1. Introduction
As coal mining operations extend to greater depths, the precise and rapid monitoring of roadway stability is critical for ensuring safe and efficient extraction [
1,
2]. The geomechanical environment of deep roadways is characterized by a confluence of challenging conditions, including high in situ stress, elevated water pressure, high geothermal temperatures, and strong mining-induced disturbances [
3,
4]. This inherent vulnerability, when compounded by factors such as inadequate support design or dynamic loading from equipment [
5,
6], can induce significant differential deformation. Traditional monitoring techniques, which rely on extrapolating overall stability from a limited number of discrete measurement points, are ill-equipped to resolve this spatial complexity [
7]. Such methods provide only sparse data, fundamentally failing to capture the comprehensive deformation behavior required for accurate stability assessments in deep mine environments. Therefore, the development and implementation of advanced monitoring methodologies capable of delivering precise and comprehensive spatial data are essential for the timely identification of potential failure zones and for guaranteeing the operational integrity of deep roadways.
Conventional methods for monitoring roadway deformation primarily include taut-wire convergence measurements [
8], direct readings with tape measures [
9,
10], the use of cross-sectional convergence meters [
11,
12], and total station surveys [
13,
14]. The operational paradigm for these techniques involves establishing discrete measurement cross-sections at intervals of several tens of meters along the roadway. At these locations, changes in the roof-to-floor and wall-to-wall distances are recorded by measuring pre-installed reference points to assess the stability of the surrounding rock mass. This approach is not only inefficient to implement but, more critically, it is incapable of capturing the non-uniform deformation characteristics of the rock mass between measurement stations. In critical situations, this reliance on sparse data can lead to a significant misassessment of roadway stability.
3D laser scanning is a non-contact measurement technology that enables the rapid acquisition of high-density, high-precision 3D point cloud data from object surfaces [
15,
16,
17,
18]. When integrated with Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) algorithms, mobile 3D laser scanning systems can efficiently generate spatially referenced models of underground roadways in real-time. This capability has led to its widespread application in geotechnical engineering [
19,
20], tunnel monitoring [
21,
22], ground subsidence analysis [
23,
24], and mine surveying [
25,
26].
In the specific domain of coal mine roadway monitoring, extensive research has been conducted utilizing this technology. To address the persistent challenges of low efficiency and poor accuracy in data alignment, Singh et al. [
27] proposed a cooperative automatic registration method that significantly enhanced the efficiency and automation of on-site point cloud acquisition. The fundamental capability of 3D laser scanning to capture deformation was validated by Kajzar et al. [
28], who performed repeat scans of roadways and coal pillars in the Ostrava-Karvina coal basin and found the results comparable to those from other survey instruments. Methodological refinements have also targeted data quality; for instance, Xu et al. [
29] developed a stepping bounding box algorithm to denoise and efficiently extract clean point clouds of the surrounding rock. Building on this, Wu et al. [
30] demonstrated the reliability of a mobile laser scanning-based analysis method in the Sanshandao Gold Mine. Furthermore, to quantify complex deformation patterns, Pu et al. [
31] introduced a point-to-surface distance calculation method, which successfully revealed the asymmetric and non-uniform deformation of expansive rock in the Taiping Mine. However, despite these advances, two critical issues continue to impede the routine application of 3D laser scanning in underground environments: the effective filtering of extensive noise generated by mining infrastructure such as belt conveyors and ventilation ducts, and the robust, high-precision registration of multi-temporal point cloud data. Addressing these challenges remains essential for leveraging the full potential of the technology.
To address these challenges, we present a complete, end-to-end workflow for analyzing surrounding rock deformation in deep mine roadways using 3D laser scanning. This framework was implemented and validated within the No. 20105 belt conveyor roadway of the Dahaize coal mine. Our methodology integrates several critical stages: initial data acquisition was performed with a GoSLAM G100 3D laser scanner, followed by a multi-stage denoising process that employed statistical, connected-component, and trimming filters. High-precision registration of multi-temporal point clouds was then achieved using a hybrid strategy that combines Principal Component Analysis (PCA) with the Iterative Closest Point (ICP) algorithm. Finally, the roadway deformation was quantified using the Cloud-to-Cloud (C2C) distance computation method. The objective of this study is to establish a robust and high-fidelity approach for characterizing the complete deformation profile of roadways, thereby providing a quantitative and timely basis for stability control.
2. Engineering Background
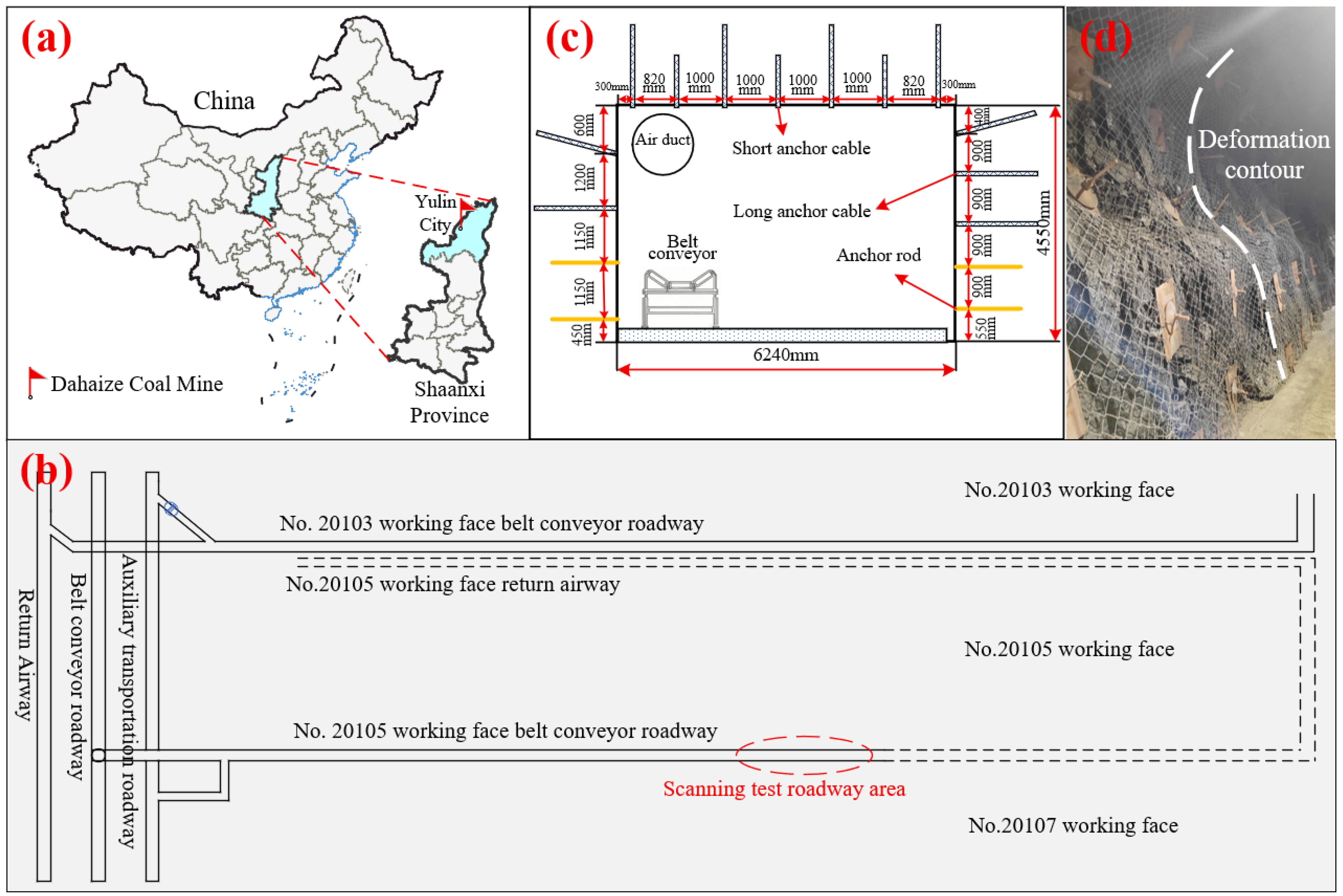
The Dahaize coal mine, located in Yulin, China (
Figure 1a), is a large-scale operation with a designed production capacity of 20.0 Mt/a. The subject of this investigation, the No. 20105 belt conveyor roadway, was designed with a length of 6250 m at a burial depth exceeding 600 m. As depicted in
Figure 1b, the roadway serves a critical long-term function. It was engineered not only to support the active No. 20105 longwall panel but also to be preserved using gob-side entry retaining to serve as the ventilation passage for the subsequent No. 20107 panel. Consequently, the precise and rapid monitoring of its stability is paramount for the safety of both excavation and extraction phases.
The roadway was excavated with a rectangular cross-section of 6240 mm in width and 4550 mm in height. A combined support system was implemented, the specific parameters of which are detailed in
Figure 1c. The roof was reinforced with an alternating pattern of four long cable bolts (Φ21.8 × 7300 mm) and three short cable bolts (Φ21.8 × 4500 mm), supplemented with wire mesh. Notably, the wall support was designed asymmetrically. The left wall was supported by two upper short cable bolts (Φ21.8 × 3000 mm) and two lower rock bolts (Φ22 × 2600 mm), whereas the right wall was reinforced with three upper short cable bolts (Φ21.8 × 3000 mm) and two lower rock bolts (Φ22 × 2600 mm).
During development, the combination of high in situ stress, elevated water pressure, and excavation-induced disturbances—all characteristic of deep mining—resulted in measurable convergence of the roadway walls. This deformation was notably asymmetric, as illustrated in
Figure 1d, with convergence in the lower sections of the walls being significantly more pronounced than in the upper sections. We hypothesize that this differential deformation is attributable to the support design, which allowed for stress to concentrate in the less reinforced and intrinsically weaker coal strata of the lower walls. Given the extended service life required of the roadway and its critical role in the gob-side entry retaining strategy, implementing a more rapid and comprehensive deformation monitoring program is a foundational prerequisite for effective, long-term stability control.
3. Materials and Methods
This section details the methodology, instrumentation, and data processing workflow employed for monitoring the deformation of the surrounding rock in the subject roadway.
3.1. Deformation Monitoring Methodology
3.1.1. Principles of 3D Laser Scanning
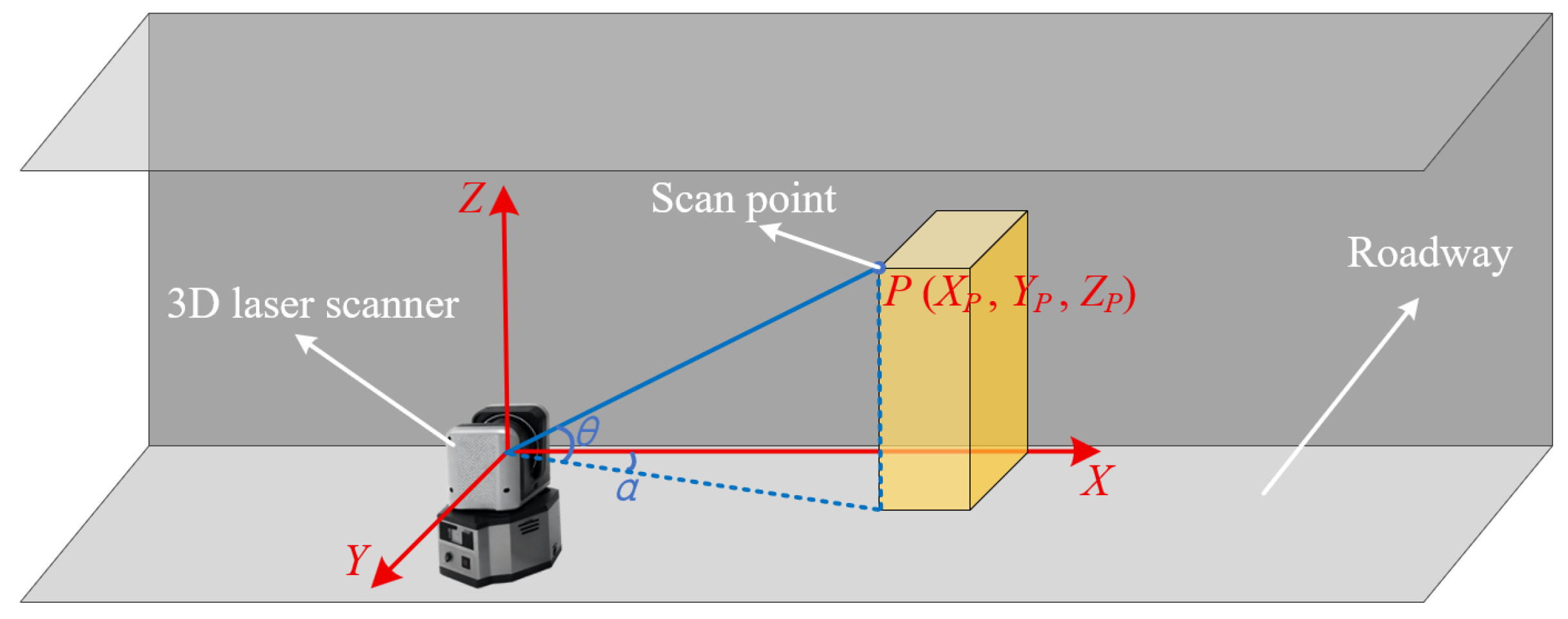
The principle of 3D laser scanning relies on precisely measuring distances and angles to generate a three-dimensional map of a target surface [
32]. The instrument’s laser emitter projects an infrared laser beam, which is directed by a rotating optical mirror onto the object of interest. The beam undergoes diffuse reflection from the surface, and a portion of the reflected light returns to the instrument’s receiver. The system records the time-of-flight, which is the interval between emission and reception, to calculate the distance (
S) between the scanner and the object.
Simultaneously, the instrument records the horizontal deflection angle (
α) and the vertical deflection angle (
θ) of the optical mirror. These three values—
S,
α, and
θ—define the position of a point in a spherical coordinate system. This system is defined with the laser source as the origin (
O), the positive
Z-axis pointing vertically upward, and the positive
X-axis aligned with the horizontal laser emission direction, forming a left-handed coordinate system. Through the continuous rotation of the instrument body and its internal optics, the scanner systematically captures this spatial information across its field of view, assembling the measurements into a dense point cloud. As illustrated in
Figure 2, the relative coordinates (
XP,
YP,
ZP) of any scanned target point
P are calculated using the following equations:
3.1.2. SLAM Technology
The 3D laser scanner employed in this study utilizes SLAM technology. SLAM is a computational framework that enables a device to operate in an unknown, GPS-denied environment by concurrently constructing a map and tracking its own pose within that map [
33]. The process integrates data from a suite of sensors, including an Inertial Measurement Unit and the laser scanner itself. This information is processed through a sophisticated architecture that includes front-end data association, back-end optimization, and loop closure detection to correct for accumulated drift. In essence, SLAM fuses sensor observations with motion information to simultaneously estimate the scanner’s trajectory while progressively building and refining a model of the surrounding environment, with the localization and mapping tasks being mutually dependent components of a unified estimation problem.
3.2. Three-Dimensional Laser Scanner
The specific instrument used for data acquisition was the GoSLAM G100 (manufactured by China Coal (Tianjin) Mining Technology Co., Ltd., Tianjin, China), a mobile 3D laser scanner specifically developed for deployment in underground mine roadways. This device integrates a multi-line LiDAR sensor with an IMU and operates on the SLAM principle, enabling it to reconstruct a complete and precise 3D spatial model without reliance on any external positioning infrastructure. Key technical specifications of the instrument are provided in
Table 1. The scanner emits 320,000 laser pulses per second, has a maximum scanning range of 120 m, and achieves a relative accuracy of better than 1 cm. As a Class I laser product, it is safe for operation in occupied areas. A critical feature for this application is the scanner’s capability for real-time data processing, allowing for immediate visualization and quality control of the acquired point cloud.
3.3. Methods
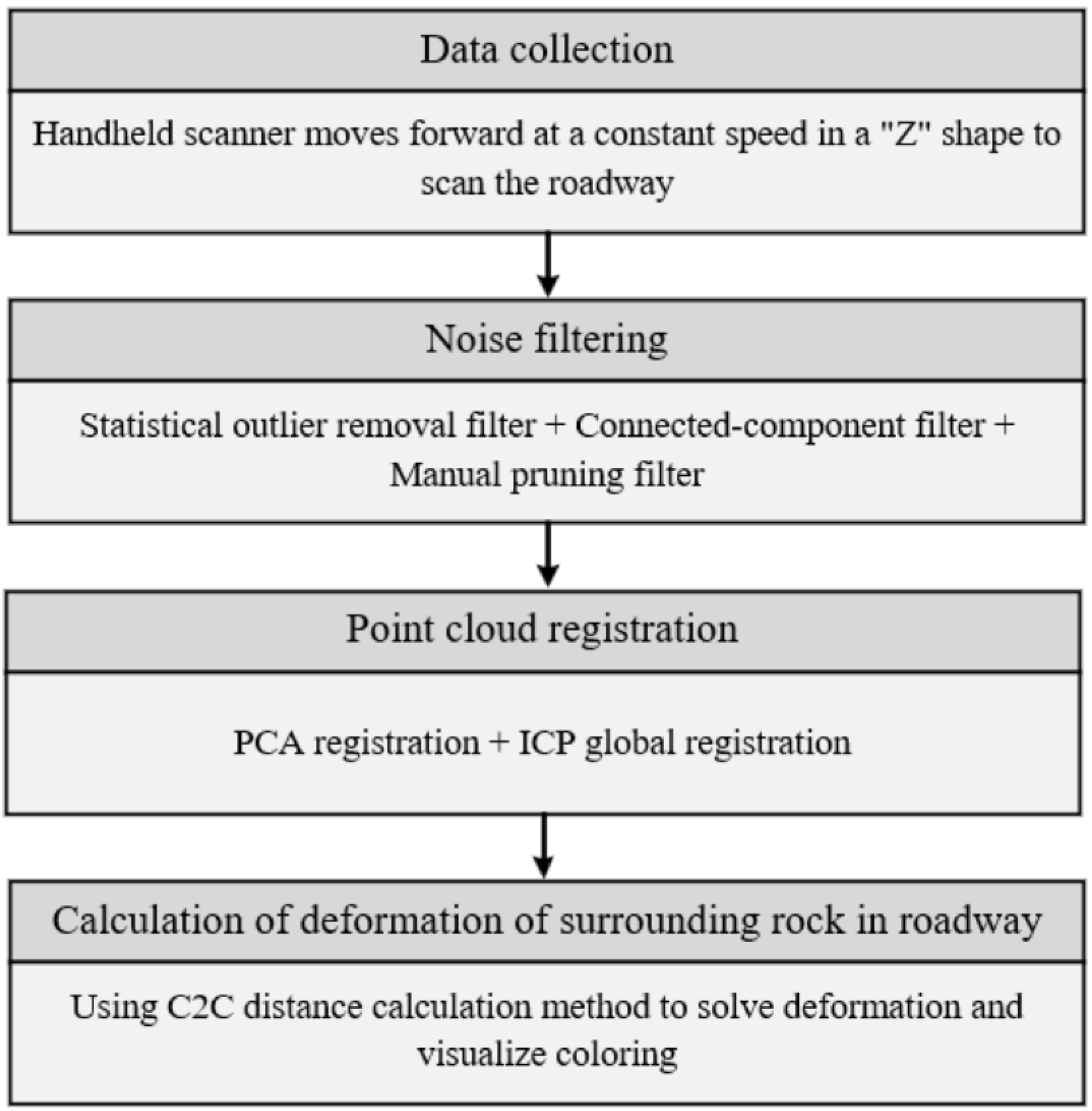
We developed a comprehensive workflow for analyzing roadway deformation using 3D laser scanning, which supports both global deformation analysis and the comparative analysis of arbitrary cross-sections. As illustrated in
Figure 3, this processing pipeline consists of four primary stages: data acquisition, data pre-processing, point cloud registration, and deformation quantification.
3.3.1. Data Acquisition
To establish the optimal parameters for field data acquisition, we first conducted a series of controlled benchtop experiments (
Figure 4a). The objective of these tests was to determine the ideal scanning duration and distance for capturing high-fidelity data with the GoSLAM G100. For this purpose, a toolbox with distinct geometric features was used as a standardized target. The scanner’s ability to resolve surface details under different parameter sets was quantified by measuring the density of the point cloud successfully captured on the target’s surface.
In the first experiment, we quantified the effect of scan duration on point cloud density. Four duration intervals were tested: 30 s, 60 s, 120 s, and 300 s. To ensure a rigorous comparison, all other variables were held constant; the scanner’s pose relative to the target remained fixed, and illumination was provided by ambient light. The results, presented in
Figure 4b–e and
Table 2, demonstrated that beyond an initial rapid increase, the number of points captured on the target surface did not significantly improve with longer scan times. The point cloud count effectively reached saturation after 60 s of scanning.
A second experiment was conducted to investigate the influence of scan distance on point cloud density. We established four distance intervals—1 m, 2 m, 5 m, and 10 m—to simulate representative scenarios, from close-range inspection of the walls, roof, and floor to comprehensive mapping of the entire roadway profile. For this test series, the scan duration was fixed at 120 s under ambient light. As shown in
Figure 4f–i and
Table 2, the acquired point cloud density decreased markedly with increasing distance. At distances of 5 m or less, the target object was clearly resolvable, and the point cloud density was optimal—neither excessively dense nor overly sparse.
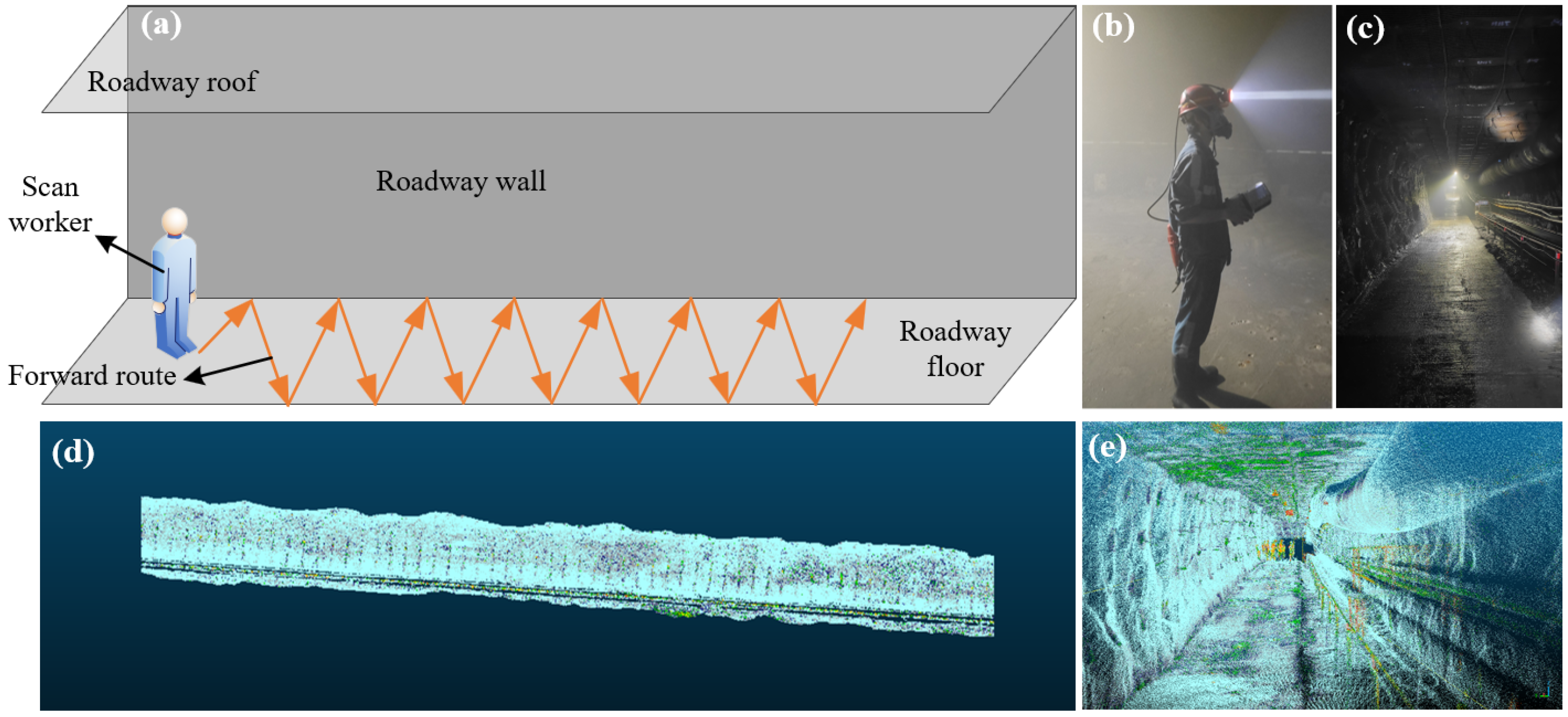
Recognizing that SLAM trajectory drift inevitably accumulates with distance, we proactively managed this potential error source by limiting the length of any single, continuous scan to approximately 100 m, ensuring the overall drift remained within a controllable range. Informed by these calibration experiments, we designed a field data acquisition strategy that employed a Z-pattern trajectory (
Figure 5a). The operator carried the scanner and moved at a slow, constant walking pace along the roadway (
Figure 5b). This strategy was specifically chosen to ensure both a sufficient scan duration for the overall roadway geometry and closer, more detailed scans of the irregular wall surfaces. The site conditions and the resulting raw point cloud are depicted in
Figure 5c–e. This methodology yielded a high-quality dataset with a final point cloud surface density of 10,363 points/m
2, a density greater than that achieved in our 5 m benchtop test (0.92 points/cm
2), which was sufficient to resolve fine geometric features, it confirms the data quality is adequate for characterizing the overall roadway geometry. This level of detail is appropriate for resolving deformations of several centimeters or more.
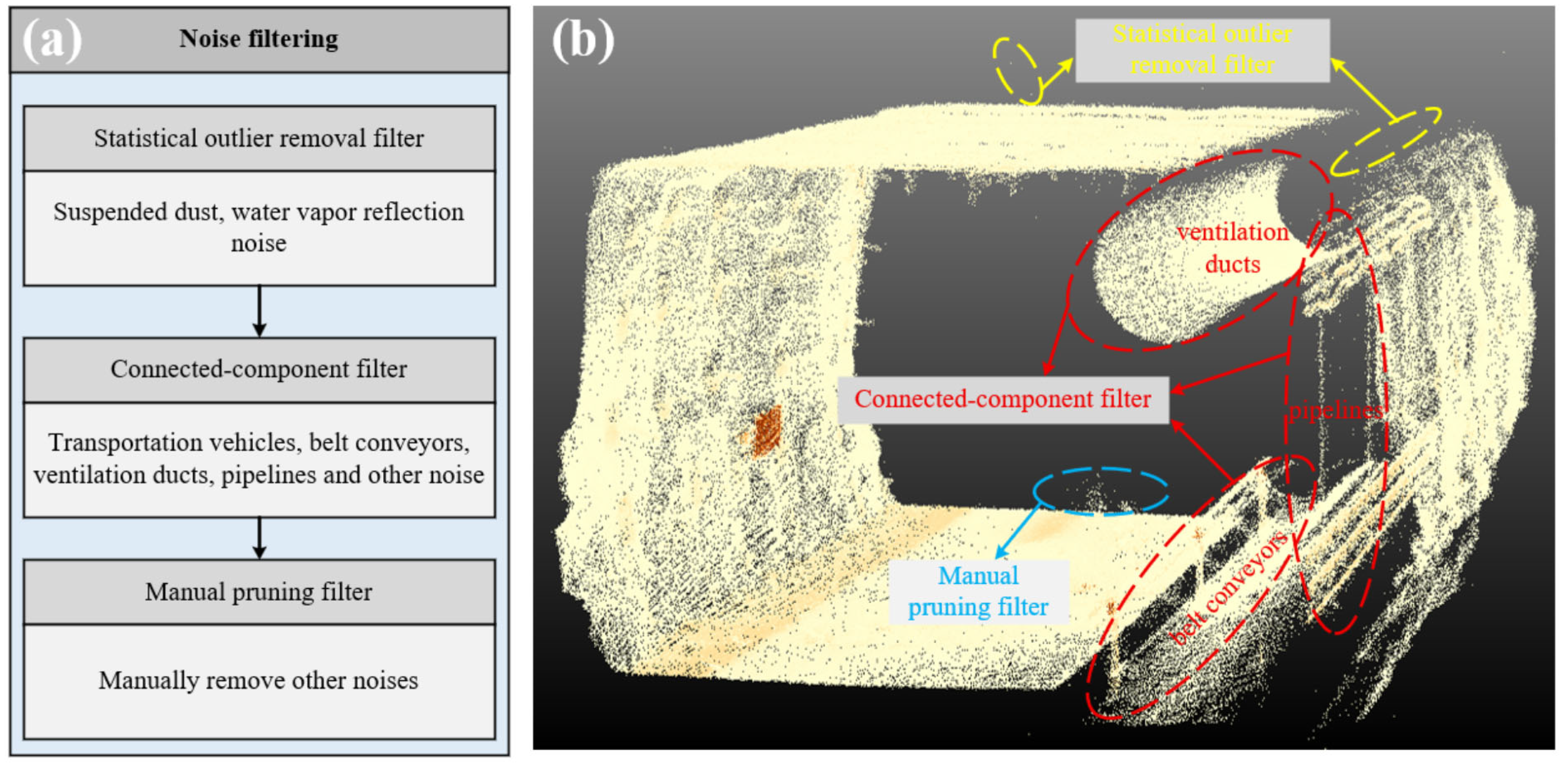
3.3.2. Noise Filtering
The raw point cloud data acquired in an active underground mine is invariably contaminated with extraneous points. These artifacts originate from various sources, including mining equipment (e.g., vehicles, conveyors, ventilation ducts) and reflections from airborne dust and water vapor. The removal of this noise is a critical prerequisite for accurate deformation analysis. To address this, we implemented a sequential, three-stage filtering process, as illustrated in
Figure 6.
The first stage employed a statistical outlier removal filter to eliminate sparse, randomly distributed noise. This algorithm functions by calculating the mean distance for each point to its k-nearest neighbors [
34]. Assuming these distances follow a Gaussian distribution, any point whose mean distance falls outside a defined threshold (mean ± n × standard deviation) is classified as an outlier and removed from the dataset. This filter is highly effective at targeting noise generated by atmospheric particulates.
The second stage utilized connected-component filtering to segment and remove large, discrete objects. This method clusters points based on their Euclidean distance in 3D space, partitioning the entire point cloud into spatially distinct components [
35]. By defining a minimum point count threshold, we isolated the largest connected component—representing the continuous roadway surface—while discarding any components with fewer points than this threshold. This filter is specifically designed to effectively remove the point clouds of large-scale equipment that is physically detached from the main rock mass, such as transport vehicles, belt conveyors, ventilation ducts, and pipelines.
As a final step, a manual pruning filter was applied. This served as a supplementary measure to meticulously remove any remaining noise that was not successfully eliminated by the automated algorithms, thereby producing a final, clean point cloud representing only the surrounding rock surface [
31].
3.3.3. Point Cloud Registration
The accurate alignment of multi-temporal point clouds is a fundamental prerequisite for deformation analysis. Datasets acquired at different epochs will inevitably be misaligned due to factors such as rock mass deformation and minor variations in the scanner’s trajectory. To resolve this, we employed a two-stage registration strategy that combined a coarse global alignment using PCA with a subsequent fine registration using the ICP algorithm.
PCA is a dimensionality reduction technique that identifies the principal axes of a point cloud by performing an eigenvalue decomposition of its covariance matrix [
36]. For an elongated structure like a mine roadway, the first principal axis aligns with the direction of greatest variance (the roadway’s longitudinal axis), the second aligns with the lateral axis (width), and the third aligns with the vertical axis (height).
PCA-based coarse registration determines the optimal rigid transformation (
), which applies a rotation followed by a translation to the source point cloud (P) to align it with the target point cloud (Q). This process is initiated by mean-centering both clouds to align their respective centroids with the coordinate origin:
where
pi ∈ P,
qi ∈ Q, and
and
are the centroids of P and Q, respectively.
Next, the covariance matrices for the centered clouds were computed, and eigenvalue decomposition yielded their respective eigenvector matrices,
Up and
Uq. The column vectors of these matrices represent the principal axes of the point clouds. From this, the initial rotation matrix (
R) and translation vector (
t) were derived:
A critical challenge in PCA-based registration is the inherent ambiguity in the direction of the principal axes (i.e., each axis has two possible opposing vectors). To resolve this, we systematically evaluated all eight possible combinations of axis orientations and computed the registration error for each:
The orientation combination that yielded the minimum error was selected as the result of the coarse alignment. Following this global alignment, the ICP algorithm was employed to perform fine registration and further enhance precision. ICP is an iterative optimization process that computes the rotation matrix (
R’) and translation vector (
t’) that minimize the sum of squared distances between corresponding points in the source and target clouds [
37]. The objective function is:
Each iteration of the ICP algorithm consists of two main steps. First, for each point in the transformed source cloud, the closest corresponding point in the target cloud was identified using a KD-Tree for efficient nearest-neighbor searching. Second, the optimal transformation (R’, t’) that minimized the distance between these newly established point pairs was computed, typically using Singular Value Decomposition (SVD). This transformation was then applied to the source cloud, and the process was repeated until the change in error between iterations fell below a predefined convergence threshold.
The final transformation is a composition of the initial PCA transformation (
R,
t) and the subsequent ICP transformation (
R’,
t’). For any point
pi in the original source cloud P, the final transformed point
pi_final is calculated as:
This expanded formulation defines the final composite rotation as and the final composite translation as . This standard geometric transformation is critical for preventing systematic bias and is robustly implemented in the Open3D library used for this study.
3.3.4. Deformation Quantification
The final stage of our workflow involved the quantification of roadway deformation. For this, we employed the C2C distance computation method. This approach was selected for its efficiency and directness, as it operates on the raw point data and bypasses the need for computationally intensive intermediate steps such as surface mesh reconstruction or the calculation of normal vectors [
38].
The analysis was performed between the two registered, multi-temporal datasets. The point cloud from the initial survey was designated as the reference cloud (
Qref), corresponding to the target cloud in the registration step. The point cloud from the subsequent survey was designated as the comparison cloud (
Pcmp), which corresponds to the fully transformed source cloud (
P’). The C2C algorithm iterates through each point (
pj) in the comparison cloud (
Pcmp) and calculates its minimum Euclidean distance to any point in the reference cloud (
Qref). This minimum distance,
Dj, is defined as the magnitude of deformation at point
pj:
To accelerate this computationally intensive nearest-neighbor search, we constructed a KD-Tree spatial index for the reference cloud (Qref) prior to the analysis. This data structure significantly reduces the time complexity of the search algorithm, enabling the efficient processing of the high-density datasets. Finally, the computed deformation magnitudes for all points were rendered onto the 3D model using a continuous color scale, providing an intuitive visualization of the spatial distribution and magnitude of the roadway deformation.
4. Results and Discussion
Point cloud data were acquired over a 100 m section of the subject roadway, from chainage 1500 m to 1600 m. The initial dataset was collected on 12 August 2025, when the excavation front was located at approximately 1660 m. A second dataset was acquired on 21 September 2025. The comparative analysis of these two epochs was designed to characterize the roadway’s deformation as it transitioned from the period of active excavation-induced disturbance to a more stable, post-development state.
4.1. Data Pre-Processing and Registration Results
A critical challenge in comparing multi-temporal SLAM datasets is the inherent inter-epoch trajectory drift, which can introduce global misalignments that may be misinterpreted as deformation. Our hybrid PCA-ICP registration process is specifically designed to measure and correct for this systematic error. Consequently, the final registration RMSE quantifies the residual uncertainty after this correction, establishing the minimum detection limit for the subsequent deformation analysis.
Application of the noise-filtering workflow described in
Section 3.3.2 to the raw data successfully produced a clean point cloud of the surrounding rock surface (
Figure 7). The resulting dataset revealed a complete and continuous surface for the roof, floor, and right wall. In contrast, the data for the left wall was incomplete and discontinuous. This was an expected outcome, as the ventilation duct and belt conveyor, positioned along the top and bottom of the left wall, respectively, created significant occlusions. Nevertheless, the filtered point cloud accurately delineated the geometric features of the non-occluded sections, providing a robust basis for subsequent deformation analysis.
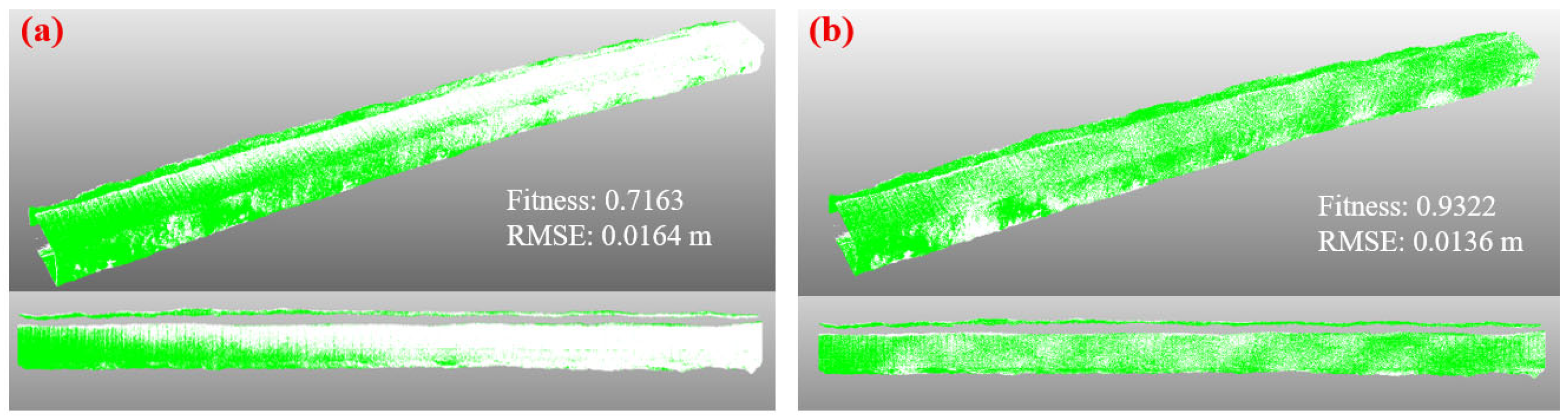
The hybrid PCA-ICP algorithm was then used to register the two denoised, multi-temporal point clouds, with the registration quality assessed by the Fitness and RMSE metrics. The initial coarse alignment via PCA, visualized by overlaying the initial (white) and subsequent (green) datasets, resulted in a non-uniform overlap (
Figure 8a). This alignment achieved a Fitness of 0.7163 and an RMSE of 0.0164 m. Following this, the fine registration with ICP substantially improved the alignment, resulting in a visually uniform overlap between the two epochs (
Figure 8b). The Fitness increased by 0.2159 to a final value of 0.9322, while the RMSE was reduced to 0.0136 m. This final registration error of only 1.36 cm validates that the datasets were aligned with sufficient precision to support a centimeter-scale deformation analysis.
4.2. Analysis of Roadway Deformation
The C2C comparison of the registered point clouds produced a comprehensive 3D deformation map for the entire surveyed section of the roadway (
Figure 9). The global analysis revealed that while the majority of the roadway remained stable, apparent large deformations were detected along the left wall and the adjacent floor (
Figure 9a,b). These were identified as edge artifacts resulting from the differing extents of occlusion caused by the ventilation duct and belt conveyor in the two surveys. As these artifacts do not represent actual rock mass displacement, these regions were excluded from the geomechanical interpretation. Analysis of the individual, non-occluded surfaces demonstrated that both the roof and the floor were stable, exhibiting negligible change between the two epochs (
Figure 9c,d). In stark contrast, the right wall displayed clear and significant convergent deformation (
Figure 9e).
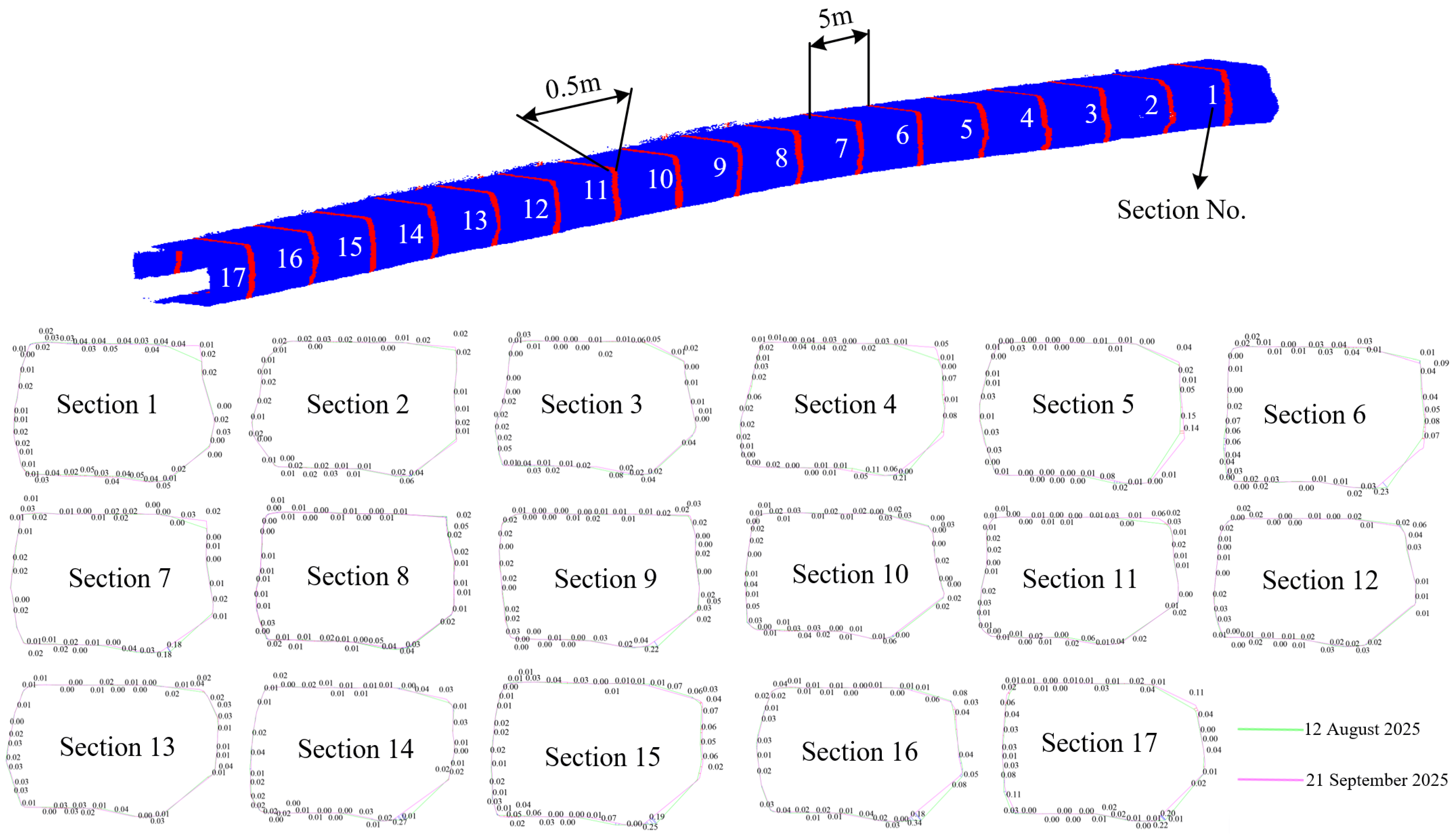
To quantify these observations, we extracted and analyzed 17 cross-sections at 5 m intervals along the roadway (
Figure 10). This quantitative analysis confirmed that the roof and floor were stable, with measured displacements generally falling between 0.01 m and 0.02 m. As this magnitude is comparable to the point cloud registration error, we concluded that any apparent displacement on these surfaces was below the detection limit of the method and that no significant deformation occurred.
However, the roadway walls exhibited substantial convergent deformation, with a maximum displacement of 11 cm recorded in the lower portion of the right wall at cross-section 17. Crucially, the analysis revealed a pronounced differential deformation pattern along the right wall, where convergence in the lower section was consistently and significantly greater than in the upper section. This pattern was particularly evident at several locations (e.g., cross-sections 3, 6, 10, 14, and 17). In these sections, the lower-wall convergence reached values as high as 0.05 m, 0.07 m, 0.05 m, 0.04 m, and 0.11 m, respectively, while the corresponding upper-wall convergence did not exceed 0.03 m. Although severe occlusion prevented a similar quantitative conclusion for the left wall, it can be inferred from the roadway and support design that both walls likely experienced a similar mode of deformation. This differential behavior is likely attributable to the support system, which appears to allow for the concentration of stress in the less-reinforced and intrinsically weaker coal strata of the lower walls, leading to a locally accelerated rate of convergence.
Due to strict access and time constraints in the deep roadway under active excavation, dedicated repeat surveys were not feasible; however, the two available scans still provide a basis for an indirect assessment of reproducibility. The Z-pattern scanning path adopted in each epoch creates multiple re-observations of the same surfaces and frequent loop closures, which contribute to a stable internal SLAM geometry. When the two epochs are compared, the roof and floor—sections expected to remain essentially undisturbed during the monitoring period—show differences of only 1–2 cm, a level consistent with the registration uncertainty. In contrast, the lower right wall exhibits a similar pattern and location of localized convergence in both datasets, with displacements reaching up to 11 cm, well above the uncertainty threshold. Taken together, these observations indicate that both the stable and deforming zones are reproduced within the expected error range, supporting the reliability of the detected deformation pattern.
5. Conclusions
This study presents a complete methodology for coal mine roadway deformation analysis using 3D laser scanning, encompassing data acquisition, noise filtering, point cloud registration, and deformation quantification. The principal conclusions are as follows:
(1) A “Z-pattern” mobile scanning trajectory, validated through both benchtop and field experiments, was demonstrated to be highly effective for acquiring dense and comprehensive roadway point cloud data. The subsequent application of a sequential filtering workflow—integrating statistical outlier removal, connected component analysis, and manual pruning—successfully isolated a clean point cloud of the surrounding rock by removing noise from both airborne particulates and large-scale mining infrastructure.
(2) The proposed hybrid PCA-ICP registration algorithm achieves centimeter-level, high-precision alignment of multi-temporal point clouds, which is critical for accurate change detection. The initial coarse alignment by PCA provided a robust starting point (RMSE = 0.0164 m; Fitness = 0.7164), and the subsequent ICP fine registration was essential for achieving the final precision, reducing the RMSE to 0.0136 m and increasing the Fitness to 0.9322.
(3) The C2C deformation analysis revealed that the roadway roof and floor remained stable during the monitoring period. Deformation was concentrated in the walls and manifested as convergence. Critically, the right wall exhibited a pronounced differential deformation pattern, where convergence in the lower section was significantly greater than in the upper section. This behavior is consistent with the transfer of stress to the less-reinforced and intrinsically weaker coal strata of the lower walls.
(4) The presented methodology has broad applications for monitoring underground infrastructure and evaluating support performance. However, key limitations remain, including hardware precision, cumulative SLAM drift, and the complexity of the data processing workflow. Consequently, future research should be directed towards developing higher-precision hardware, advancing SLAM and loop-closure algorithms to mitigate drift, and creating intelligent, automated software suitable for on-site application.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.W., Y.S., and X.F.; methodology, L.W. and Y.S.; software, C.H. and Y.F.; validation, H.S., B.Z., and Y.F.; formal analysis, C.H.; investigation, C.H. and B.Z.; resources, C.H. and B.Z.; data curation, H.S.; writing—original draft preparation, L.W. and Y.S.; writing—review and editing, Y.S. and X.F.; visualization, H.S. and Y.F.; supervision, L.W.; project administration, L.W.; funding acquisition, X.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 52474183; the Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province, grant number KYCX24_2869 and the Graduate Innovation Program of China University of Mining and Technology, grant number 2024WLKXJ036.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the Dahaize coal mine for their support in conducting the field experiments. The authors also thank the editor and anonymous reviewers for their constructive suggestions and comments, which have considerably improved the quality of this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Lixin Wang, Chengjun Hu, Baofu Zhao, Hao Shi were employed by the company China Coal (Tianjin) Underground Engineering Intelligent Research Institute Co., Ltd. and China Coal Tianjin Engineering Design Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| ICP | Iterative Closest Point |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
| C2C | Cloud-to-Cloud |
| SLAM | Simultaneous Localization and Mapping |
References
- Huang, Q.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, F.; Xiao, J.; He, Y.; Yan, F.; Shen, Y.; Ren, G. Study on Large Deformation Mechanism and Surrounding Rock Control of Entry in “Three Soft Coal Seam” of Deep Mine. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 31836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Fang, X.; Song, Y.; Li, S.; Chen, N.; Zhang, F. Research on Three-Dimensional Stress Monitoring Method of Surrounding Rock Based on FBG Sensing Technology. Sensors 2022, 22, 2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.; Gao, F.; Xu, G.; Ren, H. Mechanical Behaviors of Coal Measures and Ground Control Technologies for China’s Deep Coal Mines—A Review. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2023, 15, 37–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Kang, H.; Zhang, C.; Jiang, B. Dynamic Impact Simulation Tests of Deep Roadways Affected by High Stress and Fault Slip. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2025, 35, 519–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landar, S.; Velychkovych, A.; Ropyak, L.; Andrusyak, A. A Method for Applying the Use of a Smart 4 Controller for the Assessment of Drill String Bottom-Part Vibrations and Shock Loads. Vibration 2024, 7, 802–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velychkovych, A.; Mykhailiuk, V.; Andrusyak, A. Evaluation of the Adaptive Behavior of a Shell-Type Elastic Element of a Drilling Shock Absorber with Increasing External Load Amplitude. Vibration 2025, 8, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fang, X.; He, D.; Song, Y.; Chen, N.; Feng, H. Research on Prediction Method of Rock Uniaxial Compressive Strength Based on Interpretable INFO-Stacking Model. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2025, 179, 106390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manchao, H.; e Sousa, R.L.; Müller, A.; Vargas, E.; e Sousa, L.R.; Xin, C. Analysis of Excessive Deformations in Tunnels for Safety Evaluation. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2015, 45, 190–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryn, M.Y.; Afonin, D.A.; Bogomolova, N.N.; Nikitchin, A.A. Monitoring of Transport Tunnel Deformation at the Construction Stage. In Proceedings of the International Scientific Conference Transportation Geotechnics and Geoecology (TGG-2017), Saint Petersburg, Russia, 6–8 September 2017; Petriaev, A., Konon, A., Eds.; Elsevier Science Bv: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 189, pp. 417–420. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Liang, M.; Fang, X.; Wu, G.; Chen, N.; Song, Y. Research on Autonomous Cutting Method of Cantilever Roadheader. Energies 2022, 15, 6190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Chen, C.; Sun, Y.; Xia, K.; Wang, T. Mining-Induced Deformation for a Haulage Drift of the Hanging Wall at Jinshandian Iron Mine in China. Front. Earth Sci. 2023, 10, 998759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Yang, Y. Deep Soft Rock Tunnel Perimeter Rock Control Technology and Research. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.L.; Wang, B.; Ji, S.Y.; Liu, W.N.; Shi, H.Y. Non-Contact Monitoring and Analysis System for Tunnel, Surrounding Rock Deformation of Underground Engineering. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2005, 15, 88–91. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Xiao, H.; Jiang, W.; Bai, W.; Liu, G. Automatic Subway Tunnel Displacement Monitoring Using Robotic Total Station. Measurement 2020, 151, 107251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Yu, G.; Xia, G.; Liu, X. 3D Geometric Reconstruction of Underground Garage Based on SLAM Laser Point Cloud. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Environmental Remote Sensing and Big Data (ERSBD 2021), Wuhan, China, 29–31 October 2021; Weng, C.H., He, Y., Eds.; Spie-Int Soc Optical Engineering: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2021; Volume 12129. [Google Scholar]
- Raval, S.; Banerjee, B.P.; Singh, S.K.; Canbulat, I. A Preliminary Investigation of Mobile Mapping Technology for Underground Mining. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS 2019), Yokohama, Japan, 28 July–2 August 2019; pp. 6071–6074. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, B.; Chen, L.; Zou, Y.; Wu, X.; Washaya, P. Methods for Monitoring Fast and Large Gradient Subsidence in Coal Mining Areas Using SAR Images: A Review. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 159018–159035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marian, D.-P.; Onica, I. Analysis of the Geomechanical Phenomena That Led to the Appearance of Sinkholes at the Lupeni Mine, Romania, in the Conditions of Thick Coal Seams Mining with Longwall Top Coal Caving. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassilis, M.; Ioannis, F.; Themistoklis, C.; Dimitra, P.; Georgios, S.; Georgios, P.; Efstratios, K. Remote Sensing Integration to Geohazard Management at the Castle-Monastery of Panagia Spiliani, Nisyros Island, Greece. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Luo, Q.; Wang, T.; Connolly, D.P.; Xie, T. A Combined Experimental and DEM Investigation of Grain Interlocking in Sheared Granular Assemblies. Particuology 2024, 90, 436–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Qi, Y.; Guan, T.; Liang, Y. Efficient and Accurate 3D Reconstruction in a Featureless Tunnel Environment: A Robust LiDAR-Inertial SLAM Tightly Coupled with Wheel Odometry. J. Civ. Struct. Health Monit. 2025, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Luo, X.; Wang, Q.; Lv, G.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Xie, Q. Enhanced Tunnel Construction Safety: Drill-and-Blast Construction Tunnel Deformation Detection Using LiDAR and Cloth Simulation Filter. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2025, 36, 096012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhan, X.; Zhou, D. A New Approach for Monitoring Mining Surface 3D Deformation Using UAV-LiDAR Point Cloud Data. Measurement 2025, 253, 117745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; He, K.; Hu, X.; Liu, W.; Zhang, S.; Wu, J.; Xi, C. Mechanism of Surface Subsidence and Sinkhole Formation in Mining Areas: Insights from MPM. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2024, 83, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Shi, M.; Feng, X.-T.; Cheng, S.; Wang, F.; Zhang, X.; Yang, C.; Luo, H.; Zhao, F.; Kou, Y. Mechanisms of Long-Term Deformation and Failure in Deep Hard Fractured Rock Roadways: A Case Study on Blasting-Induced Effects. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2026, 168, 107110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, D.; Ranasinghe, P.; Banerjee, B.; Raval, S. A Deep Learning Approach to Identify Rock Bolts in Complex 3D Point Clouds of Underground Mines Captured Using Mobile Laser Scanners. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Banerjee, B.P.; Raval, S. Three-Dimensional Unique-Identifier-Based Automated Georeferencing and Coregistration of Point Clouds in Underground Mines. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajzar, V.; Kukutsch, R.; Waclawik, P.; Nemcik, J. Innovative Approach to Monitoring Coal Pillar Deformation and Roof Movement Using 3D Laser Technology. In Proceedings of the ISRM European Rock Mechanics Symposium EUROCK 2017, Ostrava, Czech Republic, 20–22 June 2017; Konicek, P., Soucek, K., Konecny, P., Eds.; Elsevier Science Bv: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 191, pp. 873–879. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Shi, B.; Wang, C.; Xing, F. Novel High-Performance Automatic Removal Method of Interference Points for Point Cloud Data in Coal Mine Roadway Environment. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2023, 44, 1433–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Li, Y.; An, L.; Dong, E.; Han, L. An MLS-Based High-Accuracy Measurement and Automatic Analysis Method for Roadway Deformation. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2023, 140, 105306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, J.; Yu, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Z.; Cao, Y.; Le, Z.; Yang, Z.; Li, X. Deformation Analysis of a Roadway Tunnel in Soft Swelling Rock Mass Based on 3D Mobile Laser Scanning. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2024, 57, 5177–5192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, A.; Wu, J. Enhancing the Functionalities of Three-Dimensional Imaging LiDAR: A Review. Precis. Eng. 2026, 97, 391–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucci, G.; Visintini, D.; Bonora, V.; Parisi, E.I. Examination of Indoor Mobile Mapping Systems in a Diversified Internal/External Test Field. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Peng, Y.; Tang, Z.; Li, Z. Three-Dimensional Reconstruction of Railway Bridges Based on Unmanned Aerial Vehicle-Terrestrial Laser Scanner Point Cloud Fusion. Buildings 2023, 13, 2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.; Wang, Q.; Sohn, H. Optimal Placement of Precast Bridge Deck Slabs with Respect to Precast Girders Using 3D Laser Scanning. Autom. Constr. 2018, 86, 81–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurunnabi, A.; Sadahiro, Y.; Teferle, F.N.; Laefer, D.F.; Li, J. Detection and Segmentation of Pole-like Objects in Mobile Laser Scanning Point Clouds. In Proceedings of the Geospatial Week 2023, Cairo, Egypt, 2–7 September 2023; El-Sheimy, N., Abdelbary, A.A., El-Bendary, N., Mohasseb, Y., Eds.; Copernicus Gesellschaft Mbh: Göttingen, Germany, 2023; Volume 48-1, pp. 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, C.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Bao, L.; Pan, J.; Ou, G.; et al. A Precise Estimation Framework for Individual Tree AGB of Pinus Kesiya Var. Langbianensis Utilizing Point Cloud Registration Optimization. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2025, 140, 104612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, T.; Wu, C.H.; Mueller, S.; Mechtcherine, V.; Brell-Cokcan, S. As-Built Monitoring of Concrete Structures. In Proceedings of the Fourth Rilem International Conference on Concrete and Digital Fabrication, DC 2024, Munich, Germany, 4–6 September 2024; Lowke, D., Freund, N., Bohler, D., Herding, F., Eds.; Springer International Publishing Ag: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; Volume 53, pp. 158–165. [Google Scholar]
Figure 1.
Geotechnical setting and site characteristics of the No. 20105 roadway at the Dahaize coal mine: (a) Geographic location of the mine in Shaanxi Province, China; (b) Plan view showing the layout of the subject roadway relative to the No. 20105 and No. 20107 longwall panels; (c) Cross-sectional diagram detailing the asymmetric design of the rock and cable bolt support system; (d) In situ photograph illustrating the pronounced convergent deformation observed in the lower section of the roadway wall.
Figure 1.
Geotechnical setting and site characteristics of the No. 20105 roadway at the Dahaize coal mine: (a) Geographic location of the mine in Shaanxi Province, China; (b) Plan view showing the layout of the subject roadway relative to the No. 20105 and No. 20107 longwall panels; (c) Cross-sectional diagram detailing the asymmetric design of the rock and cable bolt support system; (d) In situ photograph illustrating the pronounced convergent deformation observed in the lower section of the roadway wall.
Figure 2.
Geometric principle of coordinate acquisition in 3D laser scanning.
Figure 2.
Geometric principle of coordinate acquisition in 3D laser scanning.
Figure 3.
The end-to-end processing pipeline for roadway deformation analysis based on 3D laser scanning.
Figure 3.
The end-to-end processing pipeline for roadway deformation analysis based on 3D laser scanning.
Figure 4.
Benchtop calibration experiments to determine optimal data acquisition parameters: (a) The experimental setup; (b–e) A qualitative comparison of the point clouds generated using progressively longer scan durations of 30 s, 60 s, 120 s, and 300 s; (f–i) The resulting point clouds acquired at increasing scan distances of 1 m, 2 m, 5 m, and 10 m.
Figure 4.
Benchtop calibration experiments to determine optimal data acquisition parameters: (a) The experimental setup; (b–e) A qualitative comparison of the point clouds generated using progressively longer scan durations of 30 s, 60 s, 120 s, and 300 s; (f–i) The resulting point clouds acquired at increasing scan distances of 1 m, 2 m, 5 m, and 10 m.
Figure 5.
Field data acquisition strategy and the resulting high-density point cloud: (a) Schematic of the scanning trajectory; (b) The scanning process in the field; (c) Photograph of the subject roadway; (d) The acquired raw point cloud; (e) A cross-sectional view of the point cloud.
Figure 5.
Field data acquisition strategy and the resulting high-density point cloud: (a) Schematic of the scanning trajectory; (b) The scanning process in the field; (c) Photograph of the subject roadway; (d) The acquired raw point cloud; (e) A cross-sectional view of the point cloud.
Figure 6.
The sequential workflow for point cloud noise filtering: (a) Flowchart of the three-stage filtering process; (b) Visual demonstration of the filtering results on a representative section of the roadway point cloud.
Figure 6.
The sequential workflow for point cloud noise filtering: (a) Flowchart of the three-stage filtering process; (b) Visual demonstration of the filtering results on a representative section of the roadway point cloud.
Figure 7.
Comparison of the roadway point cloud before and after noise filtering: (a) Raw point cloud; (b) Cross-section of the raw point cloud; (c) Filtered point cloud; (d) Cross-section of the filtered point cloud.
Figure 7.
Comparison of the roadway point cloud before and after noise filtering: (a) Raw point cloud; (b) Cross-section of the raw point cloud; (c) Filtered point cloud; (d) Cross-section of the filtered point cloud.
Figure 8.
Point cloud registration of the multi-temporal roadway datasets: (a) Coarse registration using PCA; (b) Fine registration using ICP following the initial PCA alignment.
Figure 8.
Point cloud registration of the multi-temporal roadway datasets: (a) Coarse registration using PCA; (b) Fine registration using ICP following the initial PCA alignment.
Figure 9.
Deformation analysis of the subject roadway: (a) Deformation map; (b) Perspective view; (c) Roof view; (d) Floor view; (e) Right wall view; (f) Left wall view.
Figure 9.
Deformation analysis of the subject roadway: (a) Deformation map; (b) Perspective view; (c) Roof view; (d) Floor view; (e) Right wall view; (f) Left wall view.
Figure 10.
Deformation analysis of roadway cross-sections.
Figure 10.
Deformation analysis of roadway cross-sections.
Table 1.
Technical specifications of the GoSLAM G100 3D laser scanner.
Table 1.
Technical specifications of the GoSLAM G100 3D laser scanner.
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|
| Relative accuracy | 1 cm |
| Maximum scanning range | 120 m |
| Scan rate | 320,000 points/second |
| Field of view (fov) | 360° (horizontal) × 280° (vertical) |
| Laser lines | 16 |
| Laser class | Class I (eye-safe) |
| Operating temperature | −20 °C to 50 °C |
| Operating time | 4 h (continuous) |
| Weight | 2.1 kg |
| Storage | 512 GB |
| Processing mode | Real-time |
| Figure | ![Applsci 15 12255 i001 Applsci 15 12255 i001]() |
Table 2.
Quantitative effect of scan duration and distance on the number of points acquired on the target object.
Table 2.
Quantitative effect of scan duration and distance on the number of points acquired on the target object.
| ScanDuration(s) | 30 | 60 | 120 | 300 |
| Number ofPoints | 4675 | 5554 | 5652 | 5563 |
| ScanDistance (m) | 1 | 2 | 5 | 10 |
| Number ofPoints | 11,914 | 5652 | 1140 | 306 |
| Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).