KA-RAG: Integrating Knowledge Graphs and Agentic Retrieval-Augmented Generation for an Intelligent Educational Question-Answering Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Retrieval-Augmented Generation and Hybrid Retrieval Mechanisms
2.2. Knowledge Graph Representation and Relational Learning
2.3. Agentic Reasoning and Tool-Augmented Language Models
2.4. Fusion Strategies Between RAG and Knowledge Graphs
2.5. Comparative Analysis of RAG, KG, and Agentic-RAG Frameworks
2.6. Research Gap and Contributions
3. Methods and Materials
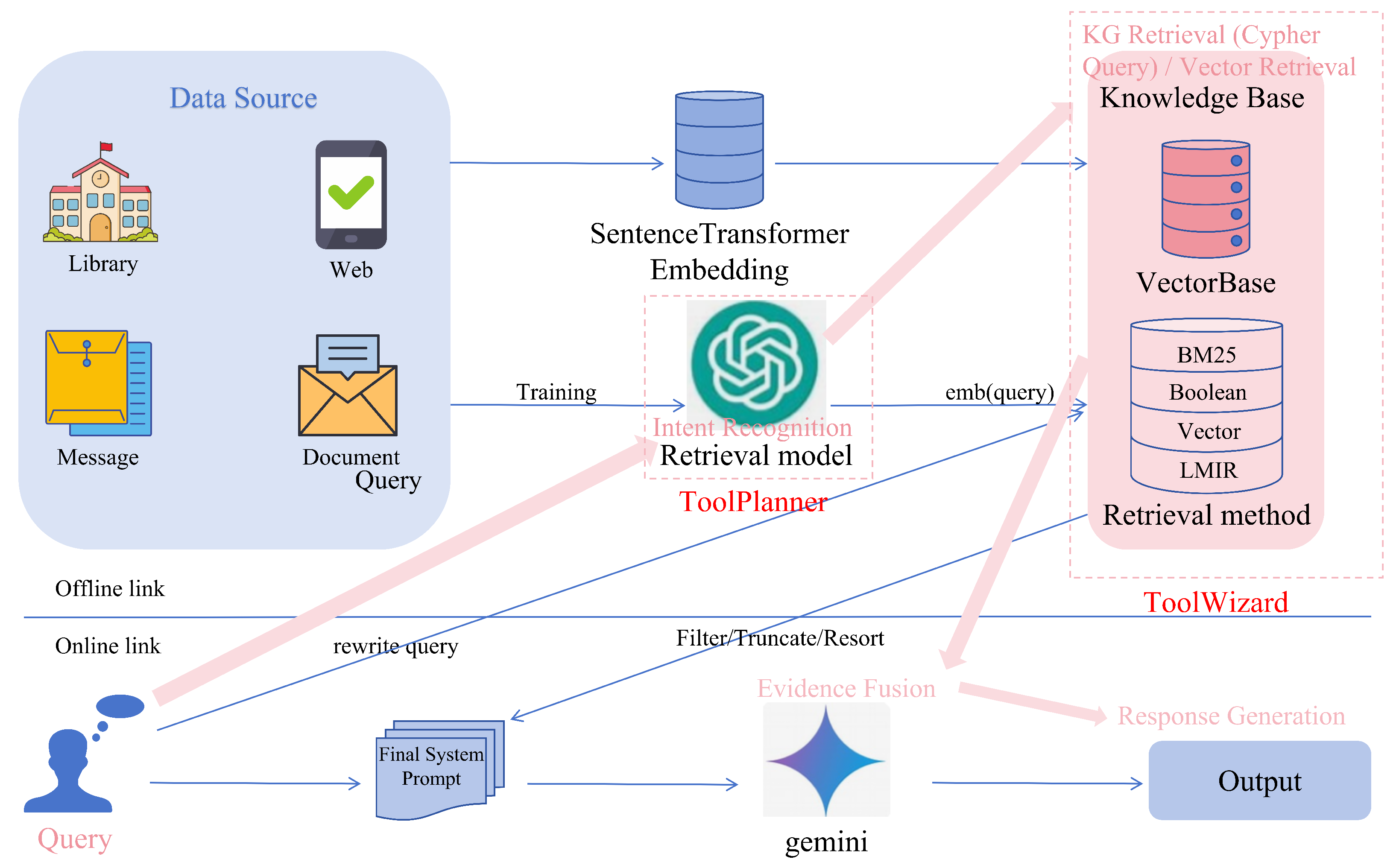
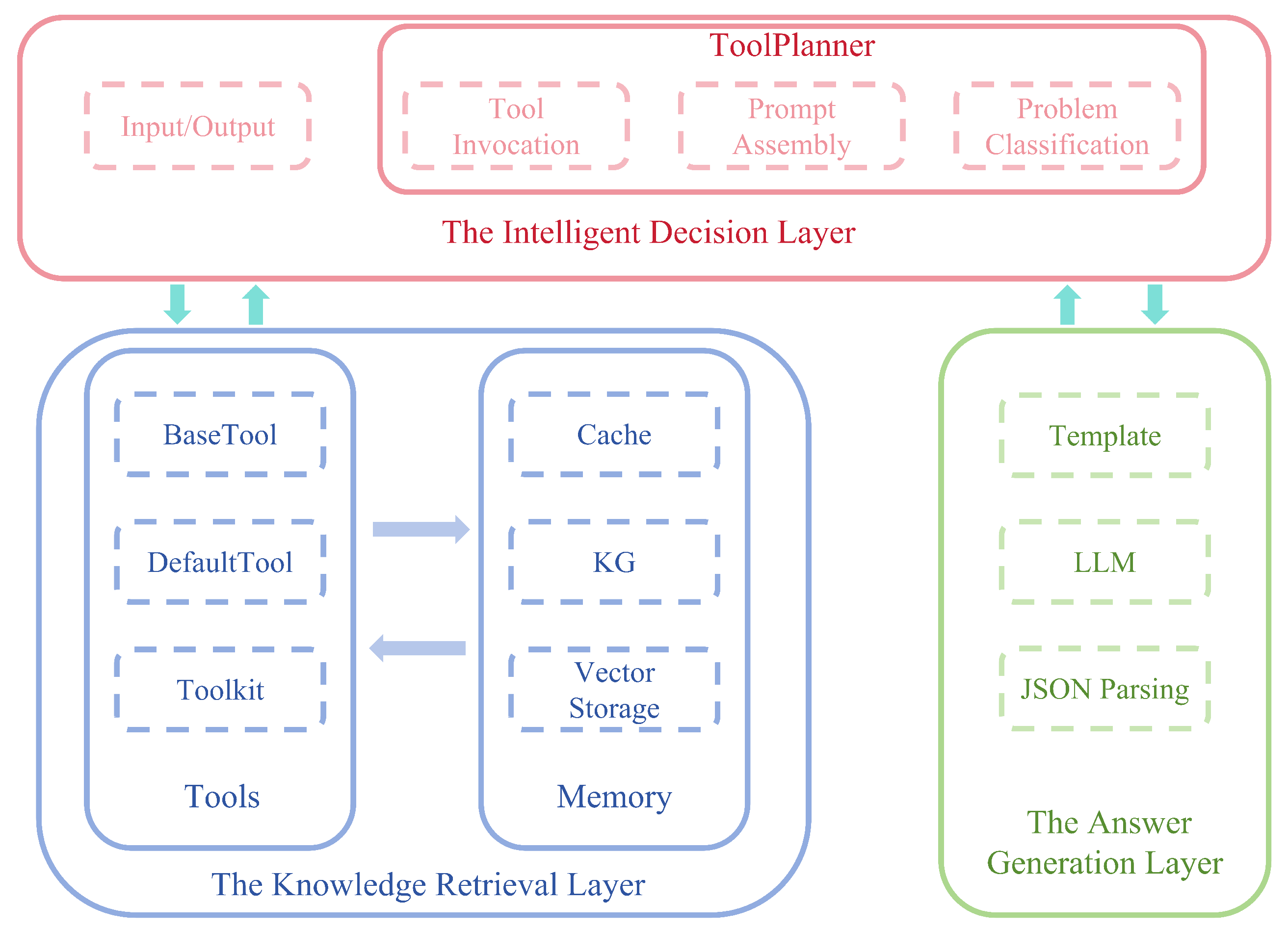
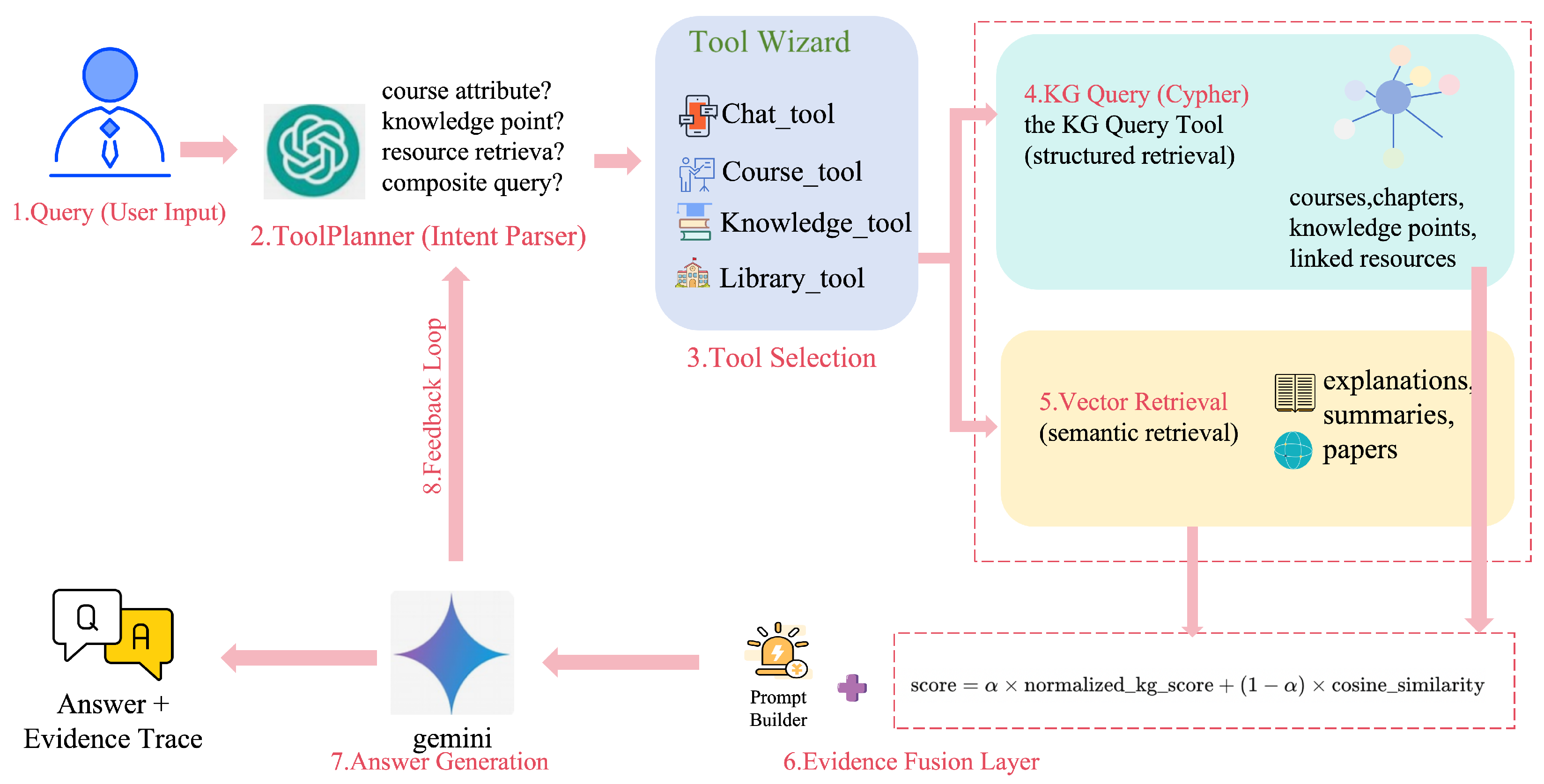
3.1. Overall Architecture
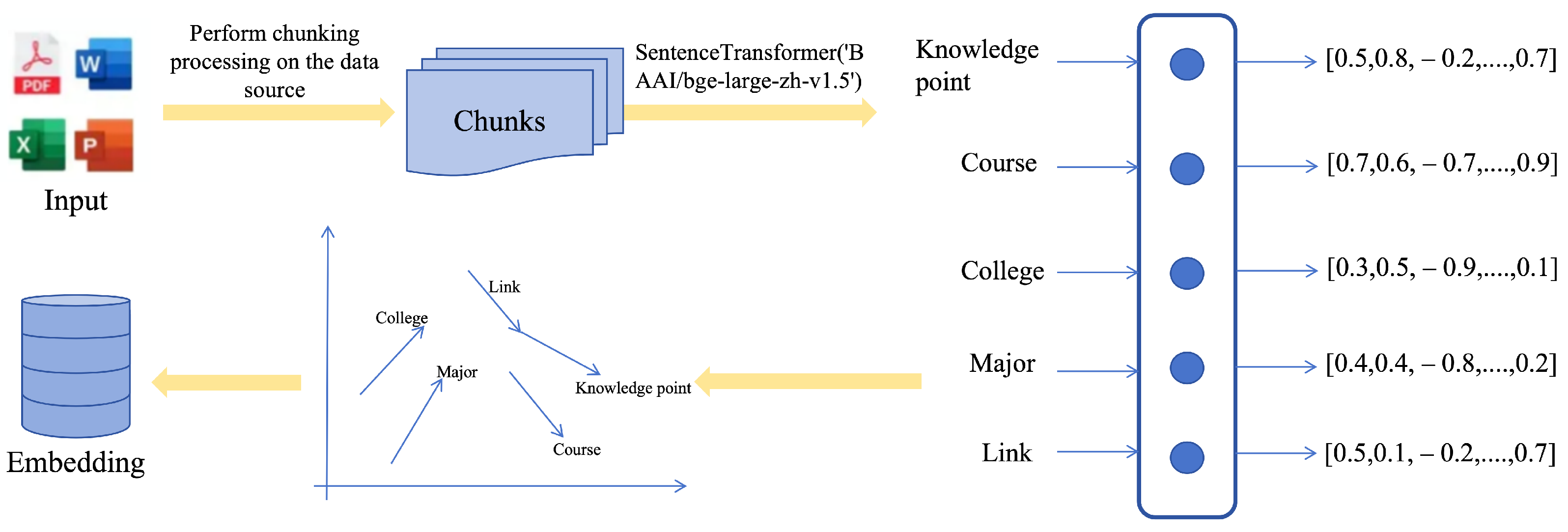
3.2. Hybrid Slicing Method for Educational Vector Databases
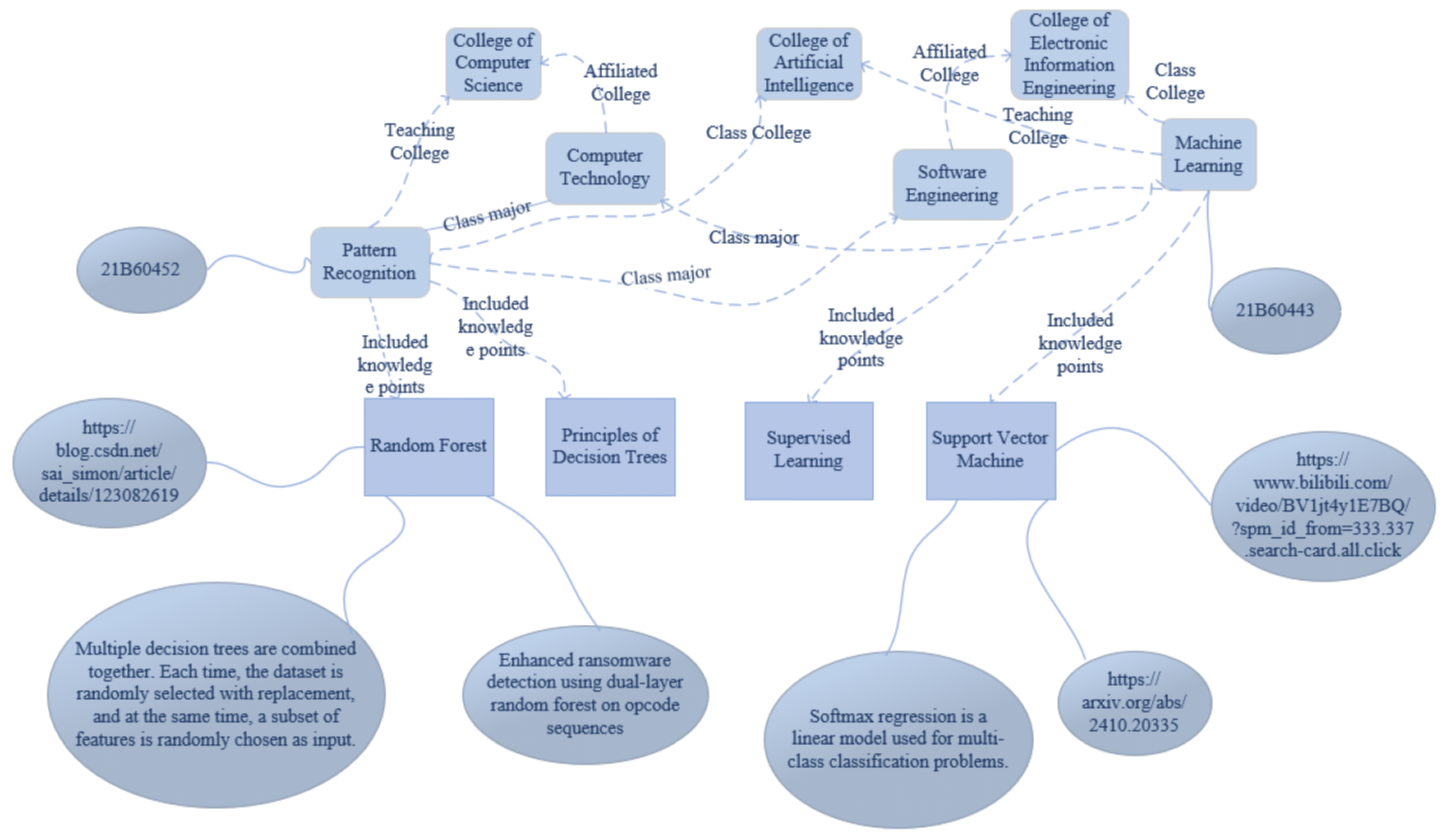
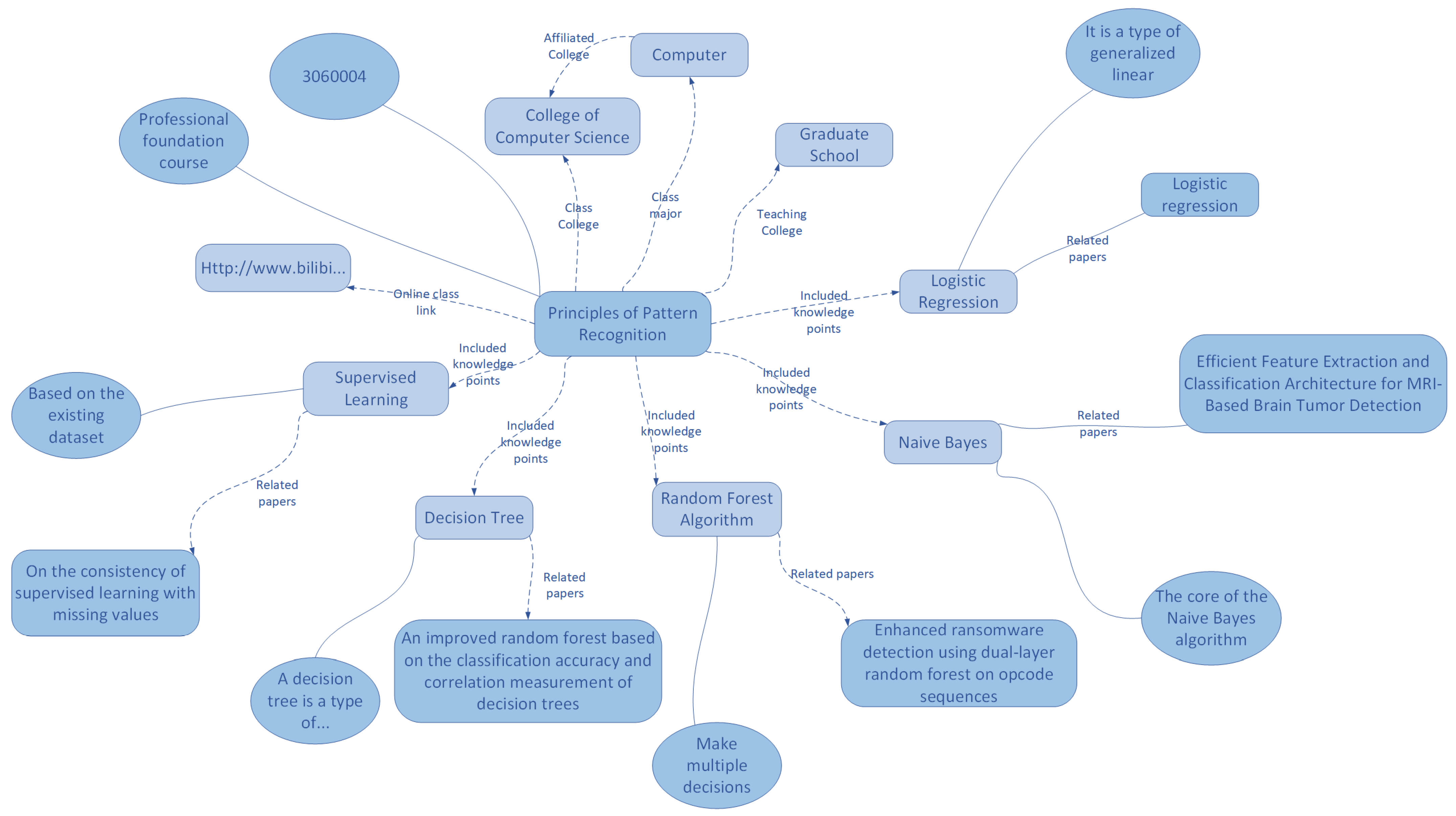
3.3. Cross-Module Knowledge Graph Construction
3.3.1. Module Definition and Structure
3.3.2. Knowledge Extraction and Relation Construction
3.3.3. Storage and Query Optimization
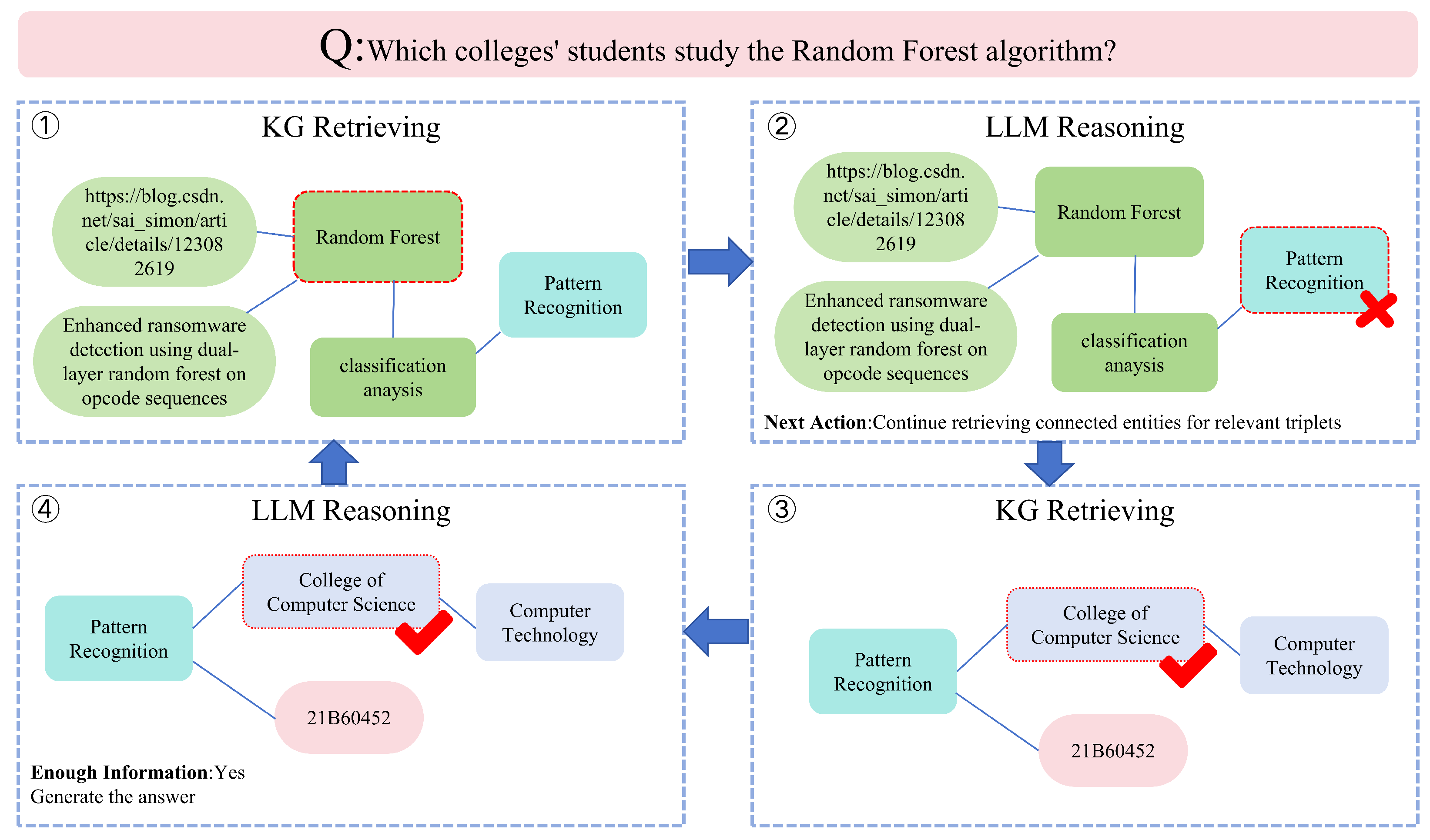
3.4. Agentic-RAG Multi-Round Tool-Calling Mechanism
Agent Decision Module Design
3.5. Joint RAG–Knowledge-Graph Retrieval Process
3.6. Generative Model and Prompt Optimization
3.6.1. Model Configuration
3.6.2. Scenario-Based Prompt Templates
- Course-attribute queries: enforce structured output following the order course name–credit–school–applicable majors.
- Knowledge-point Q&A: emphasize hierarchical reasoning (chapter–core concept–application case) and integrate textual and linked evidence.
- Composite queries: require synthesis of attributes, knowledge points, and resources into coherent multi-source answers with cited evidence.
4. Results
4.1. Experimental Design
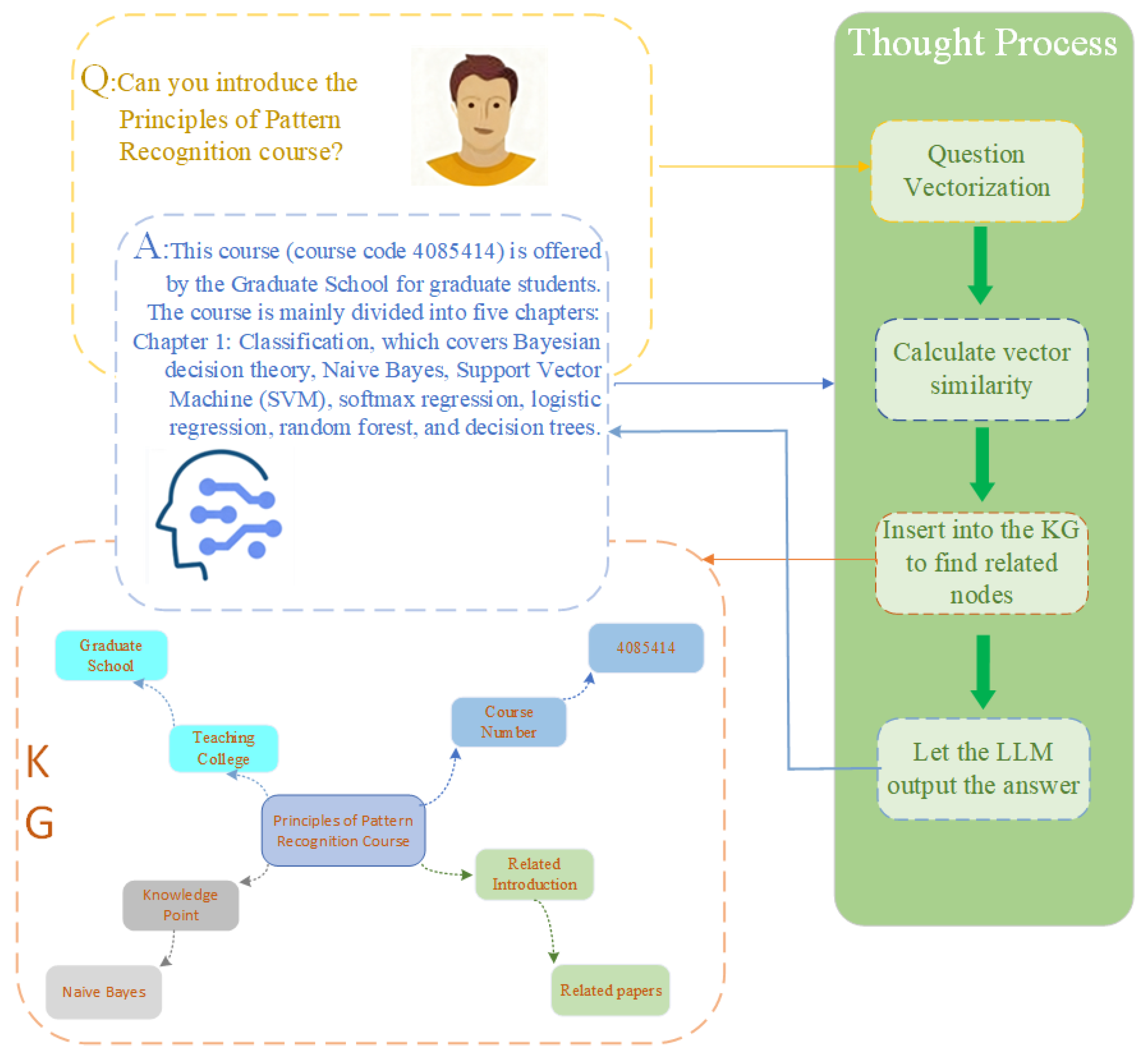
4.2. Case Selection and Analysis
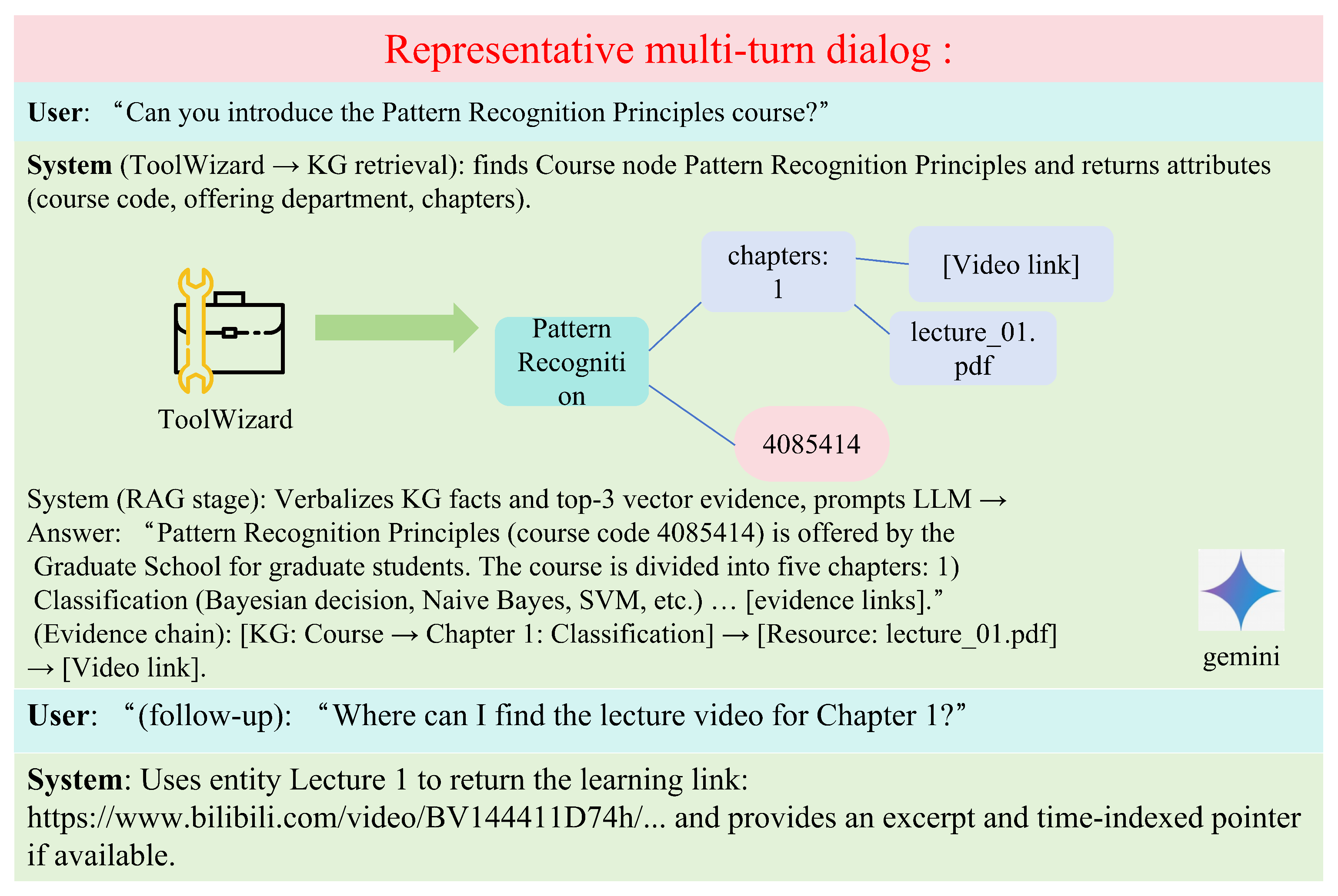
Representative Multi-Turn Dialog and UI Screenshots
4.3. Experimental Results and Discussion
4.3.1. Datasets
- Course attributes: course name, course code, credit value (3.0), offering school (School of Computer Science), and five applicable majors.
- Knowledge hierarchy: eight chapters (e.g., “Fundamentals of Pattern Recognition,” “Bayesian Classifier,” “Support Vector Machine”) containing 42 key knowledge points. Each knowledge point includes a difficulty level, concept explanation, and associated application scenarios.
4.3.2. Test Dataset Construction
4.3.3. Experimental Environment
4.3.4. Ablation Study on System Components
5. Practical Impact and Implications
5.1. Practical Impact
5.2. Implications and Future Directions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- García-Méndez, S.; e Arriba-Pérez, F.; Somoza-López, M.D.C. A Review on the Use of Large Language Models as Virtual Tutors. Sci. Educ. 2025, 34, 877–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S. Application of Large Language Models in the Field of Education. Theor. Nat. Sci. 2024, 34, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-H.; Kim, S.-J.; Lee, S.-T. AI and Creativity in Entrepreneurship Education: A Systematic Review of LLM Applications. AI 2025, 6, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.H.; Huang, J.; Chen, T. ITS-CAL: An Intelligent Tutoring System for Coding Powered by Large Language Models. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Liu, P.; Chen, X.; Yang, F.; Wu, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, W.; et al. Difficulty-Aware Programming Knowledge Tracing via Large Language Models. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 7422. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Zhan, Y.; Lian, J.; Hu, Z.; Yuan, N.J.; Zhang, Q.; Xie, X.; Xiong, H. LLM-Powered Multi-Agent Framework for Goal-Oriented Learning in Intelligent Tutoring Systems. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2501.15749. [Google Scholar]
- Gaeta, A.; Weber, F.; D’Angelo, G.; Di Adamo, D.; Persico, D.; Pinto, M.; Roselli, T.; Sessa, S.; Taibi, D.; Temperini, M. Enhancing Traditional Intelligent Tutoring Architectures with Large Language Models: Design and Evaluation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Information Systems (ICIS 2025), Nashville, TN, USA, 14–17 December 2025; AIS Electronic Library: Redmond, WA, USA, 2025; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Rashtchian, C.; Juan, P. Deeper Insights into Retrieval-Augmented Generation: The Role of Sufficient Context. Google Research Blog. 2025. Available online: https://research.google/blog/deeper-insights-into-retrieval-augmented-generation-the-role-of-sufficient-context/ (accessed on 13 November 2025).
- Wang, H.; Shi, Y. Knowledge Graph Combined with Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Enhancing LMs Reasoning: A Survey. Acad. J. Sci. Technol. 2025, 14, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klesel, M.; Wittmann, H.F. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). Bus. Inf. Syst. Eng. 2025, 67, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, X.; Luo, Y.; Gu, L. MS-RAG: Simple and Effective Multi-Semantic Retrieval-Augmented Generation. In Proceedings of the 2025 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Suzhou, China, 4–9 November 2025; Association for Computational Linguistics. 2025; pp. 22620–22636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Z.; Fan, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhengfan, W.; Huang, H.; Liu, T. RAG+: Enhancing Retrieval-Augmented Generation with Application-Aware Reasoning. In Proceedings of the 2025 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Suzhou, China, 4–9 November 2025; Association for Computational Linguistics. 2025; pp. 32001–32025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Xie, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Hu, W. Knowledge Graph-Guided Retrieval-Augmented Generation. In Proceedings of the 2025 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies (NAACL 2025), Long Papers, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 29 April–4 May 2025; pp. 8912–8924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Wang, F.; Huang, L. OctoTools: An Agentic Framework with Extensible Tools for Complex Reasoning. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.11271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osei Opoku, D.; Sheng, M.; Zhang, Y. DO-RAG: A Domain-Specific QA Framework Using Knowledge Graph-Enhanced Retrieval-Augmented Generation. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2505.17058. [Google Scholar]
- An, B.; Zhang, S.; Dredze, M. RAG LLMs Are Not Safer: A Safety Analysis of Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Large Language Models. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2504.18041. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, P.; Perez, E.; Piktus, A.; Petroni, F.; Karpukhin, V.; Goyal, N.; Küttler, H.; Lewis, M.; Yih, W.-t.; Rocktäschel, T.; et al. Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Knowledge-Intensive NLP Tasks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 9459–9474. [Google Scholar]
- Karpukhin, V.; Oguz, B.; Min, S.; Lewis, P.S.; Wu, L.; Edunov, S.; Chen, D.; Yih, W.-t. Dense Passage Retrieval for Open-Domain Question Answering. In Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP 2020), Online, 16–20 November 2020; pp. 6769–6781. [Google Scholar]
- Guu, K.; Lee, K.; Tung, Z.; Pasupat, P.; Chang, M.-W. REALM: Retrieval-Augmented Language Model Pre-Training. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.08909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izacard, G.; Grave, É. Leveraging Passage Retrieval with Generative Models for Open-Domain Question Answering. In Proceedings of the 16th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics (EACL 2021), Online, 19–23 April 2021; pp. 874–880. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Ping, W.; Liu, Z.; Wang, B.; You, J.; Zhang, C.; Shoeybi, M.; Catanzaro, B. RankRAG: Unifying Context Ranking with Retrieval-Augmented Generation in LLMs. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 37, 121156–121184. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.; Ma, X.; Chen, W. LongRAG: Enhancing Retrieval-Augmented Generation with Long-Context LLMs. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.15319. [Google Scholar]
- Bordes, A.; Usunier, N.; Garcia-Duran, A.; Weston, J.; Yakhnenko, O. Translating Embeddings for Modeling Multi-Relational Data. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2013, 26, 2787–2795. [Google Scholar]
- Kipf, T.N.; Welling, M. Semi-Supervised Classification with Graph Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), Toulon, France, 24–26 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Schlichtkrull, M.; Kipf, T.N.; Bloem, P.; Van Den Berg, R.; Titov, I.; Welling, M. Modeling Relational Data with Graph Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the European Semantic Web Conference (ESWC), Crete, Greece, 3–7 June 2018; pp. 593–607. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Wang, Z. Knowledge Graph Enhanced Intelligent Tutoring System Based on Exercise Representativeness and Informativeness. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.15076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canal-Esteve, M.; Gutiérrez, Y. Educational Material to Knowledge Graph Conversion: A Methodology to Enhance Digital Education. In Proceedings of the 1st Workshop on Knowledge-Augmented Language Models (KaLLM); Association for Computational Linguistics: Bangkok, Thailand, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, K.; Li, K.C.; Wong, B.T.M.; Wu, M.M.; Liu, M. A Survey of Knowledge Graph Approaches and Applications in Education. Electronics 2024, 13, 2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliyu, I.; Kana, A.F.D.; Aliyue, S. Development of Knowledge Graph for University Courses Management. Int. J. Educ. Manag. Eng. 2020, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Shakya, R. A Study on the Curriculum Design for K–12 AI Education Using Knowledge Graph. Eur. J. Sci. Innov. Technol. 2023, 3, 515–531. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, S.; Zhao, J.; Yu, D.; Du, N.; Shafran, I.; Narasimhan, K.R.; Cao, Y. ReAct: Synergizing Reasoning and Acting in Language Models. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2210.03629. [Google Scholar]
- Schick, T.; Dwivedi-Yu, J.; Dessì, R.; Raileanu, R.; Lomeli, M.; Hambro, E.; Zettlemoyer, L.; Cancedda, N.; Scialom, T. Toolformer: Language Models Can Teach Themselves to Use Tools. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.04761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Zhu, C.; Fang, Y.; Yu, W.; Wang, S.; Xu, Y.; Ren, X.; Yang, Y.; Zeng, M. KG-FiD: Infusing Knowledge Graphs into Fusion-in-Decoder. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.04330. [Google Scholar]
- Guu, K.; Lee, K.; Tsvetkov, Y. Multimodal Retrieval-Augmented Learning for STEM Education. In Proceedings of the 40th International Conference on Machine Learning, Honolulu, HI, USA, 23–29 July 2023; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, A. From Novice to Navigator: Students’ Help-Seeking Behavior and Perceived Usefulness of ChatGPT. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2023, 28, 5431–5450. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y. A Systematic Review of Key Retrieval-Augmented Generation Techniques. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2507.18910. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Z. LightRAG: Simple and Fast Retrieval-Augmented Generation. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2410.05779. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Xu, C. A Systematic Review of Key Retrieval-Augmented Methods for Large Language Models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.10997. [Google Scholar]
- Henkel, O.; Lindl, T.; Stöter, J. Retrieval-Augmented Generation to Improve Math Question Answering. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Educational Data Mining (EDM), Atlanta, GA, USA, 14–17 July 2024; pp. 289–298. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.; Xu, Z.; He, M.; Feng, J.; Shen, B. Graph Retrieval-Augmented Large Language Models for Rare Genetic Disease Diagnosis. NPJ Digit. Med. 2025, 8, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S. AcademicRAG: Knowledge Graph Enhanced Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Academic Contexts. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.01763. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Lei, D.; Li, S.; Yang, L.; Wu, Y. Review of Graph Neural Networks Applied to Knowledge Graph Reasoning. J. Comput. Sci. Explor. 2023, 17, 27–52. [Google Scholar]
- Bei, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, S.; Chen, W.; Zhou, S.; Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Bu, J.; Pan, S.; Yu, Y.; et al. Graphs Meet AI Agents: Taxonomy, Progress, and Future Opportunities. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2506.18019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, Y.; Duan, H.; Liu, Y.; Qin, Z. Survey on the Construction Technology of Knowledge Graphs. J. Comput. Res. Dev. 2016, 53, 582–600. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, W.; Zhang, M.; Li, Q. MAS-KCL: Knowledge Component Graph Structure Learning with Large Language Model-Based Agentic Workflow. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2505.14126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xia, L. Study on the Development History and Current Status of Semantic Networks. J. Doc. Inf. Knowl. 2019, 6, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yin, Q.W.; Hu, Y.J.; Guo, M.; Fu, X.J. A Review of Ontology Research. Comput. Res. Dev. 2004, 41, 1041–1052. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, H. Research on Smart Education Systems Driven by Knowledge Graphs. China New Telecommun. 2024, 26, 43–45. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Zhong, B. Educational Knowledge Graph: Research Progress and Future Development. Comput. Eng. 2024, 50, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Berners-Lee, T.; Hendler, J.; Lassila, O. The Semantic Web. Sci. Am. 2001, 284, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Tong, P.; Jin, Z.; Sun, Y.; Ye, J.; Xiong, H. Plan-on-Graph: Self-Correcting Adaptive Planning of Large Language Models on Knowledge Graphs. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. (NeurIPS) 2024, 37, 37665–37691. [Google Scholar]


| Criterion | RAG | Knowledge Graph | Agentic-RAG (Proposed) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Core representation | Dense embeddings (vector DB) | Symbolic triples | Hybrid semantic–structural graph embeddings |
| Retrieval mechanism | Cosine similarity in high-dimensional space | Graph traversal/Cypher query | Policy-guided hybrid retrieval |
| Reasoning depth | Shallow (context window limited) | Deep relational reasoning | Multi-hop reasoning via agent planning |
| Explainability | Low (latent space) | High (explicit relations) | High, with evidence trace and fusion weights |
| Computational complexity | retrieval + decoding | traversal | adaptive hybrid |
| Adaptivity to user intent | Static retriever | Rule-based query templates | Dynamic multi-tool orchestration |
| Performance on educational QA | Moderate accuracy, low interpretability | High structure, limited coverage | High accuracy, explainable, adaptive |
| Category | Sample Question (Subset) | Reference Answer (Example) |
|---|---|---|
| Course Attribute | Which college offers the course? | College of Computer Science. |
| Knowledge Q&A | What is Naive Bayes? | Naive Bayes is a simple and efficient classification algorithm based on Bayes’ theorem. It calculates the probability of each class given the input features and assumes all features are independent. |
| Resource Retrieval | Help me find the learning link for the Pattern Recognition Principles course. | https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV144411D74h/ |
| Cross-Dimensional | Which majors include SVM? | Artificial Intelligence; Data Science. |
| Complex Multi-Topic | Compare Naive Bayes and Random Forest. | Naive Bayes assumes independence, while Random Forest uses ensembles for variance reduction. |
| Accuracy (%) | Semantic Consistency (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Basic RAG | 87.0% | 85.5% |
| KG+ RAG | 88.3% | 86.6% |
| Agent+RAG (no KG) | 87.5% | 86.7% |
| Agent+KG+RAG | 91.4% | 87.6% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, F.; Xu, S.; Hao, W.; Lu, T. KA-RAG: Integrating Knowledge Graphs and Agentic Retrieval-Augmented Generation for an Intelligent Educational Question-Answering Model. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 12547. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312547
Gao F, Xu S, Hao W, Lu T. KA-RAG: Integrating Knowledge Graphs and Agentic Retrieval-Augmented Generation for an Intelligent Educational Question-Answering Model. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(23):12547. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312547
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Fangqun, Shu Xu, Weiyan Hao, and Tao Lu. 2025. "KA-RAG: Integrating Knowledge Graphs and Agentic Retrieval-Augmented Generation for an Intelligent Educational Question-Answering Model" Applied Sciences 15, no. 23: 12547. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312547
APA StyleGao, F., Xu, S., Hao, W., & Lu, T. (2025). KA-RAG: Integrating Knowledge Graphs and Agentic Retrieval-Augmented Generation for an Intelligent Educational Question-Answering Model. Applied Sciences, 15(23), 12547. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312547






