A Real-Time Water Level and Discharge Monitoring Station: A Case Study of the Sakarya River
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
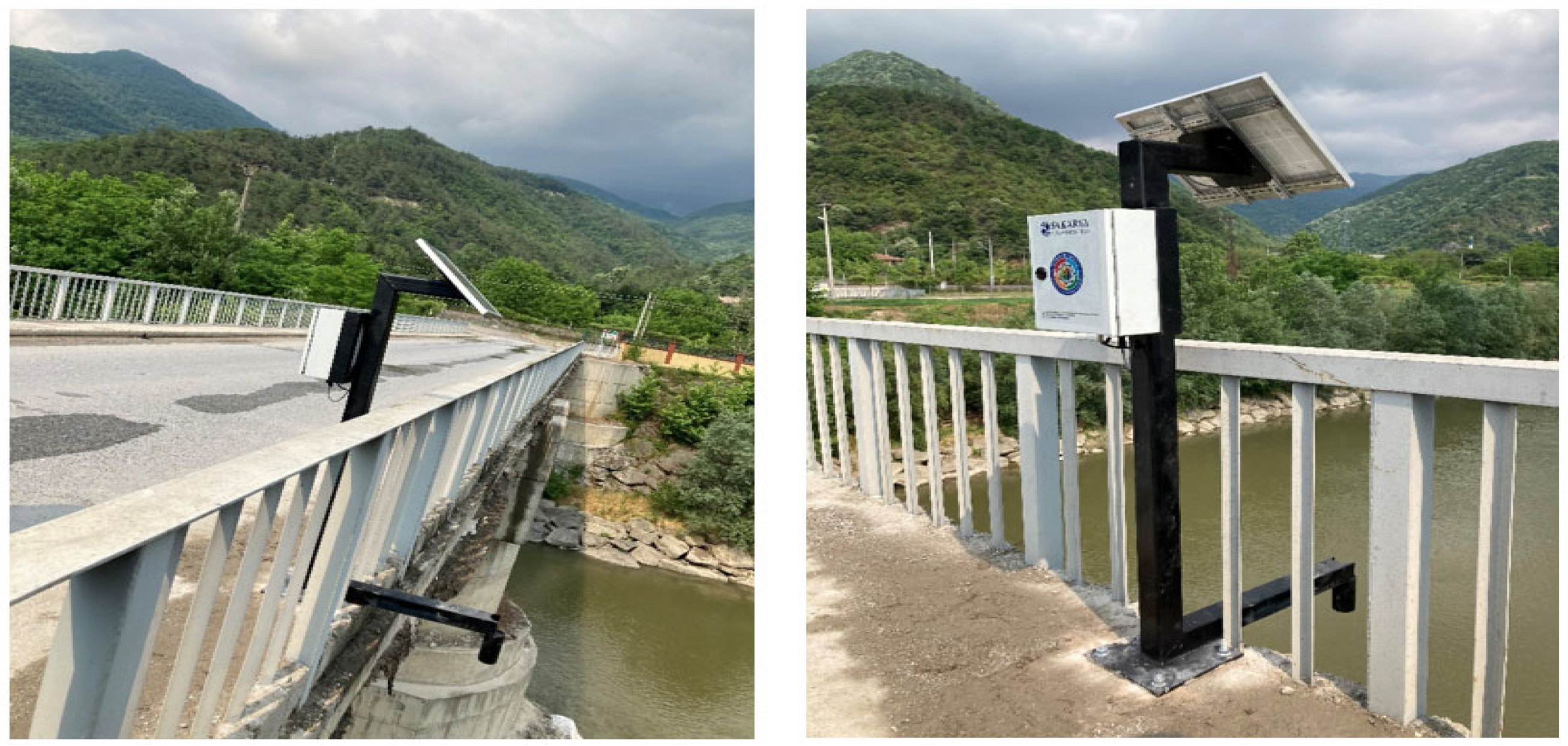
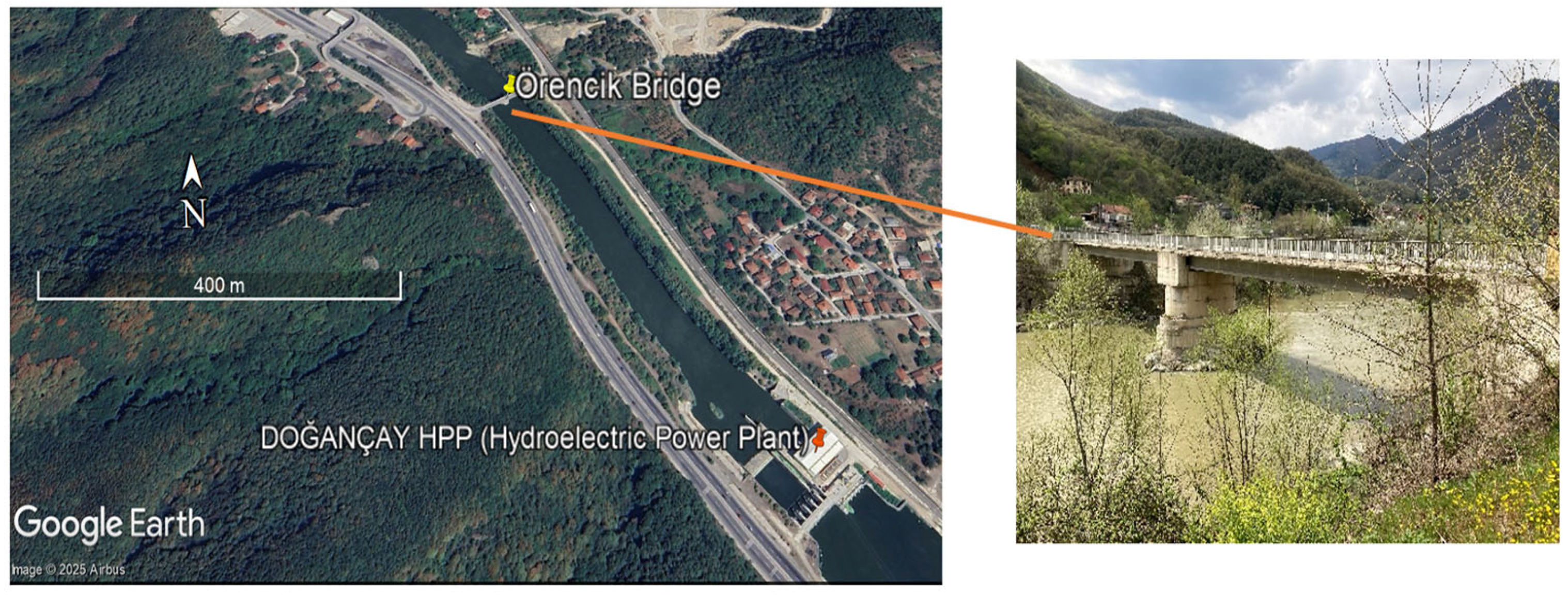
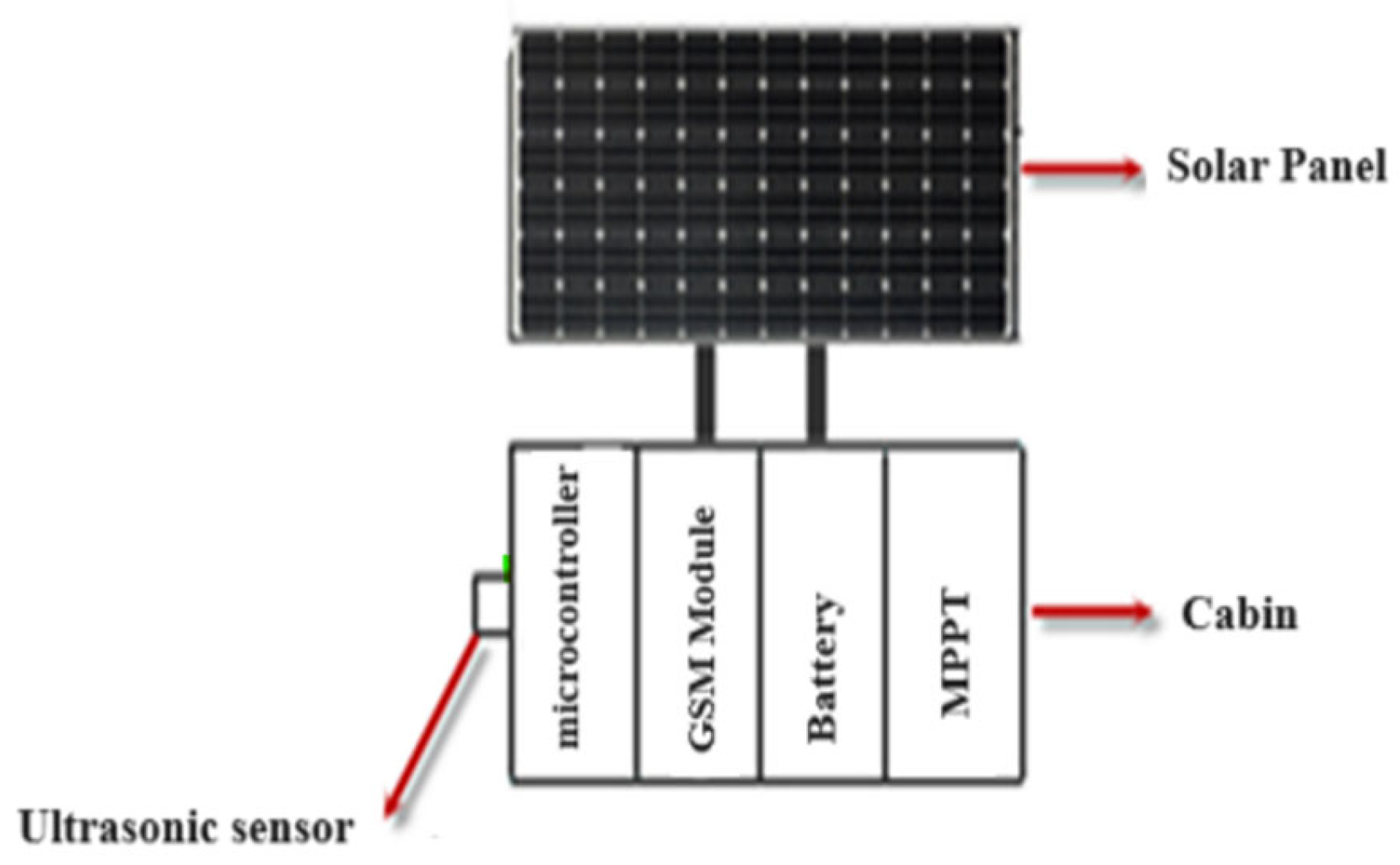
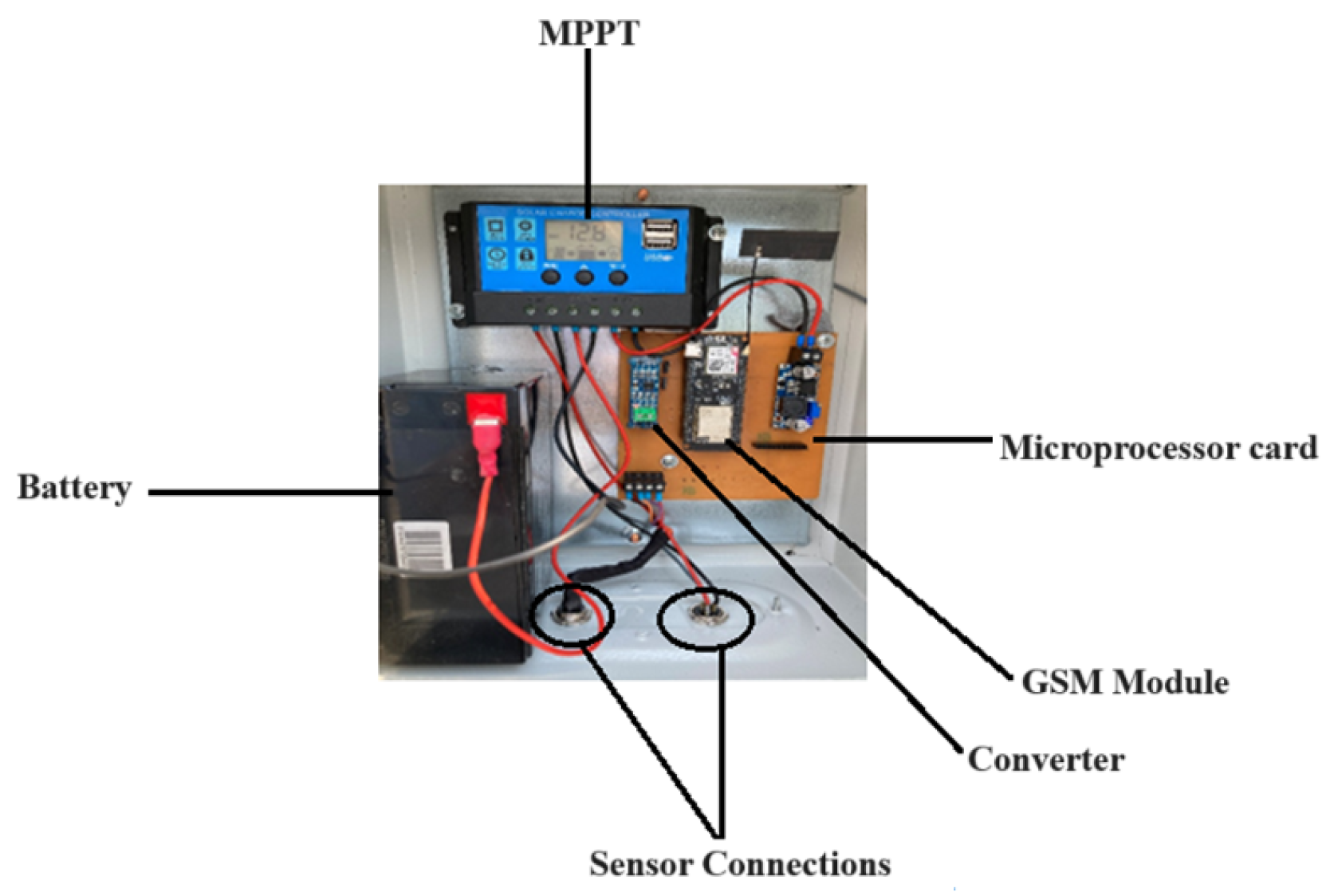
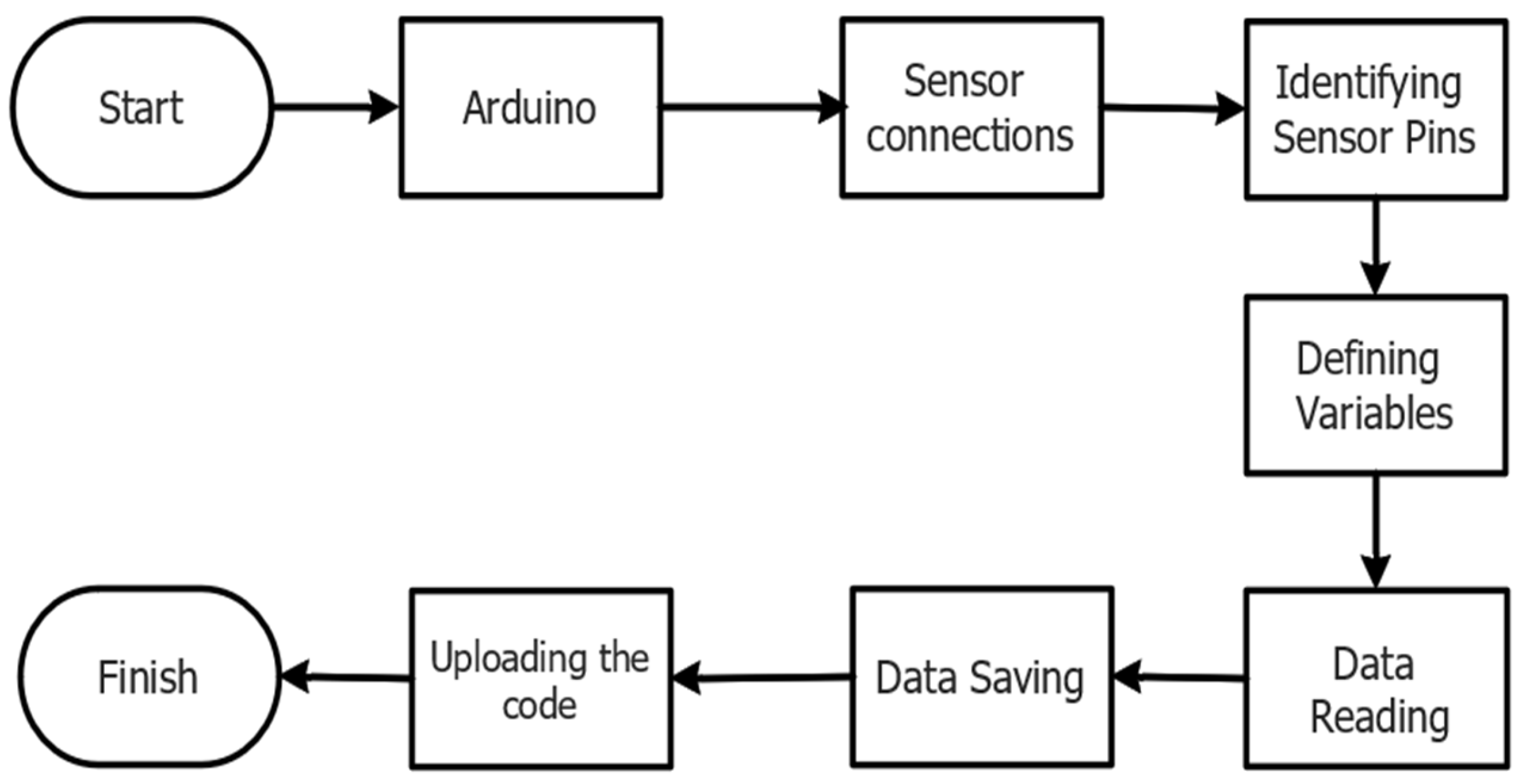
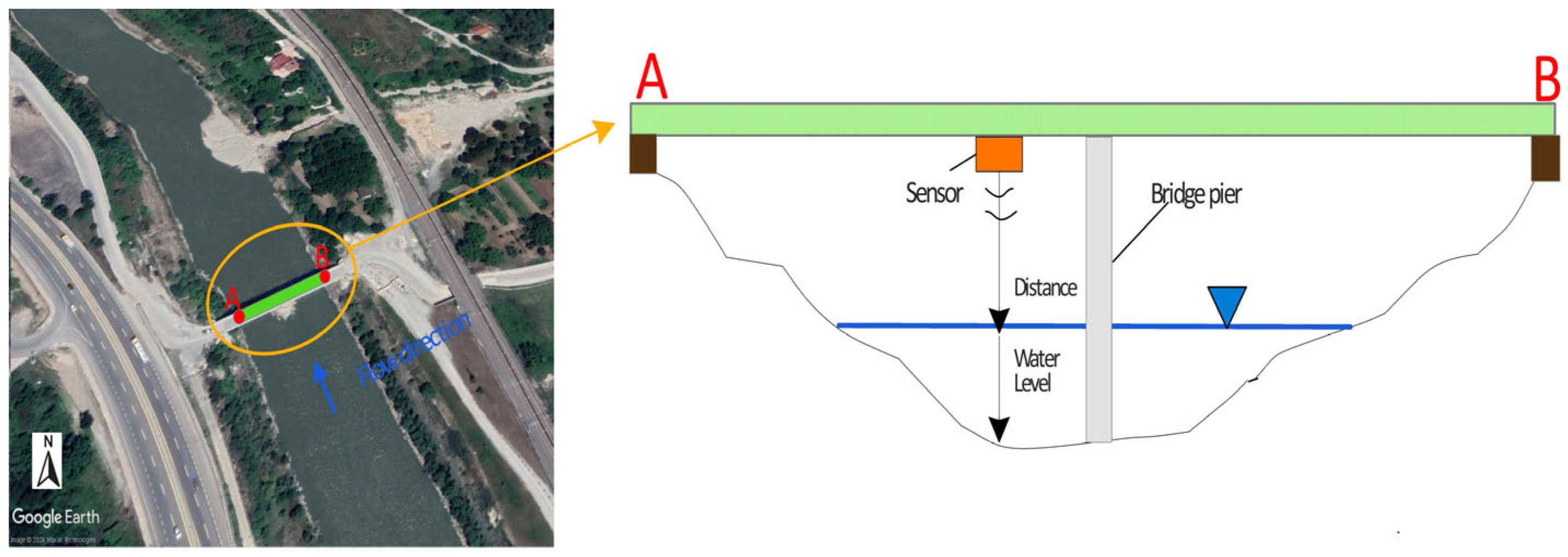
2.1. Station Design
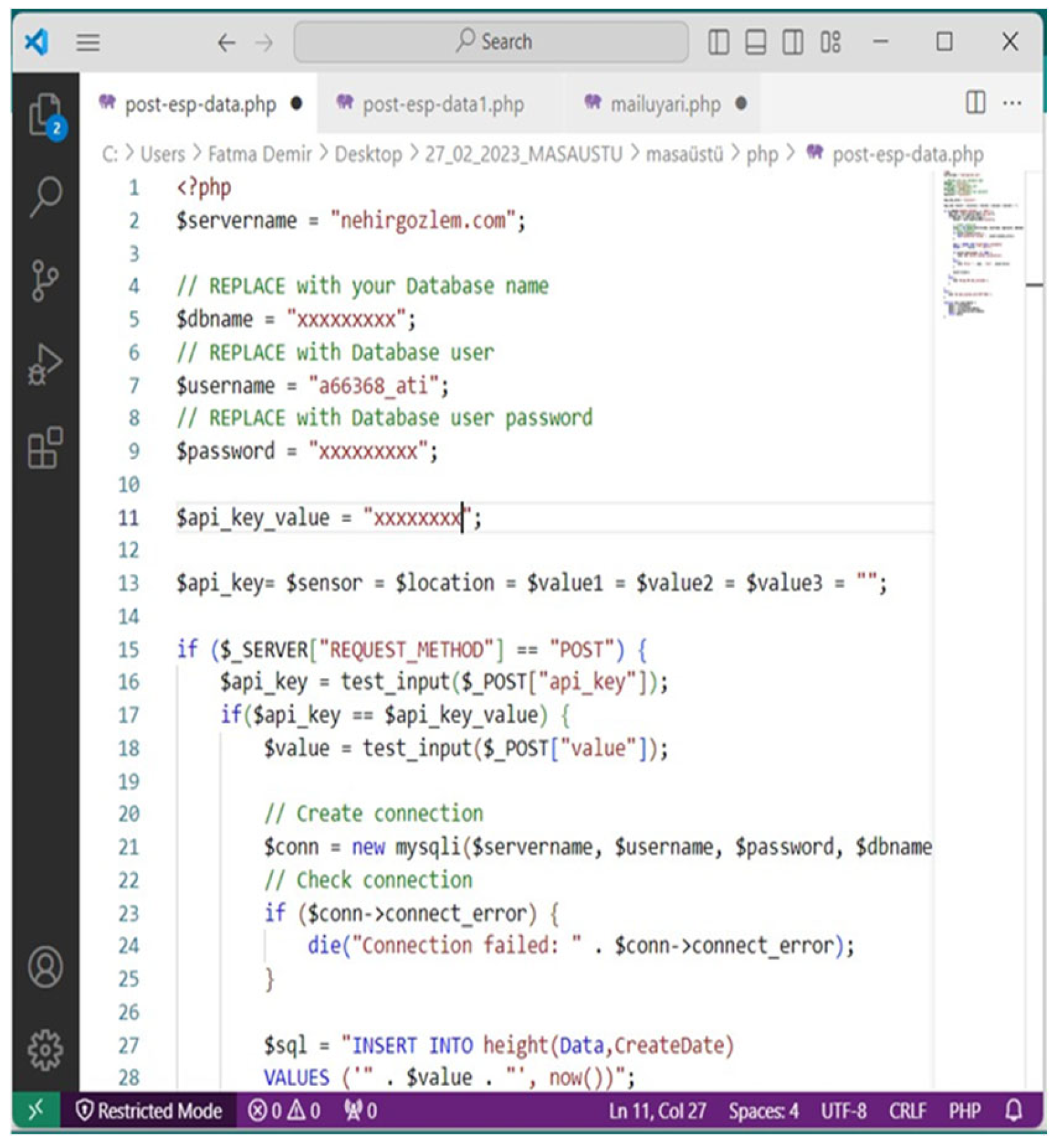
2.2. Software and Connections
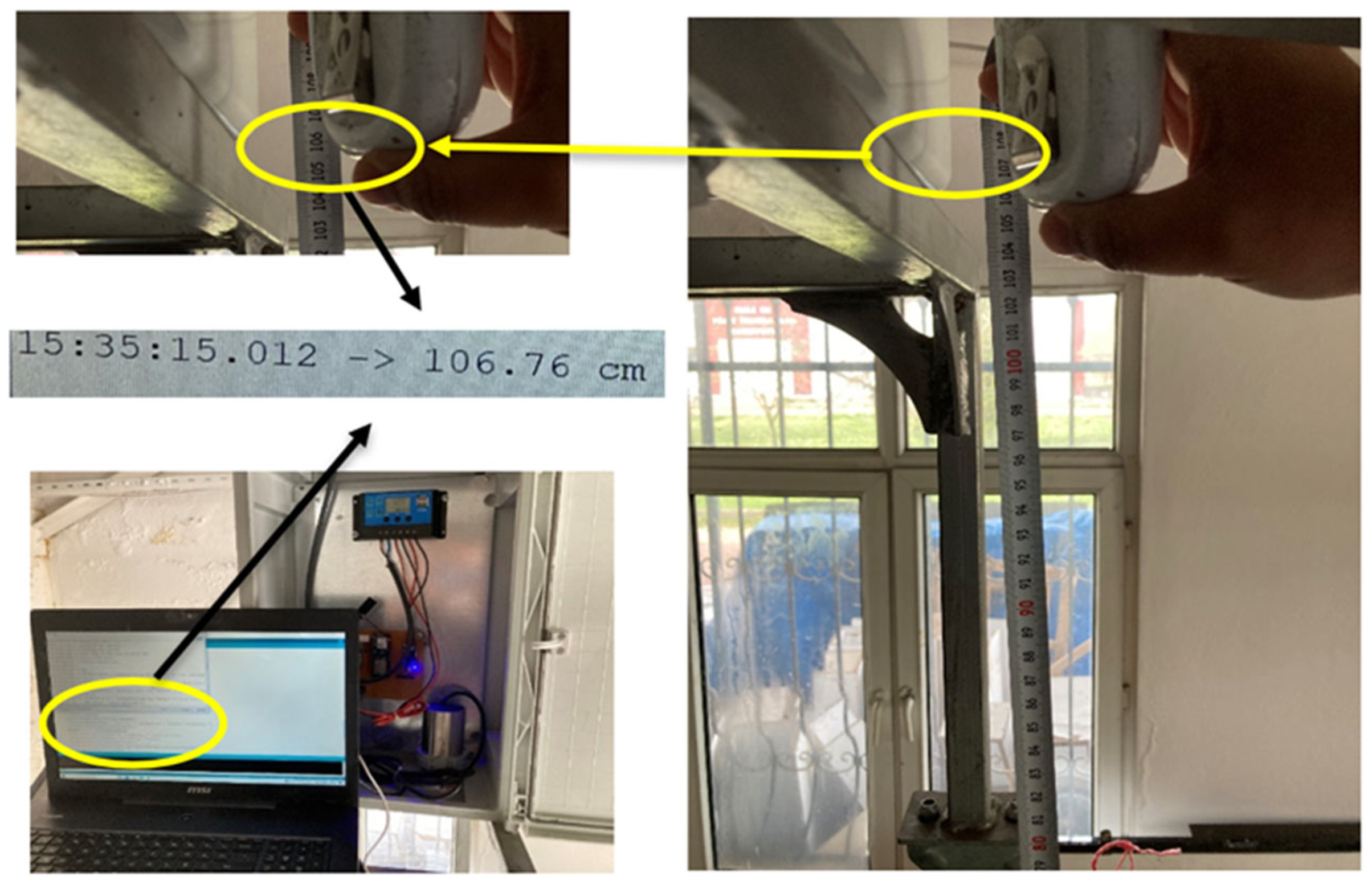
2.3. River Monitoring Station Laboratory and Field Calibration
2.4. Discharge Level Monitoring and Discharge Calculation Integration into the Web System
3. Results
3.1. Validation of River Monitoring Station Data
3.1.1. Comparison of Hourly Data
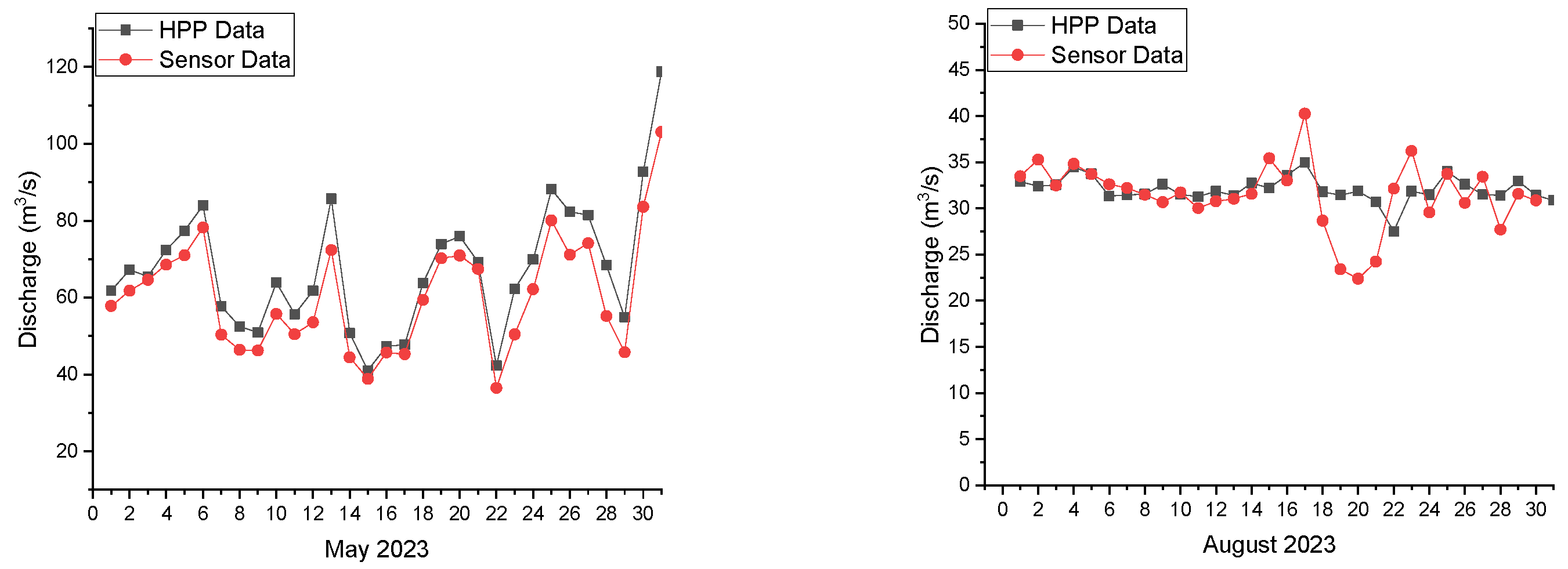
3.1.2. Comparison of Daily Data
3.1.3. Comparison of Monthly Data
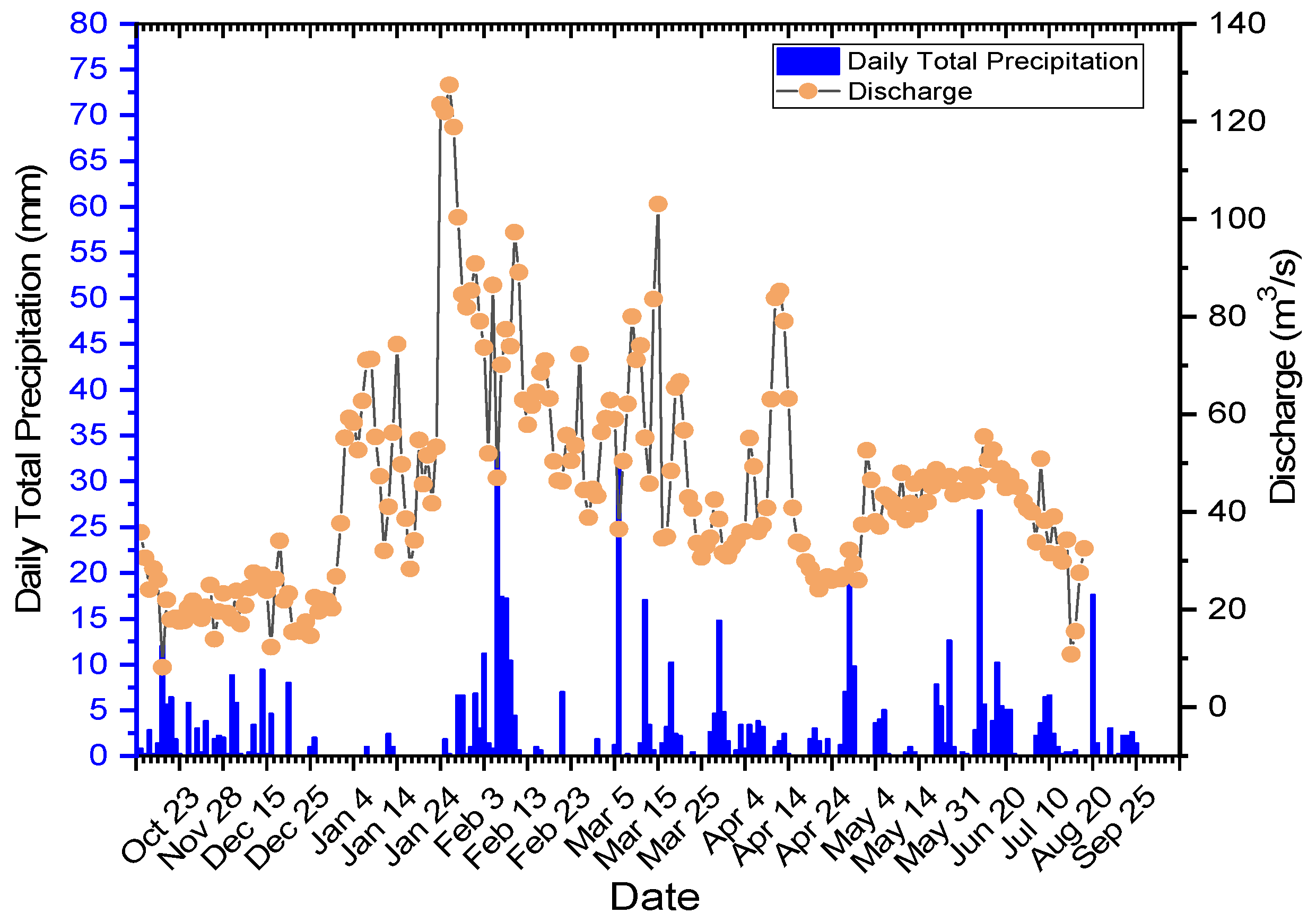
3.2. Evaluation of 2023 Hydrological Year Real-Time Monitoring Station Data
3.3. Real-Time River Monitoring Station and Early Warning System
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The real-time river monitoring station provides a robust and sustainable solution for continuous river level monitoring, integrating solar-powered energy independence and advanced IoT communication technologies.
- Calibration and validation studies conducted in both laboratory and field environments confirmed the sensor’s high measurement accuracy, with error margins within 0.1%, ensuring reliability for long-term monitoring applications.
- Validation against upstream hydropower plant (HPP) data demonstrated high correlation (r2 = 0.92) and confirmed the accuracy of the system’s measurements in real-world conditions. This high degree of consistency between the station and HPP data reinforces the station’s reliability in monitoring river water levels and discharge.
- The system’s capability to operate autonomously for up to one week without solar input highlights its resilience and adaptability to remote or poorly infrastructured locations.
- Real-time data sharing and accessibility through an open-access web interface allow users to monitor, download, and analyze measurements in various formats, supporting effective water resource management and flood prevention.
- The early warning system, triggered by ultrasonic sensor readings, provides timely alerts to relevant authorities, significantly enhancing flood risk management and disaster preparedness efforts.
- Minimal data loss during operation has been mitigated through optimized measurement intervals, with future enhancements planned to integrate artificial intelligence and statistical methods for even greater data reliability.
- The system’s flexible design allows for scalability and adaptation to various geographic and climatic conditions, making it a model for similar environmental monitoring projects worldwide.
- By addressing the limitations of existing methods, the system offers a practical and innovative tool for advancing flood risk management, water resource planning, and environmental sustainability.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Myhre, G.; Alterskjær, K.; Stjern, C.W.; Hodnebrog, Ø.; Marelle, L.; Samset, B.H.; Sillmann, J.; Schaller, N.; Fischer, E.; Schulz, M.; et al. Frequency of Extreme Precipitation Increases Extensively with Event Rareness under Global Warming. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.N.; Yun, S.-H.; Bhardwaj, A.; Hill, E.M. Urban Flood Detection with Sentinel-1 Multi-Temporal Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) Observations in a Bayesian Framework: A Case Study for Hurricane Matthew. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, T. Retracted: Simulation of Rainstorm Waterlogging Based on SWMM and Visualization Module Research. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Smart City and Systems Engineering (ICSCSE), Hunan, China, 25–26 November 2016; pp. 394–397. [Google Scholar]
- Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Kanae, S.; Seneviratne, S.I.; Handmer, J.; Nicholls, N.; Peduzzi, P.; Mechler, R.; Bouwer, L.M.; Arnell, N.; Mach, K.; et al. Flood Risk and Climate Change: Global and Regional Perspectives. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2014, 59, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain Shah, S.M.; Yassin, M.A.; Abba, S.I.; Lawal, D.U.; Hussein Al-Qadami, E.H.; Teo, F.Y.; Mustaffa, Z.; Aljundi, I.H. Flood Risk and Vulnerability from a Changing Climate Perspective: An Overview Focusing on Flash Floods and Associated Hazards in Jeddah. Water 2023, 15, 3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalnezhad, A.; Rahman, A.; Nasiri, N.; Haddad, K.; Rahman, M.M.; Vafakhah, M.; Samali, B.; Ahamed, F. Artificial Intelligence-Based Regional Flood Frequency Analysis Methods: A Scoping Review. Water 2022, 14, 2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappato, A.; Baker, E.A.; Reali, A.; Todeschini, S.; Manenti, S. The Role of Modeling Scheme and Model Input Factors Uncertainty in the Analysis and Mitigation of Backwater Induced Urban Flood-Risk. J. Hydrol. 2022, 614, 128545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furquim, G.; Filho, G.; Jalali, R.; Pessin, G.; Pazzi, R.; Ueyama, J. How to Improve Fault Tolerance in Disaster Predictions: A Case Study about Flash Floods Using IoT, ML and Real Data. Sensors 2018, 18, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, S.-W.; Wu, J.-H.; Lin, F.-P.; Hsu, C.-H. Visual Sensing for Urban Flood Monitoring. Sensors 2015, 15, 20006–20029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, P.; Orellana-Alvear, J.; Bendix, J.; Feyen, J.; Célleri, R. Flood Early Warning Systems Using Machine Learning Techniques: The Case of the Tomebamba Catchment at the Southern Andes of Ecuador. Hydrology 2021, 8, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzhizhanovskaya, V.V.; Shirshov, G.S.; Melnikova, N.B.; Belleman, R.G.; Rusadi, F.I.; Broekhuijsen, B.J.; Gouldby, B.P.; Lhomme, J.; Balis, B.; Bubak, M.; et al. Flood Early Warning System: Design, Implementation and Computational Modules. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2011, 4, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosavi, A.; Ozturk, P.; Chau, K. Flood Prediction Using Machine Learning Models: Literature Review. Water 2018, 10, 1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, D.C.; Dance, S.L.; Cloke, H.L. Floodwater Detection in Urban Areas Using Sentinel-1 and WorldDEM Data. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2021, 15, 032003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCallum, I.; Liu, W.; See, L.; Mechler, R.; Keating, A.; Hochrainer-Stigler, S.; Mochizuki, J.; Fritz, S.; Dugar, S.; Arestegui, M.; et al. Technologies to Support Community Flood Disaster Risk Reduction. Int. J. Disaster Risk Sci. 2016, 7, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, B.; Ogie, R.; Barthelemy, J.; Pradhan, B.; Verstaevel, N.; Perez, P. Computer Vision and IoT-Based Sensors in Flood Monitoring and Mapping: A Systematic Review. Sensors 2019, 19, 5012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumann, G. Preface: Remote Sensing in Flood Monitoring and Management. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 17013–17015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prafanto, A.; Budiman, E. A Water Level Detection: IoT Platform Based on Wireless Sensor Network. In Proceedings of the 2018 2nd East Indonesia Conference on Computer and Information Technology (EIConCIT), Makassar, Indonesia, 6–7 November 2018; pp. 46–49. [Google Scholar]
- Siddula, S.S.; Jain, P.C.; Upadhayay, M.D. Real Time Monitoring and Controlling of Water Level in Dams Using IoT. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 8th International Advance Computing Conference (IACC), Greater Noida, India, 14–15 December 2018; pp. 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.; Leitão, J.P.; Simões, N.E.; Moosavi, V. Data-driven Flood Emulation: Speeding up Urban Flood Predictions by Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2021, 14, e12684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinis, S.; Kersten, J.; Twele, A. A Fully Automated TerraSAR-X Based Flood Service. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 104, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rony, J.H.; Karim, N.; Rouf, M.D.A.; Islam, M.d.M.; Uddin, J.; Begum, M. A Cost-Effective IoT Model for a Smart Sewerage Management System Using Sensors. J 2021, 4, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koestoer, R.A.; Pancasaputra, N.; Roihan, I.; Harinaldi, H. A Simple Calibration Methods of Relative Humidity Sensor DHT22 for Tropical Climates Based on Arduino Data Acquisition System. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2062, 020009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Sabre, M.S.; Abdullah, S.S.; Faruq, A. Flood Warning and Monitoring System Utilizing Internet of Things Technology. Kinet. Game Technol. Inf. Syst. Comput. Netw. Comput. Electron. Control 2019, 4, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Devaraj Sheshu, E.; Manjunath, N.; Karthik, S.; Akash, U. Implementation of Flood Warning System Using IoT. In Proceedings of the 2018 Second International Conference on Green Computing and Internet of Things (ICGCIoT), Bangalore, India, 16–18 August 2018; pp. 445–448. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, F.; Pang, C.; Tang, H. Sensors on the Internet of Things Systems for Urban Disaster Management: A Systematic Literature Review. Sensors 2023, 23, 7475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, R.; McDonald, K.; Chapman, B.; Jensen, K.; Podest, E.; Tessler, Z.; Bohn, T.; Zimmermann, R. Development and Evaluation of a Multi-Year Fractional Surface Water Data Set Derived from Active/Passive Microwave Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 16688–16732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayder, I.M.; Al-Amiedy, T.A.; Ghaban, W.; Saeed, F.; Nasser, M.; Al-Ali, G.A.; Younis, H.A. An Intelligent Early Flood Forecasting and Prediction Leveraging Machine and Deep Learning Algorithms with Advanced Alert System. Processes 2023, 11, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xu, H.; Chen, X.; Simonovic, S.P. Streamflow Forecast and Reservoir Operation Performance Assessment Under Climate Change. Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 24, 83–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Coll, M.; Ballester-Merelo, F.; Martinez-Peiró, M.; De la Hoz-Franco, E. Real-Time Early Warning System Design for Pluvial Flash Floods—A Review. Sensors 2018, 18, 2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çavuş, V.; Tuna, R.; Duran, İ.U. Arduino Devreleri Için Kod Üretme ve Veri İşleme Uygulaması Tasarımın. Muş Alparslan Üniversitesi Fen Bilim. Derg. 2017, 5, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, V. Te Open-Channel Hydraulics; McGraw-Hill Book Company: New York, NY, USA, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, W.H.F.; Sandwell, D.T. Global Sea Floor Topography from Satellite Altimetry and Ship Depth Soundings. Science 1997, 277, 1956–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruise, J.F.; Sherif, M.M.; Singh, V.P. Elementary Hydraulics; Cengage Learning: Boston, MA, USA, 2007; p. 334. ISBN 978-0-534-49483-4. [Google Scholar]
- Boutahir, M.K.; Farhaoui, Y.; Azrour, M.; Sedik, A.; Nasralla, M.M. Advancing Solar Power Forecasting: Integrating Boosting Cascade Forest and Multi-Class-Grained Scanning for Enhanced Precision. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulkifli, C.Z.; Garfan, S.; Talal, M.; Alamoodi, A.H.; Alamleh, A.; Ahmaro, I.Y.Y.; Sulaiman, S.; Ibrahim, A.B.; Zaidan, B.B.; Ismail, A.R.; et al. IoT-Based Water Monitoring Systems: A Systematic Review. Water 2022, 14, 3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullo, S.L.; Sinha, G.R. Advances in Smart Environment Monitoring Systems Using IoT and Sensors. Sensors 2020, 20, 3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Demir, F.; Sonmez, O. A Real-Time Water Level and Discharge Monitoring Station: A Case Study of the Sakarya River. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 1910. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15041910
Demir F, Sonmez O. A Real-Time Water Level and Discharge Monitoring Station: A Case Study of the Sakarya River. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(4):1910. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15041910
Chicago/Turabian StyleDemir, Fatma, and Osman Sonmez. 2025. "A Real-Time Water Level and Discharge Monitoring Station: A Case Study of the Sakarya River" Applied Sciences 15, no. 4: 1910. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15041910
APA StyleDemir, F., & Sonmez, O. (2025). A Real-Time Water Level and Discharge Monitoring Station: A Case Study of the Sakarya River. Applied Sciences, 15(4), 1910. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15041910






