Unraveling the Patterns and Drivers of Multi-Geohazards in Tangshan, China, by Integrating InSAR and ICA
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area
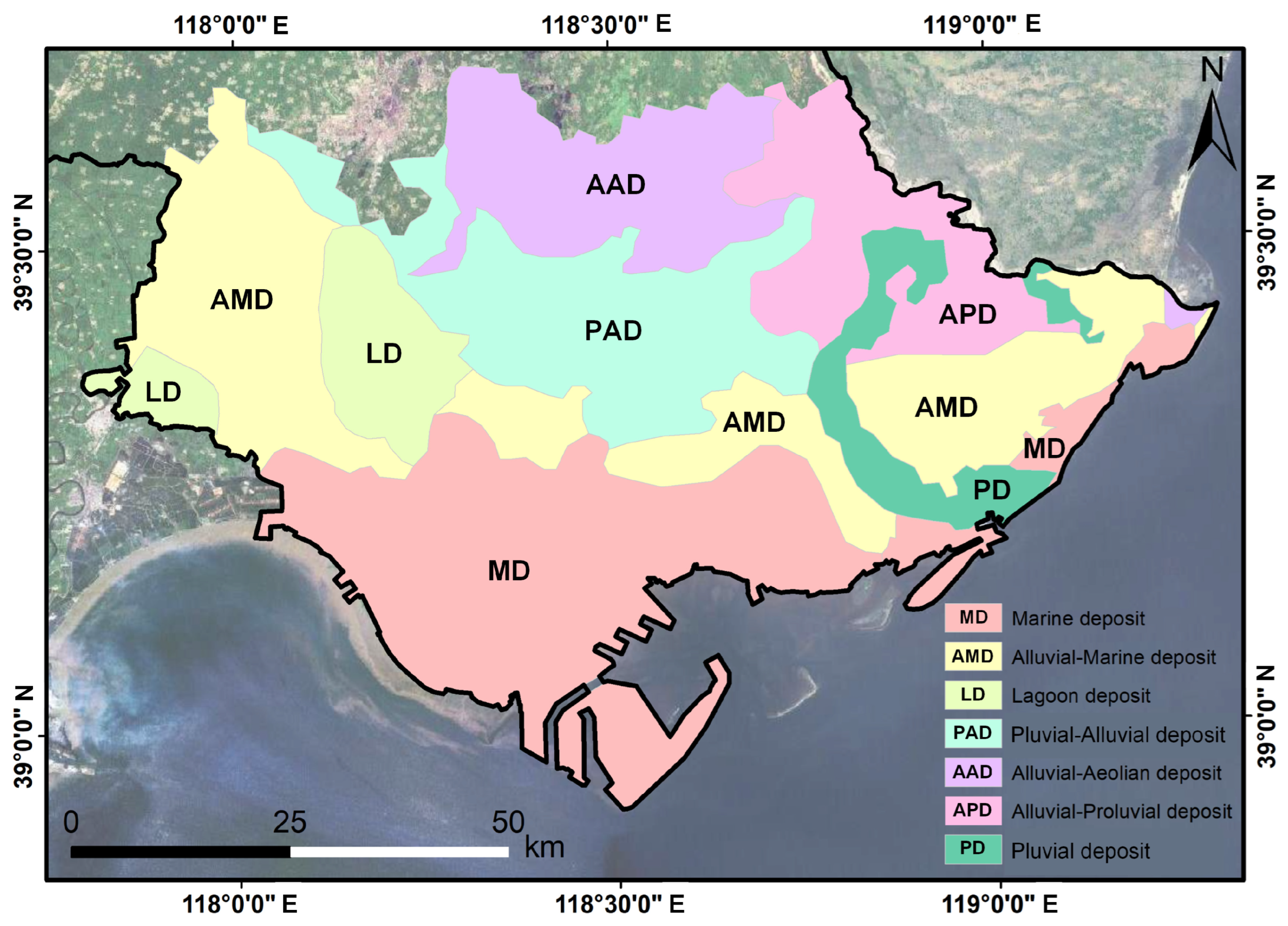
3. Methods and Datasets
3.1. Datasets
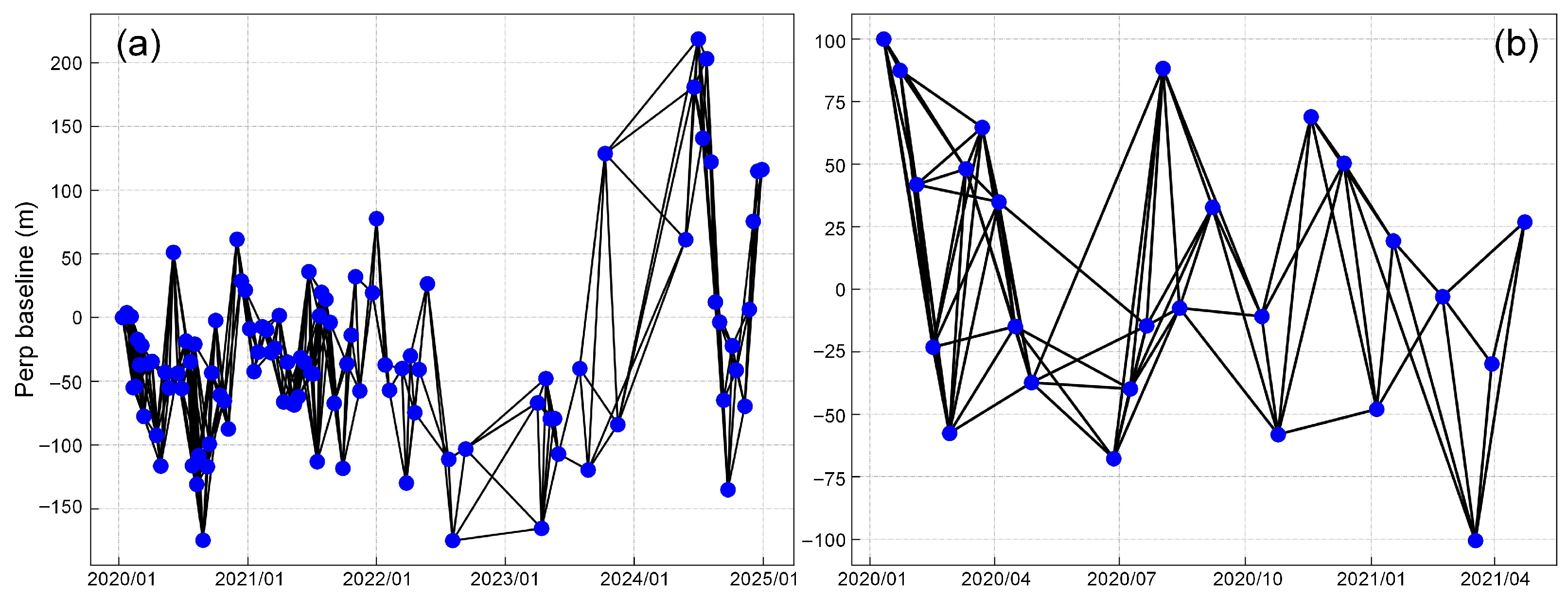
3.2. SBAS-InSAR
3.3. Independent Component Analysis
4. Results
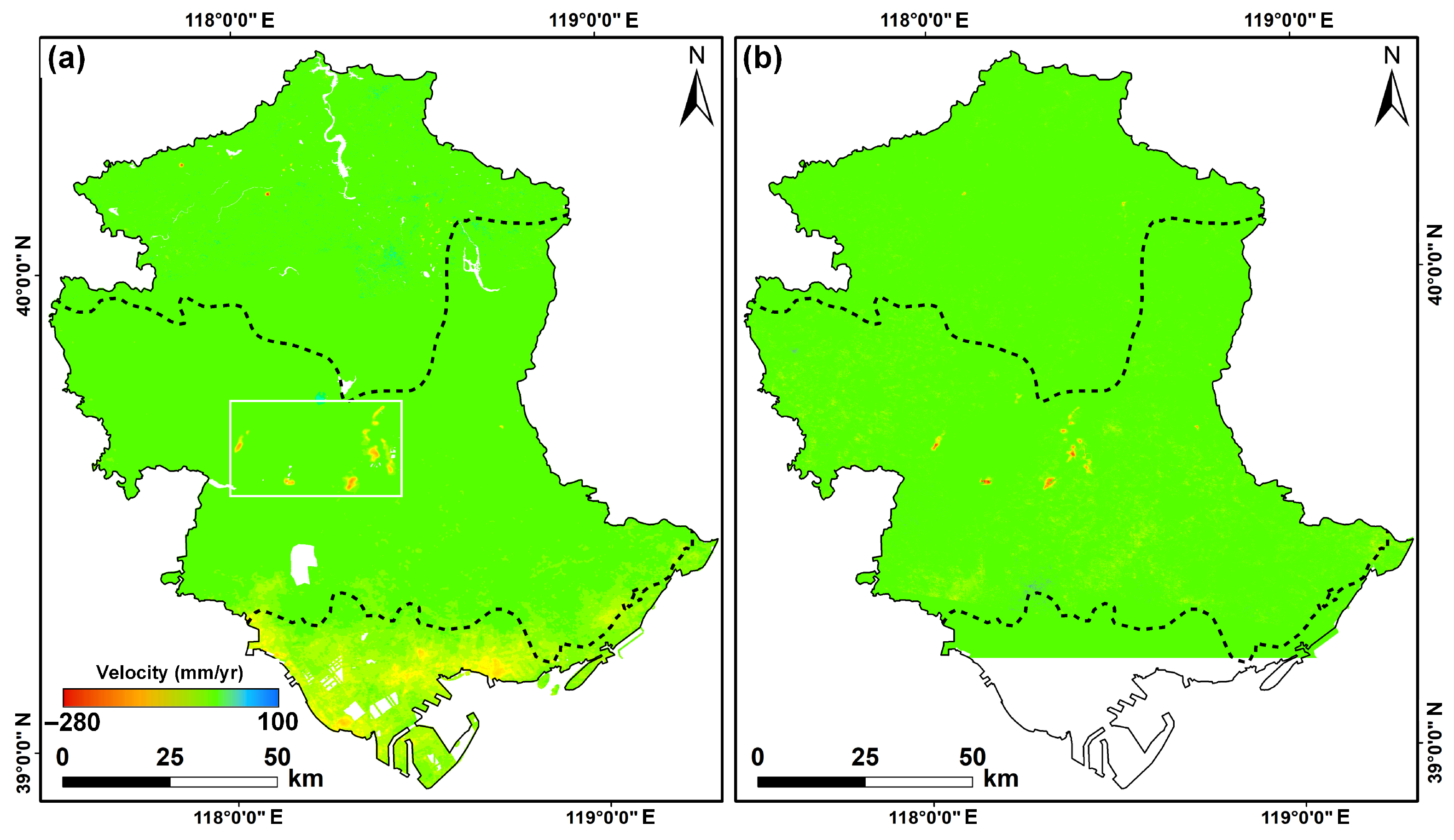
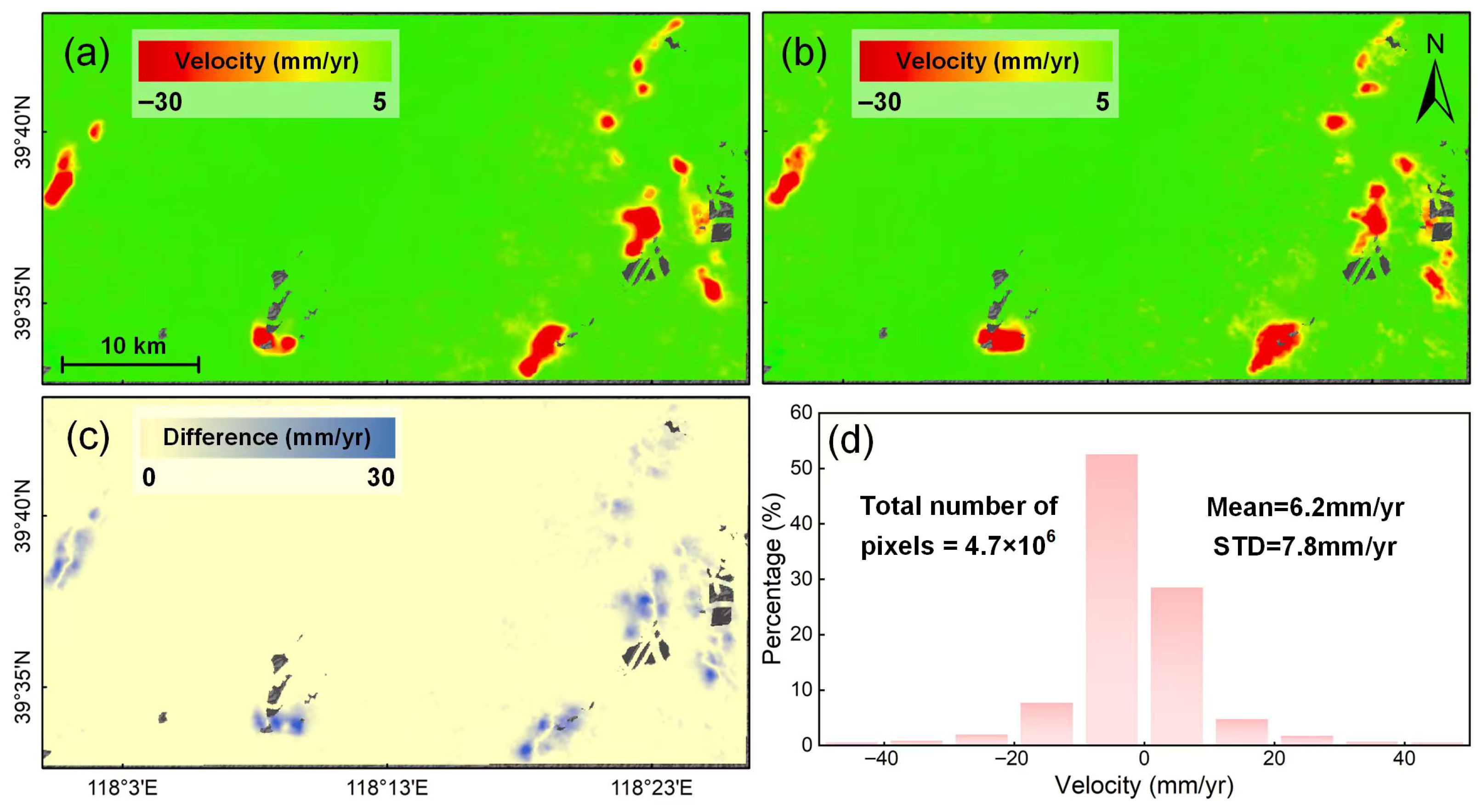
4.1. Regional Surface Deformation and Cross-Validation of InSAR Measurements
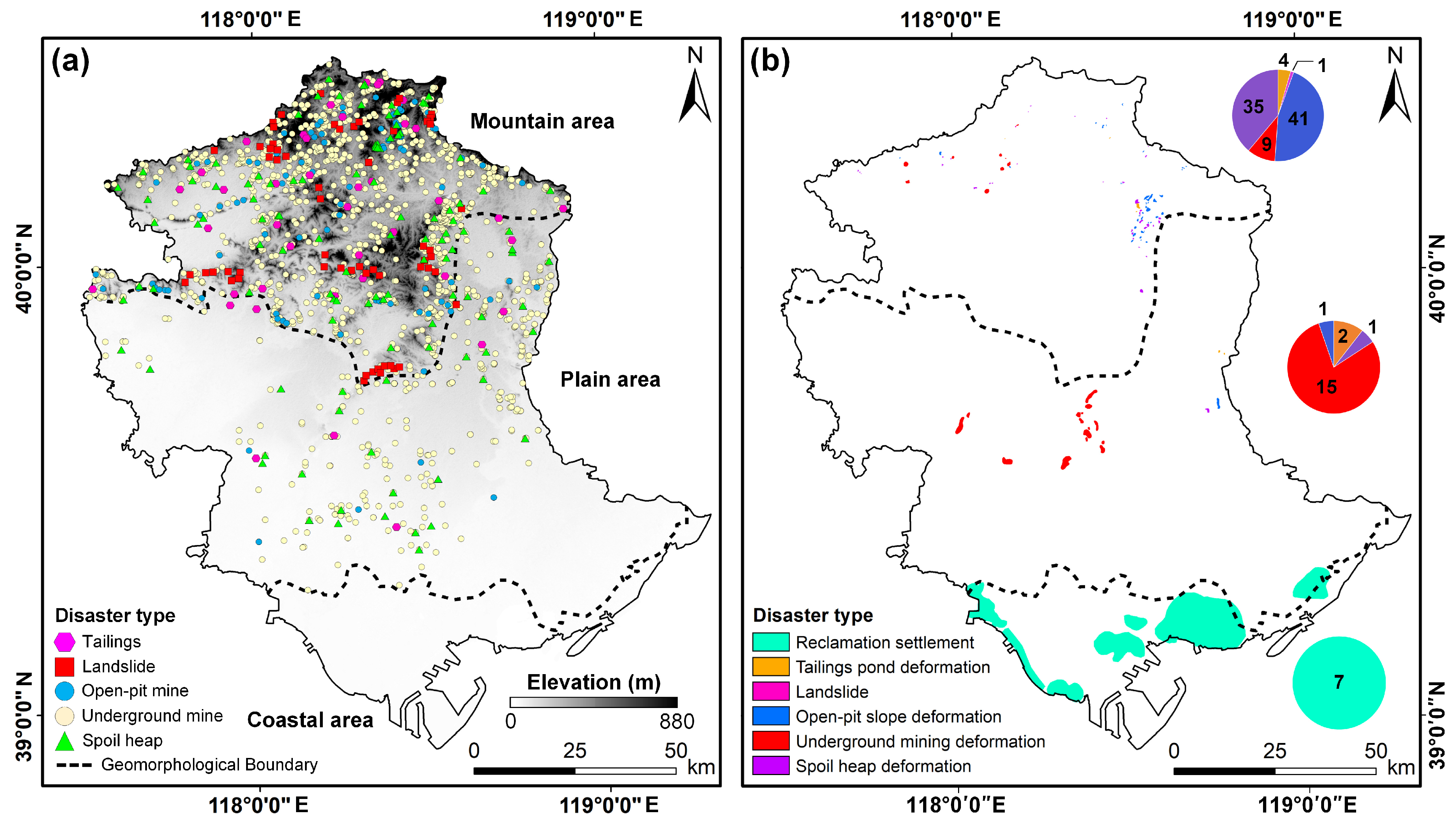
4.2. Multi-Geohazards Inventory
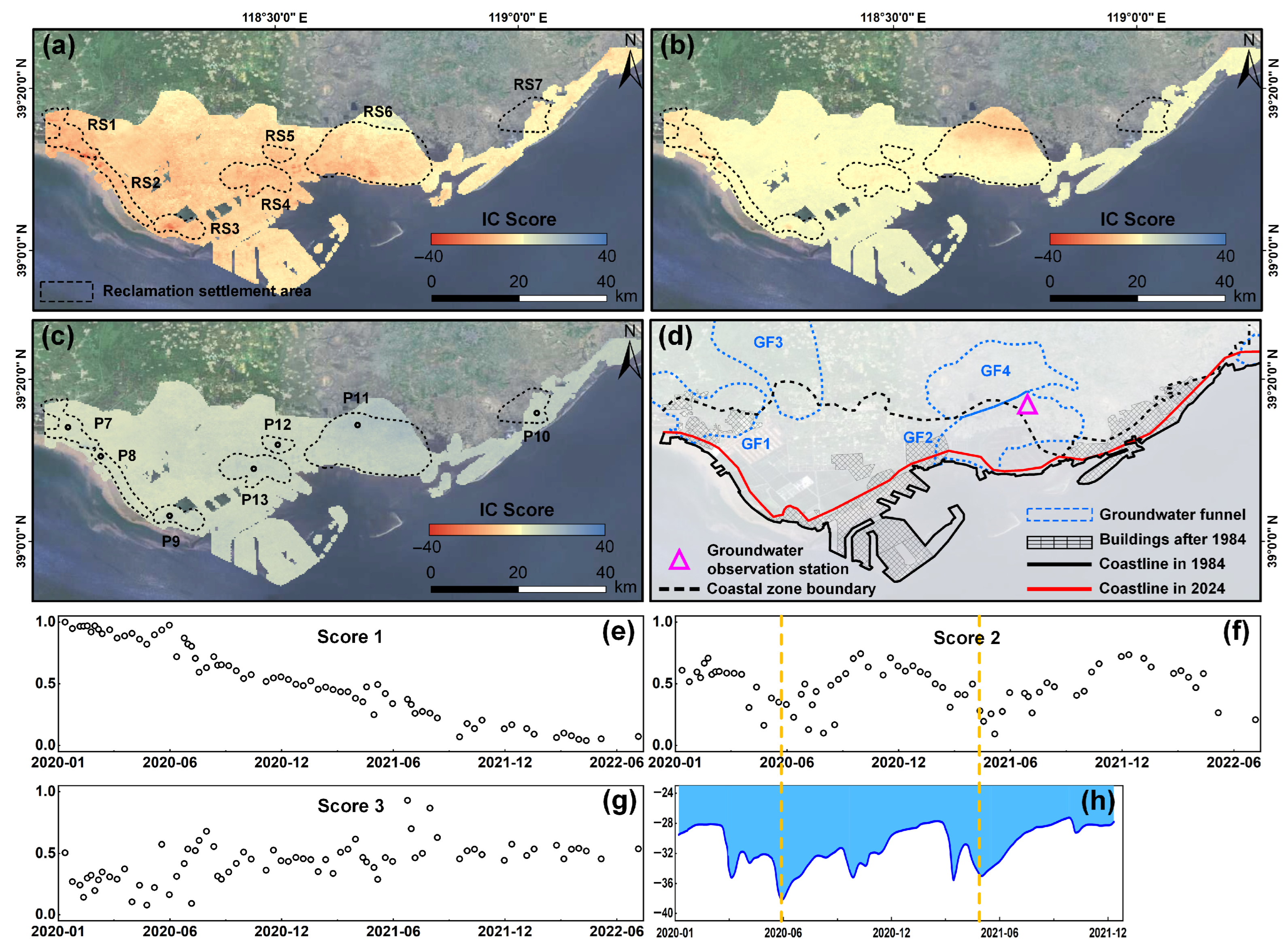
4.3. ICA-Derived Spatiotemporal Signals of Reclamation Settlement
5. Discussion
5.1. Implications of 2D Deformation and Validation Strategy in Mining Areas
5.2. Spatiotemporal Patterns and Underlying Causes of Multi-Geohazards
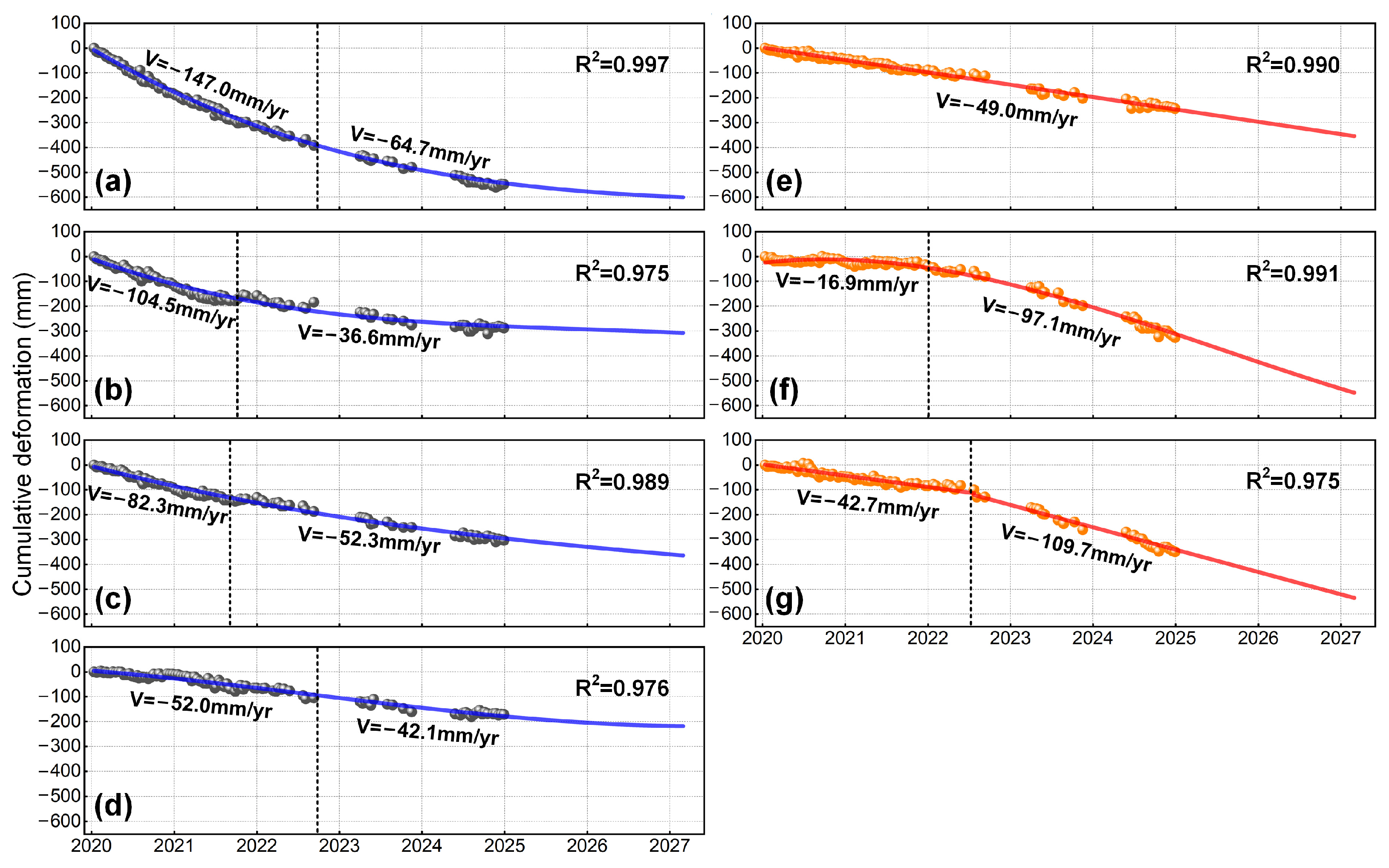
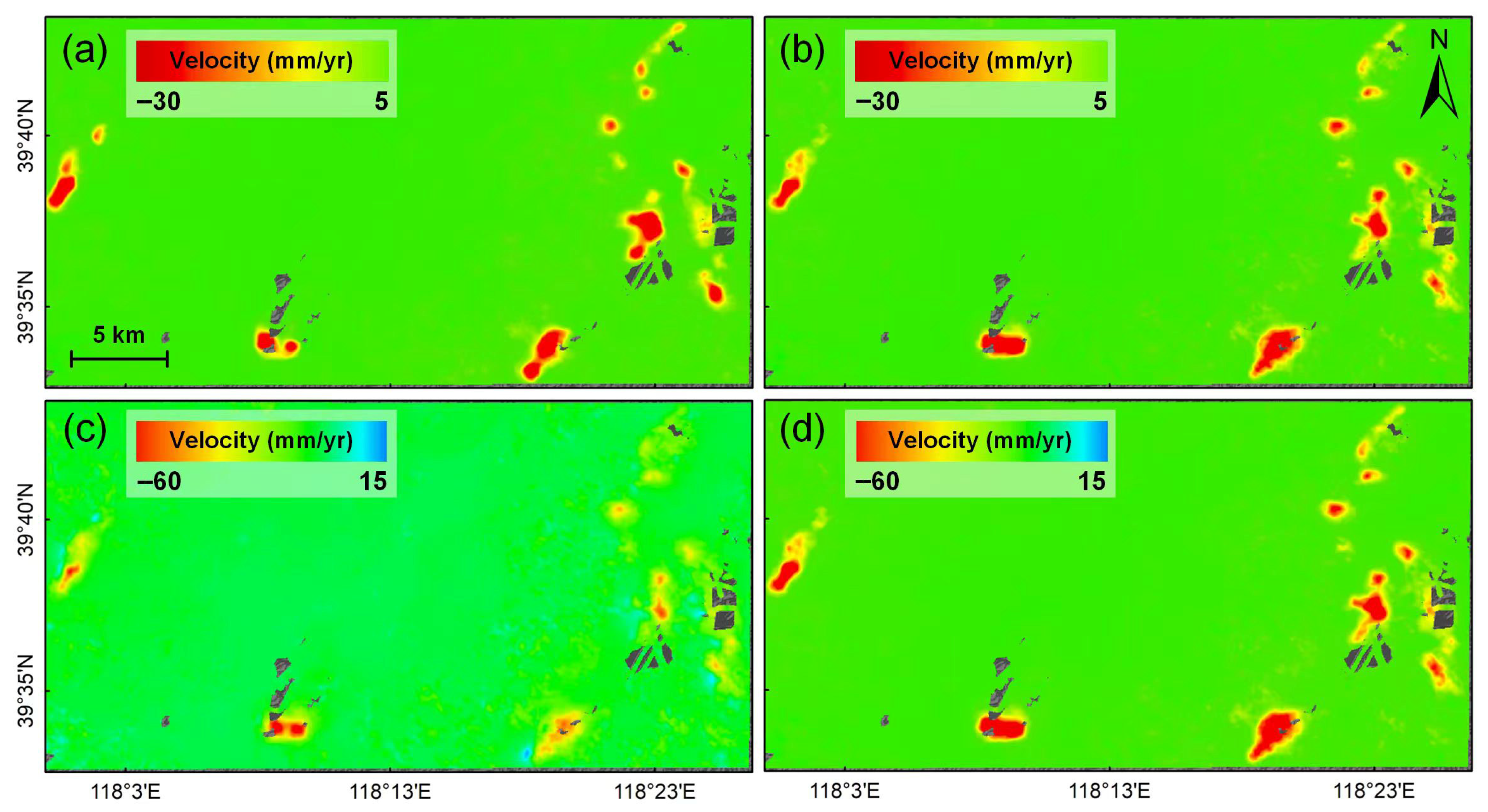
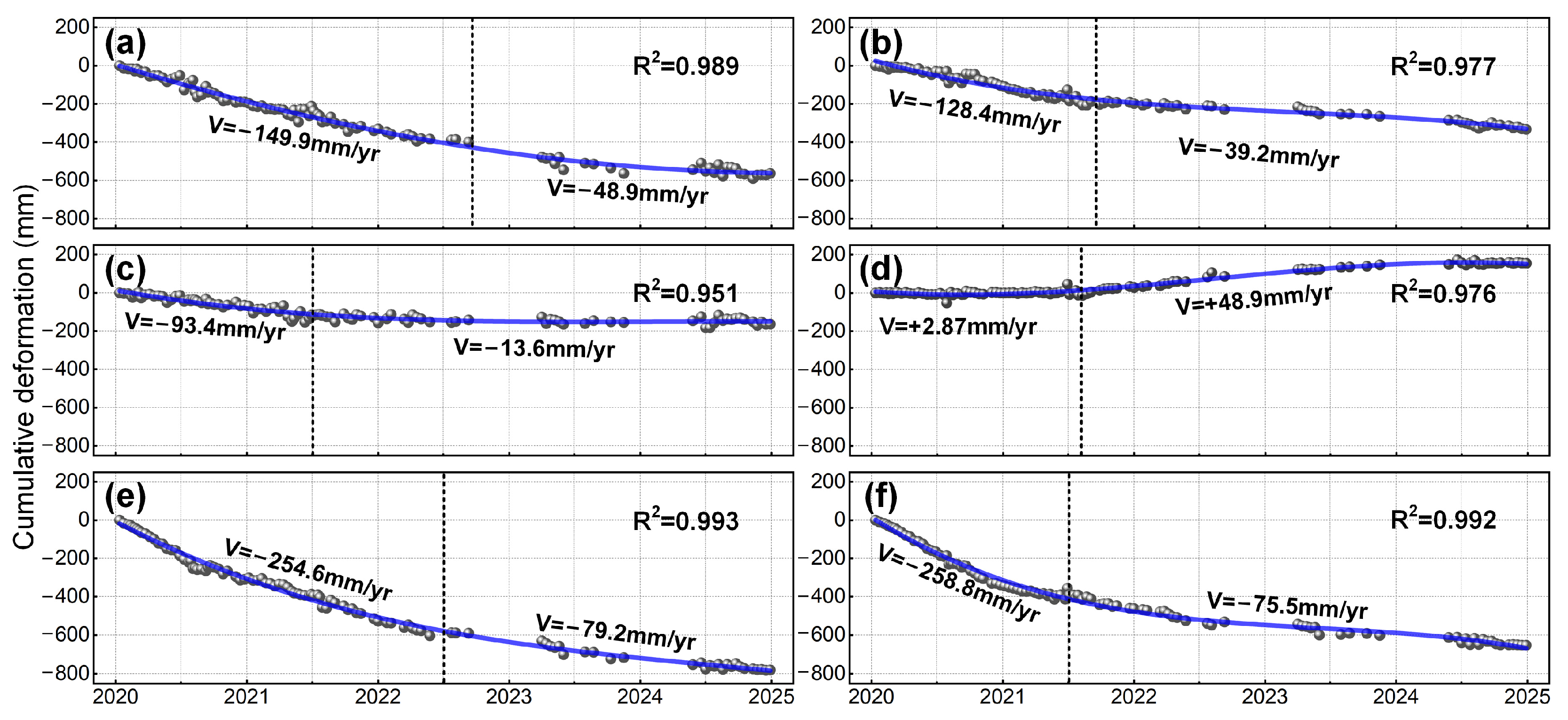
- Tailings pond deformation (Figure 10c,d): Both the eastern and western dam sections exhibit significant movement away from the satellite, governed mainly by vertical compression and consolidation of the dam materials. The notable slowdown in deformation suggests that consolidation is nearing completion (Figure 11b).
- Open-pit slope deformation (Figure 10g,h): This case displays typical instability patterns: the western slope moves southeast (away from the satellite) and the eastern slope moves northwest (toward the satellite). After June 2021, the deformation rate accelerated from 2.87 mm/yr to 48.9 mm/yr, reflecting rapid slope degradation that requires immediate monitoring and early warning (Figure 11d).
- Mining-induced subsidence (Figure 10i,j): This type is marked by large, contiguous subsidence zones with sharp boundaries and high magnitudes. Although the rate decreased from –254.6 mm/yr to –79.2 mm/yr after June 2022, it remains considerable, indicating ongoing risk and the need for continued monitoring (Figure 11e).
- Spoil heap deformation (Figure 10k,l): Deformation is mainly caused by self-weight consolidation of the piled material. Although the trend is decelerating, the rate remains high (–75.5 mm/yr) (Figure 11f). Given the considerable height of the heap, there is a notable risk of lateral collapse or sliding, necessitating sustained monitoring.
5.3. Determination of the Optimal Number of ICA Components
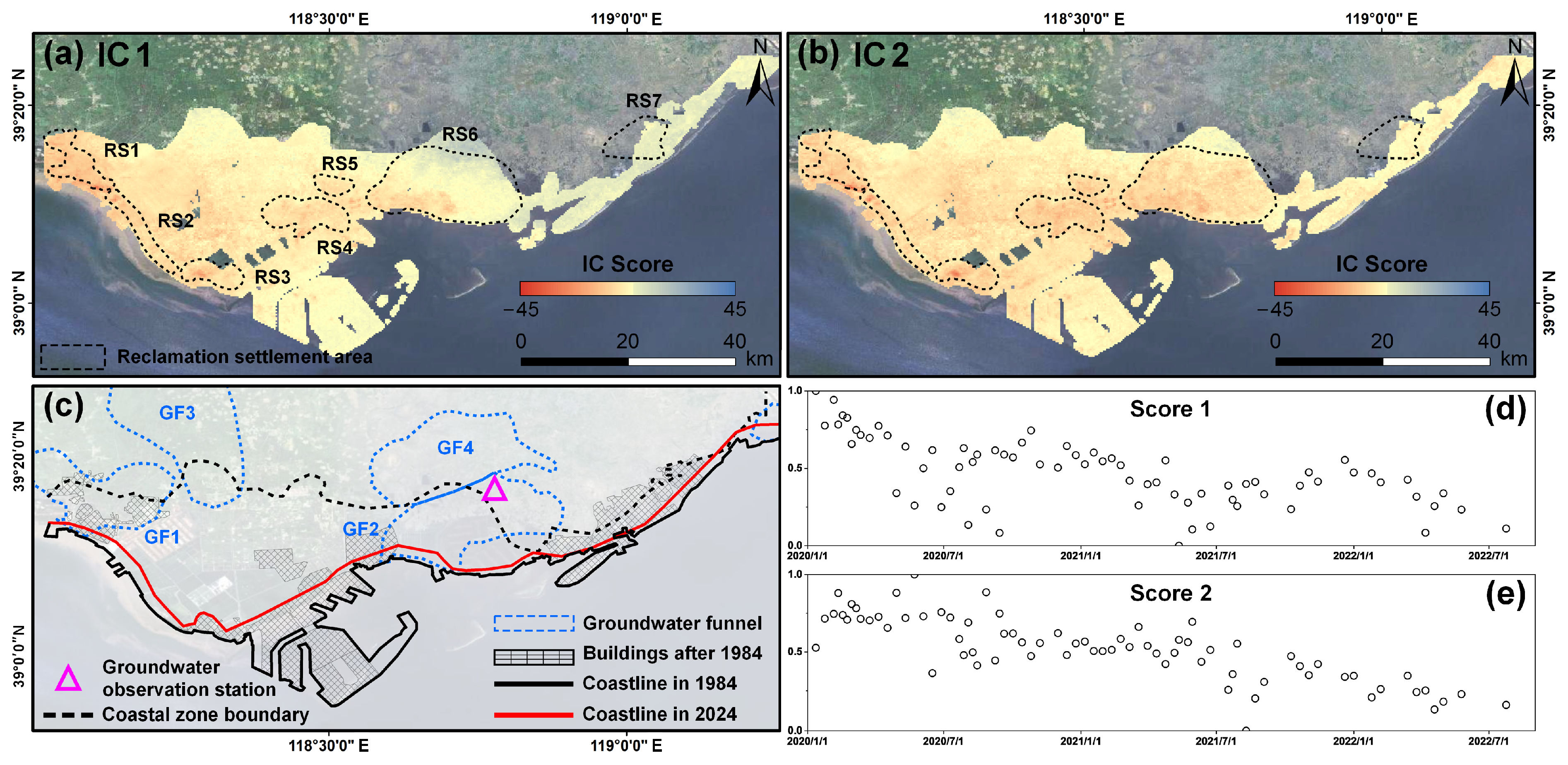
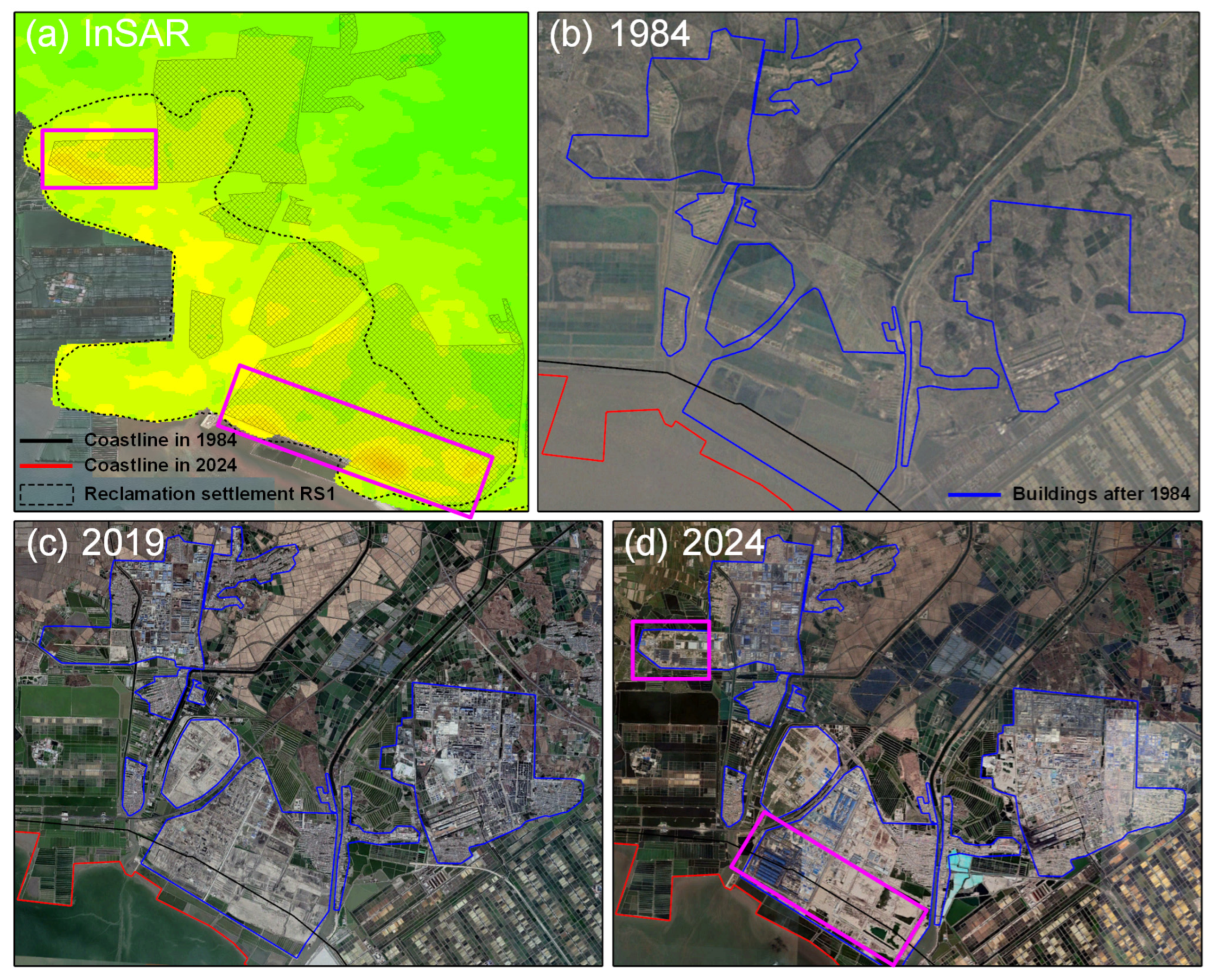
5.4. Driving Mechanisms of Coastal Reclamation Settlement Unraveled by ICA
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hasan, M.F.; Smith, R.; Vajedian, S.; Pommerenke, R.; Majumdar, S. Global Land Subsidence Mapping Reveals Widespread Loss of Aquifer Storage Capacity. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huning, L.S.; Love, C.A.; Anjileli, H.; Vahedifard, F.; Zhao, Y.; Chaffe, P.L.B.; Cooper, K.; Alborzi, A.; Pleitez, E.; Martinez, A.; et al. Global Land Subsidence: Impact of Climate Extremes and Human Activities. Rev. Geophys. 2024, 62, e2023RG000817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Xu, C.; Ma, J.; Gao, H. Escalating Risks and Impacts of Rainfall-Induced Geohazards. Nat. Hazards Res. 2025, 5, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaussard, E.; Amelung, F.; Abidin, H.; Hong, S.-H. Sinking Cities in Indonesia: ALOS PALSAR Detects Rapid Subsidence Due to Groundwater and Gas Extraction. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 128, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohenhen, L.O.; Zhai, G.; Lucy, J.; Werth, S.; Carlson, G.; Khorrami, M.; Onyike, F.; Sadhasivam, N.; Tiwari, A.; Ghobadi-Far, K. Land Subsidence Risk to Infrastructure in US Metropolises. Nat. Cities 2025, 2, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasechko, S.; Seybold, H.; Perrone, D.; Fan, Y.; Shamsudduha, M.; Taylor, R.G.; Fallatah, O.; Kirchner, J.W. Rapid Groundwater Decline and Some Cases of Recovery in Aquifers Globally. Nature 2024, 625, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, A.; Wang, T.; Yang, Y.; Lv, J.; Jiang, H.; Chen, K.; Mao, W. Reclaimed-Land Subsidence Mechanism Analysis and Evolution Prediction of Tianjin Binhai New Area, China Based on Time-Series InSAR Observations. Adv. Space Res. 2025, 76, 1368–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yan, F.; Chen, J.; Fan, X. Detection Ground Deformation Characteristics of Reclamation Land with Time-Series Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar in Tianjin Binhai New Area, China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent Scatterers in SAR Interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosetto, M.; Monserrat, O.; Cuevas-González, M.; Devanthéry, N.; Crippa, B. Persistent Scatterer Interferometry: A Review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 115, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A New Algorithm for Surface Deformation Monitoring Based on Small Baseline Differential SAR Interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Pang, H.; Li, Y.; Fan, L.; Wei, S.; Yuan, Z.; Fang, Y. Applications and Advancements of Spaceborne InSAR in Landslide Monitoring and Susceptibility Mapping: A Systematic Review. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosetto, M.; Crippa, B.; Mróz, M.; Cuevas-González, M.; Shahbazi, S. Applications Based on EGMS Products: A Review. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2025, 37, 101452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Yu, Y.; Yang, S.; Lv, Y.; Sarker, M.N.I. Urban Resilience for Urban Sustainability: Concepts, Dimensions, and Perspectives. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen-Waeber, J.; Bürgmann, R.; Chaussard, E.; Giannico, C.; Ferretti, A. Spatiotemporal Patterns of Precipitation-Modulated Landslide Deformation from Independent Component Analysis of InSAR Time Series. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 1878–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyvärinen, A.; Oja, E. Independent Component Analysis: Algorithms and Applications. Neural Netw. 2000, 13, 411–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualandi, A.; Liu, Z. Variational Bayesian Independent Component Analysis for InSAR Displacement Time-Series with Application to Central California, USA. JGR Solid Earth 2021, 126, e2020JB020845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Dong, D.; Chen, J. Application of Independent Component Analysis to GPS Position Time Series in Yunnan Province, Southwest of China. Adv. Space Res. 2022, 69, 4111–4122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Huang, J.; Zhao, Y. Coupling Coordination Analysis of Ecosystem Services and Urban Development of Resource-Based Cities: A Case Study of Tangshan City. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 136, 108706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The 1976 Tangshan Earthquake|U.S. Geological Survey. Available online: https://www.usgs.gov/publications/1976-tangshan-earthquake (accessed on 10 October 2025).
- Nábělek, J.; Chen, W.; Ye, H. The Tangshan Earthquake Sequence and Its Implications for the Evolution of the North China Basin. J. Geophys. Res. 1987, 92, 12615–12628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Z.-H.; Wei, T.-Y.; Zhao, B.-C.; Chen, Z.-Y. Clay Minerals in the Pliocene–Quaternary Sediments of the Southern Yangtze Coast, China: Sediment Sources and Palaeoclimate Implications. J. Palaeogeogr. 2014, 3, 297–308. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Ge, D.; Guo, X.; Liu, B.; Li, M.; Wang, Y. InSAR Monitoring Surface Deformation Induced by Underground Mining Using Sentinel-1 Images. Proc. Int. Assoc. Hydrol. Sci. 2020, 382, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, Y. Study on Land Subsidence Characteristics and Deformation Evolution Mechanism in Caofeidian New Area, Bohai Bay. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2023, 82, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Shi, X.; Wu, Y.; Ge, D.; Tang, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y. Monitoring Subsidence Characteristics in Southern Tangshan from 2015—2021 Using Multi-temporal Sentinel-1 Data. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2025, 50, 1648–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Wei, M.; D’Hondt, S. Subsidence in Coastal Cities Throughout the World Observed by InSAR. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2022GL098477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Wang, Y. Assessment of Reclamation-Induced Consolidation Settlement Considering Stratigraphic Uncertainty and Spatial Variability of Soil Properties. Can. Geotech. J. 2022, 59, 1215–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanari, R.; Casu, F.; Manzo, M.; Zeni, G.; Berardino, P.; Manunta, M.; Pepe, A. An Overview of the Small BAseline Subset Algorithm: A DInSAR Technique for Surface Deformation Analysis. In Deformation and Gravity Change: Indicators of Isostasy, Tectonics, Volcanism, and Climate Change; Wolf, D., Fernández, J., Eds.; Pageoph Topical Volumes; Birkhäuser Basel: Basel, Switzerland, 2007; pp. 637–661. ISBN 978-3-7643-8416-6. [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein, R.M.; Werner, C.L. Radar Interferogram Filtering for Geophysical Applications. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1998, 25, 4035–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.W.; Zebker, H.A. Two-Dimensional Phase Unwrapping with Use of Statistical Models for Cost Functions in Nonlinear Optimization. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2001, 18, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casu, F.; Manzo, M.; Lanari, R. A Quantitative Assessment of the SBAS Algorithm Performance for Surface Deformation Retrieval from DInSAR Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 102, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comon, P. Independent Component Analysis, a New Concept? Signal Process. 1994, 36, 287–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, G.R.; Kumar, D.K. An overview of independent component analysis and its applications. J. Inform. 2011, 35, 63–81. [Google Scholar]
- Hyvärinen, A.; Oja, E. A Fast Fixed-Point Algorithm for Independent Component Analysis. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1483–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaddes, M.E.; Hooper, A.; Bagnardi, M.; Inman, H.; Albino, F. Blind Signal Separation Methods for InSAR: The Potential to Automatically Detect and Monitor Signals of Volcanic Deformation. JGR Solid Earth 2018, 123, 10,226–10,251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maubant, L.; Pathier, E.; Daout, S.; Radiguet, M.; Doin, M.-P.; Kazachkina, E.; Kostoglodov, V.; Cotte, N.; Walpersdorf, A. Independent Component Analysis and Parametric Approach for Source Separation in InSAR Time Series at Regional Scale: Application to the 2017–2018 Slow Slip Event in Guerrero (Mexico). JGR Solid Earth 2020, 125, e2019JB018187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himberg, J.; Hyvärinen, A.; Esposito, F. Validating the Independent Components of Neuroimaging Time Series via Clustering and Visualization. Neuroimage 2004, 22, 1214–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Li, Z.W.; Ding, X.L.; Zhu, J.J.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Q. Resolving Three-Dimensional Surface Displacements from InSAR Measurements: A Review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2014, 133, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrmann, T.; Garthwaite, M.C. Resolving Three-Dimensional Surface Motion with InSAR: Constraints from Multi-Geometry Data Fusion. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Wang, L.; Wen, B.; Du, S. A New Model for Three-Dimensional Deformation Extraction with Single-Track InSAR Based on Mining Subsidence Characteristics. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 94, 102223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsonov, S.; d’Oreye, N. Multidimensional Time-Series Analysis of Ground Deformation from Multiple InSAR Data Sets Applied to Virunga Volcanic Province. Geophys. J. Int. 2012, 191, 1095–1108. [Google Scholar]
- Bekaert, D.P.S.; Hooper, A.; Wright, T.J. A Spatially Variable Power Law Tropospheric Correction Technique for InSAR Data. JGR Solid Earth 2015, 120, 1345–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, Z.; Li, Z.; Yang, C.; Zhu, W.; Liu-Zeng, J.; Chen, L.; Liu, C. Integration of Sentinel-1 and ALOS/PALSAR-2 SAR Datasets for Mapping Active Landslides along the Jinsha River Corridor, China. Eng. Geol. 2021, 284, 106033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, C.; Yin, Y.; Tomás, R.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, Y.; Wang, M.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.M. Refined InSAR Method for Mapping and Classification of Active Landslides in a High Mountain Region: Deqin County, Southern Tibet Plateau, China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 304, 114030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Li, Z.; Song, C.; Yu, C.; Zhu, W.; Liu, Z.; Han, B.; Du, J.; Zhang, C.; Xu, F.; et al. Automatic Detection of Active Geohazards with Millimeter-to-Meter-Scale Deformation and Quantitative Analysis of Factors Influencing Spatial Distribution: A Case Study in the Hexi Corridor, China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2024, 131, 103995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delbridge, B.G.; Bürgmann, R.; Fielding, E.; Hensley, S.; Schulz, W.H. Three-Dimensional Surface Deformation Derived from Airborne Interferometric UAVSAR: Application to the Slumgullion Landslide. JGR Solid Earth 2016, 121, 3951–3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parise, M.; Lollino, P. A Preliminary Analysis of Failure Mechanisms in Karst and Man-Made Underground Caves in Southern Italy. Geomorphology 2011, 134, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, F.; Parise, M.; De Waele, J.; Jourde, H. A Review on Natural and Human-Induced Geohazards and Impacts in Karst. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2014, 138, 61–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Hong, S. Nonlinear Modeling of Subsidence from a Decade of InSAR Time Series. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2020GL090970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Deng, K.; Feng, G.; Miao, L.; Li, K.; He, C.; He, Y. Settlement Prediction of Reclaimed Coastal Airports with InSAR Observation: A Case Study of the Xiamen Xiang’an International Airport, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, Z.; Hu, X.; Tao, S.; Hu, X.; Wang, G.; Li, M.; Wang, F.; Hu, L.; Liang, X.; Xiao, J.; et al. A National-Scale Assessment of Land Subsidence in China’s Major Cities. Science 2024, 384, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Nicholls, R.J.; Brown, S.; Lincke, D.; Hinkel, J.; Vafeidis, A.T.; Du, S.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, M.; Shi, P. Benefits of Subsidence Control for Coastal Flooding in China. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Guo, S.; Wang, N.; Zhang, L.; Ge, D.; Liao, M.; Gong, J. Tri-Decadal Evolution of Land Subsidence in the Beijing Plain Revealed by Multi-Epoch Satellite InSAR Observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 286, 113446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolivet, R.; Agram, P.S.; Lin, N.Y.; Simons, M.; Doin, M.; Peltzer, G.; Li, Z. Improving InSAR Geodesy Using Global Atmospheric Models. JGR Solid Earth 2014, 119, 2324–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekaert, D.P.S.; Walters, R.J.; Wright, T.J.; Hooper, A.J.; Parker, D.J. Statistical Comparison of InSAR Tropospheric Correction Techniques. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 170, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Shan, Q.; Zhao, D.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, F. Unraveling the Patterns and Drivers of Multi-Geohazards in Tangshan, China, by Integrating InSAR and ICA. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 12584. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312584
Ma B, Wang Y, Zhao J, Shan Q, Zhao D, Zhou Y, Jiang F. Unraveling the Patterns and Drivers of Multi-Geohazards in Tangshan, China, by Integrating InSAR and ICA. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(23):12584. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312584
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Bingtai, Yang Wang, Jianqing Zhao, Qiang Shan, Degang Zhao, Yiwen Zhou, and Fuwei Jiang. 2025. "Unraveling the Patterns and Drivers of Multi-Geohazards in Tangshan, China, by Integrating InSAR and ICA" Applied Sciences 15, no. 23: 12584. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312584
APA StyleMa, B., Wang, Y., Zhao, J., Shan, Q., Zhao, D., Zhou, Y., & Jiang, F. (2025). Unraveling the Patterns and Drivers of Multi-Geohazards in Tangshan, China, by Integrating InSAR and ICA. Applied Sciences, 15(23), 12584. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312584




