Learning to Count Crowds from Low-Altitude Aerial Views via Point-Level Supervision and Feature-Adaptive Fusion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Crowd Counting
2.2. Point-Supervised Small Object Counting Algorithms
2.3. Crowd Counting Datasets
2.3.1. UCF_CC_50
2.3.2. Shanghai Tech Part A
2.3.3. Shanghai Tech Part B
- Joint modeling of density and location for clustered small objects: Unlike methods relying solely on global density regression or single-point detection, this paper proposes a strategy combining density maps and point-level supervision, effectively addressing occlusion and dense distribution issues while maintaining small object localization accuracy.
- Multi-scale feature fusion strategy: By fusing image features at different scales, the network’s perception ability for small objects of varying sizes and uneven distributions is enhanced, reducing missed detections and duplicate counting.
- Efficient training and annotation cost optimization: While maintaining high accuracy, it combines point-level annotation with semi-supervised strategies, effectively reducing annotation costs and improving the model’s generalization ability on limited datasets.
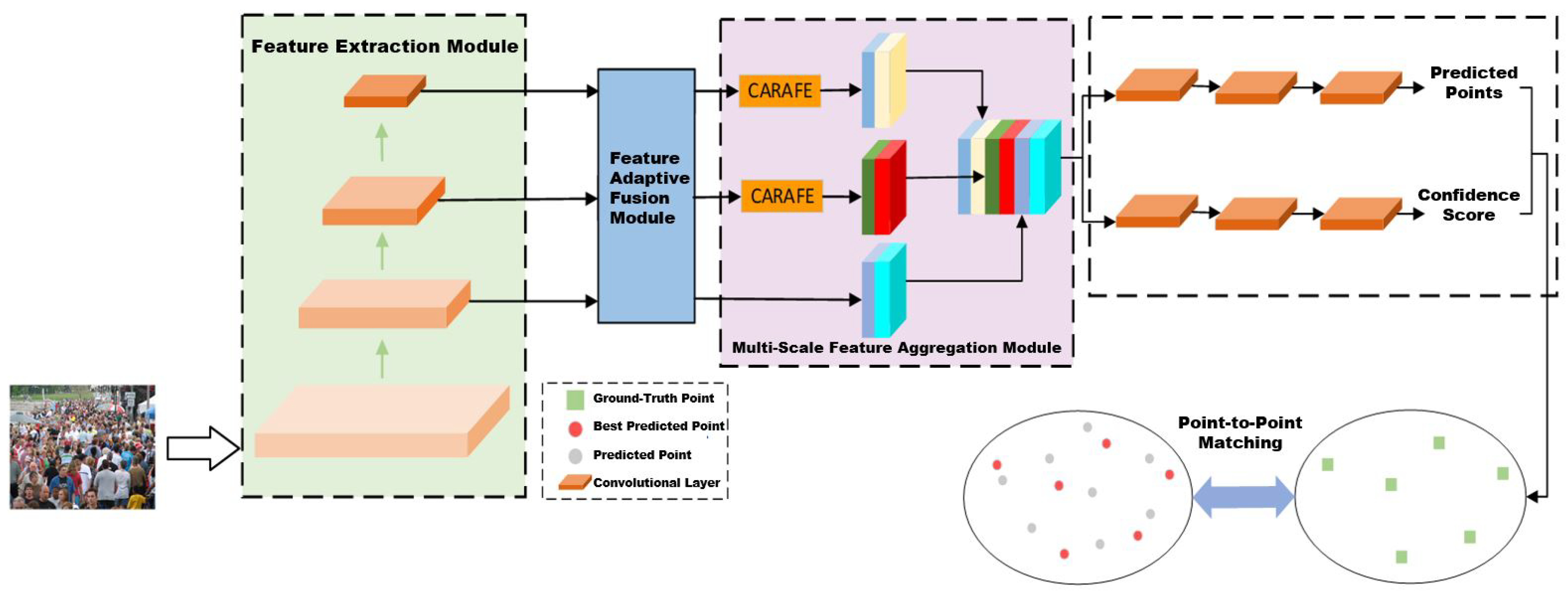
3. Crowd Counting Based on Point-Level Supervision and Feature-Adaptive Fusion
3.1. Overall Network Architecture
3.2. Feature Adaptive Fusion Module
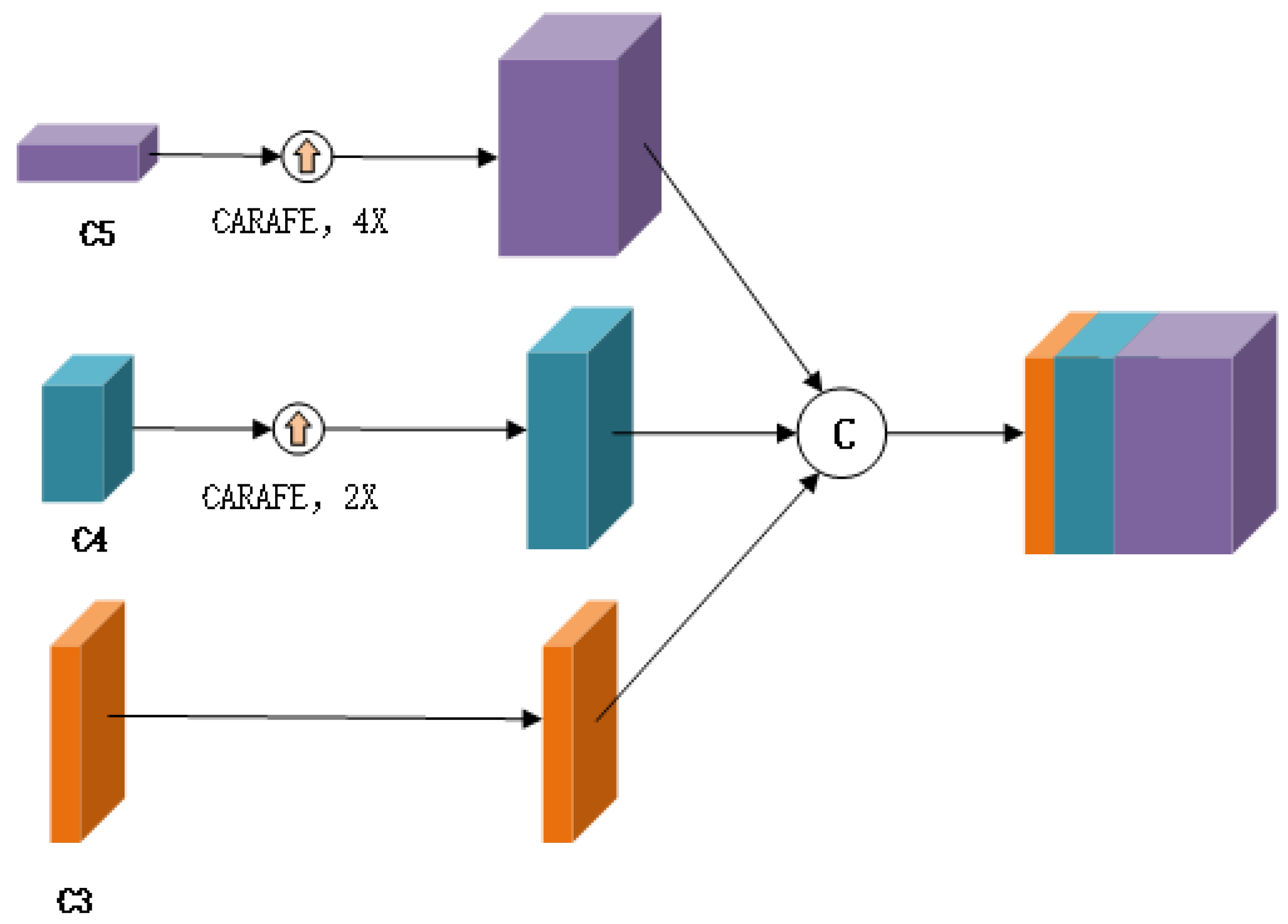
3.3. Multi-Scale Feature Aggregation Module
3.4. Design of Loss Function
4. Experimental Results and Analysis
4.1. Experimental Setup
4.1.1. Experimental Environment and Parameter Settings
4.1.2. Data Augmentation
4.2. Comparative Experimental Results and Analysis
4.2.1. Experimental Results on ShanghaiTech Part A Dataset
4.2.2. Experimental Results on ShanghaiTech Part B
4.2.3. Experimental Results on UCF_CC_50
4.3. Ablation Experiments and Analysis
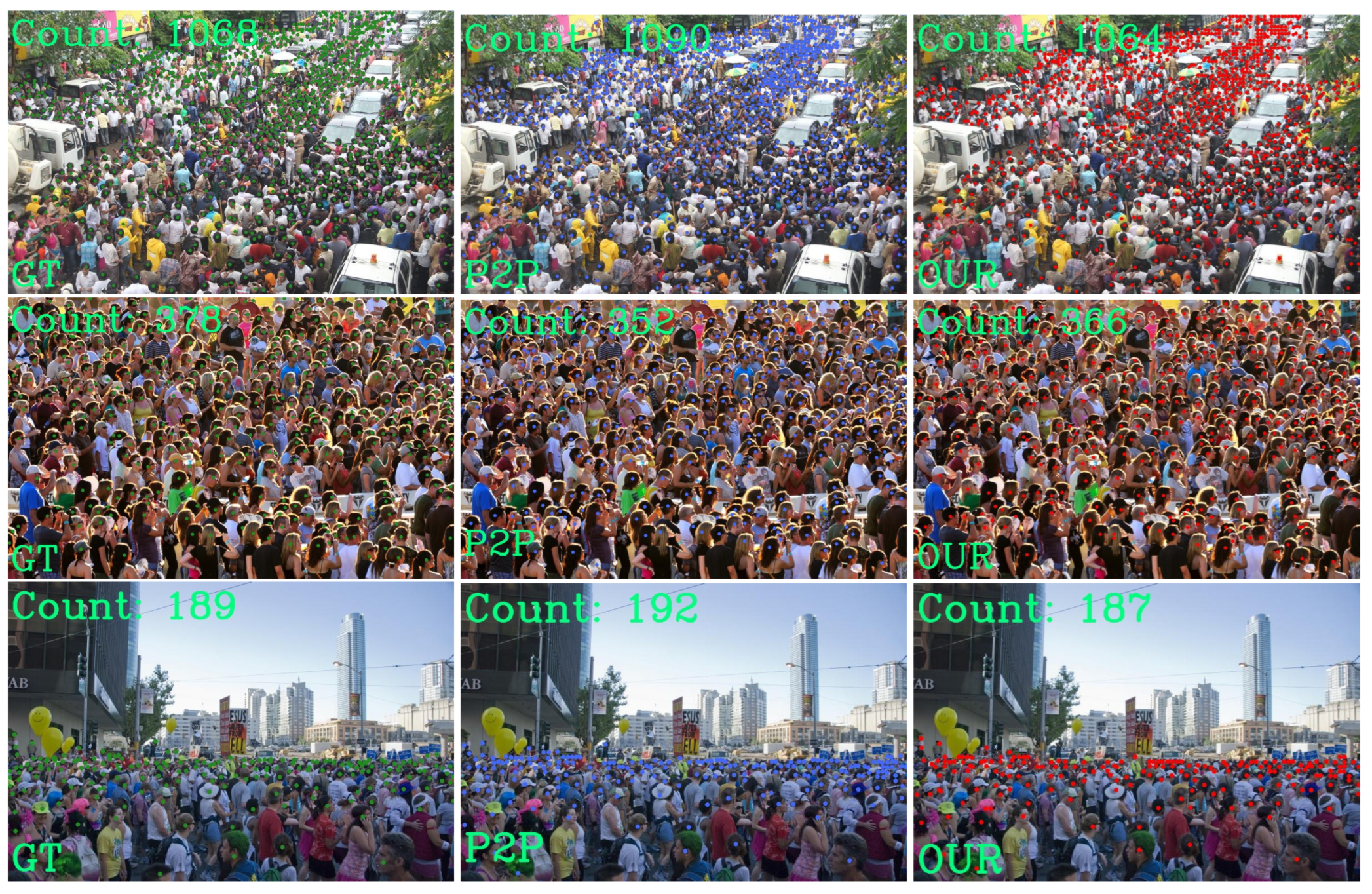
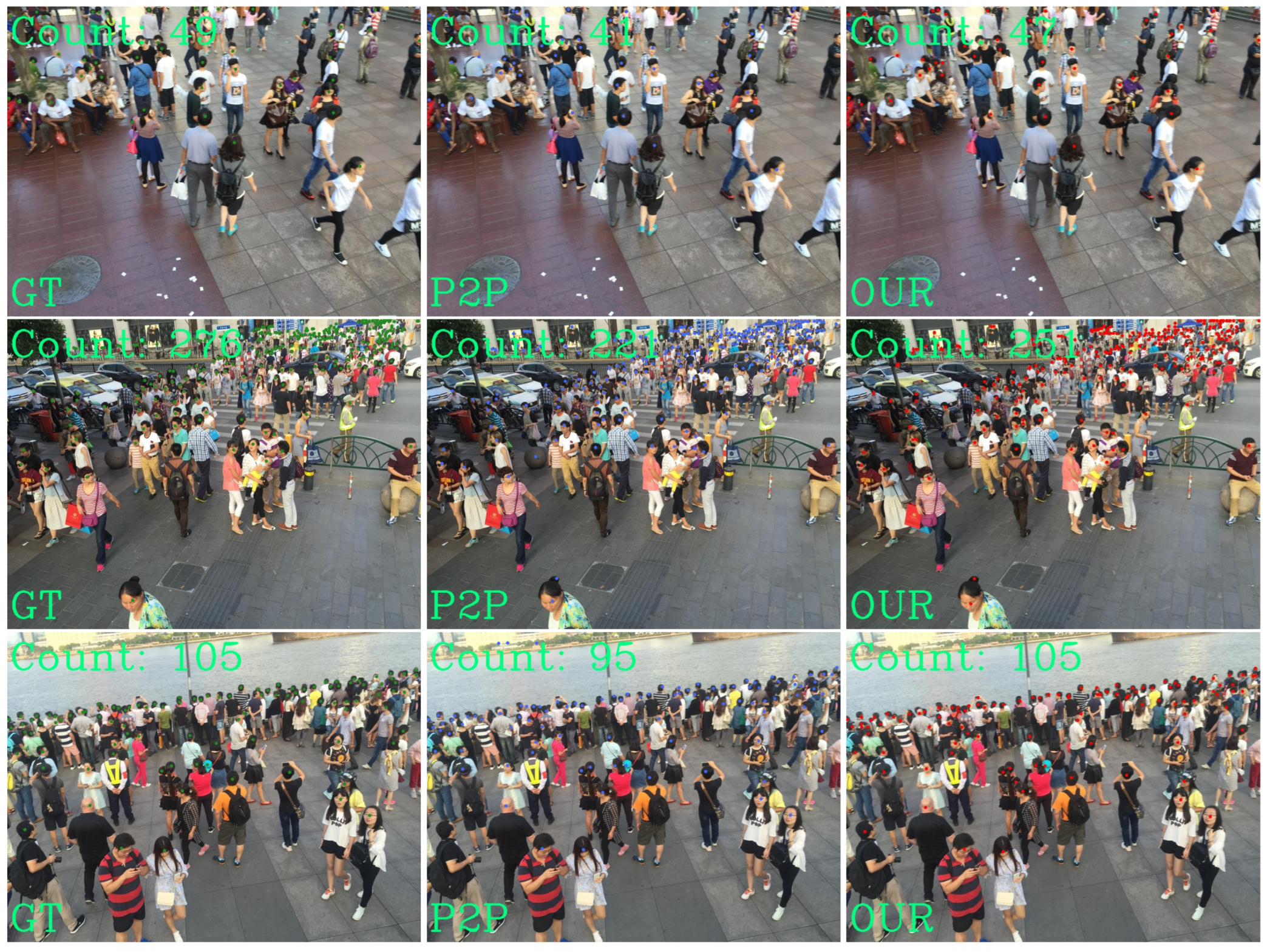
4.4. Visual Comparison
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, D.; Chen, S.; Gao, S.; Ma, Y. Single-image crowd counting via multi-column convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 589–597. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, B.; Nevatia, R. Detection of multiple, partially occluded humans in a single image by bayesian combination of edgelet part detectors. In Proceedings of the Tenth IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV’05), Beijing, China, 17–20 October 2005; Volume 1, pp. 90–97. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, M.J.; Snow, D. Pedestrian detection using boosted features over many frames. In Proceedings of the 2008 19th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Tampa, FL, USA, 8–11 December 2008; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Dalal, N.; Triggs, B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’05), San Diego, CA, USA, 20–26 June 2005; pp. 886–893. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, C.; Liu, J.; Feng, Q.; Lv, J. People-flow counting in complex environments by combining depth and color information. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2016, 75, 9315–9331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, V.Q.; Kozakaya, T.; Yamaguchi, O.; Okada, R. Count forest: Co-voting uncertain number of targets using random forest for crowd density estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 3253–3261. [Google Scholar]
- Viola, V.; Snow, D. Detecting pedestrians using patterns of motion and appearance. In Proceedings of the Ninth IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Nice, France, 13–16 October 2003; Volume 2, pp. 734–741. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, K.; Tan, T. Estimating the number of people in crowded scenes by mid based foreground segmentation and head-shoulder detection. In Proceedings of the 2008 19th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Tampa, FL, USA, 8–11 December 2008; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, T.; Nevatia, R.; Wu, B. Segmentation and tracking of multiple humans in crowded environments. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2008, 30, 1198–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, D.; Denman, S.; Sridharan, S.; Fookes, C. An evaluation of crowd counting methods, features and regression models. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2015, 130, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paragios, N.; Ramesh, V. A MRF-based approach for real-time subway monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition CVPR 2001, Kauai, HI, USA, 8–14 December 2001; p. I-I. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, A.B.; Liang, Z.-S.J.; Vasconcelos, N. Privacy preserving crowd monitoring: Counting people without people models or tracking. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Anchorage, AK, USA, 23–28 June 2008; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Lempitsky, V.; Zisserman, A. Learning to count objects in images. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2010, 23. [Google Scholar]
- LeCun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Xu, P.; Li, X.; Liu, Q.; Ye, M.; Zhu, C. Fast crowd density estimation with convolutional neural networks. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2015, 43, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Yang, L.; Liu, S.; Cao, X. Deep people counting in extremely dense crowds. In Proceedings of the 23rd ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Brisbane, Australia, 26–30 October 2015; pp. 1299–1302. [Google Scholar]
- Walach, E.; Wolf, L. Learning to count with cnn boosting. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Proceedings, Part II 14. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 660–676. [Google Scholar]
- Babu Sam, D.; Surya, S.; Venkatesh Babu, R. Switching convolutional neural network for crowd counting. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 5744–5752. [Google Scholar]
- Sindagi, V.A.; Patel, V.M. Generating high-quality crowd density maps using contextual pyramid cnns. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 1861–1870. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, D.; Li, K.; Zha, Z.-J.; Wang, M. Dadnet: Dilated-attention-deformable convnet for crowd counting. In Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Nice, France, 21–25 October 2019; pp. 1823–1832. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, D. Csrnet: Dilated convolutional neural networks for understanding the highly congested scenes. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 1091–1100. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Su, F. Scale aggregation network for accurate and efficient crowd counting. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 734–750. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, N.; Long, Y.; Zou, C.; Niu, Q.; Pan, L.; Wu, H. Adcrowdnet: An attention-injective deformable convolutional network for crowd understanding. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 3225–3234. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Q.; Wang, C.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Tai, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, J.; Huang, F.; Wu, Y. Rethinking counting and localization in crowds: A purely point-based framework. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 3365–3374. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Liu, H.; Samaras, D.; Nguyen, M.H. Distribution matching for crowd counting. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 1595–1607. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Zhao, Q.; Ma, Y.; Chong, M.O.; Zhang, Y. Bipartite Matching for Crowd Counting with Point Supervision. In Proceedings of the 30th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI), Virtual, 19–27 August 2021; pp. 860–866. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Yang, T.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Sun, J. Points as queries: Weakly semi-supervised object detection by points. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Virtual, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 8823–8832. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Su, W.; Lu, L.; Li, B.; Wang, X.; Dai, J. Deformable detr: Deformable transformers for end-to-end object detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.04159. [Google Scholar]
- Idrees, H.; Saleemi, I.; Seibert, C.; Shah, M. Multi-source multi-scale counting in extremely dense crowd images. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 2547–2554. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Salzmann, M.; Fua, P. Context-aware crowd counting. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 5099–5108. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Z.-Q.; Dai, Q.; Li, H.; Song, J.; Wu, X.; Hauptmann, A.G. Rethinking spatial invariance of convolutional networks for object counting. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 19638–19648. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, D.; Xu, W.; Bai, X. An end-to-end transformer model for crowd localization. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 38–54. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.-Y.; Zhang, L.; Wei, X.-Y. Fgenet: Fine-grained extraction network for congested crowd counting. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Multimedia Modeling (MMM), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 29 January–2 February 2024; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 43–56. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.-Y.; Zhang, L.; Shi, S. VMambaCC: A Visual State Space Model for Crowd Counting. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.03978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Dataset Name | Image Number | Annotation Count | Average Resolution | Average Count | Train Set | Test Set |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ShanghaiTech | 482 | 241,677 | 589 × 868 | 510 | 300 | 182 |
| Part A | ||||||
| ShanghaiTech | 716 | 88,488 | 768 × 1024 | 124 | 400 | 316 |
| Part B | ||||||
| UCF_CC_50 | 50 | 63,974 | 2101 × 2888 | 1280 | 40 | 10 |
| Model | Year | MAE | MSE |
|---|---|---|---|
| CSRNet [21] | 2018 | 68.2 | 115.0 |
| CAN [31] | 2019 | 62.3 | 100.0 |
| DM-Count [25] | 2020 | 59.7 | 95.7 |
| P2PNet [24] | 2021 | 52.74 | 85.06 |
| GauNet [32] | 2022 | 54.8 | 89.1 |
| CLTR [33] | 2022 | 56.9 | 95.2 |
| FGENet [34] | 2024 | 51.66 | 85.0 |
| VMambaCC [35] | 2024 | 51.87 | 81.3 |
| Proposed Method | 51.52 | 81.04 |
| Model | Year | MAE | MSE |
|---|---|---|---|
| CSRNet [21] | 2018 | 10.6 | 16.0 |
| CAN [31] | 2019 | 7.8 | 12.2 |
| DM-Count [25] | 2020 | 7.4 | 11.8 |
| P2PNet [24] | 2021 | 6.25 | 9.9 |
| GauNet [32] | 2022 | 6.2 | 9.9 |
| CLTR [33] | 2022 | 6.5 | 10.6 |
| FGENet [34] | 2024 | 6.34 | 10.53 |
| VMambaCC [35] | 2024 | 7.48 | 12.47 |
| Proposed Method | 6.78 | 9.68 |
| Model | Year | MAE | MSE |
|---|---|---|---|
| CSRNet [21] | 2018 | 215.4 | 296.4 |
| CAN [31] | 2019 | 212.2 | 243.7 |
| DM-Count [25] | 2020 | 211.0 | 291.5 |
| P2PNet [24] | 2021 | 172.7 | 256.1 |
| GauNet [32] | 2022 | 186.3 | 256.5 |
| CLTR [33] | 2024 | 142.56 | 215.87 |
| FGENet [34] | 2024 | 64.34 | 78.71 |
| Proposed Method | 64.2 | 103.62 |
| Method | MAE | MSE |
|---|---|---|
| P2PNet | 52.74 | 85.06 |
| P2PNet+ADFF | 53.77 | 82.42 |
| P2PNet+Fusion | 52.19 | 81.99 |
| P2PNet+CARAFE+Fusion | 52.02 | 81.81 |
| P2Pnet+ADFF+CARAFE+Fusion | 51.52 | 81.64 |
| Improvement | 1.22 (2.3%) | 3.42 (4.02%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mao, J.; Nai, L.; Bai, J.; Liu, C.; Xu, L. Learning to Count Crowds from Low-Altitude Aerial Views via Point-Level Supervision and Feature-Adaptive Fusion. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 13211. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152413211
Mao J, Nai L, Bai J, Liu C, Xu L. Learning to Count Crowds from Low-Altitude Aerial Views via Point-Level Supervision and Feature-Adaptive Fusion. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(24):13211. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152413211
Chicago/Turabian StyleMao, Junzhe, Lin Nai, Jinqi Bai, Chang Liu, and Liangfeng Xu. 2025. "Learning to Count Crowds from Low-Altitude Aerial Views via Point-Level Supervision and Feature-Adaptive Fusion" Applied Sciences 15, no. 24: 13211. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152413211
APA StyleMao, J., Nai, L., Bai, J., Liu, C., & Xu, L. (2025). Learning to Count Crowds from Low-Altitude Aerial Views via Point-Level Supervision and Feature-Adaptive Fusion. Applied Sciences, 15(24), 13211. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152413211





