An Innovative Approach for Forecasting Hydroelectricity Generation by Benchmarking Tree-Based Machine Learning Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
- First and foremost, Python, which is an open-source programming language, is used in this paper on a publicly available data set to present reproducible work for other researchers studying the same field and to bring the term of reproducibility to the fore in scientific writing.
- One of the main contributions of this study is to propose an innovative approach for forecasting hydroelectricity generation of an HPP by paying attention to the electricity productions of the other upstream HPPs on the same river (or within the same basin) alongside a variety of explanatory features containing meteorological, market, calendar, and historical hydroelectricity generation. The proposed methodology uniquely differs this paper from other studies in the literature that focus on a single HPP and offers a more comprehensive perspective on basin-wide hydrological and operational dynamics for future studies. Furthermore, the HGF literature is considered immature in terms of covering studies with real-time data in the short-term horizon, and it is thought that this paper will bridge the highlighted gap and reinforce the current literature.
- For the first time in the literature, this paper fulfills a thorough benchmark of state-of-the-art tree-based machine learning models, namely XGBoost, LightGBM, and CatBoost, by taking the tuning of the hyperparameters such as the number of trees and learning rates into consideration. To the best of one’s knowledge, no previous research has conducted a direct head-to-head comparison of these algorithms in forecasting hydroelectricity generation under identical constraints with the same performance and error metrics.
2. Related Work
2.1. Statistical Models
2.2. Neural Networks-Based Models
2.3. Tree-Based Models
2.4. Hybrid and Other Models
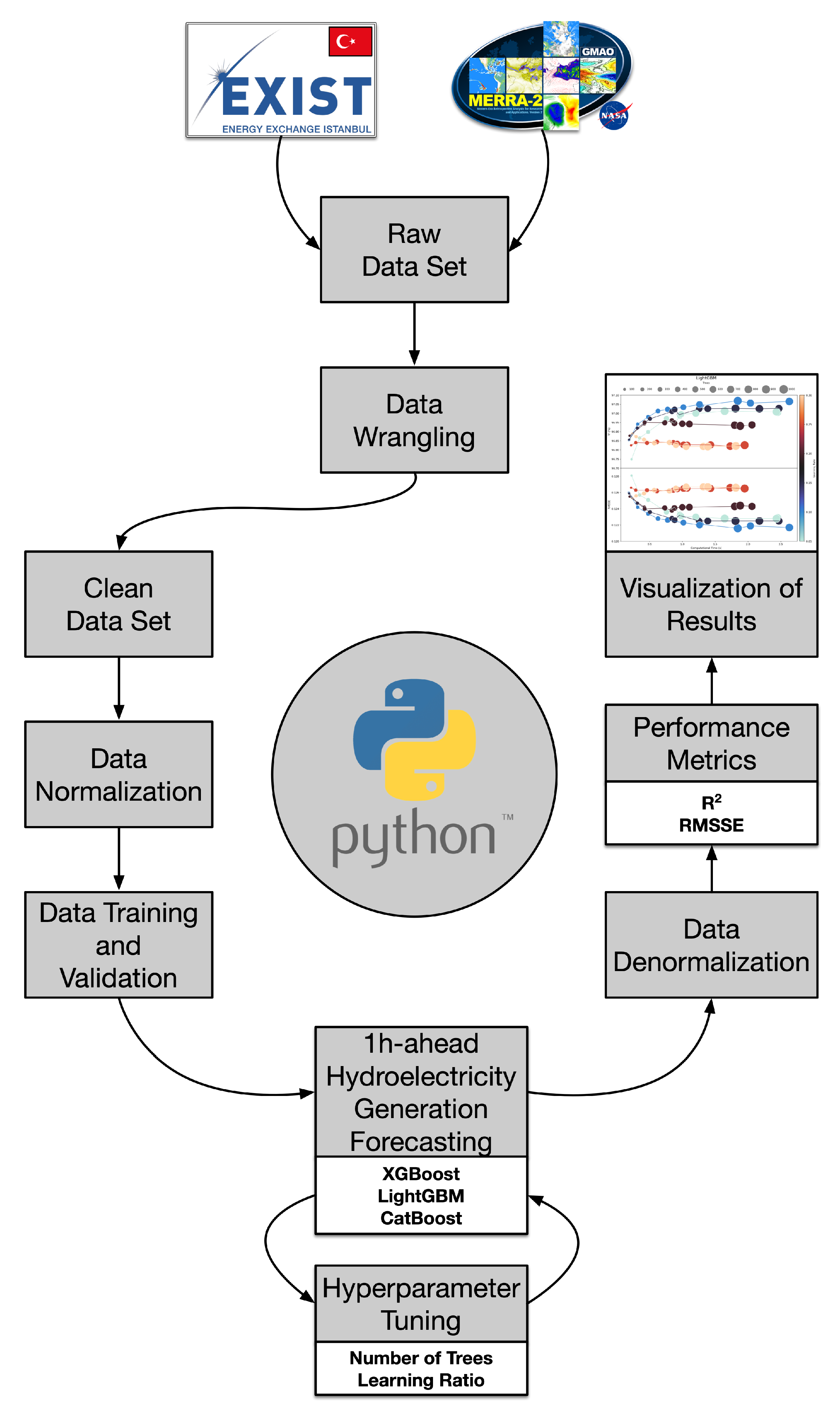
3. Material and Methods
3.1. Material
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. XGBoost
3.2.2. LightGBM
- 1.
- Rank all training instances by the absolute values of their gradients in descending order.
- 2.
- Retain the top of instances with the largest gradients to form subset A.
- 3.
- From the remaining instances with smaller gradients, randomly sample instances to create subset B, where is the complement of A.
- 4.
- Determine the optimal split by evaluating the variance gain over the combined set .
- and are the subsets of A split by threshold d.
- and are the subsets of B split similarly.
3.2.3. CatBoost
3.2.4. Model Implementation
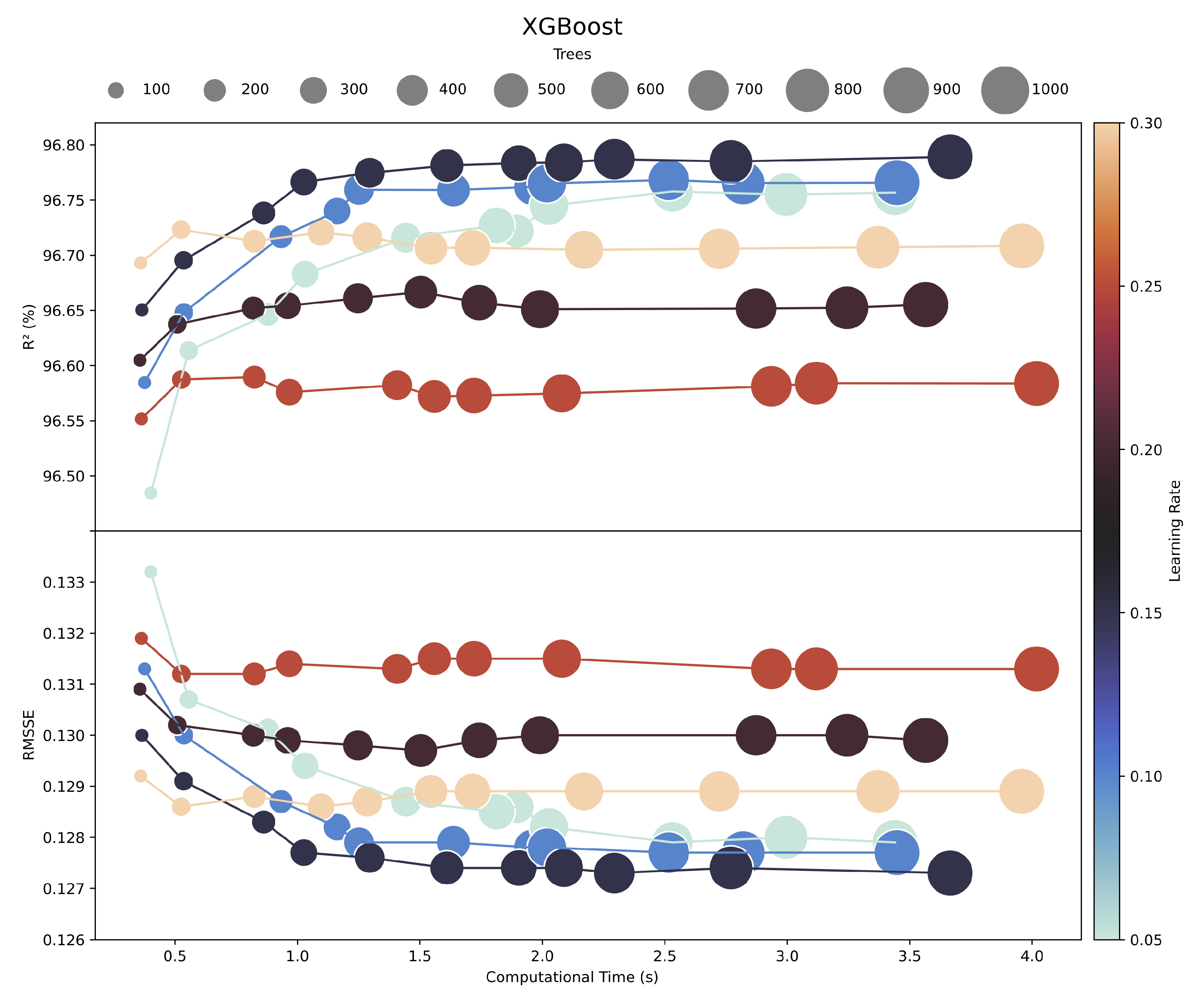
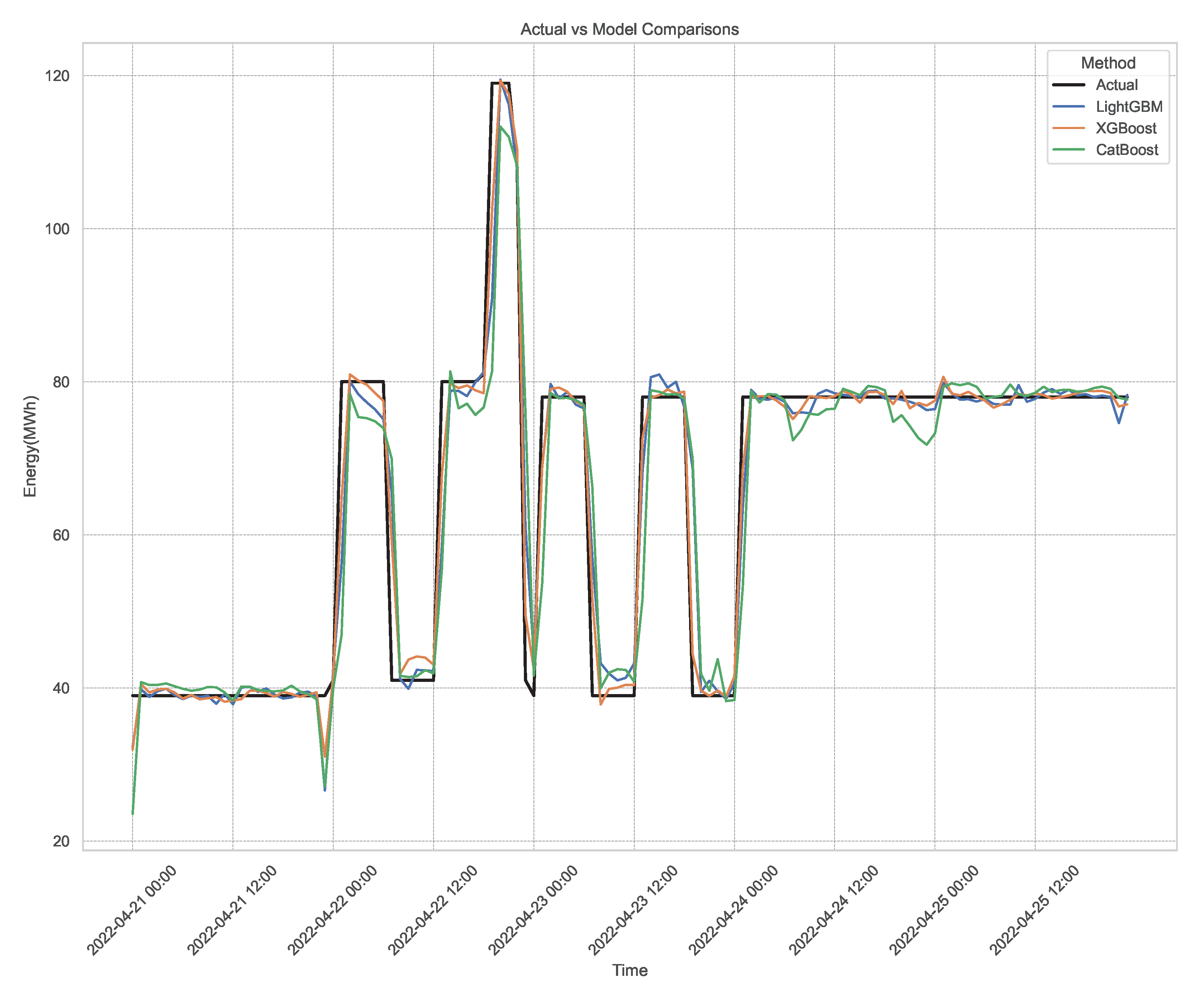
4. Results and Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABC | Artificial Bee Colony |
| ABDT | Adaptive Boosting Decision Trees |
| ABLR | Adaptive Boosting Linear Regression |
| AE | Autoencoder |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| ANFIS | Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System |
| ANN | Artificial Neural Network |
| ARIMA | Auto-Regressive Integrated Moving Average |
| AWT | Adaptive Wavelet Transform |
| CatBoost | Categorical Boosting |
| DL | Deep Learning |
| DNN | Deep Neural Network |
| EEMD | Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition |
| ELM | Extreme Learning Machines |
| EXIST | The Energy Exchange Istanbul |
| GA | Genetic Algorithm |
| GBDT | Gradient Boosted Decision Trees |
| GBM | Gradient Boosting Machine |
| GOSS | Gradient-based One Side Sampling |
| GPR | Gaussian Process Regression |
| GWO | Grey Wolf Optimization |
| HGF | Hydroelectricity Generation Forecasting |
| HPP | Hydroelectric Power Plant |
| kNN | K-Nearest Neighbor |
| LightGBM | Light Gradient Boosting Machine |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| LWNRBF | Linear Weighted Normalized Radial Basis Function |
| MAE | Mean Absolute Error |
| MAPE | Mean Absolute Percentage Error |
| MERRA-2 | Modern-Era Retrospective Analysis for Research and Applications, Version 2 |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| MLP | Multilayer Perceptron |
| MLR | Multiple Linear Regression |
| MSE | Mean Squared Error |
| NSE | Nash–Sutcliffe Efficiency |
| R2 | Coefficient of Determination |
| RBF | Radial Basis Function |
| RF | Random Forest |
| RMSE | Root Mean Squared Error |
| RMSPE | Root Mean Squared Percentage Error |
| RMSSE | Root Mean Squared Scaled Error |
| RNN | Recurrent Neural Networks |
| SARIMA | Seasonal ARIMA |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| SVR | Support Vector Regression |
| XGBoost | Extreme Gradient Boosting |
| WDS | Water Distribution Systems |
References
- Çakır, S. Renewable energy generation forecasting in Turkey via intuitionistic fuzzy time series approach. Renew. Energy 2023, 214, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Energy Institute. Statistical Review of World Energy 2024; Technical report; Energy Institute: London, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Cebeci, C.; Parker, M.; Recalde-Camacho, L.; Campos-Gaona, D.; Anaya-Lara, O. Variable-Speed Hydropower Control and Ancillary Services: A Remedy for Enhancing Grid Stability and Flexibility. Energies 2025, 18, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zor, K.; Tolun, G.G.; Şeker Zor, E. Forecasting Electricity Generation of a Geothermal Power Plant Using LSTM and GRU Networks. In Proceedings of the 2025 7th Global Power, Energy and Communication Conference (GPECOM), Bochum, Germany, 11–13 June 2025; pp. 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Hydropower Association. 2024 World Hydropower Outlook; Technical report; International Hydropower Association: London, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Bayazıt, Y. The effect of hydroelectric power plants on the carbon emission: An example of Gokcekaya dam, Turkey. Renew. Energy 2021, 170, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Farrok, O.; Haque, M.M. Environmental impact of renewable energy source based electrical power plants: Solar, wind, hydroelectric, biomass, geothermal, tidal, ocean, and osmotic. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 161, 112279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atalay, B.A. Hydroelectric Power Forecasting via Tree-Based Machine Learning Algorithms. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Graduate School, Adana Alparslan Türkeş Science and Technology University, Adana, Türkiye, 2024. Available online: https://tez.yok.gov.tr/UlusalTezMerkezi/TezGoster?key=1pwTzRXnomYf6jwqVORfUU5c3WKK1Ha5zeoRJpvV87EpgvwsiUzpV629p6yCgy4n (accessed on 23 September 2025).
- Lorca, A.; Favereau, M.; Olivares, D. Challenges in the Management of Hydroelectric Generation in Power System Operations. Curr. Sustain. Energy Rep. 2020, 7, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.W.; Fang, H.; Wang, Y.W. Short-Term Residential Load Forecasting via Pooling-Ensemble Model With Smoothing Clustering. IEEE Trans. Artif. Intell. 2024, 5, 3690–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.C.; Wang, Y.W.; Xiao, J.W. Accurate forecasting on few-shot learning with a novel inference foundation model. Inf. Fusion 2025, 124, 103370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriqi, A.; Pinheiro, A.N.; Sordo-Ward, A.; Bejarano, M.D.; Garrote, L. Ecological impacts of run-of-river hydropower plants—Current status and future prospects on the brink of energy transition. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 142, 110833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krechowicz, A.; Krechowicz, M.; Poczeta, K. Machine Learning Approaches to Predict Electricity Production from Renewable Energy Sources. Energies 2022, 15, 9146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EÜAŞ Aslantaş HPP. 2024. Available online: https://www.euas.gov.tr/en-US/power-plants/aslantas-hepp (accessed on 23 September 2025).
- Enerjiatlasi.com HPPs in Türkiye. 2025. Available online: https://www.enerjiatlasi.com/hidroelektrik/ (accessed on 23 September 2025).
- Mosavi, A.; Salimi, M.; Faizollahzadeh Ardabili, S.; Rabczuk, T.; Shamshirband, S.; Varkonyi-Koczy, A.R. State of the Art of Machine Learning Models in Energy Systems, a Systematic Review. Energies 2019, 12, 1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero Bermejo, J.; Gómez Fernández, J.F.; Olivencia Polo, F.; Crespo Márquez, A. A Review of the Use of Artificial Neural Network Models for Energy and Reliability Prediction. A Study of the Solar PV, Hydraulic and Wind Energy Sources. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Lei, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, B.; Peng, J. A review of deep learning for renewable energy forecasting. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 198, 111799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, C.; Wang, W.; Yu, J.; Li, Q.; Yu, D.; Liu, J. Deep learning for renewable energy forecasting: A taxonomy, and systematic literature review. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 384, 135414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksandrovskii, A.Y.; Borshch, P.S. Prediction of electric-power generation at hydroelectric power plants. Power Technol. Eng. 2013, 47, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, C.H.; Lall, U. Climate informed long term seasonal forecasts of hydroenergy inflow for the Brazilian hydropower system. J. Hydrol. 2010, 381, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekanayake, P.; Wickramasinghe, L.; Jayasinghe, J.M.J.W.; Rathnayake, U. Regression-Based Prediction of Power Generation at Samanalawewa Hydropower Plant in Sri Lanka Using Machine Learning. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 4913824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzola-Monteses, J.; Mite-León, M.; Espinoza-Andaluz, M.; Gómez-Romero, J.; Fajardo, W. Time Series Analysis for Predicting Hydroelectric Power Production: The Ecuador Case. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Xue, P.; Li, Y. Comparison of Holt-Winters and ARIMA Models for Hydropower Forecasting in Guangxi. In Proceedings of the 2020 3rd International Conference on Signal Processing and Machine Learning, Beijing China, 22–24 October 2020; pp. 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sousa, M.A.; Maçaira, P.M.; Souza, R.C.; Cyrino Oliveira, F.L.; Calili, R.F. Forecasting Electricity Generation of Small Hydropower Plants. In Springer Proceedings in Business and Economics; Springer Science and Business Media B.V.: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polprasert, J.; Hanh Nguyen, V.A.; Nathanael Charoensook, S. Forecasting Models for Hydropower Production Using ARIMA Method. In Proceedings of the 2021 9th International Electrical Engineering Congress (iEECON), Pattaya, Thailand, 10–12 March 2021; pp. 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu, N.; Tukimat, N.N.A.; Abu, N. Forecasting of hydropower production using Box-Jenkins model at Tasik Kenyir, Terengganu. AIP Conf. Proc. 2024, 2895, 050005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarpong, S.A.; Agyei, A. Forecasting Hydropower Generation in Ghana Using ARIMA Models. Int. J. Stat. Probab. 2022, 11, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaga, G.O.; Ikuzwe, A.; Gupta, A. Forecasting of Monthly Hydroelectric and Solar Energy in Rwanda using SARIMA. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE PES/IAS PowerAfrica, PowerAfrica 2022, Kigali, Rwanda, 22–26 August 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.T.; Miao, S.M.; Luo, B.; Sun, Y.J. Forecasting monthly energy production of small hydropower plants in ungauged basins using grey model and improved seasonal index. J. Hydroinform. 2017, 19, 993–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.X.; Li, Q.; Pei, L.L. Grey forecasting method of quarterly hydropower production in China based on a data grouping approach. Appl. Math. Model. 2017, 51, 302–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Hu, X.; Guo, H.; Xiong, X. A novel Weighted Average Weakening Buffer Operator based Fractional order accumulation Seasonal Grouping Grey Model for predicting the hydropower generation. Energy 2023, 277, 127568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, C.; Ramirez-Rosado, I.J.; Fernandez-Jimenez, L.A. Short-term forecasting model for aggregated regional hydropower generation. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 88, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulibaly, P.; Anctil, F.; Bobée, B. Neural Network-Based Long-Term Hydropower Forecasting System. Comput.-Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2000, 15, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valena, M.; Ludermir, T. Constructive neural networks in forecasting weekly river flow. In Proceedings of the Proceedings Fourth International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Multimedia Applications, ICCIMA 2001, Yokusika City, Japan, 30 October–1 November 2001; pp. 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokelj, T.; Paravan, D.; Golob, R. Enhanced Artificial Neural Network Inflow Forecasting Algorithm for Run-of-River Hydropower Plants. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2002, 128, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joaquim, P.; Rosa, J. Artificial neural networks for temporal processing applied to prediction of electric energy in small hydroelectric power stations. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Montreal, QC, Canada, 31 July–4 August 2005; Volume 4, pp. 2625–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobaner, M.; Haktanir, T.; Kisi, O. Prediction of Hydropower Energy Using ANN for the Feasibility of Hydropower Plant Installation to an Existing Irrigation Dam. Water Resour. Manag. 2008, 22, 757–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzlu, E.; Akpinar, A.; Özturk, H.T.; Nacar, S.; Kankal, M. Estimates of hydroelectric generation using neural networks with the artificial bee colony algorithm for Turkey. Energy 2014, 69, 638–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Deng, C.H.; Tan, J.; Yang, W.; Zheng, L. Research on Small Hydropower Generation Forecasting Method Based on Improved BP Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2016 3rd International Conference on Materials Engineering, Manufacturing Technology and Control, Taiyuan, China, 27–28 February 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussin, S.N.H.S.; Malek, M.A.; Jaddi, N.S.; Hamid, Z.A. Hybrid metaheuristic of artificial neural network—Bat algorithm in forecasting electricity production and water consumption at Sultan Azlan shah Hydropower plant. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Power and Energy (PECon), Melaka, Malaysia, 28–29 November 2016; pp. 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammid, A.T.; Sulaiman, M.H.B.; Awad, O.I. A robust firefly algorithm with backpropagation neural networks for solving hydrogeneration prediction. Electr. Eng. 2018, 100, 2617–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammid, A.T.; Sulaiman, M.H.B.; Abdalla, A.N. Prediction of small hydropower plant power production in Himreen Lake dam (HLD) using artificial neural network. Alex. Eng. J. 2018, 57, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucci, C.E.M.; Collischonn, W.; Fan, F.M.; Schwanenberg, D. Hydropower Forecasting in Brazil. In Handbook of Hydrometeorological Ensemble Forecasting; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 1307–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yao, F.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, F. Hydropower generation forecasting via deep neural network. In Proceedings of the 2019 6th International Conference on Information Science and Control Engineering, ICISCE 2019, Shanghai, China, 20–22 December 2019; pp. 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, C.; Wei, H.; Qin, S.; Li, Z. Trend-guided Small Hydropower System Power Prediction Based on Extreme Learning Machine. In Proceedings of the 2020 4th International Conference on Power and Energy Engineering (ICPEE), Xiamen, China, 19–21 November 2020; pp. 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, M.N.G.; da Rocha, B.R.P.; Vieira, A.C.; de Sá, J.A.S.; Rolim, P.A.M.; da Silva, A.G. Artificial neural networks approaches for predicting the potential for hydropower generation: A case study for Amazon region. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2019, 36, 5757–5772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joe, W.W.; Yuzainee, M.Y.; Zaini, N.; Malek, M.A. Methods in Forecasting Water Used and Electricity Production at Hydropower Plants. Int. J. Recent Technol. Eng. (IJRTE) 2019, 8, 6499–6505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Chen, S.; Wei, D.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y. A Comprehensive Hybrid Deep Learning Approach for Accurate Status Predicting of Hydropower Units. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 9323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Li, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, W.; Guo, J.; Qin, H.; Ni, X. Research on Medium- and Long-Term Hydropower Generation Forecasting Method Based on LSTM and Transformer. Energies 2024, 17, 5707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Grande, S.; Berlotti, M.; Cavalieri, S.; Gueli, R. A Machine Learning Approach for Hydroelectric Power Forecasting. In Proceedings of the 14th International Renewable Energy Congress (IREC), Sousse, Tunisia, 16–18 December 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Grande, S.; Berlotti, M.; Cavalieri, S.; Gueli, R. A Machine Learning Approach to Forecasting Hydropower Generation. Energies 2024, 17, 5163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, U.; Fraz, M.M.; Mahmood, I.; Shahzad, M.; Arif, O. Forecasting of Electricity Generation for Hydro Power Plants. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 17th International Conference on Smart Communities: Improving Quality of Life Using ICT, IoT and AI (HONET), Charlotte, NC, USA, 14–16 December 2020; pp. 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Rayess, H.; Ülke Keskin, A. Forecasting the hydroelectric power generation of gcms using machine learning techniques and deep learning (Almus dam, Turkey). Geofizika 2021, 38, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, T.; Xu, N.; Zhou, H.; Xiong, Z.; Long, W. A Novel Reservoir Modeling Method based on Improved Hierarchical XGBoost. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 5th Advanced Information Technology, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (IAEAC), Chongqing, China, 12–14 March 2021; pp. 1918–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepanek, R. Daily Streamflow Forecasting in Mountainous Catchment Using XGBoost, LightGBM and CatBoost. Hydrology 2022, 9, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Kedam, N.; Sharma, K.V.; Mehta, D.J.; Caloiero, T. Advanced Machine Learning Techniques to Improve Hydrological Prediction: A Comparative Analysis of Streamflow Prediction Models. Water 2023, 15, 2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Xu, F.; Zhu, X.; Liu, S. A runoff-based hydroelectricity prediction method based on meteorological similar days and XGBoost model. Front. Energy Res. 2023, 11, 1273805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciejewski, D.; Mudryk, K.; Sporysz, M. Forecasting Electricity Production in a Small Hydropower Plant (SHP) Using Artificial Intelligence (AI). Energies 2024, 17, 6401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atalay, B.A.; Zor, K. XGBoost (Aşırı Gradyan Artırımlı Karar Ağaçları) ile Hidroelektrik Enerji Tahmini. Çukurova Üniv. Mühendis. Fak. Derg. 2025, 40, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Feng, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, C. Enhancing hydropower generation Predictions: A comprehensive study of XGBoost and Support Vector Regression models with advanced optimization techniques. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2025, 16, 103206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, C.; Feng, Y.; Wang, S. Predicting hydropower generation: A comparative analysis of Machine learning models and optimization algorithms for enhanced forecasting accuracy and operational efficiency. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2025, 16, 103299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, I.; Lopes, J.E.G.; Ballini, R.; Soares, S. Verifying the Use of Evolving Fuzzy Systems for Multi-Step Ahead Daily Inflow Forecasting. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Intelligent System Applications to Power Systems, Curitiba, Brazil, 8–12 November 2009; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konica, J.A.; Staka, E. Forecasting of a hydropower plant energy production with Fuzzy logic Case for Albania. J. Multidiscip. Eng. Sci. Technol. (JMEST) 2017, 4, 2458–9403. [Google Scholar]
- Wardlaw, R.B.; Sharif, M.; Kimaite, F. Real-time hydro-power forecasting on the Victoria Nile. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng.-Water Manag. 2005, 158, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xu, D.; Qiu, L.; Ma, J. Genetic Programming for Modelling Long-Term Hydrological Time Series. In Proceedings of the 2009 Fifth International Conference on Natural Computation, Tianjian, China, 14–16 August 2009; Volume 4, pp. 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, M.; Riahi-Madvar, H.; Hooshyaripor, F.; Mosavi, A.; Shamshirband, S.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Chau, K.w. Prediction of Hydropower Generation Using Grey Wolf Optimization Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System. Energies 2019, 12, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathnayake, N.; Rathnayake, U.; Dang, T.L.; Hoshino, Y. A Cascaded Adaptive Network-Based Fuzzy Inference System for Hydropower Forecasting. Sensors 2022, 22, 2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Wang, Y.; Su, H.; Chang, J.; Huang, Q.; Li, Z. Dynamic quantitative assessment of multiple uncertainty sources in future hydropower generation prediction of cascade reservoirs with hydrological variations. Energy 2024, 299, 131447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, R.; Bai, Z. Comparative Study for Daily Streamflow Simulation with Different Machine Learning Methods. Water 2023, 15, 1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebong, N.K.; Simo, T.; Takougang, A.N. Two-level deep learning ensemble model for forecasting hydroelectricity production. Energy Rep. 2023, 10, 2793–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çakıcı, F.N.; Tezcan, S.S.; Düzkaya, H. Estimation of Hydroelectric Power Generation Forecasting and Analysis of Climate Factors with Deep Learning Methods: A Case Study in Yozgat Province in Turkey. Gazi Üniv. Fen Bilim. Derg. Part C Tasarım Teknol. 2024, 12, 819–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksoy, B. Estimation of Energy Produced in Hydroelectric Power Plant Industrial Automation Using Deep Learning and Hybrid Machine Learning Techniques. Electr. Power Components Syst. 2021, 49, 213–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gao, Z.; Ma, Y. Prediction Model of Hydropower Generation and Its Economic Benefits Based on EEMD-ADAM-GRU Fusion Model. Water 2022, 14, 3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolfaghari, M.; Golabi, M.R. Modeling and predicting the electricity production in hydropower using conjunction of wavelet transform, long short-term memory and random forest models. Renew. Energy 2021, 170, 1367–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogliari, E.; Nespoli, A.; Mussetta, M.; Pretto, S.; Zimbardo, A.; Bonfanti, N.; Aufiero, M. A Hybrid Method for the Run-Of-The-River Hydroelectric Power Plant Energy Forecast: HYPE Hydrological Model and Neural Network. Forecasting 2020, 2, 410–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huangpeng, Q.; Huang, W.; Gholinia, F. Forecast of the hydropower generation under influence of climate change based on RCPs and Developed Crow Search Optimization Algorithm. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, C.; Açikgöz, H. Forecasting diversion type hydropower plant generations using an artificial bee colony based extreme learning machine method. Energy Sources Part B Econ. Plan. Policy 2021, 16, 216–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongpaseuth, V.; Kaewarsa, S. Nam Theun 2 Hydropower Plant Energy Prediction Using Artificial Neural Network and Genetic Algorithm. In Proceedings of the Asia-Pacific Power and Energy Engineering Conference, APPEEC, Chiang Mai, Thailand, 6–9 December 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewarsa, S.; Kongpaseuth, V. An energy prediction approach using bi-directional long short-term memory for a hydropower plant in Laos. Electr. Eng. 2024, 106, 2609–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, S.A.; Shah, D.; Jayavel, K.; Mtonga, K. Hydropower Energy Generation Prediction Model: A Machine Learning Approch. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Computer Communication and Informatics (ICCCI), Coimbatore, India, 25–27 January 2022; pp. 01–04. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgili, M.; Keiyinci, S.; Ekinci, F. One-day ahead forecasting of energy production from run-of-river hydroelectric power plants with a deep learning approach. Sci. Iran. 2022, 29, 1838–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İnal, S.; Akkaya Oy, S.; Özdemir, A.E. A Neural Network Model for Estimation of Maximum Next Day Energy Generation Capacity of a Hydropower Station: A Case Study from Turkey. Celal Bayar Üniv. Fen Bilim. Derg. 2023, 19, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safaraliev, M.; Kiryanova, N.; Matrenin, P.; Dmitriev, S.; Kokin, S.; Kamalov, F. Medium-term forecasting of power generation by hydropower plants in isolated power systems under climate change. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Modeling and Assimilation Office (GMAO). MERRA-2 inst1_2d_asm_Nx: 2d,1-Hourly,Instantaneous,Single-Level,Assimilation,Single-Level Diagnostics V5.12.4 (M2I1NXASM); Global Modeling and Assimilation Office (GMAO): Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Modeling and Assimilation Office (GMAO). MERRA-2 tavg1_2d_flx_Nx: 2d,1-Hourly,Time-Averaged,Single-Level,Assimilation,Surface Flux Diagnostics V5.12.4 (M2T1NXFLX); Global Modeling and Assimilation Office (GMAO): Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Modeling and Assimilation Office (GMAO). MERRA-2 tavg1_2d_rad_Nx: 2d,1-Hourly,Time-Averaged,Single-Level,Assimilation,Radiation Diagnostics V5.12.4 (M2T1NXRAD); Global Modeling and Assimilation Office (GMAO): Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EXIST(EPIAS). Transparency Platform. 2025. Available online: https://seffaflik.epias.com.tr/home (accessed on 23 September 2025).
- Wilcox, R.R. Chapter 9 - Correlation and Tests of Independence. In Introduction to Robust Estimation and Hypothesis Testing, 5th ed.; Wilcox, R.R., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 541–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, I. Visualizations with statistical details: The “ggstatsplot” approach. J. Open Source Softw. 2021, 6, 3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolun, O.C.; Zor, K.; Tutsoy, O. A comprehensive benchmark of machine learning-based algorithms for medium-term electric vehicle charging demand prediction. J. Supercomput. 2025, 81, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolun, G.G.; Tolun, O.C.; Zor, K. An Application of Prosumer Electric Load Forecasting with Machine Learning-Based Algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2024 15th National Conference on Electrical and Electronics Engineering (ELECO), Bursa, Türkiye, 28–30 November 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Distributed (Deep) Machine Learning Community. DMLC XGBoost. Available online: https://github.com/dmlc/xgboost (accessed on 23 September 2025).
- Mitchell, R.; Adinets, A.; Rao, T.; Frank, E. XGBoost: Scalable GPU Accelerated Learning. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.11248. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, G.; Meng, Q.; Finley, T.; Wang, T.; Chen, W.; Ma, W.; Ye, Q.; Liu, T.Y. LightGBM: A Highly Efficient Gradient Boosting Decision Tree. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Guyon, I., Luxburg, U.V., Bengio, S., Wallach, H., Fergus, R., Vishwanathan, S., Garnett, R., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Tolun, G.G.; Tolun, Ö.C.; Zor, K. Advanced machine learning algorithms for reactive power forecasting in electric distribution systems. E-Prime-Adv. Electr. Eng. Electron. Energy 2025, 13, 101019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhu, C.; Zou, L.; Zhang, M.; Feng, L.; Cao, Q. Predicting surface solar radiation using a hybrid radiative Transfer–Machine learning model. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 173, 113105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Liu, Y.; Ye, X.; Tang, Q.; Gou, J.; Huang, M.; Wen, Y. Power System Transient Stability Assessment Based on Bayesian Optimized LightGBM. In Proceedings of the 2019 3rd IEEE Conference on Energy Internet and Energy System Integration: Ubiquitous Energy Network Connecting Everything, EI2 2019, Changsha, China, 8–10 November 2019; pp. 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Wang, Y.; Fang, X.; Jiang, J. To Predict the Power Generation based on Machine Learning Method. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2310, 012084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, M. Hourly solar radiation estimation and uncertainty quantification using hybrid models. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2024, 202, 114727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Hu, X.; Tian, T.; Guo, H.; Liao, H. A novel Optimized initial condition and Seasonal division based Grey Seasonal Variation Index model for hydropower generation. Appl. Energy 2022, 328, 120180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adinkrah, J.; Kemausuor, F.; Tutu Tchao, E.; Nunoo-Mensah, H.; Agbemenu, A.S.; Adu-Poku, A.; Kponyo, J.J. Artificial intelligence-based strategies for sustainable energy planning and electricity demand estimation: A systematic review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2025, 210, 115161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokhorenkova, L.; Gusev, G.; Vorobev, A.; Dorogush, A.V.; Gulin, A. CatBoost: Unbiased boosting with categorical features. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Bengio, S., Wallach, H., Larochelle, H., Grauman, K., Cesa-Bianchi, N., Garnett, R., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 31. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, L. Data-driven estimation of building energy consumption with multi-source heterogeneous data. Appl. Energy 2020, 268, 114965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasina, D.; Gorshenin, A. Application of the Catboost Gradient Boosting Method in Forecasting Solar Electricity. In Proceedings of the 2023 Dynamics of Systems, Mechanisms and Machines (Dynamics), Omsk, Russia, 14–15 November 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Microsoft. GitHub-Microsoft/LightGBM: A Fast, Distributed, High Performance Gradient Boosting (GBT, GBDT, GBRT, GBM or MART) Framework Based on Decision Tree Algorithms, Used for Ranking, Classification and Many other Machine Learning Tasks. 2024. Available online: https://github.com/Microsoft/LightGBM (accessed on 23 September 2025).
- CatBoost. CatBoost-Open-Source Gradient Boosting Library. 2025. Available online: https://catboost.ai/ (accessed on 23 September 2025).
- What is Python Used For? 8 Real-Life Python Uses. 2024. Available online: https://www.datacamp.com/blog/what-is-python-used-for (accessed on 23 September 2025).
- Timur, O.; Zor, K.; Çelik, Ö.; Teke, A.; İbrikçi, T. Application of Statistical and Artificial Intelligence Techniques for Medium-Term Electrical Energy Forecasting: A Case Study for a Regional Hospital. J. Sustain. Dev. Energy Water Environ. Syst. 2020, 8, 520–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makridakis, S.; Spiliotis, E.; Assimakopoulos, V. M5 accuracy competition: Results, findings, and conclusions. Int. J. Forecast. 2022, 38, 1346–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cebeci, C.; Zor, K. Electricity Demand Forecasting Using Deep Polynomial Neural Networks and Gene Expression Programming During COVID-19 Pandemic. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
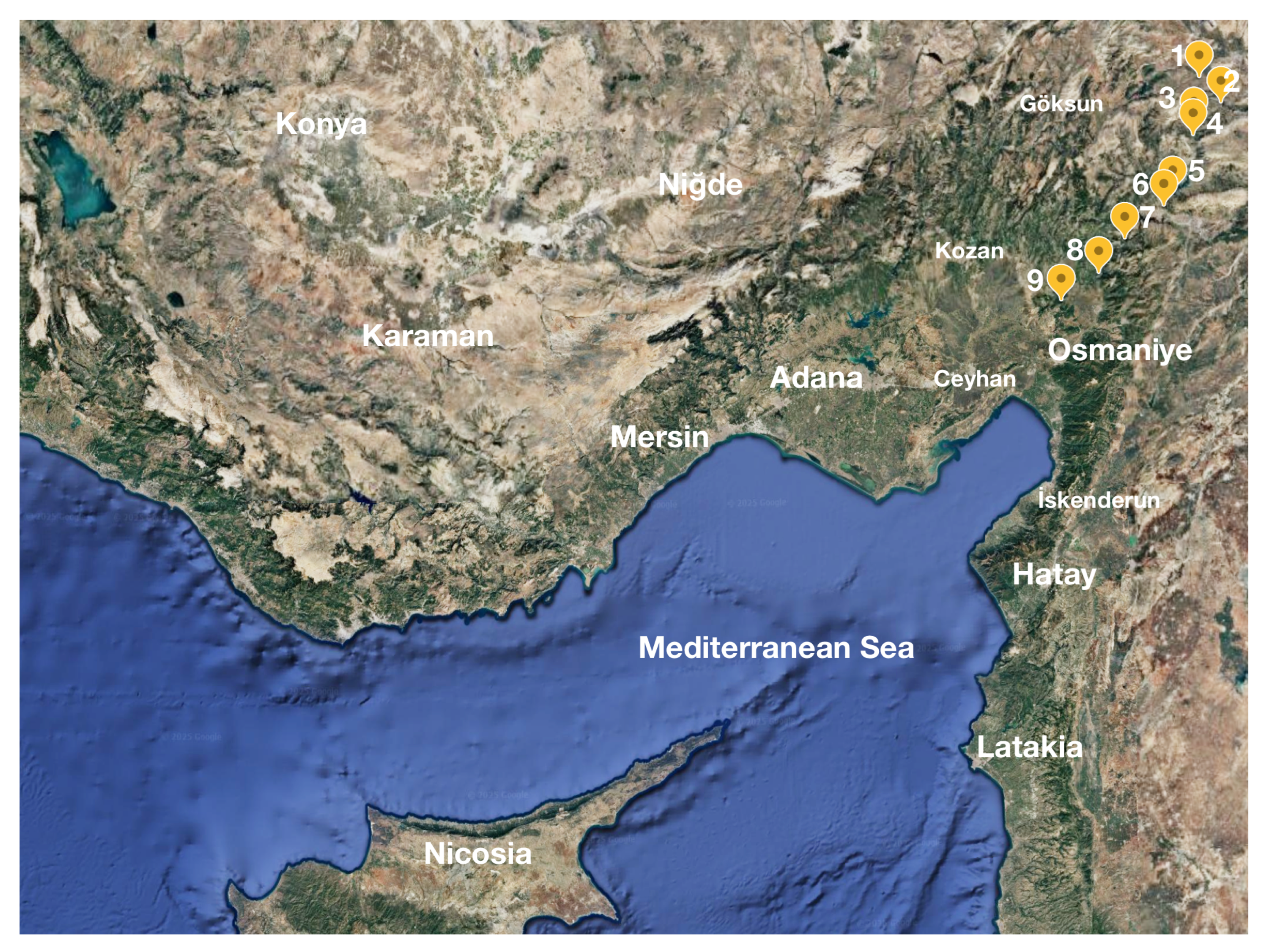





| Owner | Altitude | Installed Power | CF * | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Name | Status | (m) | (MW) | (%) |
| 1 | Dağdelen HPP | Private | 1111 | 8.00 | 37.7 |
| 2 | Kandil HPP | Private | 1087 | 207.92 | 26.7 |
| 3 | Sarıgüzel HPP | Private | 870 | 103.00 | 30.9 |
| 4 | Hacınınoğlu HPP | Private | 749 | 140.00 | 25.4 |
| 5 | Menzelet HPP | Private | 560 | 124.00 | 44.1 |
| 6 | Kılavuzlu HPP | Private | 489 | 54.00 | 38.6 |
| 7 | Sır HPP | State | 420 | 283.50 | 20.4 |
| 8 | Berke HPP | State | 340 | 510.00 | 27.6 |
| 9 | Aslantaş HPP | State | 145 | 138.00 | 36.6 |
| Year | Ref. | Location | Capacity | Methods | Output | Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | [53] | Tarbela HPP, Pakistan | 4.88 MW | MLR, kNN, SVR, RF, LSTM | Daily | 2.47 kWh (MAE), 3.98 kWh (RMSE) |
| 2021 | [54] | Almus HPP, Türkiye | 27 MW | DT, GBDT, RF, GL | Monthly | 0.717 GBDT (Corr.) |
| 2021 | [73] | Dinar 2 HPP, Türkiye | 3 MW | kNN, SVR, RF, GA, DNN, RNN, AE | Hourly | 1.904 kWh (MAE), 2.841 kWh (RMSE) |
| 2021 | [75] | Mahabad HPP, Iran | 6 MW | AWT, LSTM, RF | Daily | 2.154 kWh (MAE), 5.261 kWh (RMSE), 98.7% (R2) |
| 2022 | [84] | Gorno-Badakhshan HPPs, Tajikistan | N/A | LR, kNN, ABDT, ABLR, RF, XGBoost, MLP | Daily | 5.23% (MAPE) |
| 2023 | [58] | Yunnan, China | N/A | XGBoost, GM | Quarter Hourly | 97.14% (Acc.) |
| 2024 | [59] | Skawa HPP, Poland | 760 kW | RF, GBDT, MLP, RBF | Daily | 10.96 kWh (MAE), 3.41% (MAPE) |
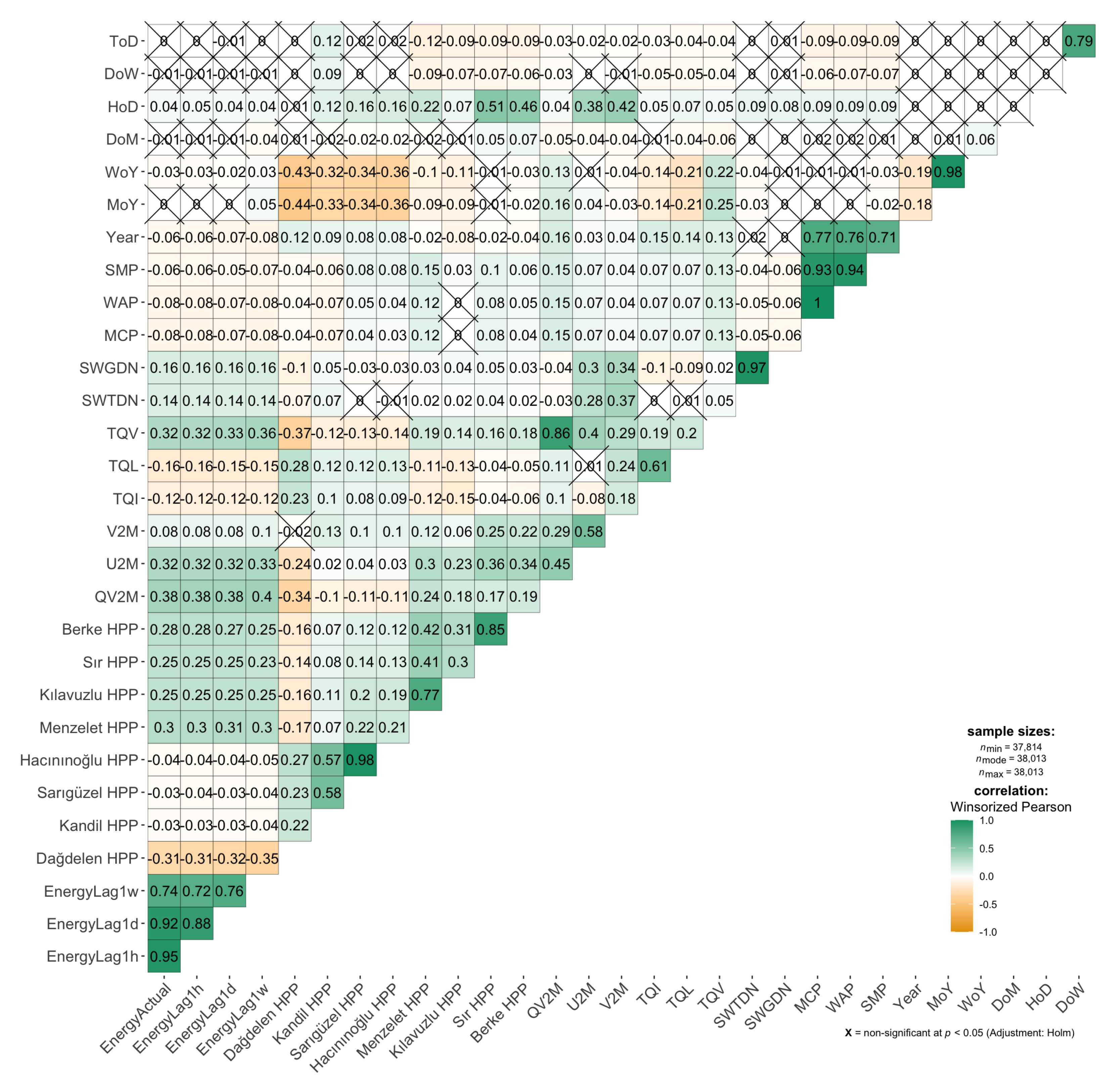
| Category | Feature | Description | Units |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy | EnergyLag1h | Hourly generation lagged by 1 h | MWh |
| Energy | EnergyLag1d | Hourly generation lagged by 1 day | MWh |
| Energy | EnergyLag1w | Hourly generation lagged by 1 week | MWh |
| Energy | Dağdelen HPP | Hourly generation | MWh |
| Energy | Kandil HPP | Hourly generation | MWh |
| Energy | Sarıgüzel HPP | Hourly generation | MWh |
| Energy | Hacınınoğlu HPP | Hourly generation | MWh |
| Energy | Menzelet HPP | Hourly generation | MWh |
| Energy | Kılavuzlu HPP | Hourly generation | MWh |
| Energy | Sır HPP | Hourly generation | MWh |
| Energy | Berke HPP | Hourly generation | MWh |
| Weather | QV2M | Specific humidity at 2 m | kg/kg |
| Weather | U2M | East–west wind components at 2 m | m/s |
| Weather | V2M | North–south wind components at 2 m | m/s |
| Weather | T2M | Temperature at 2 m | C |
| Weather | TQI | Total column ice water content | kg/m2 |
| Weather | TQL | Total column liquid water content | kg/m2 |
| Weather | TQV | Total column vapor content | kg/m2 |
| Weather | SWTDN | TOA incoming shortwave flux | W/m2 |
| Weather | SWGDN | Surface incoming shortwave flux | W/m2 |
| Weather | PRECTOT | Total precipitation | mm |
| Weather | PREVTOT | Total column re-evap of precipitation | mm |
| Weather | PRECSNO | Snowfall precipitation | mm |
| Market | MCP | Market clearing price | TRY |
| Market | WAP | Weighted average price | TRY |
| Market | SMP | System marginal price | TRY |
| Tree | Learning | R2 | Computational | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Size | Rate | (%) | RMSSE | Time (s) | |
| 1 | LightGBM | 1000 | 0.10 | 97.07 | 0.1217 | 1.240 |
| 2 | LightGBM | 900 | 0.10 | 97.06 | 0.1219 | 1.192 |
| 3 | LightGBM | 800 | 0.10 | 97.05 | 0.1220 | 1.066 |
| 4 | LightGBM | 700 | 0.10 | 97.04 | 0.1221 | 0.894 |
| 5 | LightGBM | 600 | 0.10 | 97.03 | 0.1223 | 0.768 |
| 6 | CatBoost | 1000 | 0.15 | 96.94 | 0.1242 | 4.832 |
| 7 | CatBoost | 900 | 0.15 | 96.93 | 0.1245 | 4.316 |
| 8 | CatBoost | 1000 | 0.20 | 96.91 | 0.1249 | 4.971 |
| 9 | CatBoost | 800 | 0.20 | 96.90 | 0.1250 | 3.328 |
| 10 | CatBoost | 900 | 0.20 | 96.90 | 0.1250 | 4.049 |
| 11 | XGBoost | 900 | 0.15 | 96.79 | 0.1273 | 2.007 |
| 12 | XGBoost | 600 | 0.15 | 96.78 | 0.1274 | 1.349 |
| 13 | XGBoost | 700 | 0.15 | 96.78 | 0.1274 | 1.600 |
| 14 | XGBoost | 800 | 0.15 | 96.78 | 0.1274 | 1.797 |
| 15 | XGBoost | 1000 | 0.15 | 96.78 | 0.1274 | 2.274 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Atalay, B.A.; Zor, K. An Innovative Approach for Forecasting Hydroelectricity Generation by Benchmarking Tree-Based Machine Learning Models. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 10514. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910514
Atalay BA, Zor K. An Innovative Approach for Forecasting Hydroelectricity Generation by Benchmarking Tree-Based Machine Learning Models. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(19):10514. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910514
Chicago/Turabian StyleAtalay, Bektaş Aykut, and Kasım Zor. 2025. "An Innovative Approach for Forecasting Hydroelectricity Generation by Benchmarking Tree-Based Machine Learning Models" Applied Sciences 15, no. 19: 10514. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910514
APA StyleAtalay, B. A., & Zor, K. (2025). An Innovative Approach for Forecasting Hydroelectricity Generation by Benchmarking Tree-Based Machine Learning Models. Applied Sciences, 15(19), 10514. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910514







