Frequency-Domain Importance-Based Attack for 3D Point Cloud Object Tracking
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We develop a frequency-domain attack method that targets low-frequency components, utilizing a saliency map to enhance perturbation in critical sub-bands, improving attack effectiveness and generalization.
- On the KITTI dataset, our approach effectively reduces P2B tracking performance in white-box attacks and demonstrates robust transferability to black-box models, significantly impacting their performance.
2. Related Works
2.1. 3D Point Cloud Object Tracking
2.2. Adversarial Attack for 3D Point Cloud Object Tracking
3. Methodology
3.1. Problem Setting and Framework
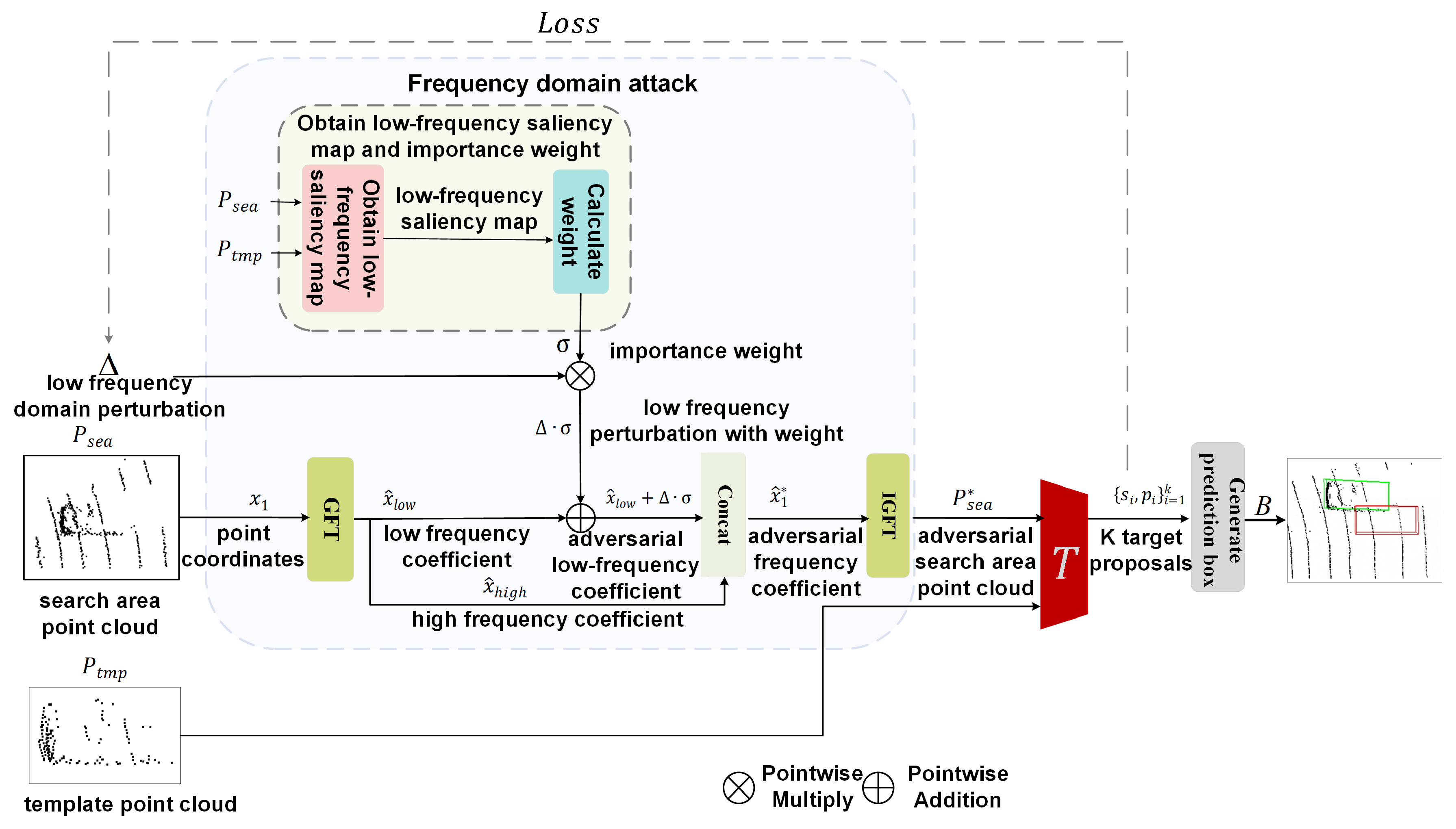
3.2. Frequency-Domain Attack Module Based on Frequency Band Importance
| Algorithm 1: Generate frequency band saliency map |
| Input: template point cloud , search area point cloud , tracking model T, ground-truth bounding box , low band range , sub-band length m Output: frequency band saliency map
|
3.3. Optimization
| Algorithm 2: Optimize frequency perturbation based on sub-band importance |
| Input: search area point cloud , frequency coefficients and , frequency band saliency map , maximum iterations T Output: adversarial point cloud
|
4. Experiments
4.1. Experiment Settings
4.2. Comprehensive Comparisons
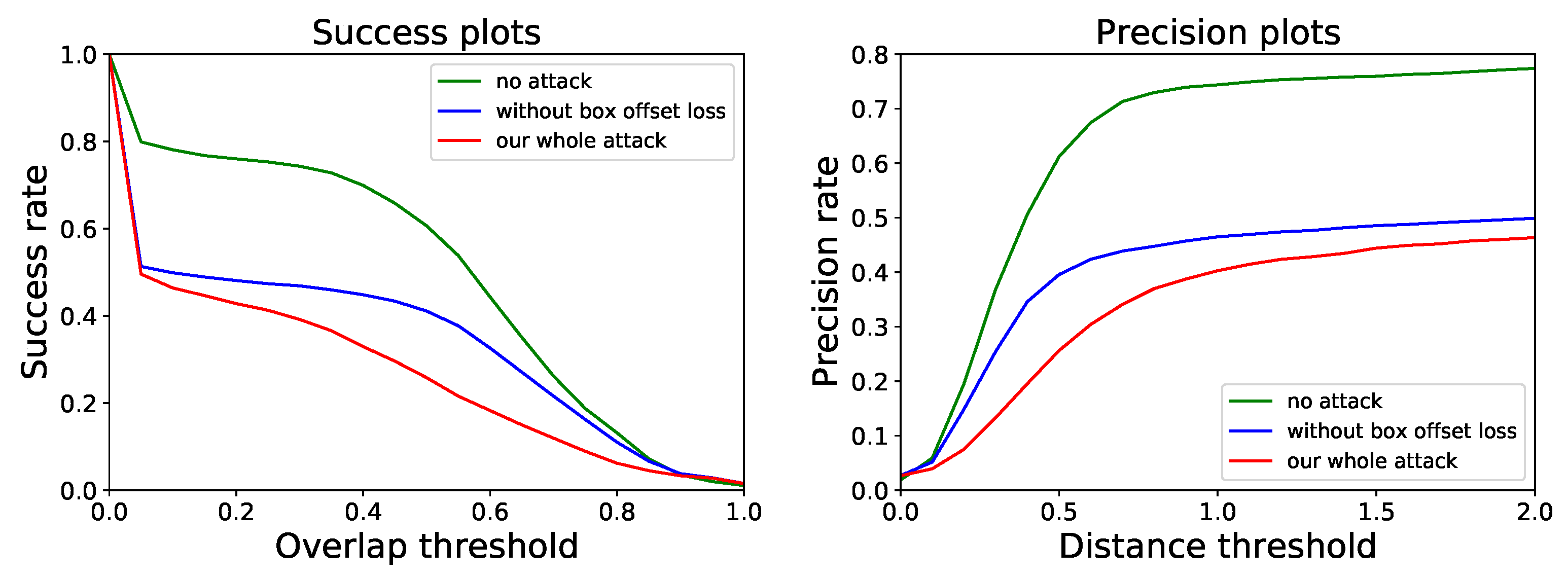
4.3. Ablation Study
4.4. Visualization Result
4.5. Defensive Strategies and Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, W.; Yang, B.; Urtasun, R. Fast and furious: Real time end-to-end 3d detection, tracking and motion forecasting with a single convolutional net. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 3569–3577. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, O.; Joo, K.; Sim, J.Y. Learning-Based Reflection-Aware Virtual Point Removal for Large-Scale 3D Point Clouds. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2023, 8, 8510–8517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingle, P.Y.; Kim, Y.G. Multiview abnormal video synopsis in real-time. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 123, 106406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Wu, J.; Cui, Y.; Hu, H. Multi-object tracking based on a novel feature image with multi-modal information. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2023, 72, 9909–9921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, K.; Kim, S.; Kwon, H. Selective Audio Perturbations for Targeting Specific Phrases in Speech Recognition Systems. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2025, 18, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Sohel, F.; Bennamoun, M.; Liao, Y.; Yu, J. Adversary distillation for one-shot attacks on 3D target tracking. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022-2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Virtual, 7–13 May 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 2749–2753. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Lin, Y.; Yang, Q.; Fan, H. Transferable adversarial attack on 3D object tracking in point cloud. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Multimedia Modeling, Nara, Japan, 8–10 January 2025; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 446–458. [Google Scholar]
- Ilyas, A.; Santurkar, S.; Tsipras, D.; Engstrom, L.; Tran, B.; Madry, A. Adversarial examples are not bugs, they are features. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 32, 125–136. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.Q.J.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, Y. Training behavior of deep neural network in frequency domain. In Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing: 26th International Conference, ICONIP 2019, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 12–15 December 2019; Proceedings, Part I 26. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 264–274. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Yu, A.W.; Meng, T.; Caine, B.; Ngiam, J.; Peng, D.; Shen, J.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, D.; Le, Q.V.; et al. Deepfusion: Lidar-camera deep fusion for multi-modal 3d object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 17182–17191. [Google Scholar]
- Giancola, S.; Zarzar, J.; Ghanem, B. Leveraging shape completion for 3d siamese tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 1359–1368. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, H.; Feng, C.; Cao, Z.; Zhao, F.; Xiao, Y. P2b: Point-to-box network for 3d object tracking in point clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 6329–6338. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Yan, J.; Wu, W.; Zhu, Z.; Hu, X. High performance visual tracking with siamese region proposal network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 8971–8980. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, C.; Yan, X.; Gao, J.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, W.; Li, Z.; Cui, S. Box-aware feature enhancement for single object tracking on point clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 13199–13208. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.; Luo, Z.; Luo, Y.; Liu, T.; Pan, L.; Cai, Z.; Zhao, H.; Lu, S. Pttr: Relational 3d point cloud object tracking with transformer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 8531–8540. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Z.; Zhou, C.; Pan, L.; Zhang, G.; Liu, T.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Z.; Lu, S. Exploring point-bev fusion for 3d point cloud object tracking with transformer. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2024, 46, 5921–5935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.X.; Guo, Y.C.; Lai, Y.K.; Zhang, S.H. CXTrack: Improving 3D point cloud tracking with contextual information. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 1084–1093. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, C.; Yan, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, B.; Cheng, S.; Cui, S.; Li, Z. Beyond 3d siamese tracking: A motion-centric paradigm for 3d single object tracking in point clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 8111–8120. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, R.; Sang, N.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X. Non-rigid transformation based adversarial attack against 3d object tracking. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022-2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Virtual, 7–13 May 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 2744–2748. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.; Frank, J.S.; Weinberger, K.Q. Low Frequency Adversarial Perturbation. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Fifth Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence, UAI 2019, Tel Aviv, Israel, 22–25 July 2019; Globerson, A., Silva, R., Eds.; AUAI Press: Corvallis, OR, USA, 2019. Proceedings of Machine Learning Research. Volume 115, pp. 1127–1137. [Google Scholar]
- Long, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zeng, B.; Gao, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Song, J. Frequency domain model augmentation for adversarial attack. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 549–566. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, X.; Tao, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhou, P.; Qu, X.; Dong, J.; Tang, K.; Sun, L. Frequency-aware gan for imperceptible transfer attack on 3d point clouds. In Proceedings of the 32nd ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 28 October–1 November 2024; pp. 6162–6171. [Google Scholar]
- Shuman, D.I.; Narang, S.K.; Frossard, P.; Ortega, A.; Vandergheynst, P. The emerging field of signal processing on graphs: Extending high-dimensional data analysis to networks and other irregular domains. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2013, 30, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, D.K.; Vandergheynst, P.; Gribonval, R. Wavelets on graphs via spectral graph theory. Appl. Comput. Harmon. Anal. 2011, 30, 129–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yan, X.; Zheng, F.; Jiang, Y.; Xia, S.T.; Zhao, Y.; Ji, R. One-shot adversarial attacks on visual tracking with dual attention. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 10176–10185. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, C.; Qi, C.R.; Li, B. Generating 3d adversarial point clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 9136–9144. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, H.; Su, H.; Guibas, L.J. A point set generation network for 3d object reconstruction from a single image. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 605–613. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, R.; Zhang, A.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, B.; El Saddik, A. Adversarial Geometric Attacks for 3D Point Cloud Object Tracking. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2025, 27, 3144–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiger, A.; Lenz, P.; Urtasun, R. Are we ready for autonomous driving? In the kitti vision benchmark suite. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 3354–3361. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Lim, J.; Yang, M.H. Online object tracking: A benchmark. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 2411–2418. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Yang, J.; Sun, K.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Salzmann, M. Mixcycle: Mixup assisted semi-supervised 3d single object tracking with cycle consistency. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 13956–13966. [Google Scholar]
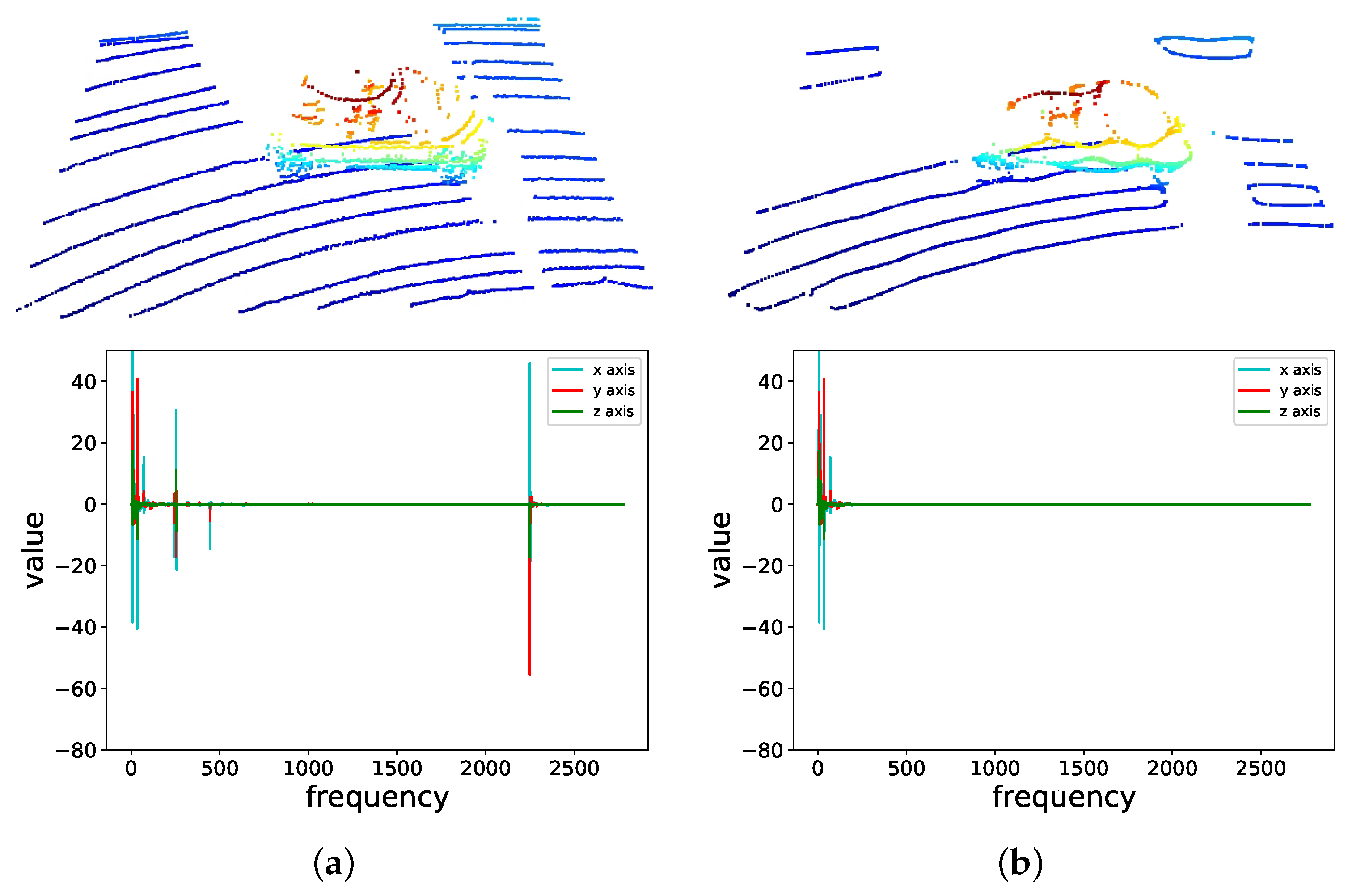

| Retained Frequency Band | Success (%) | Precision (%) |
|---|---|---|
| first 1/5 band | 39.6 | 48.8 |
| first 1/4 band | 40.0 | 49.6 |
| first 1/3 band | 46.0 | 57.5 |
| whole band | 53.3 | 68.4 |
| Metrics | Tracker | KITTI | NuScenes | Type | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ori | Random | Ours | Ori | Random | Ours | |||
| Success (%) | P2B [12] | 53.3 | 48.9 | 28.9 | 39.0 | 37.0 | 27.3 | W |
| BAT [14] | 65.3 | 55.2 | 48.7 | 40.3 | 39.6 | 31.0 | B | |
| M2Track [18] | 67.4 | 53.8 | 50.9 | 57.2 | 54.2 | 50.2 | B | |
| MixCycle [31] | 45.1 | 42.7 | 34.6 | 34.2 | 33.1 | 28.6 | B | |
| Precision (%) | P2B [12] | 68.4 | 62.5 | 35.0 | 39.9 | 37.4 | 26.5 | W |
| BAT [14] | 78.8 | 73.0 | 57.1 | 43.4 | 40.0 | 31.2 | B | |
| M2Track [18] | 81.0 | 72.2 | 61.4 | 65.7 | 61.3 | 50.2 | B | |
| MixCycle [31] | 58.8 | 55.1 | 44.6 | 35.8 | 33.8 | 28.8 | B | |
| Metrics | Tracker | KITTI | NuScenes | Type | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ori | Random | Ours | Ori | Random | Ours | |||
| Success (%) | BAT [14] | 65.3 | 55.2 | 29.5 | 40.3 | 39.6 | 25.1 | W |
| P2B [12] | 53.3 | 48.9 | 39.8 | 39.0 | 37.0 | 33.7 | B | |
| M2Track [18] | 67.4 | 53.8 | 51.5 | 57.2 | 54.2 | 49.3 | B | |
| MixCycle [31] | 45.1 | 42.7 | 37.1 | 34.2 | 33.1 | 29.0 | B | |
| Precision (%) | BAT [14] | 78.8 | 73.0 | 35.2 | 43.4 | 40.0 | 26.3 | W |
| P2B [12] | 68.4 | 62.5 | 49.4 | 39.9 | 37.4 | 32.2 | B | |
| M2Track [18] | 81.0 | 72.2 | 68.2 | 65.7 | 61.3 | 52.0 | B | |
| MixCycle [31] | 58.8 | 55.1 | 46.0 | 35.8 | 33.8 | 28.3 | B | |
| Metrics | Tracker | KITTI | NuScenes | Type | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ori | Random | Ours | Ori | Random | Ours | |||
| Success (%) | MixCycle [31] | 45.1 | 42.7 | 28.2 | 34.2 | 33.1 | 22.3 | W |
| P2B [12] | 53.3 | 48.9 | 37.5 | 39.0 | 37.0 | 28.5 | B | |
| BAT [14] | 65.3 | 55.2 | 46.2 | 40.3 | 39.6 | 30.5 | B | |
| M2Track [18] | 67.4 | 53.8 | 50.3 | 57.2 | 54.2 | 45.5 | B | |
| Precision (%) | MixCycle [31] | 58.8 | 55.1 | 35.0 | 35.8 | 33.8 | 23.5 | W |
| P2B [12] | 68.4 | 62.5 | 46.3 | 39.9 | 37.4 | 30.0 | B | |
| BAT [14] | 78.8 | 73.0 | 55.0 | 43.3 | 40.0 | 35.6 | B | |
| M2Track [18] | 81.0 | 72.2 | 65.6 | 65.7 | 61.3 | 52.0 | B | |
| Confidence Loss | Bounding-Box Offset Loss | KITTI | NuScenes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Success (%) | Precision (%) | Success (%) | Precision (%) | ||
| ✓ | ✗ | 34.0 | 40.2 | 37.6 | 31.2 |
| ✓ | ✓ | 28.9 | 35.0 | 27.3 | 26.5 |
| Hyper-Parameter | KITTI | NuScenes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Success (%) | Precision (%) | Success (%) | Precision (%) | |
| 0 | 32.5 | 40.8 | 32.8 | 33.2 |
| 1 | 31.6 | 39.2 | 30.6 | 30.8 |
| 1.5 | 28.9 | 35.0 | 27.3 | 26.5 |
| KITTI | NuScenes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Success (%) | Precision (%) | Success (%) | Precision (%) | |
| 32.8 | 41.0 | 31.6 | 40.5 | |
| 31.4 | 38.9 | 30.8 | 37.6 | |
| 30.5 | 35.8 | 28.5 | 35.0 | |
| 28.9 | 35.0 | 27.3 | 26.5 | |
| 28.4 | 34.6 | 27.1 | 34.3 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, A.; Zhang, A.; Wang, L.; Yao, R. Frequency-Domain Importance-Based Attack for 3D Point Cloud Object Tracking. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 10682. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910682
Ma A, Zhang A, Wang L, Yao R. Frequency-Domain Importance-Based Attack for 3D Point Cloud Object Tracking. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(19):10682. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910682
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Ang, Anqi Zhang, Likai Wang, and Rui Yao. 2025. "Frequency-Domain Importance-Based Attack for 3D Point Cloud Object Tracking" Applied Sciences 15, no. 19: 10682. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910682
APA StyleMa, A., Zhang, A., Wang, L., & Yao, R. (2025). Frequency-Domain Importance-Based Attack for 3D Point Cloud Object Tracking. Applied Sciences, 15(19), 10682. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910682






