Abstract
Background/Aim: The purpose of this study was to reproduce a lateral fall using a computer simulation model and to clarify the circumstances of mandible fracture caused by a lateral impact. Material and methods: Fall scenarios were reconstructed using a computer simulation with finite element models. The fall condition was set as a fall from the head direction, which would cause facial injuries. In each simulation, the effective plastic strain of the mandible and its site were determined. Analysis of variance was performed to determine which factors had a significant effect on the maximum effective plastic strain of the mandible. Results: Significant differences with p-values less than 0.001 were found for the following factors: pitch angle, lateral bending angle, impact object, combination of pitch angle and lateral bending angle, and combination of pitch angle and impact object. In most cases with higher values of effective plastic strain, which can cause mandibular fractures, the site was found at the condylar process or mandibular angle of the attacked side. Conclusion: If the patient falls laterally and their face makes contact with a protruding object, medical professionals can predict fractures of the upper part of the mandibular angle and the condyle of the affected side.
1. Introduction
Recently, aging and low birth rates have become a serious problem in developed countries. With demographic and various social changes, such as the greater number of older persons living alone and leading an active retirement, older persons may be at increased risk for trauma, including maxillofacial fractures. Because of their diminished cognitive and motor skills, poor balance, slow reflexes, and weakened eyesight, falling has become the predominant cause of unintentional injury in Japan. Falling is also a major cause of oral and maxillofacial fractures. According to a study of older patients aged 60 years or more, who were admitted to 14 maxillofacial surgery departments worldwide, the leading cause of maxillofacial fracture was falling, accounting for 66.4% [1]. Another study for older adults also suggested that the most common cause of maxillofacial fracture was falling [2]. Fasola et al. indicated that falling-related maxillofacial fractures on a level surface occurred more frequently in older adults because the ability to avoid environmental hazards was reduced by age-related changes [3]. Maxillofacial fractures result in severe morbidity, loss of function, and disfigurement. Subsequent long hospital stays and disability can influence the quality of life of a patient. According to a study of bicyclists and motorcyclists, the number of fracture lines and intermaxillary fixation were independent factors for long-term hospitalization [4]. In addition, a study of patients who had fallen suggested that the number of injured teeth and intermaxillary fixation were independent predictive factors for a treatment duration of more than 1 month [5]. Therefore, preventing maxillofacial fracture and the use of intermaxillary fixation are required to maintain the daily activities of patients and maintain a reasonable quality of life.
The mandible is the most common site of all maxillofacial fractures. A previous study reported the most common fracture site of older adults was the mandible (56.7%), followed by the middle face (36.4%), and the mandible and middle face (16.9%) [5]. Particularly for patients who had fallen, this trend was dominant and accounted for 70.6% to 79.7% of all cases of falling [5,6,7]. The anterior region of the mandible was reported to be the most frequent site impacted by falling due to its exposed position in the facial skeleton [5,6,7,8]. Therefore, the mechanism of mandibular fracture caused by anterior impact has been analyzed [9]. In real-world injuries, substantial numbers of persons fall laterally, and the lateral region of the face can also be impacted. A retrospective analysis of 185 mandibular fractures resulting from falling in 109 patients showed that the condyle was the most common fractured site (92 cases), followed by the symphysis (46 cases), body (21 cases), angle (20 cases), ramus (5 cases), and coronoid process (1 case) [10].
In biomechanical research regarding lateral impacts, Liu et al. applied a 2 kN force to the angle of the mandibular body and investigated the stress distribution using a finite element (FE) model [11]. In the presence of a third molar, the ipsilateral mandibular angle showed a higher risk of fracture than the condyle. In a study by Ma et al., a similar force was applied to the right body of the mandible, and the effects were studied using an FE model. When a third molar was absent, the stress was evenly distributed across the internal and external oblique lines of the mandible, which reduced the risk of mandibular angle fracture [12]. Hedesiu et al. applied a force corresponding to the fall of the head from a height of 2 m on the lateral region of the mandible using an FE model [13] and found that the condylar region was susceptible to fracture. However, no studies have investigated the mechanism of mandibular fracture caused by a lateral fall using a whole-body simulation. If the characteristics and mechanisms of mandibular fracture under these circumstances are elucidated, maxillofacial surgeons would be able to estimate the risk of fracture when provided with information regarding a fall and initiate prompt treatment. Furthermore, the risk of mandibular fracture could be described to older adults and the use of effective preventive measures, such as using a stick or a facial guard, could be promoted. The objectives of the present study were to reconstruct a lateral fall using a computer simulation model and to elucidate the mechanism underlying mandibular fractures caused by a lateral impact.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Computational Model
Falling scenarios were reconstructed using a computer simulation with FE models. The Total Human Model for Safety (THUMS) model (version 4.02), developed by Toyota Motor Corporation and Toyota Central R&D Laboratories, was used in this study [14]. THUMS is a virtual human body model software program for computer analysis of human body injuries. It consists of all deformable human body parts with anatomical geometry and biomechanical properties. This model consisted of approximately 0.78 million nodes and 2.0 million elements and had a height of 175.0 cm and a weight of 77.4 kg, which corresponded to 50th-percentile American adult male anthropometric values [14,15]. The cortical bone of the mandible was modeled using structural shell elements with a constant thickness of 1.5 mm, and the trabecular bone of the mandible was modeled using hexahedral solid elements. Isotropic elastoplastic constitutive equations were applied to both the cortical and trabecular bone. The Young’s modulus and the yield stress of the cortical bone were 10.5 GPa and 47.9 MPa, and those of the trabecular bone were 0.20 GPa and 0.70 MPa, respectively. Each simulation was conducted using LS-DYNA (version 971, R11.1.0) (Ansys, Canonsburg, PA, USA) configured to run in a massively parallel processing configuration on an HPCT W216s workstation (HPCTECH Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) with a Xeon Gold 6242 CPU running Windows 10 ×64 [16]. The total run time per simulation was approximately 8 h, with 16 CPU per run.
2.2. Fall Conditions
Lateral falling was modeled from a height of 1.0 m, which is similar to the height of the face of an older person, with contact between the lower face and the ground occurring at a velocity of 4.43 m/s. The falling condition was set as falling from the head direction to cause facial injuries. Since several factors affect the mechanisms associated with injuries: the pitch angle, roll angle, the body around the long axis, the angle of lateral bending of the face, and the impact object. The test factors and their possible conditions are shown in Figure 1. Detailed boundary conditions are as follows:
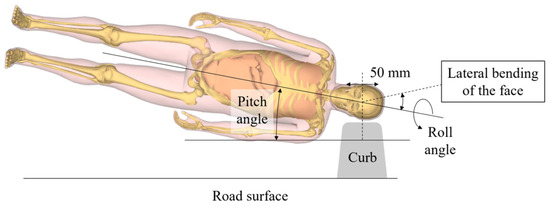
Figure 1.
Factors related to falling conditions.
- Pitch angle: Oblique orientation of the body at time of impact of 10° or 20° to the horizontal surface. Because we aimed to simulate a lateral fall, we did not set a larger pitch angle.
- Roll angle of the body around the long axis: Rolling to a prone position from a lateral position at 0° (lateral position), 15°, or 30°.
- Lateral bending of the face: Without lateral bending or bending to the opposite side to the falling direction at 20°. For this factor, we set these two conditions because we evaluated the effects of lateral bending to the opposite side.
- Impact object: At the time of impact, the face contacts the surface of a road or concrete block. A concrete block was represented as the boundary block between the sidewalk and road. The most common size of a boundary block is shown in Figure 2. The center of the block was considered to be the impact point to the center of the head. Then, the attacked site was shifted toward the head direction by 50 mm or to the toe direction by 50 mm (represented as −50 mm). The ground was modeled as an asphalt surface with a rigid wall with a friction coefficient of 0.5. Detailed boundary conditions are shown in Table 1.
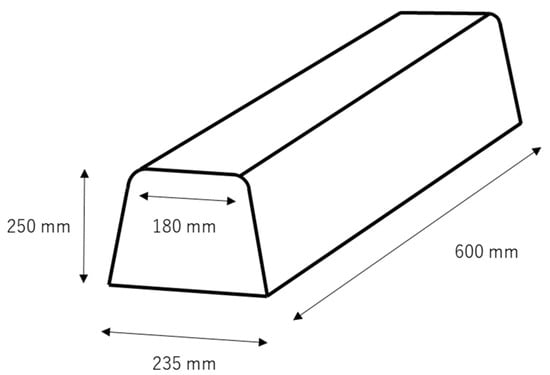 Figure 2. The shape of the simulated concrete block.
Figure 2. The shape of the simulated concrete block. Table 1. The test factors and their possible conditions during the simulation.
Table 1. The test factors and their possible conditions during the simulation.
2.3. Statistical Analyses
The Taguchi full factorial design was applied in the present analysis. Taguchi procedures were created to improve the quality of product items and have recently been used in engineering methods [17]. The full factorial method contained all feasible sets of conditions. In this study, the orientation of the body, roll angle of the body, degree of lateral bending of the face, and impact object were factors considered to be influencing factors for mandible fractures caused by a lateral impact. When considering the number of sets in each factor, the number of simulations was 48 (2 × 2 × 3 × 4). In each simulation, the effective plastic strain on the THUMS mandible and its site were determined.
To identify the factors affecting the maximum value of the effective plastic strain of the mandible, an analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed. One-way ANOVA was conducted to examine the significance of differences among the factors tested, including the orientation of the body, roll angle of the body, and degree of lateral bending of the face and impact object. A two-way ANOVA was used to determine significant differences between the combination of four factors. The contribution rate in each ANOVA was also calculated. According to previous studies, the failure plastic strain of the cortical bone of an individual aged approximately 60 years was considered to be approximately 0.015 [18,19]. Therefore, the threshold of a mandible fracture with an effective plastic strain of 0.015 was determined.
3. Results
3.1. Kinematics of the Human Model
The kinematics of the human model are shown for a representative case with a pitch role of 10°, a roll angle of 15°, and lateral bending of 20° after contact with the center of the concrete block (Figure 3). The left side of the head contacted the concrete block and rebounded 6 ms later. Following the body movement, the head moved downward again at 22 ms. At 32 ms, the left side of the mandible and left arm collided with the concrete block and the road surface, respectively. The head and face started to bend and rotate to the right following contact of the face with the concrete block. In this situation, the maximum value of the effective plastic strain was 0.089, and it occurred at the upper part of the mandible angle (close to the buccinator crest). The head and face were bent to the right following contact with the face.
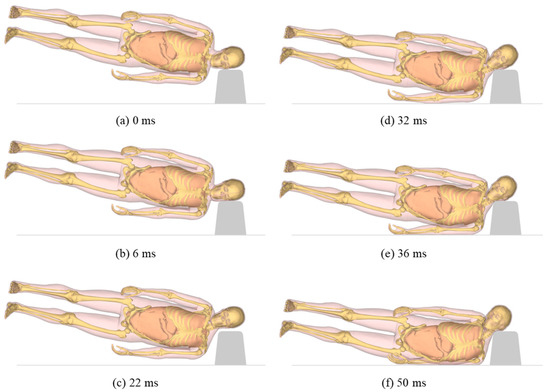
Figure 3.
A representative simulation of the kinematics of the human model, according to the time elapsed after the initial contact (pitch angle: 10°, roll angle: 15°, lateral bending of the face: 20°, impact location: center of the block).
Figure 4 shows the kinematic behavior of the skull, upper face, and mandible at impact, using the same simulation as that in Figure 3. The left temporal bone and zygomatic bone contacted the concrete block at the 10-ms time point. As a result, the neurocranium and the left temporomandibular joint stopped suddenly. However, the mandibular symphysis continued to move toward the concrete block, owing to inertia. This caused shear and torsional displacement between the neurocranium and mandible, after which the skull rebounded. At 42 ms, the mandible made contact with the concrete block surface directly, owing to the rotation of the head.
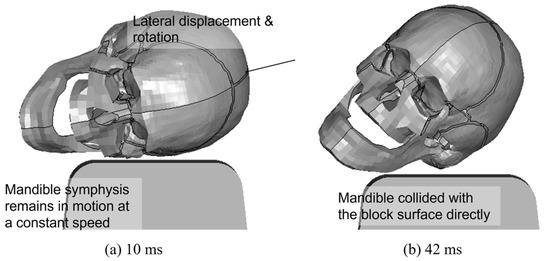
Figure 4.
Kinematic behavior of the skull, upper face, and mandible in the same simulation as in Figure 3 (pitch angle: 10°, roll angle: 15°, neck lateral bending: 20°, impact location: center of the block).
Figure 5 shows the von Mises stress distribution in the same simulation as that shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4. At 12 ms, high stress was observed in the right side of the mandible, owing to relative displacement between the neurocranium and mandible, as shown in Figure 4a. The highest stress was identified in the left side of the mandible at 44 ms, which was caused by direct contact with the concrete block surface, as shown in Figure 4b.
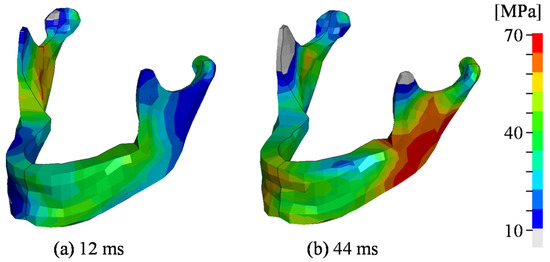
Figure 5.
Distribution of von Mises stress on the mandible in the same simulation as that shown in Figure 3 (pitch angle: 10°, roll angle: 15°, neck lateral bending: 20°, impact location: center of the block).
3.2. Distribution of the Maximum Effective Plastic Strain in the Mandible
The distribution of the maximum effective plastic strain in the mandible of the model for each simulation is shown in Figure 6. The highest values of effective plastic strain were found at the condylar process of the attacked side and the upper and lower parts of the mandibular angle on the same side. The values obtained were divided into a high value (0.015 or more), which was beyond the threshold of the fracture, and a low value (less than 0.015). Among the 48 simulations, high values were found in 27 cases, and low values were found in 21 cases, according to Figure 6. In most cases with high values, the site was at the condylar process or upper part of the mandible angle of the affected site.
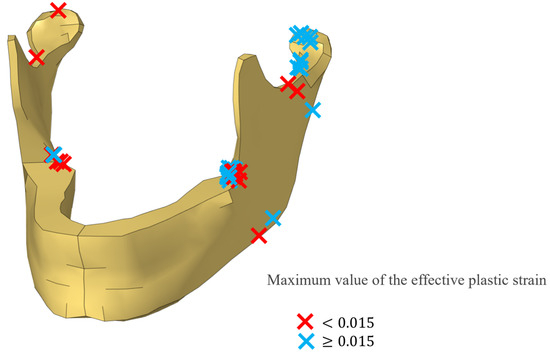
Figure 6.
Distribution of the sites with the highest effective plastic strain levels in all the simulations. The blue crosses indicate the maximum values of effective plastic strain ≥ 0.015, and the red crosses indicate values of <0.015.
In some individuals, only the left temporal bone made contact with the concrete block. Because the mandible did not make contact with the concrete block, the neurocranium stopped suddenly, but the mandible continued to move toward the concrete block, owing to inertia. This caused shear displacement between the neurocranium and mandible and bending of both the left and right temporomandibular joints. Therefore, the highest effective plastic strains were found on the right side of the mandible.
3.3. Factors That Strongly Influenced Fracture of the Mandible
The results of the ANOVA are shown in Table 2. Significant differences with p-values less than 0.001 were found for the following factors: pitch angle, lateral bending of the face, impact object, combination of pitch angle and lateral bending of the face, and combination of pitch angle and impact object. Regarding the cumulative contribution rate, among these five factors, the highest rate was 23.40% for the impact object, followed by 22.70% for lateral bending of the face.

Table 2.
Results of the analysis of variance and contribution rates.
Next, a graph of factorial effects was generated (Figure 7) to show the interval plot of effective plastic strain vs. pitch angle, roll angle, lateral bending of the face, and the impact object. The mean response was plotted against the variable level of each factor. The effective plastic strain was markedly increased when the angle of lateral bending of the face varied from 0 to 20° and when the impact object varied from road surface to concrete block contacting with the center of the lateral surface of the head. These results reflected the higher cumulative contribution rate of the lateral bending angle and impact object.
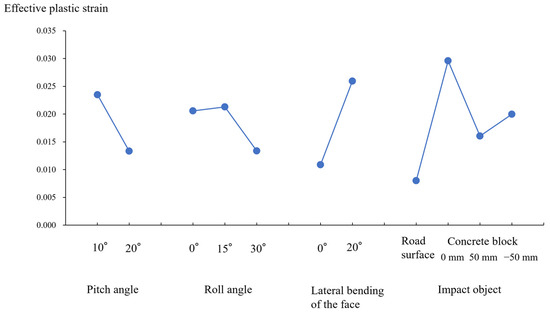
Figure 7.
Estimation of the factor effect.
4. Discussion
A previous study reported that when falling, the body position at the time of impact was a significant factor that affected injury severity and an impact to the lateral region was a significant factor that influenced the injury severity score [20]. Therefore, the mechanism of injury related to a lateral impact when falling should be analyzed to reduce the severity of injuries related to falling.
Reconstruction technology using computer simulations has been widely used to analyze injuries. Specifically, reconstructions of falls by means of computer simulation models have been performed. FE models can be used to simulate deformation modes and force responses accurately. In addition, it is possible to predict whether bones would fracture under given impact conditions by assuming their stress–strain properties around the fracture sites. Research using a human FE model is an advanced method of predicting impact behavior and mechanical responses. The mechanisms involved in mandibular injuries have been evaluated using FE models of the mandible [11,12,13,21]. Hedesiu et al. simulated the conditions of a lateral fall using an FE model of the mandible, but in the present study, we reconstructed a lateral fall using a more sophisticated whole-body FE model [13]. Tsutsumi et al. characterized the mechanisms of mandibular fractures in cyclists using the same FE model as in the present study [21]. They reconstructed cyclist injury scenarios, namely an individual falls from a bicyclist in a forward direction and their face makes contact with the road surface, using a similar simulation model to our analysis. Since the mandible was the most common fractured site, they reconstructed injuries to the frontal region of the mandible. In these simulations, higher von Mises stresses were noted in the mandible when the center of the mandibular body struck the road surface.
The conditions leading to and frequent sites of mandibular fracture due to a lateral impact as well as the main contributing factors, were examined using FE model analyses in the present study. The impact object and angle of lateral bending of the face strongly influenced the occurrence of mandibular fractures. Contact of the center of the head with the concrete block was the most probable cause of mandibular fractures. When a victim falls laterally, the shoulder or upper arm contacts the road surface before the head, and the speed of the fall of the whole body is reduced, leading to a decreased impact force on the face. However, if the protruding object contacts the center of the head, a higher stress might be produced at the face.
Regarding the lateral bending of the face, bending to the opposite side of the falling direction by 20° was the most probable condition, resulting in higher stress to the mandible. If there is no bending, the lateral head will have the dominant contact with the block, and less force will be applied to the mandible.
In addition, the pitch angle also influenced the occurrence of mandible fractures. The distance between the mandible and concrete block was less when the pitch angle was 10° compared with 20°, indicating higher stress was obtained with a pitch angle of 10°.
The condylar process and upper region of the mandibular angle of the impacted side were the most common sites of mandibular fractures. A previous study reported higher stress at impact on the alveolar and mandibular body, which are common fracture sites, after frontal impact on the mandible [21]. These phenomena were related to direct and indirect forces. When direct forces are applied to the front side of the mandible, the mandibular body is fractured. During contact, indirect forces are applied backward to the alveolar region. The present study demonstrated that even after a lateral impact, direct and indirect forces are involved in fractures. These forces were mainly applied to areas surrounding the upper region of the mandibular angle, leading to a subsequent fracture at this site. Generally, the third molar is present at this site, and this might contribute to the increased vulnerability of the mandible because the mandible loses some of its bony structure by the third molar [12,22]. Reitzik et al. [23] reported that fractures of the mandibles of monkeys with a third molar required less force compared with those without a third molar (60% of the required forces). Therefore, fractures of the upper part of the mandibular angle occur frequently after a direct lateral impact. At impact, the attacked side of the lateral body of the mandible is deflected to the opposite side, and higher indirect stress occurs at the condylar. The present study is the first to clarify the biomechanical mechanisms related to the common fracture site in the mandible after a lateral fall, using a sophisticated whole-body FE model. The results obtained herein may be useful when managing patients. According to the patients’ and witnesses’ testimonies, if the patient falls laterally and the face makes contact with a protruding object, medical professionals can predict fractures of the upper part of the mandibular angle and the condyle of the affected side. Furthermore, this information may be useful for paramedics in that they may predict the site of mandible fractures and transport patients to appropriate medical institutions with maxillofacial surgeons.
The present study reconstructed the mandibular fractures in older adults that were caused by falling laterally. Once a mandibular fracture occurs, a long hospital stay with surgery is required. According to an analysis of cyclists and motorcyclists with oral and maxillofacial injuries, the number of fractured lines and intermaxillary fixation were independent factors for long-term hospitalization [6]. Another study on patients with oral and maxillofacial injuries by falling or falls from a height suggested that the number of injured teeth and intermaxillary fixation were significant factors affecting the duration of treatment [7]. Therefore, if an individual falls laterally and the face is affected, long hospitalization is necessary. Long hospitalization by the elderly may result in frailty, such as a decline in muscle and cognitive function. Therefore, strategies to avoid falling, such as using a stick and daily exercise to prevent frailty, are recommended. Furthermore, in older adults who frequently fall, the use of a facial guard is recommended. Based on the present results, effective preventive measures need to be established in order to maintain the quality of life of older adults.
This study had some limitations. First, lateral falls were modeled from a height of 1.0 m. This height was chosen to represent a situation where an older person fell laterally from a standing position. However, there may be a variety of initial positions, such as a semi-standing position. Therefore, in the future, similar simulations should vary the initial falling height or initial body position. Second, a concrete block of a certain size was modeled. Boundary blocks used for sidewalks and roads are highly variable, and only one size was modeled. However, any object protruding from the floor can make contact with a face when a person falls; thus, various sizes and shapes of boundary blocks should be analyzed in future simulations. Third, the shape of this model was based on the anatomical geometry of human adults, but the mandibular shape differs between individuals. Also, bone mechanical properties differ mainly according to age. Furthermore, using this model, although soft tissues, such as membrane and fatty tissues, were incorporated, the cushioning effects of the soft tissues of the face were not evaluated in detail. These factors might affect the distribution of the plastic strain. In the future, the present results should be confirmed using studies of patients who had experienced a mandibular fracture owing to a lateral fall. Fourth, the threshold of the fracture was set at an effective plastic strain of 0.015. This was based on the results of previous biomechanical studies of humans aged approximately 60 years old. However, in developed countries, including Japan, aging has progressed, and falling is more common among older adults. Because the effective plastic strain, which represents the threshold of the fracture, decreases according to age, further analyses with variable fracture thresholds should be performed. Furthermore, in the present study, bone fracture was predicted using the effective plastic strain. When using this method, a fracture is considered to have occurred when the effective plastic strain of each element exceeds a threshold value. This method is simple and widely used in vehicle crash safety studies. However, there are some limitations to the representation of damage that can be achieved in this way. To represent the anisotropy and tension–compression asymmetry of the evolution of damage to the mandible and the resulting material degradation, a continuum damage mechanics model should be used to represent the material properties of both cortical and trabecular bone.
5. Conclusions
In the present study, a biomechanical approach using an FE model and Taguchi full factorial design were used to analyze the mechanism of mandible fracture caused by a lateral impact. If a patient falls laterally and their face makes contact with a protruding object, medical professionals can predict fractures to the upper part of the mandibular angle and the condyle of the affected side. To confirm the present results, further studies of patients with mandibular fractures secondary to a lateral fall should be performed. Based on the results obtained, effective preventive measures to maintain the quality of life of older adults need to be established.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.T., D.I. and M.H.; methodology, D.I., A.T. and M.H.; formal analysis, T.T., D.I. and M.H.; investigation, T.M., A.T. and S.K. writing—original draft preparation, T.T. and M.H.; writing—review and editing, M.N., S.K. and K.T.; visualization, D.I., T.M. and M.N.; supervision, M.N. and K.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was financially supported by the Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) (22K10609), Japan.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Bojino, A.; Roccia, F.; Carlaw, K.; Aquilina, P.; Rae, E.; Laverick, S.; Romeo, I.; Locca, O.; Copelli, C.; Sobrero, F.; et al. A multicentric prospective analysis of maxillofacial trauma in the elderly population. Dent. Traumatol. 2022, 38, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, K.; Matsusue, Y.; Murakami, K.; Horita, S.; Kirita, T. Maxillofacial fractures in older patients. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2011, 69, 2204–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasola, A.O.; Obiechina, A.E.; Arotiba, J.T. Incidence and pattern of maxillofacial fractures in the elderly. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2003, 32, 206–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirobe, Y.; Koshinuma, S.; Nakamura, M.; Baba, M.; Yamamoto, G.; Hitosugi, M. Factors influencing the long-term hospitalization of bicyclists and motorcyclists with oral and maxillofacial injuries. Dent. Traumatol. 2021, 37, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machida, Y.; Tomioka, T.; Koshinuma, S.; Nakamura, M.; Yamamoto, G.; Hitosugi, M. Factors predicting oral and maxillofacial fractures after falling and factors predicting the duration of treatment. Dent. Traumatol. 2023, 39, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, K.; Kuraki, M.; Kurihara, M.; Matsusue, Y.; Murakami, K.; Horita, S.; Sugiura, T.; Kirita, T. Maxillofacial fractures resulting from falls. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2010, 68, 1602–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, R.; Kubota, K.; Yaguchi, S.; Furudate, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Kobayashi, W. Falls due to loss of consciousness are associated with maxillofacial fracture severity. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 78, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roccia, F.; Boffano, P.; Bianchi, F.A.; Zavattero, E. Maxillofacial fracture due to falls: Does fall modality determine pattern of injury? J. Oral Maxillofac. Res. 2014, 5, e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DuChesne, A.; Unnewehr, M.; Schmidt, P.F.; Sotonyi, P.; Brinkmann, B.; Piffko, J.; Fischer, G.; Bajanowski, T. Deformation characteristics of the human mandible in low impact experiments. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2003, 117, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogami, S.; Yamauchi, K.; Bottini, G.B.; Otake, Y.; Sai, Y.; Morishima, H.; Higuchi, K.; Ito, K.; Gaggl, A.; Takahashi, T. Fall-related mandible fractures in a Japanese population: A retrospective study. Dent. Traumatol. 2019, 35, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.F.; Wang, R.; Baur, D.A.; Jiang, X.F. A finite element analysis of the stress distribution to the mandible from impact forces with various orientations of third molars. J. Zeijiang Univ. Sci. B 2018, 19, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Xu, X.; Liu, Q.; Xin, P. A finite element analysis on the indication for extracting partially impacted mandibular third molars considering mandibular trauma. BMC Oral Health 2024, 24, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedesiu, M.; Pavel, D.G.; Almasan, O.; Pavel, S.R.; Hedesiu, H. Three-dimentional finite element analysis on mandibular biomechanics simulation under normal and traumatic conditions. Oral 2022, 2, 221–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shigeta, K.; Kitagawa, Y.; Yasuki, T. Development of next generation human FE model capable of organ injury prediction. In Proceedings of the 21st International Technical Conference on the Enhanced Safety of Vehicles (ESV), Stuttgart, Germany, 15–18 June 2009; National Highway Traffic Safety Administration: Stuttgart, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, R.; Miyazaki, H.; Kitagawa, Y.; Yasuki, T. Research of collision speed dependency of pedestrian head and chest injuries using human FE model (THUMS Version 4). In Proceedings of the 22nd International Technical Conference on the Enhanced Safety of Vehicles (ESV), Washington, DC, USA, 13–16 June 2011; Volume 22, p. 31. [Google Scholar]
- Hallquist, J.O. LS-DYNA Keyword User’s Manual, Version 971; Livermore Software Technology Corporation: Livermore, CA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Rosa, J.L.; Robin, A.; Silva, M.B.; Baldan, C.A.; Peres, M.P. Electrodeposition of copper on titanium wires: Taguchi experimental design approach. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2009, 209, 1181–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, J.G.; Kerry, A.D.; Logan, E.M.; Joel, D.S. Injury prediction in a side impact crash using human body modek simulation. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2014, 64, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Jeffry, S.N.; Anuradha, R.; Michael, J.R.; Wang, X. Mechanical behavior of human cortical bone in cycles of advancing tensile strain for two age groups. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2009, 89A, 521–529. [Google Scholar]
- Fujii, M.; Shirakawa, T.; Nakamura, M.; Baba, M.; Hitosugi, M. Factors influencing the injury severity score and the probability of survival in patients who fell from height. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsutsumi, Y.; Ito, D.; Nakamura, M.; Koshinuma, S.; Yamamoto, G.; Hitosugi, M. Maxillofacial injuries in cyclists: A biomechanical approach for the analysis of mechanisms of mandible fractures. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2021, 79, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Harbawee, A.; Ahmed, T.; Ahmed, S.; Avery, C.; Fagiry, R.; Hamzah, H.A.; Afzaal, A.; Khan, A.; Mair, M.; Ali, M.; et al. A retrospective analysis of the impaction status of mandibular third molars as a risk factor for fractures of angle or condylar region of the mandible. Adv. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2021, 1, 100018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitzik, M.; Lownie, J.F.; Cleaton-Jones, P.; Austin, J. Experimental fractures of monkey mandibles. Int. J. Oral Surg. 1978, 7, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).