Load–Deformation Behavior and Risk Zoning of Shallow-Buried Gas Pipelines in High-Intensity Longwall Mining-Induced Subsidence Zones
Abstract
1. Introduction
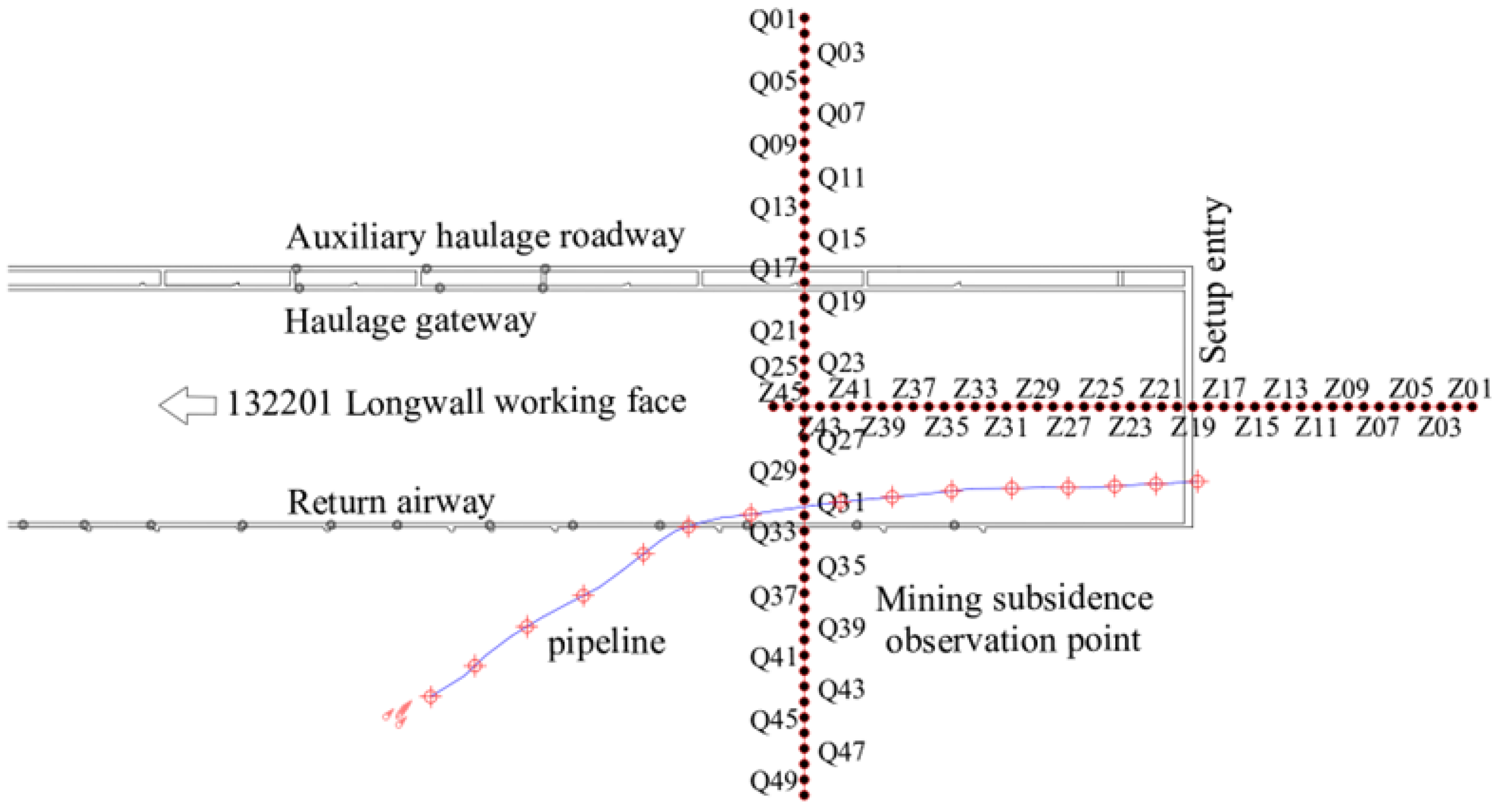
2. Engineering Background
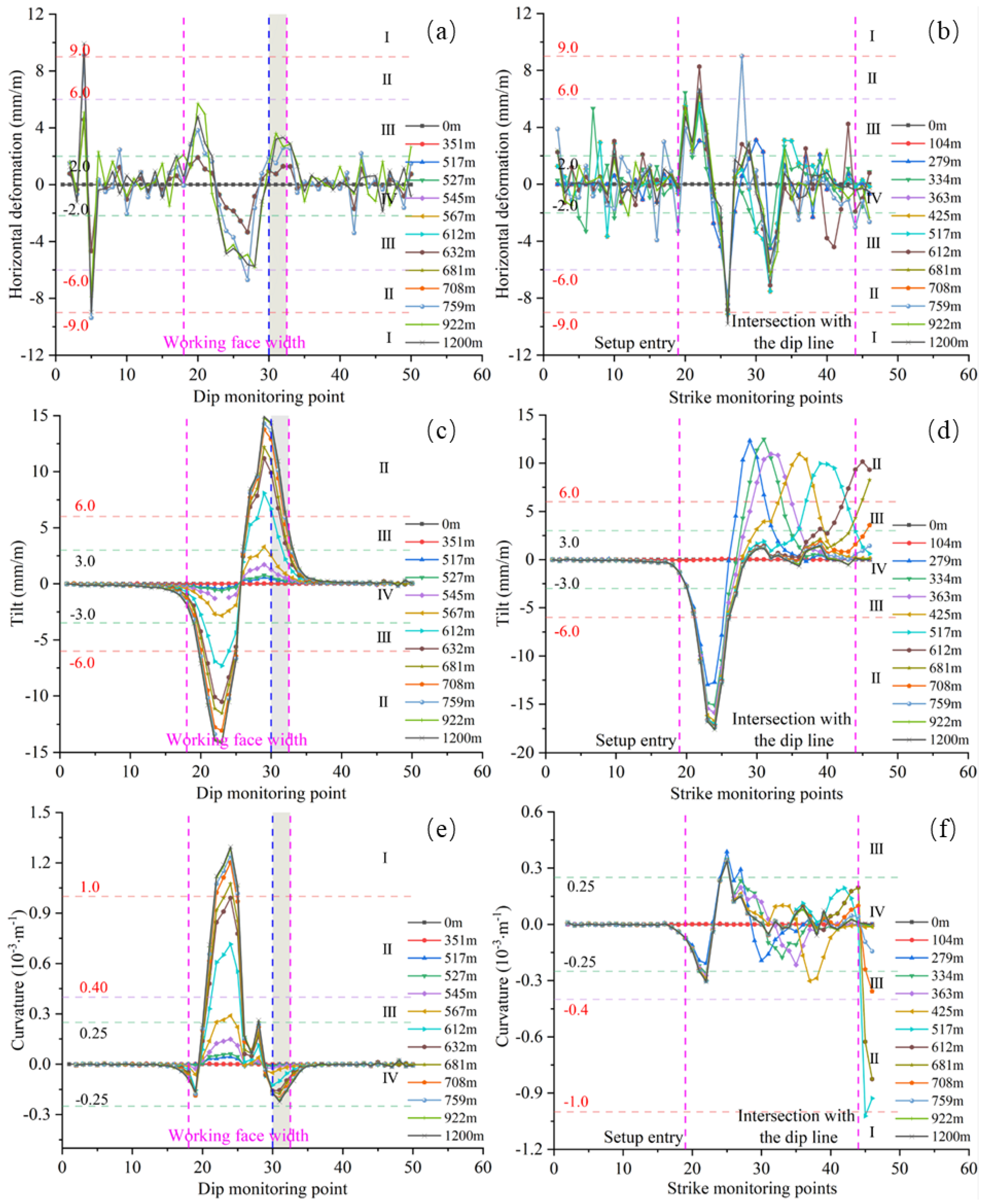
3. Hazard Zoning of Gas Pipelines in Subsidence Areas
4. Numerical Simulation of Pipeline Loading and Deformation Characteristics Under Different Mining Parameters
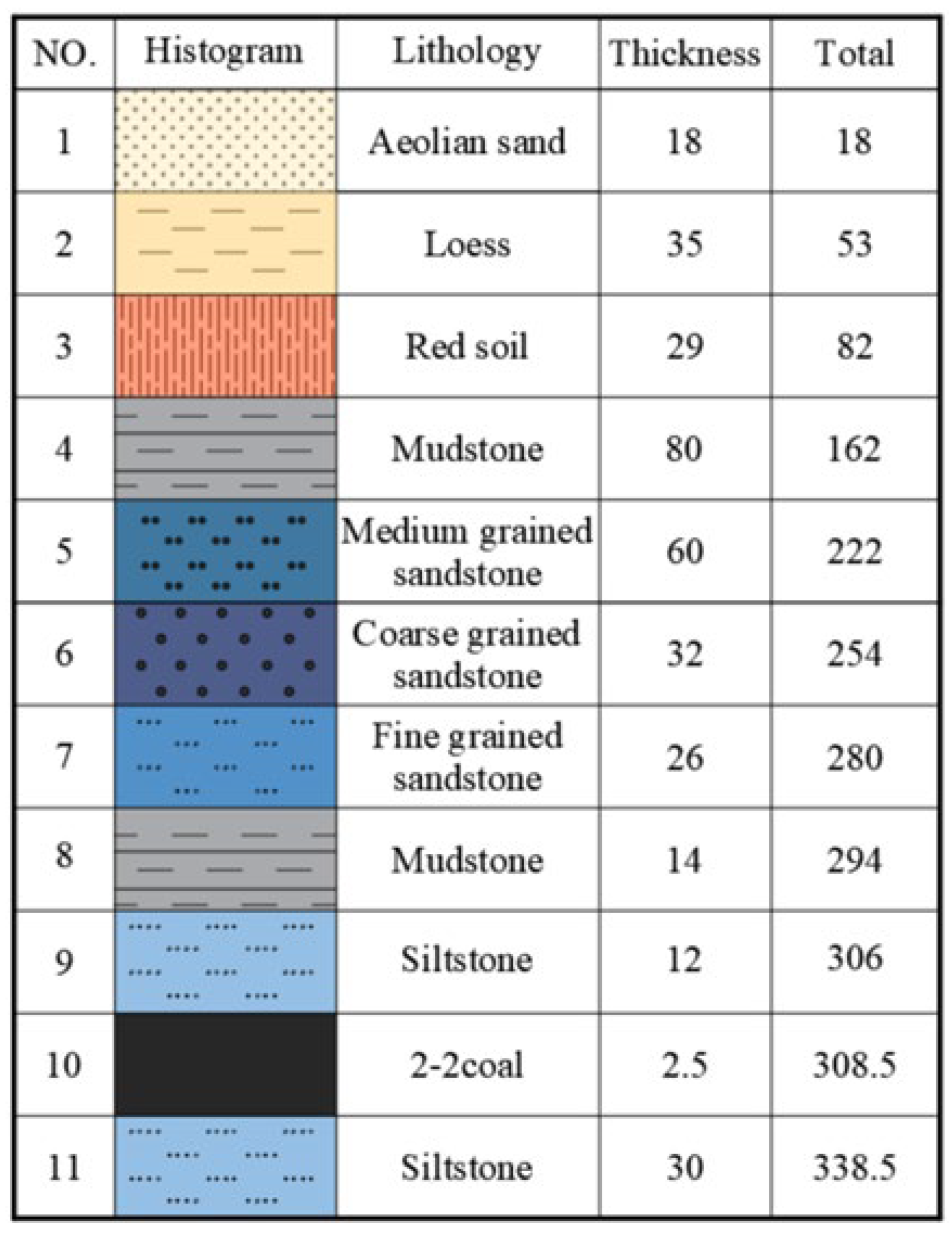
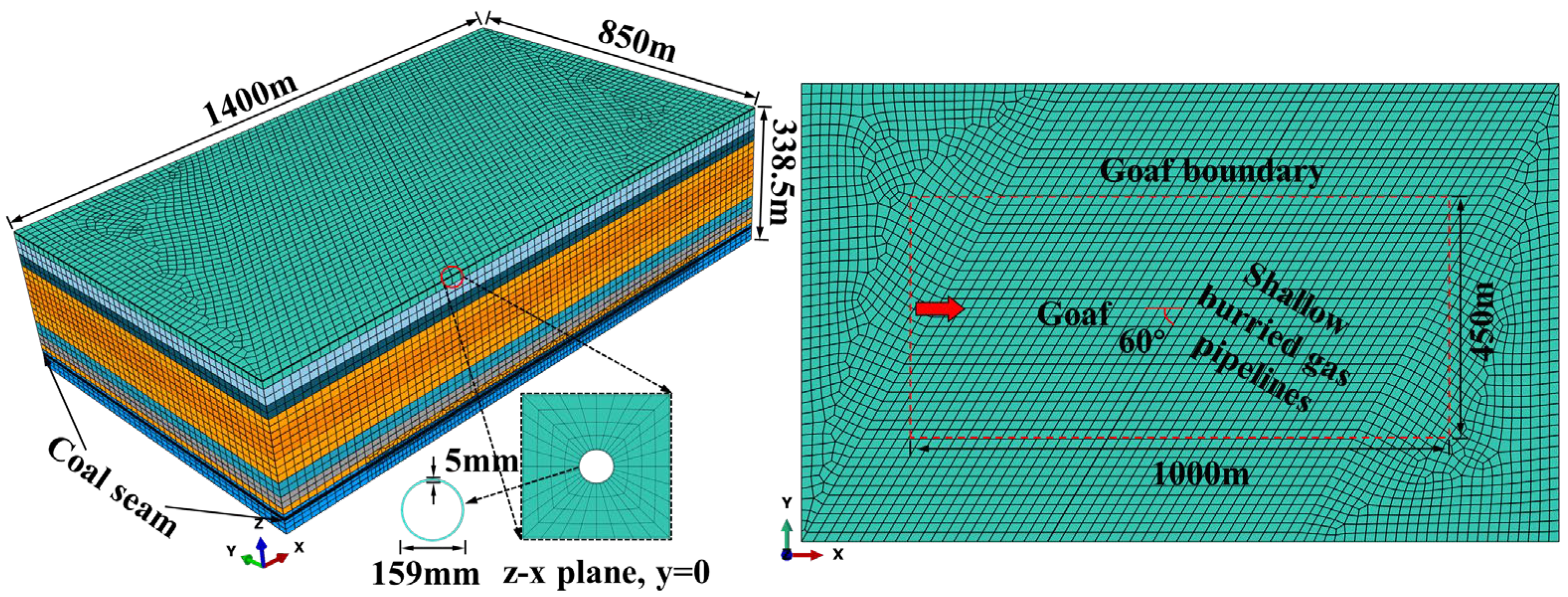
4.1. Numerical Model Development
4.1.1. Model Construction and Fundamental Assumptions
4.1.2. Model Validation and Parameter Determination
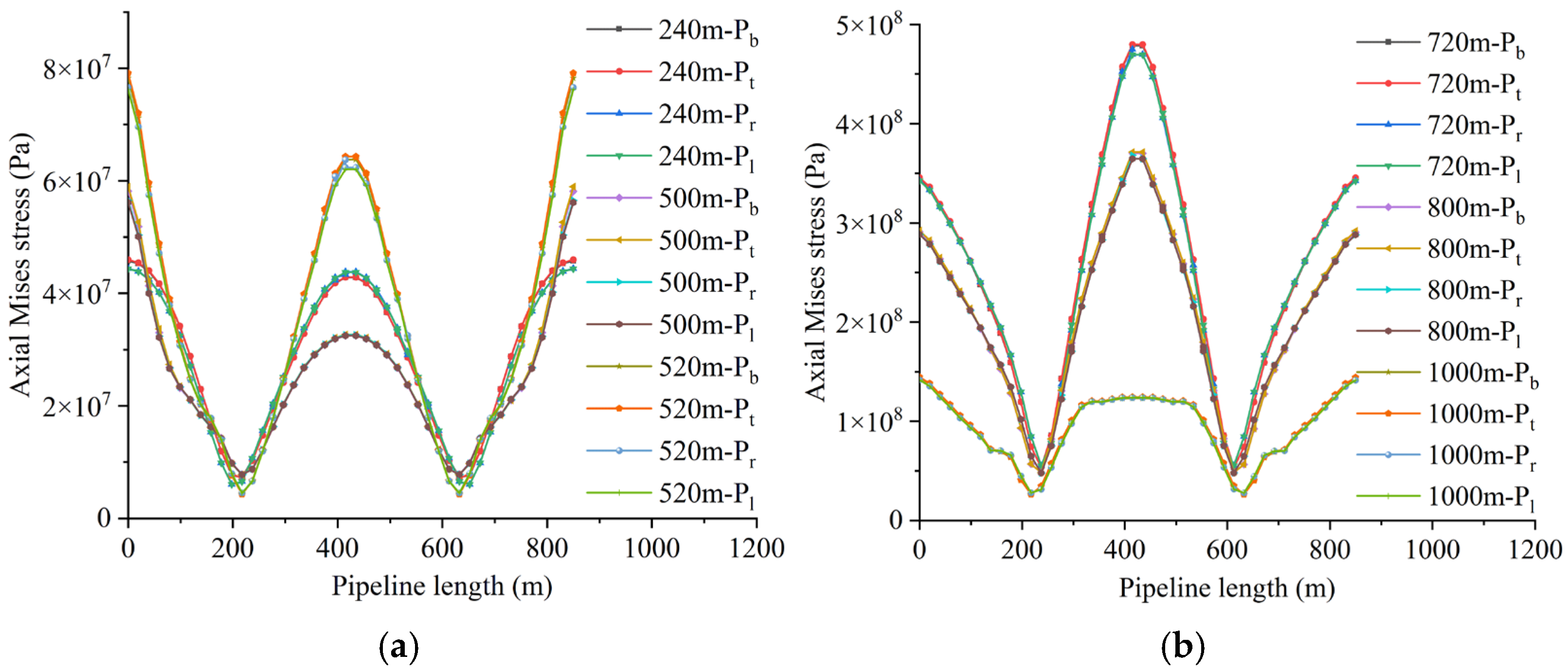
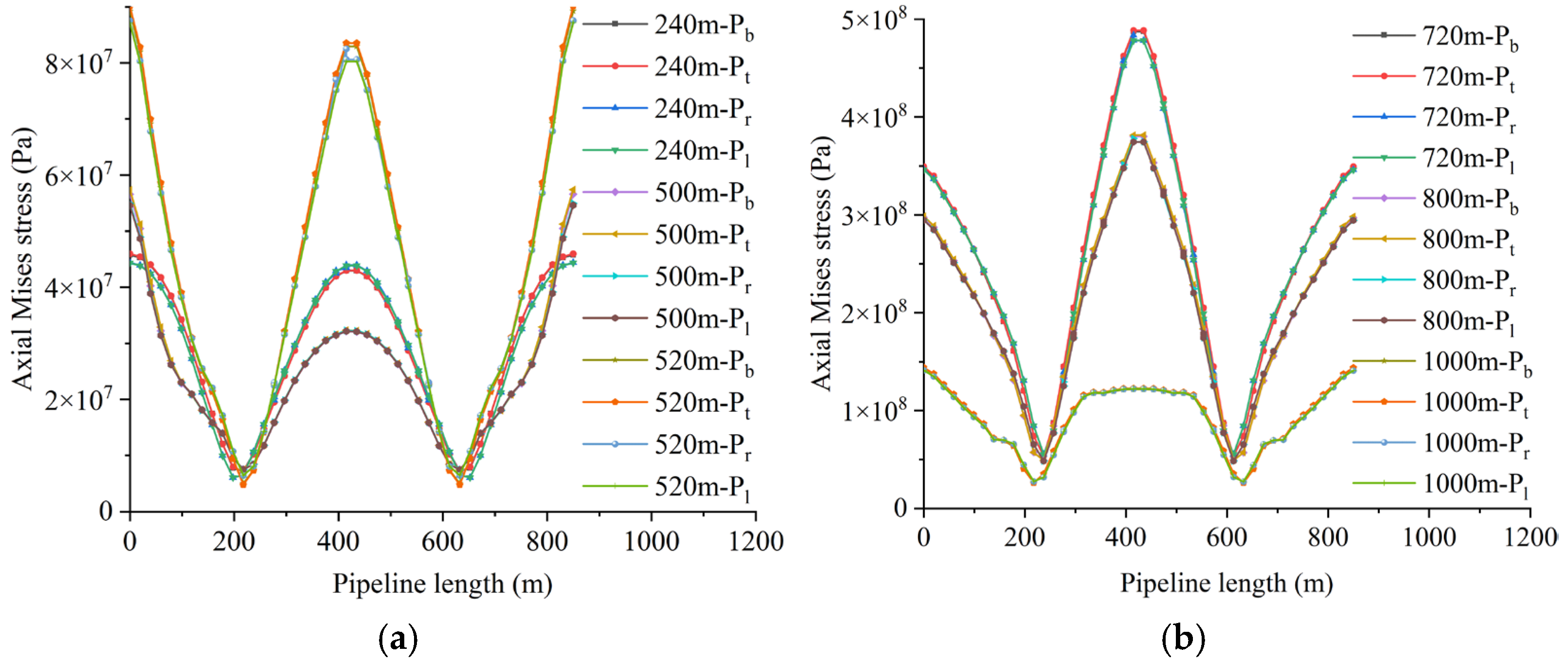
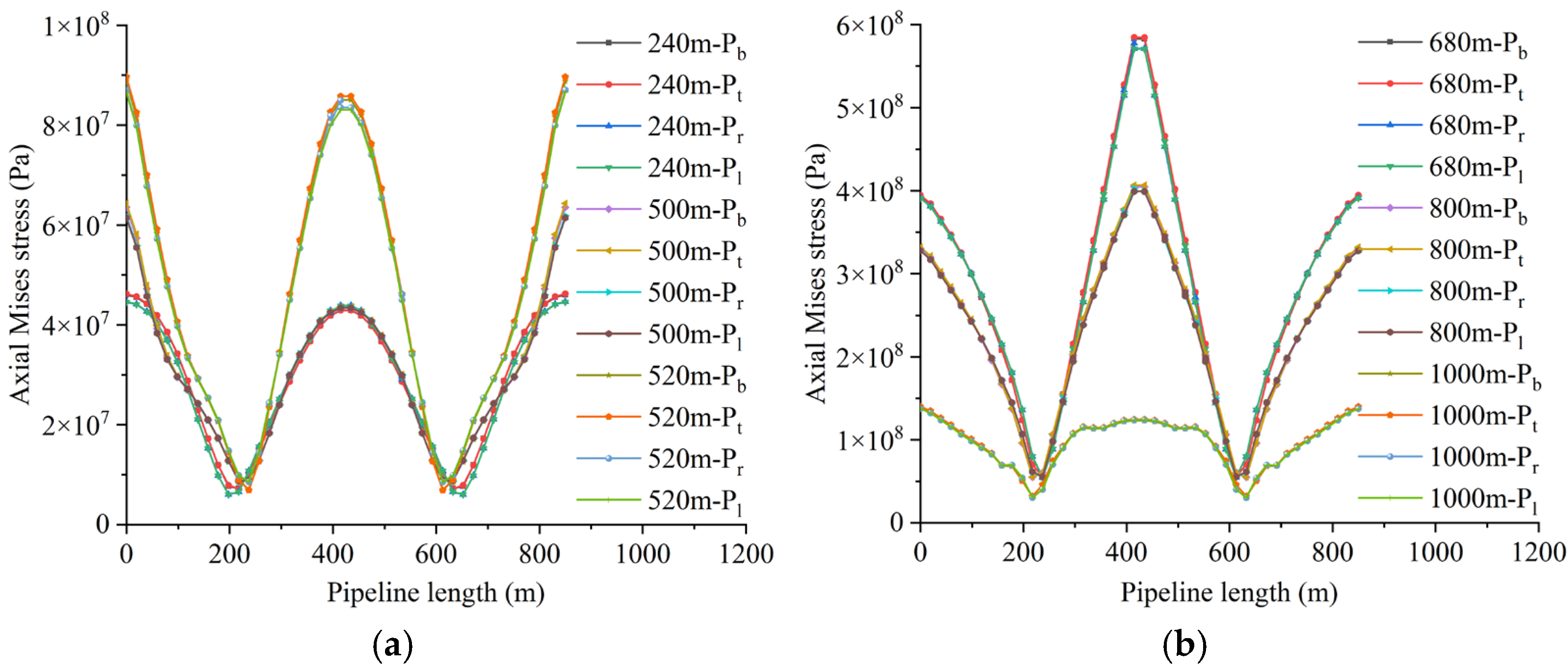
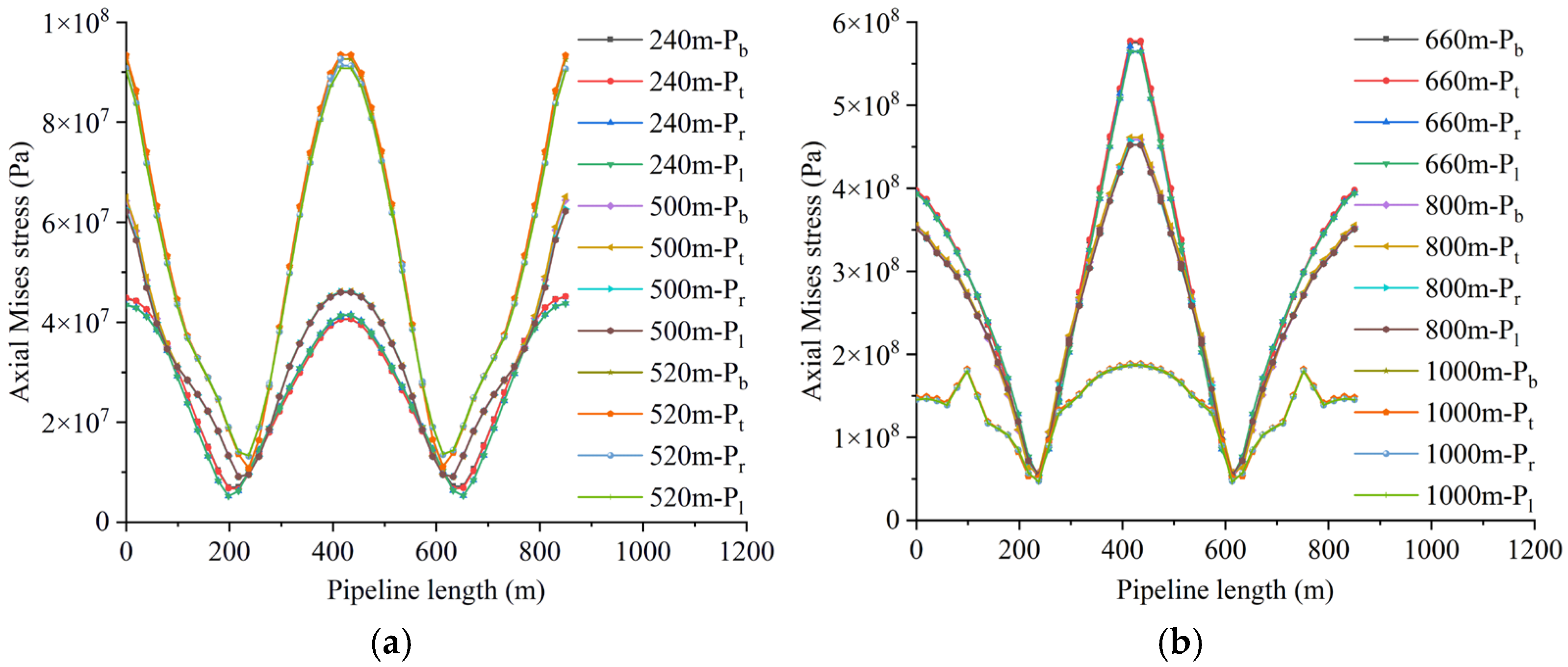
4.2. The Influence of Working Face Advance Rate on Pipeline Loading and Deformation
4.2.1. Loading Characteristics of Shallowly Buried Pipelines
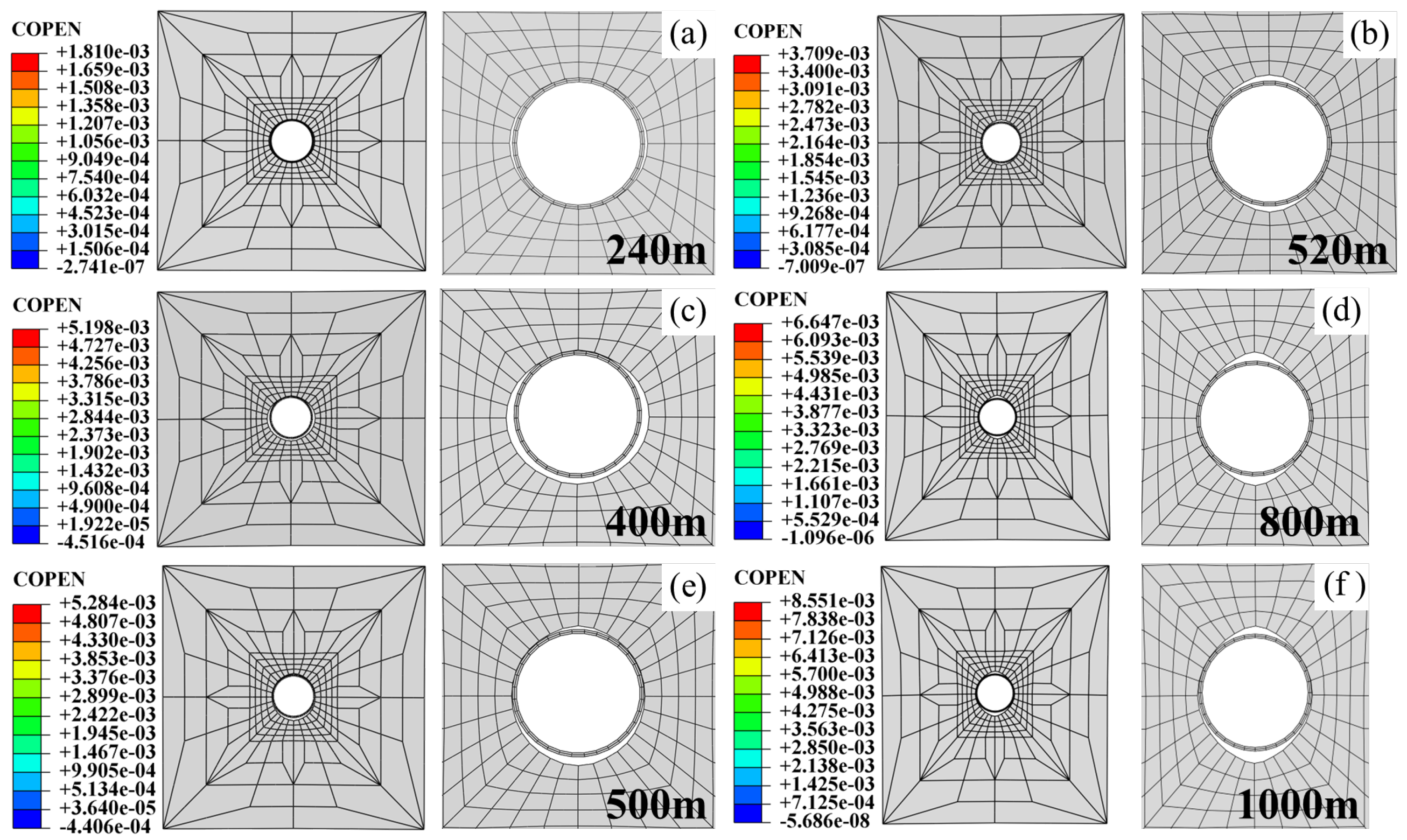
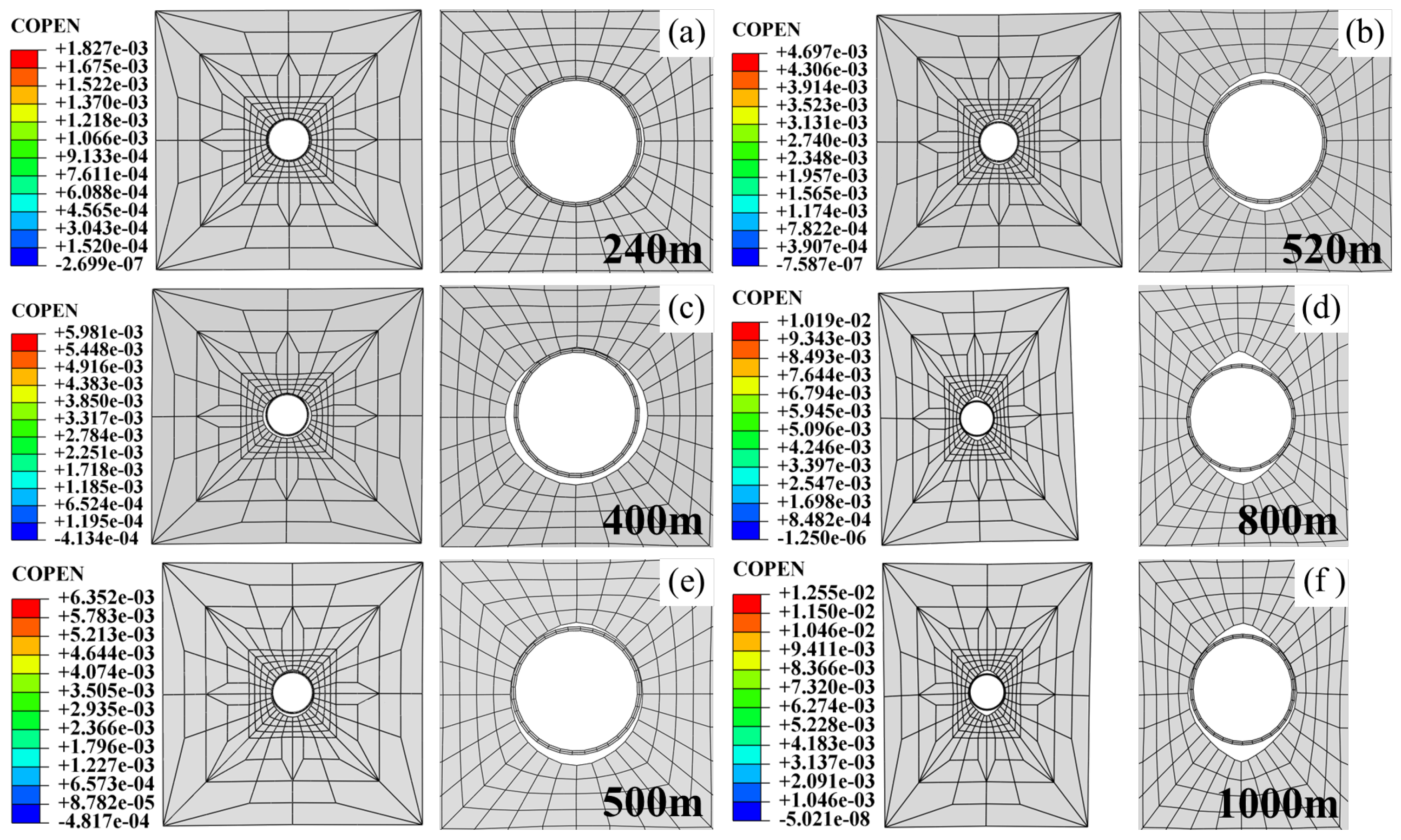
4.2.2. Settlement Deformation Characteristics of Pipeline and Surface Sandy Soil
4.3. Effect of Mining Height on Pipeline Loading and Deformation
4.3.1. Load-Bearing Characteristics of Shallow-Buried Pipelines
4.3.2. Subsidence Deformation Characteristics of Pipeline–Soil Systems
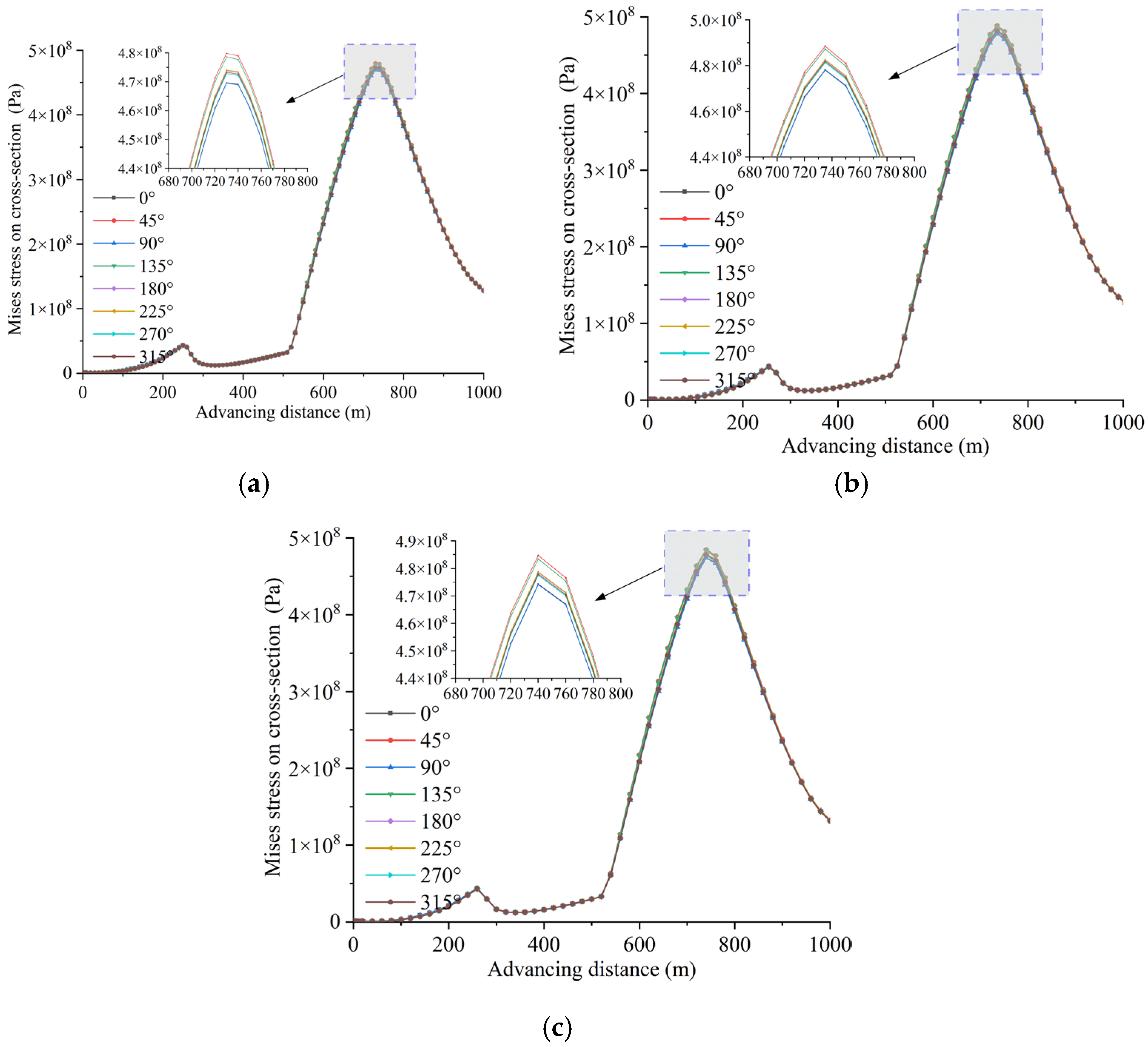
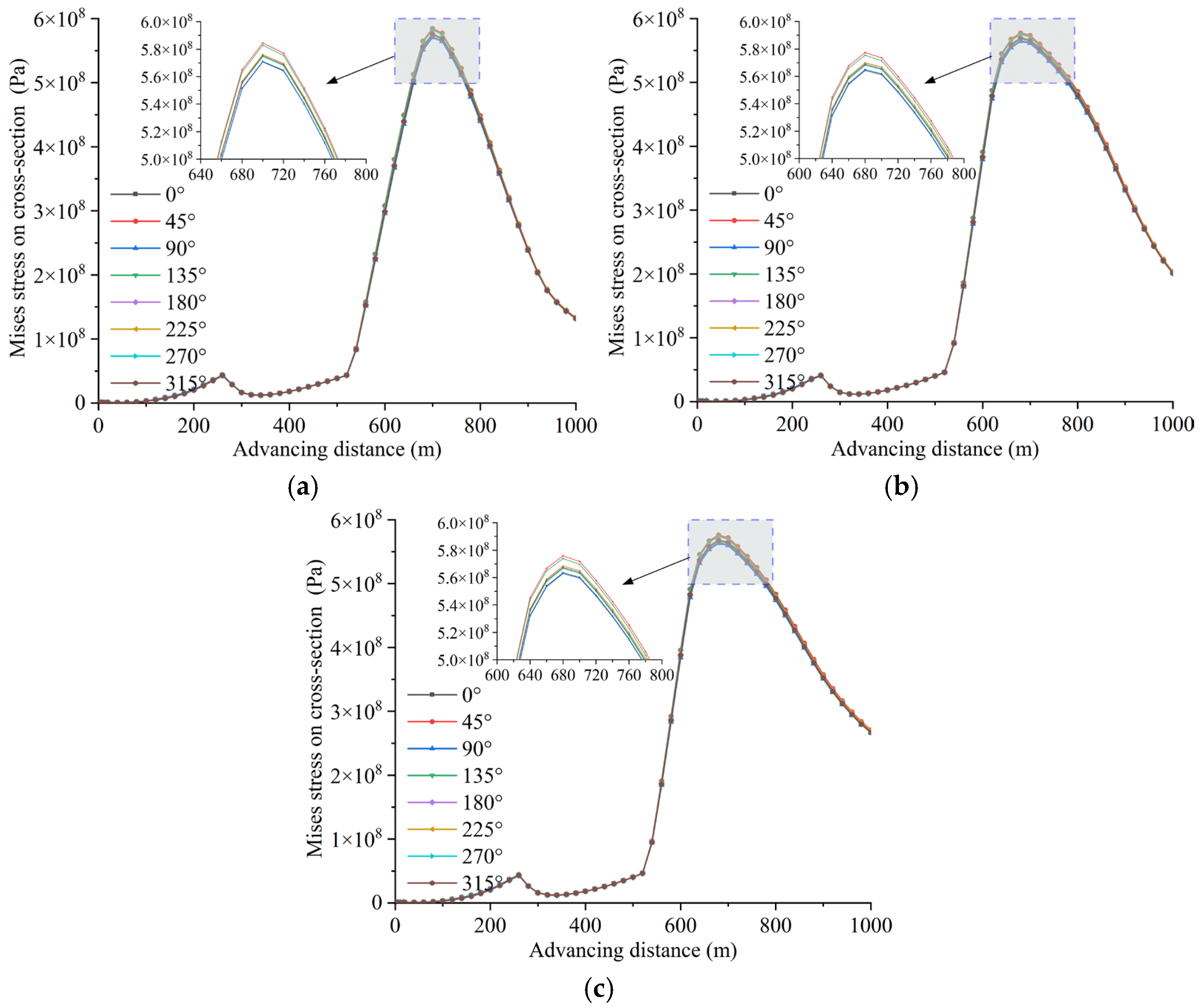
4.4. Influence of Varied Angles Between Advancement Direction and Pipeline Axis on Pipeline Loading and Deformation Behavior
4.4.1. Mechanical Response Characteristics of Shallow-Buried Pipelines
4.4.2. Settlement Deformation Characteristics of Pipeline-Soil System
5. Protective Measures for Shallow-Buried Pipelines: Discussions and Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviation
| LWWF | Longwall working face |
References
- Yuan, L. Scientific problem and countermeasure for precision mining of coal and associated resources. J. China Coal Soc. 2019, 44, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, B.X.; Zhao, X.L.; Zhang, Q. Framework of the theory and technology for simultaneous mining of coal and its associated resources. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2016, 45, 653–662. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.N.; Liang, S.; Liang, X.; Yang, B.; Shi, Z.L.; Wu, C.L.; Shen, J.H.; Yang, M.; Ma, Y.D.; Xu, P. Spatio-temporal evolution of loading and deformation of surface gas pipelines for high-intensity coalbed mining and its integrity prediction methodology. Processes 2024, 12, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Elsworth, D.; Li, X.H.; Fu, X.H.; Yang, D.; Yao, Q.L.; Wang, Y. Dynamic impacts on the survivability of shale gas wells piercing longwall panels. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2015, 26, 1130–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Elsworth, D.; Li, X.H.; Fu, X.H.; Sun, B.Y.; Yao, Q.L. Key strata characteristics controlling the integrity of deep wells in longwall mining areas. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2017, 172, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Elsworth, D.; Fu, X.H.; Li, X.H.; Yao, Q.L. Influence of Stratigraphic Conditions on the Deformation Characteristics of Oil/Gas Wells Piercing Longwall Pillars and Mining Optimization. Energies 2017, 10, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Elsworth, D.; Li, X.H.; Yang, D. Topographic influence on stability for gas wells penetrating longwall mining areas. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2014, 132, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Li, X.H.; Yao, Q.L.; Yang, D. Influence of weak interlayer contacts on the stability of shale gas wells transiting minable coal seams. J. Min. Saf. Eng. 2015, 32, 471–477. [Google Scholar]
- Parmelee, R.; Ludtke, C. Seismic soil-structure interaction of buried pipelines. In Proceedings of the U.S. National Conference on Earthquake Engineering, Oakland, CA, USA, 18–20 June 1975; Earthquake Engineering Research Institute: Oakland, CA, USA, 1975; pp. 406–415. [Google Scholar]
- Ariman, T.; Muleski, G.E. A review of the response of buried pipelines under seismic excitations. J. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 1981, 9, 133–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, D.; Liu, H. Stress effect of the interface between buried pipeline and sandy soil layer in a cold environment. J. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2020, 172, 102981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Zeng, G.; Zheng, J.; Pan, Y. Laboratory investigation on the pipeline-soil interaction under different freezing conditions. J. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2024, 217, 104050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Lai, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, L. Upheaval buckling resistance of pipelines buried in unsaturated clay backfills. J. Int. J. Geomech. 2023, 23, 04023032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Yang, H.; Xu, P.; Zhang, M.; Hou, Z. Coupling interaction of surrounding soil-buried pipeline and additional stress in subsidence soil. J. Geofluids 2021, 2021, 7941989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, Y.D.J.; Zornberg, J.G.; Costa, C.M.L. Physical modeling of buried PVC pipes overlying localized ground subsidence. J. Acta Geotech. 2021, 16, 807–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; You, X.; Zha, S. Mechanical behavior analysis of buried polyethylene pipe under land subsidence. J. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2020, 108, 104351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J. Mechanical behavior of gas-transmission pipeline in a goaf. Processes 2023, 11, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhong, M.S.; Long, Y.; Ding, K.; Xie, X.B.; Ying, L. Study on dynamic strain regularity and influencing factors of shallow buried metal pipe under collapse impact load. J. Shock Vib. 2018, 2018, 8792564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xie, R.; Zheng, T.; Lu, G.H.; Xu, J.Y. Buckling behavior of buried pipe crossing stratum subsidence area. J. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2022, 135, 106130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saberi, M.; Arabzadeh, H.; Keshavarz, A. Numerical analysis of buried pipelines with right angle elbow under wave propagation. J. Procedia Eng. 2011, 14, 3260–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazouras, P.; Tsatsis, A.; Dakoulas, P. Thermal upheaval buckling of buried pipelines: Experimental behavior and numerical modeling. J. Pipeline Syst. Eng. Pract. 2021, 12, 04020057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadaee, M.; Farzaneganpour, F.; Anastasopoulos, I. Response of buried pipeline subjected to reverse faulting. J. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2020, 132, 106090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saboya, F., Jr.; Tibana, S.; Reis, R.M.; Farfan, A.D.; Melo, C.M.D.A.R. Centrifuge and numerical modeling of moving traffic surface loads on pipelines buried in cohesionless soil. J. Transp. Geotech. 2020, 23, 100340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzabeebee, S.; Chapman, D.N.; Faramarzi, A. A comparative study of the response of buried pipes under static and moving loads. J. Transp. Geotech. 2018, 15, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Han, C.J.; Xie, R.; Wang, L. Mechanical behavior analysis of buried pipeline understratum settlement caused by underground mining. J. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 2020, 188, 104212. [Google Scholar]
- Sarvanis, G.C.; Karamanos, S.A. Analytical model for the strain analysis of continuous buried pipelines in geohazard areas. J. Eng. Struct. 2017, 152, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Tang, S.; Cui, Z.Y. Safety assessment of buried natural gas pipelines with corrosion defects under the ground settlement. J. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2021, 129, 105663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazaluk, O.; Kuchyn, O.; Saik, P.; Soltabayeva, S.; Brui, H.; Lozynskyi, V.; Cherniaiev, O. Impact of ground surface subsidence caused by underground coal mining on natural gas pipeline. J. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 19327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.S.; Luo, Y. Determination of stress field in buried thin pipelines resulting from ground subsidence due to longwall mining. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 1988, 6, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Peng, S.; Chen, H. Protection of pipelines affected by surface subsidence. J. Trans. 1998, 302, 98–103. [Google Scholar]
- Polak, M.A.; Duyvestyn, G.; Knight, M. Experimental strain analysis for polyethylene pipes installed by horizontal directional drilling. J. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2004, 19, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.B.; Wang, Y.G. The definition of high-intensity mining based on green coal mining and its index system. J. Min. Saf. Eng. 2017, 34, 616–623. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W.B.; Bai, E.H.; Yang, D.M. Study on the technical characteristics and index of thick coal seam high-intensity mining in coalmine. J. China Coal Soc. 2018, 43, 2117–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Q/SY 05487–2017; Specifications for Safety Design and Prevention Technique of Oil and Gas Pipeline in Mining Subsidence Areas. Petroleum Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Zhang, J.; Xie, R. Numerical analysis of mechanical behavior of buried pipes in subsidence area caused by underground mining. J. Press. Vessel Technol. 2019, 141, 021703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xie, R.; Zhang, H. Mechanical response analysis of the buried pipeline due to adjacent foundation pit excavation. J. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2018, 78, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P. Study on the Buried Pipeline-Soil Interaction and Its Mechanical Response by Mining Subsidence. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Mining and Technology, Xuzhou, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, P.; Zhang, M.; Lin, Z.; Cao, Z.; Chang, X. Additional stress on a buried pipeline under the influence of coal mining subsidence. J. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2018, 2018, 3245624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, F.C.; Chen, G.; Tang, M.M.; Cao, Y.B.; Cao, Y.P.; Yang, Y.L. Analysis and optimization of wellbore structure considering casing stress in oil and gas wells within coal mine goaf areas subject to overburden movement. J. Process. 2025, 13, 2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 9711-2023; Petroleum and Natural Gas Industries—Steel Pipe for Pipeline Transportation Systems. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2023.









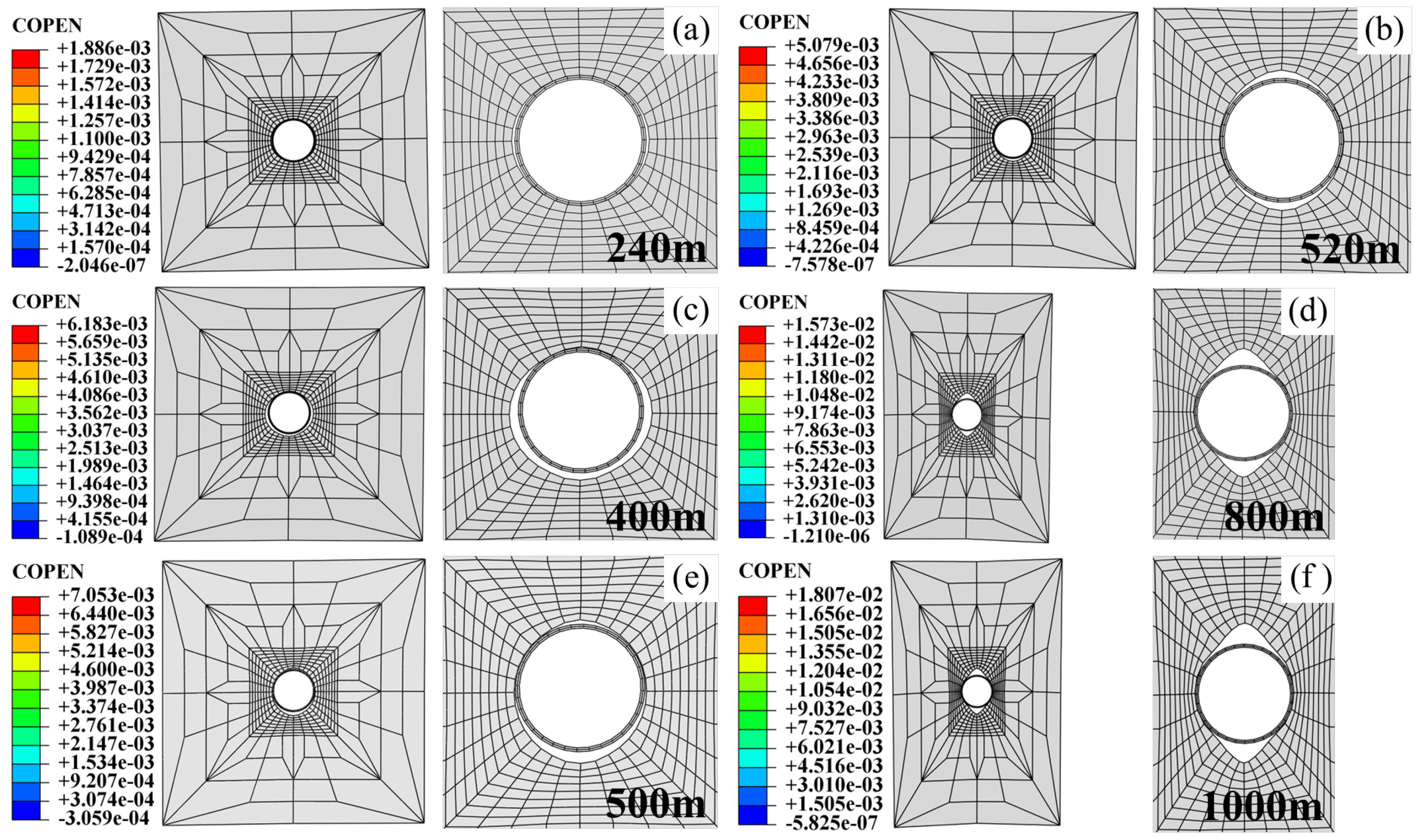
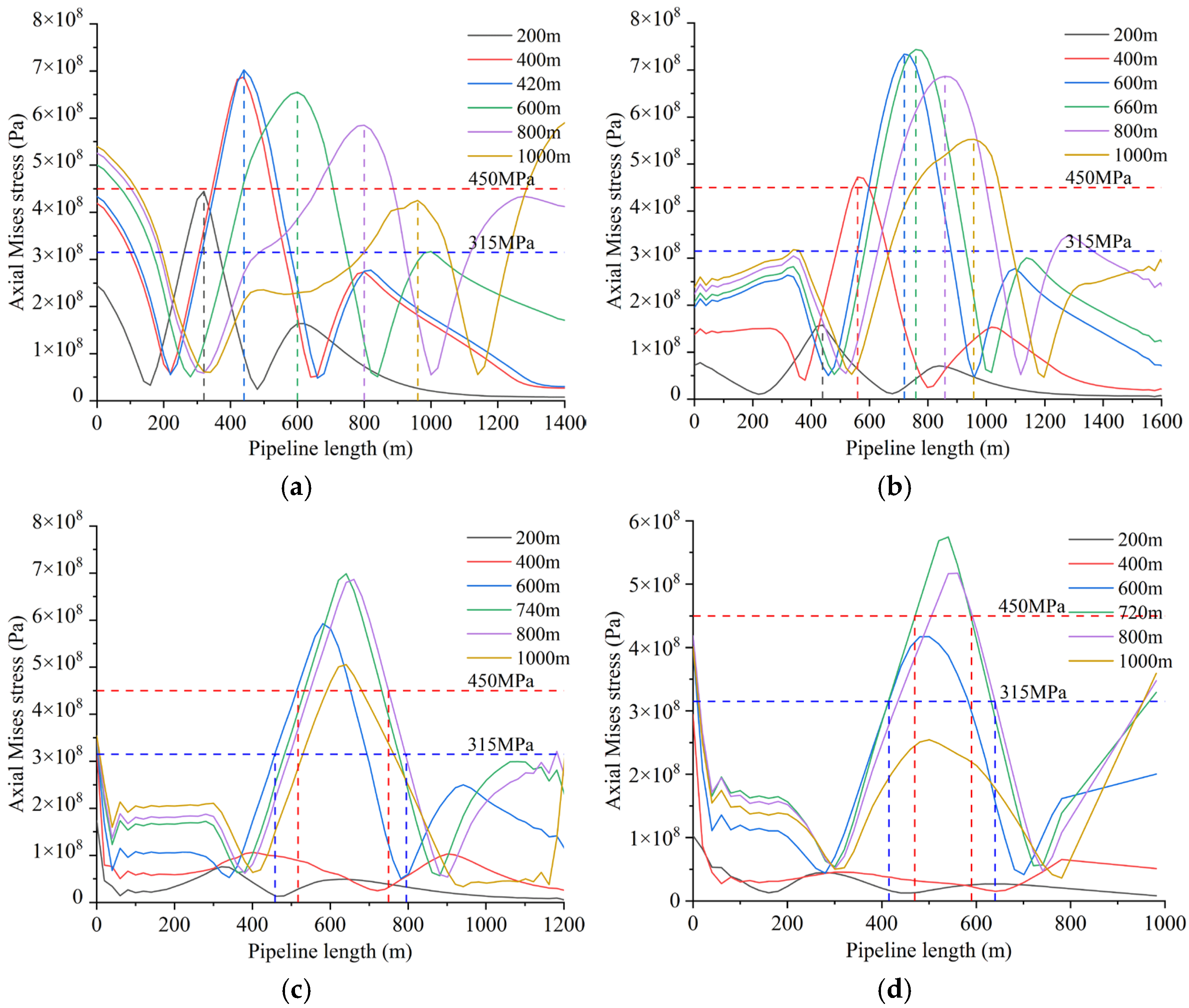
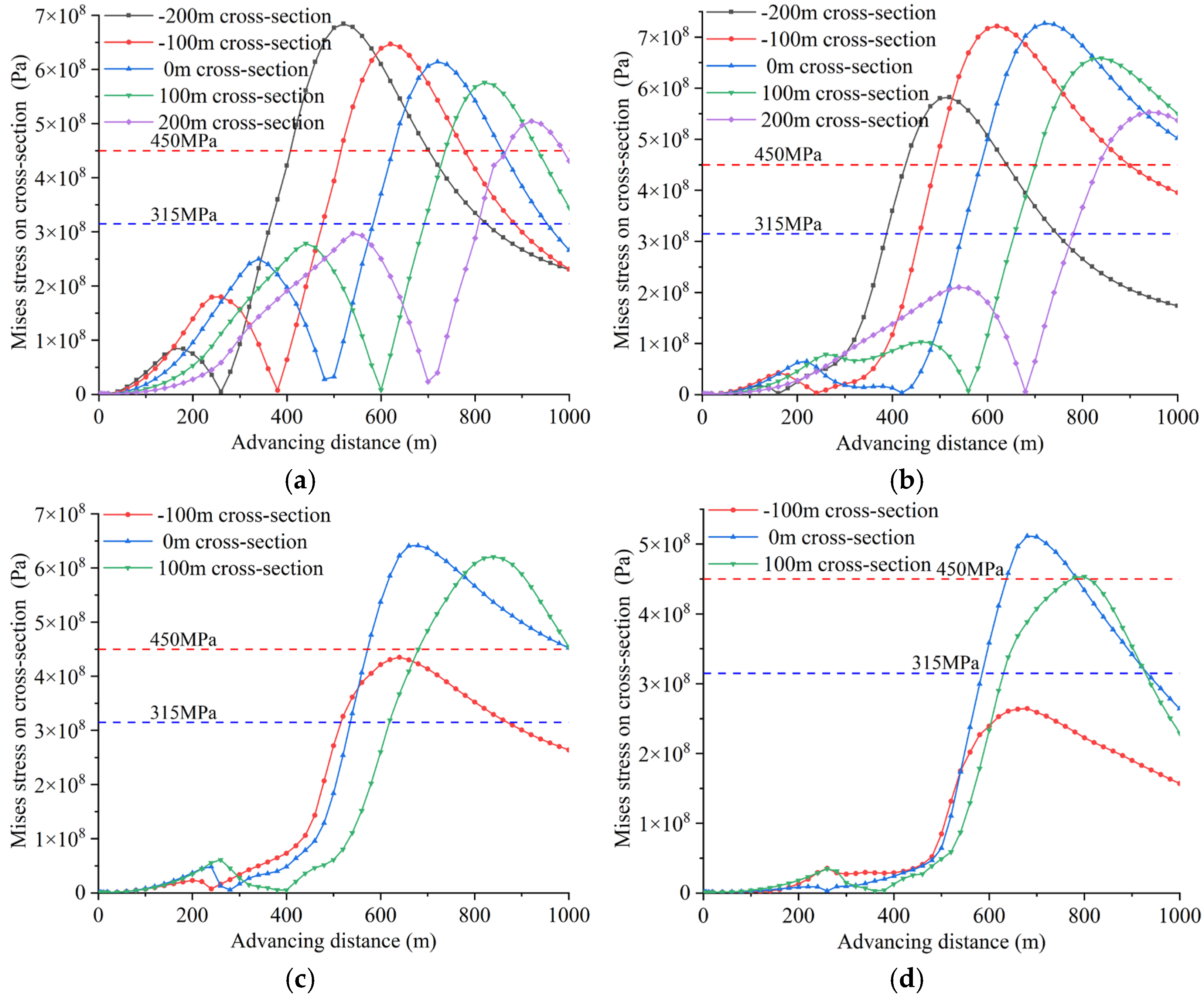


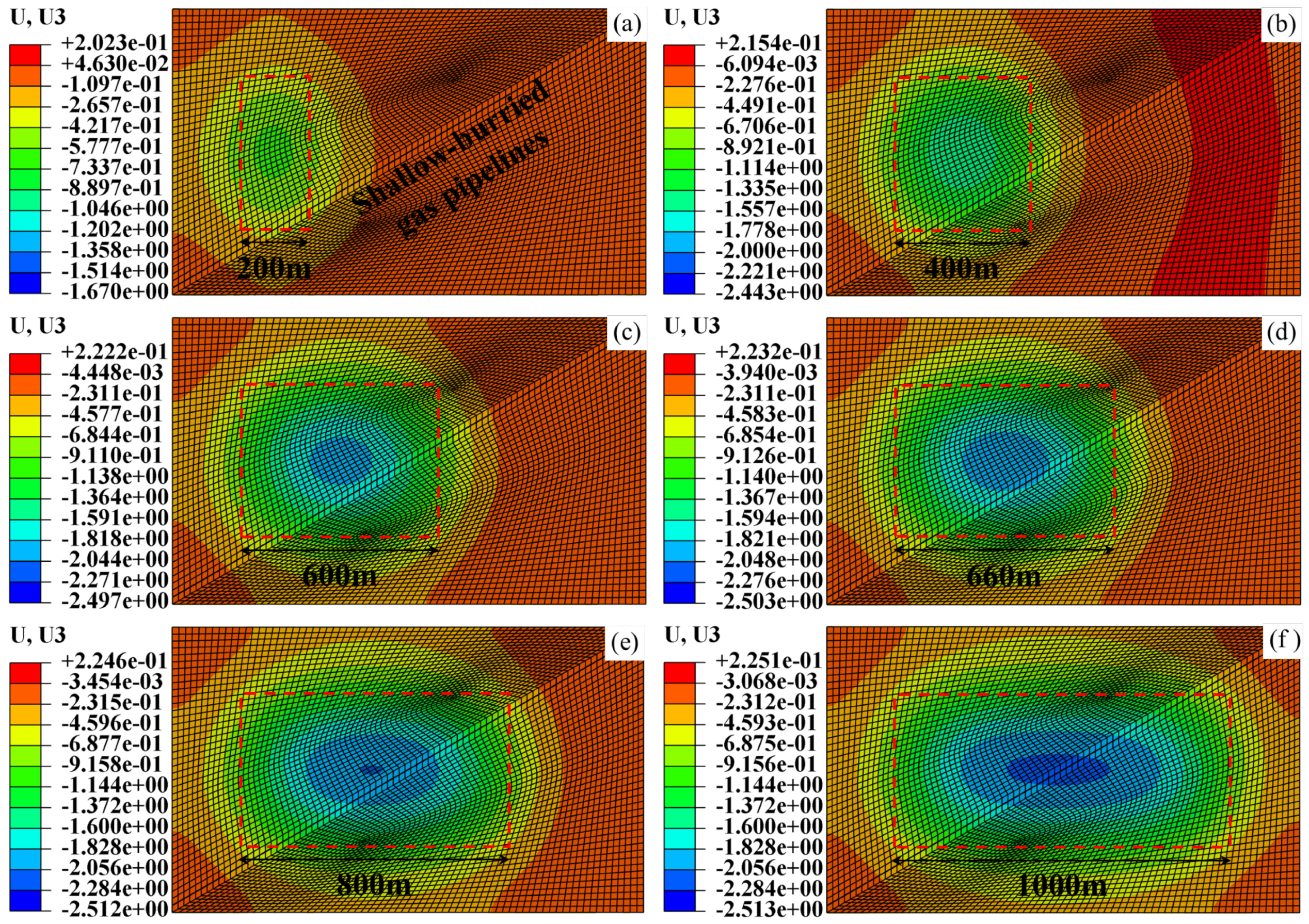
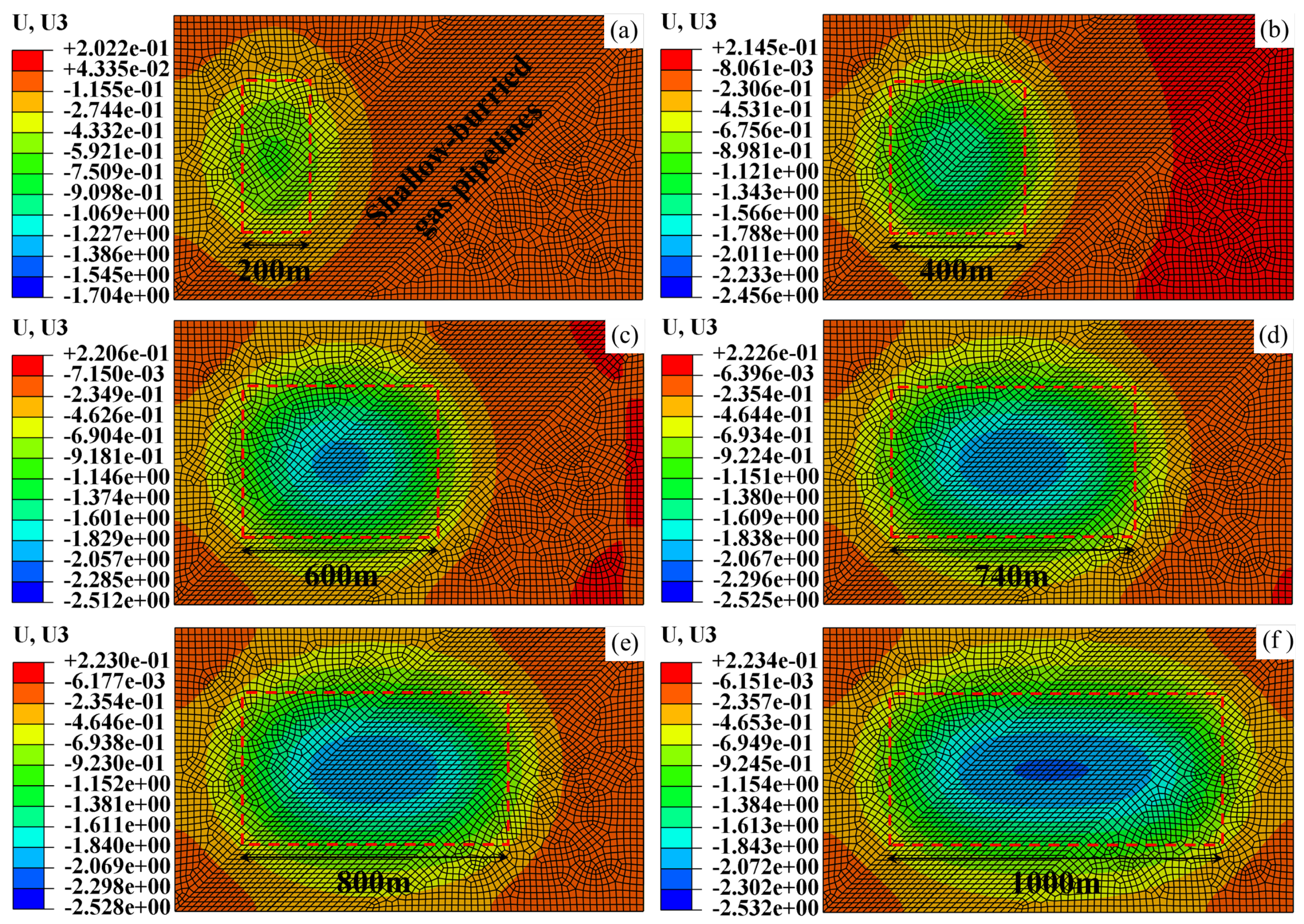
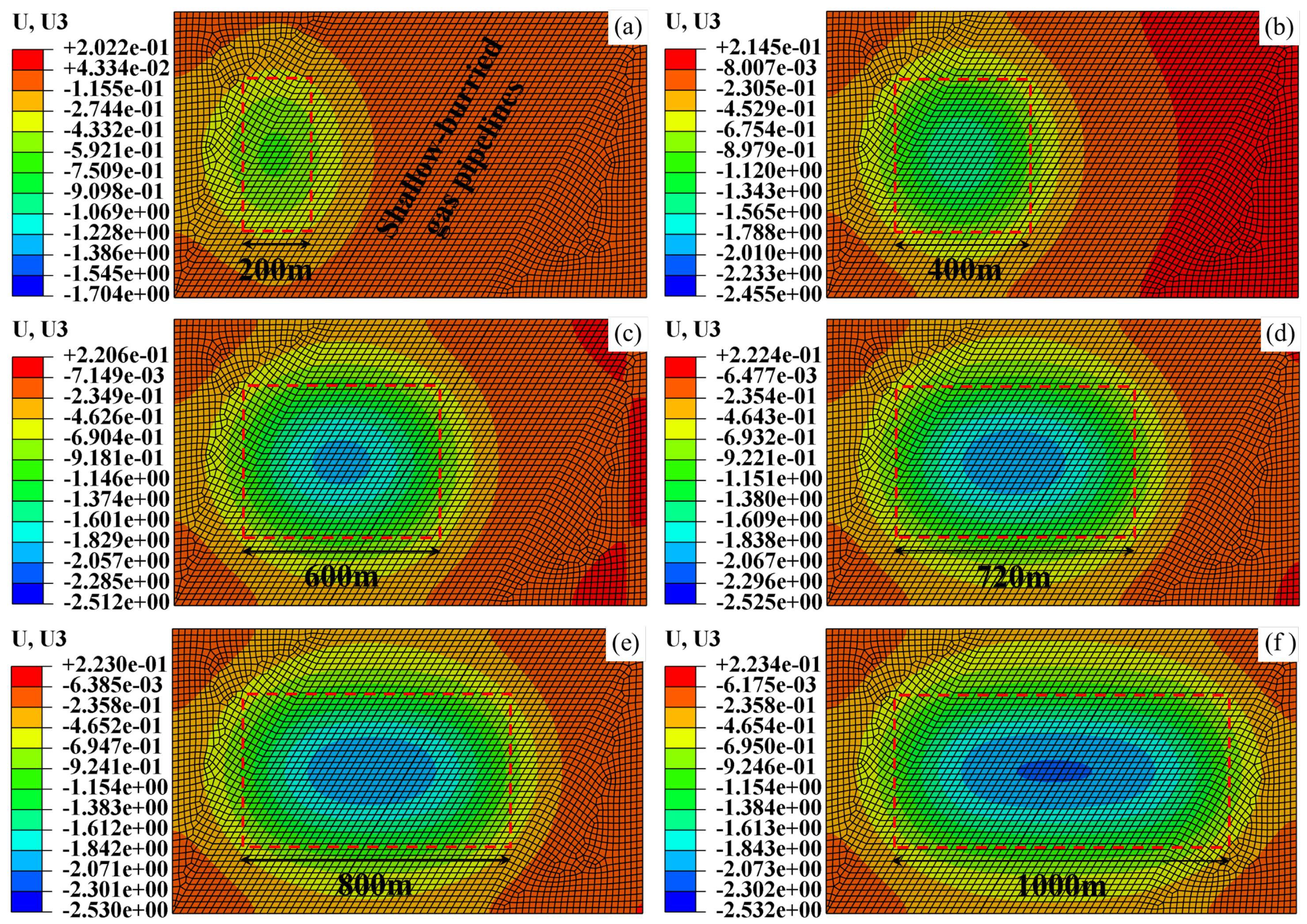

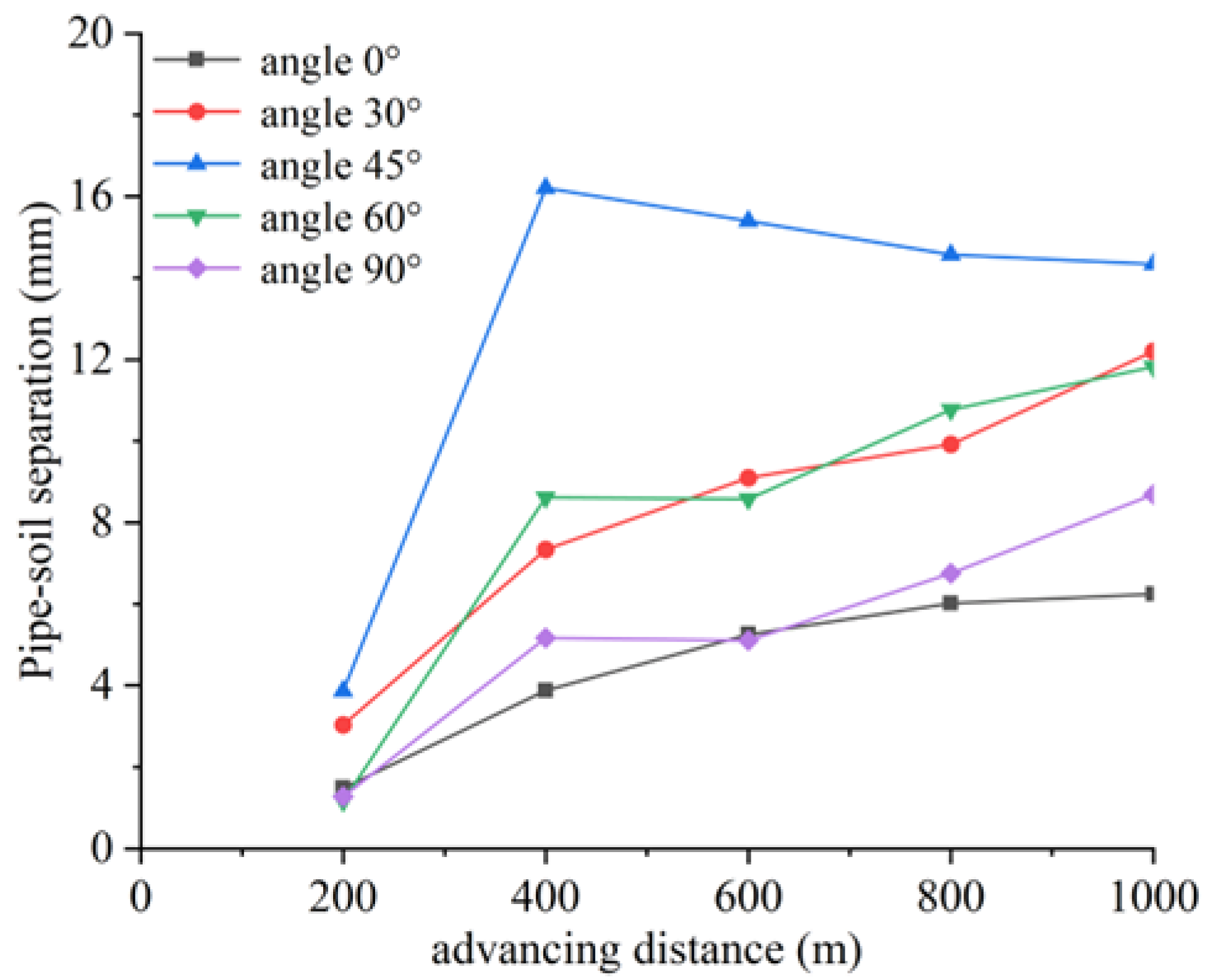
| Main Reference Index | Extremely High Intensity | High Intensity | Moderate Intensity | Low Intensity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area ratio of mined area to the total area | >0.6 | 0.3~0.6 | 0.3~0.6 | <0.1 |
| Mining dimensions of the LWWF (m) | Mining thickness: ≥4.5 Width of the LWWF: ≥200 Advancing length: ≥2000 | Mining thickness: 1.3~4.5 Width of the LWWF: 100~200 Advancing length: 1000~2000 | Mining thickness: <1.3 Width of the LWWF: No limit Advancing length: No limit | |
| Advancing speed (m/d) | ≥5 | Not required | Not required | |
| Stability Level | Surface Deformation Indicators | The Hazard Level of the Pipeline | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Horizontal Deformation ε (mm/m) | Tilt i (mm/m) | Curvature K (10−3·m−1) | ||
| I | >9.0 | / | ≥1.0 | High |
| II | 6.0~9.0 | >6.0 | 0.4~1.0 | Moderate–high |
| III | 2.0~6.0 | 3.0~6.0 | 0.25~0.4 | Moderate |
| IV | 0.5~2.0 | 0.6~3.0 | 0.05~0.25 | Moderate–low |
| V | ≤0.5 | ≤0.6 | ≤0.05 | None |
| Scheme | Advancing Speed (m/d) | Mining Thickness (m) | Different Angles from the Advancing Direction (°) |
|---|---|---|---|
| I-1 | 10 | 2.5 | 90° |
| I-2 | 15 | ||
| I-3 | 20 | ||
| II-1 | 20 | 3.5 | 90° |
| II-2 | 5.5 | ||
| II-3 | 7.5 | ||
| III-1 | 20 | 2.5 | 0° |
| III-2 | 30° | ||
| III-3 | 45° | ||
| III-4 | 60° |
| Name of Material | Density (kg/m3) | Elastic Modulus (MPa) | Poisson Ratio | Cohesive Force (MPa) | Internal Friction Angle (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aeolian sand | 1600 | 150 | 0.11 | 0.2 | 19 |
| Loess | 2100 | 525 | 0.32 | 0.8 | 30 |
| Red soil | 2260 | 500 | 0.31 | 2 | 34 |
| Mudstone | 2300 | 750 | 0.3 | 3.8 | 34 |
| Medium-grained sandstone | 2360 | 900 | 0.34 | 4.4 | 36 |
| Coarse-grained sandstone | 2340 | 1050 | 0.28 | 5.7 | 40 |
| Fine-grained sandstone | 2450 | 1200 | 0.26 | 5.2 | 42 |
| Mudstone | 2300 | 750 | 0.3 | 3.8 | 34 |
| Siltstone | 2400 | 900 | 0.31 | 4.1 | 36 |
| Coal | 1350 | 300 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 29 |
| Siltstone | 2400 | 900 | 0.31 | 4.1 | 36 |
| pipe | 7850 | 200,000 | 0.3 | / | / |
| Mining Thickness/m | 315 MPa Danger Zone | 450 MPa Danger Zone | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initiation Distance (m) | Termination Distance (m) | Initiation Distance (m) | Termination Distance (m) | |
| 2.5 | 645 | 850 | 718 | 780 |
| 3.5 | 608 | 861 | 645 | 800 |
| 5.5 | 590 | 898 | 615 | 820 |
| 7.5 | 590 | 915 | 615 | 820 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, S.; Xu, Y.; Shen, J.; Wang, Q.; Liang, X.; Xu, S.; Luo, C.; Yang, M.; Ma, Y. Load–Deformation Behavior and Risk Zoning of Shallow-Buried Gas Pipelines in High-Intensity Longwall Mining-Induced Subsidence Zones. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 10618. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910618
Liang S, Xu Y, Shen J, Wang Q, Liang X, Xu S, Luo C, Yang M, Ma Y. Load–Deformation Behavior and Risk Zoning of Shallow-Buried Gas Pipelines in High-Intensity Longwall Mining-Induced Subsidence Zones. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(19):10618. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910618
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Shun, Yingnan Xu, Jinhang Shen, Qiang Wang, Xu Liang, Shaoyou Xu, Changheng Luo, Miao Yang, and Yindou Ma. 2025. "Load–Deformation Behavior and Risk Zoning of Shallow-Buried Gas Pipelines in High-Intensity Longwall Mining-Induced Subsidence Zones" Applied Sciences 15, no. 19: 10618. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910618
APA StyleLiang, S., Xu, Y., Shen, J., Wang, Q., Liang, X., Xu, S., Luo, C., Yang, M., & Ma, Y. (2025). Load–Deformation Behavior and Risk Zoning of Shallow-Buried Gas Pipelines in High-Intensity Longwall Mining-Induced Subsidence Zones. Applied Sciences, 15(19), 10618. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910618






