Effect of Heavy Metal Contamination on Caciotta Cheese Made from Buffalo Milk
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design and Cheese Manufacturing
2.2. Extraction, Identification, and Quantification of Fatty Acids by Gas Chromatography
2.2.1. Lipid Extraction in Cheese
2.2.2. Extraction and Derivatization of Free Fatty Acids
2.2.3. Gas Chromatography (GC) Analysis
2.3. Determination of Lipid Oxidation Products
2.3.1. Peroxide Value (PV)
2.3.2. Acid Degree Value (ADV)
2.3.3. Fatty Acid Oxidation Products
2.4. Pre-Treatment for Antioxidant Activity
2.5. Protein Oxidation
2.5.1. Free Thiols Group
2.5.2. Radical Scavenging Assay (ABTS)
2.5.3. Activity by Ferric-Reducing Antioxidant Power
2.5.4. Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) Activity
2.6. Statistical Analysis
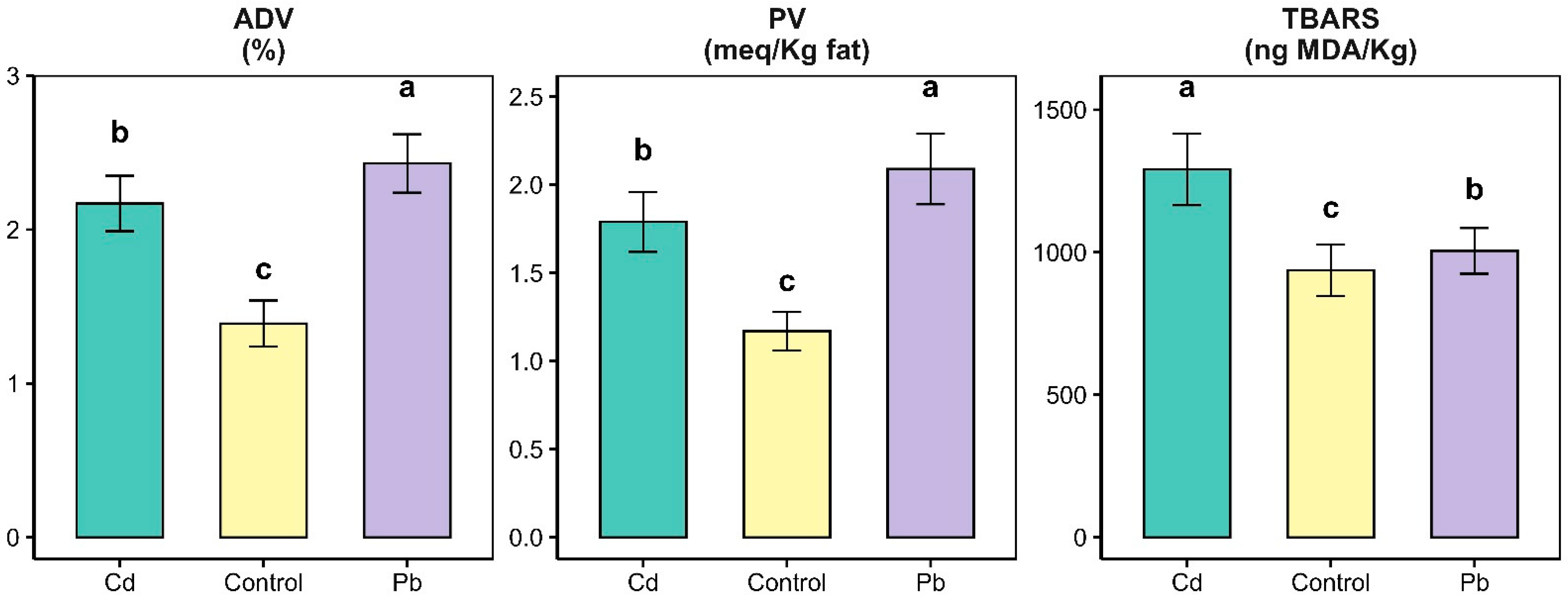
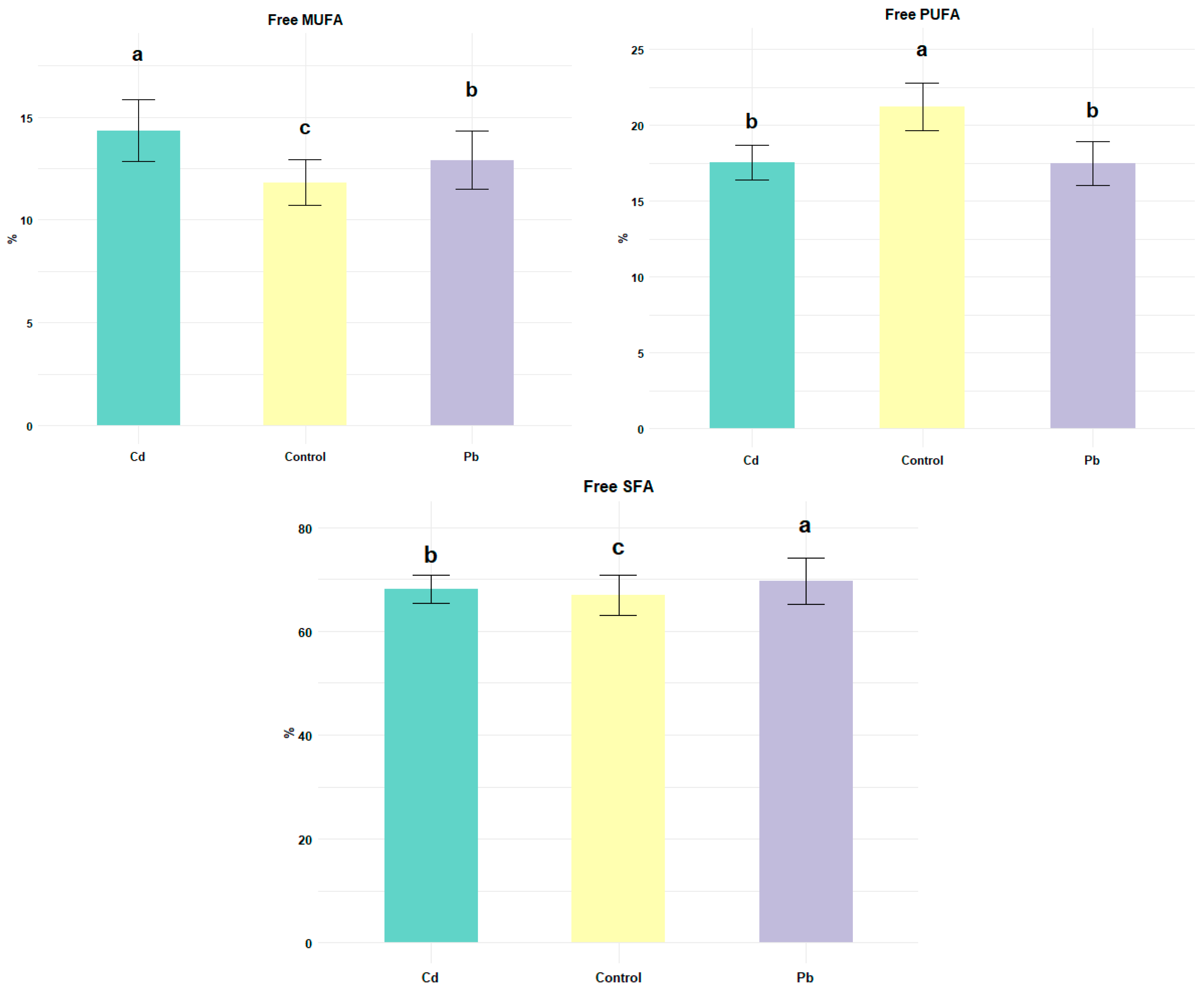
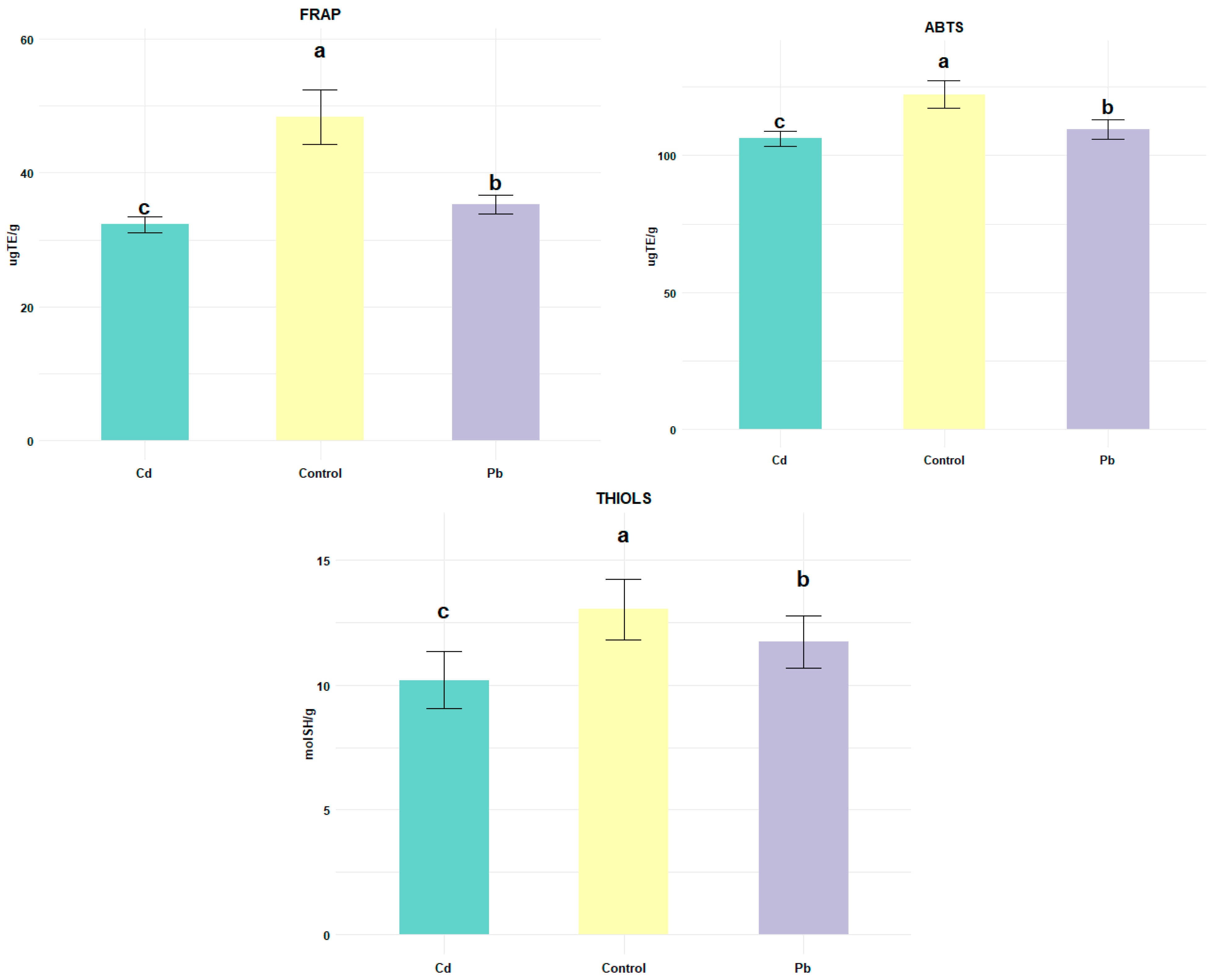
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical Composition of Cheese
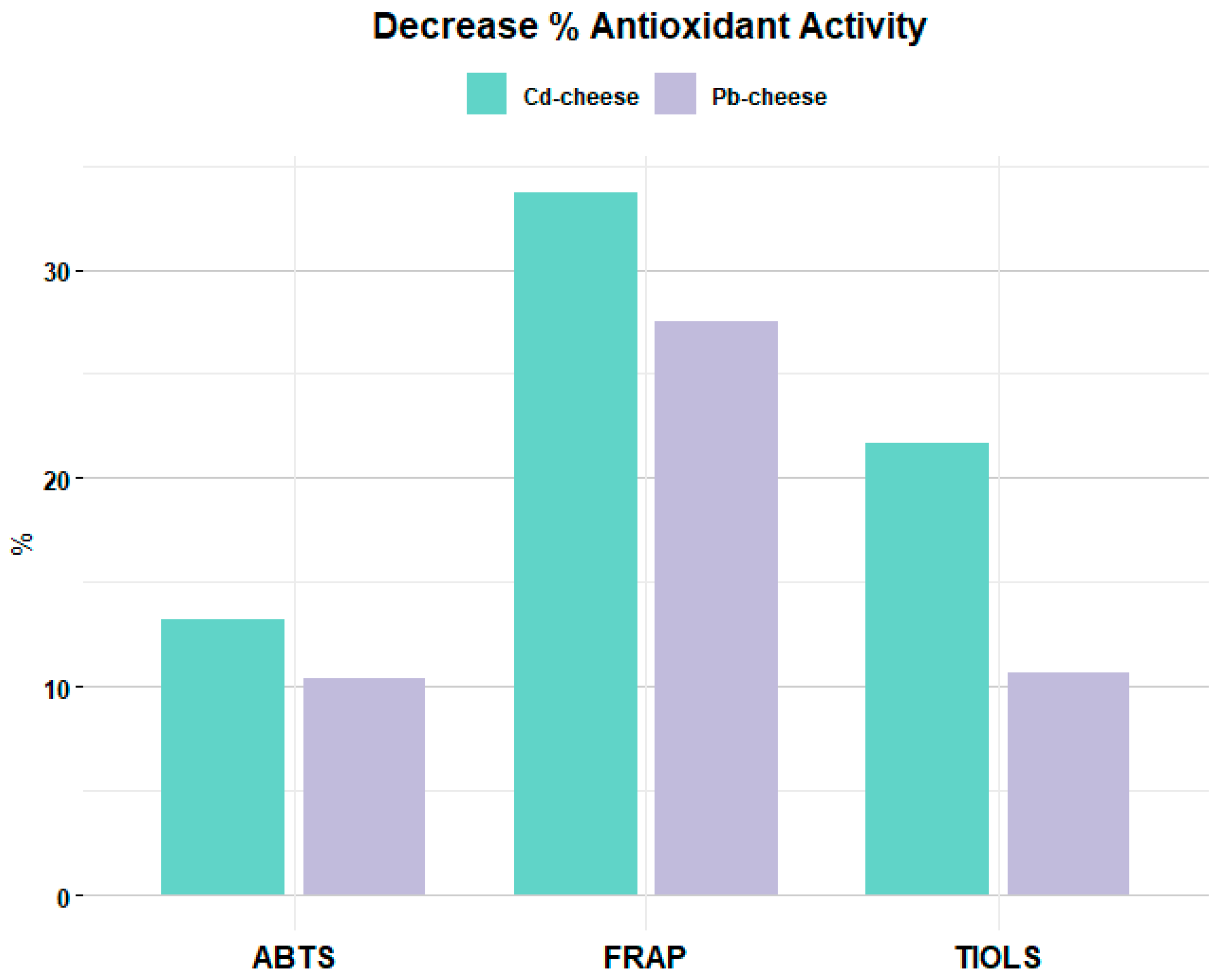
3.2. Protein Oxidation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Commission Regulation (EU) 2021/1323 of 10 August 2021 Amending Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 as Regards the Maximum Levels of Cadmium in Certain Foodstuffs. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2021/1323/oj/eng (accessed on 3 November 2025).
- Amalfitano, N.; Stocco, G.; Maurmayr, A.; Pegolo, S.; Cecchinato, A.; Bittante, G. Quantitative and Qualitative Detailed Milk Protein Profiles of 6 Cattle Breeds: Sources of Variation and Contribution of Protein Genetic Variants. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 11190–11208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, T.; Elarnaoutti, M.S. Heavy Metals Transfer from Milk into Milk Products. Turk. J. Agric.-Food Sci. Technol. 2025, 13, 900–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, K.; Das, A.P. Lead Pollution: Impact on Environment and Human Health and Approach for a Sustainable Solution. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2023, 5, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hettiarachchi, G.M.; Betts, A.R.; Chandima Wekumbura, W.G.; Lake, L.; Mayer, M.M.; Scheckel, K.G.; Basta, N.T. Chapter 6—Lead: The Most Extensively Spread Toxic Environmental Contaminant. In Inorganic Contaminants and Radionuclides; Naidu, R., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 113–150. ISBN 978-0-323-90400-1. [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis, P.; Fawell, J. Lead in Drinking Water—An Ongoing Public Health Concern? Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2021, 20, 100239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubier, A.; Wilkin, R.T.; Pichler, T. Cadmium in Soils and Groundwater: A Review. Appl. Geochem. 2019, 108, 104388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Nandi, P.; Bhattacharya, C.; Kabir, Z.; Mukherjee, S.; Maji, B.K. Cadmium Acts as a Silent Killer of Liver by Inducing Oxidative Stress and Hepatocellular Injury and a Possible Amelioration by Vitamin B12 and Folic Acid in Rat Model. Prog. Health Sci. 2019, 1, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flora, G.; Gupta, D.; Tiwari, A. Toxicity of Lead: A Review with Recent Updates. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2012, 5, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collin, F. Chemical Basis of Reactive Oxygen Species Reactivity and Involvement in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Khan, E.; Ilahi, I. Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology of Hazardous Heavy Metals: Environmental Persistence, Toxicity, and Bioaccumulation. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 6730305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briffa, J.; Sinagra, E.; Blundell, R. Heavy Metal Pollution in the Environment and Their Toxicological Effects on Humans. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juan, C.A.; Pérez de la Lastra, J.M.; Plou, F.J.; Pérez-Lebeña, E. The Chemistry of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Revisited: Outlining Their Role in Biological Macromolecules (DNA, Lipids and Proteins) and Induced Pathologies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, L.; Liu, K.; Zhang, H. Lipid Oxidation in Foods and Its Implications on Proteins. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1192199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehm, R.; Baldensperger, T.; Raupbach, J.; Höhn, A. Protein Oxidation—Formation Mechanisms, Detection and Relevance as Biomarkers in Human Diseases. Redox Biol. 2021, 42, 101901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Jin, L.; Li, J.; Chen, G. Association of Cadmium and Lead Exposure with Mortality in Cancer Survivors: A Prospective Cohort Study. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 292, 117960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, A.; Mahreen, N. Emerging Insights into the Impacts of Heavy Metals Exposure on Health, Reproductive and Productive Performance of Livestock. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1375137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visioli, F.; Strata, A. Milk, Dairy Products, and Their Functional Effects in Humans: A Narrative Review of Recent Evidence. Adv. Nutr. 2014, 5, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basilicata, M.G.; Pepe, G.; Adesso, S.; Ostacolo, C.; Sala, M.; Sommella, E.; Scala, M.C.; Messore, A.; Autore, G.; Marzocco, S.; et al. Antioxidant Properties of Buffalo-Milk Dairy Products: A β-Lg Peptide Released after Gastrointestinal Digestion of Buffalo Ricotta Cheese Reduces Oxidative Stress in Intestinal Epithelial Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Ramella, M.; Pateiro, M.; Maggiolino, A.; Faccia, M.; Franco, D.; De Palo, P.; Lorenzo, J.M. Buffalo Milk as a Source of Probiotic Functional Products. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grassi, G.; Simonetti, A.; Gambacorta, E.; Perna, A. Effect of Species on the Distribution and Oxidative Stability of Milk Added of Lead and Cadmium. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2023, 22, 1162–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fucà, N.; McMahon, D.J.; Caccamo, M.; Tuminello, L.; La Terra, S.; Manenti, M.; Licitra, G. Effect of Brine Composition and Brining Temperature on Cheese Physical Properties in Ragusano Cheese. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 460–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horwitz, W. (Ed.) AOAC Official Methods of Analysis of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists, 13th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists (AOAC): Rockville, MA, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Sloane Stanley, G.H. A Simple Method for the Isolation and Purification of Total Lipides from Animal Tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 226, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilcawley, K.N.; Mannion, D.T. Free Fatty Acids Quantification in Dairy Products. In Fatty Acids; Catala, A., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2017; ISBN 978-953-51-3301-8. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 3976:2006-IDF 74:2006; Milk Fat—Determination of Peroxide Value Published. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006.
- Thomas, T.D.; Pearce, K.N. Influence of Salt on Lactose Fermentation and Proteolysis in Cheddar Cheese. J. Dairy Sci. Technol. 1981, 16, 253–259. [Google Scholar]
- Sacchetti, G.; Di Mattia, C.; Pittia, P.; Martino, G. Application of a Radical Scavenging Activity Test to Measure the Total Antioxidant Activity of Poultry Meat. Meat Sci. 2008, 80, 1081–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellman, G.L. Tissue Sulfhydryl Groups. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1959, 82, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant Activity Applying an Improved ABTS Radical Cation Decolorization Assay. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, G.; Simonetti, A.; Gambacorta, E.; Perna, A. Decrease of Activity of Antioxidant Enzymes, Lysozyme Content, and Protein Degradation in Milk Contaminated with Heavy Metals (Cadmium and Lead). JDS Commun. 2022, 3, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAS User’s Guide: Statistics; Cary, N.C., Ed.; SAS Institute: Cary, NC, USA, 1985; ISBN 978-0-917382-66-6. [Google Scholar]
- Morsy, M.K.; Elsabagh, R. Quality Parameters and Oxidative Stability of Functional Beef Burgers Fortified with Microencapsulated Cod Liver Oil. LWT 2021, 142, 110959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Ojeda, F.J.; Olza, J.; Gil, Á.; Aguilera, C.M. Chapter 1—Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome. In Obesity; del Moral, A.M., Aguilera García, C.M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 1–15. ISBN 978-0-12-812504-5. [Google Scholar]
- Semeniuc, C.A.; Mandrioli, M.; Socaci, B.S.; Socaciu, M.-I.; Fogarasi, M.; Podar, A.S.; Michiu, D.; Jimborean, A.M.; Mureşan, V.; Ionescu, S.R.; et al. Changes in Lipid Composition and Oxidative Status during Ripening of Gouda-Type Cheese as Influenced by Addition of Lavender Flower Powder. Int. Dairy J. 2022, 133, 105427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, X.; Yao, Y.; Qu, X.; Chen, J.; Xie, K.; Wang, X.; Qi, Y.; Xiao, B.; He, C. Effects of Different Levels of Hermetia Illucens Larvae Meal on Performance, Egg Quality, Yolk Fatty Acid Composition and Oxidative Status of Laying Hens. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2021, 20, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroga-Roger, D.; Babul, J.; Guixé, V. Role of Monovalent and Divalent Metal Cations in Human Ribokinase Catalysis and Regulation. Biometals 2015, 28, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thierry, A.; Collins, Y.F.; Abeijón Mukdsi, M.C.; McSweeney, P.L.H.; Wilkinson, M.G.; Spinnler, H.E. Chapter 17—Lipolysis and Metabolism of Fatty Acids in Cheese. In Cheese, 4th ed.; McSweeney, P.L.H., Fox, P.F., Cotter, P.D., Everett, D.W., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2017; pp. 423–444. ISBN 978-0-12-417012-4. [Google Scholar]
- Charkiewicz, A.E.; Omeljaniuk, W.J.; Nowak, K.; Garley, M.; Nikliński, J. Cadmium Toxicity and Health Effects—A Brief Summary. Molecules 2023, 28, 6620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteverde, V.; Camilleri, G.; Arfuso, F.; Pennisi, M.; Perillo, L.; Patitò, G.; Gioia, G.; Castronovo, C.; Piccione, G. Heavy Metal Levels in Milk and Serum of Dairy Cows from Different Farms Located near an Industrial Area. Animals 2022, 12, 2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsaturyan, V.; Poghosyan, A.; Toczyłowski, M.; Pepoyan, A. Evaluation of Malondialdehyde Levels, Oxidative Stress and Host–Bacteria Interactions: Escherichia Coli and Salmonella Derby. Cells 2022, 11, 2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stapelfeldt, H.; Nielsen, B.R.; Skibsted, L.H. Effect of Heat Treatment, Water Activity and Storage Temperature on the Oxidative Stability of Whole Milk Powder. Int. Dairy J. 1997, 7, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkowska, D.; Słowik, J.; Chilicka, K. Heavy Metals and Human Health: Possible Exposure Pathways and the Competition for Protein Binding Sites. Molecules 2021, 26, 6060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai, S.; Shimizu, S.; Tatara, Y.; Mimura, J.; Itoh, K. Regulation of Nrf2 by Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species in Physiology and Pathology. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snezhkina, A.V.; Kudryavtseva, A.V.; Kardymon, O.L.; Savvateeva, M.V.; Melnikova, N.V.; Krasnov, G.S.; Dmitriev, A.A. ROS Generation and Antioxidant Defense Systems in Normal and Malignant Cells. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2019, 2019, 6175804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haidar, Z.; Fatema, K.; Shoily, S.S.; Sajib, A.A. Disease-Associated Metabolic Pathways Affected by Heavy Metals and Metalloid. Toxicol. Rep. 2023, 10, 554–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, S. Reactive Species in Advanced Oxidation Processes: Formation, Identification and Reaction Mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 401, 126158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, R.; Pateiro, M.; Gagaoua, M.; Barba, F.J.; Zhang, W.; Lorenzo, J.M. A Comprehensive Review on Lipid Oxidation in Meat and Meat Products. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ighodaro, O.M.; Akinloye, O.A. First Line Defence Antioxidants-Superoxide Dismutase (SOD), Catalase (CAT) and Glutathione Peroxidase (GPX): Their Fundamental Role in the Entire Antioxidant Defence Grid. Alex. J. Med. 2018, 54, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elarabany, N.; Bahnasawy, M. Comparative and Interactive Biochemical Effects of Sub-Lethal Concentrations of Cadmium and Lead on Some Tissues of the African Catfish (Clarias gariepinus). Toxicol. Res. 2019, 35, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cangelosi, V.; Ruckthong, L.; Pecoraro, V.L. Lead(II) Binding in Natural and Artificial Proteins. In Lead: Its Effects on Environment and Health; Sigel, A., Sigel, H., Sigel, R.K.O., Eds.; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany; Boston, UK, 2017; Volume 17, pp. 271–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jomova, K.; Valko, M. Advances in Metal-Induced Oxidative Stress and Human Disease. Toxicology 2011, 283, 65–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, A.; DeGheselle, O.; Smeets, K.; Van Kerkhove, E.; Cuypers, A. Cadmium-Induced Pathologies: Where Is the Oxidative Balance Lost (or Not)? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 6116–6143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausen, M.R.; Connolly, C.; Skibsted, L.H.; Stagsted, J. Oxidative Stability of Bovine Milk Determined by Individual Variability in Herd Irrespective of Selenium Status. Int. Dairy J. 2010, 20, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revilla, I.; González-Martín, M.I.; Vivar-Quintana, A.M.; Blanco-López, M.A.; Lobos-Ortega, I.A.; Hernández-Hierro, J.M. Antioxidant Capacity of Different Cheeses: Affecting Factors and Prediction by near Infrared Spectroscopy. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 5074–5082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zeng, G.; Qu, D.; Gu, J.; Zhou, M.; Chai, L. Cadmium-Induced Oxidative Stress and Response of the Ascorbate–Glutathione Cycle in Bechmeria Nivea (L.) Gaud. Chemosphere 2007, 69, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lučić, M.; Miletić, A.; Savić, A.; Lević, S.; Ignjatović, I.S.; Onjia, A. Dietary Intake and Health Risk Assessment of Essential and Toxic Elements in Pepper (Capsicum annuum). J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 111, 104598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Control | Cd | Pb | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| µ | SD | µ | SD | µ | SD | |
| Moisture (%) | 33.66 | 2.90 | 33.35 | 1.97 | 33.82 | 3.28 |
| Total fat (%) | 35.82 | 2.70 | 36.03 | 2.46 | 35.70 | 2.16 |
| Total protein (%) | 26.96 | 2.17 | 26.96 | 1.64 | 26.86 | 1.42 |
| Ash (%) | 3.55 | 0.28 | 3.64 | 0.30 | 3.80 | 0.20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grassi, G.; Perna, A.M. Effect of Heavy Metal Contamination on Caciotta Cheese Made from Buffalo Milk. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 11881. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152211881
Grassi G, Perna AM. Effect of Heavy Metal Contamination on Caciotta Cheese Made from Buffalo Milk. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(22):11881. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152211881
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrassi, Giulia, and Anna Maria Perna. 2025. "Effect of Heavy Metal Contamination on Caciotta Cheese Made from Buffalo Milk" Applied Sciences 15, no. 22: 11881. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152211881
APA StyleGrassi, G., & Perna, A. M. (2025). Effect of Heavy Metal Contamination on Caciotta Cheese Made from Buffalo Milk. Applied Sciences, 15(22), 11881. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152211881








