Performance Evaluation of Readily Available Iron–Carbon Micro-Electrolysis Materials for Domestic Sewage Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
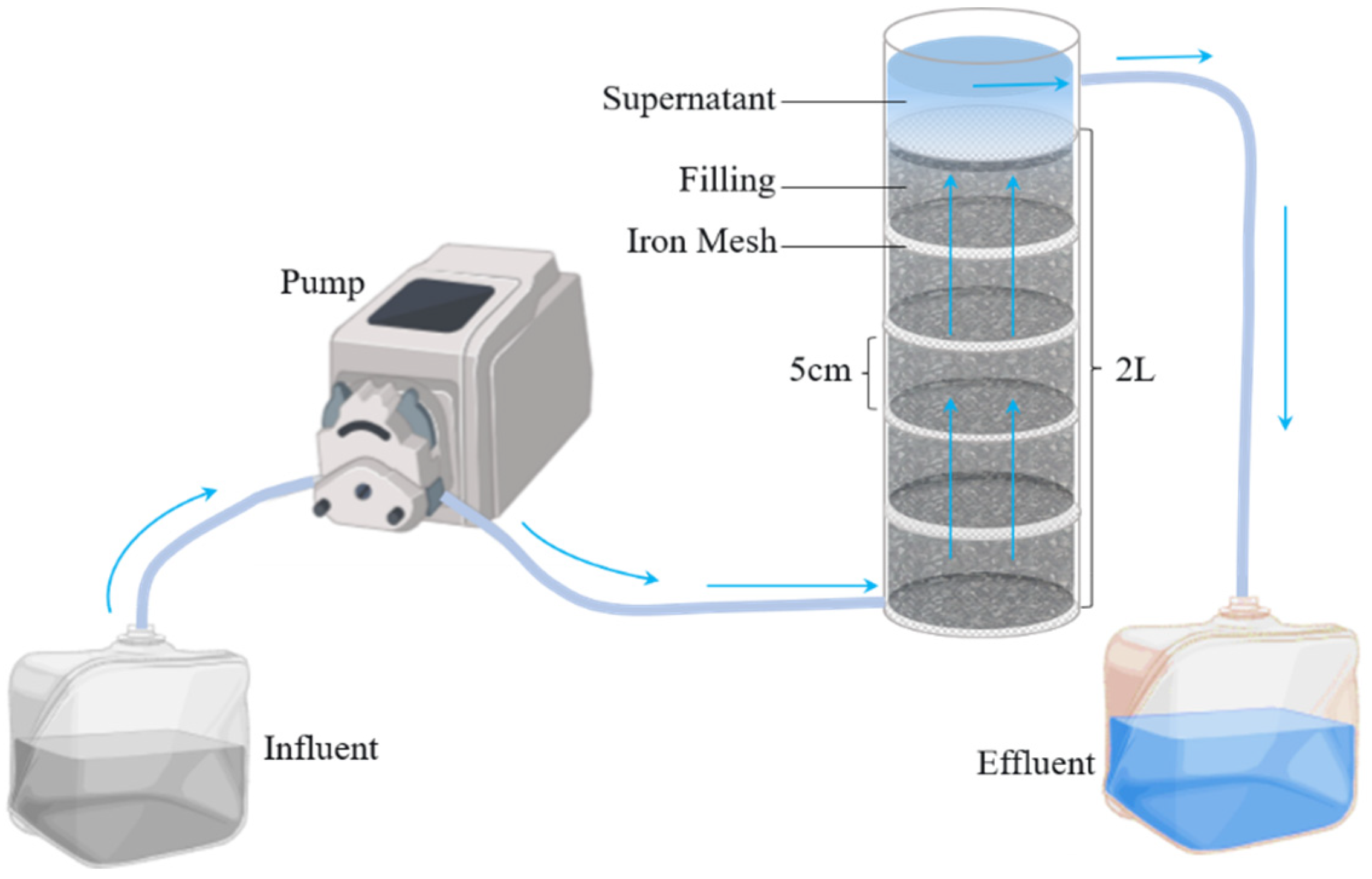
2.1. Fe/C Micro-Electrolysis Material Experimental Setup
2.2. Experimental Materials
2.3. Experimental Design
2.3.1. Static Removal Experiment of IFs and CSC with Different Ratios
2.3.2. Effect of SS as a Substitute for IF
2.3.3. Continuous Domestic Wastewater Treatment Experiment
2.3.4. Performance Differences in Fillers Prepared at Various Temperatures and Ratios
2.4. Experimental Methods and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Static Simulation Experiment for Phosphorus Removal via Fe/C Physical Mixture
3.1.1. Phosphorus Removal Performance
3.1.2. Organic Matter Removal Performance
3.1.3. Nitrogen Removal Performance
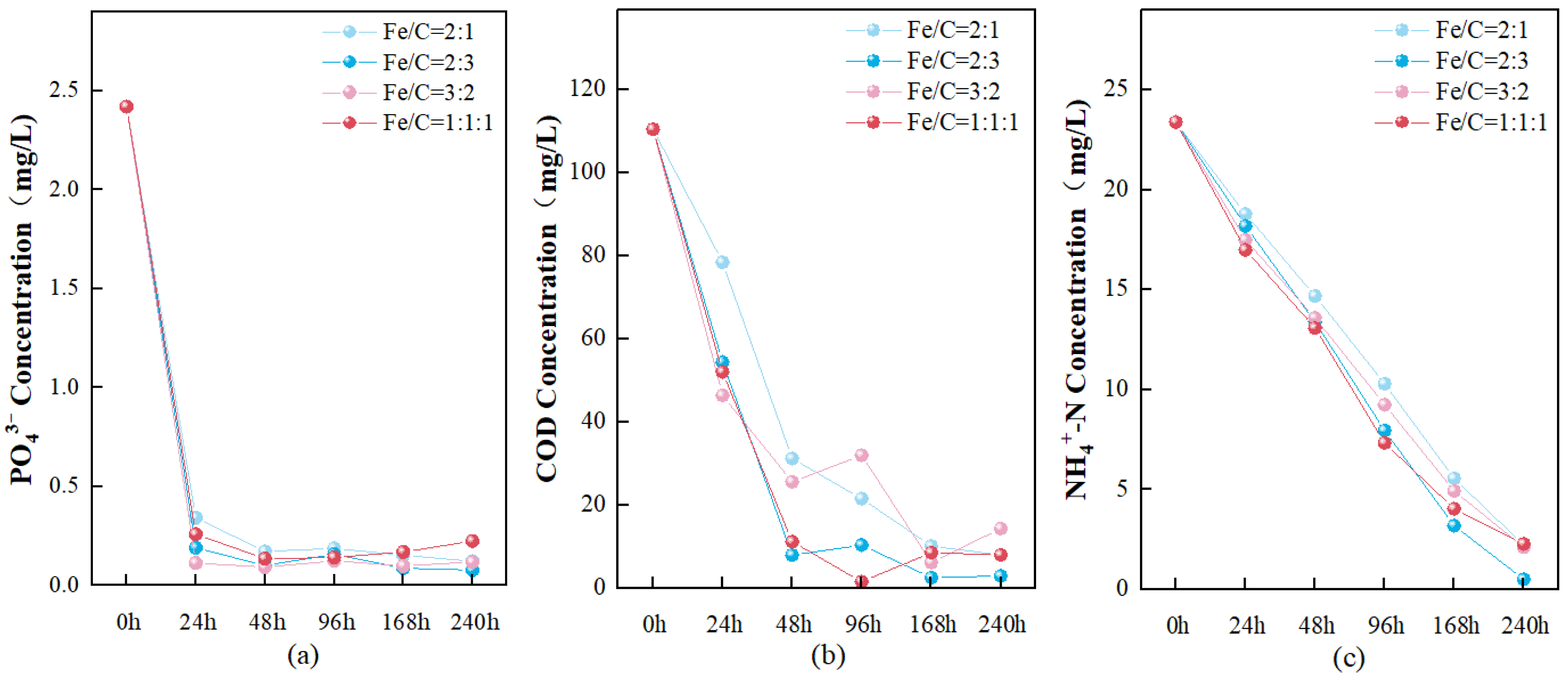
3.2. Static Removal Simulation Experiment of SS as a Substitute for IF
3.2.1. Treatment Effects on N, P, and COD
3.2.2. Release of N, P, and COD from Materials
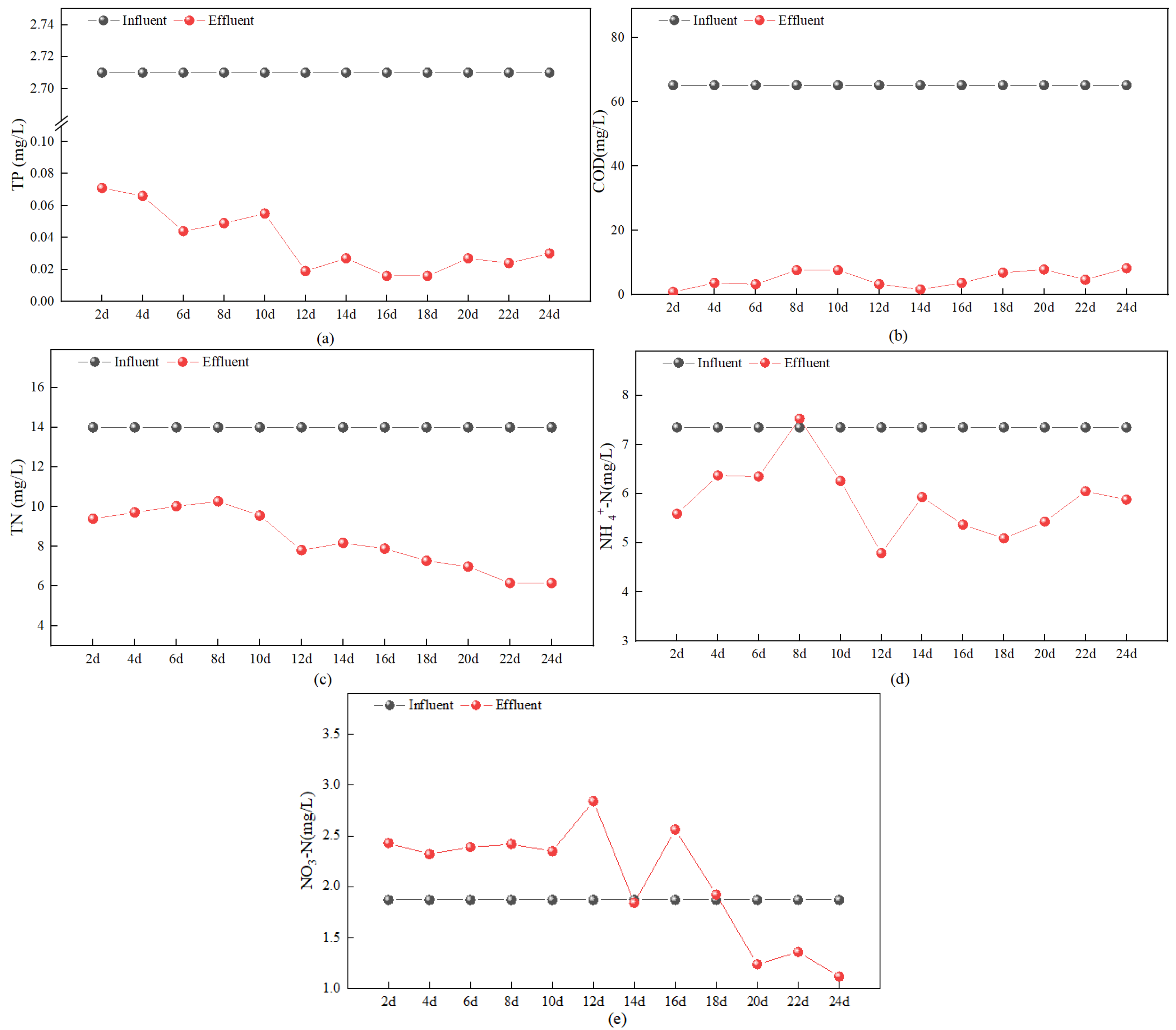
3.3. Continuous Experiment on Domestic Sewage
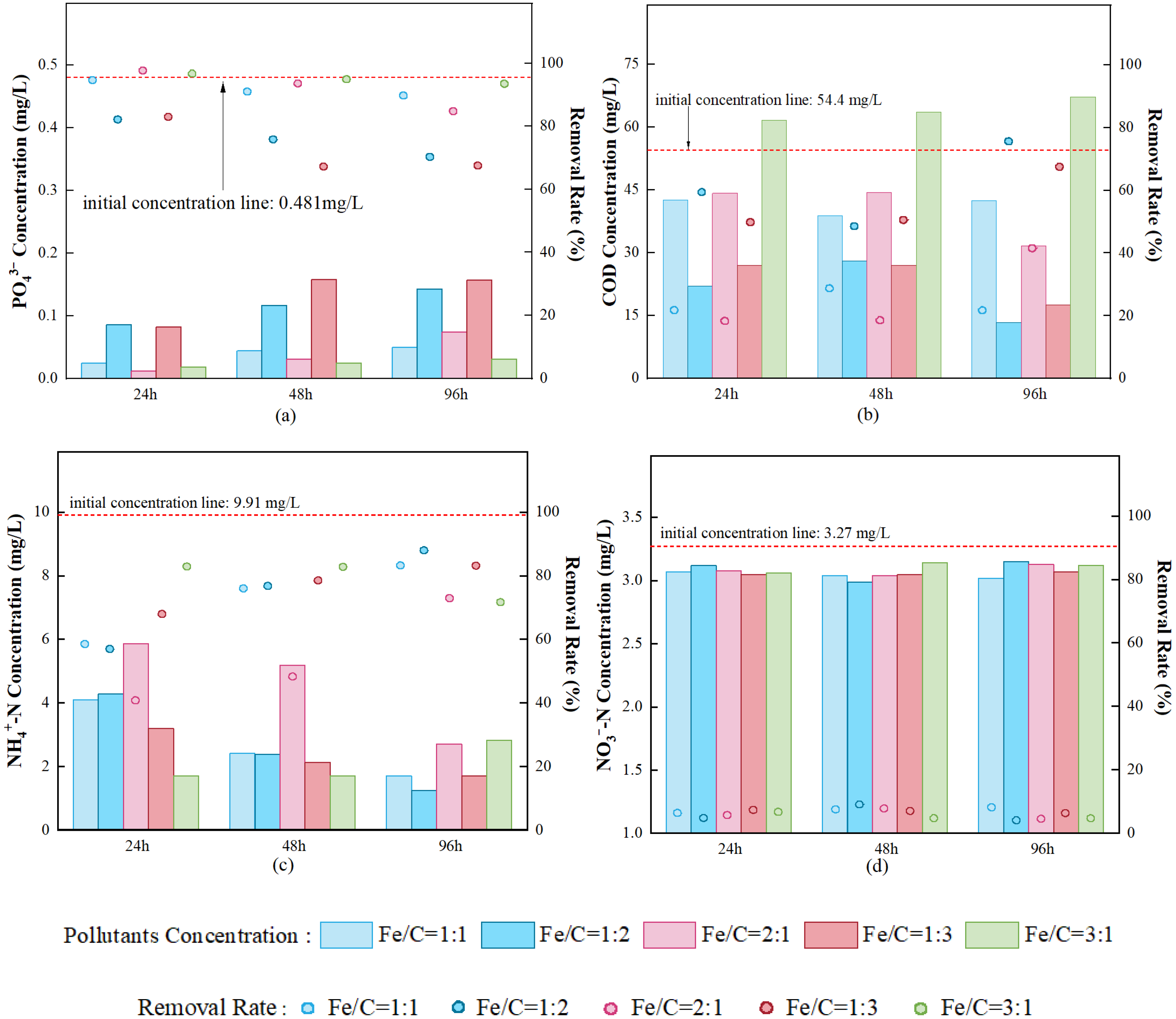
3.3.1. Performance Comparison of Different Fe/C Fillers
3.3.2. Treatment Efficiency for Actual Wastewater Using Selected Fe/C Mixed Fillers
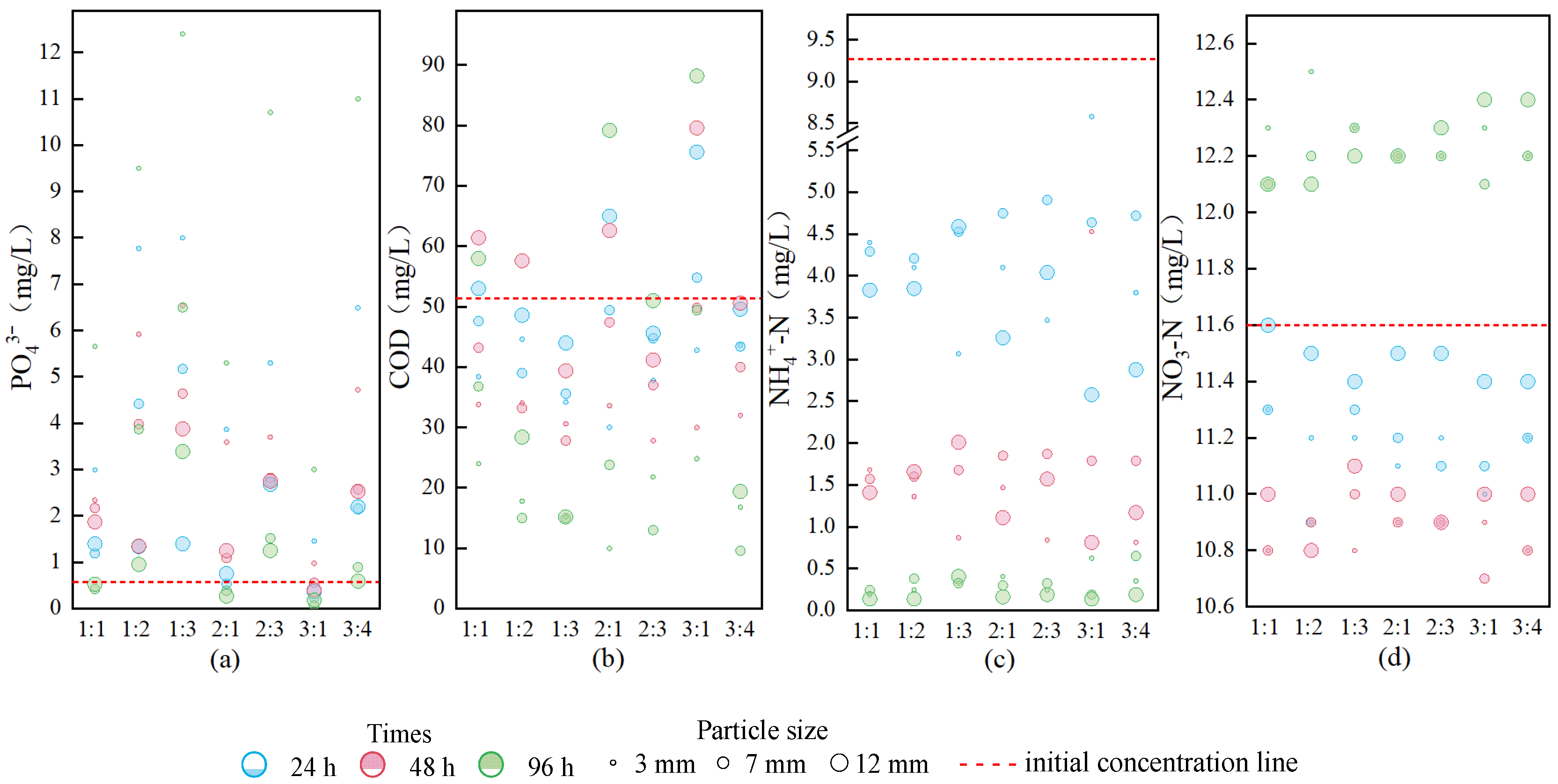
3.4. Static Simulation Experiments for Phosphate Removal by Fillers Prepared at Different Temperatures and Ratios
4. Discussion
4.1. Performance of Fe/C Physical Mixture
4.2. Comparison of Physical Mixing and Preparation Methods for Filler Performance
4.3. Effects of Relatively Low Temperature + Binder
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, C.; Wu, A.; Zhao, X.; He, G.; Zhao, S.; He, L.; Wu, F. Challenges and solutions for rural domestic sewage treatment at the grassroots level in developing countries. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2025, 201, 107480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Huang, J.; Xv, J.; Yao, J. Macrophytes stimulate microbial interaction and carbon, nitrogen, sulfur, and iron cycling in iron-carbon micro-electrolysis constructed wetlands. Environ. Res. 2025, 286, 122982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Fang, W.; Cheng, M.; Li, W.; Cen, Q.; Li, B.; Liu, Z. A review on the application of iron-carbon composites prepared from red mud and organic solid waste for wastewater treatment. Desalination 2025, 614, 119202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Guo, X.; Wang, A.; Pan, Y.; Ma, J.; Lu, S.; Liu, D. A comprehensive review on iron–carbon microelectrolysis constructed wetlands: Efficiency, mechanism and prospects. Water Res. 2025, 268, 122648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Song, P.; Cheng, H.; Liu, C.; Chen, R. Enhanced treatment of decentralized domestic sewage using gravity-flow multi-soil-layering systems coupled with iron-carbon microelectrolysis. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Zhuang, J.; Wu, W.; Sheng, M.; Pei, H.; Xu, X.; Huang, T. Enhancement of nitrogen and phosphorus removal from municipal wastewater treatment plant effluents by iron-modified solid carbon source in constructed wetlands: Performance and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 519, 165161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Chen, S.; Chen, J.; Zhou, N.; Yu, G. Effect of iron–carbon–zeolite substrate configuration on cadmium removal in vertical-flow constructed wetlands. Separations 2025, 12, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Deng, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Shan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, D. Iron-carbon galvanic cells enhance an anaerobic-aerobic-anoxic baffled reactor pretreatment for simultaneous organic and nitrogen removal from decentralized black water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 115898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.; Loebsack, G.; Sarchami, T.; Klinghoffer, N.B.; Papari, S.; Yeung, K.K.C.; Berruti, F. Production of a bio-magnetic adsorbent via co-pyrolysis of pine wood waste and red mud. Waste Manag. 2022, 149, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, C.; Du, Y.; Teng, G.; Wu, Z. Functional biochar fabricated from waste red mud and corn straw in China for acidic dye wastewater treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 320, 128887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Lin, K.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, D.; Ahmad, M.; Yu, J.; Fu, H.; Xu, L.; Wu, S.; Huang, L. Functionalizing biochar by co-pyrolysis shaddock peel with red mud for removing acid orange 7 from water. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 299, 118893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Xue, S.; Zhao, S.; Yan, J.; Qian, L.; Chen, M. Biochar supported nanoscale iron particles for the efficient removal of methyl orange dye in aqueous solutions. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latrach, L.; Ouazzani, N.; Hejjaj, A.; Zouhir, F.; Mahi, M.; Masunaga, T.; Mandi, L. Optimization of hydraulic efficiency and wastewater treatment performances using a new design of vertical flow Multi-Soil-Layering (MSL) technology. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 117, 140–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Chen, N.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, W.; Feng, C. Redefining multi-soil-layering systems: Structural innovation and sulfur-autotrophic denitrification for decentralized wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 523, 168392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Feng, C.; Zhan, Y.; Deng, B.; Mei, D.; Chen, N.; Hu, W. Disentangling microbial coupled fillers mechanisms for the permeable layer optimization process in multi-soil-layering systems. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 147, 538–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghotbi, S.; Abedini, A.; Akbarpour, A.; Malakooti, R. The efficiency and capabilities assessment of some local materials in wastewater treatment using the multi soil layering. Results Eng. 2025, 26, 104618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.L.; Hameed, B.H. Insight into the adsorption kinetics models for the removal of contaminants from aqueous solutions. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 74, 25–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Lawluvy, Y.; Shi, Y.; Ighalo, J.O.; He, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yap, P.-S. Adsorption of cadmium and lead from aqueous solution using modified biochar: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 106502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, J.; Zhang, L.; Chang, N. Phosphate adsorption on hydroxyl–iron–lanthanum doped activated carbon fiber. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 215–216, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, X. Adsorption kinetic models: Physical meanings, applications, and solving methods. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 390, 122156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HJ/T 399-2007; Water Quality—Determination of the Chemical Oxygen Demand—Fast Digestion-Spectrophotometric Method. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2008.
- GB 11893-89; Water Quality—Determination of Total Phosphorus—Ammonium Molybdate Spectrophotometric Method. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 1989.
- HJ/T 636-2012; Water Quality—Determination of Total Nitrogen—Alkaline Potassium Persulfate Digestion UV spectrophotometric method. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2012.
- HJ/T 535-2009; Water Quality―Determination of Ammonia Nitrogen―Nessler’s Reagent Spectrophotometry. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2009.
- HJ/T 346-2007; Water Quality—Determination of Nitrate-Nitrogen—Ultraviolet Spectrophotometry. State Environmental Protection Administration: Beijing, China, 2007.
- HJ/T 91-2002; Technical Specifications Requirements for Monitoring of Surface Water and Waste Water. State Environmental Protection Administration: Beijing, China, 2002.
- Genz, A.; Kornmüller, A.; Jekel, M. Advanced phosphorus removal from membrane filtrates by adsorption on activated aluminium oxide and granulated ferric hydroxide. Water Res. 2004, 38, 3523–3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, D.; Liu, G.; Liu, T.; Feng, Y. Intensified nitrogen and phosphorus removal and mechanism revelation in constructed wetlands amended with iron-carbon based substrate towards low C/N ratio wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 481, 148931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Zhou, Y.; Xie, Q.; Chen, T.; Liu, H.; Xue, S.; Zou, X.; Wei, L.; Xu, L.; Zhang, X.; et al. Phosphate adsorption kinetics and equilibria on natural iron and manganese oxide composites. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 323, 116222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yu, H.; Zhu, R.; Zhang, X.; Yan, L. Phosphate adsorption performance and mechanisms by nanoporous biochar–iron oxides from aqueous solutions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 28132–28145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Yan, D. Addition of Fe2+ increase nitrate removal in vertical subsurface flow constructed wetlands. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 91, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Han, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Ge, L.; An, X.; Liu, X.; Gao, W.; Sun, L.; Ren, Z.; et al. Study of enhanced nitrogen removal performance and mechanism of iron-modified activated carbon in low-temperature environments. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 116951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Qiu, B.; Hu, Q. The enhancement of nutrients removal performance in a vertical up-flow constructed wetland system using iron-carbon substrates. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 110036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Xu, J.; Kang, X.; Li, B.; Zhang, Y. Experimental study on the treatment of printing and dyeing wastewater by iron–carbon micro-electrolysis and combined processes. Processes 2025, 13, 2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DB53/T 953-2019; Water Pollutant Discharge Standard for Domestic Wastewater Treatment Facilities in Rural Areas. Yunnan Administration for Market Regulation: Yunnan, China, 2019.
- GB 3838-2002; Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water. State Environmental Protection Administration: Beijing, China, 2002.
- Yang, Z.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Ren, Z. Degradation of organic pollutants in near-neutral pH solution by Fe-C micro-electrolysis system. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 315, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, X.; Li, R.; Zhao, B.; Liang, W. Arsenate removal from water by zero-valent iron/activated carbon galvanic couples. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 182, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Gao, J.; Liu, J. Preparation of a new iron-carbon-loaded constructed wetland substrate and enhanced phosphorus removal performance. Materials 2020, 13, 4739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhou, Q.; Zeng, L.; He, F.; Wu, Z. Synergistic removal effect of P in sediment of all fractions by combining the modified bentonite granules and submerged macrophyte. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 626, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, H. Iron modified bentonite: Enhanced adsorption performance for organic pollutant and its regeneration by heterogeneous visible light photo-Fenton process at circumneutral pH. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 302, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamparas, M.; Gianni, A.; Stathi, P.; Deligiannakis, Y.; Zacharias, I. Removal of phosphate from natural waters using innovative modified bentonites. Appl. Clay Sci. 2012, 62–63, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, L.; Yu, L.; Hua, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Lu, Y.; Dong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Removing nutrients from wastewater by constructed wetlands under perfluoroalkyl acids stress. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Zhou, C.; Wu, F.; Xu, H.; Zhao, Z.; Han, Z.; Zhang, H.; Yang, S. Enhanced removal of organic, nutrients, and PFCs in the iron-carbon micro-electrolysis constructed wetlands: Mechanism and iron cycle. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 457, 141174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Q.; Li, G. Potassium phosphate/magnesium oxide modified biochars: Interfacial chemical behaviours and Pb binding performance. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 759, 143452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Xiao, J.; Wang, T.; Chen, G.; Chen, L.; Tian, X. Engineering of phosphate-functionalized biochars with highly developed surface area and porosity for efficient and selective extraction of uranium. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 379, 122388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wei, C.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Ding, X. MgO-modified biochar increases phosphate retention and rice yields in saline-alkaline soil. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 235, 901–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Pang, H.; Song, G.; Chen, J.; Wang, X. Efficient removal of uranium(VI) by layered double hydroxides supported nanoscale zero-valent iron: A combined experimental and spectroscopic studies. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 365, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yue, X.; Xu, W.; Zhang, H.; Li, F. Amino modification of rice straw-derived biochar for enhancing its cadmium (II) ions adsorption from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 379, 120783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, A.; Hussain, B.; Waqar, M.; Khan, M.R.; Jehanzeb, J.; Alam, K.; Rosaiah, P.; Ali, M.; Annu, M.; Akkinepally, B.; et al. Synergistic effects of carbon nanotubes on α-MnO2 electrocatalysts for improved oxygen reduction in alkaline fuel cells. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2024, 149, 111611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaled, Z.; Mohsen, A.; Soltan, A.; Kohail, M. Optimization of kaolin into metakaolin: Calcination conditions, mix design and curing temperature to develop alkali activated binder. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2023, 14, 102142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
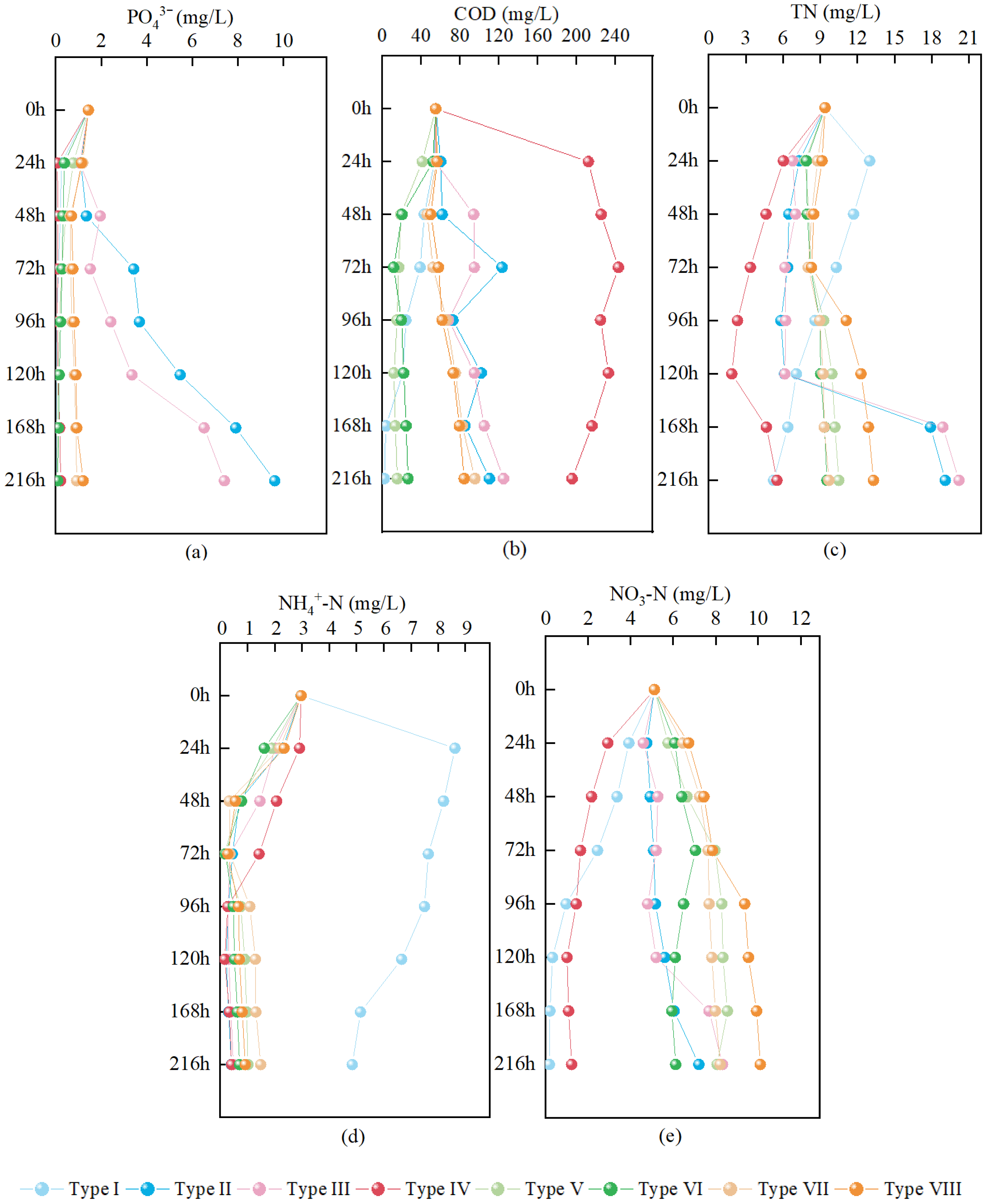
| Parameter | Type I | Type II | Type III | Type IV | Type V | Type VI | Type VII | Type VIII |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Iron (%) | 20 | 10 | 20 | 40 | 10 | 20 | 10 | 20 |
| Carbon (%) | 10 | 20 | 10 | 20 | 20 | 10 | 20 | 10 |
| Kaolin (%) | 30 | / | / | / | 50 | 50 | / | / |
| Bentonite (%) | / | 50 | 50 | 25 | / | / | 50 | 50 |
| Ammonium Bicarbonate (%) | 10 | 10 | 10 | / | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Quartz Sand (%) | 30 | 10 | 10 | / | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Lime (%) | / | / | / | 10 | / | / | / | / |
| Aluminum Powder (%) | / | / | / | 5 | / | / | / | / |
| Sintering Temperature (°C) | 400 | 400 | 400 | Natural drying | 800 | 800 | 800 | 800 |
| Indicator | Treatment Time (h) | CSC | IF | SS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PO43− (mg/L) | 24 | 4.31 | 0.04 | 0.02 |
| 48 | 4.43 | 0.06 | 0.02 | |
| 96 | 5.60 | 0.07 | 0.02 | |
| COD (mg/L) | 24 | 17.10 | 53.20 | 46.40 |
| 48 | 39.80 | 44.50 | 49.00 | |
| 96 | 12.00 | 110.60 | 52.80 | |
| NH4+-N (mg/L) | 24 | 0.05 | 3.42 | 2.52 |
| 48 | 0.11 | 6.13 | 0.30 | |
| 96 | 0.00 | 4.29 | 5.32 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Y.; Ren, X.; Wu, D.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Y.; Sun, S.; Feng, J.; Shen, J.; Wang, X. Performance Evaluation of Readily Available Iron–Carbon Micro-Electrolysis Materials for Domestic Sewage Treatment. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 12355. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312355
Xu Y, Ren X, Wu D, Zhou X, Liu Y, Sun S, Feng J, Shen J, Wang X. Performance Evaluation of Readily Available Iron–Carbon Micro-Electrolysis Materials for Domestic Sewage Treatment. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(23):12355. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312355
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Yong, Xiaojiao Ren, Di Wu, Xuejin Zhou, Yanping Liu, Shanshan Sun, Jimeng Feng, Jian Shen, and Xinze Wang. 2025. "Performance Evaluation of Readily Available Iron–Carbon Micro-Electrolysis Materials for Domestic Sewage Treatment" Applied Sciences 15, no. 23: 12355. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312355
APA StyleXu, Y., Ren, X., Wu, D., Zhou, X., Liu, Y., Sun, S., Feng, J., Shen, J., & Wang, X. (2025). Performance Evaluation of Readily Available Iron–Carbon Micro-Electrolysis Materials for Domestic Sewage Treatment. Applied Sciences, 15(23), 12355. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312355








