LM3D: Lightweight Multimodal 3D Object Detection with an Efficient Fusion Module and Encoders †
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose three efficient modules (DWLE, ELIF, and MCPT), which enable lightweight yet accurate multimodal 3D object detection by reducing computational cost and enhancing feature representation.
- Our method improves 3D detection accuracy (mAP) compared to baseline approaches, providing robust and discriminative feature representations even in complex driving scenarios.
- The proposed LM3D achieves higher inference speed (FPS) while maintaining competitive accuracy, resulting in a superior trade-off among accuracy, efficiency, and model size compared to existing methods.
2. Related Work
2.1. Camera-Based 3D Object Detection
2.2. LiDAR-Based 3D Object Detection
2.3. Multimodal 3D Object Detection
3. Method
3.1. Overall Architecture
3.2. DepthWise Lightweight Encoder (DWLE) Module
- Depthwise Convolution (DW): Performs spatial convolution independently on each input channel.
- Pointwise Convolution (PW): Applies a convolution to integrate information across channels.
3.3. Efficient LiDAR Image Fusion (ELIF) Module
3.4. Mixture of CNN and Point Transformer (MCPT) Module
- CNN Branch: A convolutional layer is used to extract localized geometric features. Batch Normalization and ReLU activation follow to stabilize and transform the feature maps.
- Point Transformer Branch: This branch employs a point-based transformer architecture to capture long-range dependencies and spatial context based on self-attention mechanisms.
3.5. Overall Loss Function
4. Experimental Setup
4.1. Datasets
4.2. Network Training
4.3. Evaluation Metrics
5. Experiments
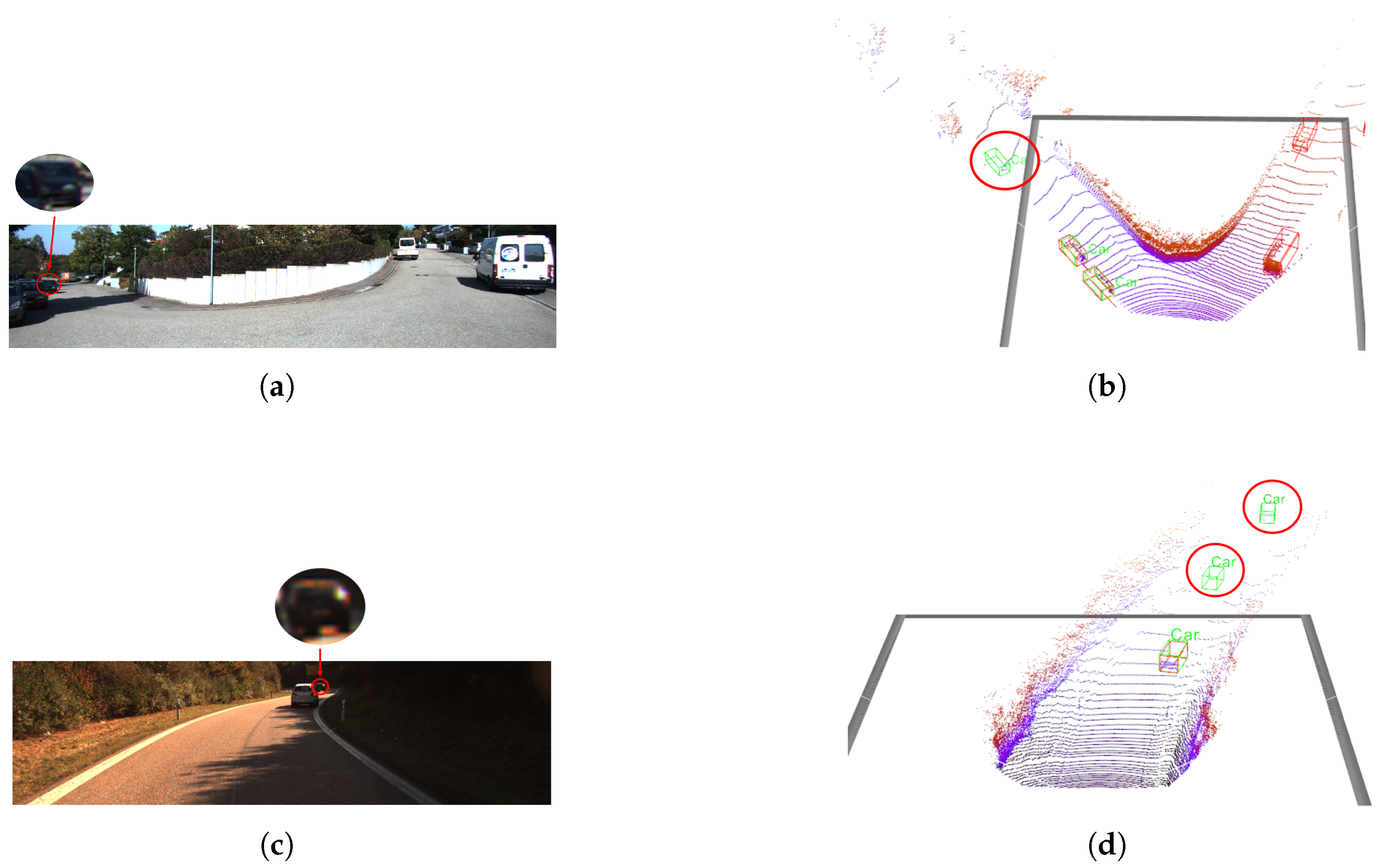
5.1. Main Results on KITTI
5.2. Results on the nuScenes Night-Time Subset
5.3. Ablation Study
5.4. Placement Strategy of MCPT Module
5.5. Kernel Size Strategy of MCPT Module
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2012, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16 × 16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.; Shi, S.; Wang, X.; Li, H. 3D object detection for autonomous driving: A comprehensive survey. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2023, 131, 1909–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Kong, X.; Nishikawa, H.; Lian, Q.; Tomiyama, H. Dynamic Point-Pixel Feature Alignment for Multimodal 3-D Object Detection. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 11327–11340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Mao, Q.; Zhu, H.; Deng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y. Multi-modal 3D object detection in autonomous driving: A survey. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2023, 131, 2122–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yu, A.W.; Meng, T.; Caine, B.; Ngiam, J.; Peng, D.; Shen, J.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, D.; Le, Q.V.; et al. Deepfusion: Lidar-camera deep fusion for multi-modal 3D object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 17182–17191. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, C.R.; Liu, W.; Wu, C.; Su, H.; Guibas, L.J. Frustum pointnets for 3D object detection from rgb-d data. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 918–927. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Ma, T.; Hou, Y.; Shi, B.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, X.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.; Qiao, Y.; et al. Logonet: Towards accurate 3D object detection with local-to-global cross-modal fusion. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 17524–17534. [Google Scholar]
- Sakai, Y.; Shimada, T.; Kong, X.; Tomiyama, H. MCPT: Mixture of CNN and Point Transformer for Multimodal 3D Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 40th International Technical Conference on Circuits/Systems, Computers, and Communications (ITC-CSCC), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 7–10 July 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; He, Y.; Zhu, H.; Wang, C.; Li, H.; Jiang, Q. Monocular 3D object detection: An extrinsic parameter free approach. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 7556–7566. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Sun, F.; Huang, W. Fine-grained multilevel fusion for anti-occlusion monocular 3D object detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 31, 4050–4061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Huo, Y.; Yi, H.; Wang, Z.; Shi, J.; Lu, Z.; Luo, P. Learning depth-guided convolutions for monocular 3D object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 1000–1001. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, W.; Xu, B.; Chen, Z. Monofenet: Monocular 3D object detection with feature enhancement networks. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 29, 2753–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Wang, J.; Lu, Y. Monogrnet: A general framework for monocular 3D object detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 44, 5170–5184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Chen, X.; Shen, S. Stereo r-cnn based 3D object detection for autonomous driving. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 7644–7652. [Google Scholar]
- You, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chao, W.-L.; Garg, D.; Pleiss, G.; Hariharan, B.; Campbell, M.; Weinberger, K.Q. Pseudo-LiDAR++: Accurate Depth for 3D Object Detection in Autonomous Driving. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), Virtual Only Conference, 26 April–1 May 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, E.; Al-Jarrah, O.Y.; Dianati, M.; Fallah, S.; Oxtoby, D.; Mouzakitis, A. A survey on 3D object detection methods for autonomous driving applications. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2019, 20, 3782–3795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Wang, X.; Li, H. Pointrcnn: 3D object proposal generation and detection from point cloud. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 770–779. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, C.R.; Yi, L.; Su, H.; Guibas, L.J. Pointnet++: Deep hierarchical feature learning on point sets in a metric space. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, C.R.; Litany, O.; He, K.; Guibas, L.J. Deep Hough Voting for 3D Object Detection in Point Clouds. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.09664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Mao, Y.; Li, B. SECOND: Sparsely Embedded Convolutional Detection. Sensors 2018, 18, 3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, A.H.; Vora, S.; Caesar, H.; Zhou, L.; Yang, J.; Beijbom, O. Pointpillars: Fast encoders for object detection from point clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 12697–12705. [Google Scholar]
- Vora, S.; Lang, A.H.; Helou, B.; Beijbom, O. Pointpainting: Sequential fusion for 3D object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 4604–4612. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Peng, L.; Yang, H.; Xie, L.; Huang, C.; Deng, C.; Liu, H.; Cai, D. Sparse fuse dense: Towards high quality 3D detection with depth completion. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 5418–5427. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Cai, G.; Song, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zeng, B.; Li, J.; Wang, Z. LVP: Leverage Virtual Points in Multimodal Early Fusion for 3-D Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 5700415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Qiu, B.; Khong, A.W. ViKIENet: Towards Efficient 3D Object Detection with Virtual Key Instance Enhanced Network. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Conference, Nashville, TN, USA, 10–17 June 2025; pp. 11844–11853. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, S.; Morris, D.; Radha, H. CLOCs: Camera-LiDAR object candidates fusion for 3D object detection. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 24 October–24 January 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 10386–10393. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Tang, H.; Amini, A.; Yang, X.; Mao, H.; Rus, D.L.; Han, S. Bevfusion: Multi-task multi-sensor fusion with unified bird’s-eye view representation. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), London, UK, 29 May–2 June 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 2774–2781. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Hou, J.; Yuan, Y.; Xing, G. Unleash the potential of image branch for cross-modal 3D object detection. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2023, 36, 51562–51583. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, T.; Liu, Z.; Chen, X.; Bai, X. Epnet: Enhancing point features with image semantics for 3D object detection. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Proceedings, Part XV 16. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 35–52. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Huang, T.; Li, B.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Bai, X. EPNet++: Cascade bi-directional fusion for multi-modal 3D object detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 45, 8324–8341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. Mobilenets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, B.; Zhu, P.; Li, P.; Zuo, W.; Hu, Q. ECA-Net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11534–11542. [Google Scholar]
- Dutta, P.; Sathi, K.A.; Hossain, M.A.; Dewan, M.A.A. Conv-ViT: A convolution and vision transformer-based hybrid feature extraction method for retinal disease detection. J. Imaging 2023, 9, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Z.; Liu, H.; Le, Q.V.; Tan, M. Coatnet: Marrying convolution and attention for all data sizes. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 3965–3977. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollár, P. Focal loss for dense object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2980–2988. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R. Fast r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1440–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Geiger, A.; Lenz, P.; Urtasun, R. Are we ready for autonomous driving? The kitti vision benchmark suite. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 3354–3361. [Google Scholar]
- Caesar, H.; Bankiti, V.; Lang, A.H.; Vora, S.; Liong, V.E.; Xu, Q.; Krishnan, A.; Pan, Y.; Baldan, G.; Beijbom, O. nuScenes: A Multimodal Dataset for Autonomous Driving. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11621–11631. [Google Scholar]
- Hegde, D.; Lohit, S.; Peng, K.C.; Jones, M.; Patel, V. Multimodal 3D Object Detection on Unseen Domains. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Conference, Nashville, TN, USA, 11–12 June 2025; pp. 2499–2509. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Velodyne Acoustics, Inc. HDL-64E: High Definition Lidar Sensor; Product Data Sheet, Rev. B; Velodyne Acoustics: San Jose, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Sun, J.; Jia, J. Focal sparse convolutional networks for 3D object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 5428–5437. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Duan, T. Real-Time Multimodal 3D Object Detection with Transformers. World Electr. Veh. J. 2024, 15, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Shao, J.; Iqbal, M.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, Z. CFPC: The Curbed Fake Point Collector to Pseudo-LiDAR-Based 3D Object Detection for Autonomous Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2025, 74, 1922–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Hou, Z.; Huang, W.; Hu, Y.; Wang, J.; Yan, J. Sparse Query Dense: Enhancing 3D Object Detection with Pseudo Points. In Proceedings of the 32nd ACM International Conference on Multimedia (ACM MM 2024), Melbourne, Australia, 28 October–1 November 2024; pp. 409–418. [Google Scholar]

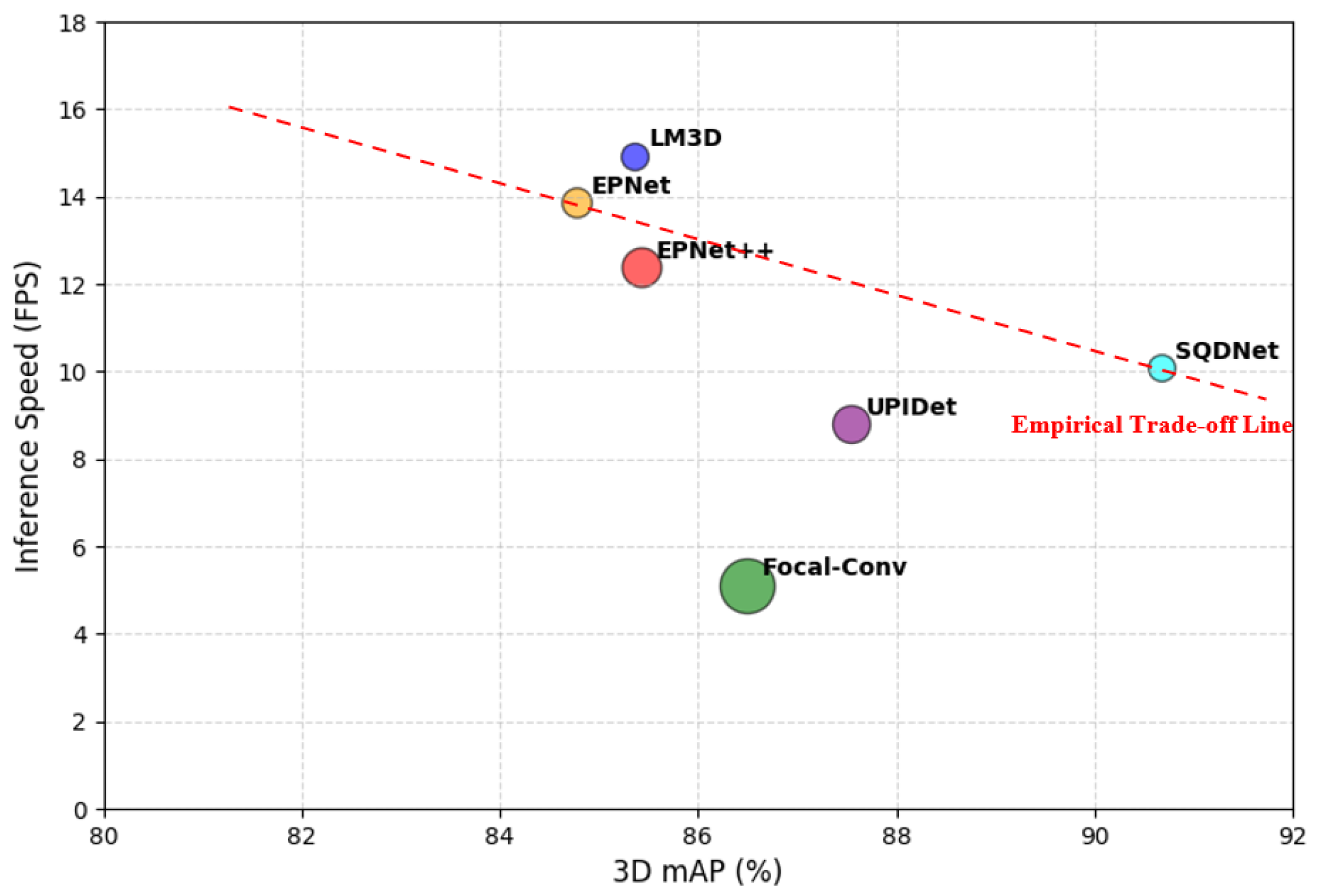
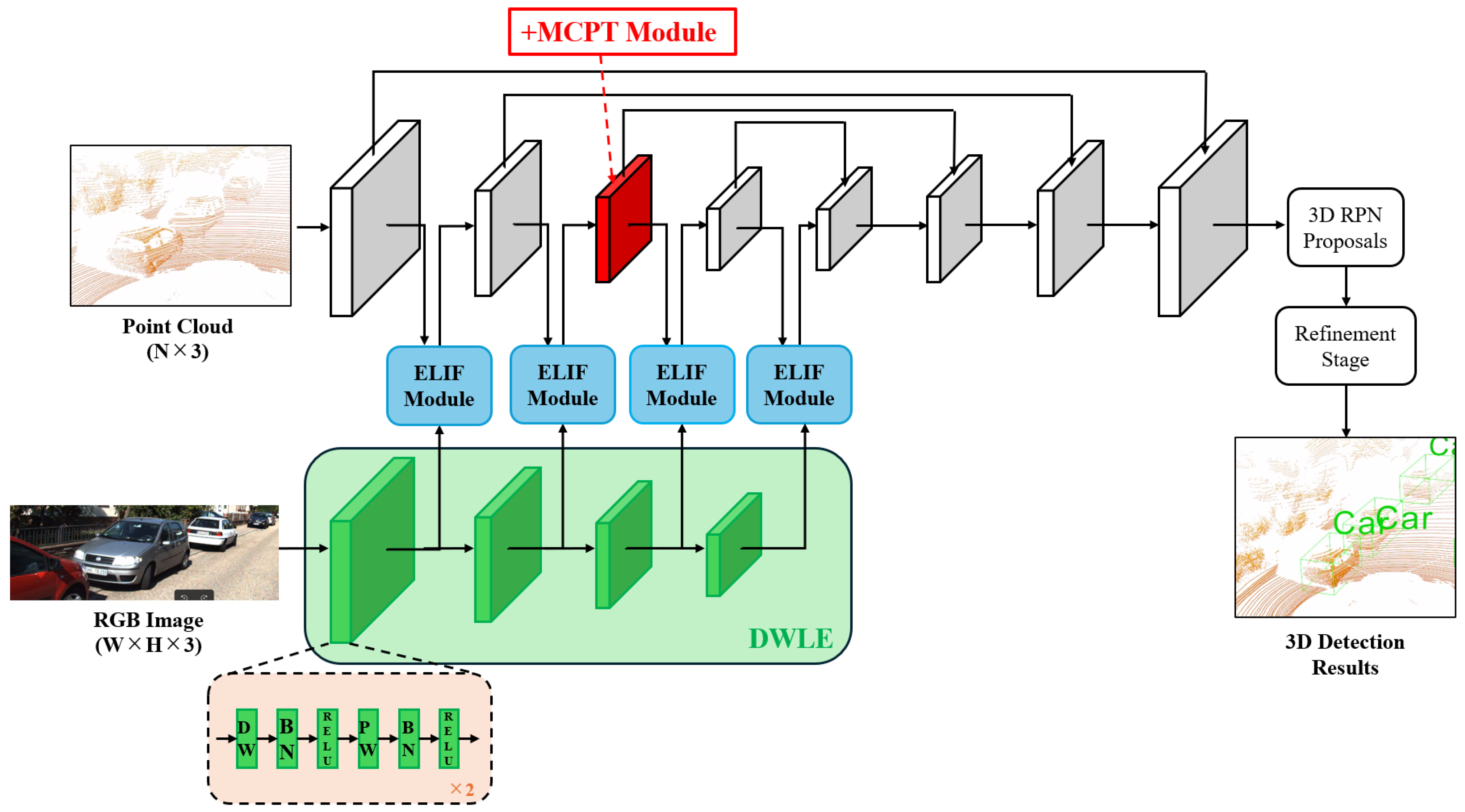
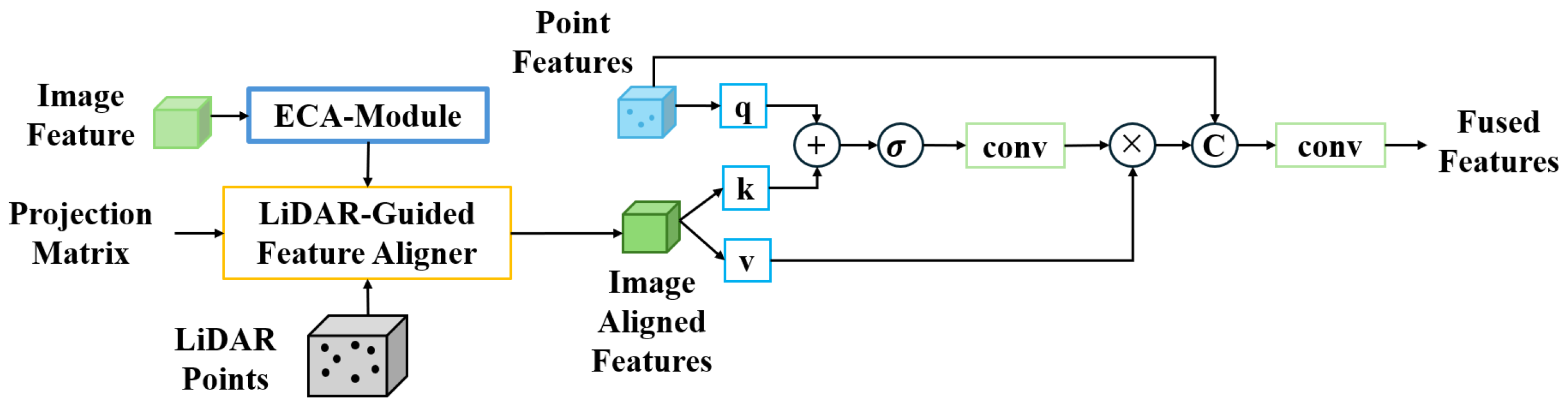


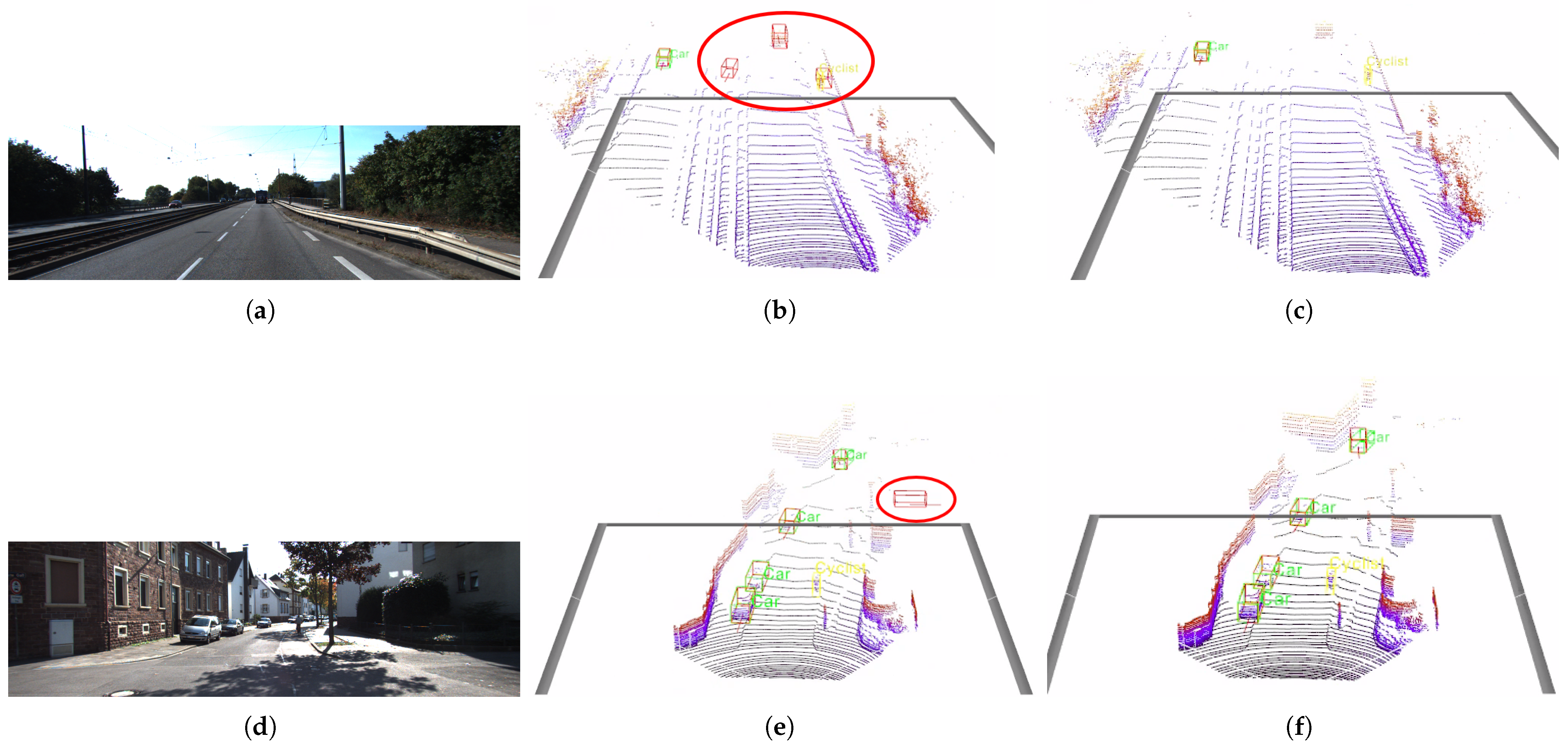

| 3D Detection | BEV Detection | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Reference | Modality | Add. Sup. | Easy | Mod. | Hard | mAP | Easy | Mod. | Hard | mAP |
| PointRCNN [19] | CVPR 2019 | L | – | 87.69 | 74.32 | 72.23 | 78.08 | 92.18 | 85.74 | 83.78 | 87.23 |
| PointPillars [23] | CVPR 2019 | L | – | 81.82 | 71.46 | 68.50 | 73.93 | 90.99 | 86.78 | 84.16 | 87.31 |
| SECOND [22] | Sensors 2018 | L | – | 87.35 | 75.73 | 73.03 | 78.70 | 93.14 | 88.00 | 87.04 | 89.39 |
| Focal-Conv [44] | CVPR 2022 | L + R | Yes | 91.72 | 84.75 | 83.04 | 86.50 | 93.94 | 90.26 | 88.55 | 90.92 |
| EPNet (base) [31] | ECCV 2020 | L + R | No | 92.13 | 82.18 | 80.00 | 84.77 | 96.23 | 88.89 | 88.59 | 91.24 |
| EPNet++ [32] | TPAMI 2022 | L + R | No | 92.39 | 83.24 | 80.62 | 85.42 | 96.23 | 89.55 | 89.15 | 91.64 |
| UPIDet [30] | NeurIPS 2023 | L + R | No | 92.82 | 86.22 | 83.57 | 87.54 | 95.49 | 91.75 | 89.27 | 92.17 |
| Fast Transfusion * [45] | WEVJ 2024 | L + R | No | 88.06 | 79.43 | 71.58 | 79.69 | 90.99 | 83.14 | 76.85 | 83.66 |
| CFPC * [46] | IEEE TVT 2024 | L + R | Yes | 92.01 | 83.39 | 82.35 | 87.42 | – | – | – | – |
| SQDNet [47] | ACM MM 2024 | L + R | Yes | 95.84 | 88.30 | 87.88 | 90.67 | 96.45 | 93.48 | 91.47 | 93.80 |
| LM3D | Appl. Sci 2025 | L + R | No | 92.50 | 82.96 | 80.54 | 85.36 | 95.94 | 89.12 | 88.70 | 91.25 |
| Method | Reference | Modality | Add. Sup. | Parameters | Inference Speed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PointRCNN [19] | CVPR 2019 | L | – | 4.04 M | 18.85 FPS |
| PointPillars [23] | CVPR 2019 | L | – | 4.83 M | 48.95 FPS |
| SECOND [22] | Sensors 2018 | L | – | 5.30 M | 31.15 FPS |
| Focal-Conv [44] | CVPR 2022 | L + R | Yes | 53.01 M | 5.12 FPS |
| EPNet (base) [31] | ECCV 2020 | L + R | No | 15.68 M | 13.88 FPS |
| EPNet++ [32] | TPAMI 2022 | L + R | No | 27.25 M | 12.40 FPS |
| UPIDet [30] | NeurIPS 2023 | L + R | No | 24.99 M | 8.79 FPS |
| Fast Transfusion * [45] | WEVJ 2024 | L + R | No | – | 10.64 FPS |
| SQDNet [47] | ACM MM 2024 | L + R | Yes | 12.71 M | 10.10 FPS |
| LM3D | Appl. Sci 2025 | L + R | No | 13.03 M | 14.94 FPS |
| Method | 3D mAP (%) | BEV mAP (%) | Inference Speed (FPS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| EPNet (base) | 30.24 | 47.92 | 13.46 |
| EPNet++ | 32.49 | 48.88 | 12.72 |
| LM3D | 36.63 | 51.15 | 14.25 |
| DWLE | ELIF | MCPT | 3D mAP (%) | BEV mAP (%) | Params (M) | Inference Speed (FPS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 84.77 | 91.24 | 15.68 | 13.88 | |||
| ✓ | 84.73 | 90.85 | 9.09 | 15.11 | ||
| ✓ | ✓ | 85.08 | 91.11 | 9.09 | 15.41 | |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 85.36 | 91.25 | 13.03 | 14.94 |
| Configuration | 3D mAP (%) | BEV mAP (%) | Params (M) | Inference Speed (FPS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placed at the 1st | 85.38 | 91.28 | 10.83 | 12.13 |
| Placed at the 2nd | 85.33 | 91.21 | 11.39 | 14.37 |
| Placed at the 3rd | 85.36 | 91.25 | 13.03 | 14.94 |
| Placed at the 4th | 85.18 | 90.48 | 19.06 | 14.82 |
| Configuration | 3D mAP (%) | BEV mAP (%) | Params (M) | Inference Speed (FPS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Point Transformer Only | 84.89 | 90.45 | 11.19 | 15.22 |
| kernel size: 1 × 1 | 85.13 | 90.48 | 11.46 | 15.26 |
| kernel size: 3 × 3 | 84.98 | 90.62 | 11.98 | 15.26 |
| kernel size: 5 × 5 | 85.32 | 91.31 | 12.51 | 15.13 |
| kernel size: 7 × 7 | 85.36 | 91.25 | 13.03 | 14.94 |
| kernel size: 9 × 9 | 85.02 | 91.12 | 13.56 | 15.15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sakai, Y.; Shimada, T.; Kong, X.; Tomiyama, H. LM3D: Lightweight Multimodal 3D Object Detection with an Efficient Fusion Module and Encoders. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 10676. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910676
Sakai Y, Shimada T, Kong X, Tomiyama H. LM3D: Lightweight Multimodal 3D Object Detection with an Efficient Fusion Module and Encoders. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(19):10676. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910676
Chicago/Turabian StyleSakai, Yuto, Tomoyasu Shimada, Xiangbo Kong, and Hiroyuki Tomiyama. 2025. "LM3D: Lightweight Multimodal 3D Object Detection with an Efficient Fusion Module and Encoders" Applied Sciences 15, no. 19: 10676. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910676
APA StyleSakai, Y., Shimada, T., Kong, X., & Tomiyama, H. (2025). LM3D: Lightweight Multimodal 3D Object Detection with an Efficient Fusion Module and Encoders. Applied Sciences, 15(19), 10676. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910676






