Abstract
Wastewater Treatment Plants (WWTPs) rely on automatic control strategies to regulate pollutant concentrations and comply with environmental standards. Among them, Proportional Integral (PI) controllers are widely adopted for their simplicity and robustness, yet their effectiveness is limited by the nonlinear and time-varying dynamics of biological processes. In this work, Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM)-based Artificial Neural Network (ANN) PI controllers are proposed as data-driven replacements for conventional PIs in key WWTP feedback loops. Using the Benchmark Simulation Model No. 1 (BSM1), ANN controllers were trained to replicate the behavior of default nitrate and nitrite nitrogen () and dissolved oxygen () loops, under both time-agnostic and time-aware strategies with three- and four-input configurations. The four-input time-aware model delivered the best results, reproducing PI behavior with high accuracy (coefficient of determination, ) and considerably reducing control errors. For instance, under storm influent conditions, the controller reduced the Integral of Squared Error () and Integral of Absolute Error () by 84.7% and 68.4%, respectively, compared with the default PI. Beyond loop-level improvements, a Transfer Learning (TL) extension was explored: the trained controller was directly applied to additional aerated reactors ( and ) without retraining, replacing fixed aeration and demonstrating adaptability while reducing design effort. Plant-wide evaluation with the loop and three dissolved oxygen loops (–), all controlled by LSTM-based PI controllers, under storm influent conditions, showed further reductions in the Effluent Quality Index () and the Overall Cost Index () by 0.84% and 1.47%, respectively, highlighting simultaneous gains in effluent quality and operational economy. Additionally, the actuator and energy analyses showed that the LSTM-based controllers produced realistic and smooth control signals, maintained consistent energy use, and ensured stable overall operation, confirming the practical feasibility of the proposed approach.
1. Introduction
Wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) are at the core of modern environmental protection, yet their operation is becoming increasingly demanding. Rising energy costs, particularly those associated with aeration, can represent more than half of a plant’s total electricity use [1], while tightening environmental regulations continues to lower permissible nutrient levels in treated effluent [2]. At the same time, climate commitments and sustainability goals demand that these facilities operate with greater efficiency and lower greenhouse gas footprints [3]. Under these pressures, effective control of treatment processes is no longer optional but a prerequisite for balancing water quality compliance, environmental responsibility, and economic viability. Early evidence of nitrous oxide emissions from municipal WWTPs was reported by Czepiel et al. [4], emphasizing the environmental trade-offs involved.
Beyond their economic and environmental challenges, WWTPs remain essential infrastructure for safeguarding public health and aquatic ecosystems. Their main task is to reduce the levels of contaminants present in residual urban waters, with nitrogen- and phosphorus-derived compounds among the most critical due to their contribution to eutrophication and aquatic toxicity [5]. Effective removal of these pollutants relies on tightly controlled biological processes such as nitrification and denitrification, which in turn require stable dissolved oxygen (DO) concentrations in aerobic tanks and low nitrate () levels in anoxic zones [6]. To meet regulatory discharge standards, modern WWTPs are equipped with automatic control systems that adjust aeration, recirculation, and related operations in real time.
Designing advanced control strategies for WWTPs, however, is far from straightforward. Biological treatment processes are highly nonlinear, subject to variable influent loads, and influenced by complex microbial interactions, making reliable plant-wide models difficult to obtain [7]. Direct testing of new controllers in full-scale facilities is expensive, site-specific, and may risk operational stability. For this reason, the wastewater research community has developed standardized benchmark models that serve as common reference platforms for testing, comparing, and improving control strategies under realistic yet safe conditions [6,7]. These frameworks provide a reproducible environment in which competing solutions can be evaluated fairly, accelerating the development of practical and robust control methodologies.
The development of mathematical frameworks has played an important role in advancing control solutions for WWTPs. The Activated Sludge Model No. 1 (ASM1) describes the underlying biochemical processes, while the Benchmark Simulation Model No. 1 (BSM1) provides a standardized plant-wide simulation platform with realistic influent profiles and evaluation metrics [8,9]. As shown in Figure 1, BSM1 represents a typical WWTP layout composed of five interconnected biological reactors followed by a secondary clarifier. Default control loops regulate nitrate () in the second reactor via the internal recycle and dissolved oxygen () in the fifth reactor via aeration, both implemented with Proportional–Integral (PI) controllers. PI control is widely applied in full-scale facilities because of its simplicity and general reliability under stable operating conditions [10].
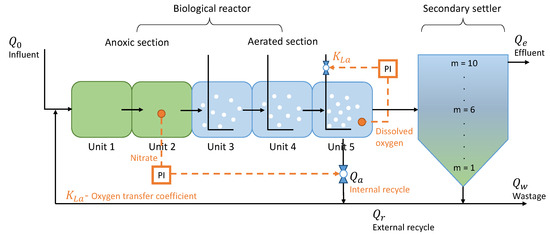
Figure 1.
Configuration of the Benchmark Simulation Model No. 1 (BSM1), consisting of an anoxic section, an aerated section, and a ten-layer secondary settler. Flows (, , , , ) represent influent, internal recycle, external recycle, effluent, and wastage, respectively. Dashed lines indicate control signals, with PI controllers regulating in Unit 2 and in Unit 5.
However, WWTPs operate in dynamic environments where influent loads fluctuate daily and seasonally, oxygen transfer efficiencies vary with operating conditions, and microbial activity shifts over time [11]. Under such nonlinear and time-varying conditions, PI controllers often struggle to maintain optimal performance, requiring frequent retuning and providing limited capability to anticipate disturbances [10].
These shortcomings have motivated the development of more advanced control strategies. Model Predictive Control (MPC), fuzzy logic, and hybrid hierarchical schemes have been applied to enhance pollutant removal and improve operational efficiency [12,13]. At the same time, Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) have emerged as data-driven tools well suited to capturing the nonlinear behavior of WWTPs without requiring explicit mechanistic models [14]. Recent reviews underscore the extensive application of neural network approaches in wastewater treatment, particularly for feature identification, parameter prediction, anomaly detection, and control optimization [15]. They have also been applied as soft sensors, effluent quality predictors, and as components in supervisory and predictive controllers [16]. Among them, recurrent neural networks such as Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) architectures have proven especially effective for time-dependent industrial processes, including wastewater treatment, as they are able to exploit temporal correlations in input–output signals [14,17,18].
Recent studies have also emphasized the importance of stability and robustness in neural control architectures. Lyapunov-based learning laws for LSTM networks have been developed to ensure practical stability in nonlinear dynamic systems [19]. Adaptive LSTM-based robust controllers have likewise been designed with formal Lyapunov stability guarantees [20]. In addition, hybrid Model Predictive Control (MPC) frameworks integrating model-based and data-driven components have been proposed to improve process control performance [21]. While the present work focuses on demonstrating feasibility within the BSM1 environment, these contributions provide a theoretical foundation for future extensions toward stability-certified and hybrid neural control strategies.
Despite these advances, most ANN-based approaches in wastewater treatment have been used as add-ons or supervisory elements rather than direct replacements of the low-level PI loops that remain central to plant operation. Addressing this gap, the present work investigates the use of LSTM-based PI controllers as drop-in substitutes for the default nitrate () and dissolved oxygen () PI controllers in BSM1. The proposed controllers were trained offline to reproduce the behavior of well-tuned PI loops under a range of influent scenarios and then integrated into the BSM1 framework for closed-loop evaluation. In addition, this study examines the potential for transferring the trained controllers to similar control loops, offering greater flexibility and reducing the need for repeated tuning and deployment efforts.
Beyond reproducing PI control, the proposed LSTM-based DO controller was successfully transferred to additional aerated reactors ( and ), replacing fixed aeration rates. This extension delivered further improvements in the Effluent Quality Index () and the Operational Cost Index (), showing that the approach can be scaled to multi-zone aeration control. Such an extension is closely related to the concept of transfer learning, where knowledge acquired in one domain is leveraged to improve performance in another, thereby reducing the demand for large amounts of task-specific data [22]. Deep transfer learning has recently been recognized as a rapidly expanding research area, particularly in industrial applications where labeled data are scarce and process dynamics are subject to change [22]. Its potential has also been demonstrated in process systems engineering, for example, in the design of soft sensors for industrial applications [23]. More recently, transfer learning strategies have been applied directly in the control of wastewater treatment plants, where transferring knowledge between neural controllers reduced design time while significantly improving performance indices such as the Integrated Absolute Error () and Integrated Squared Error () [24,25]. Similar approaches have also been adopted for prediction tasks, such as dissolved oxygen concentration modeling in industrial wastewater treatment units [26]. Building on these insights, the present work highlights the applicability of transfer learning principles for data-driven control in wastewater treatment.
In summary, this work demonstrates that LSTM-based PI controllers can serve as practical and effective replacements for conventional PI controllers in WWTP. The contributions of this study are threefold:
- 1.
- The design and evaluation of LSTM-based PI controllers that act as direct substitutes for PI controllers in the BSM1 framework, targeting nitrate and dissolved oxygen loops.
- 2.
- A comparative study of training strategies and input configurations, showing that time-aware four-input models provide the most accurate and robust performance.
- 3.
- An extension of ANN-based control beyond individual loops, where the LSTM-based dissolved oxygen (DO) controller for reactor 5 was successfully transferred to the additional aerated reactors (reactors 3 and 4), yielding measurable improvements in and .
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Characteristics and Plant Layout
The Benchmark Simulation Model No. 1 (BSM1) is one of the most widely used digital testbeds for evaluating control strategies in WWTPs [9]. It is based on the Activated Sludge Model No. 1 (ASM1) [8], which provides a mathematical description of the highly non-linear biological and biochemical reactions governing wastewater treatment. BSM1 represents a medium-sized municipal facility designed for an average dry-weather influent flow of 18,446 /day with a biodegradable chemical oxygen demand (COD) of 300 g/. The total plant capacity is 12,000 , split equally between the biological reactor (6000 ) and the secondary clarifier (6000 ). With these specifications, the system achieves an average hydraulic retention time of about 14.4 h. Sludge handling is incorporated through a wastage flow rate of 385 /day, corresponding to a solids retention time of roughly nine days, which reflects typical full-scale operations.
The biological reactor is arranged in five interconnected compartments followed by a clarifier (see Figure 1). The first two compartments operate under anoxic conditions to facilitate denitrification, while the last three are aerated to support nitrification. Each anoxic tank has a volume of 1000 , and each aerated tank holds 1333 . The downstream clarifier is modeled as a ten-layer settling unit without biological reactions, with influent entering at the sixth layer. Solids settle to form a sludge blanket that is recycled or wasted, while clarified effluent exits at the top. The clarifier dimensions of 1500 surface area and 4 m height yield a volume of 6000 , equal to that of the reactor. Together, these units mimic the essential processes of a conventional activated sludge system.
2.2. Default Control Loops
To regulate key process variables, BSM1 incorporates two default feedback loops managed by Proportional–Integral (PI) controllers. These serve as the baseline against which alternative strategies can be benchmarked:
- Nitrate and Nitrite () loop in reactor 2: controls nitrate concentration by adjusting the internal recycle flow rate () to maintain a setpoint of 1 mg/L.
- Dissolved Oxygen () loop in reactor 5: controls oxygen levels by manipulating the oxygen transfer coefficient () to maintain a setpoint of 2 mg/L.
Both controllers are pre-tuned by the BSM1 designers, with fixed proportional and integral parameters. Their performance provides a standard reference for assessing improvements achieved by advanced control strategies, such as ANN- or LSTM-based controllers, and both loops are explicitly illustrated in Figure 1.
2.3. Simulation Protocols and Performance Assessment
BSM1 simulations are designed to test control systems under realistic dynamic conditions. Each run begins with a 100-day initialization under constant influent conditions to stabilize biomass and reactor states. This is followed by 14 days of dynamic operation using one of three influent scenarios:
- Dry-weather influent: Influent profile showing diurnal variations of concentrations, without any perturbations induced by weather changes.
- Rain-weather influent: Influent profile with daily variations, including an extended wet-weather disturbance during the second week (days 9–10).
- Storm-weather influent: Influent profile with daily variations, superimposed by two short but intense storm disturbances (days 8 and 11).
Figure 2 illustrates the influent flow-rate () variations under dry-, rain-, and storm-weather scenarios. The dry-weather profile shows regular diurnal oscillations, while the rain and storm cases introduce extended and short-term flow disturbances, respectively, consistent with the BSM1 specification.
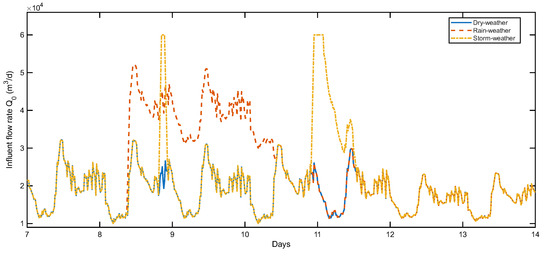
Figure 2.
Influent flow-rate () profiles for dry, rain, and storm scenarios in the BSM1.
Although the simulation covers 14 days, only the final 7 days are used for evaluation, following BSM1 guidelines.
Performance is assessed on two levels. At the local loop level, control accuracy is quantified using the Integrated Absolute Error (IAE) and Integrated Squared Error (ISE) between process measurements and their setpoints or reference values :
At the plant-wide level, two indices are used: the Effluent Quality Index (EQI), which reflects the pollutant load in the discharge, and the Operational Cost Index (OCI), which captures energy and pumping costs. These metrics allow fair comparison of control strategies across different influent conditions. The detailed definitions of EQI and OCI are provided in the BSM1 specification [9]; in summary, EQI aggregates effluent pollutants such as COD, , and into a single water-quality measure, while OCI combines aeration, pumping, and sludge-handling energy demands into a unified cost index.
2.4. LSTM-Based Controller Design
Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks extend the classical recurrent neural network framework with a structure that can selectively store and update information across time. Instead of processing each input in isolation, LSTMs use a memory cell in combination with three regulating gates (commonly referred to as input, forget, and output gates) that determine what past information is carried forward, what is updated, and what is discarded [14]. This architecture enables them to capture long- and short-term temporal patterns while reducing the influence of noise, making them particularly suitable for representing the nonlinear and time-varying dynamics of wastewater treatment systems.
In this study, LSTMs were adopted to replace the default Proportional–Integral (PI) controllers in BSM1. The proposed LSTM-based PI controllers were designed to operate as direct feedback regulators, mimicking the input–output behavior of the PI loops while offering the ability to exploit temporal correlations in the data.
2.4.1. Input Configurations
Two controller configurations were tested:
- Three-input model: consisting of the current process variable ( or ), the reference setpoint ( setpoint or setpoint), and the previous control action ( or ).
- Four-input model: extending the three-input design by including the influent flow rate (), enabling the network to anticipate load disturbances.
Figure 3 illustrates the two controller configurations considered in this work. In the three-input design, the network receives the current process variable, its corresponding setpoint, and the previous control action (). The four-input variant extends this structure by including the influent flow rate (), allowing the controller to better anticipate load disturbances.
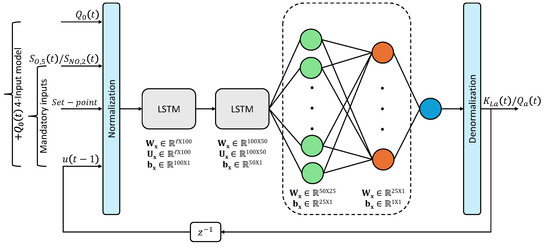
Figure 3.
LSTM-based controller architecture with three or four inputs, two stacked LSTM layers, and two dense layers. The final linear output is denormalized to yield the actuator signal ( or ).
As shown in Figure 3, both configurations are built upon the same LSTM-based neural structure, which is explained in detail in Section 2.4.3. In short, the controller combines recurrent LSTM layers with fully connected feedforward layers, ending in a linear output neuron that generates the control action. The only difference between the two configurations lies in the number of input features: three in the baseline model and four in the extended model.
2.4.2. LSTM Network Architecture
All controller variants developed in this work relied on a common LSTM-based neural structure. The core of the architecture consisted of two stacked LSTM layers, with the first layer comprising 100 hidden units and the second containing 50 hidden units. The dimensionality of the weight matrices is shown in Figure 3: for the first LSTM block, the input weight matrix is , the recurrent weight matrix is , and the bias vector is . Here, l denotes the number of input features provided to the network, which takes the value in the baseline model (process variable, setpoint, and previous control action) and in the extended model (including influent flow rate). These two configurations were trained as separate networks; the explicit parameterization highlights that the only architectural difference lies in the input weight matrix, which changes from to . All other recurrent connections and dense layers remain identical across both models.
Both recurrent layers were regularized using an L2 penalty of , which reduced overfitting and improved generalization across the different influent scenarios. The default activation mechanisms provided by Keras were retained: hyperbolic tangent functions governed the internal memory cells, while the gating mechanisms (input, forget, and output gates) employed sigmoid activations. This configuration enables LSTM to regulate the flow of information, selectively retaining or discarding past states while capturing nonlinear dynamics.
The recurrent outputs were then passed through two fully connected feedforward layers with 50 and 25 neurons, respectively. Both layers used the Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU) activation to improve nonlinear approximation capability and to map the latent features extracted by the LSTMs onto the control domain. Finally, a single linear output neuron produced the normalized control signal. This value was subsequently rescaled in a denormalization stage to its physical range, allowing it to be directly interpreted as either the oxygen transfer coefficient in the dissolved oxygen loop or the internal recirculation flow in the nitrate loop.
Although the networks were based on LSTM cells, training was performed using a single-step temporal window (time_steps = 1). Instead of unfolding long historical sequences, short-term dynamics were embedded explicitly by including the previous control action as an input, following a NARX-style formulation. This design choice provided the networks with a degree of temporal awareness while keeping the structure compact and computationally efficient.
Prior to training, all input variables were standardized to zero mean and unit variance, while predicted outputs were denormalized during post-processing. Model development was carried out in Python using TensorFlow (https://pypi.org/project/tensorflow/, accessed on 20 October 2022) with the Keras API, and data preprocessing and scaling were performed with NumPy (https://numpy.org/, accessed on 20 October 2022) and Scikit-learn (https://scikit-learn.org/stable/, accessed on 20 October 2022).
2.4.3. Training Strategies
To investigate the effect of temporal memory on performance, two training strategies were explored:
- 1.
- Time-agnostic training, where each sample is treated independently, disregarding temporal sequence.
- 2.
- Time-aware training, where the sequential nature of the data is preserved, allowing LSTM to utilize its internal memory for learning long-term dependencies.
Each training approach was tested using two input configurations: (i) a three-input model, consisting of the process measurement, setpoint, and previous control action; and (ii) a four-input model, which additionally included the influent flow rate to account for disturbance anticipation. The time-aware, four-input model showed the closest agreement with conventional PI behavior during training, achieving a determination coefficient of about .
This setup provided a clear framework for examining how various design choices—both in input selection and training approach—influence the ability of LSTM-based controllers to reproduce and, in some cases, surpass the performance of traditional PI control within the BSM1 wastewater treatment plant model.
In this work, the term time-aware refers to preserving the chronological order of influent scenarios during training—specifically, the dry-, rain-, and storm-weather datasets were concatenated in their natural temporal sequence without random shuffling. This approach allows the network to experience realistic transitions between operating conditions and retain contextual information about process dynamics. In contrast, the time-agnostic configuration pools and randomizes samples from all scenarios, effectively removing any temporal continuity. Both strategies employ a single-step input window (time_steps = 1), with short-term memory introduced explicitly through the inclusion of the previous control action as an input feature, following a NARX-style formulation. Key training details, including the use of mean squared error (MSE) as the loss function, early stopping, and dropout regularization, are described in Section 2.5 to ensure reproducibility.
2.5. Training and Implementation Protocols
The LSTM-based PI controllers were trained offline using data generated from the BSM1 model operating under its default PI controllers. Simulation runs were conducted across three influent scenarios—dry-weather, rain-weather, and storm-weather—so that the training set would capture a wide range of operating conditions. For each run, the process measurements, control signals, and influent characteristics were recorded to form the input–output pairs needed for supervised learning.
Model development was carried out in Python (version 3.9.18), using the TensorFlow and Keras libraries. Training relied on the mean squared error (MSE) between the predicted and reference PI actions, with early stopping and dropout regularization applied to prevent overfitting. Both the time-agnostic and time-aware training strategies described in Section 2.4.3 were implemented, and model fidelity was evaluated using the coefficient of determination (). High agreement with the PI responses was achieved (), confirming the LSTMs’ ability to reproduce the control dynamics.
After training, the neural network weights were exported and integrated back into the BSM1 framework through Simulink, replacing the default PI controllers. Closed-loop simulations were then performed under each influent scenario. Controller performance was assessed using both loop-level indices—the Integrated Absolute Error (IAE) and Integrated Squared Error (ISE)—and plant-wide indices, namely the Effluent Quality Index (EQI) and the Operational Cost Index (OCI). This evaluation protocol ensured a fair comparison between the baseline PI controllers and the proposed LSTM-based alternatives in terms of accuracy, robustness, and efficiency, with all closed-loop simulations under dry-, rain-, and storm-weather conditions remaining stable. The actuator signals (, ) stayed within their physical operating ranges, and no constraint violations were observed.
The models were trained using the Adam optimizer with a learning rate of , a batch size of 64, and a maximum of 500 epochs with early stopping (patience = 5). All LSTM layers were implemented in stateless mode, and teacher forcing was not applied, as the networks learned to predict the control action directly from process measurements and setpoints. To ensure comparability and reproducibility, the same data split and random seed (random_state = 42) were used across all training configurations. These details, along with the regularization and architecture parameters described in Section 2.4.2 and Section 2.4.3, define the complete training setup used in this study.
2.6. Transfer Learning Extension
In addition to directly replacing the default PI controllers, this work explored the reuse of trained models within the BSM1 framework, following the principles of transfer learning. Specifically, the LSTM-based DO controller originally designed for reactor 5 was applied to reactors 3 and 4, the other two aerated reactors in the benchmark, which normally operate under fixed aeration rates and therefore without feedback control. By substituting these fixed oxygen transfer coefficients with ANN-driven control signals, a multi-zone aeration strategy was achieved without the need for additional training.
This approach can be interpreted as a form of inductive transfer learning, where the knowledge captured by the DO controller in reactor 5 (setpoint mg/L) was extended to reactors 3 and 4, which in the default BSM1 setup operate with fixed aeration. In the default BSM1 setup, these reactors operate with fixed aeration and no feedback regulation; here, they were instead assigned the same DO setpoint of 2 mg/L and controlled using the transferred LSTM model. The result was coordinated aeration across multiple zones, leading to further improvements in plant-wide performance indices such as the Effluent Quality Index (EQI) and the Operational Cost Index (OCI). Importantly, this demonstrates how an ANN PI controller based on a single trained model can be leveraged to enhance broader plant operation, reducing both the computational cost of retraining and the complexity of controller design. The effectiveness of this extension is evaluated in detail in Section 4.5, where its impact on loop-level tracking accuracy, effluent quality, and operational cost is compared against both the default PI controllers and the baseline ANN designs.
2.7. Evaluation Metrics
Since controller design is only meaningful when paired with rigorous assessment, the proposed LSTM-based PI controllers were benchmarked using both local and plant-wide performance indices.
At the loop level, two classical tracking metrics were considered: the Integral Squared Error (ISE) and the Integral Absolute Error (IAE). These quantify how well the controllers maintained nitrate () and dissolved oxygen () at their respective setpoints over the evaluation horizon. Lower values indicate tighter regulation and smoother error correction.
At the plant-wide level, two composite indices defined in the BSM1 framework were adopted. The Effluent Quality Index (EQI) provides a weighted measure of pollutant discharge, reflecting compliance with environmental standards. The Operational Cost Index (OCI) captures energy- and pumping-related costs, offering a proxy for operational efficiency.
This dual-level evaluation ensures that improvements are not only visible in individual control loops but also translate into tangible benefits for overall wastewater treatment plant performance.
3. Transfer Learning-Based Extension
Designing dedicated controllers for every loop in a wastewater treatment plant can be computationally demanding, especially when the process model itself is nonlinear and high-dimensional. One way to reduce this effort is to reuse knowledge from an already trained controller in related parts of the system. This idea, known as Transfer Learning (TL), allows a model that has learned the dynamics of one loop to be adapted for use in another, avoiding the need for full retraining [22].
In this work, the trained LSTM-based controller for dissolved oxygen regulation in reactor 5 () was directly applied to reactors 3 and 4. Under the default BSM1 configuration [9], these units operate with fixed oxygen transfer rates, which limit their ability to adapt to variable influent conditions and different oxygen consumption needs. By substituting the constant values with the outputs of the LSTM model, a multi-zone aeration control strategy was obtained. Importantly, no retraining was required, since the control objectives across the three aerated reactors are the same: maintaining dissolved oxygen at the desired setpoint of 2 mg/L.
This approach highlights the efficiency of transfer learning in process control [24,25]. Instead of developing three separate ANN-based controllers, a single well-trained model was repurposed across multiple reactors. Beyond reducing design and training effort, this reuse also led to measurable improvements in OCI and EQI performance, demonstrating plant-wide gains in both operational cost and effluent quality, as later shown in the Section 4.5.
4. Results
The performance of the proposed LSTM-based PI controllers was assessed under three dynamic influent scenarios—dry, rain, and storm weather—and compared with the default traditional PI controllers of the BSM1 framework. Two training strategies were investigated: time-agnostic (shuffled samples without preserving sequential order) and time-aware (sequence-preserved samples exploiting LSTM memory). Within each strategy, both three-input and four-input configurations were tested.
The detailed performance outcomes for all controller configurations and weather scenarios are summarized below. These results form the basis for the analysis in the following subsections (Table 1).

Table 1.
Performance comparison of LSTM-based and default PI controllers under dry, rain, and storm influent scenarios. Results are shown for time-agnostic and time-aware training with three- and four-input configurations.
4.1. Time-Agnostic Models
Time-agnostic training produced controllers that were stable and able to broadly replicate PI dynamics. However, their handling of transient behavior was limited, particularly under highly variable influent conditions.
- Three-input variant. For nitrate control (), the time-agnostic 3-input model did not consistently improve performance. Under dry and storm conditions, both ISE and IAE were higher than PI, while rain weather showed only modest ISE and IAE reductions (∼ and ∼, respectively). For dissolved oxygen (), ISE values were consistently worse than PI, though small IAE improvements (∼5–) were observed in rain and storm scenarios.
- Four-input variant. Adding influent flow rate () as a fourth input produced clear improvements across all weather conditions. For nitrate control, performance improved substantially in dry (∼ ISE, ∼ IAE reductions), rain (∼ ISE, ∼ IAE reductions), and storm scenarios (∼ ISE, ∼ IAE reductions). For dissolved oxygen, ISE was lower than PI under dry (∼ reduction), rain (∼ reduction), and storm (∼ reduction) conditions, while IAE improved by ∼ (dry) and ∼51– (rain and storm). Across all scenarios, EQI decreased slightly (indicating cleaner effluent), while OCI remained nearly identical to PI (<0.05% difference). These results confirm the benefit of providing disturbance-related information to the controller.
4.2. Time-Aware Models
By preserving sequential dependencies during training, time-aware models leveraged the memory capacity of LSTM cells and consistently outperformed their time-agnostic counterparts.
- Three-input variant. For nitrate control (), strong ISE reductions were observed: ∼ under dry weather, ∼ in rain, and ∼ in storm. IAE performance was also consistently better, with ∼ improvement under dry weather and ∼41– under rain and storm. For dissolved oxygen (), time-aware control did not reduce ISE (slightly worse than PI), but IAE improved modestly (∼6–).
- Four-input variant. This configuration delivered the best overall results. For nitrate control, ISE decreased by ∼ under rain and ∼ under storm, with IAE reductions of ∼50–. For dissolved oxygen, storm conditions showed dramatic gains (∼ ISE and ∼ IAE reductions). Even under dry and rain conditions, ISE decreased by ∼ (dry) and ∼ (rain), while IAE improved by ∼ (dry) and ∼ (rain). EQI values improved consistently, reflecting cleaner effluent, while OCI remained nearly unchanged from PI. These results demonstrate that combining temporal dependencies with influent flow information yields highly robust ANN-based control.
To complement the numerical results in Table 1, Figure 4 and Figure 5 present the storm weather responses for nitrate () and dissolved oxygen (), each including the four ANN configurations. In both cases, the setpoint and PI responses serve as a common baseline, while the subplots illustrate the behavior of the 3-input and 4-input models under time-agnostic and time-aware training. These profiles confirm the numerical trends, showing that the LSTM-based PI controllers track the reference values more closely than the PI controllers and demonstrating the effectiveness of the proposed approach under storm conditions.
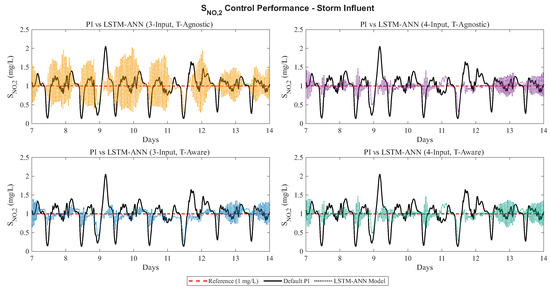
Figure 4.
Storm weather responses for the nitrate () loop. The setpoint and PI responses are shown as a common baseline (red dashed for the reference (1 mg/L), black solid for the default PI controller), while the four panels compare the behavior of the LSTM-ANN controllers, shown as black dotted lines with colors: orange for (3-Input, T-Agnostic), purple for (4-Input, T-Agnostic), blue for (3-Input, T-Aware), and green for (4-Input, T-Aware).
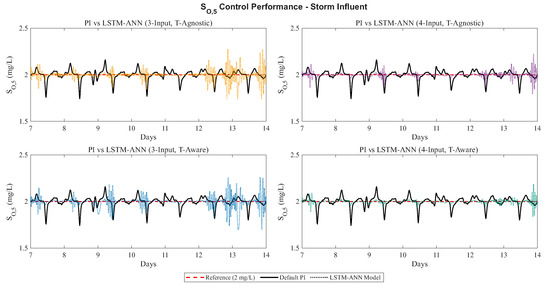
Figure 5.
Storm weather responses for the dissolved oxygen () loop. The setpoint and PI responses are shown as a common baseline (red dashed for the reference (2 mg/L), black solid for the default PI controller), while the four panels compare the behaviour of the LSTM-ANN controllers, shown as black dotted lines with colors: orange for (3-Input, T-Agnostic), purple for (4-Input, T-Agnostic), blue for (3-Input, T-Aware), and green for (4-Input, T-Aware).
4.3. Comparative Insights
From the evaluation across all models, three key conclusions emerge:
- 1.
- Time-aware training consistently outperformed time-agnostic training, especially under rain and storm scenarios where temporal correlations are dominant.
- 2.
- Adding influent flow rate () as a fourth input enhanced disturbance rejection, particularly for dissolved oxygen regulation.
- 3.
- The time-aware four-input LSTM-based PI controllers achieved the best overall performance, delivering the lowest ISE and IAE across both loops and all-weather scenarios, while simultaneously improving EQI without increasing OCI.
Taken together, these findings establish LSTM-based PI controllers—particularly in their time-aware, four-input configuration—as effective drop-in replacements for conventional PI controllers in BSM1. This provides a solid foundation for exploring transfer learning approaches, where knowledge from one well-trained controller can be repurposed to improve or accelerate the design of others.
4.4. Actuator Dynamics and Energy Implications
To further analyze loop-to-plant consistency and the energetic implications of the proposed control strategy, actuator signal behavior was examined for the oxygen transfer coefficient () and internal recirculation flow () under storm influent conditions. This analysis was performed for the default PI and the best-performing LSTM-based controllers (time-aware, four-input configuration).
Figure 6 presents the actuator time-series profiles, showing that both and signals remain within their physical bounds and exhibit smoother trajectories under LSTM control, with no saturation or abrupt switching. Quantitative checks confirmed that both actuators operated within their physical limits (0–360 for and up to 2 for ), showing realistic rate dynamics consistent with the BSM1 framework. Figure 7 shows the corresponding histograms, which provide insight into the variability and distribution of control signals. The LSTM-driven actuators demonstrate more concentrated distributions, reflecting stable yet adaptive control actions. The signal exhibited only modest variation, while displayed slightly higher-frequency responses during storm periods, associated with transient peaks in influent flow but remaining dynamically stable and within realistic limits. Figure 8 illustrates the proxy-power curves based on the squared signals ( and ), linking smoother control to comparable aeration energy and a slight increase in pumping energy. Together, these results confirm that the LSTM controller achieves improved effluent quality with realistic actuator behavior and without additional energy demand.
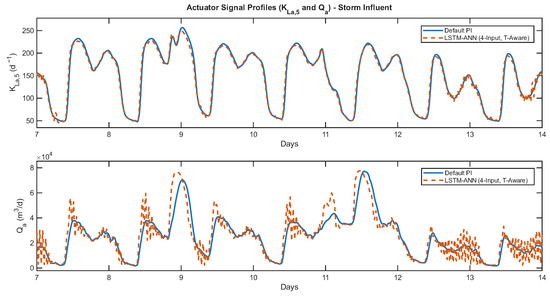
Figure 6.
Actuator signal profiles ( and ) under storm influent conditions. Comparison between the default PI and LSTM-ANN (4-input, time-aware) controllers showing smoother actuator trajectories and consistent operation within bounds.
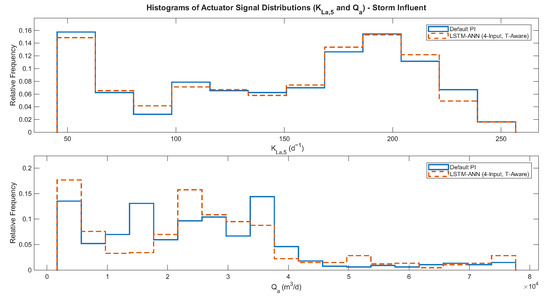
Figure 7.
Histograms of actuator signal distributions ( and ) under storm influent conditions. The normalized distributions show reduced variability and stable control actions for the LSTM-ANN compared with the PI controller.
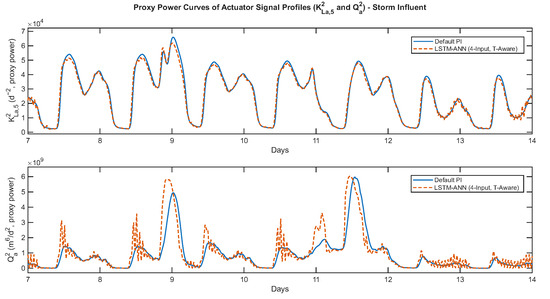
Figure 8.
Proxy power curves of actuator signal profiles ( and ) under storm influent conditions. The LSTM-ANN achieves comparable aeration energy demand and only a slight increase in pumping effort relative to the default PI.
4.5. Transfer Learning
Building upon the best-performing design (time-aware, four-input LSTM-based for ), transfer learning was used to extend the controller to reactors 3 and 4. In the default BSM1 setup, these units operate with fixed aeration, limiting their adaptability to dynamic influent. By substituting the fixed oxygen transfer rates with ANN-driven control signals, a multi-zone aeration strategy was achieved without retraining.
This approach represents inductive transfer learning, where knowledge from one control loop (DO in reactor 5) is reused in other aerated reactors with similar objectives. Together with the LSTM-based NO controller in reactor 2, the plant operated with four ANN-regulated loops. A comparative summary of the default PI setup, the standalone time-aware four-input ANN, and the transfer learning extension is provided below (Table 2).

Table 2.
Performance comparison of default PI controllers, the best LSTM-based PI configuration (time-aware, four-input), and the transfer-learning setup under dry, rain, and storm influent scenarios.
As a complement to the results in Table 2, Figure 9 presents the transfer learning responses for nitrate () under dry, rain, and storm influent conditions. In each case, the LSTM-based transfer learning controller achieves closer tracking of the setpoint compared to both the default PI and the baseline ANN controller, consistent with the numerical trends in Table 2. This figure is included as a representative example, illustrating how knowledge from a well-trained loop can be reused effectively across different operating conditions.
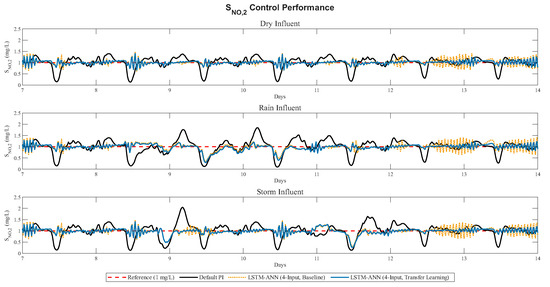
Figure 9.
Transfer learning responses for the nitrate () loop under dry, rain, and storm conditions. The figure complements Table 2, showing improved setpoint tracking compared to the default PI and standalone time-aware four-input LSTM-ANN controllers.
Across all influent scenarios, the transfer learning case yielded further plant-wide benefits:
- EQI values decreased compared to both PI and the standalone ANN, demonstrating improved effluent quality. Under dry weather, EQI was reduced by ∼1.1% relative to PI (6115.63 → 6048.19), in rain weather by ∼0.3% (8174.99 → 8148.46), and in storm conditions by ∼0.8% (7211.48 → 7151.16).
- OCI values also decreased, reflecting more efficient operation. Under dry weather, OCI dropped by ∼1.4% (16,381.94 → 16,149.08), in rain weather by ∼2.0% (15,984.85 → 15,666.39), and under storm conditions by ∼1.5% (17,253.75 → 17,000.08).
These improvements were achieved without training new models, underscoring the scalability and efficiency of transfer learning in process control.
5. Conclusions
This study demonstrated the potential of LSTM-based neural networks as drop-in replacements for conventional PI controllers in wastewater treatment plants, using the BSM1 benchmark as a test platform. By leveraging the ability of LSTM cells to capture temporal dependencies in process data, the proposed controllers achieved robust tracking of dissolved oxygen () and nitrate-nitrogen () concentrations under dry, rain, and storm influent conditions. Among the tested designs, the time-aware four-input models consistently delivered the strongest performance, with storm-weather tracking showing substantial reductions in ISE and IAE compared to baseline PI control. These improvements translated into better effluent quality (lower EQI) while maintaining operational costs (OCI) at levels comparable to or better than PI. Additional analysis of actuator dynamics confirmed that the LSTM-based controllers produced realistic, smooth control signals for and , remaining within physical bounds and achieving comparable aeration and pumping energy to the default PI setup.
Beyond direct PI replacement, this work applied transfer learning principles to extend the trained controller from reactor 5 to reactors 3 and 4, enabling a coordinated multi-zone aeration strategy without retraining. This approach not only simplified controller design but also improved plant-wide performance, with both EQI and OCI reduced relative to PI and standalone ANN setups. The results also highlighted an important trade-off: while all LSTM-based PI controllers outperformed PI, the choice of training strategy (time-agnostic vs. time-aware, three-input vs. four-input) influenced the degree of improvement, underscoring the importance of including influent context and temporal memory in the model.
Overall, the findings confirm that LSTM-based PI controllers can reliably replace conventional PI control in WWTPs while offering scalability through transfer learning. Designing a single robust ANN controller and reusing it across multiple loops not only reduces the computational burden of training but also enhances plant-wide efficiency. Moreover, their consistent actuator performance and stable energy behavior further support their suitability for real-plant implementation. Although this study focused on the BSM1 framework, the approach is generalizable to other industrial control systems where multiple loops share common objectives, making it a promising pathway for modernizing process automation with neural network-based control.
While formal robustness and stability analyses were beyond the present scope, the results demonstrate consistent closed-loop stability and safe actuator behavior across all tested scenarios. Future work will extend this framework through analytical stability assessments and robustness metrics, including delay sensitivity, constraint-violation tracking, and gain-margin testing. Furthermore, forthcoming studies will aim to establish formal stability guarantees for neural network-based feedback controllers, drawing on recent advances in Lyapunov-based analysis, hybrid MPC–ANN frameworks, and other emerging approaches to achieve theoretically grounded, stability-certified control design.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.V.; methodology, M.A. and R.V.; software, M.A.; validation, M.A. and R.V.; formal analysis, M.A. and R.V.; investigation, M.A. and R.V.; resources, R.V.; data curation, M.A. and R.V.; writing—original draft preparation, M.A.; writing—review and editing, M.A. and R.V.; visualization, M.A.; supervision, R.V.; project administration, R.V.; funding acquisition, R.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Agencia Estatal de Investigación (AEI), grant number PID2024-156522OB-C33.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data used in this study are the influent and effluent datasets generated within the Benchmark Simulation Model No. 1 (BSM1) framework, as described in [6,9].
Acknowledgments
This work has received support from the Catalan Government under Project 2021-SGR-00197 and also by the Spanish Government under MICINN projects PID2019-105434RB-C33. The authors used generative artificial intelligence tools (ChatGPT (https://chatgpt.com, accessed on 20 October 2022) by OpenAI and Grammarly) to enhance the clarity, structure, and language quality of the manuscript, limited to superficial text editing such as grammar and spelling.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ANN | Artificial Neural Network |
| ASM1 | Activated Sludge Model No. 1 |
| BSM1 | Benchmark Simulation Model No. 1 |
| DO | Dissolved Oxygen |
| EQI | Effluent Quality Index |
| IAE | Integrated Absolute Error |
| ISE | Integrated Squared Error |
| Oxygen Transfer Coefficient | |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| NO | Nitrate and Nitrite Nitrogen |
| OCI | Operational Cost Index |
| PI | Proportional Integral Controller |
| Influent Flow Rate | |
| Internal Recirculation Flow Rate | |
| Effluent Flow Rate | |
| External Recirculation Flow Rate | |
| Wastage Flow Rate | |
| Determination Coefficient | |
| Nitrate concentration in Reactor 2 | |
| Dissolved Oxygen concentration in Reactor 5 | |
| TL | Transfer Learning |
| WWTP | Wastewater Treatment Plant |
References
- Longo, S.; d’Antoni, B.M.; Bongards, M.; Chaparro, A.; Cronrath, A.; Fatone, F.; Lema, J.M.; Mauricio-Iglesias, M.; Soares, A.; Hospido, A. Monitoring and diagnosis of energy consumption in wastewater treatment plants. A state of the art and proposals for improvement. Appl. Energy 2016, 179, 1251–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriks, A.T.W.M.; Langeveld, J.; van Nieuwenhuijzen, A.; Uijterlinde, C.; van der Roest, H. Rethinking Wastewater Treatment Plant Effluent Standards: Nutrient Reduction or Nutrient Control? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 7311–7319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannina, G.; Ekama, G.; Caniani, D.; Cosenza, A.; Esposito, G.; Gori, R.; Garrido-Baserba, M.; Rosso, D.; Olsson, G. Greenhouse Gases from Wastewater Treatment—A Review of Modelling Tools. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 551–552, 254–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czepiel, P.; Crill, P.; Harriss, R. Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Municipal Wastewater Treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1995, 29, 2352–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Shi, H.; He, M. Nitrogen and Phosphorous Removal in Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants in China: A Review. Int. J. Chem. Eng. 2010, 2010, 914159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copp, J.B. The COST Simulation Benchmark: Description and Simulator Manual (COST Action 624 and Action 682); Office for Official Publications of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2002; Available online: https://op.europa.eu/en/publication-detail/-/publication/8448ef88-37dd-4d1a-823f-3143e7902429 (accessed on 12 September 2025).
- Gernaey, K.V.; Jeppsson, U.; Vanrolleghem, P.A.; Copp, J.B. Benchmarking of Control Strategies for Wastewater Treatment Plants; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2014; ISBN 9781780401171. Available online: https://library.oapen.org/handle/20.500.12657/43788 (accessed on 18 October 2025).
- Henze, M.; Grady, C.P.L., Jr.; Gujer, W.; Marais, G.V.R.; Matsuo, T. A General Model for Single-Sludge Wastewater Treatment Systems. Water Res. 1987, 21, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alex, J.; Benedetti, L.; Copp, J.; Gernaey, K.V.; Jeppsson, U.; Nopens, I.; Pons, M.N.; Rieger, L.; Rosen, C.; Steyer, J.P.; et al. Benchmark Simulation Model No. 1 (BSM1); Technical Report; Department of Industrial Electrical Engineering and Automation, Lund University: Lund, Sweden, 2008; Available online: http://iwa-mia.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/01/BSM_TG_Tech_Report_no_1_BSM1_General_Description.pdf (accessed on 10 September 2025).
- Ang, K.H.; Chong, G.; Li, Y. PID Control System Analysis, Design, and Technology. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2005, 13, 559–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alex, J. Model-based construction of wastewater treatment plant influent data for dynamic simulation studies. Water 2024, 16, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santin, I.; Pedret, C.; Vilanova, R. Fuzzy Control and Model Predictive Control Configurations for Effluent Violations Removal in Wastewater Treatment Plants. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 2763–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foscoliano, C.; Del Vigo, S.; Mulas, M.; Tronci, S. Predictive Control of an Activated Sludge Process for Long-Term Operation. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 304, 1031–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A. Deep Learning; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; Available online: http://www.deeplearningbook.org (accessed on 14 September 2025).
- Yang, W.; Li, H. Machine Learning in Wastewater Treatment: A Comprehensive Bibliometric Review. ACS ES&T Water 2025, 5, 511–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández de Cañete, J.; Del Saz-Orozco, P.; Baratti, R.; Mulas, M.; Ruano, A.; Garcia-Cerezo, A. Soft-Sensing Estimation of Plant Effluent Concentrations in a Biological Wastewater Treatment Plant Using an Optimal Neural Network. Expert Syst. Appl. 2016, 63, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.Y.; Vlachas, P.; Koumoutsakos, P.; Sapsis, T. Data-Assisted Reduced-Order Modeling of Extreme Events in Complex Dynamical Systems. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisa, I.; Santín, I.; Morell, A.; Vicario, J.L.; Vilanova, R. LSTM-Based Wastewater Treatment Plants Operation Strategies for Effluent Quality Improvement. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 159773–159786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarneros-Sandoval, A.; Ballesteros, M.; Salgado, I.; Chairez, I. Stable learning laws design for long short-term memory identifier for uncertain discrete systems via control Lyapunov functions. Neurocomputing 2022, 491, 144–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Zhao, C.; Shi, Z. LSTM-based adaptive robust nonlinear controller design of a single-axis hydraulic shaking table. IET Control Theory Appl. 2023, 17, 825–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, A.; Ghosh, D.; Zhu, L.; Xi, L.; Mhaskar, P. A novel linear hybrid model predictive control design: Application to a fed-batch crystallization process. Digit. Chem. Eng. 2022, 3, 100033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Abdulkadir, A.; Luley, P.-P.; Rosenthal, M.; Schatte, G.A.; Grewe, B.F.; Stadelmann, T. A Comprehensive Survey of Deep Transfer Learning for Anomaly Detection in Industrial Time Series: Methods, Applications, and Directions. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 3768–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curreri, F.; Patanè, L.; Xibilia, M.G. RNN- and LSTM-Based Soft Sensors Transferability for an Industrial Process. Sensors 2021, 21, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisa, I.; Morell, A.; Vilanova, R.; Vicario, J.L. Transfer Learning in Wastewater Treatment Plant Control Design: From Conventional to Long Short-Term Memory-Based Controllers. Sensors 2021, 21, 6315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisa, I.; Morell, A.; Lopez Vicario, J.; Vilanova, R. Transfer Learning in Wastewater Treatment Plants Control: Measuring the Transfer Suitability. J. Process Control 2023, 124, 36–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koksal, E.S.; Aydin, E. A Hybrid Approach of Transfer Learning and Physics-Informed Modelling: Improving Dissolved Oxygen Concentration Prediction in an Industrial Wastewater Treatment Plant. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2025, 304, 121088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).