Reinforcement Learning for Efficient Drone-Assisted Vehicle Routing
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A novel MDP formulation of the VRPD that explicitly considers multiple vehicles and drones with limited battery life. To the best of our knowledge, no prior work has simultaneously addressed multi-vehicle coordination and drone battery constraints in this manner.
- An RL-based solution approach utilizing a centralized controller to coordinate routing decisions within and across groups of drones and trucks in urban networks.
- An efficient training algorithm for RL agents, validated through comprehensive computational analyses comparing our model to state-of-the-art approaches.
2. Literature Review
2.1. The VRPD
2.2. Learning Methods to Solve VRPs
3. The Problem Formulation
3.1. The VRPD Definition
3.2. MDP Formulation of the VRPD
4. Solution Methods
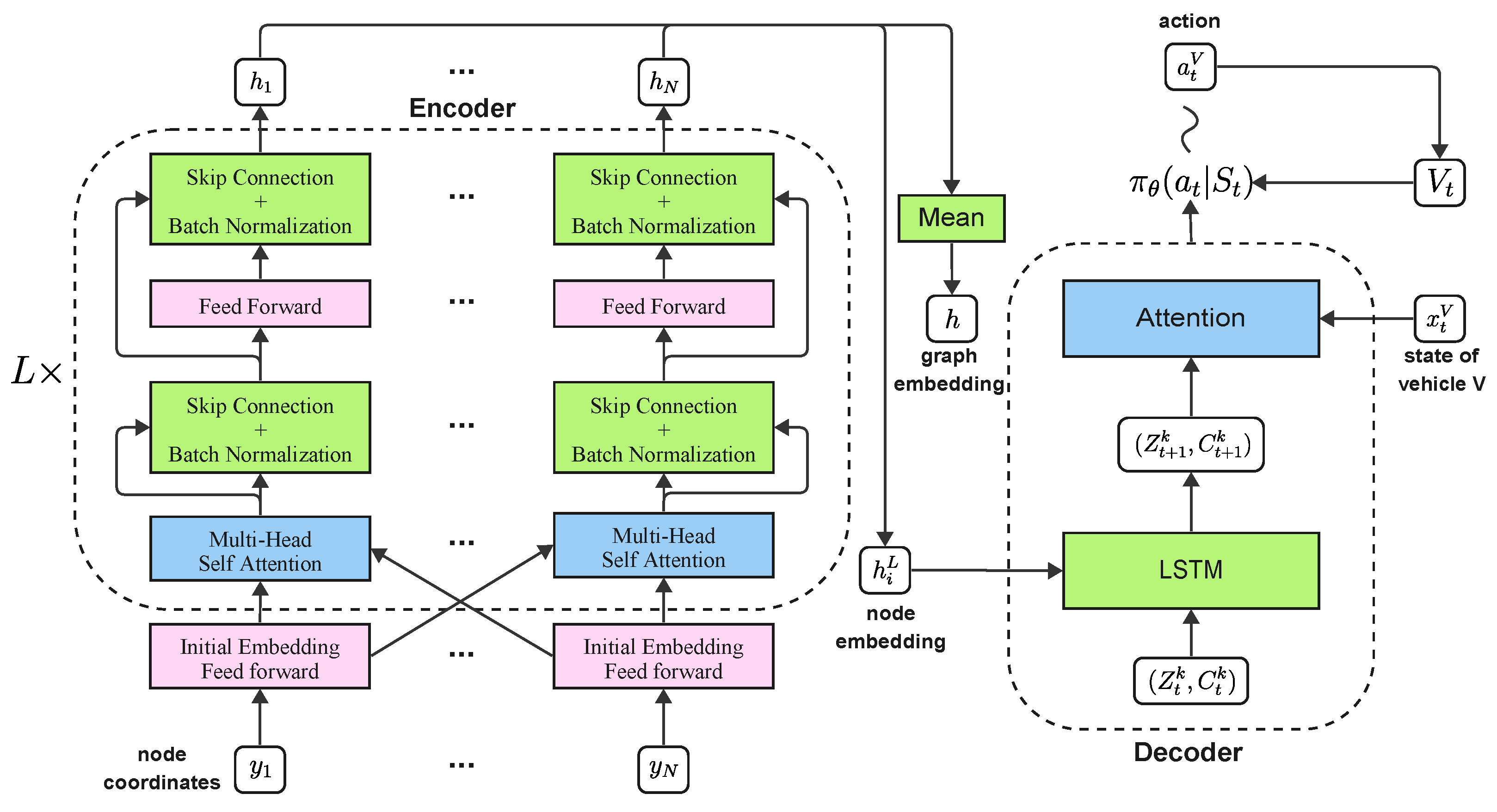
4.1. The Deep Learning Model
4.2. The Training Algorithm
| Algorithm 1: Rollout |
 |
5. Computational Studies
5.1. Training and Evaluation Configurations
5.2. Results on the VRPD with Unlimited Flying Range
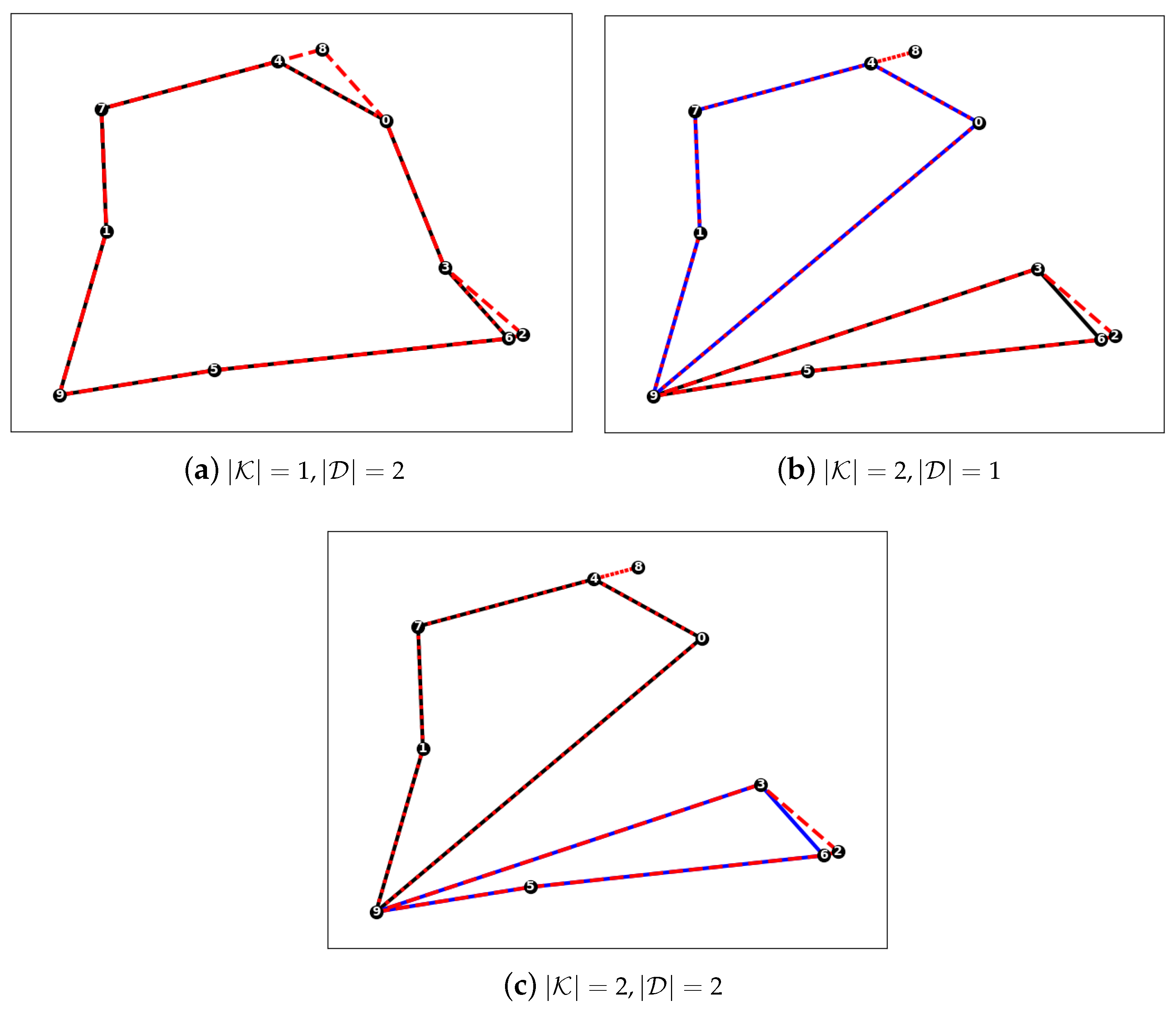
- Single vehicle with two drones
- Two vehicles with one drone assigned to each vehicle
- Two vehicles with two drones assigned to each vehicle
5.3. Results on the VRPD with Limited Flying Range
5.4. Ablation Studies
5.5. Routing Solutions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
- : – Binary variables that state whether edge belongs to the route of vehicle k.
- : – Binary variables that specify whether drone delivery is performed by a drone associated with vehicle k.
- : – Binary variables that indicate whether node i is served before (but not necessarily consecutive to) node j in the route of vehicle k.
- : – Integer variables with a lower bound of 0 that state the position of node i in the route of vehicle k, if customer i is served by vehicle k.
- : – Binary variables that specify whether the drone delivery is performed by a drone associated with vehicle k and node a precedes node i while node e follows node j in the route of vehicle k.
- : – Continuous variables with a lower bound of 0 that indicate the earliest time at which customer i is served by either the vehicle k or a drone associated with vehicle k. If i is used as a retrieval node, is the earliest time at which both the (latest) drone and the vehicle have arrived at node i.
References
- Deloison, T.; Hannon, E.; Huber, A.; Heid, B.; Klink, C.; Sahay, R.; Wolff, C. The future of the last-mile ecosystem. In Proceedings of the World Economic Forum, Davos, Switzerland, 21–24 January 2020; Volume 1, pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Mahadevan, P. The military utility of drones. CSS Anal. Secur. Policy 2010, 78. [Google Scholar]
- Restas, A. Drone applications for supporting disaster management. World J. Eng. Technol. 2015, 3, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macrina, G.; Pugliese, L.D.P.; Guerriero, F.; Laporte, G. Drone-aided routing: A literature review. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2020, 120, 102762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghetti, F.; Caballini, C.; Carboni, A.; Grossato, G.; Maja, R.; Barabino, B. The use of drones for last-mile delivery: A numerical case study in Milan, Italy. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Poikonen, S.; Golden, B. The vehicle routing problem with drones: Several worst-case results. Optim. Lett. 2017, 11, 679–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Sheu, J.B. Vehicle routing problem with drones. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2019, 122, 350–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poikonen, S.; Wang, X.; Golden, B. The vehicle routing problem with drones: Extended models and connections. Networks 2017, 70, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schermer, D.; Moeini, M.; Wendt, O. A hybrid VNS/Tabu search algorithm for solving the vehicle routing problem with drones and en route operations. Comput. Oper. Res. 2019, 109, 134–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kool, W.; van Hoof, H.; Welling, M. Attention, Learn to Solve Routing Problems! arXiv 2019, arXiv:1803.08475. [Google Scholar]
- Nazari, M.; Oroojlooy, A.; Snyder, L.; Takác, M. Reinforcement learning for solving the vehicle routing problem. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 31 (NeurIPS 2018), Montréal, QC, Canada, 3–5 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bogyrbayeva, A.; Meraliyev, M.; Mustakhov, T.; Dauletbayev, B. Machine Learning to Solve Vehicle Routing Problems: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2024, 25, 4754–4772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogyrbayeva, A.; Yoon, T.; Ko, H.; Lim, S.; Yun, H.; Kwon, C. A deep reinforcement learning approach for solving the traveling salesman problem with drone. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2023, 148, 103981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schermer, D.; Moeini, M.; Wendt, O. Algorithms for solving the vehicle routing problem with drones. In Proceedings of the Intelligent Information and Database Systems: 10th Asian Conference, ACIIDS 2018, Dong Hoi City, Vietnam, 19–21 March 2018; Proceedings, Part I 10. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 352–361. [Google Scholar]
- Schermer, D.; Moeini, M.; Wendt, O. A matheuristic for the vehicle routing problem with drones and its variants. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2019, 106, 166–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Fan, M.; Shi, J.; Feng, Y. Reinforcement learning based truck-and-drone coordinated delivery. IEEE Trans. Artif. Intell. 2021, 4, 754–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaraviglio, L.; D’andreagiovanni, F.; Choo, R.; Cuomo, F.; Colonnese, S. Joint optimization of area throughput and grid-connected microgeneration in UAV-based mobile networks. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 69545–69558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, A.; Agatz, N.; Campbell, J.; Golden, B.; Pesch, E. Optimization approaches for civil applications of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) or aerial drones: A survey. Networks 2018, 72, 411–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Lin, Y.; Li, B.; Li, R.Y.M. A bi-objective optimization model for the medical supplies’ simultaneous pickup and delivery with drones. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2022, 171, 108389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotta, A.; Andreagiovanni, F.D.; Di Felice, M.; Natalizio, E.; Chowdhury, K.R. When UAVs ride a bus: Towards energy-efficient city-scale video surveillance. In Proceedings of the IEEE Infocom 2018-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, Honolulu, HI, USA, 16–19 April 2018; pp. 1043–1051. [Google Scholar]
- Mazyavkina, N.; Sviridov, S.; Ivanov, S.; Burnaev, E. Reinforcement learning for combinatorial optimization: A survey. Comput. Oper. Res. 2021, 134, 105400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, I.; Pham, H.; Le, Q.V.; Norouzi, M.; Bengio, S. Neural combinatorial optimization with reinforcement learning. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1611.09940. [Google Scholar]
- Vinyals, O.; Fortunato, M.; Jaitly, N. Pointer networks. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 28 (NIPS 2015), Montreal, QC, Canada, 7–12 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, E.; Dai, H.; Zhang, Y.; Dilkina, B.; Song, L. Learning combinatorial optimization algorithms over graphs. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 30 (NIPS 2017), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, Y.D.; Choo, J.; Kim, B.; Yoon, I.; Gwon, Y.; Min, S. Pomo: Policy optimization with multiple optima for reinforcement learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 21188–21198. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.; Park, J. Learning Collaborative Policies to Solve NP-hard Routing Problems. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 34 (NIPS 2021), Online, 6–14 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Li, J.; Cao, Z.; Song, W.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Z.; Tang, J. Learning to Iteratively Solve Routing Problems with Dual-Aspect Collaborative Transformer. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 34 (NIPS 2021), Online, 6–14 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Agatz, N.; Bouman, P.; Schmidt, M. Optimization approaches for the traveling salesman problem with drone. Transp. Sci. 2018, 52, 965–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schermer, D.; Moeini, M.; Wendt, O. A Variable Neighborhood Search Algorithm for Solving the Vehicle Routing Problem with Drones; Technacal Report; Technische Universität Kaiserslautern: Kaiserslautern, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bogyrbayeva, A.; Jang, S.; Shah, A.; Jang, Y.J.; Kwon, C. A reinforcement learning approach for rebalancing electric vehicle sharing systems. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 23, 8704–8714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.J. Simple statistical gradient-following algorithms for connectionist reinforcement learning. Mach. Learn. 1992, 8, 229–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Methods | Costs | Gaps, % | Time, s | Costs | Gaps, % | Time, s | Costs | Gaps, % | Time, s | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solver | 158.53 | 0.51 | 175.53 | 149.53 | 1.10 | 601.33 | 125.55 | 1.09 | 481.62 | |
| Solver Lazy | 158.53 | 0.51 | 76.97 | 147.60 | 0.00 | 148.52 | 123.9 | 0.00 | 161.35 | |
| Heuristic | 158.53 | 0.51 | 154.55 | 150.32 | 1.94 | 61.84 | 125.5 | 1.06 | 65.06 | |
| RL greedy | 161.69 | 2.38 | 0.02 | 148.68 | 0.90 | 0.03 | 126.98 | 2.25 | 0.21 | |
| RL sampling | 160.23 | 1.60 | 0.87 | 148.32 | 0.59 | 1.31 | 126.87 | 2.14 | 4.00 | |
| Ensemble RL | 159.95 | 1.45 | 6.02 | 147.60 | 0.00 | 9.27 | 126.87 | 2.14 | 28.18 | |
| Solver | 196.48 | 11.25 | 601.29 | 193.75 | 16.42 | 601.52 | 171.78 | 30.89 | 601.69 | |
| Solver Lazy | 195.26 | 10.78 | 556.72 | 200.91 | 20.42 | 600.67 | 176.63 | 34.64 | 602.05 | |
| Heuristic | 178.93 | 1.42 | 308.29 | 167.59 | 0.82 | 63.68 | 131.36 | 0.23 | 99.1 | |
| RL greedy | 185.42 | 4.74 | 0.01 | 168.40 | 1.22 | 0.40 | 136.06 | 3.58 | 0.03 | |
| RL sampling | 180.26 | 1.89 | 0.43 | 167.57 | 0.71 | 1.43 | 132.40 | 0.92 | 2.06 | |
| Ensemble RL | 177.01 | 0.28 | 3.05 | 167.56 | 0.70 | 9.38 | 134.20 | 2.23 | 14.65 | |
| RL greedy | 243.06 | 3.86 | 0.02 | 219.02 | 6.91 | 0.02 | 185.88 | 8.17 | 0.32 | |
| RL sampling | 234.45 | 0.28 | 1.31 | 209.65 | 2.12 | 4.24 | 174.88 | 1.71 | 8.01 | |
| Ensemble RL | 234.09 | 0.12 | 8.94 | 205.67 | 0.15 | 29.42 | 172.64 | 0.39 | 55.60 | |
| Methods | Costs | Gaps, % | Time, s | Costs | Gaps, % | Time, s | Costs | Gaps, % | Time, s | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solver | 238.45 | 9.55 | 601.18 | 223.54 | 13.66 | 602.9 | 217.45 | 15.23 | 601.86 | |
| Solver Lazy | 246.84 | 12.89 | 601.27 | 223.58 | 13.95 | 602.1 | 215.81 | 14.33 | 601.22 | |
| Heuristic | 218.01 | 0.28 | 304.48 | 196.10 | 0.00 | 62.82 | 188.96 | 0.00 | 81.43 | |
| RL greedy | 232.24 | 6.51 | 0.03 | 205.70 | 4.77 | 0.07 | 198.47 | 5.14 | 0.02 | |
| RL sampling | 221.72 | 2.04 | 0.63 | 202.76 | 3.30 | 0.50 | 195.46 | 3.52 | 0.80 | |
| Ensemble RL | 219.78 | 1.04 | 4.54 | 200.16 | 2.03 | 3.88 | 193.17 | 2.30 | 5.44 | |
| Heuristic | 264.50 | 10.14 | 268.97 | 213.90 | 0.00 | 326.69 | 196.59 | 0.94 | 498.83 | |
| RL greedy | 252.18 | 5.09 | 0.02 | 231.80 | 8.30 | 0.03 | 218.36 | 12.02 | 0.03 | |
| RL sampling | 244.32 | 1.68 | 1.40 | 222.74 | 4.06 | 1.60 | 201.79 | 3.73 | 1.98 | |
| Ensemble RL | 240.01 | 0.00 | 9.67 | 220.63 | 3.09 | 11.36 | 201.63 | 3.58 | 11.96 | |
| Heuristic | 475.87 | 35.46 | 141.93 | 320.66 | 6.51 | 128.64 | 295.68 | 15.84 | 151.92 | |
| RL greedy | 391.58 | 11.37 | 0.04 | 318.29 | 5.71 | 0.05 | 276.61 | 8.32 | 0.05 | |
| RL sampling | 357.77 | 1.73 | 4.76 | 305.68 | 1.48 | 6.79 | 261.61 | 2.49 | 7.66 | |
| Ensemble RL | 351.63 | 0.00 | 33.18 | 301.95 | 0.25 | 47.65 | 255.74 | 0.20 | 54.45 | |
| Methods | Costs | Gaps, % | Time, s | Costs | Gaps, % | Time, s | Costs | Gaps, % | Time, s | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solver | 324.75 | 16.96 | 567.69 | 260.98 | 12.44 | 601.02 | 247.04 | 8.20 | 600.91 | |
| Solver Lazy | 282.90 | 3.95 | 476.00 | 240.47 | 4.91 | 601.71 | 238.00 | 3.98 | 601.68 | |
| Heuristic | 272.92 | 0.00 | 123.89 | 229.39 | 0.01 | 62.33 | 228.58 | 0.01 | 63.45 | |
| RL greedy | 281.62 | 1.75 | 0.01 | 231.23 | 0.80 | 0.02 | 230.99 | 1.13 | 0.02 | |
| RL sampling | 276.93 | 1.40 | 0.61 | 230.42 | 0.45 | 0.68 | 230.43 | 0.88 | 0.98 | |
| Ensemble RL | 276.32 | 1.28 | 4.47 | 229.53 | 0.08 | 4.79 | 228.84 | 0.12 | 6.80 | |
| Heuristic | 290.08 | 3.28 | 229.68 | 236.83 | 0.00 | 203.88 | 230.41 | 0.34 | 290.28 | |
| RL greedy | 292.83 | 4.32 | 0.03 | 253.66 | 7.13 | 0.02 | 248.32 | 7.81 | 0.04 | |
| RL sampling | 286.13 | 2.01 | 1.39 | 249.18 | 5.28 | 1.36 | 237.76 | 3.83 | 2.94 | |
| Ensemble RL | 283.43 | 0.96 | 9.79 | 242.89 | 2.47 | 9.47 | 235.59 | 2.66 | 15.74 | |
| Heuristic | 469.93 | 33.13 | 152.57 | 309.95 | 6.32 | 139.44 | 296.28 | 11.41 | 159.92 | |
| RL greedy | 376.76 | 6.61 | 0.06 | 306.95 | 5.24 | 0.07 | 279.95 | 5.30 | 0.07 | |
| RL sampling | 355.71 | 0.70 | 6.12 | 294.77 | 1.06 | 6.90 | 266.39 | 0.18 | 7.72 | |
| Ensemble RL | 353.27 | 0.00 | 43.15 | 291.64 | 0.00 | 48.74 | 266.68 | 0.30 | 84.59 | |
| Methods | Costs | Gaps, % | Costs | Gaps, % | Costs | Gaps, % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | RL Greedy w/t group LSTM | 234.42 | 7.26 | 209.64 | 6.83 | 214.99 | 13.79 |
| RL Greedy | 232.24 | 6.24 | 205.70 | 4.77 | 198.47 | 5.14 | |
| 2 | RL Greedy w/t group LSTM | 185.81 | 4.75 | 170.71 | 2.40 | 137.63 | 4.71 |
| RL Greedy | 185.42 | 4.50 | 168.40 | 0.98 | 136.06 | 3.58 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bogyrbayeva, A.; Dauletbayev, B.; Meraliyev, M. Reinforcement Learning for Efficient Drone-Assisted Vehicle Routing. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 2007. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15042007
Bogyrbayeva A, Dauletbayev B, Meraliyev M. Reinforcement Learning for Efficient Drone-Assisted Vehicle Routing. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(4):2007. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15042007
Chicago/Turabian StyleBogyrbayeva, Aigerim, Bissenbay Dauletbayev, and Meraryslan Meraliyev. 2025. "Reinforcement Learning for Efficient Drone-Assisted Vehicle Routing" Applied Sciences 15, no. 4: 2007. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15042007
APA StyleBogyrbayeva, A., Dauletbayev, B., & Meraliyev, M. (2025). Reinforcement Learning for Efficient Drone-Assisted Vehicle Routing. Applied Sciences, 15(4), 2007. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15042007






