Impact of Tire Microplastics on Aerobic Granular Sludge Structure and EPS Composition Under Continuous and Intermittent Aeration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Setup and Operation
2.2. Analytical Measurements
2.3. Biomass Characteristics and Activity Analysis
2.4. EPS Extraction and Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
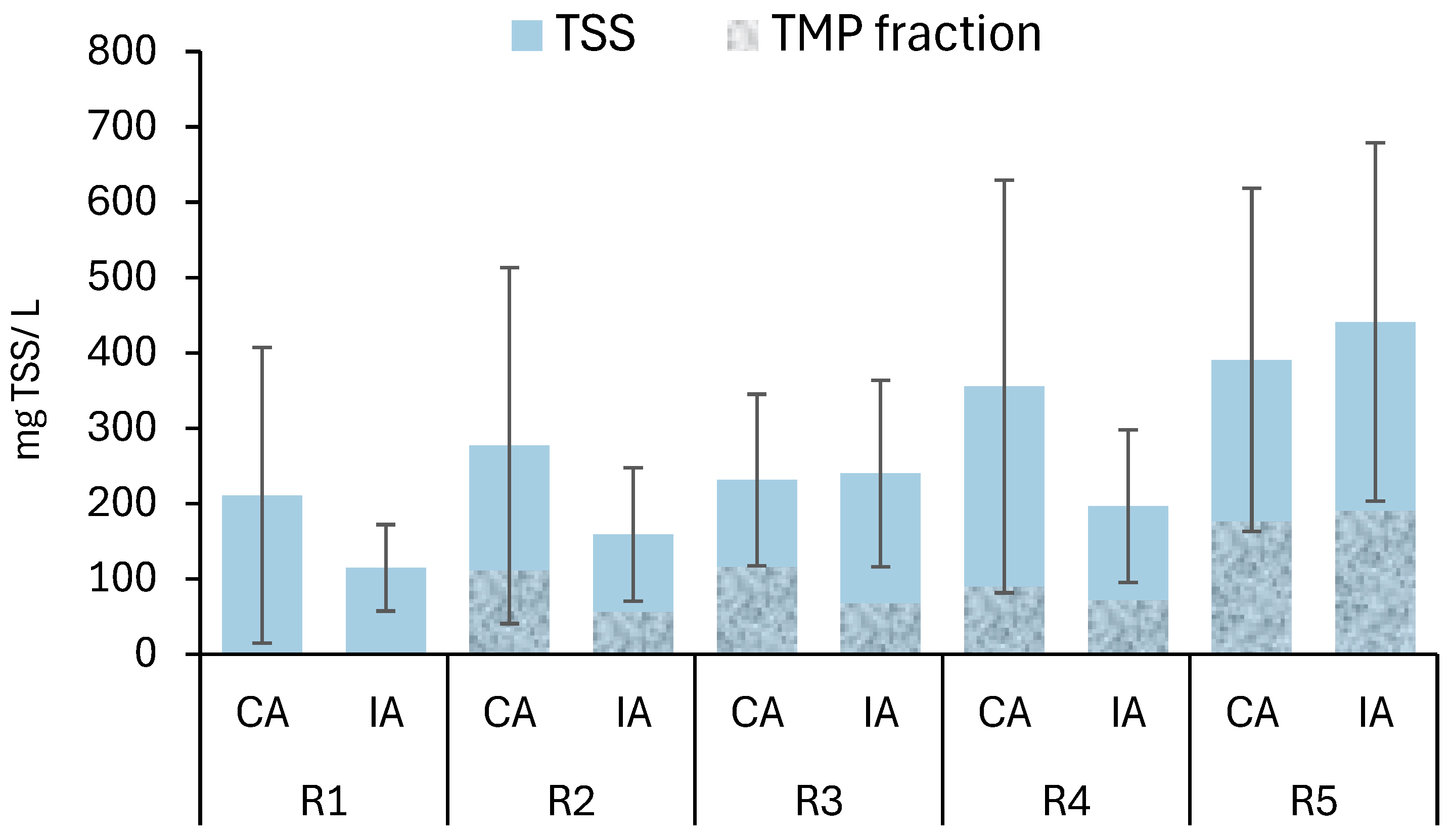
3.1. GSBRs Performance
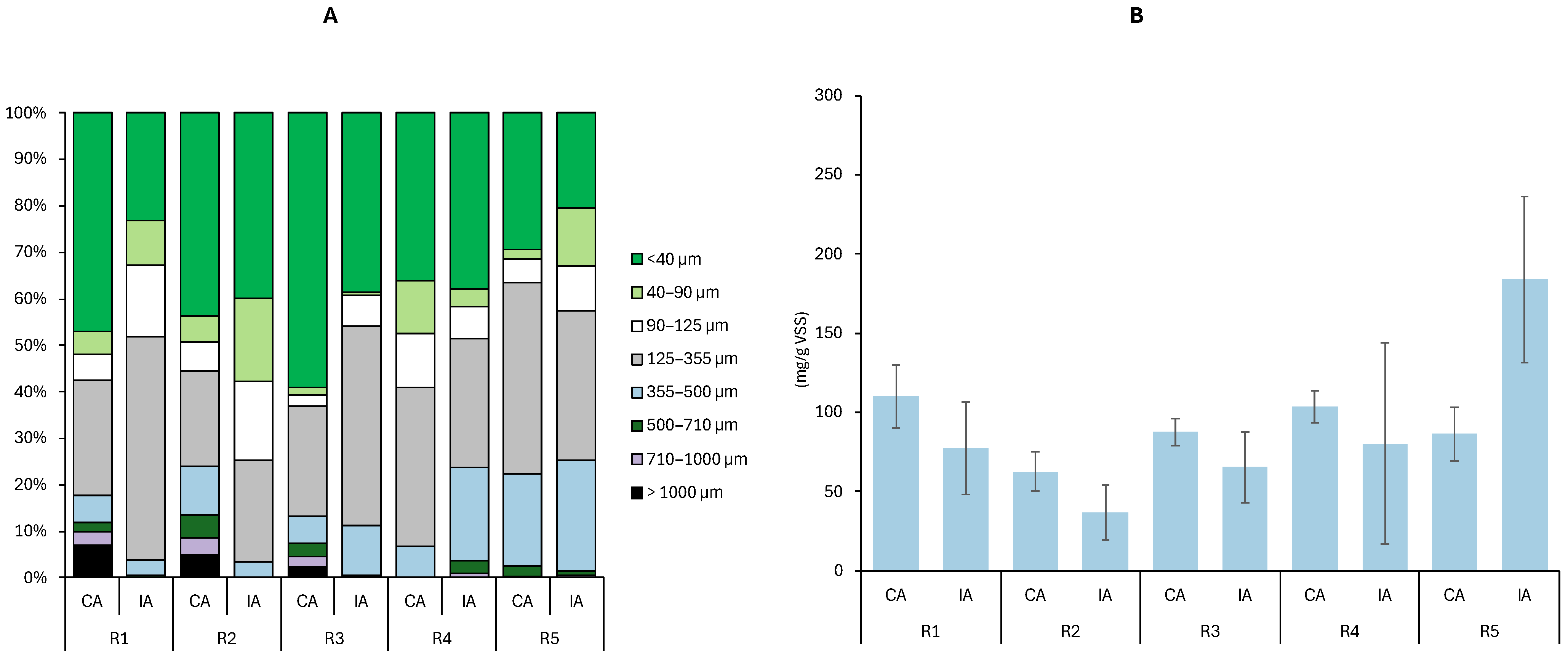
3.2. AGS Particle Size Distribution
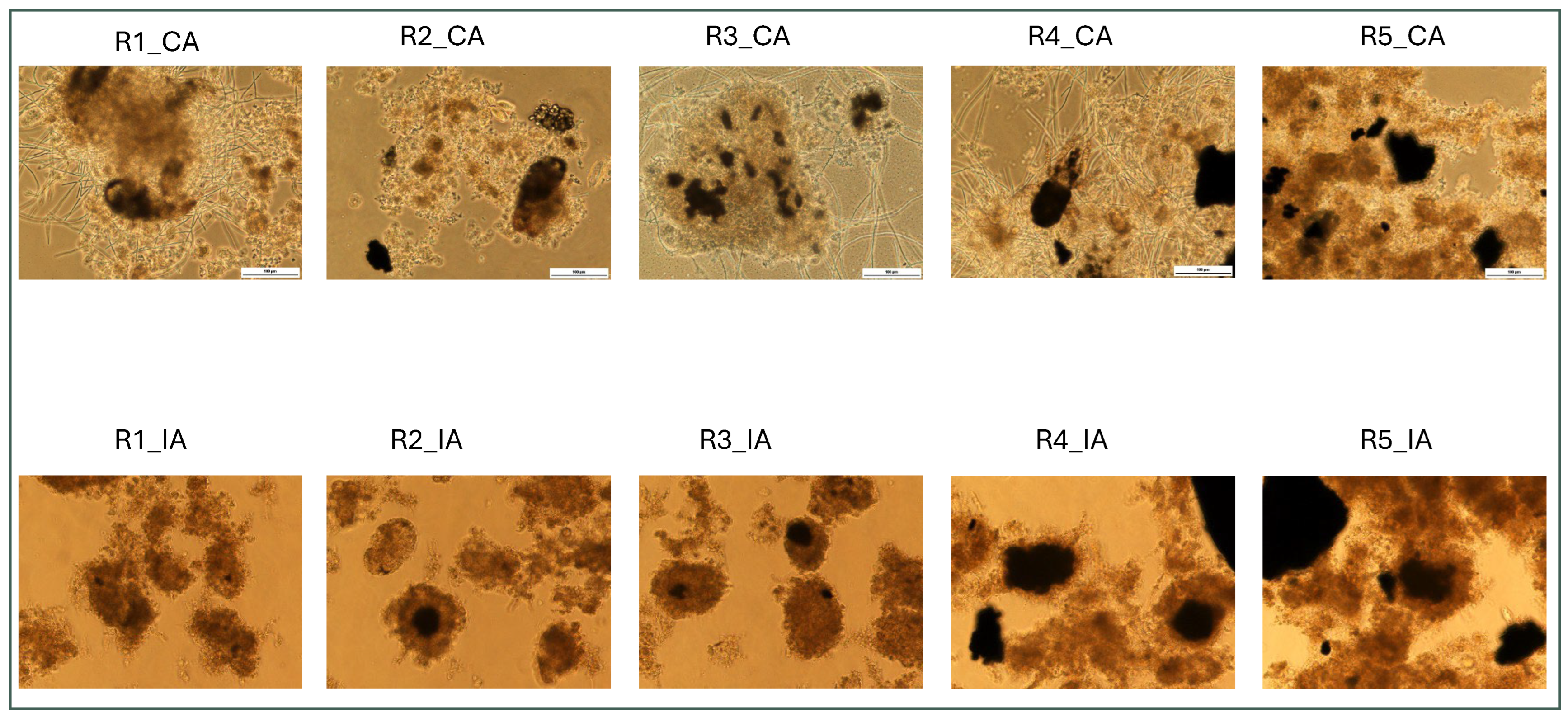
3.3. Impact of TMP on Granular Biomass
3.4. Dehydrogenase Activity
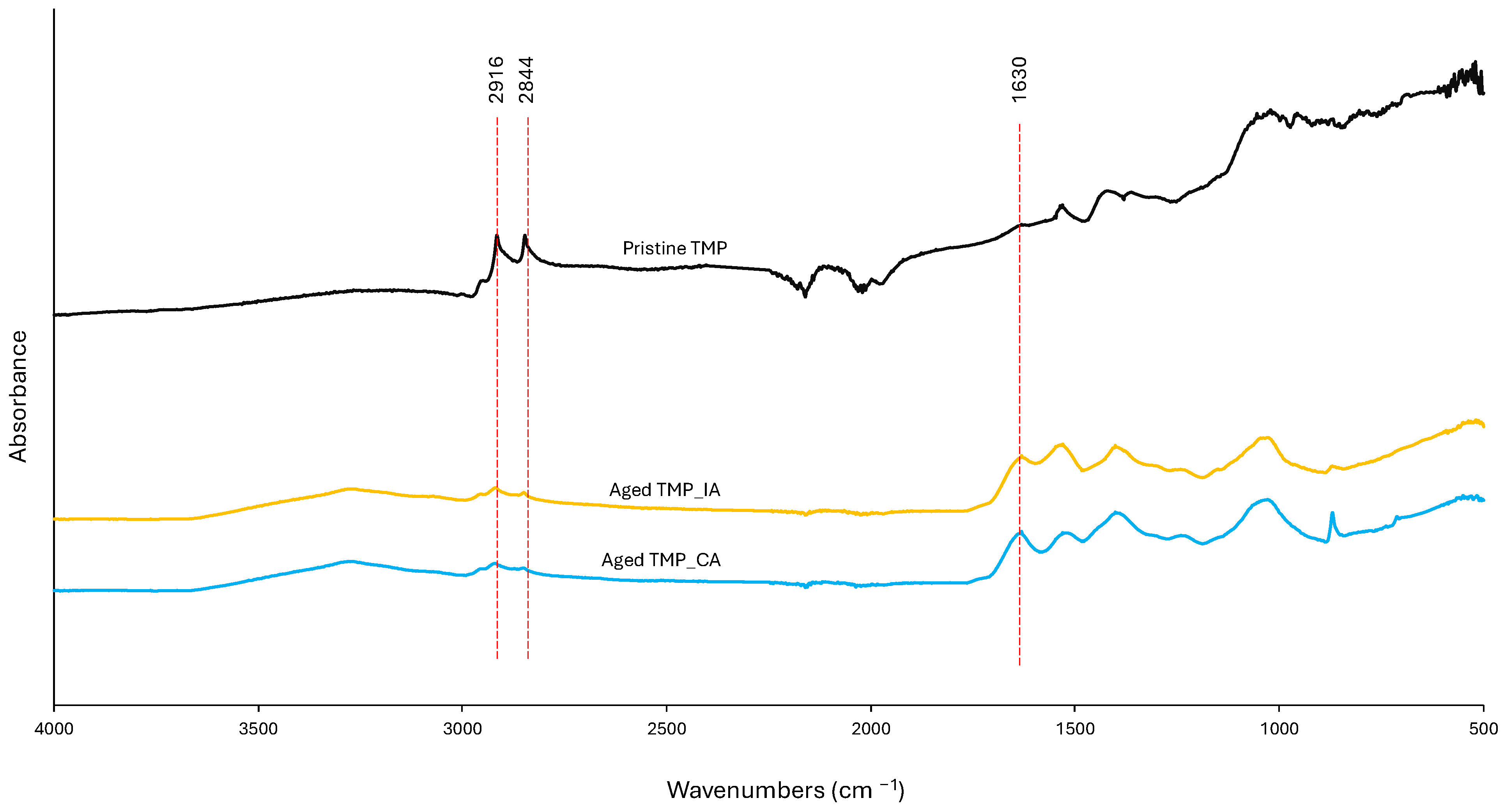
3.5. EPS Composition
3.6. EPS Interactions with Physicochemical Parameters
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| GSBR | TMPs Concentration mg/L | Obscuration (%) | Span | D[4.3]—Volume Weighted Mean (µm) | Uniformity | D[3.2]—Surface Weighted Mean (µm) | d(0.1) (µm) | d(0.5) (µm) | d(0.9) (µm) | Specific Surface Area (m2/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | 0 | 14.2 | 2.164 | 319.0 | 0.664 | 128.8 | 60.2 | 277.7 | 638.9 | 0.053 |
| R2 | 50 | 13.9 | 2.503 | 227.0 | 0.790 | 88.1 | 40.5 | 176.7 | 481.9 | 0.068 |
| R3 | 100 | 12.2 | 2.385 | 267.4 | 0.738 | 102.9 | 47.8 | 221.6 | 558.4 | 0.063 |
| R4 | 250 | 12.6 | 2.460 | 174.3 | 0.750 | 69.6 | 32.3 | 137.4 | 369.8 | 0.102 |
| R5 | 500 | 14.0 | 2.235 | 245.5 | 0.690 | 107.6 | 52.0 | 203.5 | 503.9 | 0.353 |
| GSBR | TMPs Concentration mg/L | Obscuration (%) | Span | D[4.3]—Volume Weighted Mean (µm) | Uniformity | D[3.2]—Surface Weighted Mean (µm) | d(0.1) (µm) | d(0.5) (µm) | d(0.9) (µm) | Specific Surface Area (m2/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | 0 | 18.9 | 1.715 | 105.1 | 0.539 | 49.6 | 35.5 | 91.7 | 192.8 | 0.121 |
| R2 | 50 | 13.4 | 1.693 | 203.2 | 0.534 | 98.0 | 70.6 | 177.6 | 371.2 | 0.061 |
| R3 | 100 | 13.3 | 1.728 | 250.7 | 0.534 | 151.9 | 88.9 | 217.3 | 464.2 | 0.040 |
| R4 | 250 | 15.1 | 1.678 | 212.5 | 0.554 | 130.1 | 80.4 | 177.3 | 378.0 | 0.046 |
| R5 | 500 | 16.1 | 1.645 | 286.2 | 0.508 | 165.3 | 102.1 | 254.0 | 519.9 | 0.036 |
References
- Purba, L.D.A.; Ibiyeye, H.T.; Yuzir, A.; Mohamad, S.E.; Iwamoto, K.; Zamyadi, A.; Abdullah, N. Various applications of aerobic granular sludge: A review. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 20, 101045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, S.; Hüffer, T.; Klöckner, P.; Wehrhahn, M.; Hofmann, T.; Reemtsma, T. Tire wear particles in the aquatic environment—A review on generation, analysis, occurrence, fate and effects. Water Res. 2018, 139, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mennekes, D.; Nowack, B. Tire wear particle emissions: Measurement data where are you? Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 830, 154655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Zhou, X.; Su, Y.; Wang, H.; Yu, R.; Zhou, S.; Xu, E.G.; Xing, B. Environmental occurrence, fate, impact, and potential solution of tire microplastics: Similarities and differences with tire wear particles. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 795, 148902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, P.M.; Moran, K.D.; Miller, E.L.; Brander, S.M.; Harper, S.; Garcia-Jaramillo, M.; Carrasco-Navarro, V.; Ho, K.T.; Burgess, R.M.; Hampton, L.M.T.; et al. Where the rubber meets the road: Emerging environmental impacts of tire wear particles and their chemical cocktails. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 927, 171153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giechaskiel, B.; Grigoratos, T.; Mathissen, M.; Quik, J.; Tromp, P.; Gustafsson, M.; Franco, V.; Dilara, P. Contribution of road vehicle tyre wear to microplastics and ambient air pollution. Sustainability 2024, 16, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baensch-Baltruschat, B.; Kocher, B.; Stock, F.; Reifferscheid, G. Tyre and road wear particles (TRWP)—A review of generation, properties, emissions, human health risk, ecotoxicity, and fate in the environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 137823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Järlskog, I.; Jaramillo-Vogel, D.; Rausch, J.; Gustafsson, M.; Strömvall, A.M.; Andersson-Sköld, Y. Concentrations of tire wear microplastics and other traffic-derived non-exhaust particles in the road environment. Environ. Int. 2022, 170, 107618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamis, J.E.; Koelmans, A.A.; Dröge, R.; Kaag, N.H.B.M.; Keur, M.C.; Tromp, P.C.; Jongbloed, R.H. Environmental risks of car tire microplastic particles and other road runoff pollutants. Microplast. Nanoplast. 2021, 1, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, T.S.; Almeda, R.; Koski, M.; Bournaka, E.; Nielsen, T.G. Toxicity of tyre wear particle leachates to marine phytoplankton. Aquat. Toxicol. 2022, 252, 106299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capolupo, M.; Sørensen, L.; Jayasena, K.D.R.; Booth, A.M.; Fabbri, E. Chemical composition and ecotoxicity of plastic and car tire rubber leachates to aquatic organisms. Water Res. 2019, 169, 115270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du-Carrée, J.L.; Palacios, C.K.; Rotander, A.; Larsson, M.; Alijagic, A.; Kotlyar, O.; Engwall, M.; Sjöberg, V.; Keiter, S.H.; Almeda, R. Cocktail effects of tire wear particles leachates on diverse biological models: A multilevel analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 471, 134401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Li, Y.; Yuan, F.; Yang, Q. Optimization and control strategies of aeration in WWTPs: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 418, 138008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, F.; Giuliani, A.; Martucci, I.; Pucci, L.; Race, M. Comparing continuous and intermittent aeration using BioWinTM model simulation in a full-scale wastewater treatment plant. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 68, 106530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.K.; Bhatia, A.; Kazmi, A.A. Effect of intermittent aeration strategies on treatment performance and microbial community of an IFAS reactor treating municipal waste water. Environ. Technol. 2017, 38, 2866–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burzio, C.; Ekholm, J.; Modin, O.; Falås, P.; Svahn, O.; Persson, F.; Van Erp, T.; Gustavsson, D.J.I.; Wilén, B.-M. Removal of organic micropollutants from municipal wastewater by aerobic granular sludge and conventional activated sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 438, 129528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jachimowicz, P.; Peng, R.; Hüffer, T.; Hofmann, T.; Cydzik-Kwiatkowska, A. Tire materials disturb transformations of nitrogen compounds and affect the structure of biomass in aerobic granular sludge reactors. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 465, 133223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Su, C.; Lu, Y.; Xian, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Deng, X.; Li, X. Effects of microplastics on the properties of different types of sewage sludge and strategies to overcome the inhibition: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 902, 166033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedves, A.; Kedves, O.; Mikó, E.; Kónya, Z. Micro- and nanoplastics in granular sludge systems: Mechanisms of disruption, retention, and microbial adaptation in wastewater treatment technologies. Water Res. 2025, 28, 100374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Zhang, B.; Cui, F.; He, Y.; Shi, J.; Yang, X.; Lens, P.N.L.; Shi, W. Mechanisms underlying the detrimental impact of micro(nano)plastics on the stability of aerobic granular sludge: Interactions between micro(nano)plastics and extracellular polymeric substances. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 478, 135512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrena, R.; Vazquez, F.; Sanchez, A. Dehydrogenase activity as a method for monitoring the composting process. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 99, 905–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chukhchin, D.; Varakin, E.; Rudakova, V.; Vashukova, K.; Terentyev, K. Express-Method for determination of the oxidizing capacity of activated sludge and its biofilms in pulp and paper mill. Water 2021, 13, 1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, J.M.; Koopman, B.; Bitton, G. INT–dehydrogenase test for activated sludge process control. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1986, 28, 1080–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.S.; Sheela, A.M. Microplastics alter dehydrogenase, urease, and cellulase activities in soil. Natl. Acad. Sci. Lett. 2023, 46, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Liu, Y.; Yan, K.; Wang, Z.; Lu, G.; He, Y.; He, W. Differences in the response of soil dehydrogenase activity to Cd contamination are determined by the different substrates used for its determination. Chemosphere 2016, 169, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Zou, L.F.; Cai, L.L.; Chen, G.Y. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase is required for extracellular polysaccharide production, cell motility and the full virulence of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola. Microb. Pathog. 2014, 78, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flemming, H.C.; Wingender, J. The biofilm matrix. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adav, S.S.; Lee, D.J.; Tay, J.H. Extracellular polymeric substances and structural stability of aerobic granule. Water Res. 2007, 42, 1644–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, Z.; Dai, X.; Xu, X.; Alvarez, P.J.J.; Zhu, L. Evolution and functional analysis of extracellular polymeric substances during the granulation of aerobic sludge used to treat p-chloroaniline wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 330, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Pei, Q.; Han, H.; Yin, H.; Chen, M.; Guo, C.; Li, J.; Qiu, H. Functional analysis of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) during the granulation of aerobic sludge: Relationship among EPS, granulation and nutrients removal. Environ. Res. 2022, 208, 112692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Fang, F.; Yan, P.; Liu, Z. Effect of different forms and components of EPS on sludge aggregation during granulation process of aerobic granular sludge. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 135116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusanowska, P.; Cydzik-Kwiatkowska, A.; Świątczak, P.; Wojnowska-Baryła, I. Changes in extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) content and composition in aerobic granule size-fractions during reactor cycles at different organic loads. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 272, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y. The connection between aeration regimes and EPS composition in nitritation biofilm. Chemosphere 2020, 265, 129141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Wang, C.; Kong, L.; Wang, J.; Tan, Y.; Yu, Z.; Xu, X.; Zhu, L. Spatial heterogeneity of EPS-mediated microplastic aggregation in phycosphere shapes polymer-specific Trojan horse effects. Water Res. 2025, 281, 123686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jachimowicz, P.; Cydzik-Kwiatkowska, A. Impact of polyethylene terephthalate microplastics on aerobic granular sludge structure and EPS composition in wastewater treatment. Water 2025, 17, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.T.; Wei, W.; Huang, Q.S.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Ni, B.J. Insights into the microbial response of anaerobic granular sludge during long-term exposure to polyethylene terephthalate microplastics. Water Res. 2020, 179, 115898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; De Kreuk, M.; Van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Adin, A. Characterization of alginate-like exopolysaccharides isolated from aerobic granular sludge in pilot-plant. Water Res. 2010, 44, 3355–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cydzik-Kwiatkowska, A.; Gusiatin, M.Z.; Zielińska, M.; Wojnowska-Baryła, I.; Kulikowska, D.; Bernat, K. Alginate-like polymers from full-scale aerobic granular sludge: Content, recovery, characterization, and application for cadmium adsorption. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 22260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svierzoski, N.D.S.; Castellano-Hinojosa, A.; Gallardo-Altamirano, M.J.; Mahler, C.F.; Bassin, J.P.; González-Martínez, A. Evaluating the effects of aeration intermittency on treatment performance and the granule microbiome in continuous-flow aerobic granular sludge systems. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 117660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jachimowicz, P.; Jo, Y.J.; Cydzik-Kwiatkowska, A. Polyethylene microplastics increase extracellular polymeric substances production in aerobic granular sludge. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851, 158208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandacka, D.; Durcanska, D.; Cibula, R. Concentration and inorganic elemental analysis of particulate matter in a road tunnel environment (Žilina, Slovakia): Contribution of non-exhaust sources. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 952577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreider, M.L.; Panko, J.M.; McAtee, B.L.; Sweet, L.I.; Finley, B.L. Physical and chemical characterization of tire-related particles: Comparison of particles generated using different methodologies. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 408, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leads, R.R.; Weinstein, J.E. Occurrence of tire wear particles and other microplastics within the tributaries of the Charleston Harbor Estuary, South Carolina, USA. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 145, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Wang, B.; Ouyang, W.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, H. Tire wear particles in aquatic environments: A systematic review of sources, detection, distribution, and toxicological impacts. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 305, 119236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wik, A.; Dave, G. Occurrence and effects of tire wear particles in the environment—A critical review and an initial risk assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 157, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Public Health Association (APHA). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 22nd ed.; Rice, E.W., Baird, R.B., Eaton, A.D., Clesceri, L.S., Bridgewater, L., Eds.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; ISBN 978-087553-013-0. [Google Scholar]
- Otieno, J.O.; Jachimowicz, P.; Zielińska, M.; Mądzielewska, W.I.; Cydzik-Kwiatkowska, A. The effect of tire microplastics on aerobic granular sludge performance. Emerg. Contam. 2025, 11, 100513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusanowska, P.; Cydzik-Kwiatkowska, A.; Wojnowska-Baryła, I. Microbial origin of excreted DNA in particular fractions of extracellular polymers (EPS) in aerobic granules. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2019, 230, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadi, P.; Izadi, P.; Eldyasti, A. Enhancement of simultaneous nitrogen and phosphorus removal using intermittent aeration mechanism. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 109, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.L.; Yu, S.L.; Shi, W.X.; Bao, R.L.; Zhao, Q.; Zuo, X.T. Comparative performance between intermittently cyclic activated sludge-membrane bioreactor and anoxic/aerobic-membrane bioreactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 3877–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, H.H.; Gao, J.F.; Wang, Z.Q.; Zhao, Y.F.; Zhang, D. Behavior of nitrogen, phosphorus and antibiotic resistance genes under polyvinyl chloride microplastics pressures in an aerobic granular sludge system. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 256, 120402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Huang, S.; Wu, L.; Guo, Y.; Shi, W.; Lens, P.N.L. Micro(nano)plastic size and concentration co-differentiate the treatment performance and toxicity mechanism in aerobic granular sludge systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 457, 141212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Yang, H.; Sheng, J.; Pan, Z.; Li, J. A bioreactor designed for restricting oversize of aerobic granular sludge. Processes 2021, 9, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Han, Z.; Shao, X.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Lin, T.; Yang, S.; Zhou, C. Response of aerobic granular sludge under polyethylene microplastics stress: Physicochemical properties, decontamination performance, and microbial community. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 323, 116215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, Y. Effects of chronic exposure to different sizes and polymers of microplastics on the characteristics of activated sludge. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 783, 146954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liao, X.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Fang, F.; Yan, P. New insights into filamentous sludge bulking: The potential role of extracellular polymeric substances in sludge bulking in the activated sludge process. Chemosphere 2020, 248, 126012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Ma, J.; Li, G.; Rillig, M.C.; Zhu, Y.G. Soil plastispheres as hotspots of antibiotic resistance genes and potential pathogens. ISME J. 2021, 16, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Xu, R.X.; Wang, G.X.; Zhou, Y.; Xie, B. Effects of pressurized aeration on organic degradation efficiency and bacterial community structure of activated sludge treating saline wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 222, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Y.; Gong, B.; Huang, X.; Fang, F.; Peng, T.; Liu, Z. Response of aerobic granular sludge under acute inhibition by poly-styrene microplastics: Activity, aggregation performance, and microbial analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 349, 123923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.Y.; Zhang, H.L.; Wang, H.; Hu, Y.Q.; Zhang, Y. Characteristics of the extracellular products of pure oxygen aerated activated sludge in batch mode. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 83, 1946–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, H.; Zhao, L.; Liu, X.; Wan, C. Understanding the role of cations and hydrogen bonds on the stability of aerobic granules from the perspective of the aggregation and adhesion behavior of extracellular polymeric substances. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 795, 148659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.K.; Pandey, S.; Singh, R.P.; Dahiya, S.; Gautam, S.; Kazmi, A.A. Effect of intermittent aeration cycles on EPS production and sludge characteristics in a field scale IFAS reactor. J. Water Process Eng. 2018, 23, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.S.; Kang, S.T.; Nam, S.Y. Effect of carbohydrate and protein in the EPS on sludge settling characteristics. Water Sci. Technol. 2001, 43, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.Y.; Lee, D.J.; Tay, J.H. Distribution of extracellular polymeric substances in aerobic granules. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 73, 1463–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Xu, H.; Liu, H.; Chen, L.; Hua, Y.; Yang, D.; Dai, X. Revealing the impacts of intermittent aeration on nitrogen and phosphorus removal in powder carrier system from interfacial thermodynamics and metagenomic analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 495, 153399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schambeck, C.M.; Magnus, B.S.; De Souza, L.C.R.; Leite, W.R.M.; Derlon, N.; Guimarães, L.B.; Da Costa, R.H.R. Biopolymers recovery: Dynamics and characterization of alginate-like exopolymers in an aerobic granular sludge system treating municipal wastewater without sludge inoculum. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 263, 110394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Liu, F.; Wang, L.; Sun, J. Overcoming the instability of aerobic granular sludge under nitrogen deficiency through shortening settling time. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 289, 121620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, J.; Lu, H.; Hou, J.; Fan, X.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, M.; Ren, L.; You, G. Effects of tire wear particle on growth, extracellular polymeric substance production and oxidation stress of algae Chlorella vulgaris: Performance and mechanism. Aquat. Toxicol. 2024, 276, 107118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naz, I.; Khatoon, N.; Ali, M.I.; Saroj, D.P.; Batool, S.A.; Ali, N.; Ahmed, S. Appraisal of the tire derived rubber (TDR) medium for wastewater treatment under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2014, 89, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
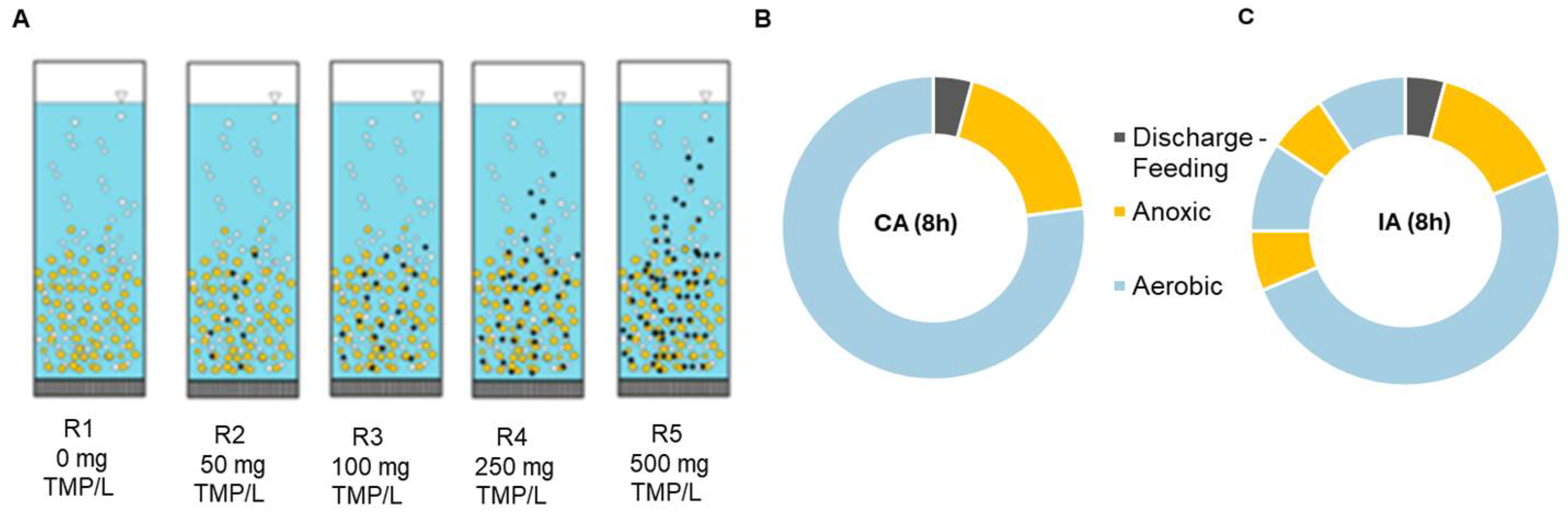
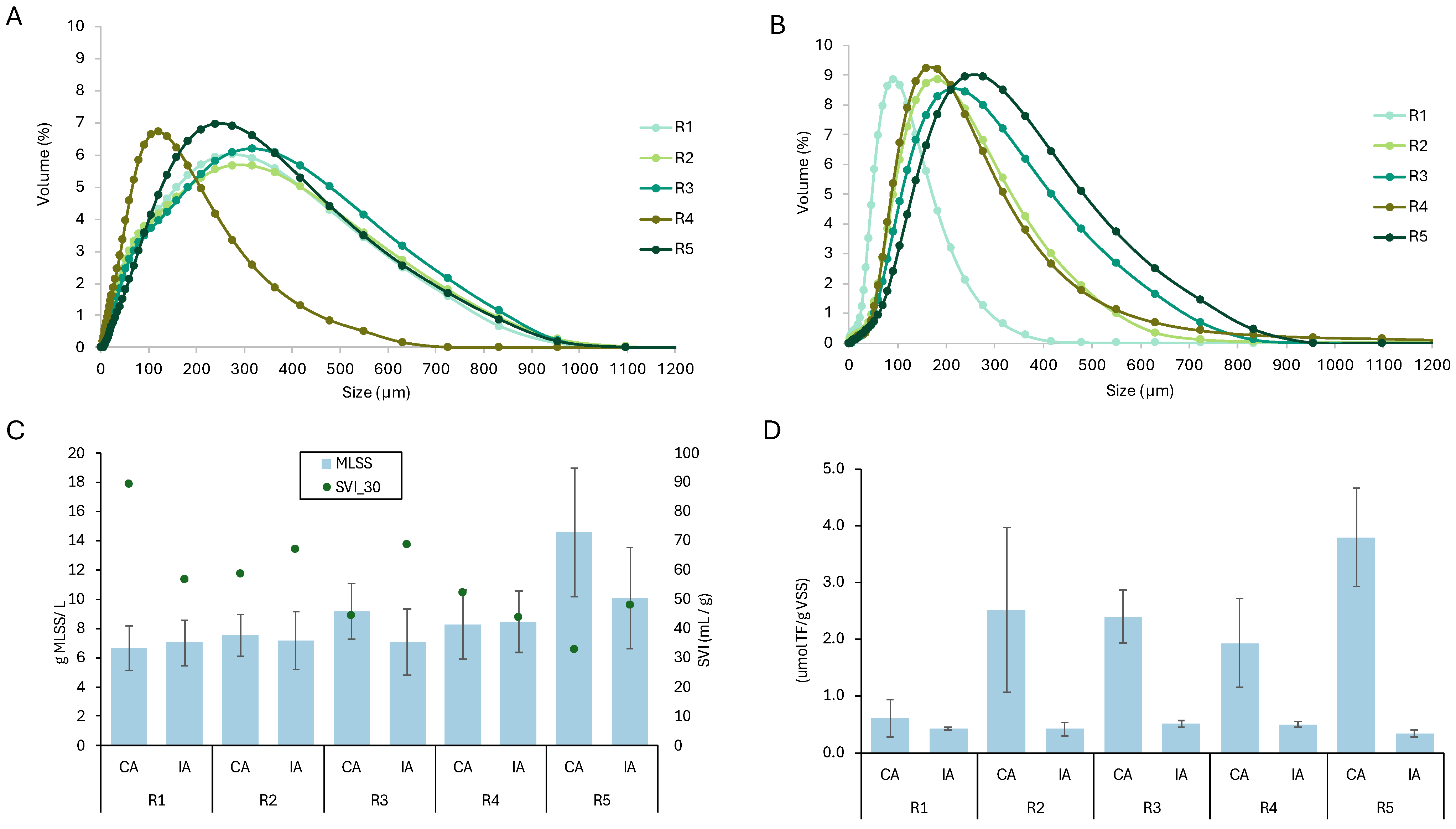
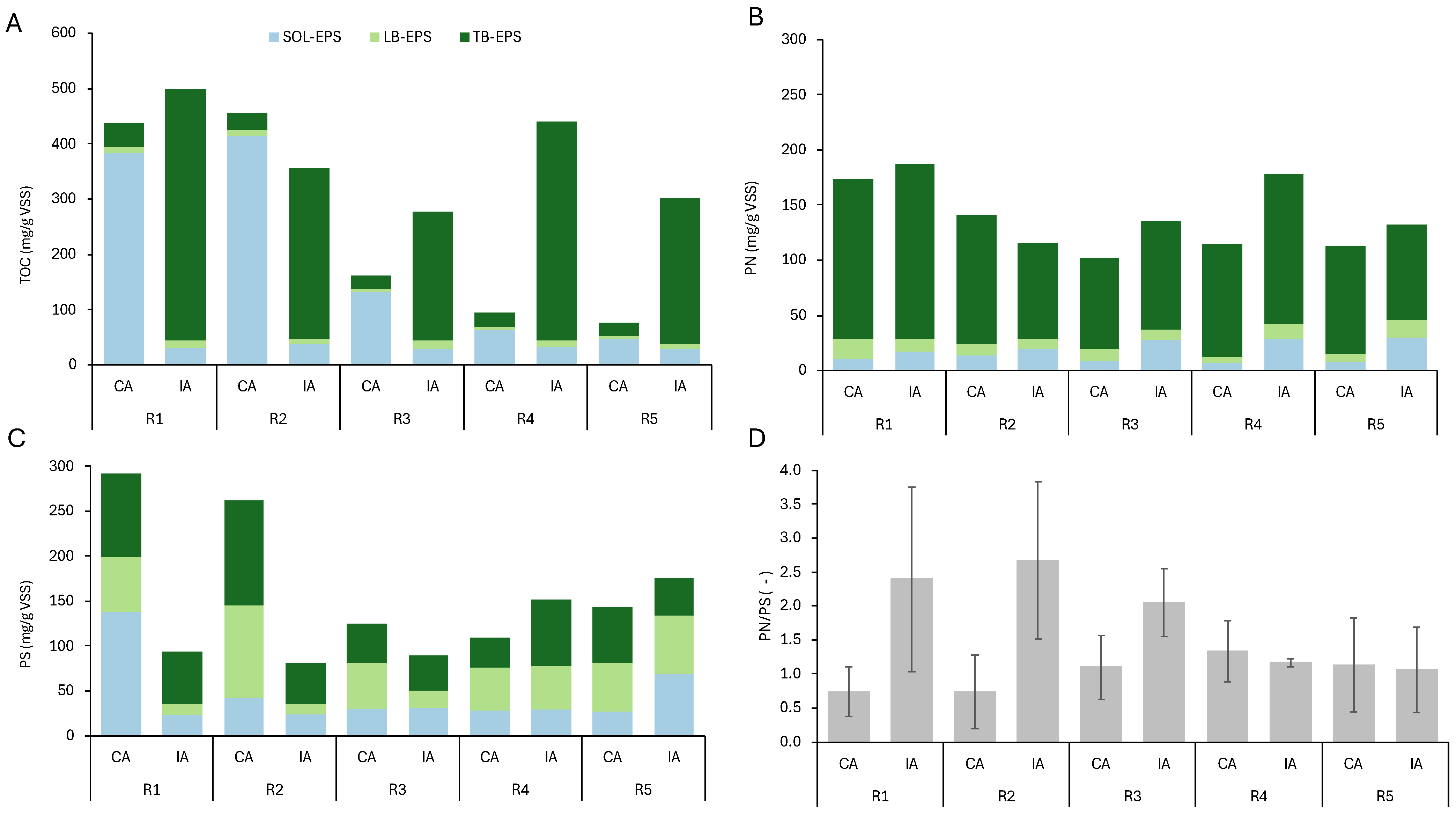
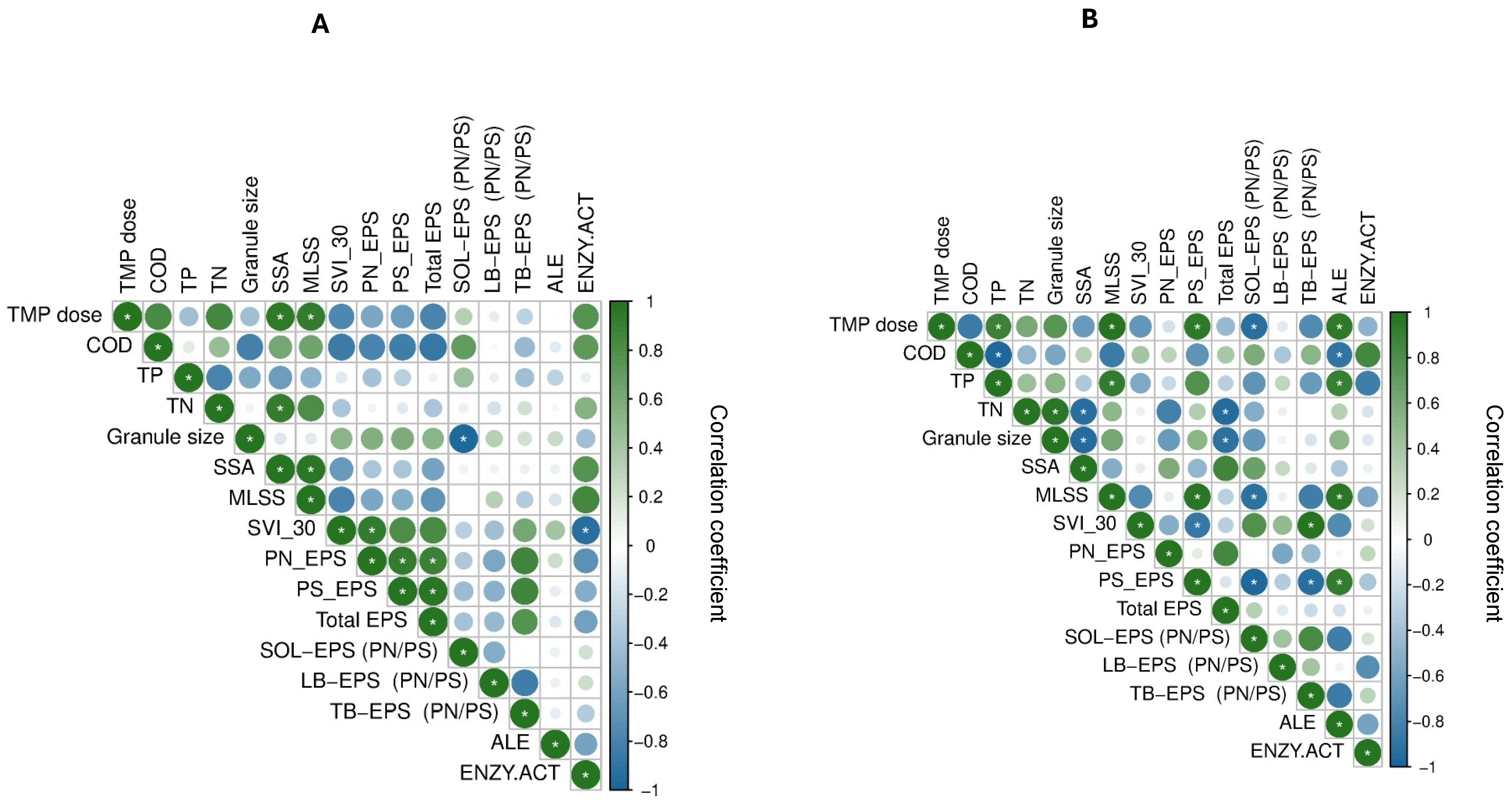
| Parameter | Aeration Regime | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COD | CA | 87.32 ± 5.86 | 88.84 ± 5.64 | 89.04 ± 5.72 | 90.66 ± 5.14 | 90.56 ± 5.31 |
| IA | 94.53 ± 2.44 | 94.58 ± 1.89 | 94.59 ± 1.45 | 94.66 ± 1.98 | 93.48 ± 2.93 | |
| TP | CA | 61.8 ± 12.0 | 66.8 ± 12.7 | 67.5 ± 16.0 | 67.4 ± 15.4 | 60.6 ± 19.2 |
| IA | 66.4 ± 17.9 | 66.6 ± 20.7 | 65.7 ± 20.4 | 66.7 ± 15.9 | 70.5 ± 19.9 | |
| TN | CA | 66.7 ± 6.6 | 65.9 ± 9.4 | 64.2 ± 9.2 | 66.7 ± 13.6 | 71.7 ± 7.6 |
| IA | 63.7 ± 8.8 | 68.4 ± 6.2 | 68.9 ± 9.2 | 67.2 ± 5.8 | 69.8 ± 6.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Otieno, J.O.; Nowak, Z.M.; Parszuto, K.; Cydzik-Kwiatkowska, A. Impact of Tire Microplastics on Aerobic Granular Sludge Structure and EPS Composition Under Continuous and Intermittent Aeration. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 12410. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312410
Otieno JO, Nowak ZM, Parszuto K, Cydzik-Kwiatkowska A. Impact of Tire Microplastics on Aerobic Granular Sludge Structure and EPS Composition Under Continuous and Intermittent Aeration. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(23):12410. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312410
Chicago/Turabian StyleOtieno, Job Oliver, Zuzanna Maja Nowak, Katarzyna Parszuto, and Agnieszka Cydzik-Kwiatkowska. 2025. "Impact of Tire Microplastics on Aerobic Granular Sludge Structure and EPS Composition Under Continuous and Intermittent Aeration" Applied Sciences 15, no. 23: 12410. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312410
APA StyleOtieno, J. O., Nowak, Z. M., Parszuto, K., & Cydzik-Kwiatkowska, A. (2025). Impact of Tire Microplastics on Aerobic Granular Sludge Structure and EPS Composition Under Continuous and Intermittent Aeration. Applied Sciences, 15(23), 12410. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312410






