Abstract
The environmental performance of natural aggregates for concrete and road construction, extracted from a dolomite quarry, was investigated. Environmental hotspots were identified, and potential optimization measures to further reduce the environmental footprint were proposed. The natural aggregates extracted from the dolomite quarry have relatively low GWP and a low environmental footprint in general. The GWP of 1 tonne of natural aggregates used in concrete production is 1.13 kg CO2 equiv., while for 1 tonne of aggregates used in road construction, it is 0.97 kg CO2 equiv. The dolomite rock in the quarry in question is tectonically fractured, such that very intensive extraction is not required, taking into account the blasting of the rock and further processing. The use of non-road mobile machinery is already optimized. Additional reductions in environmental impact could be achieved by powering the screening process exclusively with electricity from renewable sources, such as a photovoltaic system. In this context, integrating on-site battery storage systems might present a promising solution for addressing the seasonal mismatch between solar energy generation and processing demands.
1. Introduction
Aggregates are the most frequently used mineral resource. They are the main components of concrete and asphalt. Their applications include mortars, bricks, road stones, railway ballast, drainage layers, and bulk fills. Aggregates are required in almost every part of the built environment [1]. Aggregates can be primary, e.g., extracted from mineral deposits (natural stone and crushed rock from quarries; clay, sand, and gravel from alluvial deposits) [2,3,4], and secondary, which are by-products of other quarrying and mining operations (e.g., clay residues, mining waste, and tunnel excavation material) [5,6,7,8] or by-products of other industrial processes (e.g., steel slag and spent foundry sand) [9,10,11,12]. Primary aggregates are known as virgin or natural aggregates, whereas secondary aggregates are known as manufactured or artificial aggregates. The third type of aggregates is recycled aggregates, which are obtained from the processing of various mineral fractions of construction and demolition waste, or from civil engineering works [13,14,15]. As soon as a waste material is processed into a product that can be traded on the market, it ceases to be a waste and becomes a resource. At which point the material meets the criteria for end-of-waste status must be regulated by national laws [15,16].
The general criteria for achieving end-of-waste status are outlined in the Waste Framework Directive [17], which has been transposed into national law by all EU Member States. However, the degree of implementation of waste management legislation varies between EU Member States [15]. For some waste streams (metals, glass, and biodegradable waste), the end-of-waste criteria have been developed at the EU level [18,19,20]. EU Member States may set their own criteria for applying the conditions outlined in the Waste Framework Directive to other types of waste. These criteria must take into account possible adverse effects of the substance or object on the environment or human health [21,22]. Some EU Member States (France, Ireland, Italy, and the Netherlands) have already developed end-of-waste criteria for aggregates. Flanders is working at the regional level on the development of end-of-waste criteria for aggregates [23].
Global consumption of aggregates has grown exponentially, tripling in the last two decades. By 2022, the consumption of aggregates is estimated to be around 50 billion tonnes, making it the second most used resource in the world, after water [15]. Aggregate production in 42 European countries amounted to 4.20 billion tonnes in 2019, of which 91.4% were natural aggregates, 6.9% recycled aggregates, and 1.7% manufactured aggregates. Russia was the largest producer, with 723 million tonnes of aggregates produced. In 146 extraction sites (quarries and pits) in Slovenia, 11 million tonnes of aggregates were produced [24]. Worldwide reserves of natural aggregates are considered infinite on a global level; however, supply shortages may occur on a regional level. The sustainable extraction and management of aggregates are important to avoid their potential future scarcity [15,25].
The sustainable use of natural resources is one of the essential characteristics of construction products under the new Construction Products Regulation—CPR (EU) 2024/3110 (https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2024/3110/oj/eng, accessed on 5 October 2025), which came into force in January 2025. During the transition period, which lasts until 2040, both the old CPR (EU), No 305/2011 (https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A02011R0305-20241117, accessed on 5 October 2025), and the new CPR apply. The new CPR places greater emphasis on sustainability and digitalization. The declaration of the environmental performance of construction products will become mandatory between 2026 and 2032, and at the latest by 2040, when the transitional period ends. The requirements for the essential characteristics are laid down in product-specific harmonized technical specifications (e.g., harmonized standards and European Assessment Documents—EADs), but not the additional requirements (emissions to the external environment of construction works) from new CPR. Therefore, new technical specifications are being developed to address these additional requirements [26]. Under the new CPR, digital product passports will become mandatory for key categories of construction products between 2027 and 2030. These passports aim to ensure transparency across the supply chain and support the circularity of construction products, in line with the waste management hierarchy, which prioritizes reuse and recycling while preventing waste generation [27].
This study aims to assess the environmental performance of natural aggregates. Natural aggregates for road construction and concrete production are produced in a dolomite quarry in Slovenia. The environmental footprint of each type of natural aggregate was assessed. Another aim of this study was to identify potential optimizations of the production process to minimize the environmental footprint. To this end, a sensitivity analysis was performed to (i) evaluate the sensitivity of the LCA results with respect to the source of electricity (different proportions of electricity from the grid mix and from solar system photovoltaics installed in the quarry), (ii) evaluate the sensitivity of the LCA results with respect to the method of delivery of extracted rock to the screening plant (quarry dump truck versus conveyor belt), and (iii) evaluate the sensitivity of the LCA results to diesel combustion factors associated with the use of non-road mobile machinery.
A detailed LCA study on the production of natural aggregates was recently conducted by [28], who demonstrated the sensitivity of the environmental impact depending on the type of exploited rock. Most of the available LCA studies on aggregates are comparative LCAs. The environmental performance of natural aggregates and recycled aggregates is usually compared (see [29,30,31]). Recycled aggregates are usually produced from construction and demolition waste. Comparative LCA studies by [29,30] have shown that recycled aggregates have a lower environmental impact than natural aggregates. The main reason for this difference lies in the environmentally harmful extraction phase of natural aggregates, in which diesel machines are required. These machines are also required in the pre-crushing phase of recycled aggregate production; however, the energy consumption (in the form of diesel) is significantly lower [30]. Reference [31] applied LCA to compare the production of aggregates for use in road pavements. They considered the production of natural aggregates and recycled concrete aggregates. The aggregates compared—natural aggregates and recycled aggregates—must meet the same application requirements, as recycled aggregates are generally of lower quality. Their use is, therefore, often limited to road and embankment construction [32]. According to [33], aggregates intended for concrete must meet stricter geometrical, physical, and chemical requirements than those used for road construction.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Goal and Declared Unit
The Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) was used to assess the environmental footprint of the natural aggregates produced in the dolomite quarry (Poljčane, Slovenia) and to search for solutions to reduce the environmental hotspots in the production process. The LCA is a globally recognized and standardized method for environmental assessment [34,35].
The declared unit is the production of 1 tonne of natural aggregate for road construction and the production of 1 tonne of natural aggregate for concrete production.
2.2. System Boundaries
The system boundaries encompass the extraction and processing of rock, corresponding to modules A1–A3, as defined in [35] (Figure 1). The aggregates in the quarry are extracted from the dolomite bedrock. The extraction process begins with drilling holes in the rock to place explosives, which are then used to blast the bedrock into fragments. These fragments are excavated using an excavator and pushed down the slope by a bulldozer. A loader transfers the rock fragments onto a conveyor belt, which transports them to a nearby screening plant located approximately 400 m away. At the plant, the rock is screened using various mesh sizes to separate it into different fractions, including filler, fine aggregates (such as sand), and coarse aggregates (such as gravel). Finally, the aggregates are stockpiled according to size and prepared for delivery to customers for use in various construction projects. Washing and drying are not performed, as the produced aggregates meet the technical requirements for their intended applications. However, these additional processes may be introduced in the future to reduce the content of the finest fractions and enhance the quality of natural aggregates for concrete.
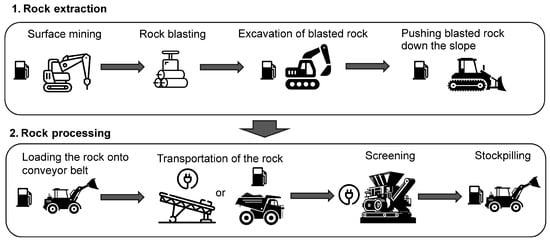
Figure 1.
System boundaries of the production of natural aggregates. Emissions associated with the production of explosives, electricity, and diesel fuel, as well as the combustion of diesel fuel in engines, are also taken into account.
The system boundaries exclude the production of non-road mobile machinery, the conveyor belt, the screening plant, and other supporting infrastructure.
2.3. Life Cycle Inventory and Assumptions
The quarry operator collects data on the amount of natural aggregates produced annually and monitors the consumption of explosives and diesel by individual machines. All collected data refer to the year 2023.
The proportion of natural aggregates used for concrete and road construction produced in 2023 was 43% versus 57%. The same types of non-road mobile machinery (surface mining machine, excavator, bulldozer, and loaders), operating under identical conditions, were used in the production of both aggregate types. Since the production processes are equivalent, the machinery consumes the same amount of diesel per tonne of aggregates produced for each type. The total diesel consumption (combusted in the engines of non-road mobile machinery) was allocated proportionally between the two production processes, based on their respective output shares (0.43 for concrete aggregates and 0.57 for road construction aggregates). Diesel consumption data were then divided by the tonnage of aggregates produced, allowing recalculation of values per functional unit—defined as the production of 1 tonne of each type of natural aggregates (see Table 1). A generic dataset related to an excavator was used to assess the environmental impacts caused by the use of all types of non-road mobile machinery. It was assumed that all types of machines emit similar emissions per liter of diesel fuel consumed. This approach enabled fuel-based normalization, which is a widely accepted method when machine-specific emission data are unavailable. We believe this generalization does not significantly affect the overall LCA results. The rationale for this simplification is the lack of relevant datasets for certain machines, such as bulldozers and surface mining machines. The same assumption was made for the loader used to store the final products (natural aggregates).

Table 1.
Life Cycle Inventory data for the production of 1 tonne of natural aggregates in the dolomite quarry (Slovenia).
The total annual (2023) electricity consumption was measured by the quarry operator. The data include electricity used to transport blasted rock via a conveyor belt, as well as the energy required for screening. Based on annual figures provided and specifications of the machinery, electricity consumption was calculated per declared unit of this LCA, specifically, per tonne of each type of natural aggregates. The conveyor belt requires 0.11 kWh of electricity to transport 1 tonne of material over a distance of 400 m. The production of natural aggregates for concrete involves more screening cycles than that for road construction, resulting in a notable difference in electricity consumption at the screening plant (1.31 kWh/t versus 0.32 kWh/t, respectively; see Table 1). Electricity for both the conveyor belt and screening plant was sourced partly from a solar system (photovoltaic panels installed at the quarry) and partly from the grid, with an annual supply ratio of 55% from solar energy and 45% from the grid.
Dust emissions are not monitored in the quarry. These emissions can be estimated, taking into account the information outlined in [36]. According to this air pollutant emission inventory guidebook, dust emissions associated with the production of natural aggregates in large quarries, including drilling, blasting, screening, loading, internal transport, and wind erosion from stockpiles, can be estimated. PM10 emissions are estimated to be 28 g per tonne of natural aggregates, and PM2.5 emissions are estimated to be 4.1 g per tonne of natural aggregates.
A dataset for explosives is not available in the MLC database and was, therefore, sourced from the Ecoinvent database (Table 1). Ecoinvent datasets typically overestimate Ozone Layer Depletion Potential (ODP) values, as they still include banned substances such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), despite their phase-out under the Montreal Protocol [37,38]. Using Ecoinvent’s dataset for explosives would lead to an unreliable and disproportionately high contribution of explosives to the overall ODP impact in the life cycle of natural aggregate production. To resolve this issue, the raw materials and energy requirements for explosive production were modeled separately within the LCA for Experts software (version 10.9). A representative ODP value for explosives was derived from this customized model, based on inventory data provided by [39].
2.4. Life Cycle Impact Assessment
The environmental impact assessment was calculated according to the impact assessment method, EN 15804:2012+A2:2019, which follows the “problem-oriented method”. This impact assessment method is preferable for reporting on the environmental footprint of construction products. In this LCA, 13 core environmental impacts were considered (Table 2). The mining sector is associated with significant dust emissions. However, particulate matter formation (expressed as “disease incidences”) is not among the core environmental impacts indicated in [35]. This impact category was reported additionally.

Table 2.
The indicators used to describe the core environmental impacts.
Under the new Construction Products Regulation, producers will be required to report on the environmental performance of their products. Mandatory reporting will be introduced gradually: GWP reporting will become mandatory from 2026, followed by the remaining core environmental indicators from 2030. Additional indicators, such as particulate matter, are expected to become mandatory after 2032 [26].
3. Results and Discussion
The production of aggregates for concrete is associated with higher burdens than the production of aggregates for road construction. The reason for this lies in the additional screening required to produce high-quality aggregate fractions suitable for the concrete industry (Table 3).

Table 3.
Environmental performance of 1 tonne of natural aggregates from the dolomite quarry (Slovenia).
The environmental impact of both types of natural aggregates produced in the dolomite quarry is relatively low compared to the data in the Environmental Product Declarations (EPDs) for natural aggregates extracted from carbonate bedrock and produced using similar technological processes, including rock blasting, crushing, and screening, without washing or drying. For example, the GWP of 1 tonne of natural aggregates from the dolomite quarry is 1.13 kg CO2 equiv. (the aggregates intended for concrete production) and 0.97 kg CO2 equiv. (the aggregates intended for road construction), while the GWP of limestone aggregates from other quarries is between 0.85 and 4.60 kg CO2 equiv., depending on the type (fraction) of aggregate [40,41]. The GWP and environmental footprint of natural aggregates are directly related to the number of crushing and screening processes (e.g., primary crushing and secondary crushing). The relatively low impact of the natural aggregates produced in the Slovenian quarry is attributed to (i) the properties of the bedrock, which consists of tectonically fractured dolomite and, as such, does not require very intensive extraction (a relatively small amount of explosive for blasting) or processing (only screening is required; there is no additional crushing of excavated rock), and (ii) optimized use of non-road mobile machinery (the duty cycles of non-road mobile machinery are maximized to minimize idle time and reduce unnecessary emissions). It is also worth noting that natural aggregates do not need to be washed and dried, as the dolomite rock has a very high purity (the dolomite is chemically homogeneous) (cf. [42]) and as such meets all market requirements.
Taking into account the data from [28], the GWP of natural aggregates from different quarries in Quebec (Canada) is between 2.28 and 3.59 kg CO2 equiv. Lower GWP values refer to the extraction of carbonate rock and higher values to the extraction of hard (volcanic) rock. Reference [28] emphasized that the environmental footprint of aggregates in quarries is directly related to rock properties (e.g., hardness). Harder rocks require more explosives, which increases the impact. Blasting carbonate rock requires 0.17–0.26 kg of explosives per tonne of rock and 0.37 kg of explosives for blasting one tonne of hard rock (volcanic rock and sandstone) [28]. In a given quarry, only 0.045 kg of explosives are needed to blast tectonically fractured dolomite rock (Table 1), which is roughly 4 to 8 times less than the values reported in [28]. This lower explosive consumption translates to a potential reduction in GWP of approximately 0.6–1.5 kg CO2 equiv. per tonne of natural aggregates, compared to extraction from massive, unfractured rock. The quantity of explosives required depends not only on the general type and hardness of the rock, but also on local geological properties, such as strength, density, and the structure of the rock mass, including the presence of discontinuities such as joints, faults, and bedding planes [43,44]. Additionally, rocks extracted from massive geological formations require crushing, which is not necessary for tectonically fractured formations, as examined in this study. Crushing harder rock involves multiple stages and consumes significantly more electrical energy, further increasing the environmental impact.
Core environmental impacts of natural aggregates intended for concrete and road construction are presented in Table 3. Particulate matter formation was additionally estimated based on secondary data [36]. The processing of natural aggregates, such as drilling, blasting, screening, loading, and internal transport, is the primary contributor to particulate matter formation. Due to limitations in the secondary data, it was not possible to estimate the reduction in dust emissions resulting from fewer screening cycles, as is typical for natural aggregates intended for road construction. The estimated particulate matter formation is 0.000001 disease incidences per tonne of natural aggregates produced.
3.1. Contribution Analysis
The contribution analysis shows which processes in the production chain have the greatest influence on the environmental footprint of natural aggregates. The use of non-road mobile machinery represents an environmental hotspot in the production process of natural aggregates. For example, it contributes to approximately 61% (in the case of natural aggregates for concrete production) or 71% (in the case of aggregates for road construction) of the total GWP impact. Non-road mobile machinery is involved in the processes of drilling (use of a drilling machine), excavation of blasted rock (use of an excavator), pushing the rock down the slope to the base of the quarry (use of a bulldozer), loading the blasted rock fragments onto a conveyor belt (use of a loader), and depositing (use of a loader) after the rock has been screened into the final fractions. These processes are identical in the production of both types of natural aggregates. The use of explosives accounts for approximately 20% of the total GWP impact. The contribution of auxiliary materials (engine oil for the working machines) is minor—less than 1% (Figure 2 and Figure 3). The details have been given in Appendix A (Table A1 and Table A2).
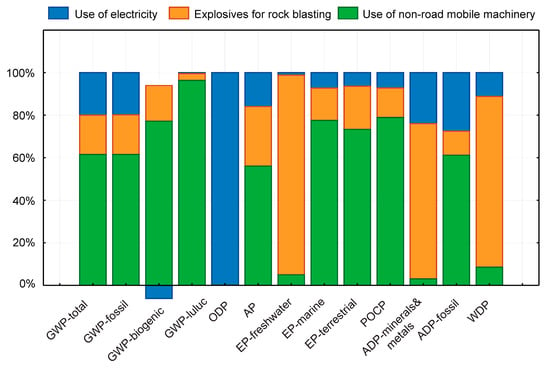
Figure 2.
Relative contributions of different processes to the environmental footprint of natural aggregates for concrete production.
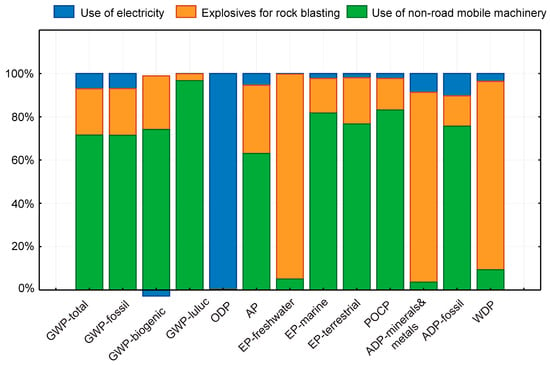
Figure 3.
Relative contributions of different processes to the environmental footprint of natural aggregates for road construction.
The contribution of the processes requiring electricity (e.g., conveying the blasted rock fragments via a conveyor belt and screening) to the total GWP value is 20% for natural aggregates used in concrete production (Figure 2) and significantly less for aggregates used in road construction, e.g., 7% (Figure 3). As shown in Table 1, 1.31 kWh of electricity per tonne of aggregates produced is required for screening blasted rock fragments into fractions suitable for concrete production (fractions 0/2, 2/4, 0/4, 0/8, 4/8, 8/16, and 16/32). In contrast, the extraction and screening of blasted rock fragments into fractions for road construction (0/16, 0/32, 0/63, and 0/125) require significantly less electrical energy, e.g., 0.32 kWh per tonne of aggregates produced. The production of natural aggregates for road construction requires fewer screening processes. The difference in electricity consumption is 84%.
As shown in Figure 2 and Figure 3, the non-road mobile machinery contributes the most to the environmental footprint of natural aggregates in most impact categories. In terms of some impact categories, the environmental hotspot is related to the use of explosives to blast the bedrock (eutrophication of freshwater, water depletion potential, and abiotic depletion of minerals and metals). The effects on these environmental parameters arise upstream, during the production of explosives. The environmental impacts associated with electricity consumption significantly predominate in terms of their potential to deplete the ozone layer. Electricity generated by photovoltaic (PV) solar systems has a relatively high impact on ozone layer depletion potential, approximately 40 times greater than the electricity supplied by the Slovenian grid. This elevated impact primarily originates from the upstream manufacturing processes of PV systems, particularly the production of aluminum frames [45].
In the production of natural aggregates for road construction, processes that require electricity contribute relatively little to other environmental parameters (Figure 3). However, processes that require electrical energy have the greatest potential for environmental optimization of the production process.
3.2. Sensitivity Analysis
- Source of electricity (share of renewable energy from photovoltaics).
The impacts associated with conveying blasted rock fragments via a conveyor belt and the screening of the rock depend on the power source. In the quarry under consideration, 55% of electricity currently comes from solar energy (photovoltaic systems installed in the quarry), and the rest of the electricity (45%) is grid mix, considering the annual demand. A sensitivity analysis was carried out to show the relationship between the different proportions of electricity from the two sources and their environmental impact, which is significantly influenced by the processes powered by electrical energy. Such environmental impacts are the GWP, the acidification potential, the abiotic depletion of fossil resources, and the abiotic depletion of minerals and metals. These parameters were selected for the sensitivity analysis because they account for more than 15% of the total impact on the value of the parameters in the case of natural aggregate production for the concrete industry (Figure 2). In the “best-case scenario”, it is assumed that all electricity is supplied by solar systems, whereas in the “worst-case scenario”, the entire electricity supply is derived from the grid mix. The GWP footprint of 1 tonne of natural aggregates for concrete production varies between 1.35 (“worst-case scenario”) and 0.95 CO2 equiv. (“best-case scenario”). The GWP footprint of 1 tonne of natural aggregates for road construction varies between 1.04 (“worst-case scenario”) and 0.92 CO2 equiv. (“best-case scenario”) (Figure 4a).
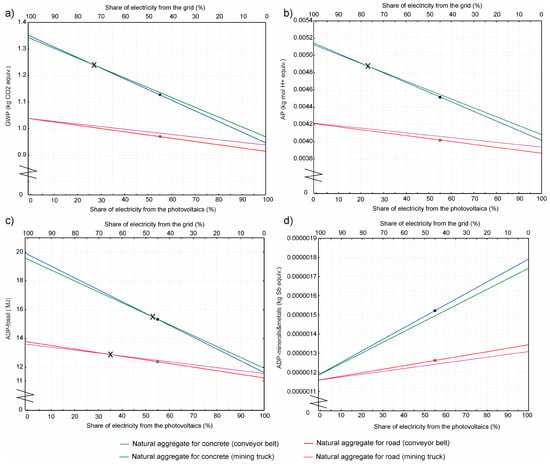
Figure 4.
Sensitivity analysis showing how different proportions of electricity sources affect the environmental footprint of the natural aggregates. (a) Impact on GWP; (b) impact on acidification; (c) impact on abiotic depletion of fossil fuels; and (d) impact on abiotic depletion of minerals and metals. Two scenarios were considered, differing in the mode of transportation for the blasted rock fragments. The dots represent the environmental impact of the aggregates, based on the actual electricity mix (55% solar energy and 45% grid mix). “X” marks the share of electricity allocated to powering the conveyor belt, resulting in equal environmental impact across both scenarios. For more details, see Appendix B.
The sensitivity analysis shows that the power source has a significant impact on the footprint of natural aggregates used in concrete production. Moving from the “worst-case scenario” to the “best-case scenario”, the abiotic depletion of fossil fuels is reduced by 42%, the GWP impact by 30%, and the acidification potential by 22% (Figure 4). These reductions are less significant for natural aggregates for road construction (e.g., 18% in terms of the abiotic depletion of fossil resources, 12% in terms of the GWP, and 8% in terms of the acidification potential), as the demand for electrical energy in the screening processes is also lower.
This study looks at electricity from the Slovenian power grid. This electricity is primarily generated in nuclear power plants (approximately one-third) and hydropower plants (approximately one-third), followed by thermal power plants (approximately 23%) [46]. The latter power plants are among the most polluting and therefore have a significantly high environmental impact, which is reflected in the footprint of the electricity in the grid.
However, electricity from photovoltaics has a greater impact on the abiotic depletion of minerals and metals compared to electricity sourced from a grid mix. For this reason, the so-called “best-case scenario”, which assumes a 100% supply of electricity from solar energy, has an adverse effect on the abiotic depletion of minerals and metals. Specifically, when considering the production of natural aggregates for the concrete industry, the abiotic depletion of minerals and metals increases by 48% compared to a scenario relying solely on grid mix electricity. For the production of natural aggregates used in road construction, the increase is 15% (Figure 4d).
The reason the electricity generated in solar power plants has a significantly high impact on the depletion of minerals and metals is that photovoltaic panels usually contain metals (such as aluminum, copper, lead, and silicon) and rare elements (including indium, gallium, and tellurium). Metals and rare elements are important components of all three generations of photovoltaic panels currently in use [47,48].
- Conveying rocks to the screening plant: conveyor belt versus quarry dump truck.
A conveyor belt is operated exclusively with electricity, whereas a quarry dump truck is operated with diesel fuel. It is assumed that the dump truck (with a 40.6-tonne payload capacity and EURO VI emission standard) travels fully loaded in one direction and returns empty. For natural aggregates intended for concrete production, the LCA results indicate that the conveyor belt scenario has a slightly higher environmental impact when electricity is sourced entirely from the grid. However, this changes when a certain portion of the electricity is supplied by photovoltaics (a renewable energy source), as shown in Figure 4. Considering the actual electricity mix (55% from photovoltaics and 45% from the grid), the conveyor belt becomes the environmentally preferable option compared to the quarry dump truck. The exception is the impact on the abiotic depletion of minerals and metals, where photovoltaic panels contribute significantly to this indicator (Figure 4d).
For natural aggregates used in road construction, the conveyor belt scenario shows a comparable impact to that of the dump truck scenario, even when powered entirely by grid electricity. One exception is the impact on the abiotic depletion of fossil fuels; however, the difference remains slight (Figure 4c). Electricity in Slovenia’s national grid is largely sourced from thermal power plants (23%), contributing to the relatively high environmental impact of grid electricity. As a result, the conveyor belt scenario (powered by 100% grid electricity) shows a higher impact on the abiotic depletion of fossil fuels than the quarry dump truck scenario.
Nevertheless, the change in transportation mode has had a relatively minor effect on the overall LCA results. For instance, when powered by grid electricity, the GWP of aggregates for concrete is only 0.62% higher in the conveyor belt scenario compared to the dump truck scenario. The GWP of both scenarios equalizes when approximately 27% of the conveyor belt’s electricity is sourced from solar energy. At higher photovoltaic shares, the conveyor belt scenario yields a lower GWP (Figure 4a). When powered entirely by solar energy, the GWP difference between the two scenarios reaches 2.4%.
- Sensitivity to diesel combustion factors associated with the use of non-road mobile machinery.
As mentioned, a generic dataset was used as a proxy for all types of non-road mobile machinery. The dataset “Excavator, 500 kW, mining (u-so)” was applied and linked to the dataset “Diesel mix at filling station (aggregated)” (Table 1). The outputs represent combustion emissions from engine operation, including regulated emissions (NOx, CO, hydrocarbons, and particulate matter), fuel-dependent emissions (CO2, SO2, benzene, toluene, and xylene), and other emissions such as CH4 and N2O. Emissions associated with machinery production, end-of-life processes, and the fuel supply chain (including exploration, refining, and transport) are excluded from this LCA [49].
CO2 emissions per liter of diesel are relatively consistent across machinery types, as CO2 output is directly linked to the carbon content of the fuel [50]. Therefore, fuel-dependent emissions are not expected to vary significantly among different types of non-road mobile machinery.
A sensitivity analysis was conducted for regulated emissions (NOx, CO, hydrocarbons, and particulate matter) from non-road mobile machinery [36], assuming a ±20% variation (Figure 5). The results show that these emissions influence the following categories: acidification potential, marine eutrophication potential, terrestrial eutrophication potential, and photochemical ozone formation potential (Figure 5). They do not affect the other nine core impact categories. The sensitivity analysis revealed that a ±20% change in regulated emissions affects acidification potential by ±8%, and marine eutrophication, terrestrial eutrophication, and photochemical ozone formation potentials by 12–13%, based on a cradle-to-gate LCA of natural aggregates for concrete. For natural aggregates used in road construction, environmental performance is slightly more sensitive to ±20% variations in regulated emissions, with acidification potential changing by ±9%, and eutrophication (marine and terrestrial) and photochemical ozone formation potentials by 13–14%. See also Appendix A (Table A3 and Table A4).
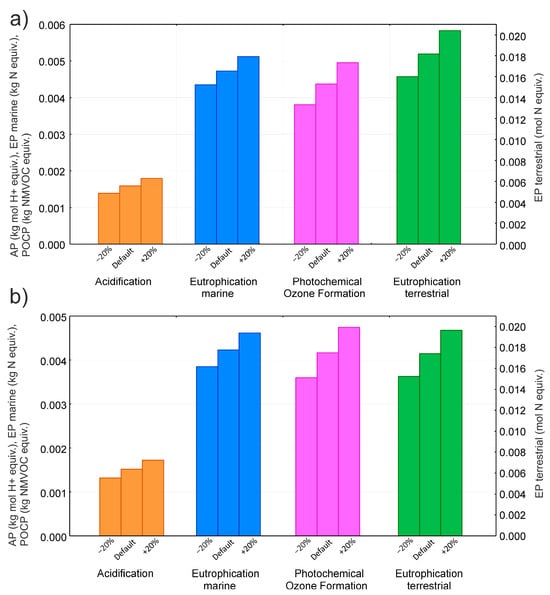
Figure 5.
A sensitivity analysis for regulated emissions (NOx, CO, hydrocarbons, and particulate matter) from non-road mobile machinery, assuming a ±20% variation. (a) Sensitivity considering cradle-to-gate LCA of natural aggregates used in concrete construction; (b) sensitivity considering cradle-to-gate LCA of natural aggregates used in road construction.
4. Conclusions
The possibilities for optimizing the quarrying process in the Poljčane quarry are currently limited. The explosives used to blast the rock will continue to significantly contribute to the environmental footprint of natural aggregates produced in quarries. Processes involving non-road mobile machinery powered by diesel fuel represent an environmental hotspot that accounts for most of the impact categories. Several of the working machines in use are already optimized, including an excavator, a bulldozer, and two loaders. Future technologies based on renewable energy sources and electrification can further improve the environmental performance of quarrying. The most promising future technology seems to be based on fuel cells that use hydrogen as fuel.
The screening process can be powered entirely by electricity from renewable energy sources, such as photovoltaics. The seasonal mismatch between the supply of solar energy and electricity demand can be mitigated by storing surplus electrical energy in batteries. Although lithium-ion batteries represent the most mature and widely adopted technology, their deployment in quarry operations may be economically unfeasible due to high capital costs, long payback periods, and uncertain returns on investment. Other renewable energy sources may become relevant for on-site power generation in the future, such as wind power, hydropower, and energy from biomass incineration. Wind turbines can complement solar generation by producing electricity during periods of low solar irradiance, such as winter or nighttime, thereby improving overall energy reliability. However, site-specific wind assessments are essential, as quarries in Slovenia are often located in valleys or forested areas where wind speeds may be insufficient for economic viability. Hydropower could be feasible in quarries situated near flowing water bodies, while biomass may be considered if organic waste streams are readily available locally. Nevertheless, all of these alternatives typically involve more complex permitting procedures, infrastructure requirements, and ecological risk assessments.
The implementation of optimization measures, such as the adoption of renewable energy sources and advanced battery storage technologies in quarry operations, is influenced by several socio-economic factors. High initial capital investment remains a significant barrier, particularly for operators who may lack access to adequate financing. Policy and regulatory frameworks, including subsidies and incentives, can play a crucial role in supporting adoption. Additionally, the local workforce’s skills and technological readiness impact feasibility, as the deployment of advanced technologies requires specialized expertise for installation, operation, and maintenance.
However, the most important aspect for improving sustainability in the production of aggregates for road construction is the substitution of natural aggregates with secondary and recycled aggregates. Almost complete substitution is possible in the construction of unbound layers and embankments. This approach aligns with the European Circular Economy policy. The partial replacement of natural aggregates with secondary and recycled aggregates in asphalt layers and concrete mixes is also a significant issue for enhancing the sustainability of the construction sector. However, such applications are relatively limited due to the high technical requirements that not all secondary and recycled aggregates fulfill. They also have to meet environmental requirements in terms of leachate emissions when the material comes into contact with water, which is another limitation for secondary aggregates compared to natural aggregates.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: J.T. and A.K.; methodology: J.T., A.K., T.Z.H. and R.C.; software: J.T. and A.K.; validation: A.K.; formal analysis: J.T. and A.K.; investigation: J.T. and A.K.; resources: T.Z.H. and R.C.; data curation: A.K., T.Z.H. and R.C.; writing—original draft: J.T. and A.K.; writing—review and editing: A.K., T.Z.H. and R.C.; supervision: T.Z.H. and R.C.; project administration: J.T., A.K., T.Z.H. and R.C.; funding acquisition: A.K., T.Z.H. and R.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was financially supported by the Slovenian Research and Innovation Agency (research core funding No. P2-0273—Building structures and materials) and DUT partnership: Driving Urban Transitions—Sustainable future for cities project (research core funding No. H2-8299—Circular Approaches in the Built Environment).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Some background data are not publicly available due to privacy restrictions. However, all inventory data necessary to ensure the repeatability of the LCA calculations are provided within this study.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Rok Cajzek and Tjaša Zupančič Hartner were employed by the company GIC GRADNJE d.o.o. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Relative contributions of different processes to the environmental footprint of natural aggregates for concrete production.
Table A1.
Relative contributions of different processes to the environmental footprint of natural aggregates for concrete production.
| Impact Category | Use of Non-Road Mobile Machinery | Explosives for Rock Blasting | Use of Electricity | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GWP—total | 61.5 | 18.5 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| GWP—fossil | 61.5 | 18.7 | 19.8 | 100.0 |
| GWP—biogenic | 77.2 | 28.7 | −5.8 | 100.0 |
| GWP—luluc | 96.3 | 3.3 | 0.4 | 100.0 |
| ODP | 0.09 | 0.05 | 99.86 | 100.0 |
| AP | 56.0 | 28.1 | 15.9 | 100.0 |
| EP—freshwater | 5.0 | 93.8 | 1.2 | 100.0 |
| EP—marine | 77.6 | 15.1 | 7.3 | 100.0 |
| EP—terrestrial | 73.3 | 20.3 | 6.4 | 100.0 |
| POCP | 78.9 | 13.8 | 7.2 | 100.0 |
| ADP—minerals and metals | 3.0 | 73.0 | 24.0 | 100.0 |
| ADP—fossil | 61.2 | 11.3 | 27.5 | 100.0 |
| WDP | 8.6 | 80.2 | 11.2 | 100.0 |

Table A2.
Relative contributions of different processes to the environmental footprint of natural aggregates for road construction.
Table A2.
Relative contributions of different processes to the environmental footprint of natural aggregates for road construction.
| Impact Category | Use of Non-Road Mobile Machinery | Explosives for Rock Blasting | Use of Electricity | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GWP—total | 71.5 | 21.4 | 7.1 | 100.0 |
| GWP—fossil | 71.3 | 21.6 | 7.0 | 100.0 |
| GWP—biogenic | 74.2 | 27.6 | −1.7 | 100.0 |
| GWP—luluc | 96.61 | 3.26 | 0.13 | 100.0 |
| ODP | 0.32 | 0.18 | 99.5 | 100.0 |
| AP | 63.0 | 31.5 | 5.5 | 100.0 |
| EP—freshwater | 5.0 | 94.6 | 0.4 | 100.0 |
| EP—marine | 81.7 | 15.9 | 2.3 | 100.0 |
| EP—terrestrial | 76.7 | 21.2 | 2.0 | 100.0 |
| POCP | 83.1 | 14.6 | 2.3 | 100.0 |
| ADP—minerals and metals | 3.6 | 87.6 | 8.8 | 100.0 |
| ADP—fossil | 75.7 | 14.0 | 10.4 | 100.0 |
| WDP | 9.3 | 87.0 | 3.7 | 100.0 |

Table A3.
Sensitivity analysis of LCA results for natural aggregates used in concrete, considering a ±20% variation in regulated emissions (NOx, CO, hydrocarbons, and particulate matter) from non-road mobile machinery.
Table A3.
Sensitivity analysis of LCA results for natural aggregates used in concrete, considering a ±20% variation in regulated emissions (NOx, CO, hydrocarbons, and particulate matter) from non-road mobile machinery.
| Impact Category | −20% Emissions | Default Emissions | +20% Emissions |
|---|---|---|---|
| AP | 0.00435 | 0.00473 | 0.00512 |
| EP—marine | 0.00139 | 0.00159 | 0.00179 |
| EP—terrestrial | 0.01600 | 0.01816 | 0.02040 |
| POCP | 0.00381 | 0.00437 | 0.00495 |

Table A4.
Sensitivity analysis of LCA results for natural aggregates used in road construction, considering a ±20% variation in regulated emissions (NOx, CO, hydrocarbons, and particulate matter) from non-road mobile machinery.
Table A4.
Sensitivity analysis of LCA results for natural aggregates used in road construction, considering a ±20% variation in regulated emissions (NOx, CO, hydrocarbons, and particulate matter) from non-road mobile machinery.
| Impact Category | −20% Emissions | Default Emissions | +20% Emissions |
|---|---|---|---|
| AP | 0.00385 | 0.00423 | 0.00462 |
| EP—marine | 0.00132 | 0.00152 | 0.00172 |
| EP—terrestrial | 0.01524 | 0.01740 | 0.01964 |
| POCP | 0.00360 | 0.00416 | 0.00474 |
Appendix B
The following formulae are used to calculate the global warming potential (GWP), acidification potential (AP), abiotic depletion potential of fossil fuels (ADP_fossil), and abiotic depletion potential of minerals and metals (ADP_minerals&metals), considering varying proportions of electricity sources (solar energy and grid mix). Two scenarios were considered in the sensitivity analysis, differing in the mode of transportation for blasted rock fragments (i) scenario with conveyor belt and (ii) scenario with quarry dump truck. The formulae correspond to Figure 4. The variable “X” represents the proportion of electricity sourced from solar photovoltaic panels.
Natural aggregates for concrete production (scenario with conveyor belt):
Natural aggregates for concrete production (scenario with quarry dump truck):
Natural aggregates for road construction (scenario with conveyor belt):
Natural aggregates for road construction (scenario with quarry dump truck):
References
- Langer, W. 9—Sustainability of aggregates in construction. In Sustainability of Construction Materials, 2nd ed.; Khatib, J.M., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2016; pp. 181–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drew, L.J.; Langer, W.H.; Sachs, J.S. Environmentalism and Natural Aggregate Mining. Nat. Resour. Res. 2002, 11, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- British Geological Survey. Construction Aggregates. Mineral Planning Factsheet 2013. Available online: https://www.nottinghamshire.gov.uk/media/120400/nd9-mineral-factsheet-construction-aggregates-june-2013.pdf (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Vijerathne, D.; Wahala, S.; Illankoon, C. Impact of Crushed Natural Aggregate on Environmental Footprint of the Construction Industry: Enhancing Sustainability in Aggregate Production. Buildings 2024, 14, 2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capasso, I.; Lirer, S.; Flora, A.; Ferone, C.; Cioffi, R.; Caputo, D.; Liguori, B. Reuse of mining waste as aggregates in fly ash-based geopolymers. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 220, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voit, K.; Kuschel, E. Rock Material Recycling in Tunnel Engineering. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnuaim, A.; Abbas, Y.M.; Khan, M.I. Sustainable application of processed TBM excavated rock material as green structural concrete aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 274, 121245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segui, P.; Safhi, A.M.; Amrani, M.; Benzaazoua, M. Mining Wastes as Road Construction Material: A Review. Minerals 2023, 13, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Xu, G.; Cheng, H.; Wang, J.; Wan, Y.; Chen, H. An Overview of Utilization of Steel Slag. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2012, 16, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, J.; Cotič, Z.; Mladenovič, A.; Šajna, A. Environmental evaluation of green concretes versus conventional concrete by means of LCA. Waste Manag. 2015, 45, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, B.; Kumar, P. Waste foundry sand in concrete: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 156, 661–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Shen, A.; Yang, X.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Y. A review of steel slag as a substitute for natural aggregate applied to cement concrete. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2022, 24, 537–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ding, L.; Li, F.; Peng, J. Recycled aggregates from construction and demolition wastes as alternative filling materials for highway subgrades in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 255, 120223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, G.S.d.; Quattrone, M.; Ambrós, W.M.; Grigore Cazacliu, B.; Hoffmann Sampaio, C. Current Applications of Recycled Aggregates from Construction and Demolition: A Review. Materials 2021, 14, 1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tost, M.; Ammerer, G. Sustainable Supply of Aggregates in Europe—An Assessment of “Non-Critical” but Essential Raw Materials with Focus on Policy and Permitting Elements; Final Report 12/2022; Commissioned by Aggregates Europe—UEPG: Leoben, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Delgado, L.; Catarino, A.S.; Eder, P.; Litten, D.; Luo, Z.; Villanueva, A. JRC 2009: End-of-Waste Criteria (Final Report); Office for Official Publications of the European Communities: Luxembourg, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- EU. Directive (EU) 2024/1785 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 24 April 2024 Amending Directive 2010/75/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council on Industrial Emissions (Integrated Pollution Prevention and Control) and Council Directive 1999/31/EC on the Landfill of Waste (Text with EEA Relevance) 2024; European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Muchová, L.; Eder, P. End-of-Waste Criteria for Iron and Steel Scrap: Technical Proposals; JRC Scientific and Policy Reports 2010; European Commission: Luxembourg; Office for Official Publications of the European Communities: Luxembourg, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez Vieitez, E.; Eder, P.; Villanueva, A.; Saveyn, H. End-of-Waste Criteria for Glass Cullet: Technical Proposals; JRC Scientific and Policy Reports 2011; European Commission: Luxembourg; Office for Official Publications of the European Communities: Luxembourg, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Saveyn, H.; Eder, P. End-of-Waste Criteria for Biodegradable Waste Subjected to Biological Treatment (Compost & Digestate): Technical Proposals; JRC Scientific and Policy Reports 2014; European Commission: Luxembourg; Office for Official Publications of the European Communities: Luxembourg, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zorpas, A.A. Sustainable waste management through end-of-waste criteria development. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 7376–7389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UEPG. UEPG Guidance: End of Waste Criteria For Recycled Aggregates From Construction & Demolition Waste; European Aggregates Association 2022; UEPG: Brussels, Belgium, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Reetsch, A.; Tessien, J.; Schröder, N.; van ‘t Zelfde, J.; Ooms, J.; van Bruggen, R.; Lundberg, P.; Zamparutti, T. Background Data Collection for Future EU EoW Criteria of Construction and Demolition Waste—GROW/2022/OP/0015; Deliverable 3 ‘Final Report on Analysis, Conclusion and Recommendations (Task 3)’ 2024; European Commission, Directorate-General for Internal Market, Industry, Entrepreneurship and SMEs: Brussels, Belgium, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- UEPG. Annual Review 2020–2021. European Aggregates Association 2021; UEPG: Brussels, Belgium, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ioannidou, D.; Meylan, G.; Sonnemann, G.; Habert, G. Is gravel becoming scarce? Evaluating the local criticality of construction aggregates. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 126, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EU No 305/2011 2024; Regulation (EU) 2024/3110 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 27 November 2024 Laying Down Harmonised Rules for the Marketing of Construction Products and Repealing Regulation (EU). European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2024.
- Zhang, A.; Seuring, S. Digital product passport for sustainable and circular supply chain management: A structured review of use cases. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2024, 27, 2513–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortoli de, A. Understanding the environmental impacts of virgin aggregates: Critical literature review and primary comprehensive life cycle assessments. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 415, 137629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.U.; Poon, C.S.; Lo, I.M.C.; Cheng, J.C.P. Comparative environmental evaluation of aggregate production from recycled waste materials and virgin sources by LCA. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2016, 109, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, M.; Abbasi, A.M.; Ravanshadnia, M. Production of natural and recycled aggregates: The environmental impacts of energy consumption and CO2 emissions. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2018, 20, 810–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Arguelles, G.; Acosta, M.P.; Dugarte, M.; Fuentes, L. Life cycle assessment of natural and recycled concrete aggregate production for road pavements applications in the northern region of Colombia: Case study. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2019, 2673, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Luo, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xiao, J. A review of life cycle assessment of recycled aggregate concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 209, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 12620: 2013; Aggregates for Concrete. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2013.
- EN ISO 14040:2006; Environmental Management—Life Cycle Assessment—Principles and Framework (EN ISO 14040:2006). European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2006.
- EN 15804:2012+A2:2019; Sustainability of Construction Works—Environmental Product Declarations—Core Rules for the Product Category of Construction Products. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2019.
- European Environment Agency. EMEP/EEA Air Pollutant EMISSION Inventory Guidebook 2023. Technical Guidance to Prepare National Emission Inventories. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/en/analysis/publications/emep-eea-guidebook-2023/part-b-sectoral-guidance-chapters/2-industrial-processes-and-product-use/2-d-2-l-other/2-d-3-i-2/@@download/file (accessed on 16 September 2025).
- Oever van den, A.; Costa, D.; Messagie, M. Revisiting the challenges of ozone depletion from a prospective LCA perspective. Qeios 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oever van den, A.E.M.; Puricelli, S.; Costa, D.; Thonemann, N.; Lavigne Philippot, M.; Messagie, M. Revisiting the challenges of ozone depletion in life cycle assessment. Clean. Environ. Syst. 2024, 13, 100196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, C.; Freire, F.; Ribeiro, J. Life-cycle assessment of a civil explosive. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 89, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPD. Environmental Product Declaration for Limestone Aggregates Xiorema Quarry 2022; EPD International: Stockholm, Sweden, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- EPD. Environmental Product Declaration of Limestone Aggregates Mesaio Quarry 2023; EPD International: Stockholm, Sweden, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kayabaşı, A.; Soypak, R.; Göz, E. Evaluation of limestone quarries for concrete and asphalt production: A case study from Ankara, Turkey. Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmi, E.F.; Sellers, E.J. A review of the methods to incorporate the geological and geotechnical characteristics of rock masses in blastability assessments for selective blast design. Eng. Geol. 2021, 281, 105970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotto, M.S.; Pourrahimian, Y. The Influence of Explosive and Rock Mass Properties on Blast Damage in a Single-Hole Blasting. Mining 2024, 4, 168–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuzaid, H.; Samara, F. Environmental and Economic Impact Assessments of a Photovoltaic Rooftop System in the United Arab Emirates. Energies 2022, 15, 8765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEA. 2023. Available online: https://www.iea.org/countries/slovenia (accessed on 6 August 2025).
- Grandell, L.; Höök, M. Assessing Rare Metal Availability Challenges for Solar Energy Technologies. Sustainability 2015, 7, 11818–11837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, Y.; Tay, Y.B.; Pham, H.K.; Mathews, N. A facile crush-and-sieve treatment for recycling end-of-life photovoltaics. Waste Manag. 2023, 156, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://lcadatabase.sphera.com/2025/xml-data/processes/2dbe076f-4a31-4348-a36a-bedf27f56715.xml (accessed on 26 September 2025).
- Babamohammadi, S.; Birss, A.R.; Pouran, H.; Pandhal, J.; Borhani, T.N. Emission control and carbon capture from diesel generators and engines: A decade-long perspective. Carbon Capture Sci. Technol. 2025, 14, 100379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).