Featured Application
The application of the HOMA index in diabetic companion animals offers veterinarians a practical tool to assess insulin resistance and β-cell function. This approach can enhance early diagnosis, guide individualized treatment strategies, and improve metabolic monitoring in diabetic dogs and cats.
Abstract
The use of the HOMA (Homeostatic Model Assessment) index in veterinary medicine is emerging as a promising and valuable method for evaluating insulin resistance and beta-cell function in companion animals, particularly in dogs and cats. Originally developed for use in human medicine, HOMA enables a minimally invasive assessment of glucose and insulin homeostasis, offering clinicians a practical tool for diagnosing and monitoring diabetes mellitus in animals. Its application in veterinary practice brings several advantages, including cost-effectiveness, ease of use, and the potential for early detection of metabolic disturbances before clinical symptoms appear. Nonetheless, important limitations persist, such as inter-individual variability, the effects of stress and comorbidities on glucose and insulin values, and the absence of standardized, species-specific reference ranges. These factors highlight the need for methodological refinement and the establishment of validated protocols tailored to the unique physiological characteristics of dogs and cats. Despite these challenges, HOMA represents a promising avenue for advancing the understanding of diabetes pathophysiology in veterinary patients. Future longitudinal studies and controlled trials are essential to confirm its reliability and enhance its clinical relevance. With further development, the HOMA index could become an essential tool in improving diagnostic accuracy and optimizing the management of diabetes in companion animal practice.
1. Introduction
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a complex endocrine and metabolic disorder with an alarmingly increasing incidence in companion animals, mirroring epidemiological trends observed in humans [1,2,3].
This pathology is characterized by chronic hyperglycemia resulting from absolute or relative insulin deficiency, insulin resistance, or a combination of both [4]. Understanding the distinct pathophysiological mechanisms, together with the use of accurate diagnostic tools, is essential for effective clinical management and for the establishment accurate prognostic indicators.
According to the veterinary classification proposed by the ALIVE Project [5], canine diabetes mellitus most frequently presents as insulin-deficient diabetes (IDD), usually resulting from immune-mediated destruction or loss of pancreatic β-cells. This leads to an absolute insulin deficiency and necessitates lifelong insulin therapy. In contrast, the predominant form in cats is insulin-resistant diabetes (IRD), often accompanied by concurrent β-cell dysfunction. This form is typically associated with risk factors such as obesity, physical inactivity, chronic inflammation, and glucolipotoxicity, all of which contribute to the progressive exhaustion of β-cells.
While insulin-deficient diabetes (IDD) in dogs generally follows an irreversible course, insulin-resistant diabetes (IRD) in cats can, in some cases, enter remission—particularly when diagnosed early and managed appropriately through interventions such as insulin therapy, dietary modification, and weight control [6,7]. Regardless of species, diabetes complications can be severe, ranging from diabetic ketoacidosis to neuropathy, cataracts, nephropathy, and increased susceptibility to infections [2,8].
A detailed metabolic evaluation is therefore essential and should go beyond simple blood glucose measurement [9,10,11]. Biomarkers such as glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), fructosamine, cholesterol, and lipid profiles provide a broader picture of glucose homeostasis, insulin secretion, and metabolic risk [4,12].
In this context, the Homeostasis Model Assessment (HOMA) indices offer a non-invasive mathematical approach for evaluating insulin sensitivity (HOMA-IR) and β-cell function (HOMA-β) [13,14]. These indices are based on fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations and model the feedback relationship between insulin production and tissue sensitivity under steady-state conditions [15].
Veterinary studies have shown that HOMA indices can provide practical insights into the early identification of insulin resistance (particularly in cats in early-stage disease) and the monitoring of treatment response [16,17]. Although the constants used in the original HOMA formulas were derived from human data, the method has shown promising applicability in dogs and cats, with potential for species-specific adaptation [18,19].
Longitudinal monitoring of HOMA indices is particularly valuable for guiding treatment adjustments, anticipating disease progression, and identifying high-risk patients—even before clinical signs appear [20,21]. When used alongside traditional markers, HOMA indices contribute to a more nuanced understanding of diabetes pathophysiology and allow for personalized treatment planning [5,22]. This integrated approach can improve glycemic control, prevent complications, and enhance the quality of life of diabetic companion animals [9,23].
2. Materials and Methods
This review was conducted in full compliance with the PRISMA 2020 guidelines. The PRISMA checklist and flow diagram are provided in the Supplementary Materials. This review was not registered in a database (e.g., PROSPERO), and no review protocol was prepared. It was conducted following the PRISMA 2020 guidelines to identify, evaluate, and synthesize available evidence on the use of the HOMA index (Homeostasis Model Assessment) in the diagnosis and monitoring of diabetes mellitus in companion animals.
A comprehensive literature search was performed using multiple international databases, including PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar. The search covered articles published between 1932 and 2024, using combinations of keywords such as “HOMA index”, “insulin resistance”, “HOMA-IR”, “HOMA-β”, “β-cell function”, “canine diabetes”, “feline diabetes”, and “companion animals”. Additional references were identified by examining the bibliographies of relevant studies.
Studies were included based on the following eligibility criteria: (1) original research articles or case series; (2) conducted on companion animals (dogs or cats); (3) involving the use of the HOMA index (HOMA-IR and/or HOMA-β); and (4) reporting relevant clinical, metabolic, or diagnostic data. Exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) studies on laboratory animals or humans; (2) review articles, editorials, or opinion pieces; and (3) articles lacking original data or sufficient methodological clarity.
Two independent reviewers screened all identified titles and abstracts, followed by full-text review of potentially eligible studies. Discrepancies were resolved by consensus. Data were extracted on species studied, study design, method of glucose and insulin measurement, HOMA calculation formulas used, and the clinical context (diagnosis, monitoring, or therapeutic evaluation).
The quality and relevance of included studies were assessed based on their methodological rigor, statistical validity, and clinical applicability. Risk of bias was considered through a qualitative appraisal of study design, sample size, and data reporting transparency. Additionally, potential publication bias was considered by assessing whether studies reported only favorable or expected outcomes and by screening reference lists for missing or unpublished studies.
Extracted data were synthesized narratively due to expected heterogeneity in study designs, species studied, and outcome measures. Comparative interpretations were supported by descriptive tables and figures illustrating HOMA-IR and HOMA-β values across species, age groups, and metabolic states.
This approach aimed to consolidate current evidence on the veterinary application of HOMA indices and to identify knowledge gaps, methodological limitations, and directions for future research.
The selection process of studies is summarized in the PRISMA 2020 flow diagram (Figure 1).
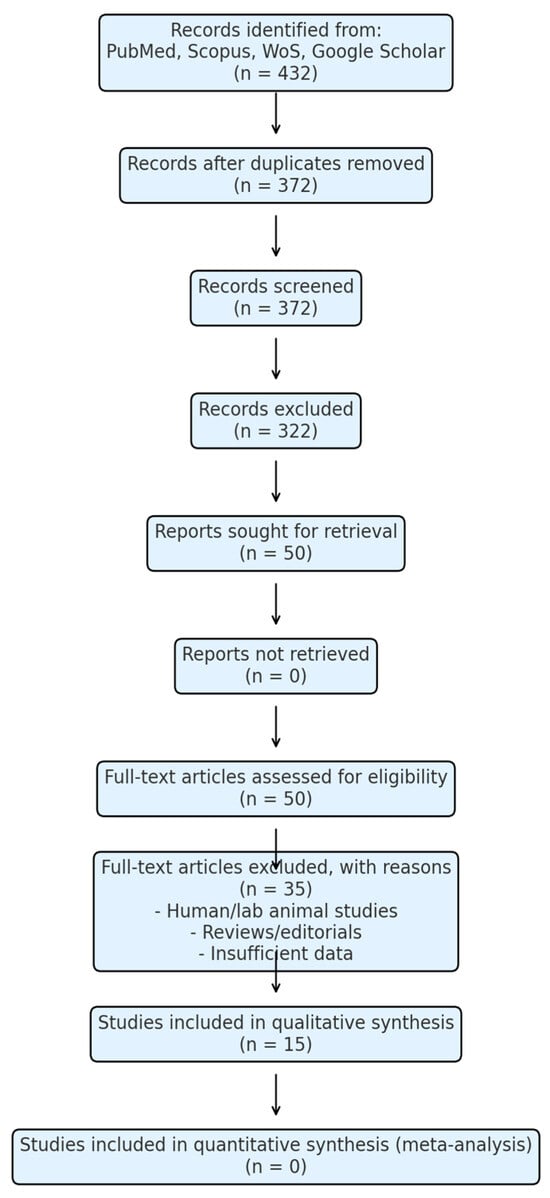
Figure 1.
PRISMA 2020 flow diagram for study selection.
The diagram illustrates the selection process of studies included in this systematic review. It details the number of records identified, screened, assessed for eligibility, excluded, and ultimately included in the synthesis, according to PRISMA 2020 guidelines.
Software and Tools: Figures and basic statistical analyses were prepared using Microsoft Excel (Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, WA, USA) and GraphPad Prism version 9.0 (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA).
Equipment: Biochemical measurements reported in the reviewed studies were obtained using standard clinical laboratory equipment (Spectrophotometer UV-1800, Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan; ELISA reader, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
AI Tools: Artificial intelligence tools (ChatGPT, OpenAI, GPT-5, accessed in September 2025) were used for figure preparation and English editing, under author supervision. The scientific content and interpretation were entirely developed and verified by the authors.
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. The Concept of HOMA and Its Relevance in Veterinary Medicine
In the study of diabetes mellitus (DM) in companion animals, the use of the HOMA (Homeostasis Model Assessment) index could become an essential tool for evaluating insulin sensitivity and pancreatic β-cell function. This mathematical model, based on fasting glucose and insulin determinations, allows for a rapid analysis of glycemic homeostasis, facilitating both diagnosis and monitoring of disease progression [15,16,24,25]. Given that DM is an increasingly common endocrine disorder in dogs and cats, characterized by chronic hyperglycemia [1,2,16,23,26,27], the identification of efficient and accessible methods for assessing metabolic status has become a pressing necessity in modern veterinary medicine [28,29] The HOMA index, through its simplicity and accuracy, offers valuable insight into the delicate balance between insulin production and tissue response [17,30,31].
According to the updated veterinary classification proposed by the ALIVE Project [5], canine diabetes mellitus most commonly manifests as insulin-deficient diabetes (IDD), typically caused by immune-mediated destruction of pancreatic β-cells, leading to absolute insulin deficiency and the need for lifelong insulin therapy. Conversely, feline diabetes is predominantly insulin-resistant diabetes (IRD), frequently accompanied by concurrent β-cell dysfunction, often associated with obesity, physical inactivity, chronic inflammation, and glucolipotoxicity and even iatrogenic steroid administration, [1,5,7,32,33], which has been shown to induce insulin resistance in cats [32]. This distinction is essential for accurate interpretation of HOMA indices in veterinary patients, as the underlying pathophysiology directly influences insulin sensitivity and β-cell performance.
A significant challenge in the extended application of this index in veterinary medicine lies in interspecies physiological differences, which can influence the interpretation of obtained values [21,34,35]. Variations in basal metabolism, circadian rhythms of hormonal secretion, and tissue insulin sensitivity among dogs, cats, and other species may necessitate cautious adaptation of interpretive thresholds [16,17,36,37]. Nevertheless, recent advancements in veterinary research have demonstrated that the HOMA index can be successfully utilized to evaluate metabolic risk and treatment efficacy in companion animals [19,38].
In dogs, this index contributes to the early identification of insulin resistance—a key factor in diabetes development—thereby allowing for timely therapeutic interventions before the onset of severe complications [39,40]. In cats, the HOMA model enhances the understanding of how carbohydrate metabolism is influenced by factors such as diet, genetic predisposition, or the animal’s general health status [18,31,41]. This provides a solid basis for personalized management strategies, considering the potential for remission of feline type 2 diabetes in early stages [1,7].
Another important aspect of using the HOMA index in veterinary medicine is its potential to reduce the need for invasive and costly tests, such as the glucose tolerance test (GTT) or the euglycemic-hyper insulinemic clamp [9,15]. While these tests are considered the gold standard for evaluating insulin sensitivity, they are difficult to perform under typical clinical conditions, requiring extensive manipulation and constant monitoring and often inducing high levels of stress in animals [4,20] These logistical and financial constraints limit their widespread applicability in current veterinary practice [11,12]. In contrast, the HOMA index offers a much more practical alternative, providing relevant information about the patient’s metabolic status based on simple, routine blood tests [13,14].
The adaptation and validation of this index for various veterinary species contribute significantly to improving prevention, diagnosis, and treatment strategies [42,43]. By correlating HOMA values with other essential metabolic markers—such as glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), fructosamine, lipid profiles, and hormonal levels—veterinarians can obtain a more detailed and nuanced picture of the pathophysiological mechanisms underlying DM [9,12]. This holistic approach allows for the individualization of therapies according to each patient’s specific needs, thus optimizing treatment response [12,44].
3.2. The Origin and Purpose of the HOMA Index
According to the updated veterinary classification proposed by the ALIVE Project [5], canine diabetes mellitus most commonly manifests as insulin-deficient diabetes (IDD), typically caused by immune-mediated destruction of pancreatic β-cells, leading to absolute insulin deficiency and the need for lifelong insulin therapy. Conversely, feline diabetes is predominantly insulin-resistant diabetes (IRD), frequently accompanied by concurrent β-cell dysfunction, associated with obesity, physical inactivity, chronic inflammation, and glucolipotoxicity [1,45]. This distinction is essential in interpreting HOMA indices, as the underlying pathophysiology directly influences insulin sensitivity (HOMA-IR) and β-cell function (HOMA-β).
The Homeostasis Model Assessment (HOMA) index was developed in the 1980s as a non-invasive and practical method for evaluating glucose homeostasis [13]. Its primary purpose was to provide an accessible alternative to invasive and costly methods, such as the euglycemic-hyperinsulinemic clamp, for estimating two fundamental metabolic parameters: insulin sensitivity (HOMA-IR) and pancreatic β-cell function (HOMA-β) [14,15,30,42]. The model is based on the premise that in the fasting state, a dynamic equilibrium exists between insulin secretion and tissue responsiveness, allowing these parameters to be estimated from basal glucose and insulin concentrations [19].
HOMA-IR quantifies the degree of insulin resistance, an indicator of the efficiency with which tissues [muscle, adipose, and hepatic] utilize glucose. Elevated HOMA-IR values suggest increased resistance, a finding particularly relevant in the pathogenesis of IRD in cats and in secondary forms of insulin resistance in dogs [19,39,46]. HOMA-β estimates the functional capacity of β-cells to secrete insulin, reflecting their health status and compensatory ability; low values indicate dysfunction or insufficiency, as seen in IDD in dogs and advanced stages of IRD in cats [12].
In veterinary medicine, the applicability of the HOMA index has been validated for assessing metabolic risk in companion animals. In dogs, HOMA-IR is valuable for early detection of insulin resistance in obese patients or those with endocrine disorders, enabling early intervention before the onset of overt hyperglycemia [39,47,48]. In cats, both HOMA-IR and HOMA-β are important for understanding how diet, genetic predisposition, and overall health influence carbohydrate metabolism—information essential for personalized management and for identifying patients with remission potential in the early stages [31,45].
The main advantages of HOMA in veterinary practice include its non-invasive nature, reduced stress and physiological alterations compared to complex procedures, accessibility and cost-effectiveness, and usefulness in repeated monitoring and longitudinal studies [9,49]. HOMA is also valuable for assessing the impact of therapeutic interventions on animal metabolism.
However, the method has limitations: it depends on strict adherence to fasting protocols and can be influenced by acute or chronic conditions. Establishing species-specific reference intervals and exploring the influence of external factors [diet, physical activity, chronic inflammation, medications] are necessary to refine its clinical utility [21,50]. Integrating HOMA values with other metabolic biomarkers—such as glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), fructosamine, lipid profile, or C-peptide—can provide a holistic view of the metabolic status and guide therapeutic decision-making.
Thus, the HOMA index represents a significant advancement in both veterinary endocrinology and comparative diabetology, offering a simple, reliable, and efficient method for evaluating metabolic status. It facilitates early diagnosis, optimizes personalized therapeutic strategies, and improves prognosis and quality of life for animals affected by metabolic disorders [51,52].
3.3. Calculation Methodology [HOMA-IR and HOMA-β]
The HOMA (Homeostatic Model Assessment) index has become an essential tool for evaluating and monitoring metabolic disorders, particularly insulin resistance and pancreatic β-cell function [12,30,53]. Its applications extend beyond human medicine and are increasingly used in veterinary medicine, offering an accessible and efficient method for diagnosing and managing various endocrine and metabolic diseases, such as diabetes mellitus [54,55,56]. HOMA-IR (for insulin resistance) and HOMA-β (for β-cell function) are straightforward formulas that allow the assessment of these parameters using only fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations, eliminating the need for invasive or costly tests—making these methods especially useful in veterinary practice [25,57,58].
The calculation methodology for evaluating insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) and pancreatic β-cell function (HOMA-β) involves two simple mathematical formulas based on plasma glucose and insulin concentrations measured under fasting conditions [13,59,60,61,62].
Originally developed for humans, these formulas have been adapted for dogs and cats through species-specific parameter adjustments [19,30,63,64]. For example, in dogs, [39] demonstrated that HOMA-IR can facilitate early diagnosis of insulin resistance, while [63] identified a threshold of 2.4 for classifying obese dogs as insulin-resistant. In cats, [19] proposed a reference interval of 0.1–3.0 for lean individuals and reported a positive correlation with body fat percentage. [64] showed that HOMA remains useful even in diabetic cats in remission, revealing persistent insulin resistance.
The formula for HOMA-IR, used to calculate insulin resistance, is as follows:
where Glu is the plasma glucose concentration (in mmol/L) and Ins is the insulin concentration (in μU/mL) [65,66]. This formula enables a rapid and non-invasive assessment of insulin resistance, a critical factor in diagnosing diabetes and other metabolic disorders [62,65,66].
HOMA-IR = (Glu × Ins)/22.5
Similarly, the formula for HOMA-β, used to evaluate pancreatic β-cell function, is as follows:
HOMA-β = (20 × Ins)/(Glu − 3.5)
This calculation reflects the pancreas’s ability to secrete insulin in response to plasma glucose and insulin levels [14,67,68]. The method is useful for assessing the health status of β-cells, with significant applications in the diagnosis and therapeutic monitoring of diabetes mellitus [14,67,69], as illustrated in Figure 2.

Figure 2.
HOMA-IR and HOMA-β indices.
The graph highlights the nonlinear relationships between these parameters. In the early stages of insulin resistance, β-cells compensate by increasing insulin secretion, resulting in elevated HOMA-β values. Over time, this compensatory capacity declines, leading to reduced insulin secretion and a progressive deterioration of β-cell function, even in the presence of persistent hyperglycemia—a hallmark of type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Interpretation of HOMA values must take into account factors such as species, physiological status, diet, and comorbidities [42,70,71]. For example, hypertriglyceridemia in Miniature Schnauzers is associated with elevated HOMA-IR values [70], while in obese dogs, HOMA-β may reflect compensatory hyperinsulinemia [71].
This figure illustrates the interrelation between plasma glucose levels, insulin secretion, and pancreatic β-cell function, as described by the HOMA-β index. Together, these trajectories demonstrate the physiological basis of the HOMA-β model and emphasize its utility in estimating the secretory capacity of β-cells under varying glycemic conditions.
It is important to note that although HOMA-IR and HOMA-β are rapid and accessible methods for assessing metabolic risks, careful interpretation of the results is required according to the species and physiological conditions of each patient to avoid diagnostic errors [57,72,73].
3.4. Reference Parameters for HOMA-IR and HOMA-β
Reference values for HOMA-IR and HOMA-β in humans are well established, are largely based on extensive clinical research, and serve as diagnostic standards for evaluating insulin sensitivity and pancreatic β-cell function [13,14], as shown in Table 1.
Generally, normal values for HOMA-IR are below 2.5, while HOMA-β values typically range between 100% and 150%, indicating adequate β-cell function [71,74]. These human-based thresholds are often used as reference points in translational studies.
When comparing these reference values to those observed in dogs and cats, notable differences emerge [19,30], as illustrated in Figure 3. For instance, overweight dogs and cats exhibited elevated HOMA-IR values (3.1 and 3.5, respectively), which surpass the typical human threshold for insulin resistance. Similarly, HOMA-β values were markedly increased in overweight dogs (180%) and moderately in overweight cats (160%), suggesting compensatory β-cell activity in response to insulin resistance [64].
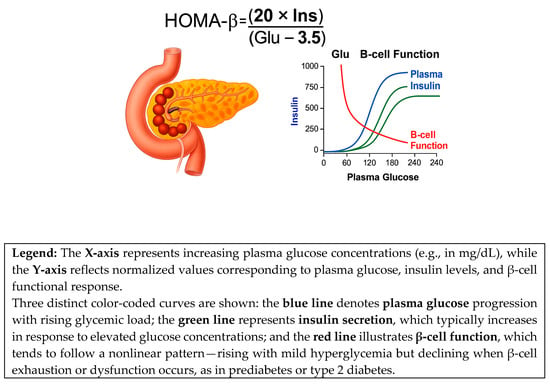
Figure 3.
The HOMA-β formula and its relevance to β-cell function.
Although the HOMA-IR and HOMA-β reference ranges are well established in humans, species-specific thresholds for dogs and cats are still under investigation. Therefore, the values illustrated in Figure 3 should be interpreted in a comparative context rather than against absolute human clinical cut-offs.
In veterinary studies, ref. [19] identified a HOMA-IR reference interval of 0.1–3.0 for lean cats, with significantly higher levels in overweight individuals (p < 0.0001). For dogs, ref. [39] suggested a HOMA-IR cutoff around 2.5 in the linear model and >4.4 in the nonlinear model, consistent with findings by [50] who proposed species-appropriate reference intervals for both HOMA-IR and HOMA-β. These results reinforce the concept that obesity-induced metabolic disturbances, including insulin resistance, are shared across species but must be evaluated within species-specific physiological frameworks (Figure 4).
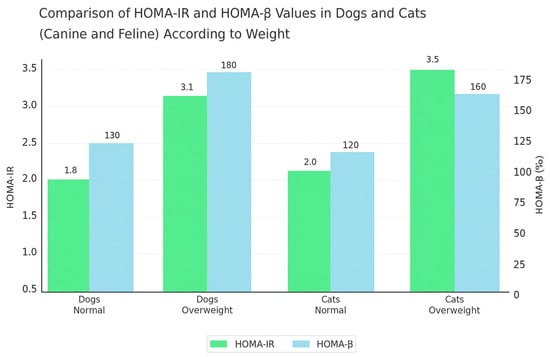
Figure 4.
Comparison of HOMA-IR and HOMA-β values in dogs and cats according to weight.
These parameters are essential for monitoring the risk of developing type 2 diabetes and for identifying metabolic problems associated with insulin resistance [19,53,71]. When HOMA-IR exceeds the value of 2.5, it is considered indicative of significant insulin resistance, an important marker in the diagnosis of diabetes [47,71], as shown in Table 1 and Table 2.

Table 1.
HOMA-IR and HOMA-β values in humans and the associated degree of diabetes [16,57,68,75].
Table 1.
HOMA-IR and HOMA-β values in humans and the associated degree of diabetes [16,57,68,75].
| HOMA-IR Value | Degree of Diabetes [Insulin Sensitivity] | HOMA-β Value | β-Cell Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Below 1.0 | Normal insulin sensitivity | 100–150% | Normal β-cell function |
| 1.0–2.5 | Normal/moderate insulin sensitivity | 100–150% | Normal β-cell function. |
| 2.5–3.0 | Mild insulin resistance | Below 100% | Slightly compromised β-cell function. |
| Above 3.0 | Severe insulin resistance | Below 100% | Compromised β-cell function. |

Table 2.
HOMA-IR and HOMA-β values in companion animals (dogs and cats) [19,53,71].
Table 2.
HOMA-IR and HOMA-β values in companion animals (dogs and cats) [19,53,71].
| Species | HOMA-IR Value | Degree of Insulin Resistance | HOMA-β Value | β-Cell Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dogs | 0.5–3.0 | Normal–mild insulin resistance | 100–150% | Normal–slightly compromised function. |
| Cats | 0.5–2.5 | Normal–mild insulin resistance | 100–150% | Normal–slightly compromised function. |
| Overweight Dogs | 2.5–3.0 | Moderate insulin resistance | Below 100% | Compromised β-cell function. |
| Overweight Cats | 2.0–2.5 | Moderate insulin resistance | Below 100% | Compromised β-cell function. |
Adapting these values for companion animals is more complex due to significant physiological differences between species [31,39,40,71]. Studies conducted on dogs suggest that an upper HOMA-IR threshold of 3.0 is associated with insulin resistance, while in cats, this threshold is usually lower, reflecting the metabolic particularities of each species [47,53]. For example, older or overweight dogs may develop insulin resistance even at higher HOMA-IR values, making the evaluation of this parameter essential for early diagnosis of metabolic issues [47,71,76]. In cats, studies show that diet can significantly influence HOMA values, with cats on low-carbohydrate diets exhibiting a different metabolic response compared to those on standard diets [77,78,79]. Additionally, adapting HOMA values according to the animal’s age and weight is crucial, as older animals or those with increased body weight have a higher risk of developing insulin resistance, as shown in Table 2 [30,43,80,81].
The physiology of insulin differs significantly between dogs and cats, highlighting the importance of adjusting reference values according to the respective species [9,16,55]. For example, dogs tend to develop insulin resistance more readily as they age or gain weight, making it necessary to consider these variables when interpreting HOMA-IR values [39,47]. Cats, on the other hand, may exhibit greater variability in HOMA values due to differences in insulin metabolism, and conditions such as obesity or chronic inflammation can significantly alter the results [30,31].
Factors such as obesity, chronic inflammation, and other metabolic disorders can significantly influence HOMA-IR and HOMA-β values, and these conditions are often correlated with an increased risk of developing diabetes or other metabolic diseases [60,71,82,83].
The interpretation of HOMA-IR and HOMA-β values should therefore be species-specific and aligned with the ALIVE classification. For example, elevated HOMA-IR in an IRD (insulin-resistant diabetes) cat suggests a potentially reversible stage if early intervention is initiated, whereas similar values in a dog with IDD usually indicate concurrent insulin resistance superimposed on an irreversible β-cell loss, requiring different therapeutic priorities.
Therefore, the interpretation of HOMA values in companion animals must take into account a variety of physiological and clinical factors, including age, weight, general health status, and diet [30,49,84]. These variable constants can significantly affect the results; thus, a reference framework adapted for each species is necessary [30,84]. The validation and adjustment of HOMA values for dogs and cats represent an essential step in developing an effective diagnostic and monitoring tool in veterinary practice [9,30,85].
3.5. Differences in the Use of HOMA Between Humans and Companion Animals
The use of HOMA indices (HOMA-IR and HOMA-β) in veterinary medicine requires significant adaptations due to physiological and metabolic differences between humans, dogs, and cats [16,18,19,50,71]. It is important to note that the original HOMA models were designed and validated exclusively for use in humans, and their direct application to other species may violate the model’s core assumptions [14]. This is further complicated by the absence of standardized insulin immunoassays for dogs and cats, which results in considerable variability between analytical methods and limits cross-study comparability. Therefore, while HOMA-derived indices can offer valuable insights in veterinary contexts, they must be interpreted cautiously, in conjunction with species-specific validation data and complementary metabolic markers (e.g., fructosamine, HbA1c, lipid profile, C-peptide).
In human studies, these indices have been validated on well-characterized physiological models, with established clinical thresholds for diagnosing insulin resistance and assessing β-cell function [14], as illustrated in Figure 5.
Figure 5.
Differences in the use of the HOMA index: humans vs. companion animals.
In humans, the mechanisms by which insulin regulates glucose concentrations and the ways in which imbalances occur in type 1 and type 2 diabetes are well understood [14,74]. In contrast, in companion animals, insulin physiology is influenced by a broader set of variables, and the types of diabetes differ significantly. According to the updated veterinary classification proposed by the ALIVE Project [5], canine diabetes mellitus most frequently manifests as insulin-deficient diabetes (IDD), typically caused by immune-mediated destruction of pancreatic β-cells, leading to absolute insulin deficiency and the need for lifelong insulin therapy. Conversely, feline diabetes is predominantly insulin-resistant diabetes (IRD), often accompanied by concurrent β-cell dysfunction, associated with obesity, physical inactivity, chronic inflammation, and glucolipotoxicity [32,86]
The use of the HOMA index to evaluate diabetes risk in companion animals faces additional challenges due to variability in basal blood glucose levels. In dogs, glucose values are generally more stable but can still be affected by stress, concurrent diseases, or medications [1]. In cats, stress-induced hyperglycemia is a well-known phenomenon that can significantly overestimate HOMA-IR [31]. Dietary composition, feeding patterns, and differences in carbohydrate metabolism between species can also influence both glucose and insulin dynamics [16,18].
Moreover, concurrent endocrine disorders such as hypothyroidism or hyperadrenocorticism can significantly alter HOMA values, impacting the correct interpretation of test results [5]. These conditions complicate the accurate assessment of insulin resistance and β-cell function in dogs and cats, often requiring species-specific reference ranges or even alternative diagnostic approaches.
It is important to note that the Homeostatic Model Assessment was originally developed and validated for humans [13,14]. Direct extrapolation to other species must be approached with caution. Nonetheless, several veterinary studies have investigated the potential of HOMA-derived indices as surrogate markers for insulin sensitivity in companion animals. For example, [19] reported that overweight cats had significantly higher HOMA-IR and fasting insulin concentrations compared to lean cats, with a positive correlation between HOMA-IR and body fat percentage, and proposed a tentative reference range for this species. Similarly [63] found that obese dogs with HOMA-IR > 2.4 could be classified as insulin resistant, supporting the discriminative ability of the index in clinical veterinary practice.
These findings indicate that while HOMA indices should be interpreted within the context of species-specific physiology, they remain valuable, non-invasive tools for estimating insulin sensitivity and β-cell function in both dogs and cats. When combined with additional diagnostic markers and clinical context, they can contribute to improved disease monitoring, early intervention, and individualized treatment strategies.
3.6. Protocol for Sample Collection and HOMA Determination
The protocol for blood sample collection to determine HOMA values involves measuring plasma glucose and insulin concentrations under fasting conditions [13,14,42]. This method is essential for obtaining accurate results, allowing a correct assessment of insulin sensitivity and β-cell function [16,17].
To ensure result accuracy, blood samples should be collected in the morning before feeding [20,42]. This precaution helps prevent postprandial hormonal fluctuations that could significantly alter measured values [13,20]. Standardizing the collection process is important to maintain consistency and facilitate comparisons between different studies and patients [16,20,87,88].
Plasma glucose concentrations are typically determined using enzymatic–colorimetric methods, which are recognized for their precision and efficiency in producing reliable results [13,42].
Another essential aspect of this protocol is the proper handling of blood samples immediately after collection [20,31,42,89]. It is imperative that samples be processed promptly to avoid degradation of biochemical components such as insulin, which can be affected by improper storage conditions [19,20]. Additionally, the use of appropriate materials for storage and transport helps maintain the stability of the analyzed biochemical parameters [31,40].
The entire workflow of the sampling and HOMA determination protocol, applicable to both humans and animals, is illustrated in Figure 6.
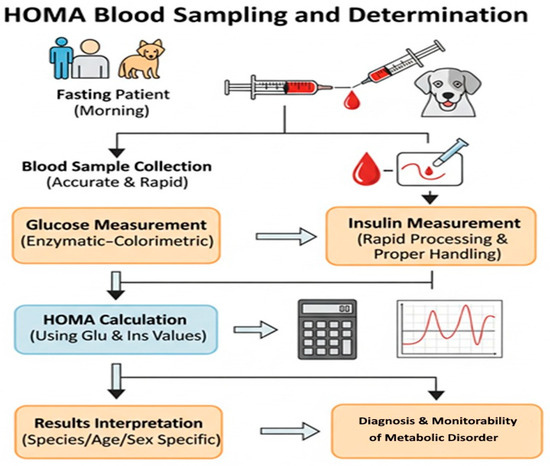
Figure 6.
Blood sample collection and HOMA index determination protocol (human and veterinary).
In companion animals, reference values for glucose and insulin can vary significantly depending on species, sex, and age [16,17]. Therefore, interpreting the results requires an individualized approach tailored to each patient [20,31]. By rigorously applying this protocol, an accurate evaluation of the HOMA index is ensured, thus contributing to the diagnosis and monitoring of diabetes mellitus and other metabolic dysfunctions [16,20,31].
3.7. Correlation Between HOMA-IR and Diabetes Severity
The correlation between the HOMA-IR (Homeostasis Model Assessment—Insulin Resistance) index and the severity of diabetes mellitus in companion animals represents a major area of interest in veterinary endocrinology [16,21]. Numerous studies have analyzed this relationship, highlighting the usefulness of this parameter in monitoring disease progression and optimizing therapeutic strategies [19,38]. An elevated HOMA-IR is an indicator of increased insulin resistance, a key pathophysiological factor that can negatively affect metabolic balance and often necessitates significant treatment adjustments to improve glycemic control [14]. A profound understanding of this correlation allows veterinarians to personalize therapeutic approaches and anticipate the risk of complications, contributing to a more effective management of the condition [17,23].
The severity of diabetes mellitus is defined not only by the magnitude of hyperglycemia but also by the degree of underlying metabolic dysfunction [4,8]. Insulin resistance, quantified by HOMA-IR, is a central element of this dysfunction, particularly in the context of insulin-resistant diabetes, which is prevalent in cats but also relevant in certain forms of canine diabetes [5]. At a physiological level, marked insulin resistance means that peripheral tissues [muscle, adipose tissue] and the liver respond inefficiently to the insulin signal [15]. This leads to reduced glucose uptake by cells and excessive hepatic glucose production, culminating in persistent hyperglycemia [4,21]. The pancreas initially attempts to compensate for this resistance by increasing insulin secretion (hyperinsulinemia), maintaining blood glucose within relatively normal limits. However, this compensation is often unsustainable, and pancreatic β-cells may eventually experience functional exhaustion [13,14]. As insulin resistance worsens, an increasingly larger amount of insulin is required to maintain adequate glycemic control. A high HOMA-IR, reflecting this increased insulin demand, is directly associated with poor glycemic control and difficulties in achieving therapeutic targets [31,63].
In line with the ALIVE classification, most canine diabetes cases correspond to IDD [insulin-deficient diabetes], whereas feline diabetes is typically IRD (insulin-resistant diabetes) [5,90]. This categorization is more accurate than directly mapping veterinary cases to human type 1 or type 2 diabetes, as it reflects species-specific pathophysiology and aids in targeted interpretation of HOMA values. Although canine diabetes is predominantly insulin-deficient due to β-cell destruction, insulin resistance can play a significant role in certain cases or complications. A high HOMA-IR in dogs may indicate intrinsic insulin resistance or resistance induced by factors such as obesity, chronic systemic inflammation, or endocrine comorbidities like hyperadrenocorticism or hypothyroidism [42]. This resistance can complicate management even in insulin-dependent dogs, requiring higher doses of exogenous insulin to achieve satisfactory glycemic control. Similarly, in cats, steroid administration (e.g., methylprednisolone acetate) has been shown to induce significant insulin resistance, which can be detected through HOMA indices [32]. Persistently high HOMA-IR in dogs has been associated with a poor metabolic response to insulin therapy and less stable glycemia, reflected by wide glycemic fluctuations or persistent hyperglycemic episodes [39].
In cats, where insulin-resistant diabetes is the predominant form, the correlation between HOMA-IR and disease severity is of particular importance [1,7]. Insulin resistance is a central pathophysiological event in feline diabetes, often exacerbated by obesity and physical inactivity [20]. High HOMA-IR values in cats reflect a significant degree of insulin resistance, which, if left unaddressed, can lead to pancreatic β-cell exhaustion and progression towards permanent insulin dependence [19,23]. Monitoring HOMA-IR in diabetic cats allows for the evaluation of therapeutic intervention efficacy. Specific dietary interventions—such as high-protein, low-carbohydrate diets—combined with weight management and, in some cases, oral hypoglycemic agents can significantly reduce insulin resistance, manifested by a decrease in HOMA-IR [1,7]. Such reductions are often correlated with improved glycemic control and, in early-stage cases, even diabetes remission.
Analyzing the correlation between HOMA-IR and diabetes severity provides crucial information for clinical management [16,17]. A high HOMA-IR signals the need for more vigorous therapeutic adjustments, which may include intensifying insulin therapy, implementing targeted dietary modifications, managing weight, and addressing comorbidities that exacerbate insulin resistance [1]. Longitudinal monitoring of HOMA-IR enables the evaluation of treatment response and the dynamic adjustment of therapy, ensuring that interventions remain aligned with the patient’s changing metabolic needs. Beyond its diagnostic and management utility, HOMA-IR also plays a predictive role [12,15]. A rising HOMA-IR, even without major glycemic changes, can indicate worsening insulin resistance and an increased risk of disease progression or complications. This is particularly valuable in screening programs for predisposed breeds or animals in a prediabetic state, such as obese cats with transient hyperglycemia [1,20]. Early detection enables preventive measures—dietary adjustments, exercise programs—that can delay or prevent clinical diabetes, improving quality of life and reducing the economic and emotional burden of chronic disease management.
While HOMA-IR is a valuable metric, it must be interpreted within the context of a complete clinical evaluation and additional metabolic markers such as fructosamine, HbA1c, lipid profiles, and C-peptide [13,14,91]. This integrated approach provides a comprehensive understanding of the patient’s metabolic state, supporting evidence-based and personalized treatment decisions.
4. Conclusions
The use of the Homeostasis Model Assessment (HOMA) indices for evaluating insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) and pancreatic β-cell function (HOMA-β) in companion animals provides a non-invasive, cost-effective, and repeatable method with significant potential for improving the diagnosis, classification, and management of diabetes mellitus [13,14]. Within the ALIVE veterinary classification [5], correct interpretation of HOMA indices must be species-specific. In dogs, where insulin-deficient diabetes (IDD) predominates, elevated HOMA-IR values may indicate concurrent insulin resistance superimposed on irreversible β-cell loss, complicating glycemic control [18]. In cats, where insulin-resistant diabetes (IRD) is the predominant form, high HOMA-IR often reflects an early, potentially reversible stage of the disease, particularly when addressed promptly with dietary modification, weight control, and pharmacological intervention [1,7,35].
Despite its advantages, the application of HOMA in veterinary practice faces challenges, including interindividual variability, the influence of comorbidities, and the absence of standardized reference values for different species, sexes, and ages [16,20].
These limitations underline the need for standardized protocols and large-scale, longitudinal studies to establish clinically relevant cut-off points.
Therefore, HOMA should be used as a complementary diagnostic and monitoring tool, integrated with other metabolic markers such as fructosamine, HbA1c, lipid profiles, and C-peptide, alongside a complete clinical evaluation. This integrated approach allows for personalized therapeutic adjustments, improved glycemic control, prevention of complications, and an overall enhancement of the quality of life in diabetic companion animals [9,23].
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/app151910342/s1; File S1: PRISMA 2020 Checklist, indicating compliance of the review with all 27 reporting items (Reference [92] is cited in the File S1). Table S1: Detailed list of included studies with species, sample size, HOMA indices, and main findings.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.D.H. and V.B.; Methodology, L.D.H., T.D.H. and M.C.S.; Validation, A.S. and L.C.B.; Formal Analysis, L.D.H. and T.D.H.; Investigation, L.D.H., A.S. and M.C.S.; Resources, V.B. and G.P.; Data Curation, T.D.H. and L.C.B.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, L.D.H.; Writing—Review and Editing, G.P., V.B. and L.C.B.; Visualization, T.D.H. and M.C.S.; Supervision, G.P. and L.C.B.; Project Administration, G.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research will be financed from the funds of the University of Life Sciences “Ion Ionescu de la Brad” Iasi Romania.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study, as it is a systematic review of previously published data and did not involve new studies with humans or animals.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable. This study did not involve humans; it is a systematic review of previously published data.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in the article and Supplementary Materials.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the use of ChatGPT (OpenAI, GPT-5) for assistance in figure preparation and English editing. All scientific content and interpretations were conceived, developed, and verified by the authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Rand, J.S.; Fleeman, L.M.; Farrow, H.A.; Appleton, D.J.; Lederer, R. Canine and feline diabetes mellitus: Nature or nurture? J. Nutr. 2004, 134 (Suppl. S8), 2072S–2080S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niessen, S.J.M.; Forcada, Y.; Mantis, P.; Lamb, C.R.; Harrington, N.; Smyth, J.B.; Mahoney, P.; Dunning, M.D.; Church, D.B. Studying cat (Felis catus) diabetes: Beware of the pitfalls and challenges. Vet. J. 2010, 184, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattin, M.; O’Neill, D.G.; Church, D.B.; McGreevy, P.D.; Thomson, P.C. An epidemiological study of diabetes mellitus in dogs attending first-opinion practice in the UK. Vet. Rec. 2014, 174, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, R.W. Canine Diabetes Mellitus. In Canine and Feline Endocrinology, 4th ed.; Feldman, E.C., Nelson, R.W., Reusch, C.E., Eds.; Saunders: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2015; pp. 213–257. [Google Scholar]
- Niessen, S.J.; Bjornvad, C.; Church, D.B.; Davison, L.; Esteban-Saltiveri, D.; Fleeman, L.M.; Forcada, Y.; Fracassi, F.; Gilor, C.; Hanson, J.; et al. Agreeing Language in Veterinary Endocrinology (ALIVE): Diabetes mellitus—A modified Delphi-method-based system to create consensus disease definitions. Vet. J. 2022, 287, 105910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rand, J. Feline diabetes mellitus. In BSAVA Manual of Canine and Feline Endocrinology; BSAVA Library: Gloucester, UK, 2012; pp. 133–147. [Google Scholar]
- Roomp, K.; Rand, J. Evaluation of detemir in diabetic cats managed with a protocol for intensive blood glucose control. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2012, 14, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reusch, C.E.; Nelson, R.W.; Feldman, E.C. Diabetic ketoacidosis. In Canine and Feline Endocrinology, 4th ed.; Elsevier Saunders: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2015; pp. 315–347. [Google Scholar]
- Behrend, E.N.; Holford, A.; Lathan, P.; Rucinsky, R.; Schulman, R. 2018 AAHA Diabetes Management Guidelines for Dogs and Cats. J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 2018, 54, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hritcu, L.D.; Borcea, D.; Burtan, L. Experimental induction of DM in rats and the role of bariatric surgery for the recovery of pancreatic β cells. J. Biotechnol. 2019, 305, S75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catchpole, B.; Ristic, J.M.; Fleeman, L.M.; Davison, L.J. Canine diabetes mellitus: Can old dogs teach us new tricks? Diabetologia 2005, 48, 1948–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reusch, C.E. Feline Diabetes Mellitus. In Canine and Feline Endocrinology, 4th ed.; Feldman, E.C., Nelson, R.W., Reusch, C.E., Scott-Moncrieff, J.C.R., Behrend, E.N., Eds.; Saunders Elsevier: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2015; pp. 258–314. [Google Scholar]
- Matthews, D.R.; Hosker, J.P.; Rudenski, A.S.; Naylor, B.A.; Treacher, D.F.; Turner, R.C. Homeostasis model assessment: Insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985, 28, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, T.M.; Levy, J.C.; Matthews, D.R. Use and abuse of HOMA modeling. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 1487–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muniyappa, R.; Lee, S.; Chen, H.; Quon, M.J. Current approaches for assessing insulin sensitivity and resistance in vivo: Advantages, limitations, and appropriate usage. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 294, E15–E26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appleton, D.J.; Rand, J.S.; Sunvold, G.D. Insulin sensitivity decreases with obesity, and lean cats with low insulin sensitivity are at greatest risk of glucose intolerance with weight gain. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2001, 3, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoenig, M.; Thomaseth, K.; Brandao, J.; Waldron, M.; Ferguson, D.C. Assessment and mathematical modeling of glucose turnover and insulin sensitivity in lean and obese cats. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2006, 31, 373–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkest, K.R.; Rand, J.S.; Fleeman, L.M.; Morton, J.M.; Richards, A.A.; Rose, F.J.; Taylor, R.M. Evaluation of beta-cell function in obese dogs. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2012, 42, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strage, E.M.; Björnsdottir, S.; Fall, T.; Hansson-Hamlin, H.; Lundgren, B.; Häggström, J.; Höglund, K. Evaluation of the homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) for predicting the development of diabetes mellitus in cats. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2021, 35, 2720–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoenig, M.; Thomaseth, K.; Waldron, M.; Ferguson, D.C. Insulin sensitivity, fat distribution, and adipocytokine response to different diets in lean and obese cats before and after weight loss. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2007, 292, R227–R234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkest, K.R.; Rand, J.S.; Fleeman, L.M.; Morton, J.M. Spontaneously obese dogs exhibit greater postprandial glucose, triglyceride, and insulin concentrations than lean dogs. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2012, 42, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, R.W.; Reusch, C.E. Animal models of disease: Classification and etiology of diabetes in dogs and cats. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 222, T1–T9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reusch, C.E.; Fracassi, F.; Peterson, M.E.; Boretti, F.S.; Germain, J.; Lutz, T.A.; Kley, S.; Riederer, A.; Sieber-Ruckstuhl, N.S. Classification of diabetes mellitus in dogs and cats: A new approach. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2022, 36, 1781–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mari, A.; Tura, A.; Grespan, E.; Bizzotto, R. Mathematical modeling for the physiological and clinical investigation of glucose homeostasis and diabetes. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 575789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Ali, H.; Daneshkhah, A.; Boutayeb, A.; Merabet, N.; Mukandavire, Z. A Comprehensive Review of Mathematical and Data-Driven Models in Glucose Homeostasis and Diabetes Pathways. In Computational Mathematics and Modelling for Diabetes; Springer: Singapore, 2025; pp. 133–165. [Google Scholar]
- Hritcu, L.D.; Borcea, D.; Anton, E.; Morosan, S.; Pasca, S.; Trinca, C.; Spataru, M.C.; Petrariu, F.D.; Burtan, L.C.; Ciobica, A.; et al. Experimental induction of type 2 diabetes mellitus and the efficiency of bariatric surgery in its reversal in rats. Acta Endocrinol. 2021, 17, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roșca, M.; Hrițcu, L.D.; Solcan, G. Feline diabetes mellitus: Diagnosis, management, and prognosis. Rev. Română Med. Vet. 2013, 23, 43–52. [Google Scholar]
- Catchpole, B.; Kennedy, L.J.; Davison, L.J.; Ollier, W.E.R. Canine diabetes mellitus: From phenotype to genotype. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2008, 49, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, R.W. Disorders of the endocrine pancreas. In Small Animal Internal Medicine, 5th ed.; Elsevier: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2015; pp. 823–869. [Google Scholar]
- Appleton, D.J.; Rand, J.S.; Sunvold, G.D. Basal plasma insulin and homeostasis model assessment (HOMA) are indicators of insulin sensitivity in cats. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2005, 7, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strage, E.M.; Ley, C.J.; Forkman, J.; Öhlund, M.; Stadig, S.; Bergh, A.; Ley, C. Homeostasis model assessment, serum insulin and their relation to body fat in cats. BMC Vet. Res. 2021, 17, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, K.M.; Rocha, M.B.; Varela, F.V.; Rodrigues, L.; Furtado, P.V.; da Costa, F.V.A.; Pöppl, Á.G. Is methylprednisolone acetate-related insulin resistance preventable in cats? Top. Companion Anim. Med. 2022, 49, 100648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, M.; Hoenig, M. Feline comorbidities: Pathophysiology and management of the obese diabetic cat. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2021, 23, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockham, S.L.; Scott, M.A. Fundamentals of Veterinary Clinical Pathology, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Weaver, S.; Hynd, P.; Ralph, C.; Edwards, J.H.; Burnard, C.; Narayan, E.; Tilbrook, A. Chronic elevation of plasma cortisol causes differential expression of predominating glucocorticoid in plasma, saliva, fecal, and wool matrices in sheep. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2021, 74, 106503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobelli, C.; Dalla Man, C.; Sparacino, G.; Magni, L.; De Nicolao, G.; Kovatchev, B.P. Diabetes: Models, signals, and control. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2009, 2, 54–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijnberk, A.; Kooistra, H.S. (Eds.) Clinical Endocrinology of Dogs and Cats: An Illustrated Text; Schlütersche: Hannover, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Uchańska, O.; Ochota, M.; Eberhardt, M.; Niżański, W. Dead or Alive? A Review of Perinatal Factors That Determine Canine Neonatal Viability. Animals 2022, 12, 1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González Villar, D.; German, A.J.; Holden, S.L.; Biourge, V.; Morris, P.J.; Courcier, E.A. Insulin resistance and its determinants in overweight and obese dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2022, 36, 2303–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarıkaya, E.; Turan, N.; Cihan, H.; Özkanlar, S. Evaluation of insulin resistance in dogs: HOMA-IR thresholds and clinical implications. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 121. [Google Scholar]
- Verbrugghe, A.; Hesta, M.; Daminet, S.; Janssens, G.P. Nutritional modulation of insulin resistance in the true carnivorous cat: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2012, 52, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkest, K.R.; Fleeman, L.M.; Rand, J.S.; Morton, J.M. Evaluation of beta-cell sensitivity to glucose and first-phase insulin secretion in obese dogs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2011, 72, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strage, E.M.; Björklund, H.; Holst, B.S. Body fat percentage, plasma insulin, and glucose concentrations in lean and overweight cats. Acta Vet. Scand. 2021, 63, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Niessen, S.J.M.; Forcada, Y.; Mantis, P.; Lamb, C.R.; Harrington, N.; Fowkes, R.; Korbonits, M.; Smith, K.; Church, D.B.; Wolfe, A. Studying cat (Felis catus) diabetes: Beware of the acromegalic imposter. PLOS ONE 2015, 10, e0127794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roomp, K.; Rand, J. Intensive blood glucose control is safe and effective in diabetic cats using home monitoring and treatment with glargine. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2012, 14, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toffolo, G.; Bergman, R.N.; Finegood, D.T.; Bowden, C.R.; Cobelli, C. Quantitative estimation of beta cell sensitivity to glucose in the intact organism: A minimal model of insulin kinetics in the dog. Diabetes 1980, 29, 979–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, J.R.; Castillo, V. Evaluation of insulin resistance in overweight and obese dogs. Int. J. Vet. Sci. Res. 2020, 6, 58–63. [Google Scholar]
- Torsahakul, C. Development of a preliminary clinical approach for detecting insulin resistance for normoglycemic control in canine diabetes. Thai J. Vet. Med. 2024, 53, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar, F.I.G.; Bravo, F.P. HOMA metabolic assessment in normoglycemic and diabetic canines. Rev. Vet. Y Zootec. 2019, 13, 14–23. [Google Scholar]
- Sarıkaya, F.G.; Yıldırım, S.; Gökçe, E.; Erbaş, O. Evaluation of insulin resistance by HOMA-IR and its relation with obesity in dogs. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2023, 76, 106683. [Google Scholar]
- Dhama, K.; Latheef, S.K.; Dadar, M.; Samad, H.A.; Munjal, A.; Khandia, R.; Karthik, K.; Tiwari, R.; Yatoo, M.I.; Bhatt, P.; et al. Biomarkers in stress related diseases/disorders: Diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic values. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2019, 6, 465402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perera, T.R.; Skerrett-Byrne, D.A.; Gibb, Z.; Nixon, B.; Swegen, A. The future of biomarkers in veterinary medicine: Emerging approaches and associated challenges. Animals 2022, 12, 2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzlez-Villar, F.; Pérez-Bravo, F. Analysis of insulin resistance using the non-linear homeostatic model assessment index in overweight canines. Vet. World 2022, 15, 1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truett, A.A.; Borne, A.T.; Monteiro, M.P.; West, D.B. Composition of dietary fat affects blood pressure and insulin responses to dietary obesity in the dog. Obes. Res. 1998, 6, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rucinsky, R.; Cook, A.; Haley, S.; Nelson, R.; Zoran, D.L.; Poundstone, M. AAHA diabetes management guidelines for dogs and cats. J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 2010, 46, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacks, D.B.; Arnold, M.; Bakris, G.L.; Bruns, D.E.; Horvath, A.R.; Lernmark, Å.; Metzger, B.E.; Nathan, D.M.; Kirkman, M.S. Guidelines and recommendations for laboratory analysis in the diagnosis and management of diabetes mellitus. Clin. Chem. 2023, 69, 808–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminathan, S.; Elanthendral; King David Edward, T.; Abirami, M.J. ++ Diagnostic Usefulness of HOMA-β and HOMA-IR in Diabetes Mellitus—A Review. Int. J. Pharm. Res. Allied Sci. 2019, 8, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Harbuwono, D.S.; Pramono, L.A.; Subekti, I.; Putradi, C.; Waspadji, S. Pathophysiology of insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes. Acta Medica Indones. 2013, 45, 274–282. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, B.; Saxena, A. Surrogate markers of insulin resistance: A review. World J. Diabetes 2010, 1, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andonova, M.; Dzhelebov, P.; Trifonova, K.; Yonkova, P.; Kostadinov, N.; Nancheva, K.; Ivanov, V.; Gospodinova, K.; Nizamov, N.; Tsachev, I.; et al. Metabolic markers associated with progression of type 2 diabetes induced by high-fat diet and single low dose streptozotocin in rats. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Gautier, J.F.; Chon, S. Assessment of insulin secretion and insulin resistance in human. Diabetes Metab. J. 2021, 45, 641–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borai, A.; Livingstone, C.; Ferns, G.A. The biochemical assessment of insulin resistance. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2007, 44, 324–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, L.C.; Sousa, A.J.; Carreira, L.M.; Guedes, R.M.C.; Matos, A.J.F.; Sequeira, J.L.; Magalhães, A.M. Evaluation of Insulin Resistance in Obese Dogs: Use of the Homeostatic Model Assessment (HOMA). Vet. Res. Commun. 2022, 46, 115–123. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34918191/ (accessed on 17 September 2025).
- Gottlieb, S. Diabetic Cats in Remission. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reaven, G.M. What do we learn from measurements of HOMA-IR? Diabetologia 2013, 56, 1867–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhosle, D.; Sayyed, A.; Bhagat, A.; Sheikh, H.; Londhe, V. Homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) in the diagnosis of insulin resistance and prediabetes. J. Med. Sci. Clin. Res. 2016, 4, 12705–12710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Zou, J.; Gao, M.; Huang, J.; Li, Y.; Li, N.; Qian, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, M.; Liu, Y. A comparative study of the relationship between time in range assessed by self-monitoring of blood glucose and continuous glucose monitoring with microalbuminuria outcome, HOMA-IR and HOMA-β test. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2024, 38, 108831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Nakagawa, T.; Honda, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Mizoue, T. Should insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), insulin secretion (HOMA-β), and visceral fat area be considered for improving the performance of diabetes risk prediction models. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2024, 12, e003680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermúdez-Pirela, V.J.; Cano, C.; Medina, M.T.; Souki, A.; A Lemus, M.; Leal, E.M.; A Seyfi, H.; Cano, R.; Ciscek, A.; Bermúdez-Arias, F.; et al. Metformin plus low-dose glimeperide significantly improves homeostasis model assessment for insulin resistance (HOMAIR) and β-cell function (HOMAβ-cell) without hyperinsulinemia in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am. J. Ther. 2007, 14, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xenoulis, P.G.; Levinski, M.D.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Steiner, J.M. Association of hypertriglyceridemia with insulin resistance in healthy Miniature Schnauzers. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2011, 238, 1011–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarıkaya, E.E.; Gökce, H. Investigations of Insulin Resistance in Obese Dogs. Medit. Vet. J. 2024, 9, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Li, X.; Song, P.; Xu, L. Optimal cut-off values for the homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) and pre-diabetes screening: Developments in research and prospects for the future. Drug Discov. Ther. 2015, 9, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madsen, S.M.; Thorup, A.C.; Overgaard, K.; Jeppesen, P.B. High intensity interval training improves glycaemic control and pancreatic β cell function of type 2 diabetes patients. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahapary, D.L.; Pratisthita, L.B.; Fitri, N.A.; Marcella, C.; Wafa, S.; Kurniawan, F.; Rizka, A.; Tarigan, T.J.E.; Harbuwono, D.S.; Purnamasari, D.; et al. Challenges in the diagnosis of insulin resistance: Focusing on the role of HOMA-IR and Tryglyceride/glucose index. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2022, 16, 102581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hakeim, H.K.; Abdulzahra, M.S. Correlation between glycated hemoglobin and homa indices in type 2 diabetes mellitus: Prediction of beta-cell function from glycated hemoglobin. J. Med. Biochem. 2015, 34, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HB, I.A. Insulin Resistance and its Significant Co-Morbidities in Young Individuals-Including Homa (Homeostatic Model Assessment). Doctoral Dissertation, Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Bengaluru, India, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.; Rand, J.S.; Coradini, M.; Morton, J.M. Effect of acarbose on postprandial blood glucose concentrations in healthy cats fed low and high carbohydrate diets. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2015, 17, 848–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbrugghe, A.; Hesta, M. Cats and carbohydrates: The carnivore fantasy? Vet. Sci. 2017, 4, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, N.; Greco, D.S.; Peterson, M.E.; Kirk, C.; Mathes, M.; Fettman, M.J. Comparison of a low carbohydrate–low fiber diet and a moderate carbohydrate–high fiber diet in the management of feline diabetes mellitus. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2006, 8, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-López, L.; Boronat, M.; Melián, C.; Brito-Casillas, Y.; Wägner, A.M. Kidney function and glucose metabolism in overweight and obese cats. Vet. Q. 2020, 40, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott-Moncrieff, J.C. Insulin resistance in cats. Vet. Clin. Small Anim. Pract. 2010, 40, 241–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; An, X.; Yang, C.; Sun, W.; Ji, H.; Lian, F. The crucial role and mechanism of insulin resistance in metabolic disease. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1149239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emir, S.N.; Emir, S. Association of insulin resistance and ectopic fat accumulation with HOMA indices: A Single-Centre observational study. Türkiye Diyabet Ve Obezite Derg. 2024, 8, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, M.; Cunningham, S.; Lund, E.M.; Khanna, C.; Naramore, R.; Patel, A.; Day, M.J. Obesity and associated comorbidities in people and companion animals: A one health perspective. J. Comp. Pathol. 2017, 156, 296–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Öztürk, M.; Mamak, N. Importance and Areas of Use of Biomarkers in Veterinary Medicine Clinical Practice. In Current Research and Treatment in Animals; Kabu, M., Tunç, A.C., Eds.; Livre de Lyon: Lyon, France, 2024; Available online: https://bookchapter.org/kitaplar/Current_research_and_treatment_in_animals.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2025).
- Patra, S.; McMillan, C.J.; Snead, E.R.; Warren, A.L.; Cosford, K.; Chelikani, P.K. Feline Diabetes Is Associated with Deficits in Markers of Insulin Signaling in Peripheral Tissues. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 15197:2013; In Vitro Diagnostic Test Systems—Requirements for Blood-Glucose Monitoring Systems for Self-Testing in Managing Diabetes Mellitus. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013.
- ISO 5725-2:2019; Accuracy (Trueness and Precision) of Measurement Methods and Results—Part 2: Basic Method for the Determination of Repeatability and Reproducibility of a Standard Measurement Method. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019.
- ASTM D638-14; Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2014.
- Pöppl, Á.G.; Lopes, J.L.X.; Nogueira, T.B.; Da Silva, D.I.; dos Santos Machado, B. Estrus Cycle, Pyometra, and Insulin-Resistant Diabetes in the Bitch: What Is Known and Why It Is Relevant? Preprints 2024. Available online: https://www.preprints.org/manuscript/202402.1006/v1 (accessed on 15 September 2025).
- Jagannatha, S.B. Study of Serum High Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein, Ferritin, Insulin, C-Peptide and Glycated Hemoglobin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Ph.D. Thesis, Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences, Bengaluru, India, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).