A Physics-Constrained Method for the Precise Spatiotemporal Prediction of Rock-Damage Evolution
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source and Hyperparameter Setup
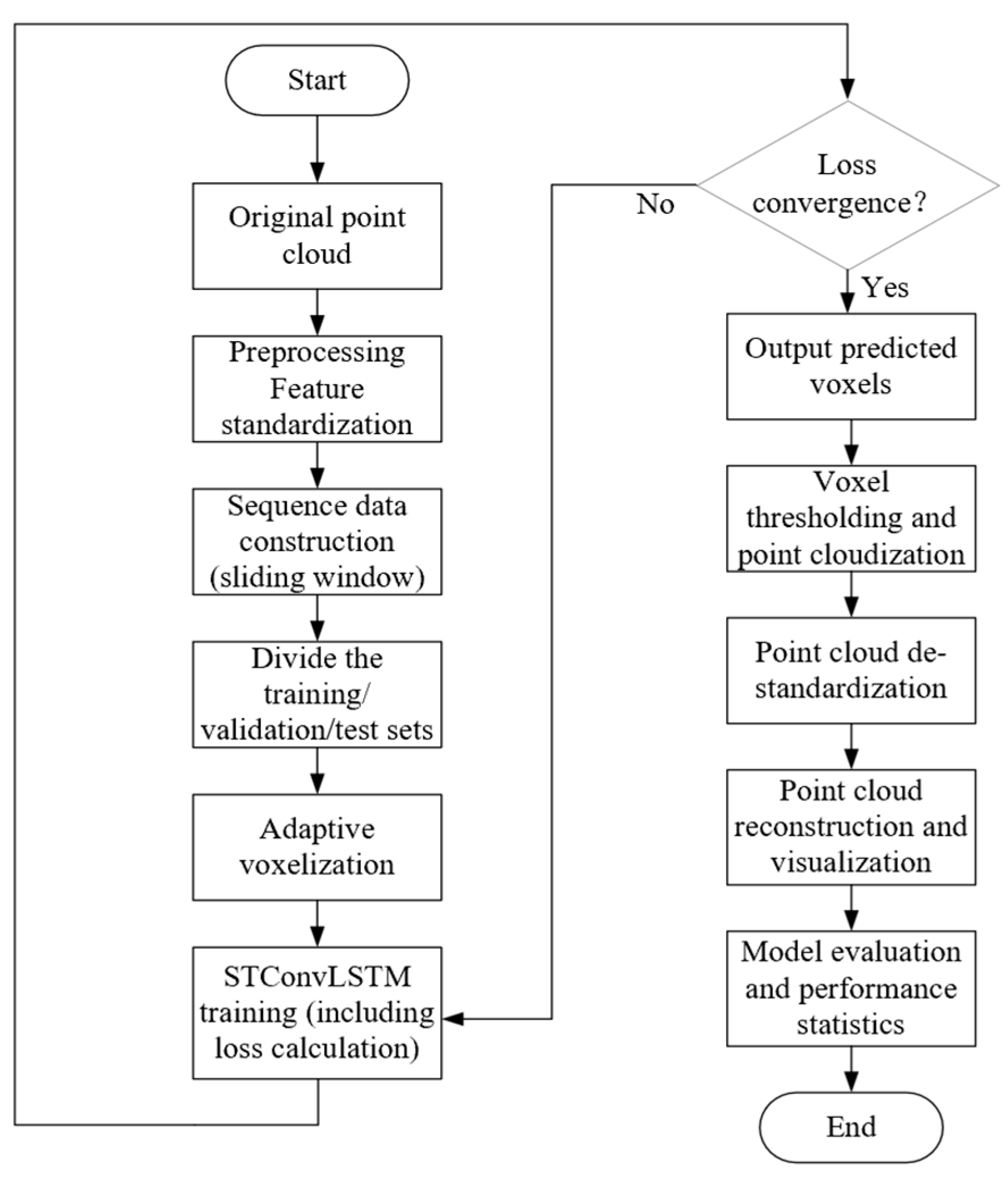
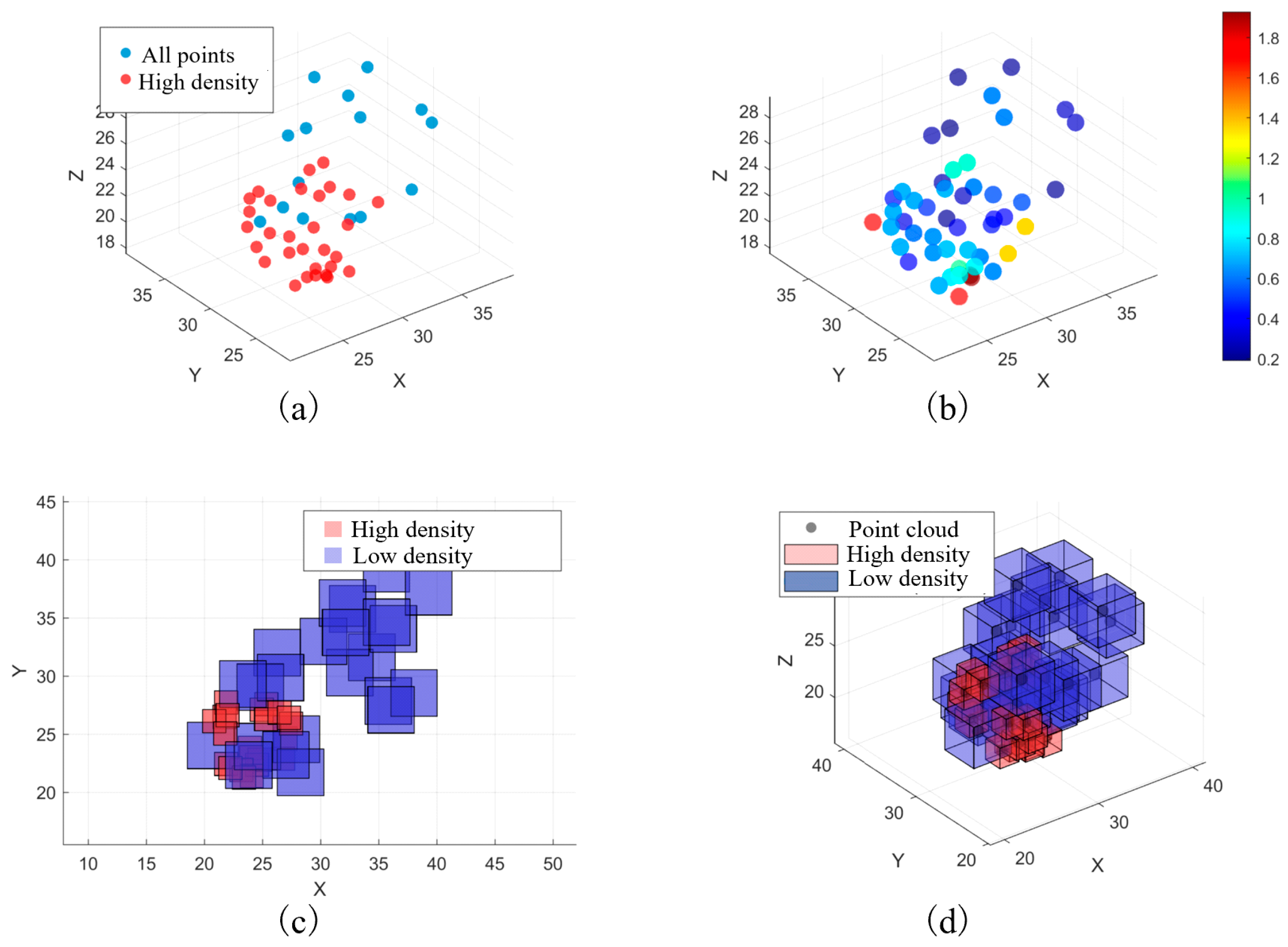
2.2. Methods, Procedures, and Adaptive Voxelization
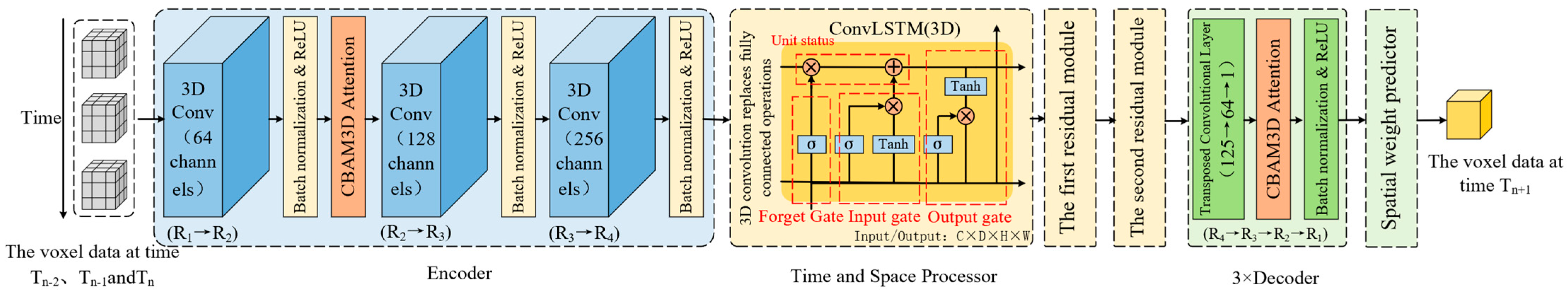
2.3. Physics-Constrained STConvLSTM Architecture
2.4. Composite Loss with Physical Constraints
2.5. Training Protocol and Evaluation Metrics
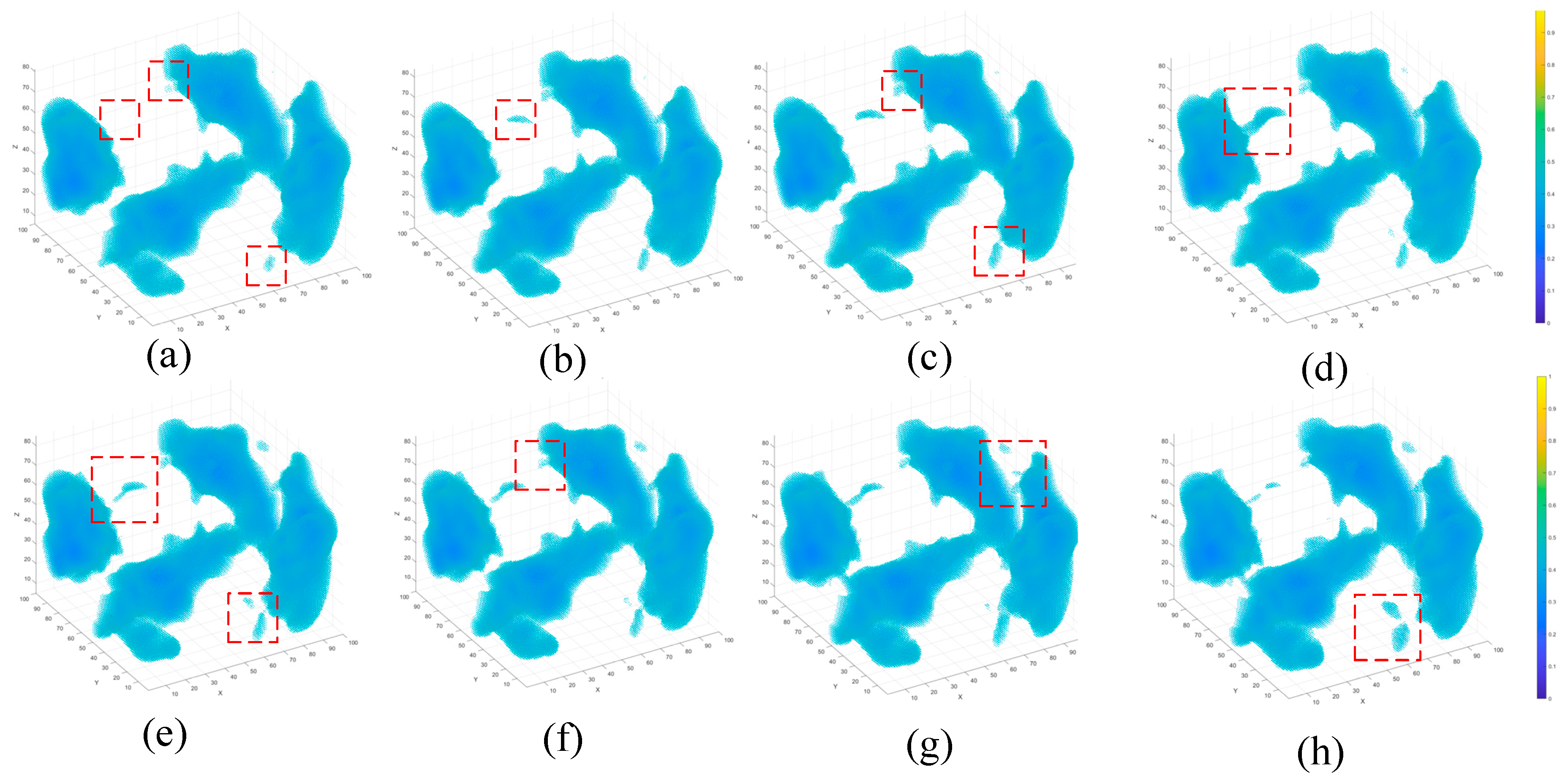
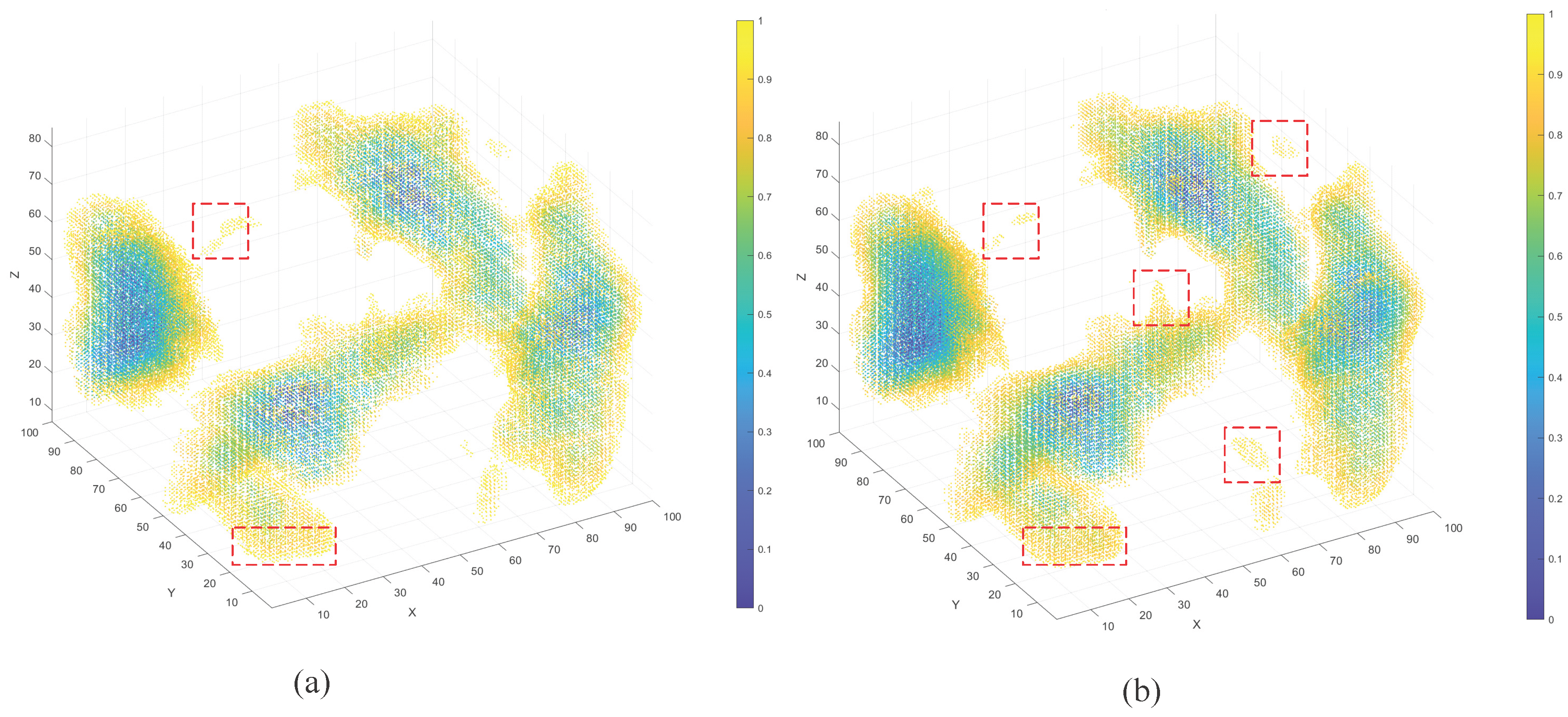
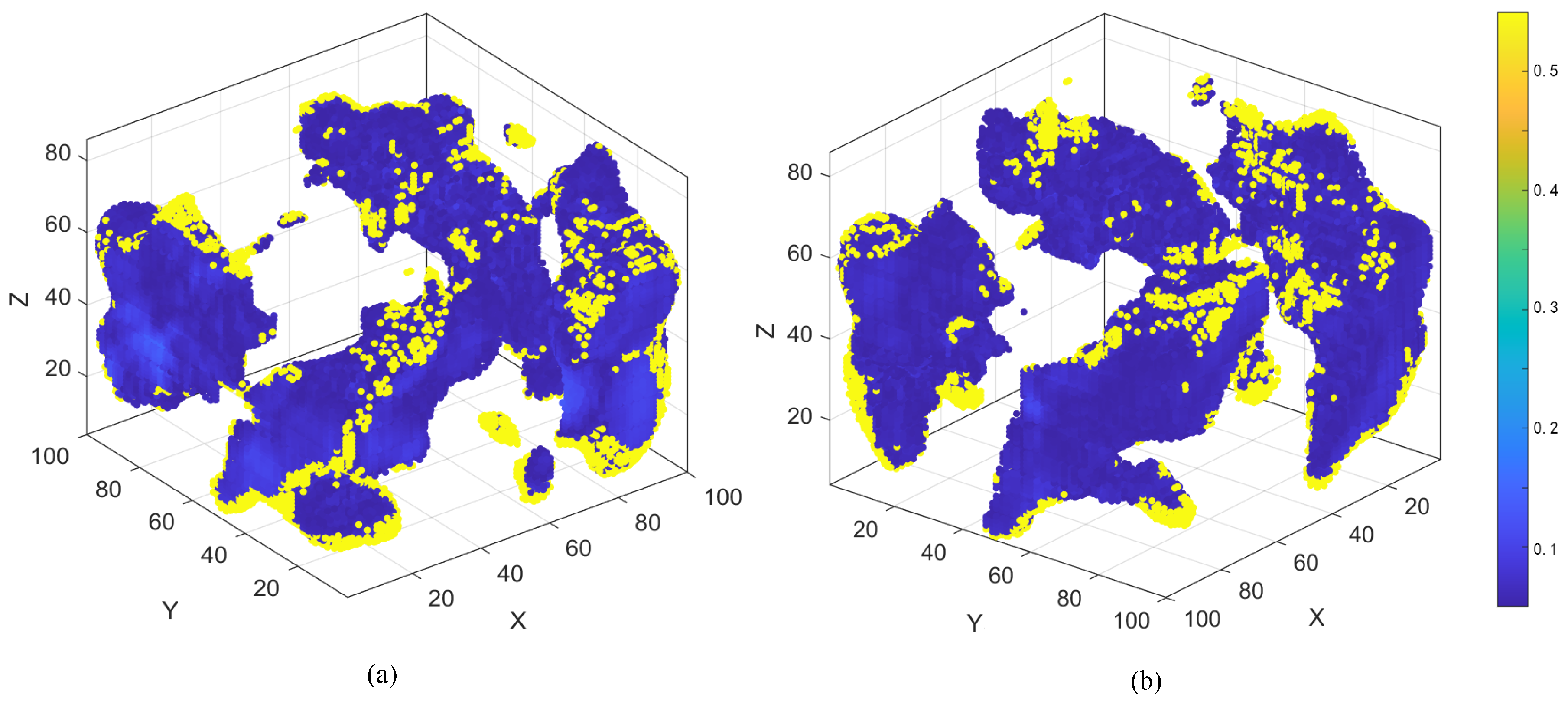
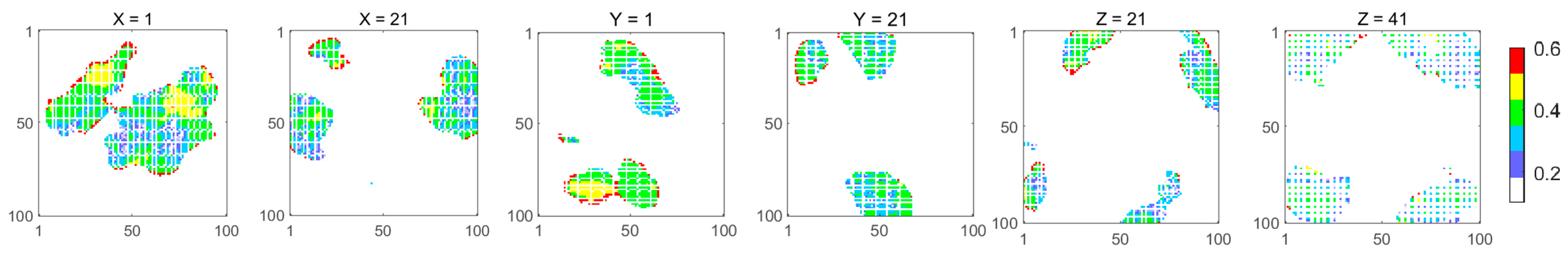
3. Results
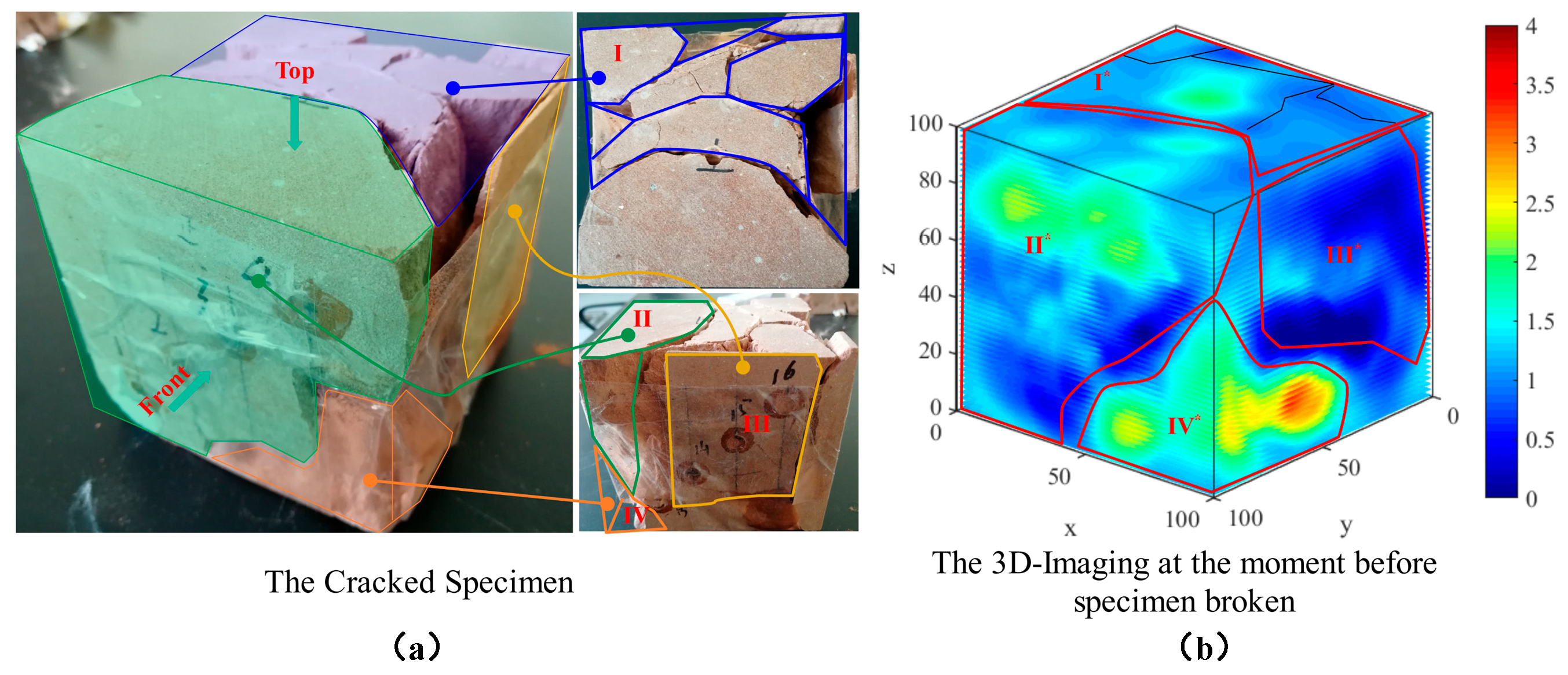
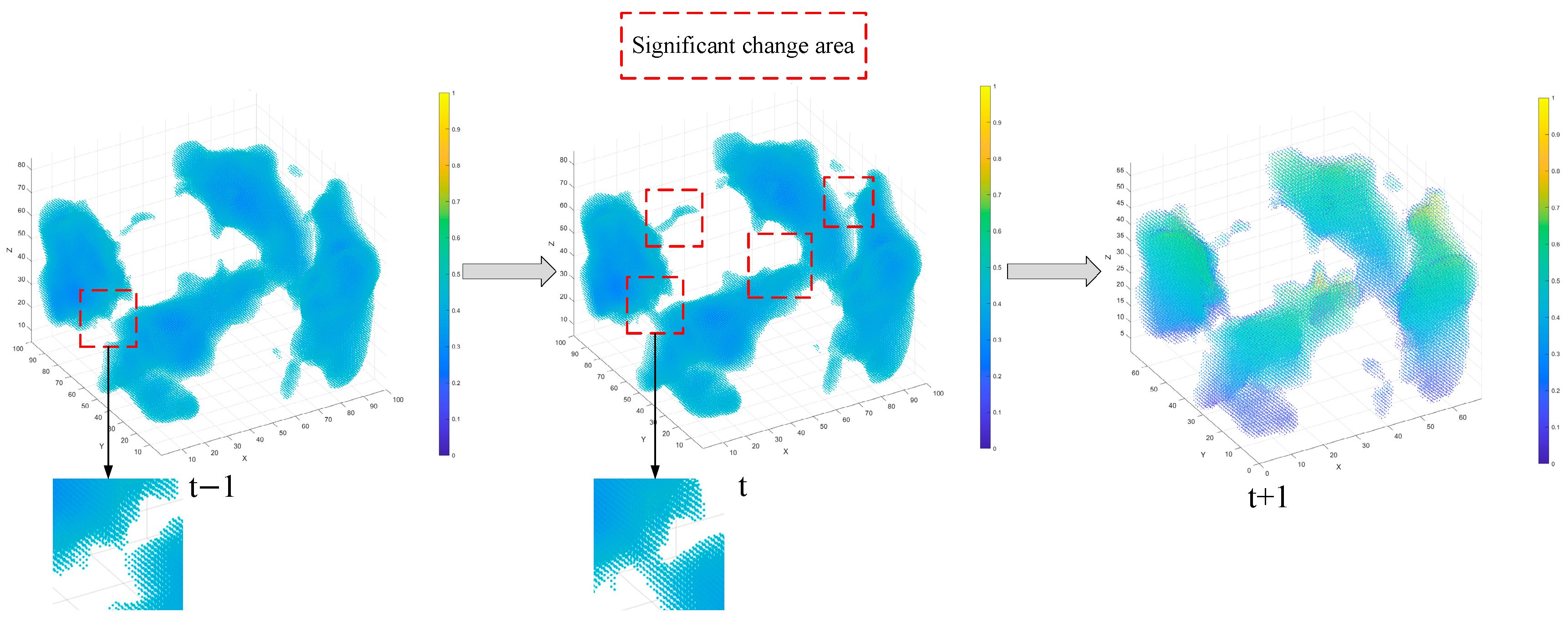
3.1. Visualization of Damage Evolution
3.2. Single-Step Prediction and Spatial Fidelity
3.3. Error Distribution Analysis
3.4. Cross-Sectional Validation
3.5. Temporal-Step Prediction Verification
3.6. Comparative Study with Baseline Models
3.7. Ablation Experiments
- Removing adaptive voxelization (fixed voxels + composite loss);
- Replacing the composite loss with simple MSE (adaptive voxels + MSE only);
- The complete model.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, L.; Xiong, H.; Zeng, T.; Wang, J.; Xiao, S.; Yang, L. In-situ micro-CT damage analysis of carbon and carbon/glass hybrid laminates under tensile loading by image reconstruction and DVC technology. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2024, 176, 107844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Ye, Q.; Guo, A. Gravity Gradient Inversion of Gravity Field and Steady-State Ocean Circulation Explorer Satellite Data for the Lithospheric Density Structure in the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau Region and the Surrounding Regions. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2021, 126, e2020JB021291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Qin, R.; Han, K.N.; Wei, Z.Y.; Ma, L.H. Progressive damage visualization and tensile failure analysis of three-dimensional braided composites by acoustic emission and micro-CT. Polym. Test. 2021, 93, 106881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Cheng, Z.; Wu, D. Deep learning driven prediction and comparative study of surrounding rock deformation in high speed railway tunnels. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 24104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.L.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Q.Z.; Sun, H.H. Long-term and short-term constitutive model of rock based on deep learning and deformation prediction of sandy limestone. Rock Soil Mech. 2025, 46, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, X.; Yan, S.; Chen, Z.; Wang, S.; Li, H.; Wang, Q. Research on rock fracture evolution prediction model based on Adam-ConvLSTM and transfer learning. Discov. Appl. Sci. 2025, 7, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Jiao, S.; Zhao, Y.; Deng, W.; Xue, B.; Wen, X. Prediction Method for Surface Settlement during Underground Mining in Mines Based on LSTM-DCNN and Transfer Learning. Min. Res. Dev. 2025, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, Y.; Luo, H.; Liu, X. Rockburst Intensity Prediction Model Based on Newton–Raphson Algorithm and BP Neural Network. Min. Res. Dev. 2025, 45, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Liang, P.; Li, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, T.; Wang, J. CNN-LSTM Rockburst Intensity Grade Prediction Model Based on Fusion Optimization Algorithm under Unbalanced Data. Min. Res. Dev. 2025, 45, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Tuzel, O. VoxelNet: End-to-End Learning for Point Cloud-Based 3D Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 4490–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.R.; Yi, L.; Su, H.; Guibas, L.J. PointNet++: Deep hierarchical feature learning on point sets in a metric space. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 5099–5108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Xiao, Z. PVLF: Point–Voxel Local Feature Fusion for 3D Detection. Discov. Artif. Intell. 2025, 5, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, H.; Hu, Q.; Liu, H.; Liu, L.; Bennamoun, M. Deep Learning for 3D Point Clouds: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 43, 4338–4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Tang, H.; Lin, Y.; Han, S. Point–Voxel CNN for Efficient 3D Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, B.; van der Maaten, L. Submanifold Sparse Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choy, C.; Gwak, J.; Savarese, S. 4D Spatio-Temporal ConvNets: Minkowski Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raissi, M.; Perdikaris, P.; Karniadakis, G.E. Physics-informed neural networks. J. Comput. Phys. 2019, 378, 686–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpatne, A.; Atluri, G.; Faghmous, J.H.; Steinbach, M.; Banerjee, A.; Ganguly, A.; Shekhar, S.; Samatova, N.; Kumar, V. Theory-Guided Data Science: A New Paradigm for Scientific Discovery from Data. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2022, 34, 3924–3938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manav, M.; Molinaro, R.; Mishra, S.; De Lorenzis, L. Phase-field modeling of fracture with physics-informed deep learning. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2024, 429, 117104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karniadakis, G.E.; Kevrekidis, I.G.; Lu, L.; Perdikaris, P.; Wang, S.; Yang, L. Physics-informed machine learning. Nat. Rev. Phys. 2021, 3, 422–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çiçek, Ö.; Abdulkadir, A.; Lienkamp, S.S.; Brox, T.; Ronneberger, O. 3D U-Net: Learning dense volumetric segmentation from sparse annotationn. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2016, Proceedings of the 19th International Conference, Athens, Greece, 17–21 October 2016; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; Volume 9901, pp. 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lu, L.; Wang, X.; Zhu, R.M.; Bagheri, M.; Summers, R.M.; Yao, J. Spatio-Temporal ConvLSTMs for Tumor Growth Prediction by Learning 4D Longitudinal Patient Data. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1902.08716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, L.; Yang, Z.; Liu, X.; Liang, P. Research on Rock Damage Acoustic Emission Detection and Imaging Method Based on Regional Correlation. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2017, 36, 2113–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Tao, Z.; Liang, P.; Zhao, J. Effect of regionalized structures on rock fracture process. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 10490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Hagan, P.; Mitra, R.; Wang, S.; Yang, H.-W. Experimental investigation of progressive failure using 3D acoustic emission tomography. Front. Earth Sci. 2021, 9, 765030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, X. Three-Dimensional AE Source Localization for Layered Rock Considering Anisotropic P-Wave Velocity. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2024, 83, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kweon, I.S. CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yu, Z.; Luan, Z.; Ren, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, G. RDAU-Net: Residual CNN with DFP and CBAM for Brain Tumor Segmentation. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 805263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Xu, W.; Yang, M.; Yu, K. 3D convolutional neural networks for human action recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 35, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Yeung, D.-Y.; Wong, W.-K.; Woo, W.-C. Convolutional LSTM network: A machine learning approach for precipitation nowcasting. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 28 (NeurIPS 2015, Montreal, QC, Canada, 7–12 December 2015; pp. 802–810. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Wu, Y.; Bai, Y.; Han, H.; Chen, L.; Gao, H.; Wei, H.; Wang, M. A lightweight 3D UNet model for glioma grading. Phys. Med. Biol. 2022, 67, 155006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, Y.; Wang, E.; Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Huang, T.; Yao, J. Comprehensive early warning of rockburst from MS–AE–EMR signals via deep learning. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2023, 170, 105519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kervadec, H.; Bouchtiba, J.; Desrosiers, C.; Granger, E.; Dolz, J.; Ben Ayed, I. Boundary loss for highly unbalanced segmentation. Med. Image Anal. 2021, 67, 101851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Hyperparameter | Value/Setting | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Base grid resolution for adaptive voxelization | 100 × 100 × 100 | Preserve spatial detail features |
| Input time step (sliding window) | 2 | Capture the recent evolutionary history |
| Hyperparameter | Value/Setting | Purpose |
| Prediction time step | 1 | Evaluate the accuracy of single-step predictions |
| Learning rate scheduling strategy | Cosine annealing | Stabilize and converge to the optimal solution |
| Optimizer | AdamW | Improve training stability |
| Composite loss weight , , | Balance various optimization objectives |
| Model Name | MSE | MAE | Accuracy | Recall | F1 Score | PC-Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3D CNN | 0.0181 ± 0.0017 | 0.0604 ± 0.0051 | 0.9122 ± 0.0041 | 0.9541 ± 0.0053 | 0.9332 ± 0.0043 | 0.9541 ± 0.0053 |
| ConvLSTM | 0.0152 ± 0.0013 | 0.0503 ± 0.0042 | 0.9030 ± 0.0049 | 0.9781 ± 0.0038 | 0.9391 ± 0.0037 | 0.9781 ± 0.0038 |
| UNet3D | 0.0301 ± 0.0022 | 0.1103 ± 0.0074 | 0.8420 ± 0.0062 | 0.8941 ± 0.0071 | 0.8670 ± 0.0064 | 0.8941 ± 0.0071 |
| STConvLSTM | 0.0121 ± 0.0011 | 0.0451 ± 0.0033 | 0.9261 ± 0.0034 | 0.9751 ± 0.0042 | 0.9470 ± 0.0035 | 0.9751 ± 0.0042 |
| Model Configuration | Accuracy | Recall | F1 Score | PC-Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| STConvLSTM (Fixed Voxel + Composite Loss) | 0.868 | 0.991 | 0.925 | 0.991 |
| STConvLSTM (Adaptive Voxel + MSE Only) | 0.853 | 0.996 | 0.906 | 0.966 |
| STConvLSTM (Complete Model) | 0.924 | 0.970 | 0.947 | 0.970 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, S.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, X.; Tao, Z.; Wang, S. A Physics-Constrained Method for the Precise Spatiotemporal Prediction of Rock-Damage Evolution. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 12801. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312801
Yan S, Tian Z, Zhang Y, Yao X, Tao Z, Wang S. A Physics-Constrained Method for the Precise Spatiotemporal Prediction of Rock-Damage Evolution. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(23):12801. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312801
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Shaohong, Zikun Tian, Yanbo Zhang, Xulong Yao, Zhigang Tao, and Shuai Wang. 2025. "A Physics-Constrained Method for the Precise Spatiotemporal Prediction of Rock-Damage Evolution" Applied Sciences 15, no. 23: 12801. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312801
APA StyleYan, S., Tian, Z., Zhang, Y., Yao, X., Tao, Z., & Wang, S. (2025). A Physics-Constrained Method for the Precise Spatiotemporal Prediction of Rock-Damage Evolution. Applied Sciences, 15(23), 12801. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312801






