Modern Honey-Based Delivery Systems for Wound Healing: A Review of Current Trends and Future Perspectives
Abstract
1. Introduction
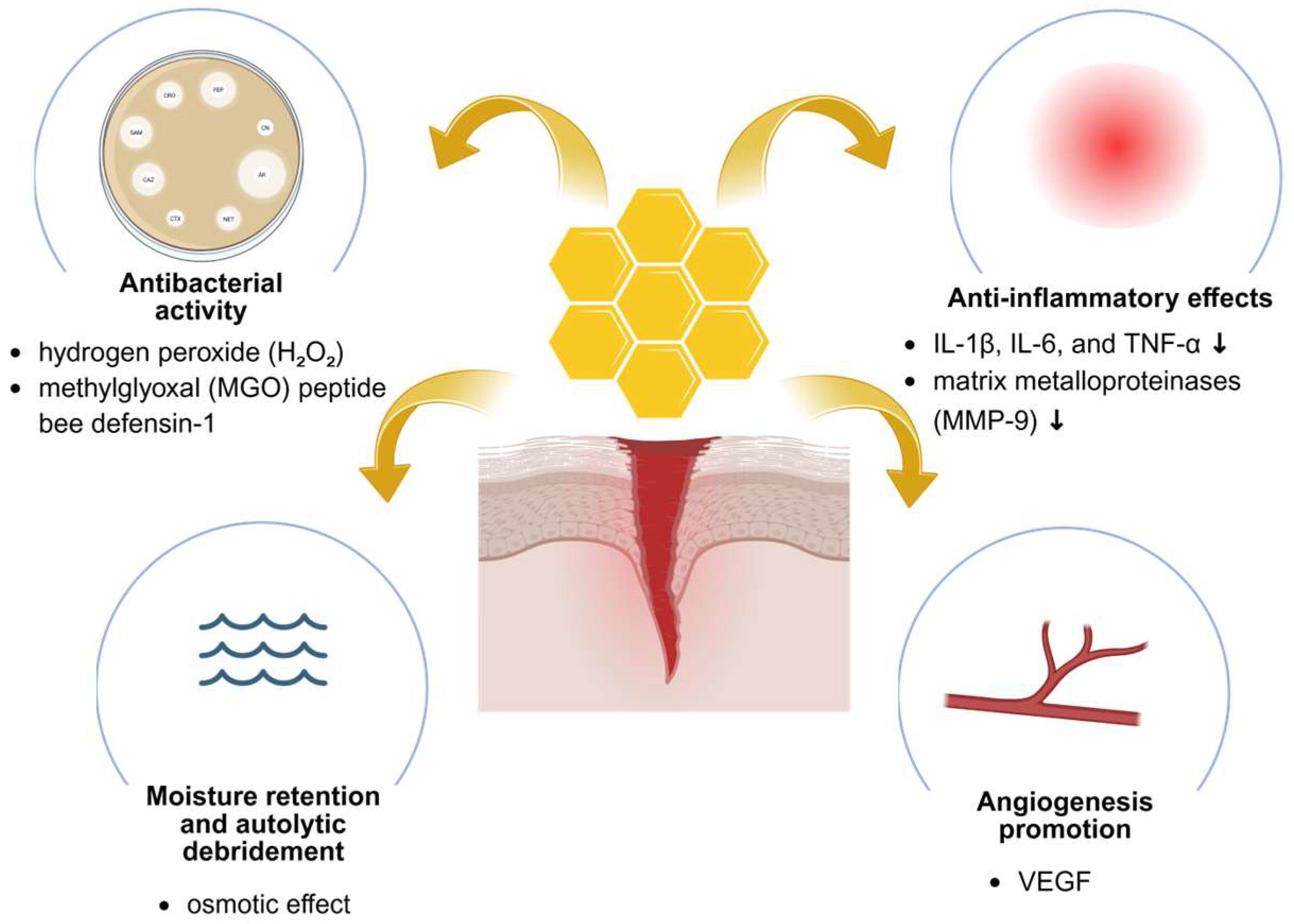
2. Therapeutic Properties of Honey in Wound Healing
2.1. Bioactive Compounds Responsible for Honey’s Therapeutic Properties
2.2. Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Activity
2.3. Anti-Inflammatory and Regenerative Effects
2.4. Therapeutic Honey Types Used in Wound Management
2.4.1. Manuka Honey
2.4.2. Tualang Honey
2.4.3. Local and Regional Honeys
2.5. Safety of Honey in Wound Healing
2.6. Challenges in Clinical Application of Honey
3. Advanced Honey Delivery Systems
3.1. Nanoparticle-Based Delivery
3.2. Electrospun Honey-Based Nanofibers
3.3. Honey-Based Hydrogels
4. Limitations
5. Conclusions and Future Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DLS | Dynamic Light Scattering |
| DSC | Differential Scanning Calorimetry |
| ECM | Extracellular Matrix |
| EDAX | Energy Dispersive Analysis of X-rays |
| EDC | 1-Ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide |
| EEP | Ethanolic Propolis Extract |
| FTIR | Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy |
| GOx | Glucose Oxidase |
| HR | Hazard Ratio |
| HR-TEM | High Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy |
| IC50 | Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration |
| MBC | Minimum Bactericidal Concentration |
| MDR | Multidrug-Resistant |
| MIC | Minimum Inhibitory Concentration |
| MMP | Matrix Metalloproteinase |
| MMP-9 | Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 |
| MPO | Myeloperoxidase |
| MRSA | Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus |
| NETosis | Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Formation |
| PAAc | Poly(acrylic acid) |
| PCL | Polycaprolactone |
| PDO | Polydioxanone |
| PET | Polyethylene Terephthalate |
| PLA | Polylactic Acid |
| PVA | Polyvinyl Alcohol |
| PVP | Polyvinylpyrrolidone |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| SNAP | S-nitroso-N-acetylpenicillamine |
| SSD | Silver Sulfadiazine |
| TGA | Thermogravimetric Analysis |
| UV-VIS | Ultraviolet–Visible Spectroscopy |
| VEGF | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor |
| WVTR | Water Vapor Transmission Rate |
| XRD | X-ray Diffraction |
| ZOI | Zone of Inhibition |
| ZnO | Zinc Oxide |
References
- Frykberg, R.G.; Banks, J. Challenges in the Treatment of Chronic Wounds. Adv. Wound Care 2015, 4, 560–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindholm, C.; Searle, R. Wound Management for the 21st Century: Combining Effectiveness and Efficiency. Int. Wound J. 2016, 13, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalik, M.; Podbielska-Kubera, A.; Dmowska-Koroblewska, A. Antibiotic Resistance of Staphylococcus aureus Strains—Searching for New Antimicrobial Agents—Review. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pachori, P.; Gothalwal, R.; Gandhi, P. Emergence of Antibiotic Resistance Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Intensive Care Unit; a Critical Review. Genes Dis 2019, 6, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLoone, P.; Oladejo, T.O.; Kassym, L.; McDougall, G.J. Honey Phytochemicals: Bioactive Agents with Therapeutic Potential for Dermatological Disorders. Phytother. Res. 2024, 38, 5741–5764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogwu, M.C.; Izah, S.C. Honey as a Natural Antimicrobial. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoială, A.; Ilie, C.-I.; Ficai, D.; Ficai, A.; Andronescu, E. Synergic Effect of Honey with Other Natural Agents in Developing Efficient Wound Dressings. Antioxidants 2022, 12, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharaf El-Din, M.G.; Farrag, A.F.S.; Wu, L.; Huang, Y.; Wang, K. Health Benefits of Honey: A Critical Review on the Homology of Medicine and Food in Traditional and Modern Contexts. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. Sci. 2025, 12, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, K.I.; Malik, M.N.; Aslam, A. Honey Compared with Silver Sulphadiazine in the Treatment of Superficial Partial-thickness Burns. Int. Wound J. 2010, 7, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.; Adcock, L. Honey for Wound Management: A Review of Clinical Effectiveness and Guidelines; CADTH Rapid Response Reports; Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Qiu, Y.; Zhu, F. An Updated Review of Functional Ingredients of Manuka Honey and Their Value-Added Innovations. Food Chem. 2024, 440, 138060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feknous, N.; Boumendjel, M. Natural Bioactive Compounds of Honey and Their Antimicrobial Activity. Czech J. Food Sci. 2022, 40, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brudzynski, K. A Current Perspective on Hydrogen Peroxide Production in Honey. A Review. Food Chem. 2020, 332, 127229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y. Antibacterial Properties of Manuka Honey and the Role of Methylglyoxal. Sch. Rev. J. 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucekova, M.; Sojka, M.; Valachova, I.; Martinotti, S.; Ranzato, E.; Szep, Z.; Majtan, V.; Klaudiny, J.; Majtan, J. Bee-Derived Antibacterial Peptide, Defensin-1, Promotes Wound Re-Epithelialisation in Vitro and in Vivo. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cianciosi, D.; Forbes-Hernández, T.Y.; Afrin, S.; Gasparrini, M.; Reboredo-Rodriguez, P.; Manna, P.P.; Zhang, J.; Bravo Lamas, L.; Martínez Flórez, S.; Agudo Toyos, P.; et al. Phenolic Compounds in Honey and Their Associated Health Benefits: A Review. Molecules 2018, 23, 2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, D.M.; Krishnakumar, K.; Batres, M.A.; Hakola-Parry, A.; Cokcetin, N.; Harry, E.; Carter, D.A. A Cost-Effective Colourimetric Assay for Quantifying Hydrogen Peroxide in Honey. Access Microbiol. 2019, 1, e000065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tama, A.; Bartosz, G.; Sadowska-Bartosz, I. Phenolic Compounds Interfere in the Ampliflu Red/Peroxidase Assay for Hydrogen Peroxide. Food Chem. 2023, 422, 136222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, P.; Ahmed, M. Evaluation of Biological Activities and Medicinal Properties of Honey Drops and Honey Lozenges. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, C.E.; Barker, D.; Deed, R.C.; Pilkington, L.I. Quantification of Methyl Glyoxal in New Zealand Mānuka Honey and Honey Meads. Food Chem. 2025, 478, 143697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultanbawa, Y.; Cozzolino, D.; Fuller, S.; Cusack, A.; Currie, M.; Smyth, H. Infrared Spectroscopy as a Rapid Tool to Detect Methylglyoxal and Antibacterial Activity in Australian Honeys. Food Chem. 2015, 172, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappalardo, M.; Pappalardo, L.; Brooks, P. Rapid and Reliable HPLC Method for the Simultaneous Determination of Dihydroxyacetone, Methylglyoxal and 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural in Leptospermum Honeys. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valachová, I.; Bučeková, M.; Majtán, J. Quantification of Bee-Derived Peptide Defensin-1 in Honey by Competitive Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay, a New Approach in Honey Quality Control. Czech J. Food Sci. 2016, 34, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawag, I.L.; Nolden, E.S.; Schaper, A.A.M.; Lim, L.Y.; Locher, C. A Modified Folin-Ciocalteu Assay for the Determination of Total Phenolics Content in Honey. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dżugan, M.; Tomczyk, M.; Sowa, P.; Grabek-Lejko, D. Antioxidant Activity as Biomarker of Honey Variety. Molecules 2018, 23, 2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, M.D.; Mandal, S. Honey: Its Medicinal Property and Antibacterial Activity. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2011, 1, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeswari, T.; Venugopal, A.; Viswanathan, C.; Kishmu, L.; Venil, C.; Sasikumar, J. Antibacterial Activity of Honey against Staphylococcus aureus from Infected Wounds. Pharmacol. Online 2010, 1, 537–541. [Google Scholar]
- Agbagwa, O.; Frank-Peterside, N. Effect of Raw Commercial Honeys from Nigeria on Selected Pathogenic Bacteria. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2010, 4, 1801–1803. [Google Scholar]
- Sherlock, O.; Dolan, A.; Athman, R.; Power, A.; Gethin, G.; Cowman, S.; Humphreys, H. Comparison of the Antimicrobial Activity of Ulmo Honey from Chile and Manuka Honey against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2010, 10, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen-Silva, E.; Gordillo-Fuenzalida, F.; Velásquez, P.; Llancalahuen, F.M.; Carvajal, R.; Cabaña-Brunod, M.; Otero, M.C. Antibacterial, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory properties of monofloral honeys from Chile. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.T.; Rahman, R.A.; Gan, S.H.; Halim, A.S.; Hassan, S.A.; Sulaiman, S.A.; BS, K.-K. The Antibacterial Properties of Malaysian Tualang Honey against Wound and Enteric Microorganisms in Comparison to Manuka Honey. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2009, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almasaudi, S. The Antibacterial Activities of Honey. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 2188–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Rubaie, W.K.; Al-Fekaiki, D.F.; Niamah, A.K.; Verma, D.K.; Singh, S.; Patel, A.R. Current Trends and Technological Advancements in the Study of Honey Bee-Derived Peptides with an Emphasis on State-of-the-Art Approaches: A Review. Separations 2024, 11, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Cokcetin, N.N.; Burke, C.M.; Turnbull, L.; Liu, M.; Carter, D.A.; Whitchurch, C.B.; Harry, E.J. Honey Can Inhibit and Eliminate Biofilms Produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balázs, V.L.; Nagy-Radványi, L.; Bencsik-Kerekes, E.; Koloh, R.; Szabó, D.; Kocsis, B.; Kocsis, M.; Farkas, Á. Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Effect of Unifloral Honeys against Bacteria Isolated from Chronic Wound Infections. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, K.; Fukushima, A.; Hayashi-Nishino, M.; Nishino, K. Effect of Methylglyoxal on Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Üsküdar-Güçlü, A.; Şimşek, D.; Ata-Vural, I.; Ünlü, S.; Başustaoğlu, A.; Üsküdar-Güçlü, A.; Şimşek, D.; Ata-Vural, I.; Ünlü, S.; Başustaoğlu, A. Antibacterial, Antifungal and Antibiofilm Activity of Methylglyoxal: A Phytochemical from Manuka Honey. Mediterr. J. Infect. Microbes Antimicrob. 2021, 10, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, V.K.; Srivastava, V. Honey Debridement. In Skin Necrosis; Téot, L., Meaume, S., Akita, S., Del Marmol, V., Probst, S., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 399–404. ISBN 978-3-031-60954-1. [Google Scholar]
- Nahak, B.K.; Roy Chowdhury, J.; Sharma, M.K.; Khan, A.; Ganguly, A.; Singh, U.K.; Parashar, P.; Kuan, C.-H.; Cheng, N.-C.; Lin, Z.-H. Advancements in Multimodal Approaches for Enhanced Wound Healing: From Chemical to Physical Strategies. Mater. Today 2025, 88, 1087–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Privrodski, B.; Jovanović, M.; Delić, N.; Ratajac, R.; Privrodski, V.; Stanojković, A.; Gavlik, B.; Čapo, I. Harnessing Manuka Honey: A Natural Remedy for Accelerated Burn Wound Healing in a Porcine Model. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleeging, C.C.F.; Wagener, F.A.D.T.G.; de Rooster, H.; Cremers, N.A.J. Revolutionizing Non-Conventional Wound Healing Using Honey by Simultaneously Targeting Multiple Molecular Mechanisms. Drug Resist. Updates 2022, 62, 100834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmi, M.F.; Abd Ghafar, N.; Che Hamzah, J.; Chua, K.H.; Ng, S.L. The Role of Gelam Honey in Accelerating Reepithelialization of Ex Vivo Corneal Abrasion Model. J. Food Biochem. 2021, 45, e13645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, A.; Bag, S.; Banerjee, P.; Chatterjee, J. Wound Healing Efficacy of Jamun Honey in Diabetic Mice Model through Reepithelialization, Collagen Deposition and Angiogenesis. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2020, 10, 529–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sell, S.A.; Wolfe, P.S.; Spence, A.J.; Rodriguez, I.A.; McCool, J.M.; Petrella, R.L.; Garg, K.; Ericksen, J.J.; Bowlin, G.L. A Preliminary Study on the Potential of Manuka Honey and Platelet-Rich Plasma in Wound Healing. Int. J. Biomater. 2012, 2012, 313781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munshi, R.M.; Bhalerao, S.S.; Kalekar, S.A.; Patil, T.A. Exploration of the Angiogenic Potential of Honey. BJPR 2014, 4, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashkandi, H. Honey in Wound Healing: An Updated Review. Open Life Sci. 2021, 16, 1091–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranzato, E.; Martinotti, S.; Burlando, B. Honey Exposure Stimulates Wound Repair of Human Dermal Fibroblasts. Burn. Trauma 2013, 1, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Malik, N.; Mohamed, M.; Mustafa, M.Z.; Zainuddin, A. In Vitro Modulation of Extracellular Matrix Genes by Stingless Bee Honey in Cellular Aging of Human Dermal Fibroblast Cells. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kased, R.F.; Amer, R.I.; Attia, D.; Elmazar, M.M. Honey-Based Hydrogel: In Vitro and Comparative In Vivo Evaluation for Burn Wound Healing. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadagali, M.D.; Chua, L.S. The Anti-Inflammatory and Wound Healing Properties of Honey. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2014, 239, 1003–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.L.; Lim, L.Y.; Hammer, K.; Hettiarachchi, D.; Locher, C. Honey-Based Medicinal Formulations: A Critical Review. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chijioke, O.C.; Aliyu, R.M.; Ohams, O.E.; Onyebuchi, A.D.; Fountain, A.I.; Nwaforcha, N.B. Natural Honey and Diabetic Wound Healing: A Review of Literature. Magna Sci. Adv. Res. Rev. 2023, 7, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yupanqui Mieles, J.; Vyas, C.; Aslan, E.; Humphreys, G.; Diver, C.; Bartolo, P. Honey: An Advanced Antimicrobial and Wound Healing Biomaterial for Tissue Engineering Applications. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Senduny, F.F.; Hegazi, N.M.; Abd Elghani, G.E.; Farag, M.A. Manuka Honey, a Unique Mono-Floral Honey. A Comprehensive Review of Its Bioactives, Metabolism, Action Mechanisms, and Therapeutic Merits. Food Biosci. 2021, 42, 101038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, M.; McBride, M.; Dahiya, D.; Owusu-Apenten, R.; Nigam, P.S. Antibacterial Activity of Manuka Honey and Its Components: An Overview. AIMS Microbiol. 2018, 4, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolan, V.C.; Harrison, J.; Wright, J.E.E.; Cox, J.A.G. Clinical Significance of Manuka and Medical-Grade Honey for Antibiotic-Resistant Infections: A Systematic Review. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, N.; Yadav, R. Manuka Honey: A Promising Wound Dressing Material for the Chronic Nonhealing Discharging Wounds: A Retrospective Study. Natl. J. Maxillofac. Surg. 2021, 12, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, J.; Lalitha, A.V.; Rameshkumar, R.; Mahadevan, S.; Kabra, S.K.; Lodha, R. Use of Honey Versus Standard Care for Hospital-Acquired Pressure Injury in Critically Ill Children: A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 22, e349–e362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onuoha, E.O.; Adekunle, A.A.; Ajike, S.O.; Gbotolorun, O.M.; Adeyemo, W.L. Effect of Manuka Honey Socket Dressing on Postoperative Sequelae and Complications Following Third Molar Extraction: A Randomized Controlled Study. J. Cranio-Maxillofacial Surg. 2023, 51, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Kamal, D.A.; Ibrahim, S.F.; Kamal, H.; Kashim, M.I.A.M.; Mokhtar, M.H. Physicochemical and Medicinal Properties of Tualang, Gelam and Kelulut Honeys: A Comprehensive Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, N.-A.M.; Halim, A.S.; Singh, K.-K.B.; Dorai, A.A.; Haneef, M.-N.M. Antibacterial Properties of Tualang Honey and Its Effect in Burn Wound Management: A Comparative Study. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2010, 10, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mat Lazim, N.; Abdullah, B.; Salim, R. The Effect of Tualang Honey in Enhancing Post Tonsillectomy Healing Process. An Open Labelled Prospective Clinical Trial. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2013, 77, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumarasamy, G.; Ramli, R.R.; Singh, H.; Abdullah, B. Tualang Honey versus Steroid Impregnated Nasal Dressing Following Endoscopic Sinus Surgery: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Complement. Integr. Med. 2020, 18, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chopra, H.; Bibi, S.; Kumar, S.; Khan, M.S.; Kumar, P.; Singh, I. Preparation and Evaluation of Chitosan/PVA Based Hydrogel Films Loaded with Honey for Wound Healing Application. Gels 2022, 8, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, L.M.; Hassanein, K.M.A.; Mohamed, F.A.; Elfaham, T.H. Formulation and Evaluation of Simvastatin Cubosomal Nanoparticles for Assessing Its Wound Healing Effect. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 17941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attard, E.; Douglas, A.B. Physicochemical Characterization of Maltese Honey. Honey Anal. 2017, 8, 171–191. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.; Chen, L.; Ran, X. Efficacy and Safety of Honey Dressings in the Management of Chronic Wounds: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jull, A.B.; Cullum, N.; Dumville, J.C.; Westby, M.J.; Deshpande, S.; Walker, N. Honey as a Topical Treatment for Wounds. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 2015, CD005083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainuddin, A.N.Z.; Mustakim, N.N.; Rosemanzailani, F.A.; Fadilah, N.I.M.; Maarof, M.; Fauzi, M.B. A Comprehensive Review of Honey-Containing Hydrogel for Wound Healing Applications. Gels 2025, 11, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojkovska, J.; Petrovic, P.; Jancic, I.; Milenkovic, M.T.; Obradovic, B. Novel Nano-Composite Hydrogels with Honey Effective against Multi-Resistant Clinical Strains of Acinetobacter baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 8529–8543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omidian, H.; Gill, E.J. Nanofibrous Scaffolds in Biomedicine. J. Compos. Sci. 2024, 8, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahari, N.; Hashim, N.; Md Akim, A.; Maringgal, B. Recent Advances in Honey-Based Nanoparticles for Wound Dressing: A Review. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venmathi Maran, B.A.; Jeyachandran, S.; Kimura, M. A Review on the Electrospinning of Polymer Nanofibers and Its Biomedical Applications. J. Compos. Sci. 2024, 8, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikzamir, M.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Panahi, Y. An Overview on Nanoparticles Used in Biomedicine and Their Cytotoxicity. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 102316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M.; Simões, M.; Vitorino, C.; Mascarenhas-Melo, F. Hydrogels in Cutaneous Wound Healing: Insights into Characterization, Properties, Formulation and Therapeutic Potential. Gels 2024, 10, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsareva, A.D.; Shtol, V.S.; Klinov, D.V.; Ivanov, D.A. Electrospinning for Biomedical Applications: An Overview of Material Fabrication Techniques. Surfaces 2025, 8, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshar, M.; Rezaei, A.; Eghbali, S.; Nasirizadeh, S.; Alemzadeh, E.; Alemzadeh, E.; Shadi, M.; Sedighi, M. Nanomaterial Strategies in Wound Healing: A Comprehensive Review of Nanoparticles, Nanofibres and Nanosheets. Int. Wound J. 2024, 21, e14953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyarzun-Ampuero, F.; Vidal, A.; Concha, M.; Morales, J.; Orellana, S.; Moreno-Villoslada, I. Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Wounds. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2015, 21, 4329–4341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, A.; Wang, X.Y.; Kaplan, D.L.; Garlick, J.A.; Egles, C. Biofunctionalized Electrospun Silk Mats as a Topical Bioactive Dressing for Accelerated Wound Healing. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 2570–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çerçi, A.; Akgün, O.; Karaca, E.; Bakhshpour-Yücel, M.; Arı, F.; Yiğit Çınar, A.; Bozkurt Güzel, Ç.; Osman, B. Molecularly Imprinted Nanoparticle-Embedded Electrospun Mat as an Antibacterial Wound Dressing. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2025, 36, e70100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zu, Q.; Deng, C.; Gao, X.; Liu, H.; Jin, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, E. Biodegradable Double-Layer Hydrogels with Sequential Drug Release for Multi-Phase Collaborative Regulation in Scar-Free Wound Healing. J. Funct. Biomater. 2025, 16, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastulyavichus, A.; Tolordava, E.; Saraeva, I.; Ulturgasheva, E.; Shelygina, S.; Egorova, D.; Babina, S.; Kudryashov, S. Nanoparticles Make the Difference: Bacteriocidic, Biocompatibility and Wound Healing Merits of Laser-Transferred Metal Nanoparticles. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2025, 771, 152044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, B.; Maleki, H.; Zavagna, L.; De la Ossa, J.G.; Linari, S.; Lazzeri, A.; Danti, S. Bio-Based Electrospun Fibers for Wound Healing. J. Funct. Biomater. 2020, 11, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kou, J.; Li, Y.; Zhou, C.; Wang, X.; Ni, J.; Lin, Y.; Ge, H.; Zheng, D.; Chen, G.; Sun, X.; et al. Electrospinning in Promoting Chronic Wound Healing: Materials, Process, and Applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2025, 13, 1550553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gounden, V.; Singh, M. Hydrogels and Wound Healing: Current and Future Prospects. Gels 2024, 10, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrasco, S.; González, L.; Tapia, M.; Urbano, B.F.; Aguayo, C.; Fernández, K. Enhancing Alginate Hydrogels as Possible Wound-Healing Patches: The Synergistic Impact of Reduced Graphene Oxide and Tannins on Mechanical and Adhesive Properties. Polymers 2024, 16, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushwaha, A.; Goswami, L.; Kim, B.S. Nanomaterial-Based Therapy for Wound Healing. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Ma, Y.; Yang, M.; Cheng, Y.; Ma, X.; Li, B.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, X.; Liu, M.; Long, Y.; et al. Wound Dressings Using Electrospun Nanofibers: Mechanisms, Applications, and Future Directions. Eur. Polym. J. 2025, 231, 113900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, T.K.N.; Truong, T.T.; Phan, T.N.L.; Nguyen, T.X.; Doan, V.H.M.; Vo, T.T.; Choi, J.; Pal, U.; Dhar, P.; Lee, B.; et al. Hydrogel-Based Smart Materials for Wound Healing and Sensing. Aggregate 2025, 6, e70047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouke, P.B.; Shrirame, T.; Potbhare, A.K.; Mondal, A.; Chaudhary, A.R.; Mondal, S.; Thakare, S.R.; Nepovimova, E.; Valis, M.; Kuca, K.; et al. Bioinspired Metal/Metal Oxide Nanoparticles: A Road Map to Potential Applications. Mater. Today Adv. 2022, 16, 100314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srujana, T.L.; Rao, K.J.; Korumilli, T. Natural Biogenic Templates for Nanomaterial Synthesis: Advances, Applications, and Environmental Perspectives. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2025, 11, 1291–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.F.; Melo, A.L.P.; Uchôa, A.F.C.; Pereira, G.M.A.; Alves, A.E.F.; Vasconcellos, M.C.; Xavier-Júnior, F.H.; Passos, M.F. Biomedical Approach of Nanotechnology and Biological Risks: A Mini-Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neupane, B.P.; Chaudhary, D.; Paudel, S.; Timsina, S.; Chapagain, B.; Jamarkattel, N.; Tiwari, B.R. Himalayan Honey Loaded Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization and Study of Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 3533–3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahid, H.; Shah, A.A.; Shah Bukhari, S.N.U.; Naqvi, A.Z.; Arooj, I.; Javeed, M.; Aslam, M.; Chandio, A.D.; Farooq, M.; Gilani, S.J.; et al. Synthesis, Characterization, and Biological Properties of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Synthesized from Apis mellifera Honey. Molecules 2023, 28, 6504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, N.A.; Shameli, K.; Wong, M.M.-T.; Teow, S.-Y.; Chew, J.; Sukri, S.N.A.M. Antibacterial and Cytotoxic Effect of Honey Mediated Copper Nanoparticles Synthesized Using Ultrasonic Assistance. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 104, 109899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghramh, H.A.; Ibrahim, E.H.; Kilany, M. Study of Anticancer, Antimicrobial, Immunomodulatory, and Silver Nanoparticles Production by Sidr Honey from Three Different Sources. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayani Nivethitha, P.; Carolin Jeniba Rachel, D. A Study of Antioxidant and Antibacterial Activity Using Honey Mediated Chromium Oxide Nanoparticles and Its Characterization. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 48, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atapakala, S.; Sana, S.S.; Kuppam, B.; Varma, R.S.; Aly Saad Aly, M.; Kim, S.-C.; Vadde, R. Honey Mediated Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles, and Evaluation of Antimicrobial, Antibiofilm Activities against Multidrug Resistant Clinical Bacterial Isolates. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2024, 135, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskin, M.; Kaya, G.; Bayram, S.; Kurek-Górecka, A.; Olczyk, P. Green Synthesis, Characterization, Antioxidant, Antibacterial and Enzyme Inhibition Effects of Chestnut (Castanea sativa) Honey-Mediated Silver Nanoparticles. Molecules 2023, 28, 2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czernel, G.; Bloch, D.; Matwijczuk, A.; Cieśla, J.; Kędzierska-Matysek, M.; Florek, M.; Gagoś, M. Biodirected Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Aqueous Honey Solutions and Evaluation of Their Antifungal Activity against Pathogenic Candida spp. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldeiu, A.; Simion, M.; Mihalache, I.; Radoi, A.; Banu, M.; Varasteanu, P.; Nadejde, P.; Vasile, E.; Acasandrei, A.; Popescu, R.C.; et al. Comparative Analysis of Honey and Citrate Stabilized Gold Nanoparticles: In Vitro Interaction with Proteins and Toxicity Studies. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2019, 197, 111519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghramh, H.A.; Ibrahim, E.H.; Ahmad, Z. Antimicrobial, Immunomodulatory and Cytotoxic Activities of Green Synthesized Nanoparticles from Acacia Honey and Calotropis procera. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 3367–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, A.A.; Bakhtiar, H.; Bidin, N.; Ghoshal, S.K. Antibacterial Activity of Decahedral Cinnamon Nanoparticles Prepared in Honey Using PLAL Technique. Mater. Lett. 2018, 232, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, A.; Şimşek, M.; Aldemir, S.D.; Kazaroğlu, N.M.; Gümüşderelioğlu, M. Honey-Based PET or PET/Chitosan Fibrous Wound Dressings: Effect of Honey on Electrospinning Process. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2014, 25, 999–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minden-Birkenmaier, B.A.; Smith, R.A.; Radic, M.; van der Merwe, M.; Bowlin, G.L. Manuka Honey Reduces NETosis on an Electrospun Template Within a Therapeutic Window. Polymers 2020, 12, 1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maleki, H.; Gharehaghaji, A.A.; Dijkstra, P.J. A Novel Honey-Based Nanofibrous Scaffold for Wound Dressing Application. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 127, 4086–4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarhan, W.A.; Azzazy, H.M.E. High Concentration Honey Chitosan Electrospun Nanofibers: Biocompatibility and Antibacterial Effects. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 122, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abolhassani, S.; Alipour, H.; Alizadeh, A.; Nemati, M.M.; Najafi, H.; Alavi, O. Antibacterial Effect of Electrospun Polyurethane-Gelatin Loaded with Honey and ZnO Nanoparticles as Potential Wound Dressing. J. Ind. Text. 2022, 51, 954S–968S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, A.S.; Najem Obaid Thewaini, Q.; Al-Musawi, S. Honey/Polymeric Nanofiber Enriched with Clove (Syzygium aromaticum L.) Extract and Al2O3 Nanoparticles: Antibacterial and in Vitro Wound Healing Studies. AIP Conf. Proc. 2022, 2437, 020029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.N.; Mohebbullah, M.; Islam, S.M.; Uddin, M.A.; Jobaer, M. Nigella/Honey/Garlic/Olive Oil Co-Loaded PVA Electrospun Nanofibers for Potential Biomedical Applications. Prog. Biomater. 2022, 11, 431–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvinzadeh Gashti, M.; Dehdast, S.A.; Berenjian, A.; Shabani, M.; Zarinabadi, E.; Chiari Fard, G. PDDA/Honey Antibacterial Nanofiber Composites for Diabetic Wound-Healing: Preparation, Characterization, and In Vivo Studies. Gels 2023, 9, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheradvar Kolour, A.; Ghoraishizadeh, S.; Zaman, M.S.; Alemzade, A.; Banavand, M.; Esmaeili, J.; Shahrousvand, M. Janus Films Wound Dressing Comprising Electrospun Gelatin/PCL Nanofibers and Gelatin/Honey/Curcumin Thawed Layer. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2024, 7, 8642–8655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, J.; Ghosh, M.; Das, P.; Basak, P.; Saha, P. Polycaprolactone Assisted Electrospinning of Honey/Betel with Chitosan for Tissue Engineering. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 57, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parin, F.N.; Terzioğlu, P.; Sicak, Y.; Yildirim, K.; Öztürk, M. Pine Honey–Loaded Electrospun Poly (Vinyl Alcohol)/Gelatin Nanofibers with Antioxidant Properties. J. Text. Inst. 2021, 112, 628–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri Azizabad, Z.; Haghbin Nazarpak, M.; Nayeb Habib, F. Modification of Cotton Gauze by Electrospinning of Gelatin and Honey Biopolymer Solution. J. Text. Inst. 2023, 114, 1199–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, M.; Ramezani, S.; Rashidi, M.-R. Fabrication of Honey-Loaded Ethylcellulose/Gum Tragacanth Nanofibers as an Effective Antibacterial Wound Dressing. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 621, 126615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghalei, S.; Li, J.; Douglass, M.; Garren, M.; Handa, H. Synergistic Approach to Develop Antibacterial Electrospun Scaffolds Using Honey and S-Nitroso-N-Acetyl Penicillamine. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuhladen, K.; Raghu, S.N.V.; Liverani, L.; Neščáková, Z.; Boccaccini, A.R. Production of a Novel Poly(ɛ-Caprolactone)-Methylcellulose Electrospun Wound Dressing by Incorporating Bioactive Glass and Manuka Honey. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2021, 109, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Mora-López, D.S.; Madera-Santana, T.J.; Olivera-Castillo, L.; Castillo-Ortega, M.M.; López-Cervantes, J.; Sánchez-Machado, D.I.; Ayala-Zavala, J.F.; Soto-Valdez, H. Production and Performance Evaluation of Chitosan/Collagen/Honey Nanofibrous Membranes for Wound Dressing Applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 275, 133809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahid, M.A.; Ali, A.; Uddin, M.N.; Miah, S.; Islam, S.M.; Mohebbullah, M.; Jamal, M.S.I. Antibacterial Wound Dressing Electrospun Nanofibrous Material from Polyvinyl Alcohol, Honey and Curcumin Longa Extract. J. Ind. Text. 2021, 51, 455–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arianto, D.; Edikresnha, D.; Suciati, T.; Khairurrijal, K. The Initial Study of Polyvinyl Alcohol/Honey/Glycerin Composite Fibers. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 44, 3408–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, C.; Girón-Hernández, J.; Honey, D.A.; Fox, E.M.; Cassa, M.A.; Tonda-Turo, C.; Camagnola, I.; Gentile, P. Synergistic Nanocoating with Layer-by-Layer Functionalized PCL Membranes Enhanced by Manuka Honey and Essential Oils for Advanced Wound Healing. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 20715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radoor, S.; Karayil, J.; Jayakumar, A.; Siengchin, S.; Parameswaranpillai, J. A Low Cost and Eco-Friendly Membrane from Polyvinyl Alcohol, Chitosan and Honey: Synthesis, Characterization and Antibacterial Property. J. Polym. Res. 2021, 28, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, J.; Chen, X.; Li, Z.; Dai, F. Silk Fibroin/Polycaprolactone Nanofibrous Membranes Loaded with Natural Manuka Honey for Potential Wound Healing. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, 51686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Lan, X.; Liang, C.; Zhong, Z.; Xie, R.; Zhou, Y.; Miao, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, W. Honey Loaded Alginate/PVA Nanofibrous Membrane as Potential Bioactive Wound Dressing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 219, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanzada, H.; Munir, M.U.; Kumpikaite, E.; Riaz, S. Development of Iodine and Honey Based PVP Electrospun Fibers for Biomedical Applications. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2024, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaydhane, M.K.; Kanuganti, J.S.; Sharma, C.S. Honey and Curcumin Loaded Multilayered Polyvinylalcohol/Cellulose Acetate Electrospun Nanofibrous Mat for Wound Healing. J. Mater. Res. 2020, 35, 600–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassem, L.M.; El-Deen, A.G.; Zaki, A.H.; El-Dek, S.I. Electrospun Manuka honey@PVP Nanofibers Enclosing Chitosan-Titanate for Highly Effective Wound Healing. Cellulose 2023, 30, 6487–6505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Musawi, S.; Albukhaty, S.; Al-Karagoly, H.; Sulaiman, G.M.; Alwahibi, M.S.; Dewir, Y.H.; Soliman, D.A.; Rizwana, H. Antibacterial Activity of Honey/Chitosan Nanofibers Loaded with Capsaicin and Gold Nanoparticles for Wound Dressing. Molecules 2020, 25, 4770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, M.; Mirhaj, M.; Varshosaz, J.; Al-Musawi, M.H.; Almajidi, Y.Q.; Danesh Pajooh, A.M.; Shahriari-Khalaji, M.; Sharifianjazi, F.; Alizadeh, M.; Labbaf, S.; et al. Keratin- and VEGF-Incorporated Honey-Based Sponge–Nanofiber Dressing: An Ideal Construct for Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 55276–55286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samraj.S, M.D.; Kirupha, S.D.; Elango, S.; Vadodaria, K. Fabrication of Nanofibrous Membrane Using Stingless Bee Honey and Curcumin for Wound Healing Applications. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 63, 102271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelu, M.; Popa, M.; Calderón Moreno, J.M. Applications of Hydrogels in Emergency Therapy. Gels 2025, 11, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liang, H.; Chen, X.; Tan, H. Natural Polymer-Based Hydrogels: From Polymer to Biomedical Applications. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satchanska, G.; Davidova, S.; Petrov, P.D. Natural and Synthetic Polymers for Biomedical and Environmental Applications. Polymers 2024, 16, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Gogoi, B.; Sharma, I.; Das, D.K.; Azad, M.A.; Pramanik, D.D.; Pramanik, A. Hydrogels as a Potential Biomaterial for Multimodal Therapeutic Applications. Mol. Pharm. 2024, 21, 4827–4848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamloo, A.; Aghababaie, Z.; Afjoul, H.; Jami, M.; Bidgoli, M.R.; Vossoughi, M.; Ramazani, A.; Kamyabhesari, K. Fabrication and Evaluation of Chitosan/Gelatin/PVA Hydrogel Incorporating Honey for Wound Healing Applications: An in Vitro, in Vivo Study. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 592, 120068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koosha, M.; Aalipour, H.; Sarraf Shirazi, M.J.; Jebali, A.; Chi, H.; Hamedi, S.; Wang, N.; Li, T.; Moravvej, H. Physically Crosslinked Chitosan/PVA Hydrogels Containing Honey and Allantoin with Long-Term Biocompatibility for Skin Wound Repair: An In Vitro and In Vivo Study. J. Funct. Biomater. 2021, 12, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giusto, G.; Beretta, G.; Vercelli, C.; Valle, E.; Iussich, S.; Borghi, R.; Odetti, P.; Monacelli, F.; Tramuta, C.; Grego, E.; et al. Pectin-Honey Hydrogel: Characterization, Antimicrobial Activity and Biocompatibility. BME 2018, 29, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasquez, J.M.; Idrees, A.; Carmagnola, I.; Sigen, A.; McMahon, S.; Marlinghaus, L.; Ciardelli, G.; Greiser, U.; Tai, H.; Wang, W.; et al. In Situ Forming Hyperbranched PEG—Thiolated Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogels with Honey-Mimetic Antibacterial Properties. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 742135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, K.; Panicker, S.S.; Adler, C.L.; O’Toole, G.A.; Hixon, K.R. Antibacterial Efficacy of Manuka Honey-Doped Chitosan-Gelatin Cryogel and Hydrogel Scaffolds in Reducing Infection. Gels 2023, 9, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, A.; Rajput, M.; Barui, A.; Chatterjee, S.S.; Pal, N.K.; Chatterjee, J.; Mukherjee, R. Dual Cross-Linked Honey Coupled 3D Antimicrobial Alginate Hydrogels for Cutaneous Wound Healing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 116, 111218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, B.; Majie, A.; Roy, K.; Lim, W.M.; Gorain, B. Glycyrrhizic Acid-Loaded Poloxamer and HPMC-Based In Situ Forming Gel of Acacia Honey for Improved Wound Dressing: Formulation Optimization and Characterization for Wound Treatment. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2025, 8, 310–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phonrachom, O.; Charoensuk, P.; Kiti, K.; Saichana, N.; Kakumyan, P.; Suwantong, O. Potential Use of Propolis-Loaded Quaternized Chitosan/Pectin Hydrogel Films as Wound Dressings: Preparation, Characterization, Antibacterial Evaluation, and in Vitro Healing Assay. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 241, 124633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, J.; Tang, Y. Honey/PVA Hybrid Wound Dressings with Controlled Release of Antibiotics: Structural, Physico-Mechanical and in-Vitro Biomedical Studies. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 77, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomić, S.L.; Vuković, J.S.; Babić Radić, M.M.; Filipović, V.V.; Živanović, D.P.; Nikolić, M.M.; Nikodinovic-Runic, J. Manuka Honey/2-Hydroxyethyl Methacrylate/Gelatin Hybrid Hydrogel Scaffolds for Potential Tissue Regeneration. Polymers 2023, 15, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noori, S.; Kokabi, M.; Hassan, Z.M. Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)/Chitosan/Honey/Clay Responsive Nanocomposite Hydrogel Wound Dressing. J Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giusto, G.; Vercelli, C.; Comino, F.; Caramello, V.; Tursi, M.; Gandini, M. A New, Easy-to-Make Pectin-Honey Hydrogel Enhances Wound Healing in Rats. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfinia, F.; Norouzi, M.-R.; Ghasemi-Mobarakeh, L.; Naeimirad, M. Anthocyanin/Honey-Incorporated Alginate Hydrogel as a Bio-Based pH-Responsive/Antibacterial/Antioxidant Wound Dressing. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaleghi, M.; Mani, F.; Salimi, H.; Hajibeygi, M.; Pashazadeh, R.; Zayerzadeh, E.; Babanejad, N.; Shabanian, M. Synthesis and Characterization of New Honey Incorporated Double-Network Hydrogels Based on Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) and Acylated Chitosan. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2018, 37, 3596–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saberian, M.; Seyedjafari, E.; Zargar, S.J.; Mahdavi, F.S.; Sanaei-rad, P. Fabrication and Characterization of Alginate/Chitosan Hydrogel Combined with Honey and Aloe Vera for Wound Dressing Applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 51398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmod, Z.; Zulkifli, M.F.; Masimen, M.A.A.; Ismail, W.I.W.; Sharifudin, M.A.; Amin, K.A.M. Investigating the Efficacy of Gellan Gum Hydrogel Films Infused with Acacia Stingless Bee Honey in Wound Healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 296, 139753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercelli, C.; Re, G.; Iussich, S.; Odore, R.; Morello, E.M.; Gandini, M.; Giusto, G. In Vivo Evaluation of a Pectin-Honey Hydrogel Coating on Polypropylene Mesh in a Rat Model of Acute Hernia. Gels 2021, 7, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshari, M.J.; Sheikh, N.; Afarideh, H. PVA/CM-Chitosan/Honey Hydrogels Prepared by Using the Combined Technique of Irradiation Followed by Freeze-Thawing. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2015, 113, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şalva, E.; Akdağ, A.E.; Alan, S.; Arısoy, S.; Akbuğa, F.J. Evaluation of the Effect of Honey-Containing Chitosan/Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogels on Wound Healing. Gels 2023, 9, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momin, M.; Kurhade, S.; Khanekar, P.; Mhatre, S. Novel Biodegradable Hydrogel Sponge Containing Curcumin and Honey for Wound Healing. J. Wound Care 2016, 25, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abohamzeh, E.; Sheikholeslami, M.; Shafee, A. Toxicity of Nanomaterials. In Nanomaterials and Nanotechnology in Medicine; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 447–478. ISBN 978-1-119-55802-6. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Gómez, F.D.; Monferrer, D.; Penon, O.; Rivera-Gil, P. Regulatory Pathways and Guidelines for Nanotechnology-Enabled Health Products: A Comparative Review of EU and US Frameworks. Front. Med. 2025, 12, 1544393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yammine, P.; El Safadi, A.; Kassab, R.; El-Nakat, H.; Obeid, P.J.; Nasr, Z.; Tannous, T.; Sari-Chmayssem, N.; Mansour, A.; Chmayssem, A. Types of Crosslinkers and Their Applications in Biomaterials and Biomembranes. Chemistry 2025, 7, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, M.; Basha, N.S.; Sahu, K.K.; Yadav, K.; Sucheta; Dubey, A.; Pradhan, H.K.; Kirubakaran, J. Engineering Nanofibers for Cutaneous Drug Delivery Systems and Therapeutic Applications. Med. Nov. Technol. Devices 2025, 27, 100386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberts, A.; Moldoveanu, E.-T.; Niculescu, A.-G.; Grumezescu, A.M. Hydrogels for Wound Dressings: Applications in Burn Treatment and Chronic Wound Care. J. Compos. Sci. 2025, 9, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Honey Type | Botanical/Geographical Origin | Distinct Characterization (Key Bioactives/Markers) | Mechanistic Highlights in Wound Care | Practical Notes/Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manuka | Leptospermum scoparium (New Zealand) | High methylglyoxal (MGO); also H2O2; bee defensin-1; polyphenols | Strong antibacterial incl. MRSA and biofilms; anti-inflammatory; supports re-epithelialization | Widely available as medical-grade dressings; potency closely linked to MGO; as with all honeys, batch standardization remains important |
| Tualang | Koompassia excelsa (Malaysia) | Phenolics/flavonoids; H2O2-dependent activity | Antibacterial—particularly strong vs. Gram-negative; anti-inflammatory; supports mucosal healing | Lower activity vs. Gram-positive than some comparators; praised for handling when incorporated in dressings; long-term evidence still developing |
| Local/regional honeys (e.g., Egyptian, Indian, Nigerian, Maltese, multifloral) | Varies with floral and geographic source | Polyphenols, enzymes; typically H2O2-mediated activity; wide variability across samples | Antimicrobial activity present but ranges widely by origin; supports wound healing via antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and moist-environment effects | Major challenge: lack of standardization (composition, sterility, potency); antimicrobial potency varies markedly (e.g., Nigerian honeys ZOI 1.4–17 mm; Maltese honeys vary by floral source) |
| Feature | Nanoparticles | Electrospun Nanofibers | Hydrogels | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Structure | Dispersed sub-micron particles (spherical or anisotropic) | Continuous fibrous mats (nano- to micro-scale fibers) | Three-dimensional cross-linked hydrophilic polymer networks | [72,73] |
| Main Components | Metal/metal-oxide or polymeric cores; honey or methylglyoxal as cargo/surface modifier | Natural or synthetic polymers with incorporated honey | Natural or synthetic polymers with incorporated honey | [74,75,76,77] |
| Release Profile | Burst-to-sustained; governed by particle matrix/coatings and the surrounding medium; often delivered within a secondary carrier | Sustained and tunable; influenced by fiber diameter, porosity and composition | Sustained and tunable; diffusion and network relaxation controlled by crosslink density and water content | [78,79,80,81] |
| Biocompatibility | Formulation-dependent; ion release and leachables for metal oxides; residual crosslinkers/endotoxin for biopolymers | Generally favorable; depends on polymer choice and residual solvents; low irritation when purified | Generally favorable; depends on polymer and crosslinker chemistry; high water content supports tolerance | [82,83,84,85] |
| Mechanical behavior | Not load-bearing as a dispersion; mechanical support provided by the host dressing | Moderate to high sheet strength; conformability improved by fiber alignment and basis weight | Soft and elastic; lower tensile strength; stiffness adjustable via crosslinking or reinforcement | [85,86,87] |
| Moisture Retention | Determined by the host dressing or gel carrier rather than the particles themselves | Moderate water-vapor transmission with in-plane wicking; tunable by layer design | High moisture retention; water-vapor transmission depends on network density and thickness | [88,89] |
| Form factor and application | Sheet-like, trim-to-size; straightforward placement over wound beds | Sheet-like, trim-to-size; straightforward placement over wound beds | Conformable gels or films; easy to inject or spread over irregular surfaces | [75,88,89] |
| Aim of the Study | Material | Methods | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| To synthesize iron oxide nanoparticles loaded with Himalayan honey and evaluate their antioxidant and antimicrobial activities. | Composition: iron oxide nanoparticles (IO-NPs) loaded with Himalayan honey (Apis laboriosa), referred to as HHLIO-NPs | In vitro Physicochemical characterization (XRD, SEM, UV-VIS), antioxidant activity (DPPH assay, IC50), antibacterial activity (agar well diffusion against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus), comparison of activity between HH, IO-NPs and HHLIO-NPs | Neupane et al. [93] |
| To synthesize copper nanoparticles using honey as a reducing and stabilizing agent, and evaluate their antibacterial and cytotoxic effects. | Composition: copper nanoparticles synthesized with and without honey via ultrasonic irradiation | In vitro Antibacterial activity (MIC50, MBC against E. coli and E. faecalis), cytotoxicity on normal colon cells (CCD112) and colorectal cancer cells (HCT116), physicochemical characterization (UV-VIS, XRD, HRTEM, FESEM-EDX, FTIR), particle size distribution | Ismail et al. [95] |
| To investigate the anticancer, antimicrobial, and immunomodulatory activities of silver nanoparticles synthesized using two types of honey | Composition: silver nanoparticles synthesized using Sider and Dharm honey as reducing agents (green synthesis) | In vitro Cytotoxicity (on MCF-7, HepG2, HCT-116, A-549 cancer cell lines), antimicrobial activity (agar well diffusion against E. coli, S. aureus, P. aeruginosa, C. albicans), immunomodulatory activity (phagocytic index in mice macrophages), physicochemical characterization (UV-VIS, FTIR, SEM) | Ghramh et al. [96] |
| To compare gold nanoparticles synthesized with honey and with citrate in terms of their colloidal behavior, protein interactions, and cytotoxicity. | Composition: gold nanoparticles synthesized via green method with honey (AuNPs@honey) and via Turkevich method with citrate (AuNPs@citrate) | In vitro Nanoparticle stability in cell media, protein corona formation, cytotoxicity (L929 fibroblasts, B16 melanoma), ROS generation, apoptosis induction | Boldeiu et al. [101] |
| To synthesize iron oxide (Fe2O3) nanoparticles using honey from Apis mellifera as a green reducing and capping agent, and to evaluate their antibacterial, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory properties. | Composition: Iron oxide nanoparticles (Fe2O3-NPs) synthesized via green method using Apis mellifera honey as reductant and stabilizer | In vitro Physicochemical characterization (UV-Vis at 350 nm, XRD, SEM, EDX, ICP-MS, VSM), antibacterial activity (inhibition zones, MIC against clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae), antioxidant activity (IC50 = 22 µg/mL), anti-inflammatory activity (IC50 = 70 µg/mL) | Shahid et al. [94] |
| To biosynthesize silver nanoparticles using aqueous honey at various concentrations and evaluate their antifungal efficacy against Candida albicans and Candida parapsilosis. | Composition: Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs-C for citrate, AgNPs-H2, H10, H20 for 2%, 10%, 20% honey-mediated synthesis) | In vitro Physicochemical characterization (UV–Vis, fluorescence spectroscopy, SEM, DLS including size, zeta potential), antifungal activity (MIC determination, disk diffusion assay against C. albicans and C. parapsilosis), effect of honey concentration on synthesis | Czernel et al. [100] |
| To synthesize chromium oxide nanoparticles using honey as a reducing agent and evaluate their antioxidant and antibacterial properties. | Composition: Chromium oxide nanoparticles (Cr2O3 NPs) synthesized by reduction of potassium dichromate using natural honey | In vitro Physicochemical characterization (UV–Vis, FT-IR, XRD, SEM, EDAX, AFM), total antioxidant activity (phosphomolybdenum method), antibacterial activity (zone of inhibition against E. coli, Bacillus spp., and S. aureus) | Nivethitha et al. [97] |
| To synthesize AgNPs using chestnut honey as reducing and stabilizing agent and to evaluate their antioxidant, antibacterial, and enzyme inhibition properties. | Composition: silver nanoparticles (CH-AgNPs) synthesized with Castanea sativa (chestnut) honey at 30, 60, 90 °C | In vitro Physicochemical characterization (UV-Vis, FT-IR, SEM, EDX, DLS), antioxidant activity (DPPH assay), antibacterial activity (MIC, inhibition zones against various bacteria), enzyme inhibition | Keskin et al. [99] |
| To evaluate antimicrobial, immunomodulatory, and cytotoxic activities of silver and selenium nanoparticles synthesized using Acacia honey and Calotropis procera leaf extract. | Composition: Silver (AgNPs) and selenium (SeNPs) nanoparticles synthesized using Acacia honey and Calotropis procera leaf extract | In vitro Physicochemical characterization (UV–Vis, TEM, SEM, FTIR, XRD), antimicrobial activity (disk diffusion assay against S. aureus, B. subtilis, E. coli, P. aeruginosa, C. albicans), immunomodulatory activity (phagocytic index in mice macrophages), cytotoxicity (MTT assay on HepG2 and HCT116 cell lines) | Ghramh et al. [102] |
| To synthesize zinc oxide nanoparticles using honey as a green reductant and evaluate their antibacterial, antibiofilm, antioxidant, and membrane-damaging activity against multidrug-resistant clinical bacterial strains. | Composition: zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnONPs) synthesized by auto-combustion method using natural honey as reducing and stabilizing agent | In vitro Physicochemical characterization (UV–Vis, FTIR, XRD, FE-SEM, TEM, DLS, zeta potential), antioxidant activity (DPPH, ABTS assays), antibacterial activity (against K. pneumoniae, E. coli, MRSA, P. aeruginosa, S. aureus), antibiofilm activity, membrane integrity analysis (leakage of nucleic acids and proteins) | Atapakala et al. [98] |
| To synthesize decahedral cinnamon nanoparticles (DCNPs) in honey using pulsed laser ablation in liquid (PLAL) and to evaluate their antibacterial activity against Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. | Composition: cinnamon nanoparticles synthesized from solid cinnamon sticks in 5 mL honey solution using pulsed laser ablation (Nd:YAG laser at 1064 nm, 30–180 mJ) | In vitro Nanoparticle morphology (HR-TEM, EDX), FTIR spectroscopy, antibacterial activity (agar well diffusion, optical density OD600) against E. coli and B. subtilis, dependence of antibacterial effect on laser ablation energy | Salim et al. [103] |
| Aim of the Study | Material | Methods | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| To evaluate the effect of honey and chitosan on the electrospinning process and structural properties of PET-based fibrous mats for potential use in wound dressings | Electrospun PET, PET/chitosan, and PET/honey fibers with 10–40% honey | In vitro Fiber morphology, fiber diameter, water uptake, wettability, porosity, and cytotoxicity (L929 fibroblasts) | Arslan et al. [104] |
| To evaluate the effect of Manuka honey incorporated into electrospun tissue engineering templates on neutrophil extracellular trap formation (NETosis), aiming to modulate inflammatory responses and reduce MMP-9 release. | Electrospun polydioxanone (PDO) with 0–10% Manuka honey | In vitro Fiber morphology, honey release, NETosis (fluorescence + MPO), MMP-9 and cytokine release | Minden-Birkenmaier et al. [105] |
| To fabricate electrospun polyurethane/gelatin nanofibers loaded with honey and ZnO nanoparticles and evaluate their antibacterial, mechanical, and cytotoxic properties for wound dressing applications | Electrospun PU/Gel nanofibers with 10% honey and 1% ZnO nanoparticles | In vitro Fiber morphology, mechanical properties (tensile strength, elongation), antibacterial activity (E. coli, S. aureus, B. subtilis), and cytotoxicity (MTT assay on HEK cells) | Abolhassani et al. [108] |
| To develop high-concentration honey–chitosan–PVA nanofibers with dexamethasone and evaluate their potential as biocompatible wound dressings. | Electrospun PVA/honey nanofiber meshes (ratios 100/0 to 60/40) ± 5/10/15% of dexamethasone | In vitro Fiber morphology, diameter, presence of beads, drug (dexamethasone) release profile, burst release dynamics | Maleki et al. (2013) [106] |
| To develop and evaluate electrospun PVA/chitosan/honey nanofibers with different compositions for potential use as wound dressings, focusing on fiber morphology, mechanical properties, antimicrobial activity, and biocompatibility. | Electrospun PVA/chitosan/honey nanofibers (ratios: PVA/chitosan 7/1.5–7/3.5, PVA/honey 10/20–10/30, honey/PVA/chitosan 30/7/1.5–40/7/3.5 crosslinked (glutaraldehyde vapor + thermal/freeze–thaw)) | In vitro Fiber morphology (SEM), FTIR spectroscopy, swelling and degradation behavior, tensile strength, antibacterial activity (S. aureus, E. coli), cytotoxicity (MTT assay on human fibroblasts), crosslinking (glutaraldehyde vapor, freezing/thawing, heating) | Sarhan et al. [107] |
| To optimize electrospinning parameters for honey/betel-loaded PCL/chitosan nanofibrous scaffolds and evaluate their morphology, physicochemical, mechanical, and biological properties for tissue engineering applications | Electrospun scaffolds of 12% w/v PCL with honey and betel, blended with 2% chitosan (PCL:honey/betel:chitosan, 2:7 ratio and crosslinked via glutaraldehyde vapor) | In vitro Electrospinning optimization, fiber morphology (bead-free, random), hydrophilicity (contact angle), thermal behavior (DSC), mechanical strength (tensile), degradation, cell viability (PBMC), and hemocompatibility | Adhikari et al. [113] |
| To fabricate pine honey-loaded electrospun poly(vinyl alcohol)/gelatin nanofibers and evaluate their structural and antioxidant properties | Electrospun PVA/gelatin nanofibers loaded with 0–15% pine honey | In vitro Fiber morphology (SEM), diameter, wettability (contact angle), FTIR, and antioxidant activity (DPPH, ABTS, β-carotene-linoleic acid, CUPRAC) | Parin et al. [114] |
| To create a dual-layer wound dressing by electrospinning gelatin/honey biopolymer solutions | Electrospun gelatin/honey biopolymer solution applied as a dual-layer dressing on cotton gauze (gelatin:honey ratios from 95:5 to 70:30) | In vitro Fiber morphology (bead formation, diameter), hydrophobicity (contact angle), chemical integration (FTIR), and potential for dermal applications | Azizabad et al. [115] |
| To develop electrospun EC/gum tragacanth nanofibers with varying honey concentrations and evaluate their physicochemical and biological properties for wound dressing applications. | Electrospun ethylcellulose/gum tragacanth nanofibers loaded with 5–20% w/w multifloral honey | In vitro Fiber morphology (bead-free, smooth), honey release profile, antioxidant capacity, cytotoxicity | Ghorbani et al. [116] |
| To fabricate electrospun PLA scaffolds incorporating Manuka honey and SNAP for dual antibacterial and regenerative functionality. | Electrospun PLA nanofibers co-loaded with Manuka honey and SNAP (a nitric oxide donor) | In vitro Fiber morphology, sustained nitric oxide release, tensile strength, wettability, water retention, water vapor transmission, antibacterial activity (against S. aureus and E. coli), and fibroblast attachment/proliferation | Ghalei et al. [117] |
| To develop electrospun PCL–methylcellulose mats functionalized with Manuka honey and bioactive glass for wound dressing applications | Electrospun PCL/methylcellulose fiber mats cross-linked with Manuka honey and loaded with bioactive glass (BG) particles | In vitro Fiber morphology and chemistry (SEM, FT-IR), wettability, mechanical strength (3–5 MPa), bioactivity (simulated body fluid tests), fibroblast and HaCaT cell proliferation and migration, antibacterial activity | Schuhladen et al. [118] |
| To fabricate electrospun PVA/chitosan/collagen nanofibers with honey and evaluate their antibacterial, mechanical, and biological properties for wound dressing applications. | Electrospun nanofibrous membranes from polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), chitosan, collagen, and honey at 0%, 5%, 10%, and 15% honey concentrations | In vitro Fiber morphology (diameter, porosity), water vapor transmission rate (WVTR), adsorption, mechanical properties (elastic modulus, elongation), antibacterial efficacy (against S. aureus, P. aeruginosa, E. coli, L. monocytogenes), and biocompatibility (cytotoxicity, fibroblast and keratinocyte viability) | Servín de la Mora-López et al. [119] |
| To develop electrospun PVA nanofibers incorporating Nigella sativa, honey, garlic, and olive oil, and evaluate their antibacterial and biological performance for wound dressing use. | Electrospun PVA nanofibers co-loaded with 3 mL Nigella sativa extract, 2 mL honey, 2 mL garlic extract, and 2 mL olive oil (per 20 mL PVA solution) | In vitro Fiber morphology, thermal stability, antibacterial activity (S. aureus), moisture absorption, cytocompatibility | Uddin et al. [110] |
| To fabricate electrospun PVA nanofibers co-loaded with honey and turmeric extract, and assess their structural and antimicrobial properties for wound care applications | Electrospun PVA nanofibers containing honey and Curcumin longa extract (CL-1: 20 mL PVA + 10 mL honey + 1 g turmeric; CL-2: same with 2 g turmeric) | In vitro Fiber morphology (SEM), moisture management, FTIR chemical composition, and antibacterial activity against S. aureus | Shahid, Ali. [120] |
| To fabricate electrospun PVA fibers with glycerin and honey and evaluate their morphology and polymer integration | Electrospun composite fibers from 10% PVA solution containing 1% v/v glycerin and 1% v/v multifloral honey | In vitro Fiber morphology, glycerin-induced plasticity, and incorporation efficiency of honey (FTIR, SEM) | Arianto et al. [121] |
| To develop Layer-by-Layer-coated PCL membranes with Manuka honey, chitosan, and essential oils for antibacterial wound dressing. | Electrospun PCL membranes functionalized by Layer-by-Layer assembly with 16 alternating layers of 20% (w/v) Manuka honey (MH) and 1% (w/v) chitosan, plus 4 additional spray layers containing cinnamon or tea tree essential oil (EO)nanoemulsions (EO:MH ratio 1:15) | In vitro Fiber morphology (SEM), chemical composition (XPS, FTIR), EO/MGO release, fibroblast viability and gene expression (VEGF, COL1, TGF-β1), antibacterial activity against S. aureus and P. aeruginosa | Gallo et al. [122] |
| To fabricate crosslinked PVA/chitosan/honey membranes and assess their mechanical, structural, and antibacterial performance. | Solution-cast membranes composed of 1.80 g PVA, 0.3 g chitosan, and honey at 1%, 5%, 10%, and 15% w/w (0.35 g, 1.75 g, 3.5 g, and 5.25 g, respectively), crosslinked with glutaraldehyde | In vitro Crystallinity (XRD), chemical structure (FTIR), surface morphology (SEM, AFM), mechanical strength and elongation, wettability (contact angle), swelling behavior, and antibacterial activity against E. coli and S. aureus | Radoor et al. [123] |
| To create silk fibroin/PCL bilayer nanofibrous membranes with Manuka honey for skin-related wound healing. | Electrospun nanofibers composed of silk fibroin (SF), polycaprolactone (PCL), and Manuka honey | In vitro Fiber morphology (SEM), mechanical properties (stress, flexibility), hydrophilicity (for cell adhesion), antibacterial activity (S. aureus, E. coli, C. albicans), cytocompatibility (cell proliferation/adhesion) | Lan et al. (2021) [124] |
| To compare the antibacterial efficacy and biocompatibility of natural clove extract and aluminum oxide nanoparticles incorporated into honey/chitosan-based nanofibrous wound dressings | Electrospun nanofibers prepared from 15% honey, 10% chitosan, 5% TPP, optionally 13% clove extract and 3% Al2O3 nanoparticles, dissolved in 1% HCl | In vitro Fiber morphology, antibacterial efficacy (S. aureus, E. coli), in vitro wound healing (fibroblast scratch assay), and nanoparticle distribution | Jawad et al. [109] |
| To fabricate alginate/PVA nanofibers with honey and assess their antioxidant, antibacterial, and cytocompatibility features. | Electrospun nanofibers composed of 7.2% PVA and 0.8% alginate with 0%, 5%, 10%, 15%, and 20% (v/v) acacia honey, crosslinked with glutaraldehyde | In vitro SEM (fiber morphology), FTIR (chemical structure), swelling ratio, weight loss, DPPH assay (antioxidant), antibacterial activity (disk diffusion and dynamic contact), cytotoxicity (MTT), cell adhesion (light microscopy) | Tang et al. [125] |
| To develop PVP nanofibers with honey and iodine and evaluate their synergistic antibacterial properties. | Electrospun PVP fibers containing 2% v/v honey and 0–5% w/v iodine | In vitro Fiber morphology (SEM), chemical composition (FTIR), thermal stability (TGA), fiber diameter changes (decrease with iodine, increase with honey), and antibacterial efficacy against S. aureus and E. coli | Khanzada et al. [126] |
| To fabricate multilayer electrospun PVA wound dressings with honey and curcumin and assess their antioxidant and antibacterial activity. | Electrospun nanofibers composed of 6% (w/v) PVA, 6% (w/v) honey, and/or 1% (w/v) curcumin; plus 16% cellulose acetate + 1% curcumin solution in acetone:DMAc (2:1) | In vitro Fiber morphology, chemical compatibility (FTIR), water absorption, water vapor transmission rate (MVTR), contact angle antioxidant activity, and antibacterial activity against E. coli | Gaydhane et al. (2020) [127] |
| To fabricate crosslinked PDDA/honey nanofibers and assess their fluid uptake, antibacterial performance, and diabetic wound healing in vivo. | Electrospun nanofibers composed of PDDA with 50% and 60% (w/w) Manuka honey; mixed with ethanol to 5 mL total volume; crosslinked with glutaraldehyde | In vitro and in vivo SEM (fiber morphology), FTIR (chemical structure), contact angle (surface wettability), swelling and degradation analysis, tensile strength (mechanical testing), antibacterial activity (S. aureus, E. coli—zone of inhibition, bacterial adhesion), in vivo wound healing in mice (wound closure measurement, H&E histological analysis) | Gashti et al. [111] |
| To create PVP-based nanofibers with Manuka honey and titanate nanotubes and evaluate their healing effects in vivo. | Electrospun nanofibers composed of 15% (w/v) polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) and 15–25% (v/v) Manuka honey; combined with chitosan–titanate hybrid prepared from 2.5% (w/v) chitosan and 2.5% (w/v) titanium dioxide nanotubes (TiONTs) in acetic acid, crosslinked via glutaraldehyde vapor | In vitro and in vivo SEM (fiber morphology), FTIR and XRD (structure), mechanical strength (tensile test), water contact angle, MGO release, antibacterial activity (S. aureus, E. coli), in vivo wound healing in rats (macroscopic wound closure, histology with re-epithelialization markers) | Kassem et al. [128] |
| To fabricate chitosan/honey nanofibers with capsaicin and/or gold nanoparticles and assess their antibacterial and healing efficacy in rabbits. | Electrospun mats based on 25% (w/v) honey, 3% (w/v) chitosan, and 8% (w/v) tripolyphosphate (TPP); variants include addition of 1 mg/mL capsaicin and 10% (v/v) gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) | In vitro and in vivo Nanofiber morphology, viscosity, antibacterial activity (against P. multocida, K. rhinoscleromatis, S. pyogenes, V. vulnificus), cytotoxicity and cell proliferation (Vero fibroblasts), and wound-closure efficacy (In vivo (rat full-thickn ess dorsal wounds)) | Al musawi et al. [129] |
| To develop a bilayer electrospun/hydrogel gelatin-based scaffold containing honey and curcumin for enhanced wound healing, and evaluate its in vivo performance compared to commercial dressings | Bilayer scaffold: enzymatically cross-linked gelatin hydrogel loaded with honey and curcumin (bottom layer), reinforced with gelatin/polycaprolactone (PCL) electrospun nanofibers (top layer) | In vitro and in vivo Mechanical properties (tensile strength, elongation), swelling rate, water vapor permeability, MTT cytocompatibility, histopathology (collagen deposition, granulation, immune response, re-epithelialization), and wound closure rate | Kheradvar Kolour et al. [112] |
| To design a bilayer dressing of honey sponge and VEGF/keratin-loaded nanofibers and assess their angiogenic and regenerative capacity. | Bilayer scaffold: top layer—sponge of poly(acrylic acid) (PAAc) with honey (Hny); bottom layer—electrospun nanofibers of keratin (Kr), honey (Hny), and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), forming PAAc–Hny/Hny–Kr–VEGF system | In vitro and in vivo (Morphology (SEM), VEGF release (7 days), mechanical strength, cytocompatibility (keratinocytes), angiogenesis (CAM), wound closure, blood vessel formation, collagen synthesis, re-epithelialization) | Tavakoli et al. [130] |
| To develop polycaprolactone (PCL) nanofibrous membranes incorporating stingless bee honey and curcumin for wound healing, and to evaluate their physicochemical, antibacterial, and biological performance | Electrospun nanofibers made from 12% (w/v) polycaprolactone (PCL) solution with stingless bee honey and curcumin; optimized blend mixed with 2% (w/v) chitosan in formic acid:acetone (4:6) solvent (CS:PCL ratio 2:7) | In vitro and in vivo SEM (morphology), ATR-FTIR (functional groups), DSC (thermal properties), tensile strength test, water degradation, contact angle (hydrophilicity), in vitro cytotoxicity (MTT on PBMCs), hemocompatibility, in vivo wound healing in rats (histology and closure rate) | Samraj et al. [131] |
| Aim of the Study | Material | Methods | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| To develop honey–PVA hydrogels crosslinked with borax for wound dressing applications and evaluate their mechanical, antimicrobial, and antibiotic-release properties | Hydrogels composed of PVA and 60% honey (v/v) with varying concentrations of borax (0–3% w/v) as crosslinker | In vitro Morphology (SEM), swelling kinetics, permeability, bioadhesion, mechanical strength (tensile test), cytotoxicity (fibroblasts), antibacterial activity (S. aureus, E. coli), amoxicillin release profile | Tavakoli et al. [144] |
| To develop chitosan/PVA hydrogel films incorporating honey via solvent-casting and evaluate their potential as wound dressings | Hydrogel films from chitosan (0.25–2%), PVA (5% w/v) and local honey (variable proportions) | In vitro Thickness, weight variation, folding endurance, moisture content, moisture uptake, WVTR, swelling, morphology (SEM), interactions (FTIR, DSC); In vitro honey release, antimicrobial activity (S. aureus), in silico docking of honey compounds; | Chopra et al. [64] |
| To create an injectable, fast-forming hydrogel that mimics honey’s antimicrobial hydrogen peroxide release for treating bacterially colonized wounds | Hydrogel formed via thiol-ene click chemistry between hyperbranched PEGDA (10% w/w) and thiolated hyaluronic acid (1% w/w), loaded with glucose oxidase (0–500 U/L) and 2.5% w/w glucose to simulate honey-like H2O2 production | In vitro Gelation time, swelling, stability, H2O2 release, cytocompatibility (L929, HaCaT), antibacterial activity (MRSA, MRSE, S. aureus, E. coli, P. aeruginosa, A. baumannii) | Vasquez et al. [139] |
| To develop hybrid hydrogel scaffolds combining Manuka honey with 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA) and gelatin, and to investigate their suitability for tissue regeneration applications | Scaffolds made from HEMA and gelatin with Manuka honey at three concentrations: 10%, 20%, and 30% (w/w) | In vitro Porosity, pH- and temperature-dependent swelling, in vitro degradation, biocompatibility (MTT assay on MRC-5 and HaCaT) | Tomić et al. [145] |
| To evaluate how Manuka honey incorporation into chitosan–gelatin cryogels and hydrogels enhances antibacterial efficacy and scaffold properties | Cryogel and hydrogel scaffolds composed of chitosan:gelatin (1:4) doped with 0%, 1%, 5% or 10% Manuka honey | In vitro SEM, swelling capacity, pore size, bacterial clearance (S. aureus), biofilm formation, cytotoxicity/cellular infiltration (likely fibroblasts or relevant cell lines) | Mitchell et al. [140] |
| To develop honey-based nanocomposite hydrogels with enhanced antimicrobial activity against multi-resistant pathogens for wound healing applications | Hydrogel matrix composed of honey, alginate, and nanocrystalline cellulose (NCC), with silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) synthesized in situ from honey and silver nitrate | In vitro Antibacterial activity (disk diffusion, MIC/MBC against A. baumannii, P. aeruginosa, S. aureus), morphology (SEM), EDX for Ag distribution, FTIR, XRD, water content, stability, biocompatibility (human dermal fibroblasts) | Stojkovska et al. [70] |
| To develop a multifunctional PVA/chitosan/honey/clay hydrogel with responsive properties for enhanced wound healing | Hydrogel composed of 10% PVA, 1.5% chitosan, 1% honey, 2% clay (montmorillonite) | In vitro Water absorption, swelling behavior, WVTR, mechanical properties (tensile strength, elongation), cytocompatibility (MTT), antibacterial activity (S. aureus, E. coli) | Noori et al. [146] |
| To develop and evaluate a pectin-honey hydrogel (PHH) as a wound healing membrane and compare its effect with pectin hydrogel and liquid honey | Hydrogel composed of Manuka honey and citrus pectin (1:1 v/v with water, then pectin added) | In vivo (Sprague Dawley rats model) Wound area reduction rate, histological evaluation (inflammation, re-epithelialization, fibrous tissue), wound contraction | Giusto et al. [147] |
| To develop sodium alginate hydrogel films incorporating honey and red cabbage-derived anthocyanins as pH-sensitive, antibacterial, and antioxidant wound dressings | Films composed of 8% (w/v) sodium alginate with 400% (w/w relative to alginate) honey and added red cabbage extract, crosslinked with 36 mM CaCl2 | In vitro Porosity; mechanical properties (tensile strength, elongation); swelling; water retention; pH-responsive color change; antibacterial activity (S. aureus, E. coli); antioxidant activity (DPPH scavenging); biocompatibility (L929 fibroblasts proliferation) | Lotfinia et al. [148] |
| To develop novel double-network hydrogels composed of acylated chitosan and PVA, incorporating honey for improved wound dressing functionality | Double-network hydrogel consisting of poly(vinyl alcohol), acylated chitosan (ACS), and honey (formulations with 5%, 10%, 15% w/w honey) | In vitro Swelling capacity, mechanical strength (tensile test), thermal properties (TGA, DSC), porosity (SEM), FTIR, degradation, antibacterial activity (S. aureus, E. coli), cytocompatibility (L929 cells), pH-responsiveness | Khaleghi et al. [149] |
| To develop chitosan–alginate–honey hydrogel films with optimized physicochemical, mechanical, and antibacterial properties for wound dressing | Hydrogel films prepared from chitosan, sodium alginate, and 2.5–10% (w/v) natural honey, crosslinked with calcium chloride (CaCl2) | In vitro Swelling index, moisture retention, water vapor transmission rate (WVTR), mechanical strength, morphology (SEM), FTIR, thermal stability (TGA), antibacterial activity (S. aureus, E. coli) | Saberian et al. [150] |
| To develop and characterize quaternized chitosan/pectin hydrogel films loaded with ethanolic propolis extract for enhanced wound healing and antibacterial activity | Hydrogel films based on quaternized chitosan, pectin (2.5%), glycerol (plasticizer), crosslinked with CaCl2, with 5–15% ethanolic propolis extract | In vitro Mechanical properties (tensile strength, elongation), swelling ratio, degradation, antibacterial activity (S. aureus, E. coli), DPPH antioxidant activity, hemolysis, in vitro wound healing (scratch assay, HaCaT cells) | Phonrachom et al. [143] |
| To evaluate the therapeutic properties of gellan gum hydrogels incorporated with varying concentrations of Acacia stingless bee honey (SBH) for wound healing | Hydrogel films based on low-acyl gellan gum with 10%, 15%, and 20% (v/v) SBH (from Heterotrigona itama, Acacia mangium); crosslinked with CaCl2 | In vitro Swelling ratio, water vapor transmission rate, disk diffusion antibacterial activity (E. coli), cell viability and proliferation (3T3-L1 fibroblasts), wound closure rate, scratch assay, FTIR, UV-vis, XRD | Mahmod et al. [151] |
| To evaluate whether coating polypropylene mesh with pectin-honey hydrogel (PHH) improves peritoneal regeneration and reduces adhesions in an acute hernia rat model | Polypropylene mesh coated with PHH prepared from 1:1 (v/v) aqueous honey solution and pectin added at 0.5:1 (w/v), dried and gamma-irradiated before implantation | In vivo Adhesion formation scores, peritoneal regeneration (histology), COX-2 expression (IHC), inflammation grade, mesh integration | Vercelli et al. [152] |
| To develop honey-based hydrogels using irradiation and freeze-thawing for wound dressing | Hydrogels composed of 10 parts PVA, 1.5–3.5 parts CM-chitosan, and 1.5–3.5 parts honey, total polymer conc. 15 wt% | In vitro and in vivo Gel content, degree of swelling, evaporation rate, mechanical strength, antibacterial activity (E. coli), wound healing efficacy in mice | Afshari et al. [153] |
| To develop and optimize an in situ forming thermoresponsive gel containing Acacia honey and glycyrrhizic acid for wound healing | Optimized gel composed of 20% poloxamer 407, 2% HPMC K100M, 2% Acacia honey, 0.1% glycyrrhizic acid | In vitro and in vivo Rheological properties, gelation temperature/time, drug release kinetics, antioxidant activity (DPPH), antibacterial activity (S. aureus, E. coli), cytocompatibility (L929), wound healing in rats (epithelialization, re-epithelialization score, collagen deposition) | Jha et al. [142] |
| To prepare honey-based hydrogels and assess their antimicrobial and burn-healing efficacy compared to a commercial product | Six hydrogel formulations with 25%, 50%, and 75% (w/w) honey prepared using either Carbopol 934 or chitosan; hydrogel base included triethanolamine (TEA), methyl paraben, and deionized wate | In vitro and in vivo (mice model) Visual assessment (homogeneity, color), pH measurement, swelling index (PBS pH 5.5), spreadability test, in vitro honey release (dialysis, UV-Vis 340 nm), antimicrobial activity (disk diffusion, S. aureus, P. aeruginosa, K. pneumoniae, S. pyogenes), daily wound contraction, histology (capillary formation, epidermal regeneration, acanthosis), bacterial swabs and culture | El-Kased et al. [49] |
| To investigate the effect of honey-enriched chitosan/hyaluronic acid hydrogels on wound healing performance | Chitosan–HA hydrogels with honey: CH1–CH4 (1–6% HA, 0–3% honey), CHB1–CHB4 with balanced honey to chitosan/HA ratios | In vitro and in vivo Physicochemical (swelling, morphology SEM), in vivo wound closure (histology: H&E staining), biocompatibility | Salva et al. [154] |
| To develop physically cross-linked chitosan/PVA hydrogels incorporating honey and allantoin via freeze–thaw cycles, and assess their wound healing potential | Hydrogels made from chitosan:PVA (30:70 v/v) with honey (diluted 1:1 w/w) and allantoin (4%), combined via freeze–thaw (3 cycles) | In vitro and in vivo Physicochemical: swelling (324–476%), gel content (<10%), mass loss, crystallinity (FTIR, XRD, DSC) | Koosha et al. [137] |
| To develop and evaluate a new pectin-honey hydrogel dressing with antibacterial and biocompatible properties | Hydrogel composed of pectin and Manuka honey (1:1 v/v), dried into films and sterilized by gamma irradiation | In vitro and in vivoSwelling, WVTR, hydrogen peroxide and MGO content, antibacterial activity (S. aureus, E. coli), cytotoxicity (L929 fibroblasts via MTT) subcutaneous and intraperitoneal implantation, histological evaluation, IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, and PGE2 levels | Giusto et al. [138] |
| To develop dual cross-linked alginate hydrogels incorporating honey and assess their structural, antimicrobial, and healing efficacy | Sodium alginate hydrogel crosslinked ionically (Ca2+) and covalently (EDC/NHS), with honey concentrations of 2%, 4%, 6%, 8%, and 10% | In vitro and in vivo FTIR, XRD, nanoindentation, swelling behavior, degradation time, SEM, cytocompatibility (HaCaT, 3T3), antibacterial activity (MRSA, E. coli), in vivo wound contraction (4% HSAG: 94.56% after 14 days), histology, OCT imaging | Mukhopadhyaya et al. [141] |
| To develop and evaluate a hydrogel sponge composite containing curcumin and honey for enhanced wound healing | Hydrogel sponge composed of chitosan (1–3% w/v), sodium alginate (1–3% w/v), 1% w/v curcumin in ethanol, 10 mL honey (per batch), crosslinked with acrylamide; prepared via solvent casting and in situ polymerization | In vitro and in vivo (excision wound model in rats); In vitro and in vivo Swelling capacity, moisture retention, tensile strength, WVTR, SEM, in vitro release, bioadhesion, hemocompatibility, biodegradability, stability, wound closure rate, histological evaluation | Momin et al. [155] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gościniak, A.; Attard, E.; Malesza, I.J.; Kamiński, A.; Cielecka-Piontek, J. Modern Honey-Based Delivery Systems for Wound Healing: A Review of Current Trends and Future Perspectives. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9997. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15189997
Gościniak A, Attard E, Malesza IJ, Kamiński A, Cielecka-Piontek J. Modern Honey-Based Delivery Systems for Wound Healing: A Review of Current Trends and Future Perspectives. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(18):9997. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15189997
Chicago/Turabian StyleGościniak, Anna, Everaldo Attard, Ida Judyta Malesza, Adam Kamiński, and Judyta Cielecka-Piontek. 2025. "Modern Honey-Based Delivery Systems for Wound Healing: A Review of Current Trends and Future Perspectives" Applied Sciences 15, no. 18: 9997. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15189997
APA StyleGościniak, A., Attard, E., Malesza, I. J., Kamiński, A., & Cielecka-Piontek, J. (2025). Modern Honey-Based Delivery Systems for Wound Healing: A Review of Current Trends and Future Perspectives. Applied Sciences, 15(18), 9997. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15189997










