Abstract
This study aimed to evaluate the impact of increasing total protein content on the rheological properties of liquid whole eggs. The study fills the gap between fundamental science and industrial application by exploring the potential for developing high-protein, functional egg products for health-conscious consumers and the food industry. Liquid whole egg samples were enriched with different percentages of egg white and whey proteins. Proteins were added either before or after heat treatment, followed by homogenization, to analyze the effects on rheological behavior. Results indicated that whey protein samples exhibit near-Newtonian behavior due to their high solubility and minimal protein interactions, while egg white protein samples, especially at higher concentrations, induce shear thinning behavior and increased viscosity due to their water-binding capacity and partial heat-induced denaturation. Flow behavior index (n) decreased by 62.7 ± 5.7% and 25.2 ± 1.8% for heat treated with 10% added egg white and whey protein samples, respectively; meanwhile, it decreased by 2.64 ± 0.06% for 10% of added egg white protein and increased by 12.0 ± 1.0% for 10% of whey protein when heat treatment was induced prior to protein additions. The findings from this study offer valuable insights for developing functional food enriched with whey and egg white proteins.
1. Introduction
Protein is an essential macronutrient of a healthy diet. Consumers believe that adding a high amount of protein to their dietary intake has multiple benefits, such as weight management, satiety, and weight loss. Egg and whey proteins are two widely recognized sources of high-quality protein, each offering distinct advantages for muscle growth, recovery, and overall health benefits. Egg protein, derived from egg white, is a complete protein known for its superior digestibility and bioavailability [1]. As for whey protein, sourced from milk during the cheese-making process, it is known for its rapid absorption and comprehensive amino acid profile. Whey protein is often favored for post-exercise supplementation due to its fast digestion and stimulation of muscle protein synthesis [2].
Egg products are all forms of eggs that are removed from the shell and processed, making them more microbiologically stable, more commercial, and more industrially used [3]. There is a large supply of egg derivatives, such as dried, liquid, and frozen eggs, all being used as ingredients in food services or formulas. Liquid eggs and liquid egg fractures possess a desirable functionality that is used widely in different manufacturing processes such as foaming, gelation, coloring, and flavoring as well as emulsification. For their functional properties, liquid egg products are used in several products, such as pasta preparation, baked goods, meat and seafood products, mayonnaise, and salad dressing [4].
Rheology properties are used to understand the response of a certain food toward stress and forces, offering useful information regarding its structure and interaction with other components [5]. It plays a crucial role in food development, knowing the rheological behavior of food can enhance its texture and quality, resulting in an increase in customer satisfaction.
Low-fat mayonnaise, for example, was developed by studying the texture and mimicking the rheological behavior of full-fat mayonnaise [6,7]. Many vegan alternatives are created using the same concept. Milk alternatives, whether derived from nuts or legumes, and vegan ice creams are developed with careful consideration of the rheological properties of their traditional products to replicate texture, mouthfeel, and overall sensory experience [8]. Similarly, studying the rheological behavior of traditional chocolate, including its melting profile and mouthfeel, allowed food developers to create sugar-free chocolate with sugar substitutes like erythritol and stevia [9].
Knowing the importance of liquid eggs in the food industry, studying their properties is a must to determine quality, sensory evaluation, and the right processing method and instrument. Understanding the flow velocity of liquid whole eggs makes it easier to predict its behavior in tubes and pipes during pasteurizing, cooling, drying, and transporting [10].
Several studies found that the rheological characteristics of eggs lean toward a Newtonian as well as time-dependent non-Newtonian shear thinning behavior [11,12,13]. A study investigating the rheological behavior of egg whites, for both thick and thin portions and at different temperatures, found that the viscosity of egg whites decreases with an increase in temperature. Different rheological behavior was observed for the thin and thick portions of egg white at 5 °C; the thin portion showed no decrease in viscosity with shearing time at constant shear rates, while the thick portion showed a decrease within the first 6 min of shearing and then remained constant [14].
More studies investigating liquid egg rheological properties found that liquid egg white and liquid whole egg rheological behavior are more heat sensitive than liquid egg yolk; liquid whole egg showed a fluctuation in apparent viscosity around pasteurization temperature leaning toward thixotropic behavior in comparison to liquid egg white, which was more stable. On the other hand, the apparent viscosity of liquid egg white and liquid whole egg at 4 °C was constant over the given time, showing time-independent behavior [15].
Increasing the content of protein in liquid whole eggs was the aim of the study; this increase can change the overall rheological behavior of liquid whole eggs.
Currently, foods with high protein content are seen as functional foods providing several health benefits [16]. A study on European consumer preferences for protein beverages found that the most important factor influencing their choice was the amount of protein, followed by the type of protein [17]. Whey, milk, and plant proteins were the most appealing proteins for consumer preference [17]. This study was designed to evaluate the effect of different proteins and protein percentages on the rheological behavior of liquid whole eggs in an effort to create a new product with a higher protein content per portion, aligning with the growing demand for protein-rich functional foods. The study addresses a significant research gap by focusing on the effects of protein supplementation in liquid whole eggs, an area that has received limited attention compared to other food matrices, such as dairy or plant-based products. While liquid whole eggs are widely used in food processing, there is a lack of systematic studies on how protein supplementation interacts with native egg proteins and impacts rheological properties, including viscosity, gelation, and flow behavior. These interactions are critical for understanding the functional and sensory properties of the final product yet remain underexplored.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
A quantity of 2800 g of raw homogenized liquid whole egg was acquired from a liquid egg plant operated by Capriovus Ltd., located in Szigetcsép, Hungary. Powdered egg white protein was procured from the same company, while whey protein isolate (WPI90) was obtained from Buda Family kft (Kóny, Hungary).
2.2. Sample Preperation
In total, 1400 g of raw liquid whole eggs was divided into 7 different beakers, with 200 g each. Powdered egg white protein was added to 3 samples with different percentages—3, 5, and 10% W/W; meanwhile, the other 3 beakers were fortified with 3, 5, and 10% of whey protein W/W. The 7th sample served as the control. All samples were homogenized at 10,000 rpm for 3 min using IKA T-18 Ultra Turrax Digital Homogenizer (Staufen im Breisgau, Germany) [18]. They were then heat treated at 60 ± 0.2 °C, with a holding time of 3.5 min in a water bath [19], followed by immediate cooling to 4 °C using an ice bath. The second batch of 1400 g of liquid whole egg was divided into 7 different beakers in the same way. The samples were heat treated at 60 ± 0.2 °C, with a holding time of 3.5 min in a water bath, then cooled down immediately to 4 °C using an ice bath. The same added percentages of the proteins were used, then the samples were homogenized using the IKA T-18 Ultra Turrax Digital Homogenizer (Staufen im Breisgau, Germany) at 10,000 rpm for 3 min. The 7th sample served as a control group. Finally, all samples were measured.
Typically, the protein content of a product should meet 10–20% of the recommended dietary allowance per serving for it to be labeled as an excellent source of protein [20]. Both proteins have a protein digestibility-corrected amino acid score of 1, indicating that these proteins provide all essential amino acids in proportions optimal for human nutrition and are highly digestible [21]. Liquid whole eggs naturally contain approximately 12 g of protein per 100 g. The increase of 3, 5, and 10% W/W of added protein was part of a trial to create a product which can be labeled as “High protein”, where at least 20% of total energy comes from protein. To achieve this, liquid whole egg total protein content should be increased by 3 g to reach 15 g or by 5 g to reach 18 g. As for the 10% increase, the total amount of protein will be around 22 g, which can be considered for sports nutrition-type products [20].
2.3. Examination of Rheological Properties
On the day of production, samples were used to examine the rheological behavior of liquid whole egg. The analysis was conducted using a MCR 92 rheometer (Anton Paar, Les Ulis, France) in rotational mode, equipped with a concentric cylinder (cup diameter 28.920 mm, bob diameter 26.651 mm, bob length 40.003 mm, active length 120.2 mm, positioning length 72.5 mm). To control the equipment, Anton Paar RheoCompass software version 1.30.1164 was used. A constant temperature of 15 °C was kept throughout the rheological measurements. Shear stress was measured by logarithmically increasing and decreasing shear rate between 1 and 1000 1/s for 32 measurement points, with each sample tested in triplicate [22].
Following the literature, this study chose the Herschel–Bulkley model to describe the rheological behavior of liquid whole egg. The Herschel–Bulkley model is often chosen for liquid egg products because it accounts for both yield stress and shear thinning behavior, which are the characteristics of liquid whole eggs. The model effectively incorporates these factors, making it suitable for analyzing the rheological properties for liquid whole eggs [13,15,18].
Equation (1) was used to analyze the flow curves (shear rate–shear stress diagrams).
where the following hold:
τ = τ0 + Kγ˙n
τ = shear stress (Pa)
τ0 = yield stress (Pa)
γ˙ = the shear rate (1/s)
K = the consistency coefficient (Pasn)
n = the flow behavior index.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
To analyze data statistically, the statistical package for social science (SPSS, version 27.0, 2020, Chicago, IL, USA) was used. A two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) test was performed to test the difference between the treatments, followed by mean separation using Tukey HSD Analysis. Means with a star sign differ significantly at p < 0.05.
3. Results
Rheological properties are essential for understanding high-protein liquid whole egg behavior, because they directly influence critical aspects of food processing and product development [23]. In processes like extrusion, rheology affects fluid flow, pump selection, equipment design, and the adaptation of raw materials to meet specific processing and product design requirements. Proteins, which exhibit both elastic and viscous behavior, play an important role in determining the texture, mouthfeel, and structural integrity of foods. By examining rheological behavior, researchers can better customize protein-based ingredients for improved performance and sensory attributes in food products [24].
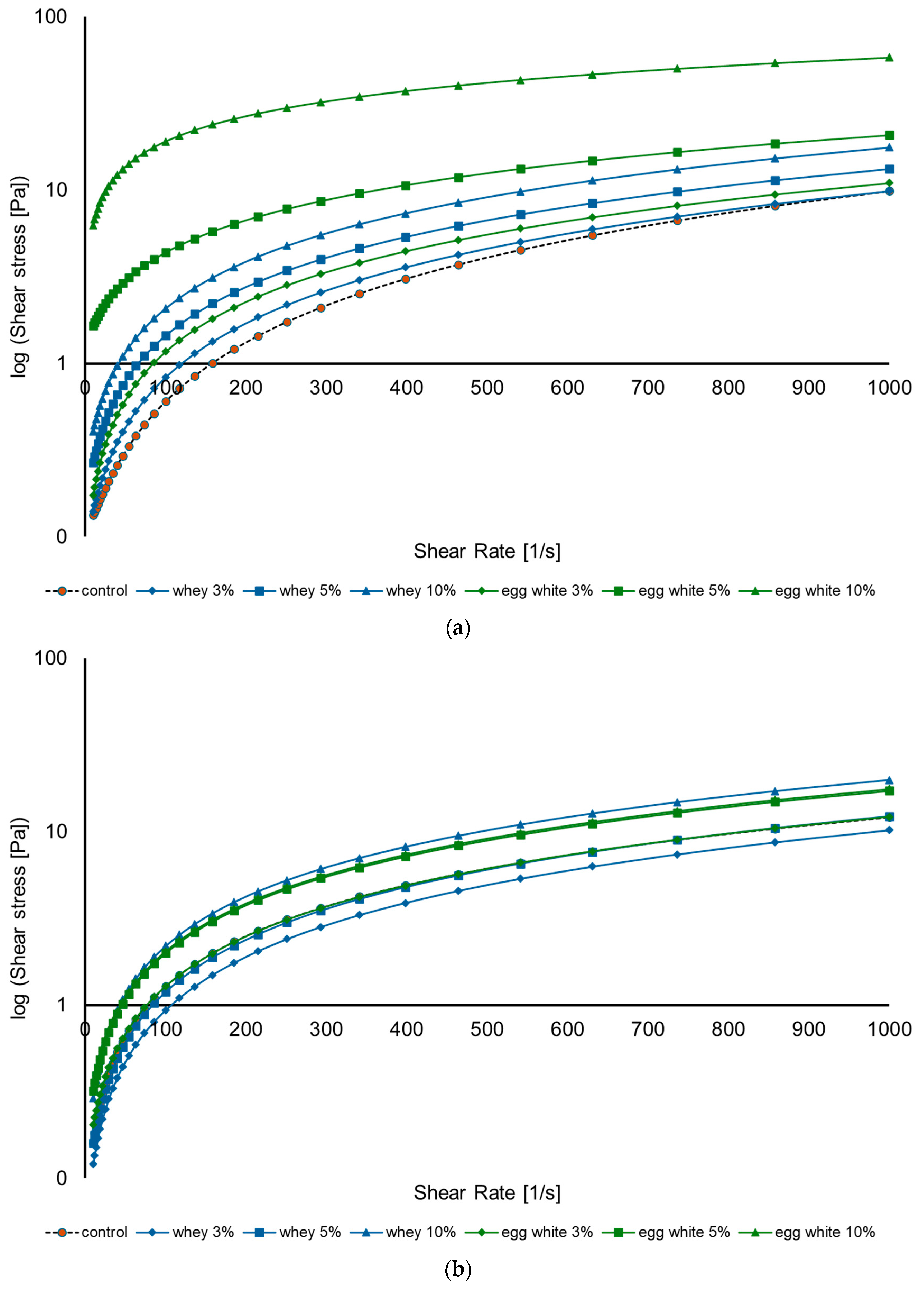
The flow properties of added-protein liquid whole eggs were shown to exhibit pseudoplastic behavior. Figure 1a,b illustrate the flow behavior for samples that were heat treated after adding proteins and those that were heat treated before, respectively. The figures show the relationship between shear stress (Pa) on the y-axis and shear rate (1/s) on the x-axis.
Figure 1.
The flow curves of different concentrations of added whey and egg white protein to liquid whole egg: (a) pasteurizing after adding proteins at 60 ± 0.2 °C with 3.5 min of holding time; (b) pasteurizing before adding proteins at 60 ± 0.2 °C with 3.5 min of holding time.
Figure 1a shows that adding whey and egg white protein then heat treating the samples increases the shear stress, which indicates that liquid whole egg is becoming thicker. At equivalent concentrations, egg white protein-enriched samples show a higher shear stress than whey-fortified samples; this shows that egg white protein has a higher influence on the overall flow behavior of liquid whole egg, making it more viscous and resistant to flow. Meanwhile, Figure 1b shows that without heat treatment, liquid whole eggs with added proteins show a Newtonian-like behavior, meaning that the viscosity of the samples remains constant despite of the applied shear rate.
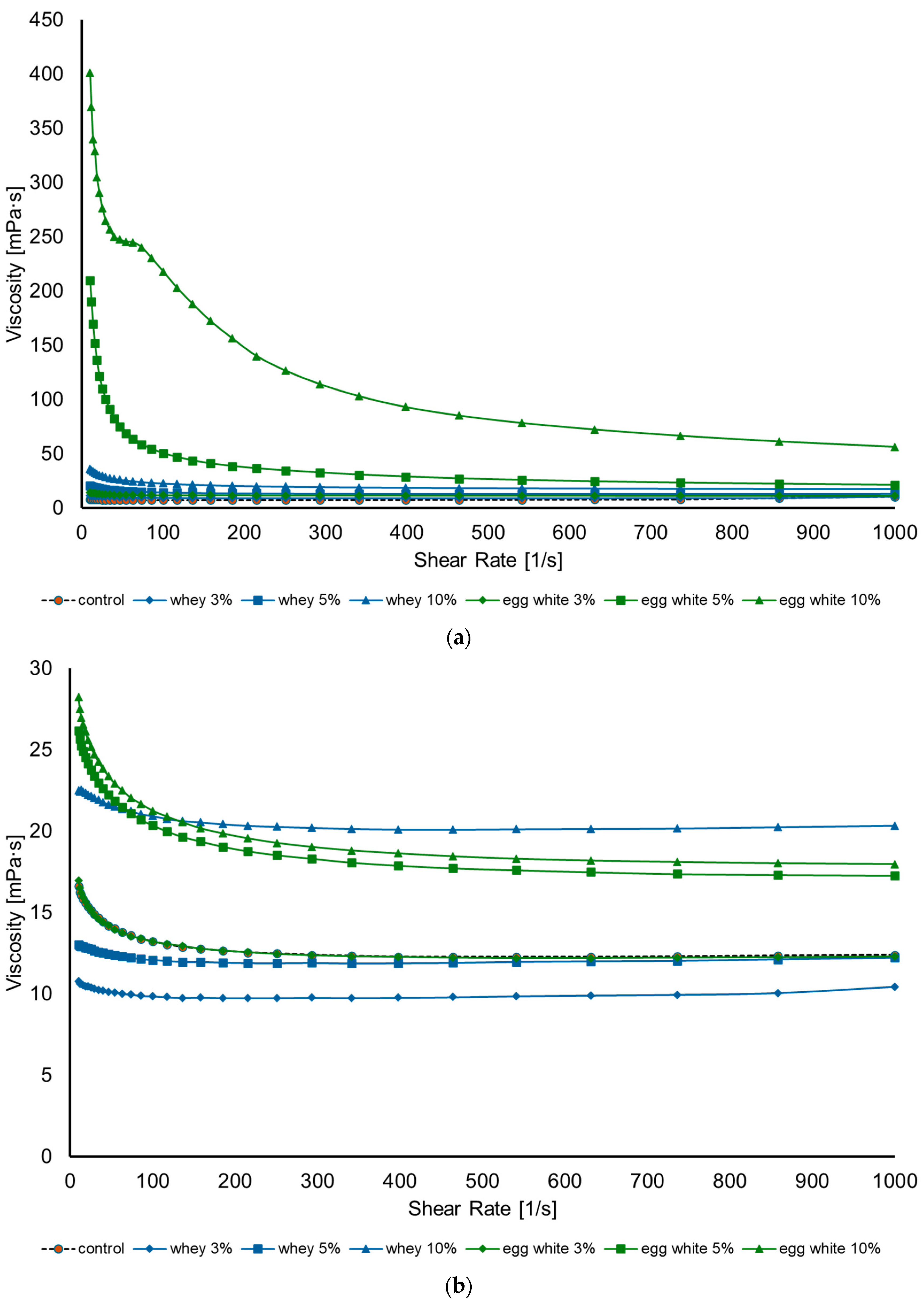
Figure 2a,b display viscosity (mPa·s) on the y-axis against shear rate (1/s) on the x-axis for samples that were heat treated after adding proteins and those which were heat treated before, respectively. Figure 2a shows that the viscosity of samples decreases with increasing shear rate for all samples, indicating a shear thinning behavior when proteins were added before heat treatment. Although all samples show a shear thinning behavior, the highest shear thinning behavior was observed in samples with 5% and 10% added egg white protein. These samples start with the highest viscosity at low shear rates and decreased significantly as the shear rate increases. As for Figure 2b, it is clearly seen that whey protein samples exhibit nearly a Newtonian behavior, where viscosity remains constant with the increase in shear rate. Meanwhile, egg white protein samples show a thinning behavior, which was more obvious with the increase in egg white protein concentrations and almost identical to the control group behavior in the sample with 3% added egg white protein.
Figure 2.
The viscosity curves (shear rate vs. viscosity) of different concentrations of added whey and egg white protein to liquid whole egg: (a) pasteurizing after adding proteins at 60 ± 0.2 °C with 3.5 min of holding time; (b) pasteurizing before adding proteins at 60 ± 0.2 °C with 3.5 min of holding time.
The flow behavior and viscosity data collected experimentally align well with the calculated values using the Herschel–Bulkley model. This alignment confirms that the samples exhibit the predicted flow behavior characteristics, validating the Herschel–Bulkley model’s accuracy in describing these non-Newtonian properties [22,25].
Table 1 shows the Herschel–Bulkley model parameters describing the flow behavior of samples that pasteurized after adding the proteins at 60 ± 0.2 °C with 3.5 min of holding time. τ0 (Tau0), K, and n for all samples were calculated to evaluate the flow behavior in reference to a control group with no added proteins. The yield stress (τ0) for the control group was 0.108 ± 0.044, representing the lowest amount of stress needed to start the flow. τ0 increased with the increase in added powered proteins percentages, whether it was whey protein or egg white protein. τ0 shifted from 0.108 ± 0.044 for the control group to 0.083 ± 0.062, 0.134 ± 0.008, and 0.204 ± 0.006, respectively, for 3, 5, and 10% added whey protein samples. All these changes where insignificant in comparison to the control group. On the other hand, τ0 shifted to 0.061 ± 0.076, 1.088 ± 0.068, and 1.937± 0.057 for 3, 5, and 10% added egg white protein samples, respectively. This increment was significant when it comes to 5 and 10% added egg white protein but an insignificant decrement was observed at 3% added egg white protein. Regarding the consistency index (K), which reflects the thickness or viscosity of a fluid, it increased from 0.001 ±0.001 to 0.004 ± 0.001, 0.013 ± 0.002, and 0.022 ± 0.005 Pa.sn for the 3, 5, and 10% added whey protein samples, respectively, and to 0.011 ± 0.002, 0.097 ± 0.045, and 2.064 ± 0.002 Pa.sn for the 3, 5, and 10% added egg white protein samples, respectively. This shift in K was significant only in the case of 5% and 10% added egg white protein, indicating that with the addition of both, protein increased the viscosity of liquid whole eggs. As for the flow behavior index (n), it shifted from 1.296 ± 0.054 for the control group, which shows a shear thickening behavior, to 1.117 ± 0.031, 0.997 ± 0.016, and 0.969 ± 0.029 for the 3, 5, and 10% added whey protein, respectively, showing more of a pseudoplastic behavior. This decrease was significant in the case of 10% but insignificant for 5% and 3% added whey protein. On the other hand, the calculated n value for 3, 5, and 10% added egg white dropped significantly to 0.994 ± 0.023, 0.783 ± 0.084, and 0.483 ± 0.021, respectively, which shows a strong shear thinning behavior.

Table 1.
Measured results of Herschel–Bulkley model at different concentrations of added whey and egg white protein after pasteurizing at 60 ± 0.2 °C with 3.5 min of holding time in comparison to liquid whole egg control group. * represents significantly different groups (Tukey’s p < 0.05).
Table 2 shows the measured results of the Herschel–Bulkley model at different concentrations of added whey and egg white protein to pasteurized liquid whole egg. Liquid whole egg was pasteurized at 60 ± 0.2 °C with 3.5 min of holding time, then cooled down in an ice bath to 4 °C, and after that, left to rest at room temperature. Proteins were added at this stage, and measurements were made in comparison to the liquid whole egg control group. τ0 started to increase with the increase in added powered proteins percentages whether it was for whey protein or egg white protein. No significant difference was observed in τ0 for the 3, 5, and 10% added whey protein samples in comparison to the control group. Meanwhile, τ0 changed significantly for the 3, 5, and 10% added egg white protein samples in comparison to the control group.

Table 2.
Measured results of Herschel–Bulkley model at different concentrations of added whey and egg white protein to pasteurized liquid whole eggs in comparison to the liquid whole egg control group. * are for significantly different groups (Tukey’s p < 0.05).
As for K, it increased for all added proteins percentages. This increase was significant for 10% added whey protein, and 3%, 5%, and 10% added egg white protein in comparison to the control group, indicating that the mixture tended to become more viscous with the increase in protein percentage. On the other hand, n values showed an increasing trend for all added concentrations, except for 10% of added egg white protein, where n slightly decreased. The changes in n values were minimal, with all samples exhibiting near-Newtonian behavior.
4. Discussion
The viscosity of liquids, in general, is influenced by several factors, including temperature, molecular structure, and the interactions between molecules. Usually, as temperature increases, the viscosity of a liquid decreases, due to the fact that molecules line up easier, allowing it to flow easier [26]. Molecular structure also has a huge effect on viscosity; the more complex the structure is, the more it resists flowing. This resistance can happen due to the strong intermolecular bond between the liquid molecules, which increases the overall viscosity [10].
In the case of liquid whole egg, viscosity is primarily affected by the protein content and how these proteins interact with each other. Proteins in the egg, such as ovalbumin and ovotransferrin, can form networks that trap water and increase resistance to flow, especially when subjected to heat [26]. This explanation is clearly seen in the results of τ0; it increased significantly with the increase in added protein percentages, and drastically increased when heat was applied after adding the protein. Adding different percentages of whey or egg white powdered proteins influences liquid whole egg viscosity. With the increase in protein content, the viscosity increases; this is due to the several types of protein interactions that occur in the solution [27].
Whey protein solution shows near-Newtonian behavior at a low concentration when no heat treatment is applied, but tends to show shear thinning behavior at a high concertation or when heat treatment near the whey protein denaturation temperature is applied, which ranges from 65 to above 70 °C. In this experiment, whey protein was dissolved in liquid whole eggs, then heated to 60 °C; this temperature is a relatively mild heat treatment for whey protein [28]. At this temperature setting, ovalbumin in egg whites and β-lactoglobulin in whey may start to partially unfold, leading to the exposure of hydrophobic regions and reactive sites on the proteins. This could facilitate hydrophobic interactions and some degree of aggregation between whey and egg proteins, but the extent of bonding is limited at this temperature [29].
Another interaction that may affect the mixture properties is disulfide bonds. Both egg and whey proteins contain the sulfhydryl group. Although 60 °C is not the optimal temperature for disulfer cross-links to occur, a weak interaction can occur [29].
The previous explained interactions and linkages also occur in egg white added-protein solutions, but more factors are involved, which contribute to more severe results. Shifting from a shear thickening to a strong shear thinning behavior when adding egg white protein to liquid whole egg can be caused by a crowding effect of the increase in total protein concentration. Although this crowding applies for samples with whey protein as well, its impact is more significant in the case of egg white protein due to its high water holding capacity [30]. When egg white protein powder is dissolved in liquid egg and heat treated at 60 °C, partial denaturation occurs, exposing polar regions that strongly bind water molecules. The reduction in free water in the mixture affects its flowing behavior and increases its viscosity. Meanwhile, as the concentration of egg white protein in liquid whole egg increases, and when combined with moderate heating, a weak gel-like structure may form. Although full gelation of egg proteins typically requires higher temperatures, partial aggregation and mild cross-linking of proteins can occur in these conditions. This results in a semi-structured network that is not a fully solid gel but behaves as a viscous, cohesive matrix, which resists flow and increases the overall thickness of the mixture [31]. The shear thinning behavior, which was clearly seen when high concentrations of egg white protein were added, is due to the denser and more interconnected protein network. As shear rate increases, the protein network aligns in the direction of flow, leading to a reduction in viscosity [32].
In regards to samples that were not heat treated, since no heat treatment was applied, the added proteins remained in their native form. In this state, protein–protein interactions were limited, as the hydrophobic and reactive regions of the proteins remained unexposed, preventing significant intermolecular interactions [33]. Additionally, whey protein’s high solubility and low intrinsic viscosity in solution contribute to its minimal impact on viscosity. Although egg white protein is less soluble than whey protein, the concentrations used were insufficient to reach saturation or to induce notable changes in the viscosity profile of the mixture [34].
5. Conclusions
The study evaluated the rheological and functional properties of liquid whole eggs enriched with whey and egg white proteins, providing significant insights into the impact of protein fortification on food systems. The results found that whey protein maintains near-Newtonian behavior across concentrations due to its high solubility and minimal protein–protein interactions in the native state. Meanwhile, egg white protein enrichment, particularly at higher concentrations, introduced substantial viscosity changes and shear thinning behavior attributed to its high water-binding capacity and partial denaturation upon heat treatment. These effects were more pronounced when proteins were added prior to heating, highlighting the influence of thermal processing on protein interactions. Since the current food trend for consumers focuses on a high protein content as a part of functional food diet, these finding are promising in terms of the ability to create a high-protein liquid egg product from a high-quality protein source.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.E. (Majd Elayan) and A.V.-T.; methodology, A.V.-T.; validation, I.D., formal analysis, I.D.; investigation, M.E. (Majd Elayan); resources, C.N.; data curation, M.E. (Majd Elayan); writing—original draft preparation, M.E. (Majd Elayan); writing—review and editing, M.E. (Munkhnasan Enkhbold) and L.F.; visualization, I.D.; supervision, L.F. and A.V.-T.; project administration, A.V.-T.; funding acquisition, L.F. and A.V.-T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Acknowledgments
We owe a great thanks to project 2023-1.1.1-PIACI_FÓKUSZ-2024-00035, “Development of age- and condition-specific functional foods focusing on active aging”, and the Department of Livestock Products and Food Preservation Technology, MATE, for providing their help for the experiment introduced in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Puglisi, M.J.; Fernandez, M.L. The Health Benefits of Egg Protein. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S. Functional Food Relevance of Whey Protein: A Review of Recent Findings and Scopes Ahead. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 19, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechevalier, V.; Guérin-Dubiard, C.; Anton, M.; Beaumal, V.; David Briand, E.; Gillard, A.; Le Gouar, Y.; Musikaphun, N.; Tanguy, G.; Pasco, M.; et al. Pasteurisation of Liquid Whole Egg: Optimal Heat Treatments in Relation to Its Functional, Nutritional, and Allergenic Properties. J. Food Eng. 2017, 195, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidas, K.I.; Nyulas-Zeke, I.C.; Visy, A.; Baranyai, L.; Nguyen, L.P.L.; Tóth, A.; Friedrich, L.; Nagy, A.; Németh, C. Effect of Combination of Salt and pH on Functional Properties of Frozen-Thawed Egg Yolk. Agriculture 2021, 11, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, P.M.; Fernández, A. Rheological Properties and Protein Quality of UV-C Processed Liquid Egg Products. Food Hydrocolloids 2013, 31, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xu, X.M.; Guo, S.D. Rheological, Texture and Sensory Properties of Low-Fat Mayonnaise with Different Fat Mimetics. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 40, 946–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Barbosa-Cánovas, G.V. Rheological Characterization of Mayonnaise. Part II: Flow and Viscoelastic Properties at Different Oil and Xanthan Gum Concentrations. J. Food Eng. 1995, 25, 409–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekiroglu, H.; Goktas, H.; Karaibrahim, D.; Bozkurt, F.; Sagdic, O. Determination of Rheological, Melting and Sensorial Properties and Volatile Compounds of Vegan Ice Cream Produced with Fresh and Dried Walnut Milk. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2022, 28, 100521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aidoo, R.P.; Afoakwa, E.O.; Dewettinck, K. Rheological Properties, Melting Behaviours and Physical Quality Characteristics of Sugar-Free Chocolates Processed Using Inulin/Polydextrose Bulking Mixtures Sweetened with Stevia and Thaumatin Extracts. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 62, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telis-Romero, J.; Thomaz, C.E.P.; Bernardi, M.; Telis, V.R.N.; Gabas, A.L. Rheological Properties and Fluid Dynamics of Egg Yolk. J. Food Eng. 2006, 74, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Sharma, H.K.; Premi, M.; Kumari, K. Effect of Storage Conditions of Egg on Rheological Properties of Liquid Whole Egg. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 51, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, J.; Ramaswamy, H.S.; Alli, I.; Ngadi, M. Effect of High Pressure on Rheological Characteristics of Liquid Egg. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2003, 36, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumbár, V.; Strnková, J.; Nedomová, Š.; Buchar, J. Fluid Dynamics of Liquid Egg Products. J. Biol. Phys. 2015, 41, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, E.R.; Rha, C. Apparent Shear Viscosity of Native Egg White. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 1982, 17, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atılgan, M.R.; Unluturk, S. Rheological Properties of Liquid Egg Products (LEPS). Int. J. Food Prop. 2008, 11, 296–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banovic, M.; Arvola, A.; Pennanen, K.; Duta, D.E.; Brückner-Gühmann, M.; Lähteenmäki, L.; Grunert, K.G. Foods with Increased Protein Content: A Qualitative Study on European Consumer Preferences and Perceptions. Appetite 2018, 125, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovai, D.; Watson, M.E.; Barbano, D.M.; Drake, M.A. Consumer Acceptance of Protein Beverage Ingredients: Less Is More. J. Dairy Sci. 2025, 108, 1392–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uysal, R.S.; Boyaci, I.H.; Sumnu, G. Determination of Pasteurization Treatment of Liquid Whole Egg by Measuring Physical and Rheological Properties of Cake Cream. J. Food Process Eng. 2019, 42, e13167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yogesh, K. Pulsed Electric Field Processing of Egg Products: A Review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 934–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission. What Is a Nutrition Claim? Food Safety. Available online: https://food.ec.europa.eu/food-safety/labelling-and-nutrition/nutrition-and-health-claims/nutrition-claims_en (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Matsuoka, R.; Kurihara, H.; Nishijima, N.; Oda, Y.; Handa, A. Egg White Hydrolysate Retains the Nutritional Value of Proteins and Is Quickly Absorbed in Rats. Sci. World J. 2019, 2019, 5475302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga-Tóth, A.; Németh, C.; Dalmadi, I.; Csurka, T.; Csorba, R.; Elayan, M.; Enkhbold, M.; Hidas, K.; Friedrich, L.F. Investigation of the Effects of Bovine Collagen Peptides and Mixed Berries on Rheological Properties and Biological Activity of Egg White-Based Beverage via Central Composite Design. Front. Nutr. 2023, 9, 1011553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittek, P.; Walther, G.; Karbstein, H.P.; Emin, M.A. Comparison of the Rheological Properties of Plant Proteins from Various Sources for Extrusion Applications. Foods 2021, 10, 1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Jiménez, N.T.; Ulloa, J.A.; Urías-Silvas, J.E.; Hidalgo-Millán, A. Modification of Rheological Properties of Animal and Vegetable Proteins Treated with High-intensity Ultrasound: A Review. Food Front. 2023, 4, 700–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovato, S.; Keetels, G.H.; Toxopeus, S.L.; Settels, J.W. An Eddy-Viscosity Model for Turbulent Flows of Herschel–Bulkley Fluids. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 2022, 301, 104729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumbár, V.; Nedomová, Š.; Strnková, J.; Buchar, J. Effect of Egg Storage Duration on the Rheology of Liquid Egg Products. J. Food Eng. 2015, 156, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.; Iwashita, K.; Shiraki, K. Viscosity Control of Protein Solution by Small Solutes: A Review. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2018, 19, 746–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yang, J.; Li, J.; Gantumur, M.-A.; Wei, X.; Oh, K.-C.; Jiang, Z. Structure and Rheological Properties of Extruded Whey Protein Isolate: Impact of Inulin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 226, 1570–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonchamp, J.; Clegg, P.S.; Euston, S.R. Functional Enhancement of Whey Protein Concentrate and Egg by Partial Denaturation and Co-Processing. Food Biosci. 2022, 49, 101895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Foegeding, E.A. The Stability and Physical Properties of Egg White and Whey Protein Foams Explained Based on Microstructure and Interfacial Properties. Food Hydrocolloids 2011, 25, 1687–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, C.; Gu, L.; Su, Y.; Chang, C.; Yang, Y. Gel Properties of Salty Liquid Whole Egg as Affected by Preheat Treatment. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollister, J.C.P.; Wang, A.C.; Kim, W.; Giza, C.C.; Prins, M.L.; Kavehpour, H.P. Shear Thinning Behavior of Cerebrospinal Fluid with Elevated Protein or Cellular Concentration. Front. Phys. 2023, 11, 1308136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhao, T.; Li, H.; Yu, J. Effect of Heat Treatment on the Property, Structure, and Aggregation of Skim Milk Proteins. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 714869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farjami, T.; Babaei, J.; Nau, F.; Dupont, D.; Madadlou, A. Effects of Thermal, Non-Thermal, and Emulsification Processes on the Gastrointestinal Digestibility of Egg White Proteins. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 107, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).