A Combined Dynamic–Kinematic Extended Kalman Filter for Estimating Vehicle Sideslip Angle
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Combined Extended Kalman Filter
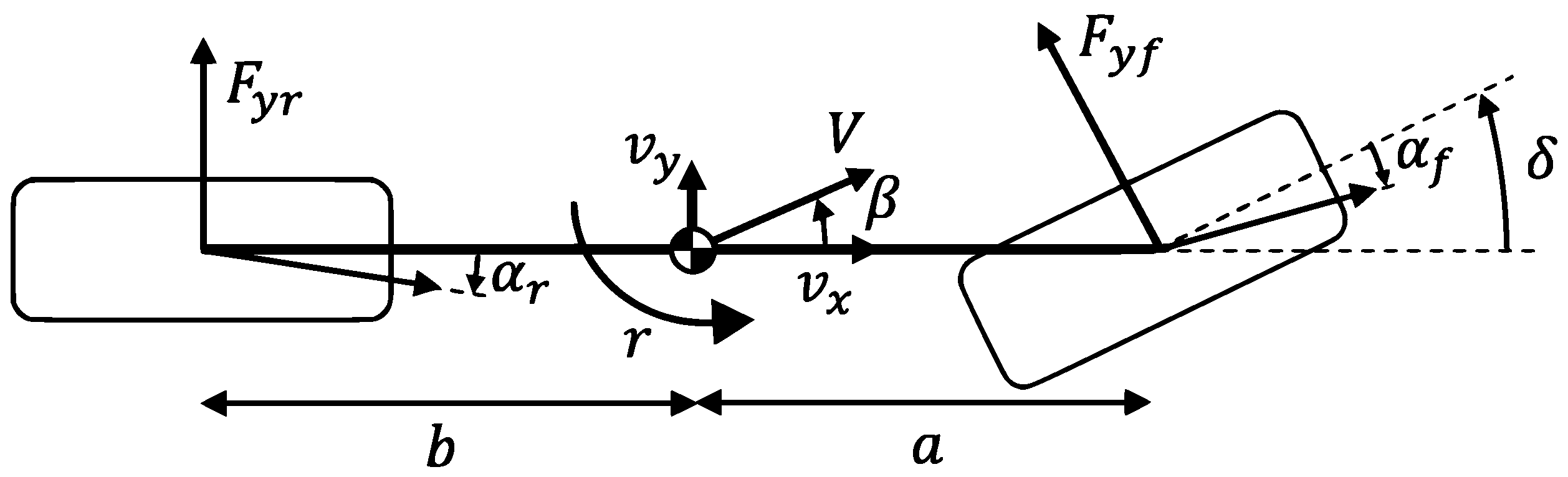
2.1. Dynamic Model
2.2. Kinematic Model
2.3. Combined Dynamic–Kinematic EKF
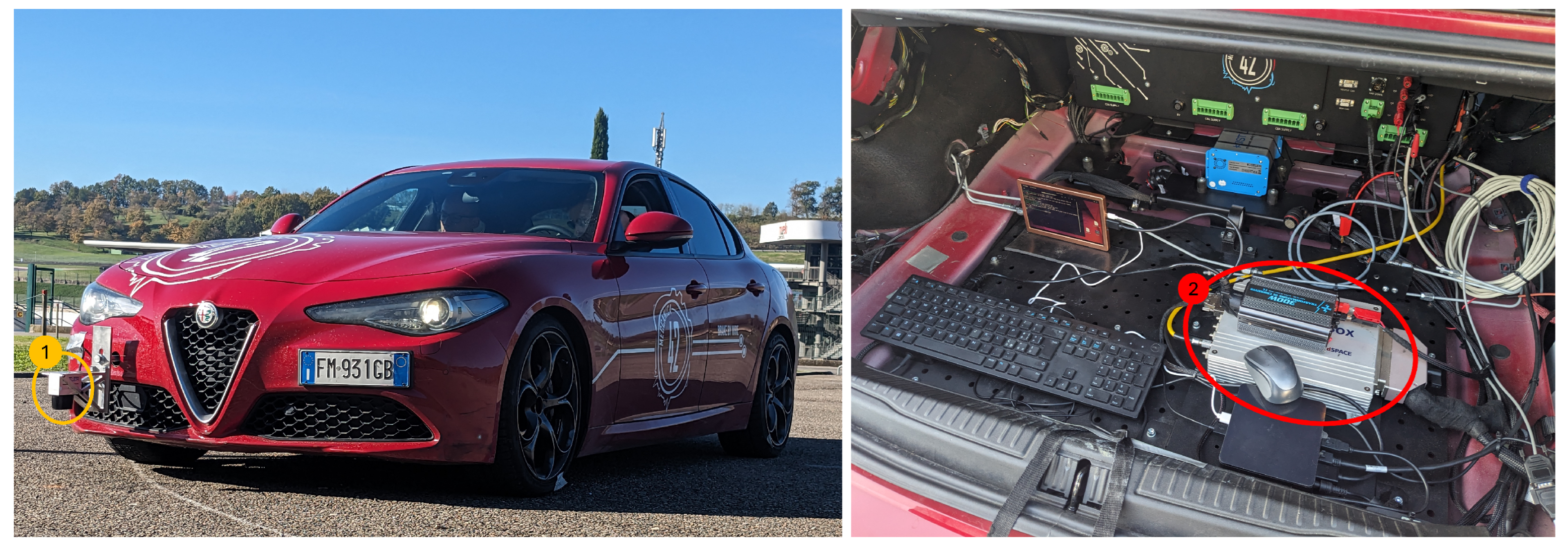
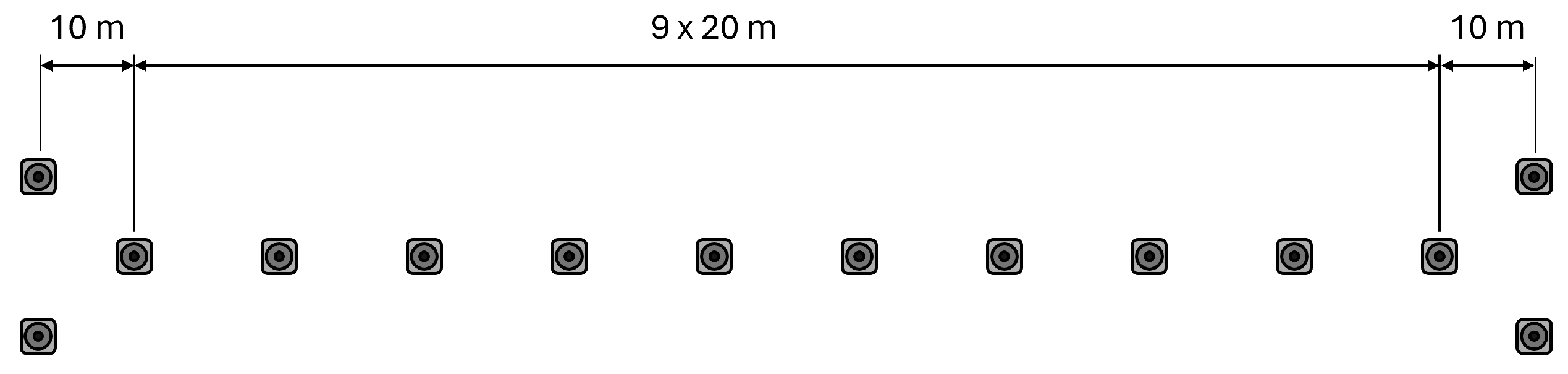
3. Experimental Setup
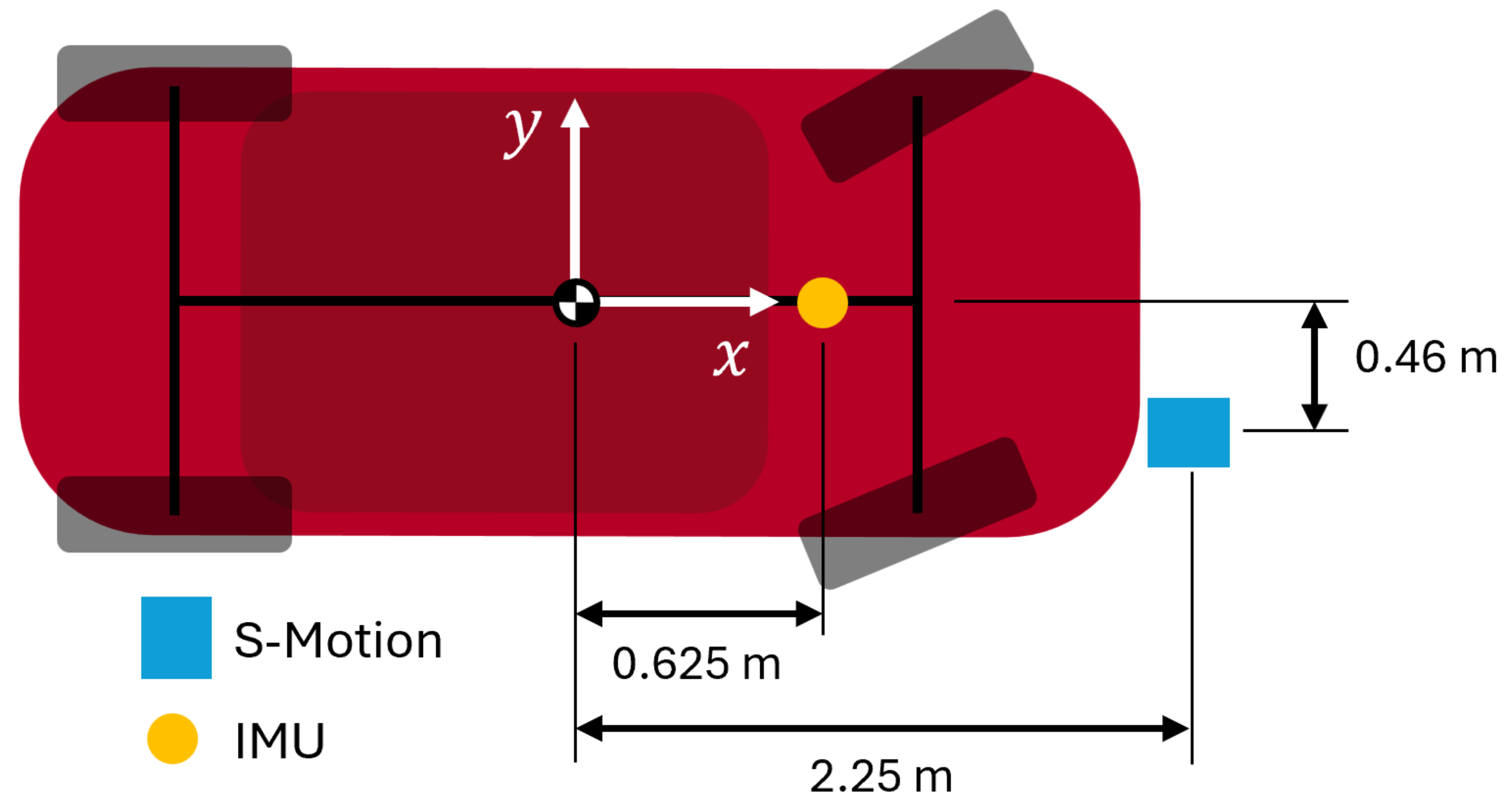
- Kistler Correvit S-motion. It is an optical sensor for measuring the overall vehicle velocity V and the sideslip angle . It is herein used to provide a reliable ground-truth comparison.
- dSPACE MicroAutoBox II. It serves as a signal logger, ensuring the synchronization of all recorded signals. Signals logged from the vehicle CAN include accelerations , , yaw rate r, wheel velocities and the steering angle, . Additionally, the dSPACE MicroAutoBox is a powerful real-time system with a high-performance multi-core processor, adept at handling complex control tasks with low latency, making it an excellent candidate for an ECU validation platform.
3.1. Signal Pre-Processing
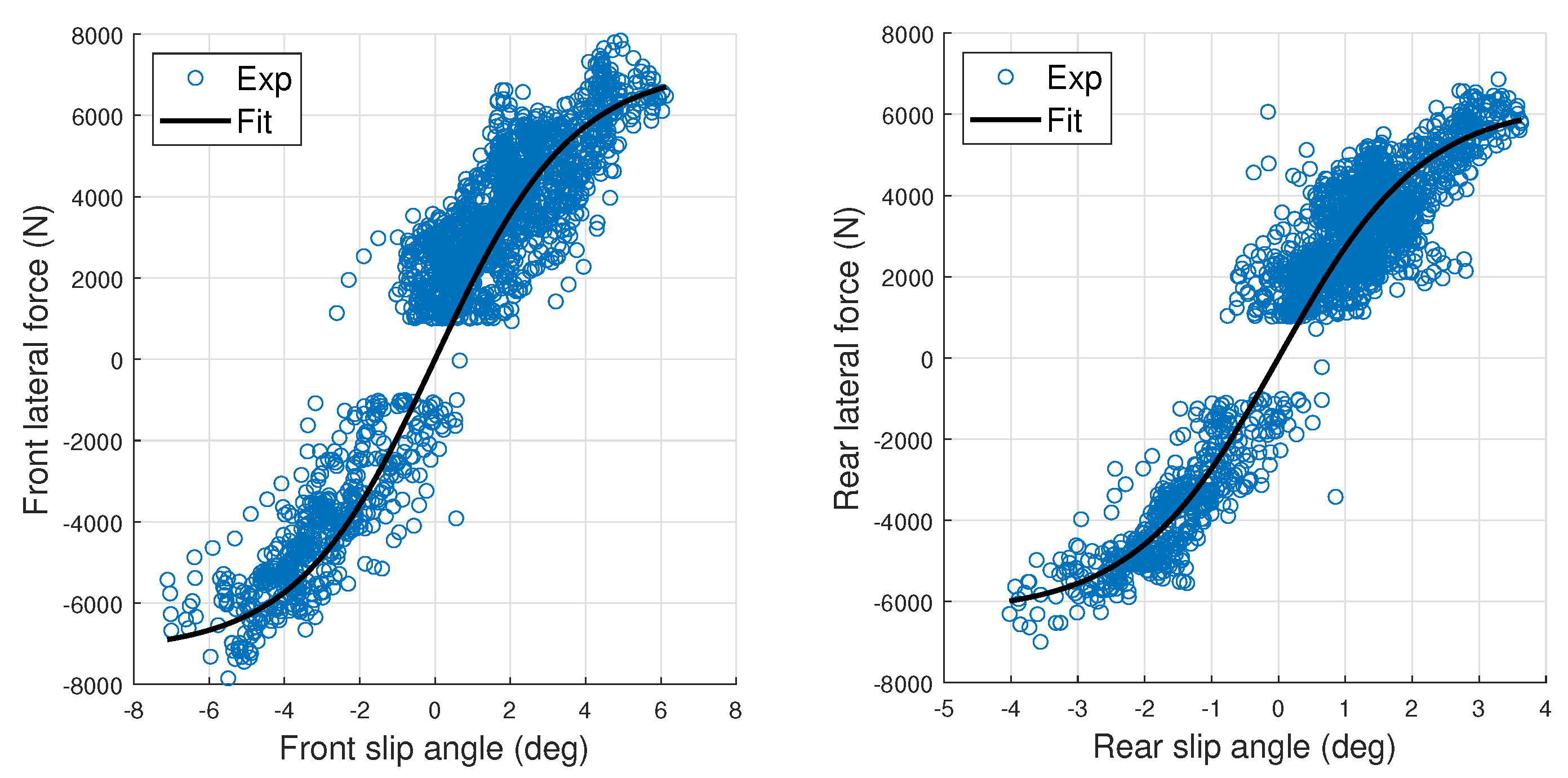
3.2. Experimental Lateral Characteristics of Front and Rear Axles
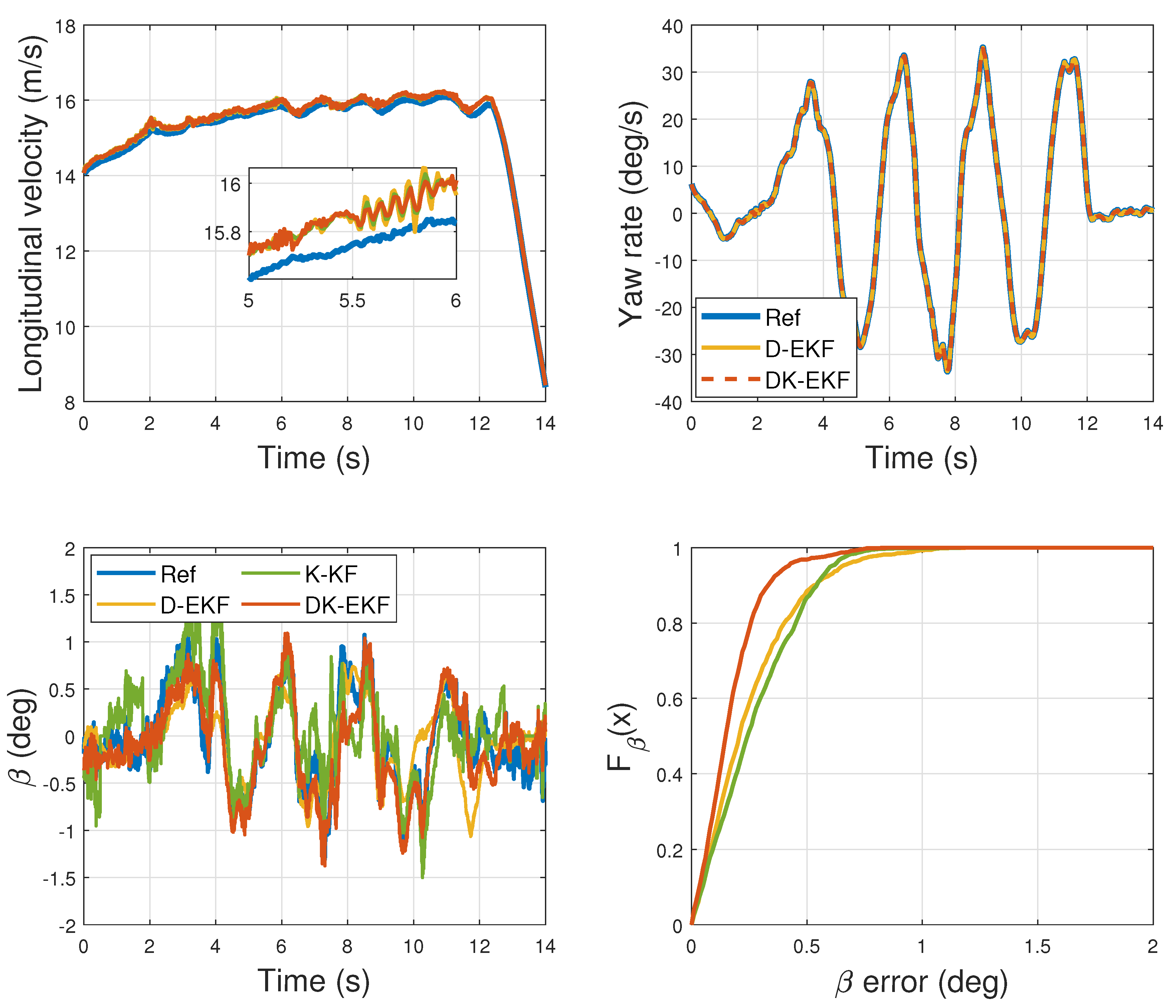
4. Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bertipaglia, A.; de Mol, D.; Alirezaei, M.; Happee, R.; Shyrokau, B. Model-Based vs Data-Driven Estimation of Vehicle Sideslip Angle and Benefits of Tyre Force Measurements. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.15119. [Google Scholar]
- Melzi, S.; Sabbioni, E. On the vehicle sideslip angle estimation through neural networks: Numerical and experimental results. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2011, 25, 2005–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Sun, H.; Qian, K.; Li, Y.; Lu, L. A prediction model for vehicle sideslip angle based on neural network. In Proceedings of the 2010 2nd IEEE International Conference on Information and Financial Engineering, Chongqing, China, 17–19 September 2010; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 451–455. [Google Scholar]
- Gurney, K. An Introduction to Neural Networks; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zhang, J. Vehicle sideslip angle estimation based on hybrid Kalman filter. Math. Probl. Eng. 2016, 2016, 3269142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungoren, A.Y.; Peng, H.; Tseng, H. A study on lateral speed estimation methods. Int. J. Veh. Auton. Syst. 2004, 2, 126–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.C.; Hsieh, F.C. Sideslip angle estimation using extended Kalman filter. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2008, 46, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chindamo, D.; Lenzo, B.; Gadola, M. On the vehicle sideslip angle estimation: A literature review of methods, models, and innovations. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Aalst, S.; Naets, F.; Boulkroune, B.; De Nijs, W.; Desmet, W. An adaptive vehicle sideslip estimator for reliable estimation in low and high excitation driving. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2018, 51, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naets, F.; van Aalst, S.; Boulkroune, B.; El Ghouti, N.; Desmet, W. Design and experimental validation of a stable two-stage estimator for automotive sideslip angle and tire parameters. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2017, 66, 9727–9742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnier, S.; Corno, M.; Savaresi, S.M. Hybrid Kinematic-Dynamic Sideslip and Friction Estimation. J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control. 2023, 145, 051004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villano, E.; Lenzo, B.; Sakhnevych, A. Cross-combined UKF for vehicle sideslip angle estimation with a modified Dugoff tire model: Design and experimental results. Meccanica 2021, 56, 2653–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahangarnejad, A.H.; Başlamışlı, S.Ç. Adap-tyre: DEKF filtering for vehicle state estimation based on tyre parameter adaptation. Int. J. Veh. Des. 2016, 71, 52–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonov, S.; Fehn, A.; Kugi, A. Unscented Kalman filter for vehicle state estimation. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2011, 49, 1497–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, J. Estimation of vehicle speed and tire-road adhesion coefficient by adaptive unscented Kalman filter. J. Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. 2016, 50, 68–75. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, H.; Chen, S.; Liu, G.; Zheng, K. Vehicle state information estimation with the unscented Kalman filter. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2014, 6, 589397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righetti, G.; Binetti, E.; de Castro, R.P.; Lot, R.; Massaro, M.; Lenzo, B. On the Investigation of Car Steady-State Cornering Equilibria and Drifting; Technical Report, SAE Technical Paper, Detroit; SAE International: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Selmanaj, D.; Corno, M.; Panzani, G.; Savaresi, S.M. Vehicle sideslip estimation: A kinematic based approach. Control. Eng. Pract. 2017, 67, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hautus, M.L. Controllability and observability conditions of linear autonomous systems. Ned. Akad. Wet. 1969, 72, 443–448. [Google Scholar]
- Mosconi, L.; Farroni, F.; Sakhnevych, A.; Timpone, F.; Gerbino, F.S. Adaptive vehicle dynamics state estimator for onboard automotive applications and performance analysis. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2023, 61, 3244–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 3888-2: 2011; Passenger Cars—Test Track for a Severe Lane-Change Manoeuvre—Part 2: Obstacle Avoidance. International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2011.
- GB/T 6323-2014; Controllability and Stability Test Procedure for Automobile [S]. China Standard Press: Beijing, China, 2014.
- Selmanaj, D.; Corno, M.; Panzani, G.; Savaresi, S.M. Robust vehicle sideslip estimation based on kinematic considerations. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2017, 50, 14855–14860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guiggiani, M. The Science of Vehicle Dynamics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, D. Optimal State Estimation: Kalman, H Infinity, and Nonlinear Approaches; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Madhusudhanan, A.K.; Corno, M.; Holweg, E. Vehicle sideslip estimator using load sensing bearings. Control. Eng. Pract. 2016, 54, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameter | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Mass | m | 1525 kg |
| Yaw moment of inertia | 2130 kg m2 | |
| COG to front axle distance | a | 1.315 m |
| COG to rear axle distance | b | 1.505 m |
| Front track | 1.557 m | |
| Rear track | 1.625 m | |
| Front cornering stiffness | 115 kN/rad | |
| Rear cornering stiffness | 165 kN/rad | |
| Tyre-road friction coefficient | 0.9 |
| Strategy | DLC | Slalom |
|---|---|---|
| D-EKF | 0.40 deg | 0.33 deg |
| K-KF | 0.60 deg | 0.33 deg |
| DK-EKF | 0.27 deg | 0.22 deg |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Righetti, G.; Lenzo, B. A Combined Dynamic–Kinematic Extended Kalman Filter for Estimating Vehicle Sideslip Angle. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 1365. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15031365
Righetti G, Lenzo B. A Combined Dynamic–Kinematic Extended Kalman Filter for Estimating Vehicle Sideslip Angle. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(3):1365. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15031365
Chicago/Turabian StyleRighetti, Giovanni, and Basilio Lenzo. 2025. "A Combined Dynamic–Kinematic Extended Kalman Filter for Estimating Vehicle Sideslip Angle" Applied Sciences 15, no. 3: 1365. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15031365
APA StyleRighetti, G., & Lenzo, B. (2025). A Combined Dynamic–Kinematic Extended Kalman Filter for Estimating Vehicle Sideslip Angle. Applied Sciences, 15(3), 1365. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15031365







