Physics-Informed Weighting Multi-Scale Deep Learning Inversion for Deep-Seated Fault Feature Identification: A Case Study of Aeromagnetic Data in the Dandong Region
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Methods
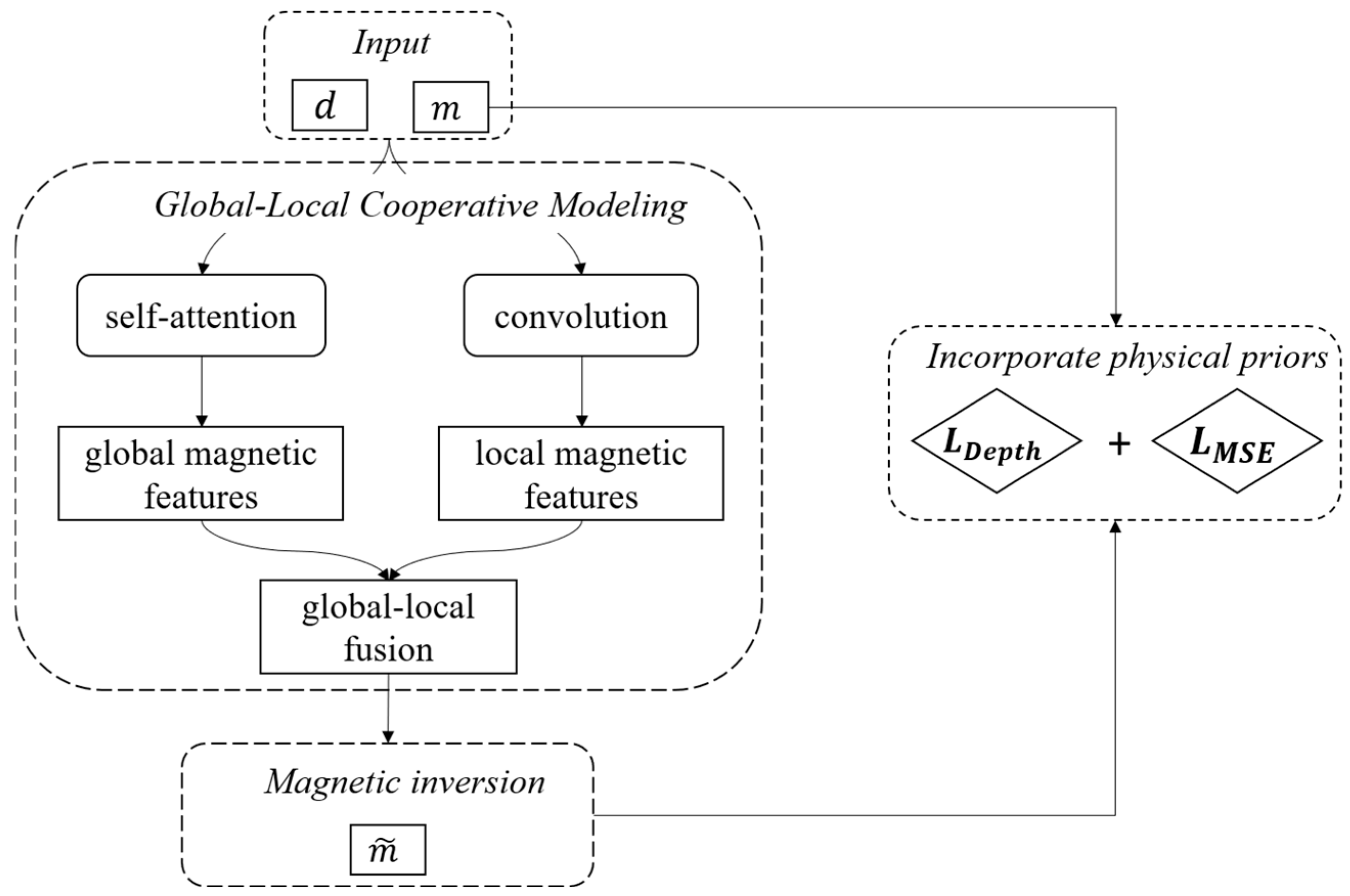
3.1. Inverse Problem
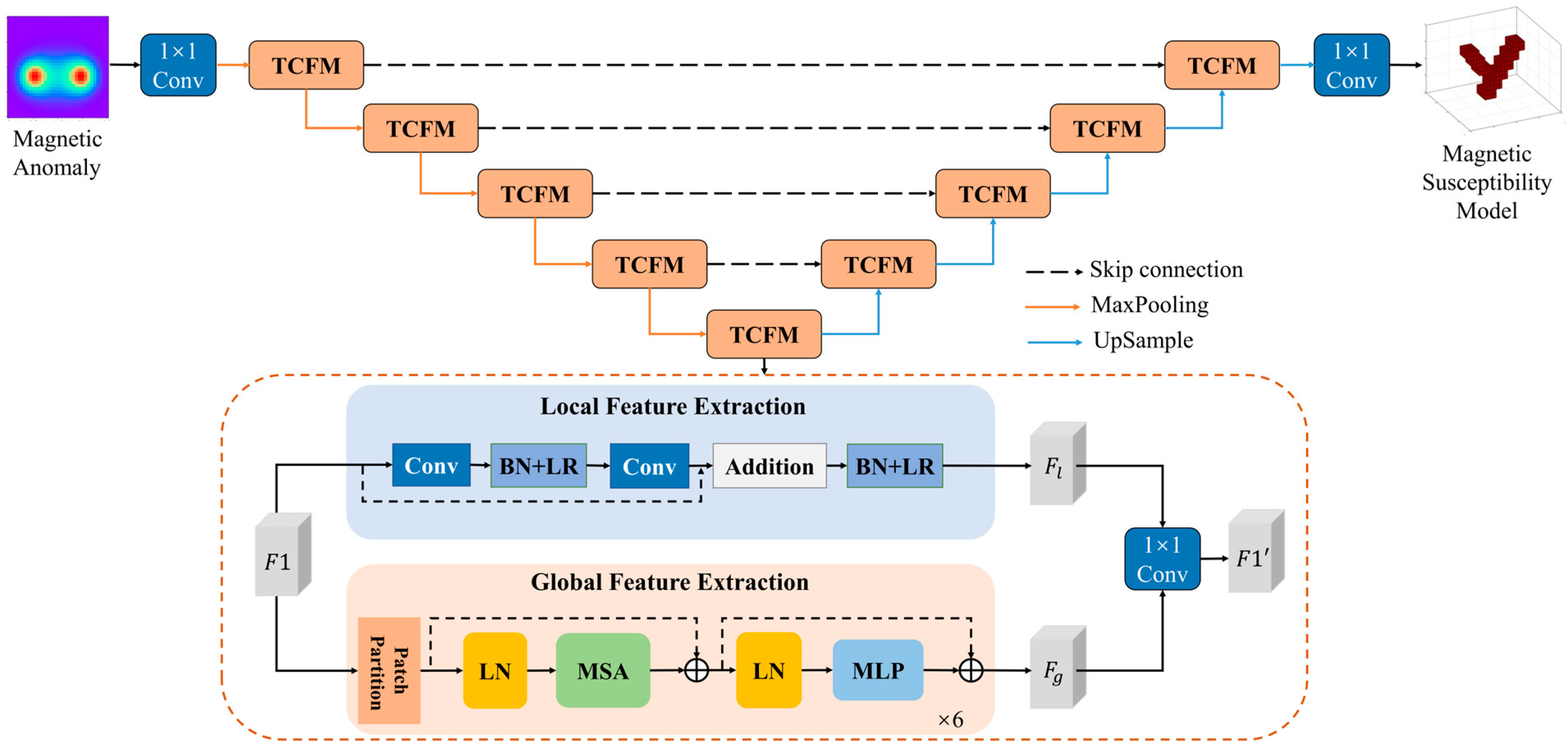
3.2. Network
3.3. Physical Constraint Loss Function
3.4. Dataset Construction and Network Training
4. Model Testing
4.1. Evaluation Metrics
4.2. Test Model Analysis
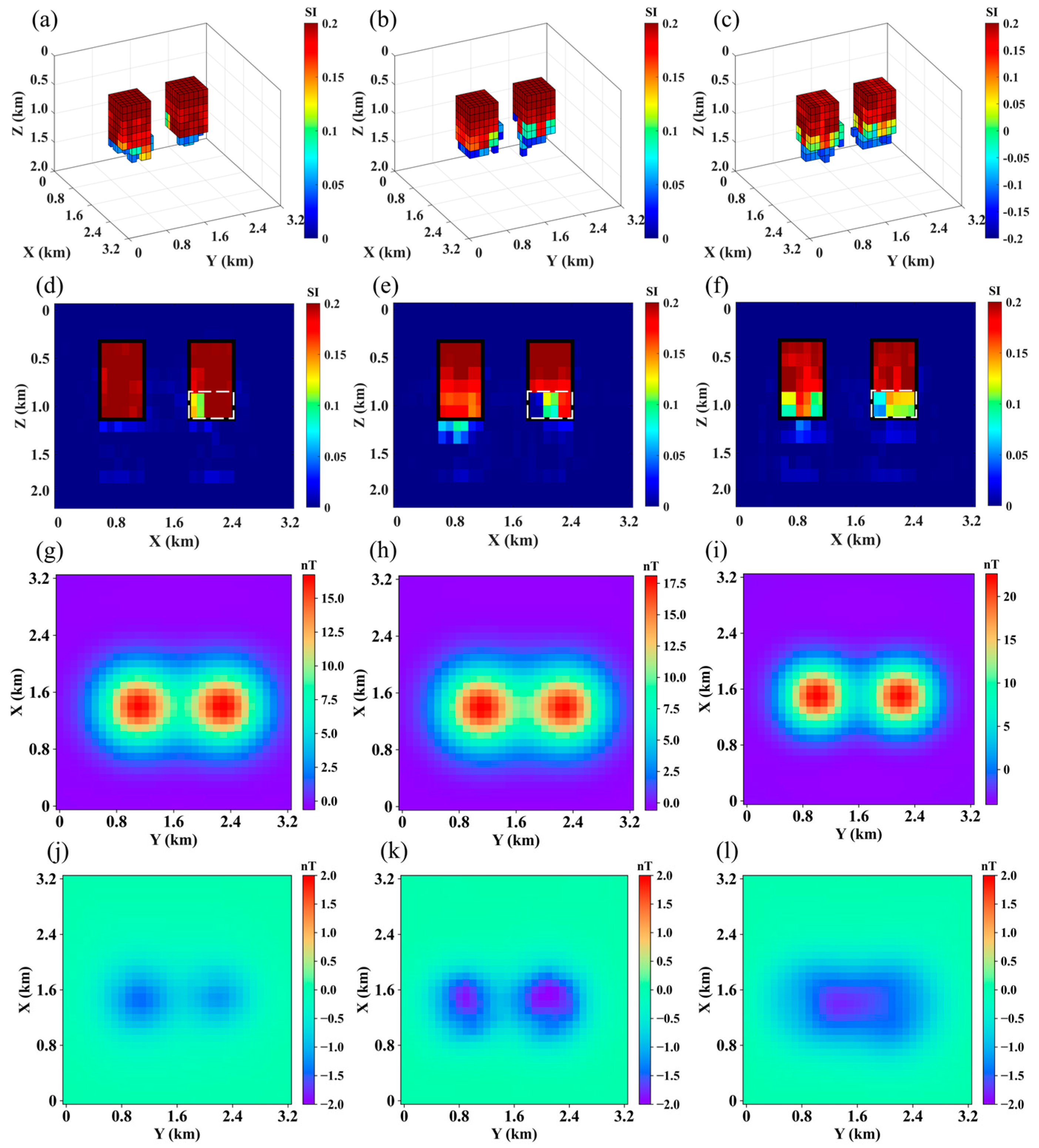
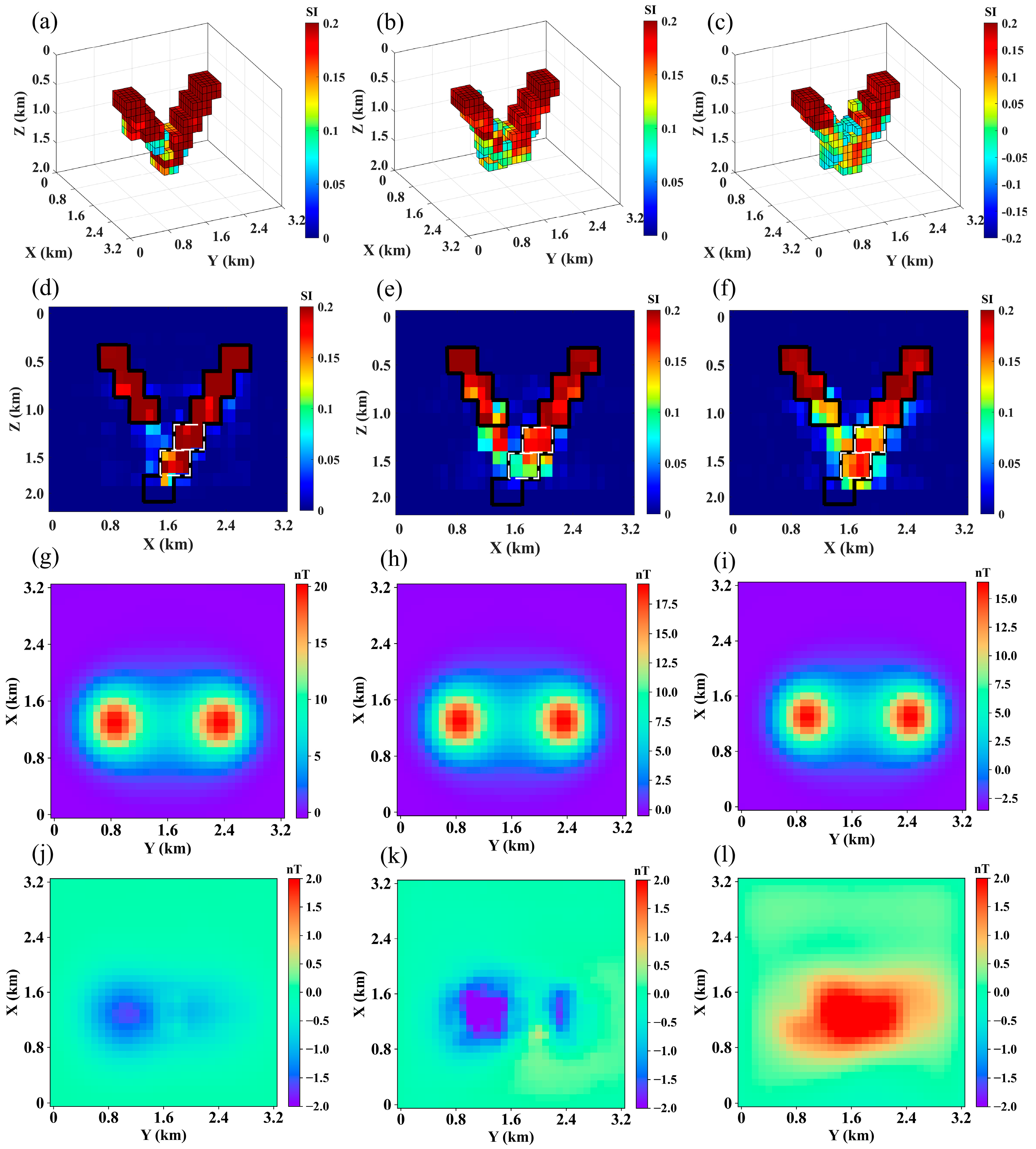
4.2.1. Test Model One
4.2.2. Test Model Two
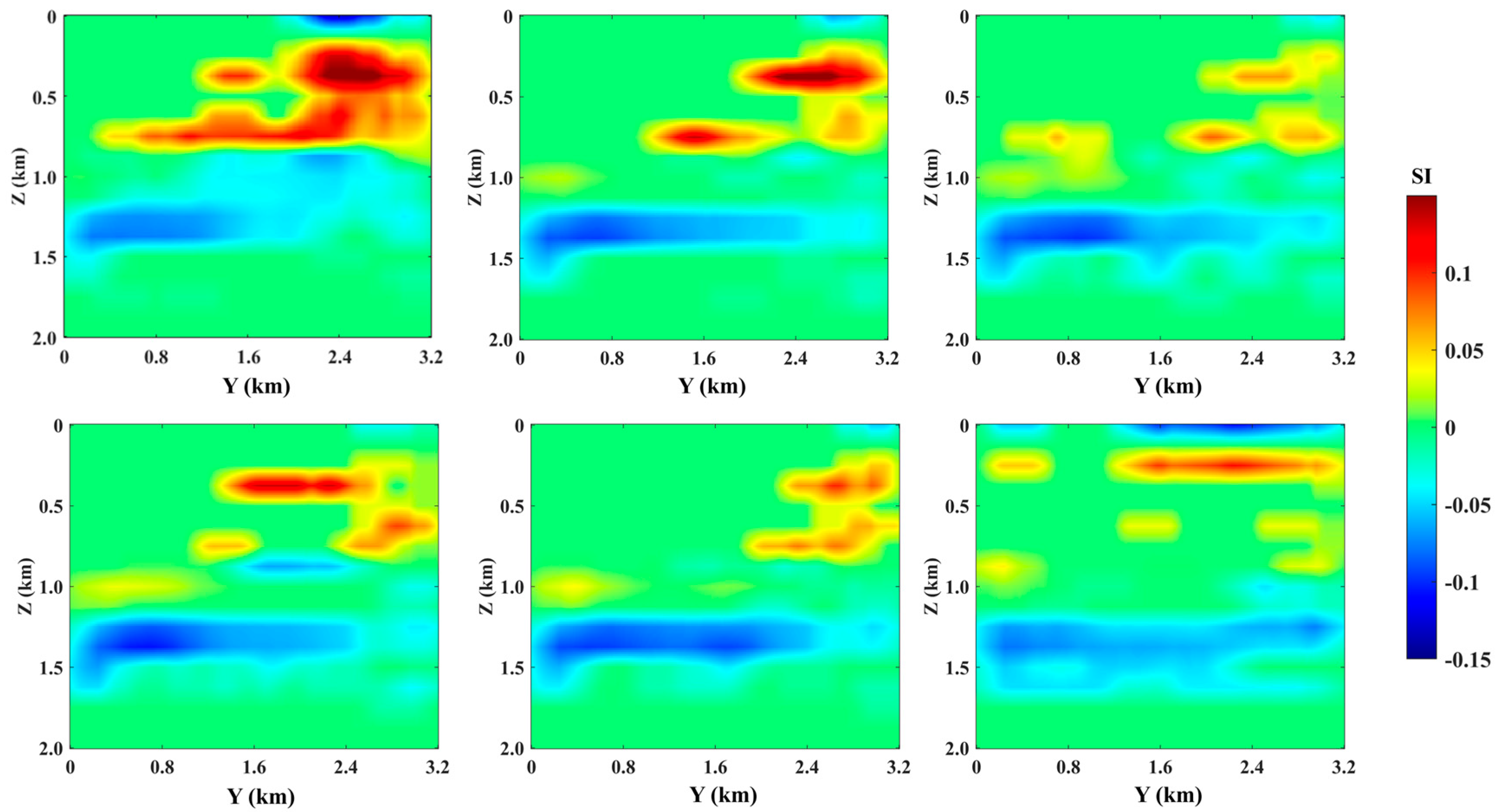
4.2.3. Test Model Three
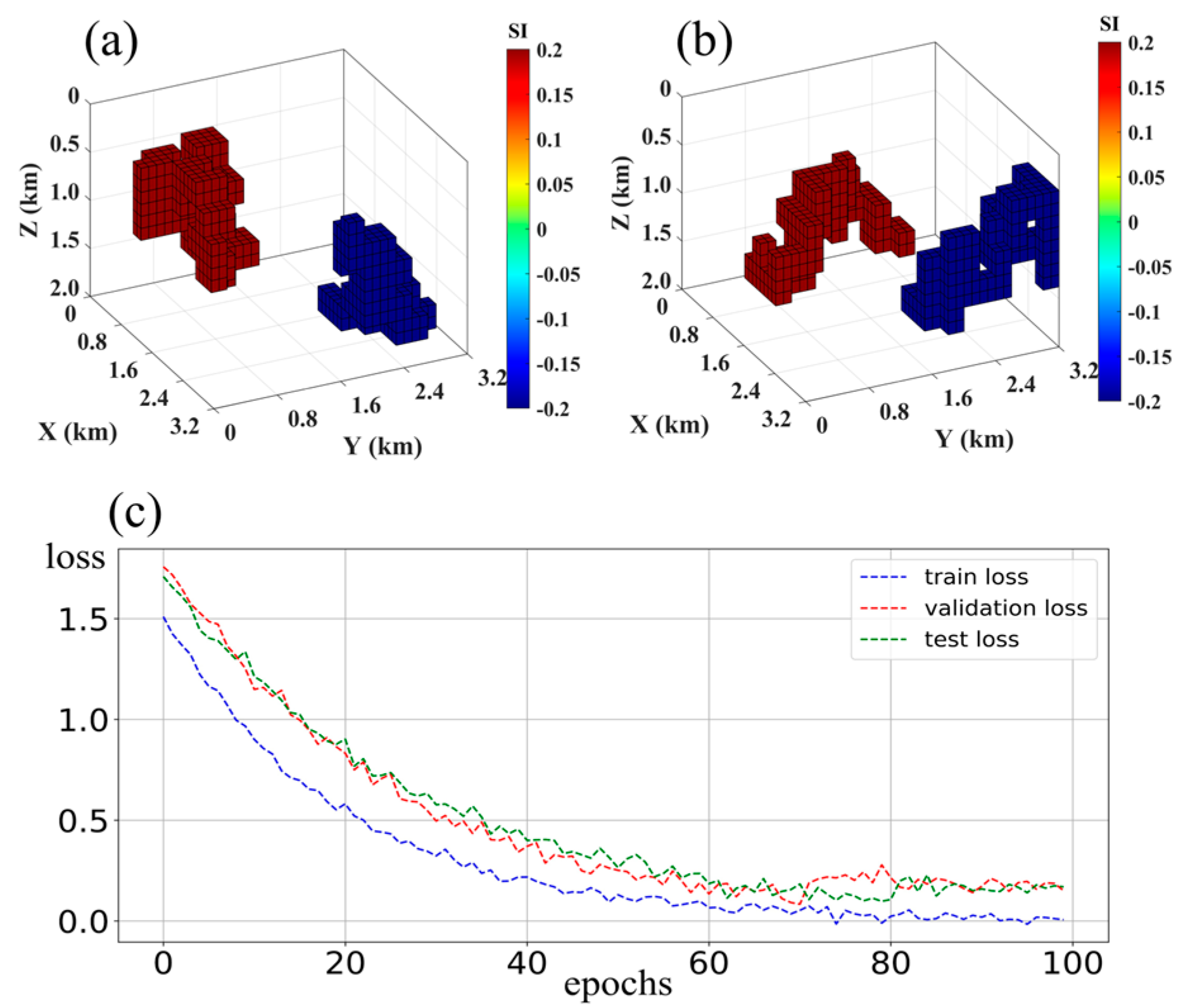
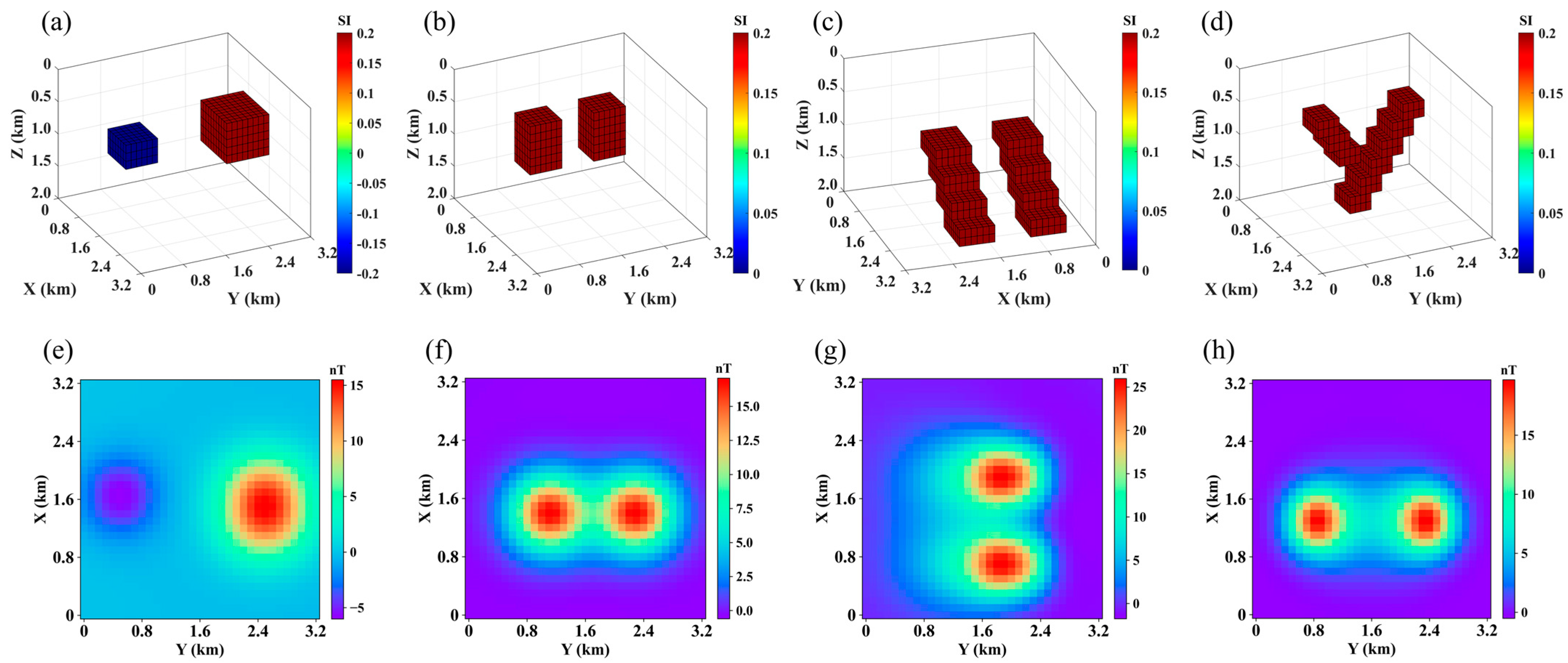
4.2.4. Test Model Four
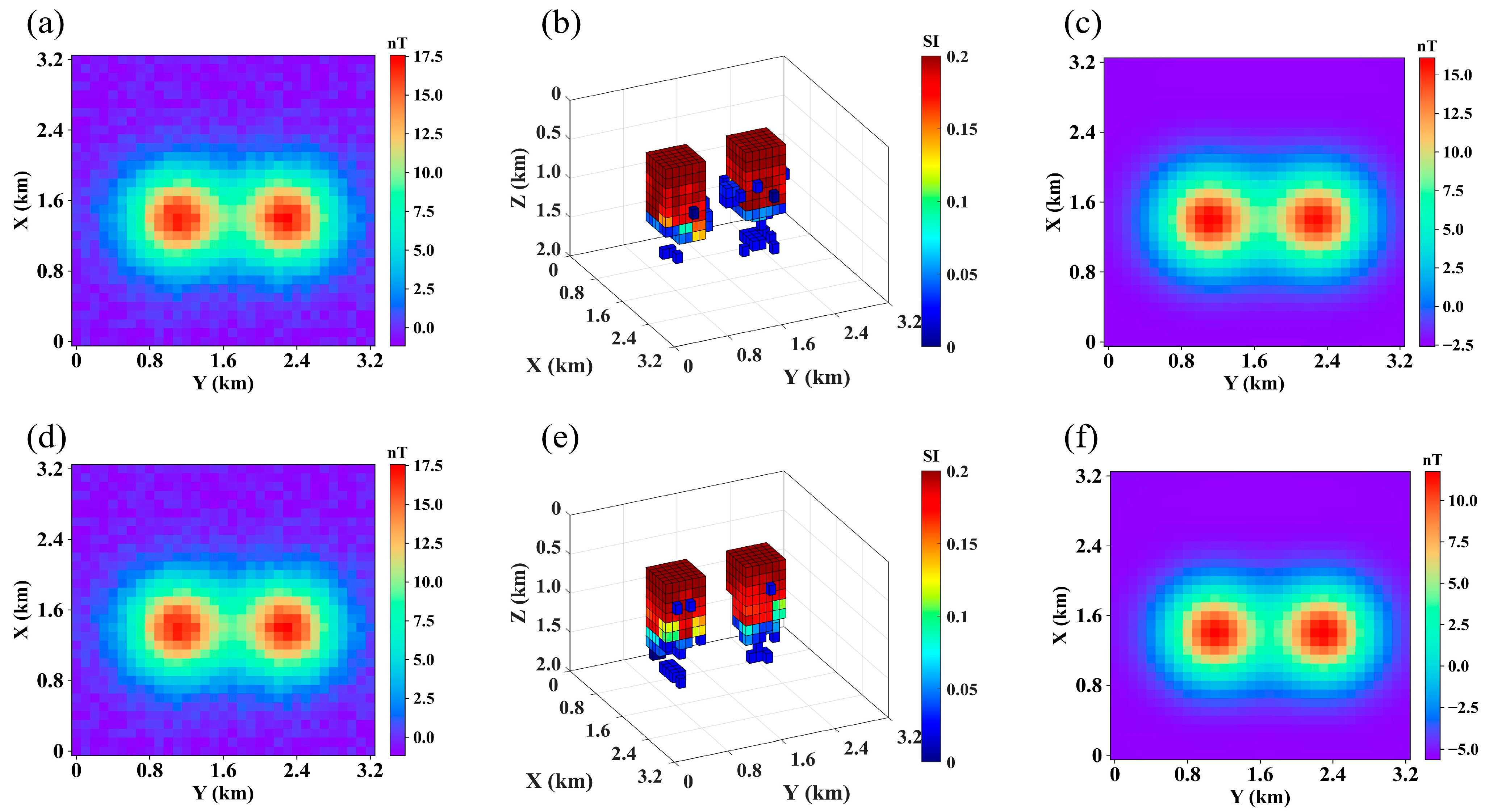
4.3. Noise Robustness Test
4.4. Ablation Study
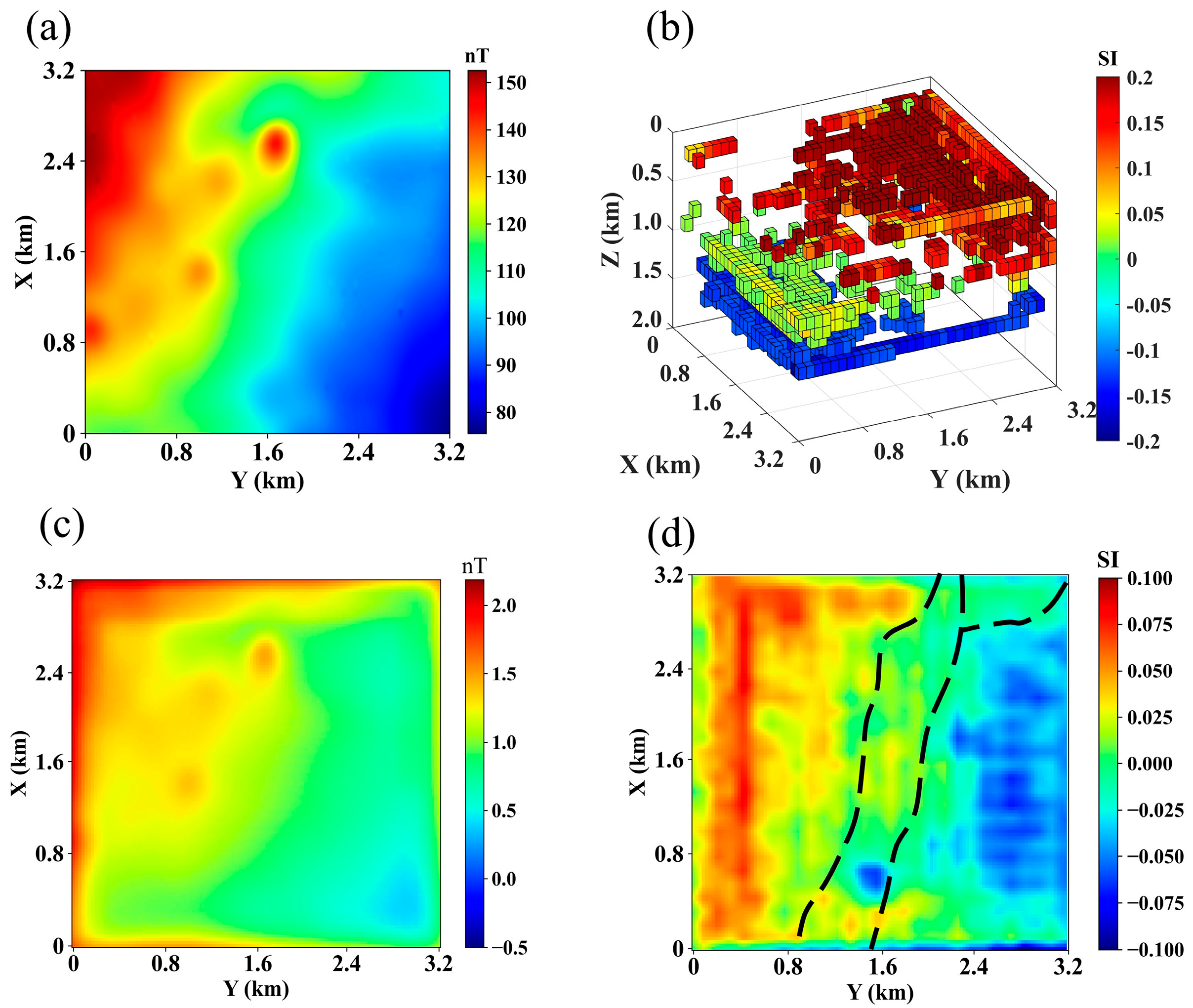
5. Field Data
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DL | Deep Learning |
| DNN | Deep Neural Network |
| TF | Transformer |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| TCFM | Transformer-CNN Fusion Module |
| MSE | Mean Squared Error |
| FPR | False Positive Rate |
| ViT | Vision Transformer |
| U-Net++ | U-Net Plus Plus (a variation in U-Net for semantic segmentation) |
| UAV | Unmanned Aerial Vehicle |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
References
- Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Zheng, M. Establishment and Geological Significance of the South Margin Fault Belt of Bogda. Acta Geol. Sin. 2025, 60, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Jiang, D.; Li, K.; Zhuang, J. Fault-geomorphology-sedimentary slope fold control sand model and its significance for oil and gas exploration—A case study of the northern section of the Baocui Slope in the West Lake Depression, East China Sea Basin. Lithol. Oil Gas Reserv. 2025, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.G.; Oldenburg, D.W. Fast inversion of large-scale magnetic data usingwavelet transforms and a logarithmic barrier method. Geophys. J. Int. 2003, 152, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paige, C.C.; Saunders, M.A. LSQR: An Algorithm for Sparse Linear Equations and Sparse Least Squares; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Pilkington, M. 3-D magnetic imaging using conjugate gradients. Geophysics 1997, 62, 1132–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.G.; Oldenburg, D.W. 3D inversion of magnetic data. Geophysics 1996, 61, 392–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, E.A.; Weiss, B.P.; Baratchart, L.; Hardin, D.P.; Saff, E.B. Fast inversion of magnetic field mapsof unidirectional planar geological magnetization. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2013, 118, 2723–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tontini, F.C.; De Ronde, C.E.J.; Scott, B.J.; Soengkono, S.; Stagpoole, V.; Timm, C.; Tivey, M. Interpretation of gravity and magnetic anomalies at lake Rotomahana: Geological and hydrothermal implications. J. Volcanol. Geothermal. Res. 2016, 314, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhonov, A.N.; Arsenin, V.Y. Solution Off Ill-Posed Problems; John Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Oldenburg, D.W. 3-D inversion of gravity data. Geophysics 1998, 63, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portniaguine, O.; Zhdanov, M.S. Focusing geophysical inversion images. Geophysics 1999, 64, 874–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhdanov, M.S.; Ellis, R.; Mukherjee, S. Three-dimensional regularized focusing inversion of gravity gradient tensor component data. Geophysics 2004, 69, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Shen, J.; Zhu, B. A review of the research and application of deep learning-based computer vision in structural damage detection. Earthq. Eng. Eng. Vib. 2022, 21, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.-W.; Kwak, K.-C. Speech Emotion Recognition Using Deep Learning Transfer Models and Explainable Techniques. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Hu, X.; Cai, H.; Liu, S.; Peng, R.; Liu, Y.; Han, B. 3D inversion of magnetic gradient tensor data based on convolutional neural networks. Minerals 2022, 12, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Liu, H.L.; Wang, W.; Ma, J. Swin Transformer for Seismic Denoising. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2024, 21, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Liu, S.; Qi, R.; Zhang, Y. Deep learning 3D sparse inversion of gravity data. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2021, 126, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.Y.; Jiao, S.; Lu, P.Y.; Zeng, S.F. 3-D Gravity Data Inversion Based on Enhanced Dual U-Net Framework. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Liao, X.L.; Cao, Y.Y.; Hou, Z.L.; Fan, X.T. Joint inversion of gravity anomalies and gravity gradient anomalies based on deep learning. J. Geophys. 2021, 64, 1435–1452. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, X.; Jiang, L.; Li, W.; Yu, Z.; Xie, J.; Li, L.; Tiwari, P.; Alonso-Fernandez, F. Swin-MGNet: Swin Transformer based Multi-view Grouping Network for 3D Object Recognition. IEEE Trans. Artif. Intell. 2024, 6, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Jia, Z.; Geng, H.; Liu, S.; Li, Y. Deep Learning Inversion for Multivariate Magnetic Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 62, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, R.J.; Xiong, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y. Magnetic Anomaly Inversion Based on Convolutional Neural Network. Geoscience 2023, 37, 173–183. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Zhu, H.; Jia, Z.; Ma, P. DiffSwinTr: A diffusion model using 3D Swin Transformer for brain tumor segmentation. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2024, 34, e23080. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M.; Qian, Y.; Liao, X.; Wang, Q.; Heng, P.-A. Hepatic vessel segmentation based on 3D swin-transformer with inductive biased multi-head self-attention. BMC Med. Imaging 2023, 23, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Deng, F.; Yan, X. A microseismic first break picking method based on Swin Transformer feature extraction. Prog. Geophys. 2023, 38, 1132–1142. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L.; Shen, H.; Min, F. Swin Transformer for simultaneous denoising and interpolation of seismic data. Comput. Geosci. 2024, 183, 105510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Huang, Z.; Lin, G. A physics-constrained neural network for multiphase flows. Phys. Fluids 2022, 34, 102102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedi, M.; Rapolla, A. 3-D inversion of gravity and magnetic data with depth resolution. Geophysics 1999, 64, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakely, R.J. Potential Theory in Gravity and Magnetic Applications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.; Wang, Z.; Lu, X.; Cheng, P.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, L. Physics-Guided Deep Learning 3-D Inversion Based on Magnetic Data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2025, 22, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, W.; Pan, K.; Zhang, J.; He, D.; Zhong, X.; Ren, Z.; Tang, J. A 3-D Magnetotelluric Inversion Method Based on the Joint Data-Driven and Physics-Driven Deep Learning Technology. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Li, F.; Meng, X.; Zheng, S. Improved 3-D Joint Inversion of Gravity and Magnetic Data Based on Deep Learning with a Multitask Learning Strategy. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumelhart, D.E.; Hinton, G.E.; Williams, R.J. Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Nature 1986, 323, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, X.; Guo, J.; Liu, Z.; Tang, Y.; Xiao, A.; Xu, C.; Xu, Y.; et al. A Survey on Vision Transformer. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 87–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, H.; Xia, Z.; Ge, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, L.; Li, B.; Dai, J. Development of a High-Stability FHD (Total-Field F, Horizontal Component H, and Declination D) Geomagnetic Vector Magnetometer Based on Bias and Compensation Fields. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2025, 96, 025103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celaya, A.; Denel, B.; Sun, Y.; Araya-Polo, M.; Price, A. Inversion of time-lapse surface gravity data for detection of 3-D CO2 plumes via deep learning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lin, Y. Data-driven seismic waveform inversion: A study on the robustness and generalization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 58, 6900–6913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, H.; Jiao, J. A High-Precision Edge Detection Technique for Magnetic Anomaly Signals Based on a Self-Attention Mechanism. Front. Earth Sci. 2025, 13, 1600631. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.Z.; Kusky, T.M.; Zhao, G.; Wu, F.; Liu, J.-Z.; Sun, M.; Wang, L. Mesozoic Tectonics in the Eastern Block of the North China Craton: Implications for Subduction of the Pacific Plate Beneath the Eurasian Plate; Geological Society, London, Special Publications: London, UK, 2007; Volume 280, pp. 171–188. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, B.; Zeng, Q.; Frimmel, H.E.; Wang, Y.; Guo, W.; Sun, G.; Zhou, T.; Li, J. Genesis of the Wulong gold deposit, northeastern North China Cra ton: Constraints from fluid inclusions, H-O-S-Pb isotopes, and pyrite trace element concentrations. Ore Geol. Rev. 2018, 102, 313–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, H.; Yang, Y.C.; Qu, H.C. Deep Geological Structures and Orebody Prediction in the Wulong Gold Mining Area, Dandong City, Liaoning Province. J. Jilin Univ. Earth Sci. Ed. 2025, 43, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, C.Q.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J. Genetic Origin of Late Jurassic Granites in the Dandong Area of the Liaodong Peninsula and Their Constraints on the Destruction of the North China Craton. Geotecton. Miner. Resour. 2023, 47, 149–164. [Google Scholar]




| Model | Parameters (Million) | Training Time | Inference Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transformer-CNN | 20.6 | 4.8 h | 0.35 s |
| U-Net++ | 10.1 | 2.3 h | 0.25 s |
| Traditional Tikhonov | N/A | N/A | 1.8 min |
| The Deep Weighting Function Proposed in This Paper | MSE + Li & Oldenburg Depth Weighting | MSE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transformer-CNN | 0.523 1.012 | 0.609 1.206 | 0.664 1.215 | |
| U-Net++ | 0.682 1.371 | 0.774 1.585 | 0.806 1.684 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ju, H.; Xia, Z.; Yang, J.; Zhou, L.; Dai, B.; Jiao, J.; Wang, D.; Wang, R. Physics-Informed Weighting Multi-Scale Deep Learning Inversion for Deep-Seated Fault Feature Identification: A Case Study of Aeromagnetic Data in the Dandong Region. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 12323. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152212323
Ju H, Xia Z, Yang J, Zhou L, Dai B, Jiao J, Wang D, Wang R. Physics-Informed Weighting Multi-Scale Deep Learning Inversion for Deep-Seated Fault Feature Identification: A Case Study of Aeromagnetic Data in the Dandong Region. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(22):12323. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152212323
Chicago/Turabian StyleJu, Haihua, Zhong Xia, Jie Yang, Longran Zhou, Bo Dai, Jian Jiao, Duo Wang, and Runqi Wang. 2025. "Physics-Informed Weighting Multi-Scale Deep Learning Inversion for Deep-Seated Fault Feature Identification: A Case Study of Aeromagnetic Data in the Dandong Region" Applied Sciences 15, no. 22: 12323. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152212323
APA StyleJu, H., Xia, Z., Yang, J., Zhou, L., Dai, B., Jiao, J., Wang, D., & Wang, R. (2025). Physics-Informed Weighting Multi-Scale Deep Learning Inversion for Deep-Seated Fault Feature Identification: A Case Study of Aeromagnetic Data in the Dandong Region. Applied Sciences, 15(22), 12323. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152212323






