Study on the Mechanical Behavior of a Large-Segment Fully Prefabricated Subway Station During the Construction Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
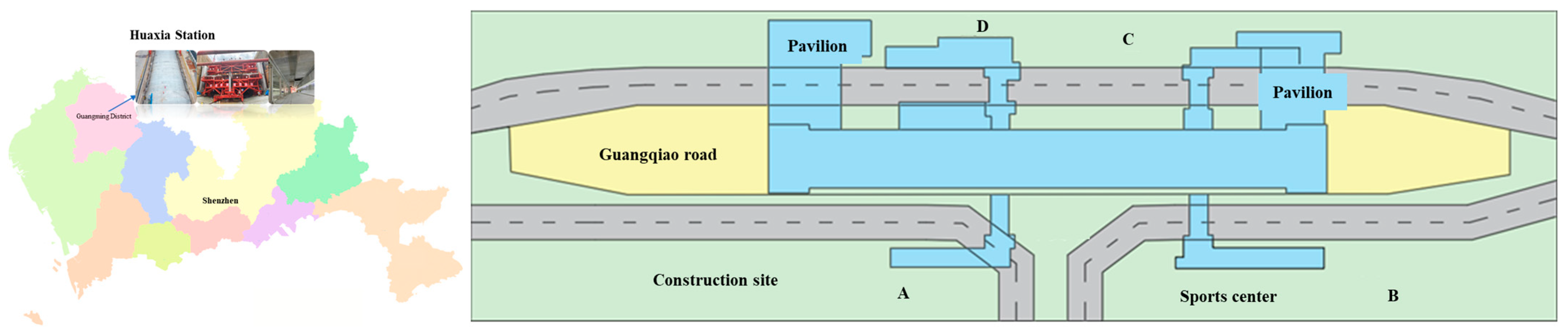
2. Project Overview
3. Study on the Mechanical Behavior of a Large-Segment Fully Prefabricated Subway Station During the Construction Process
3.1. Numerical Model Establishment
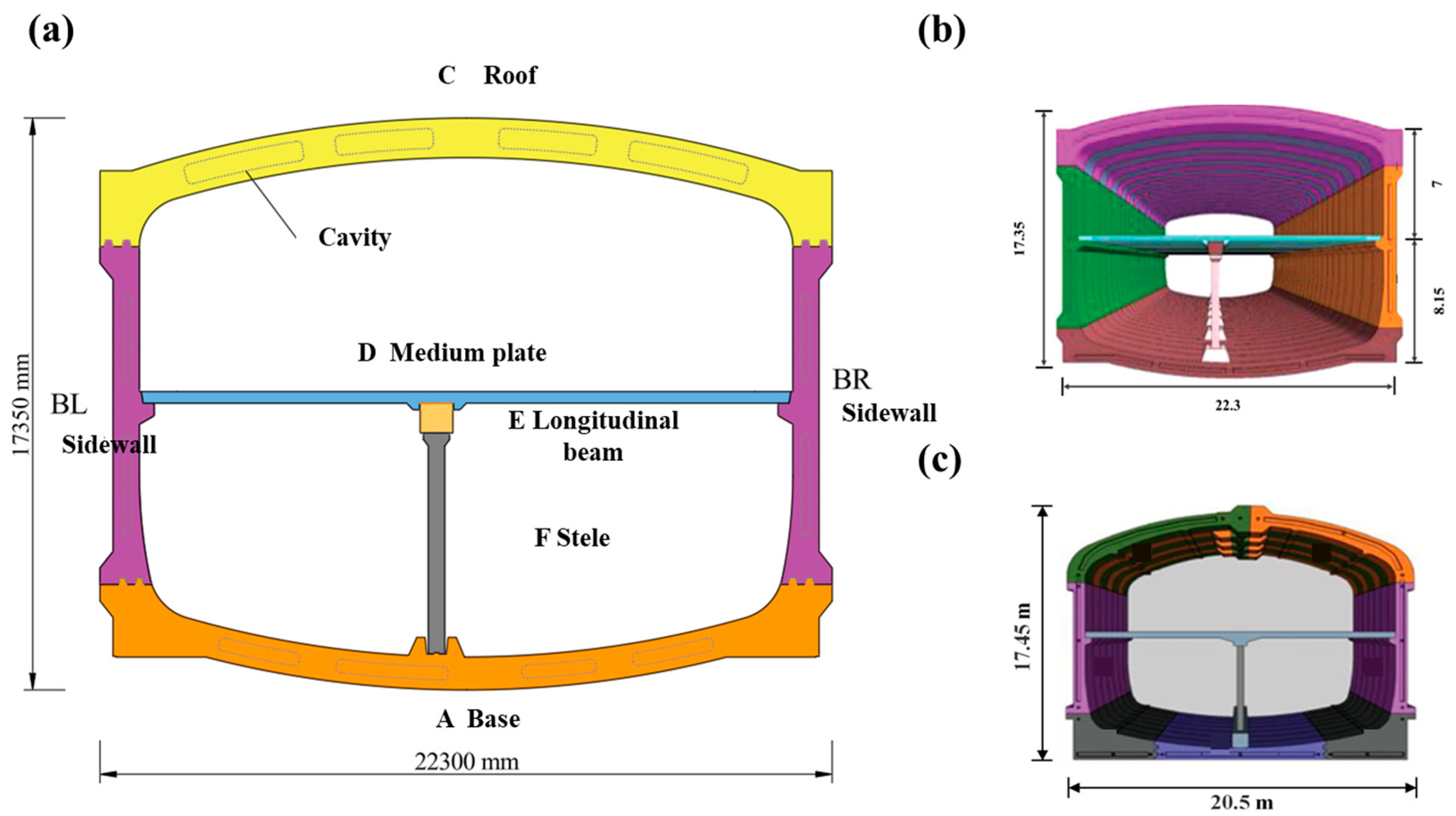
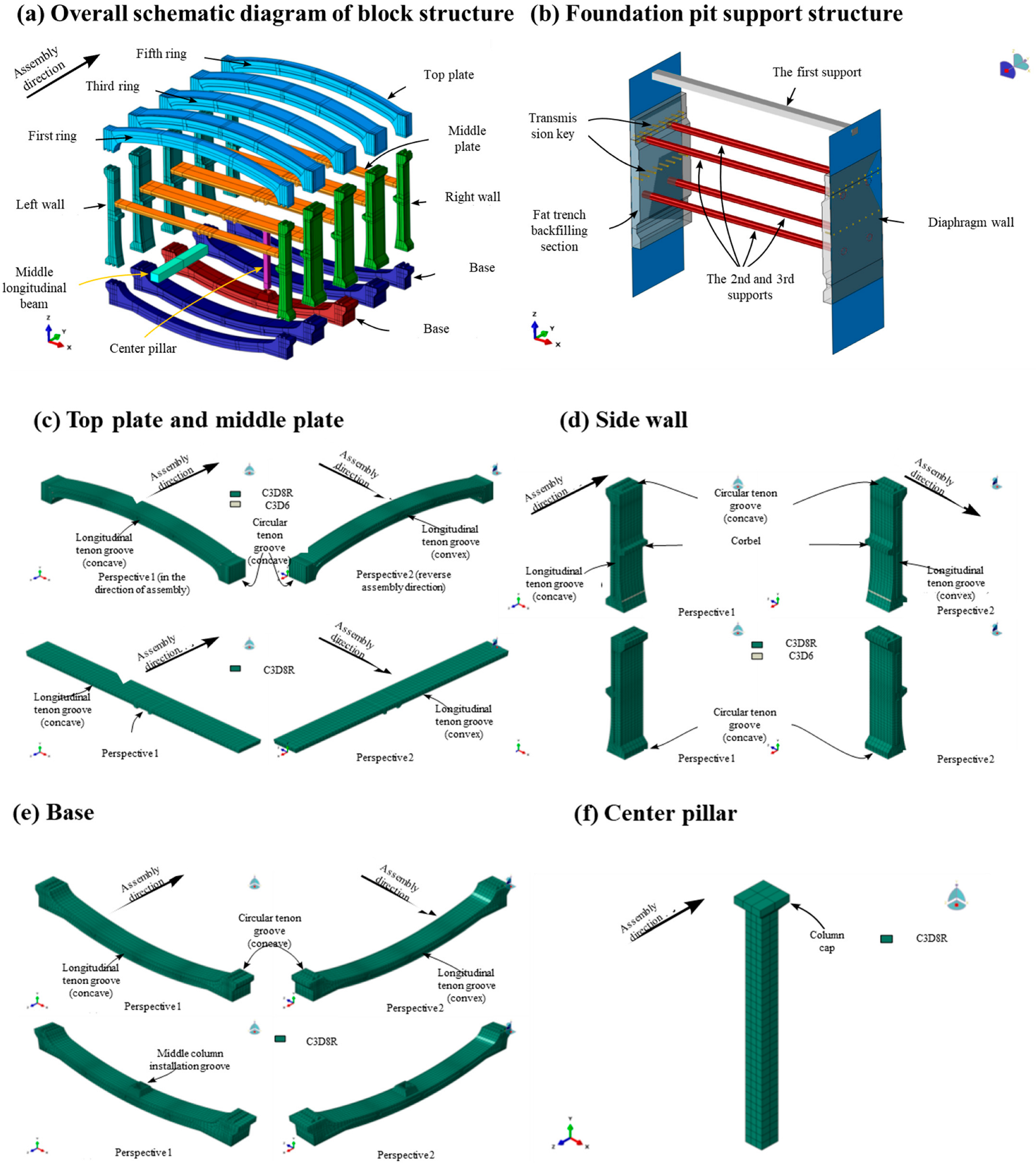
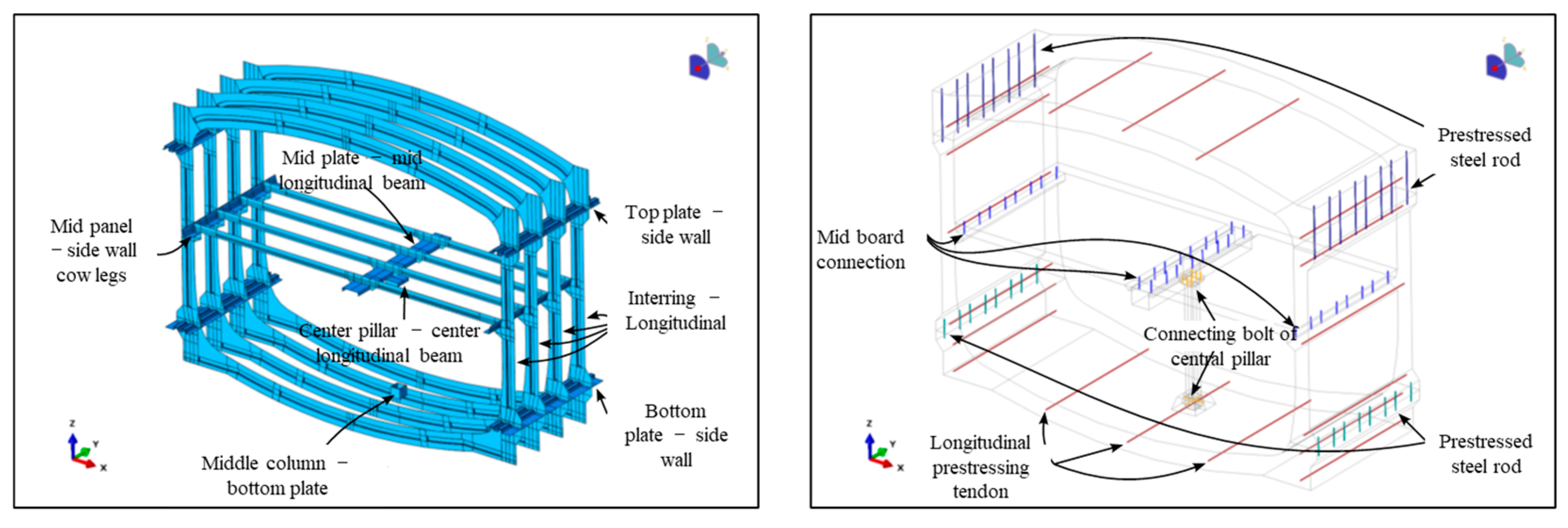
3.1.1. Model Geometry and Mesh Division
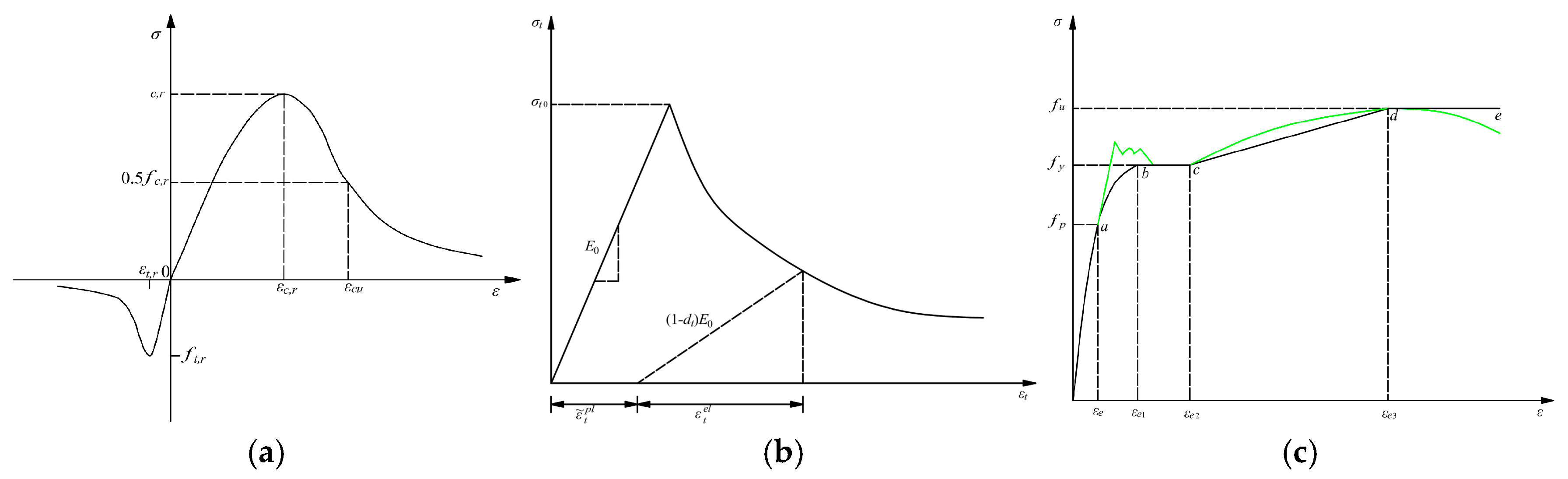
3.1.2. Constitutive Model and Material Parameters
3.1.3. Rationality Analysis of Numerical Models Based on Structural Monitoring
3.1.4. Interaction Between Components
3.1.5. Simulation Process and Boundary Conditions
3.2. Simulation Results and Analysis
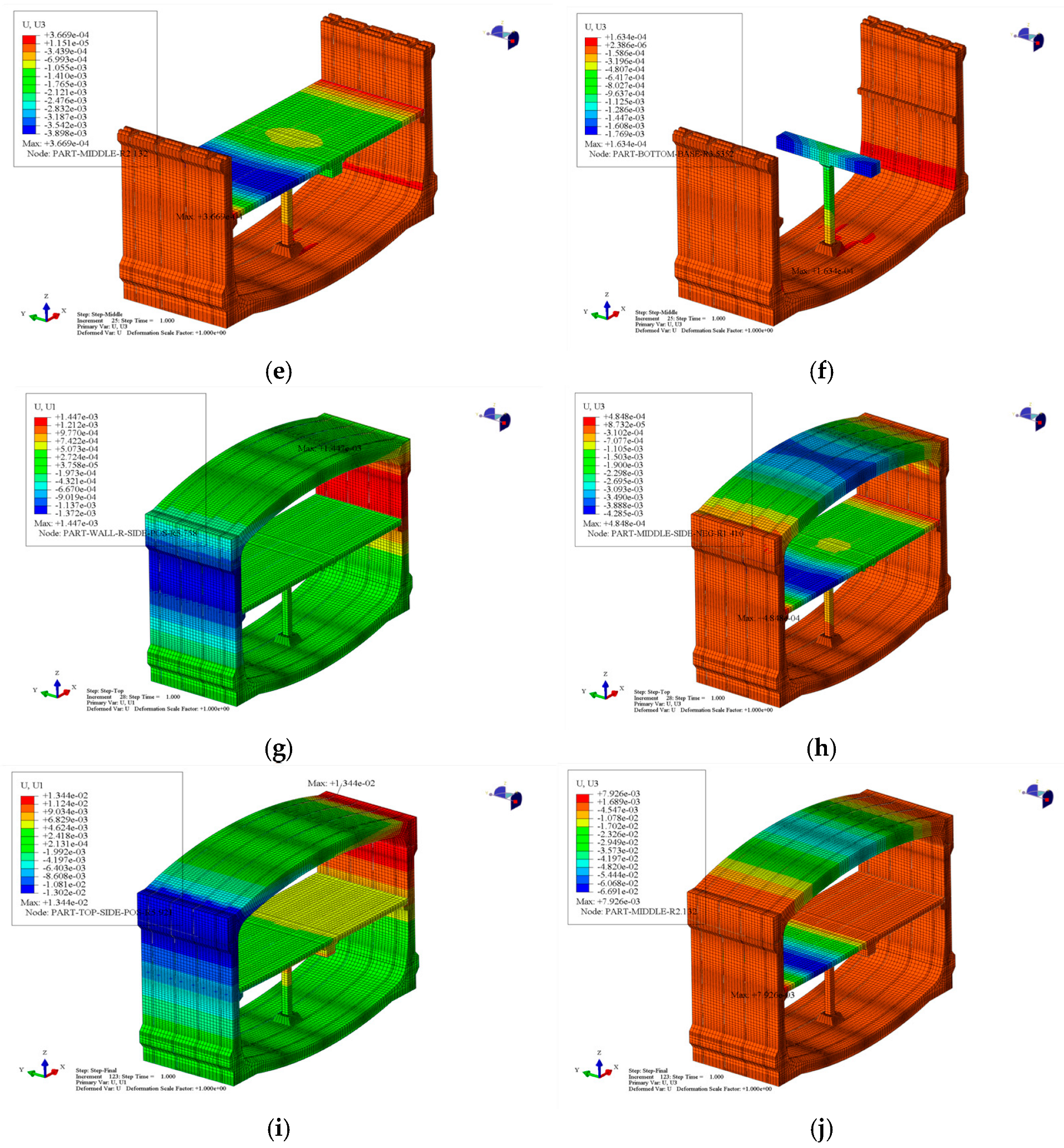
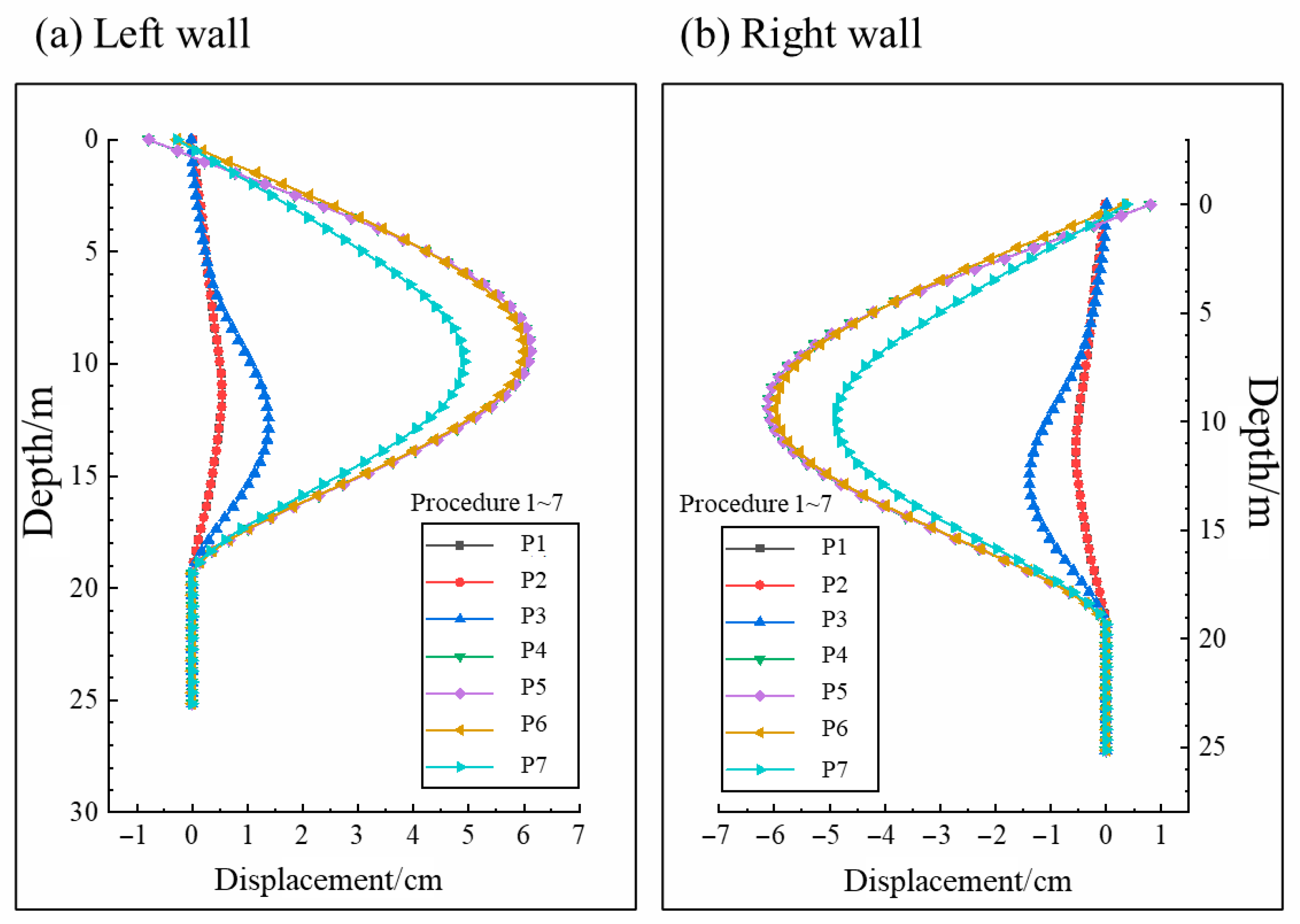
3.2.1. Displacement Analysis of Different Process Structures
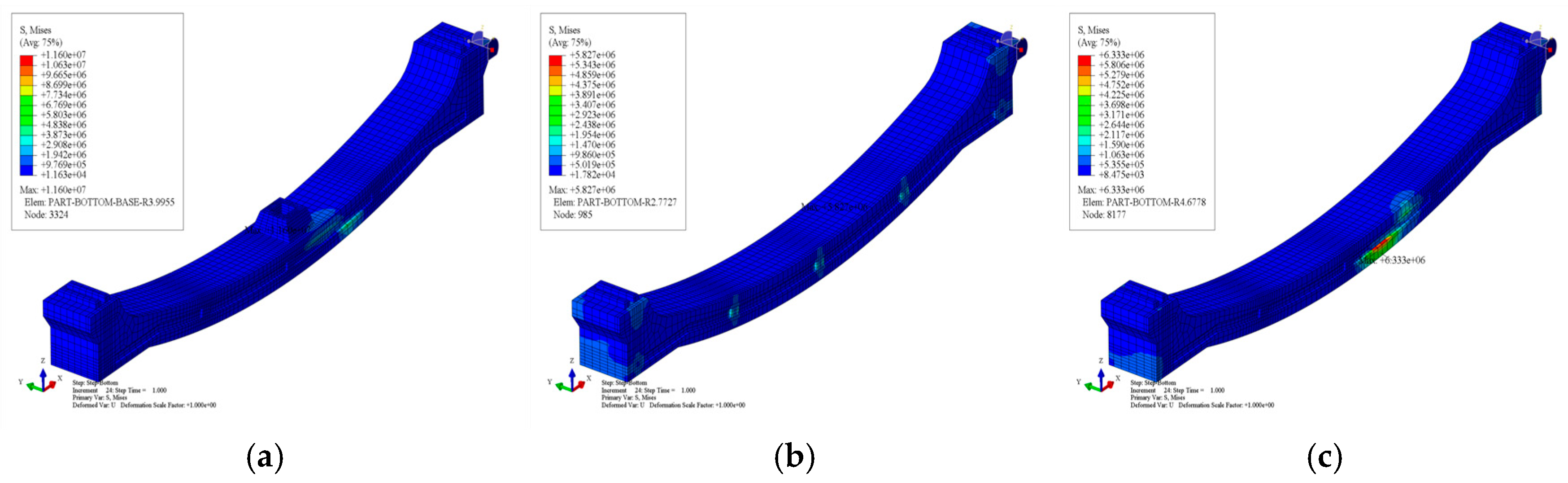
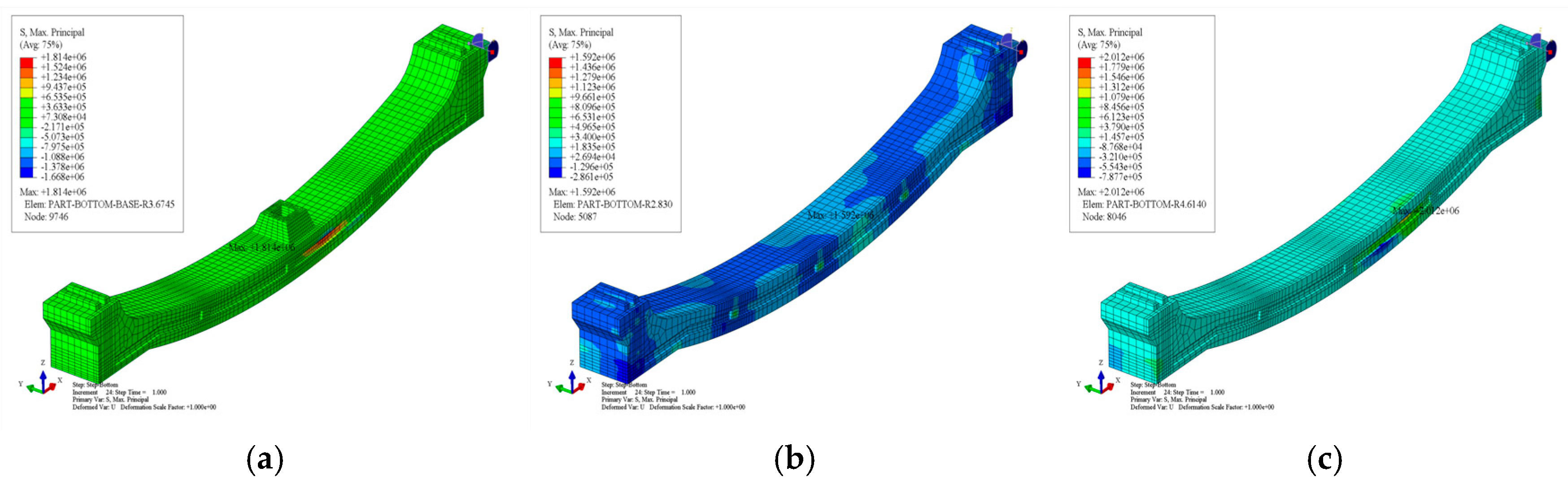
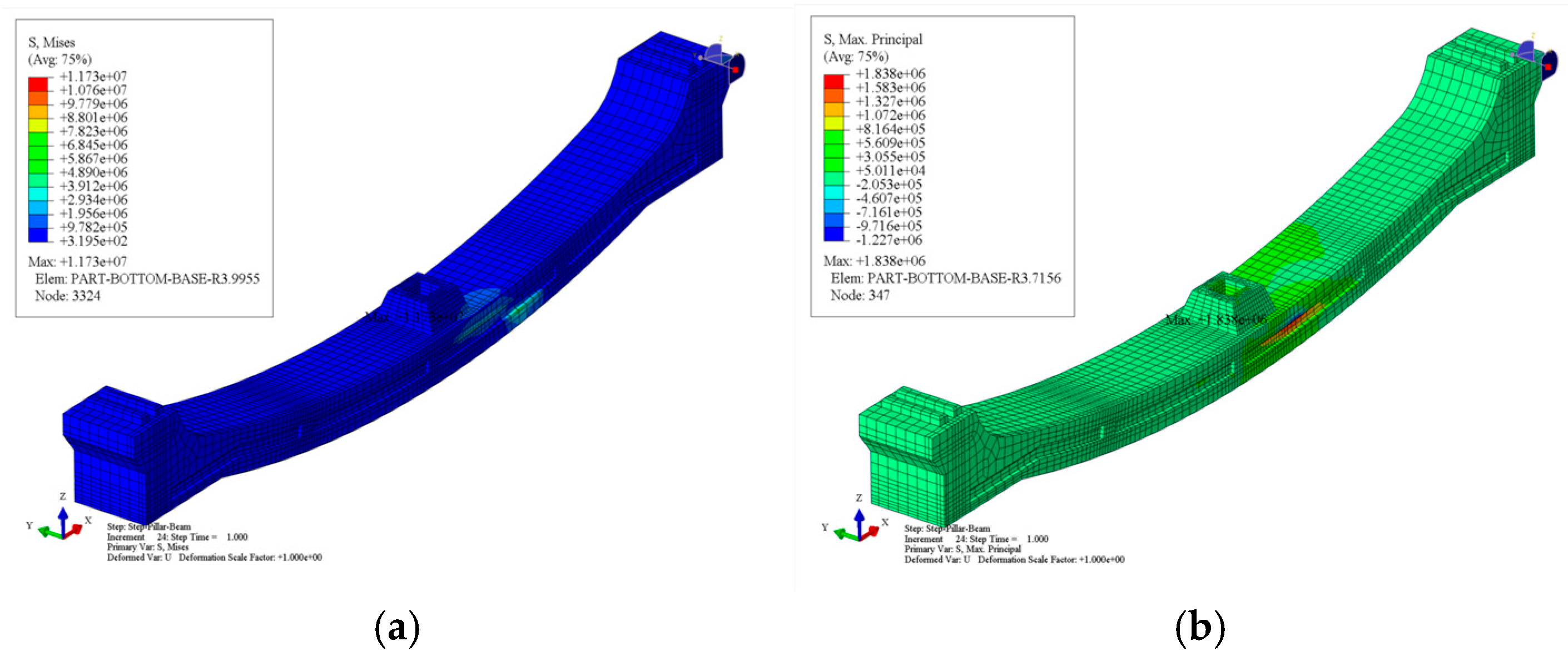
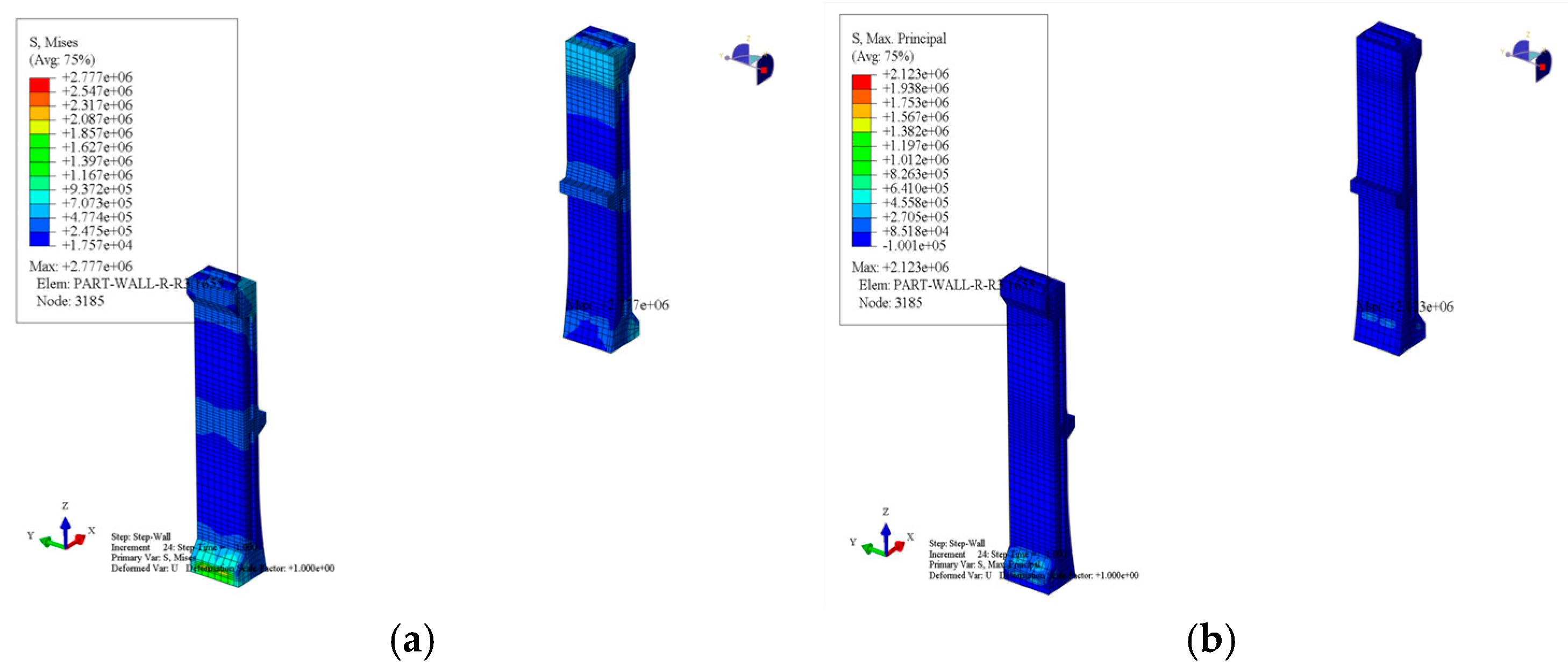
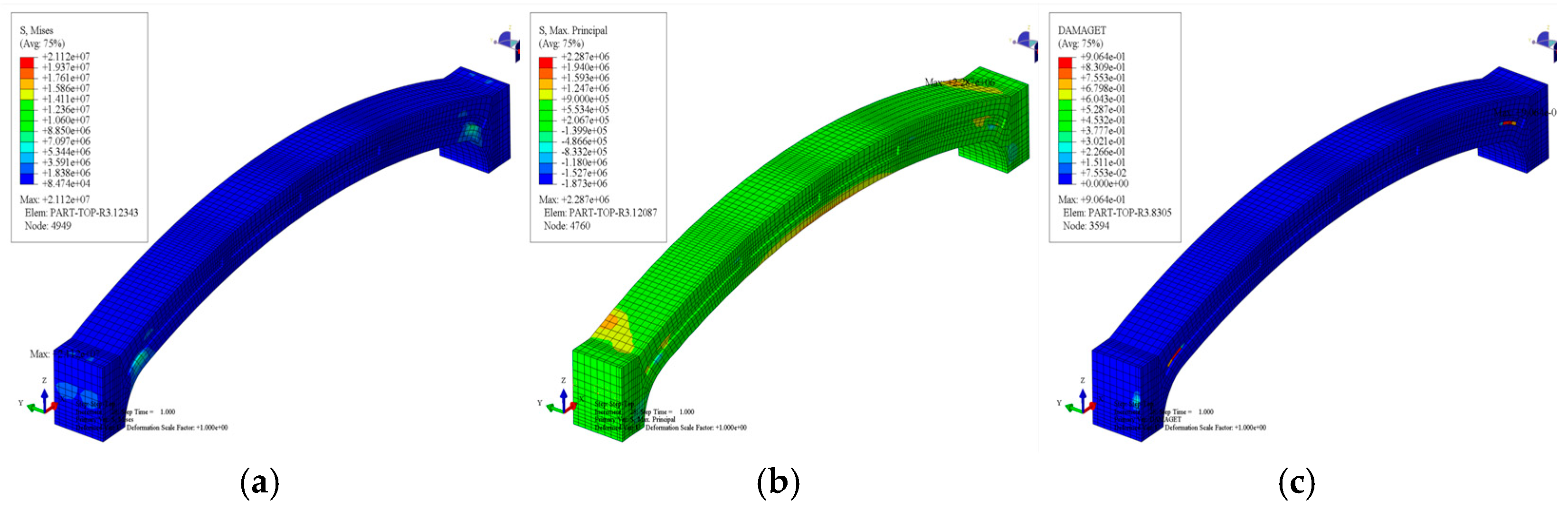
3.2.2. Stress Analysis of Different Process Structures
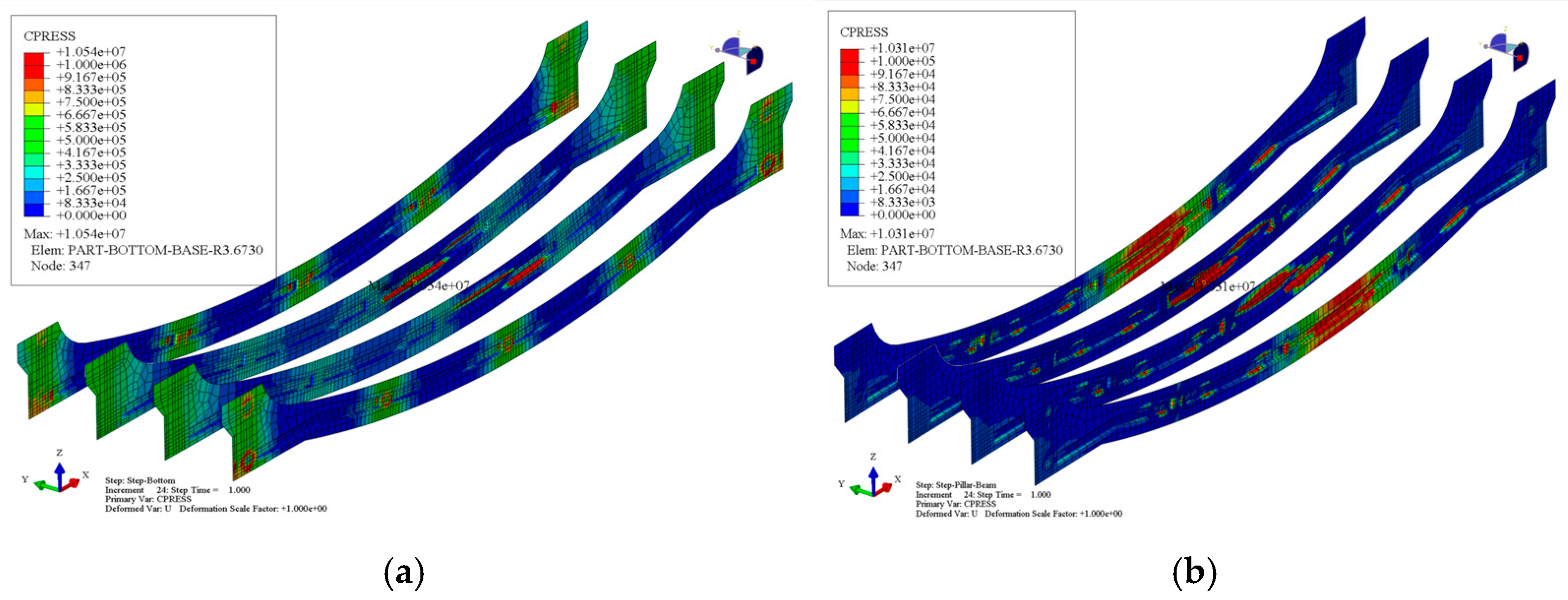
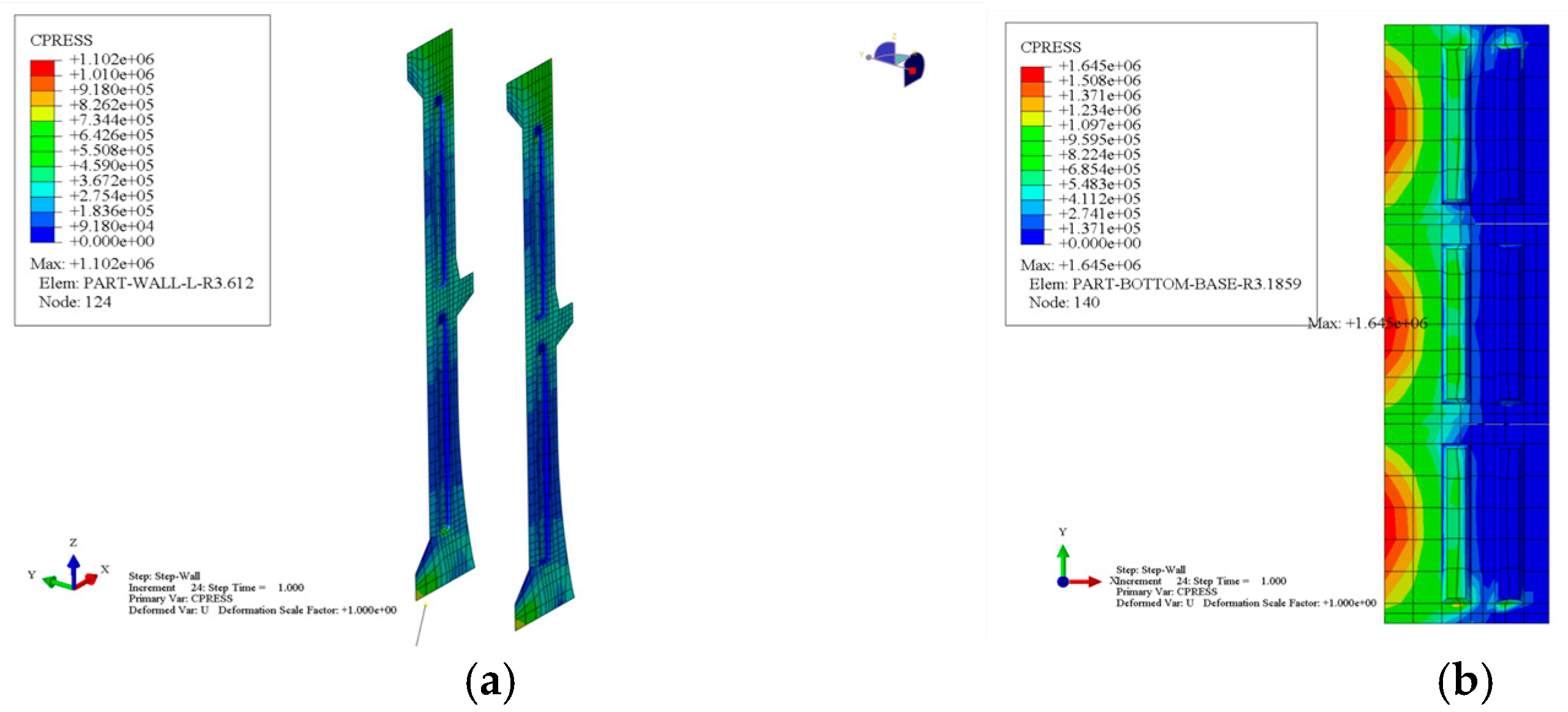
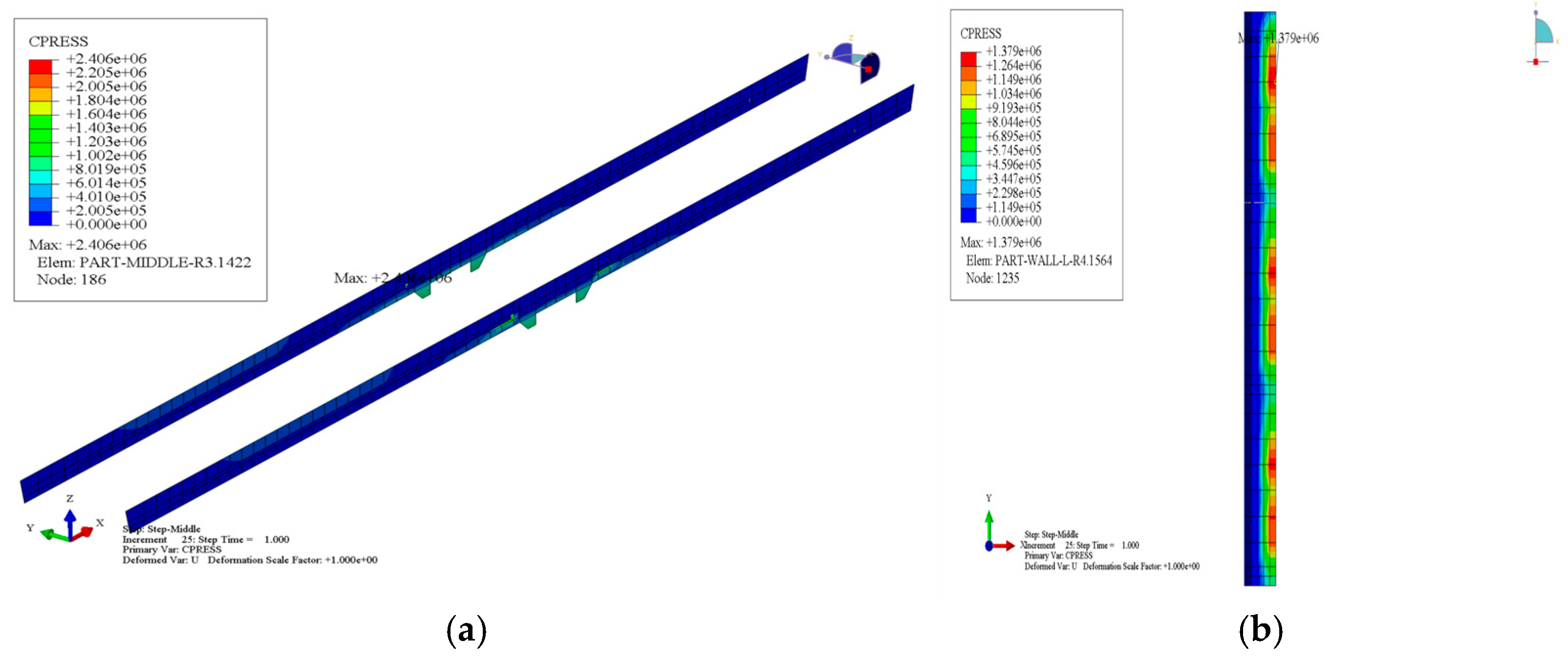
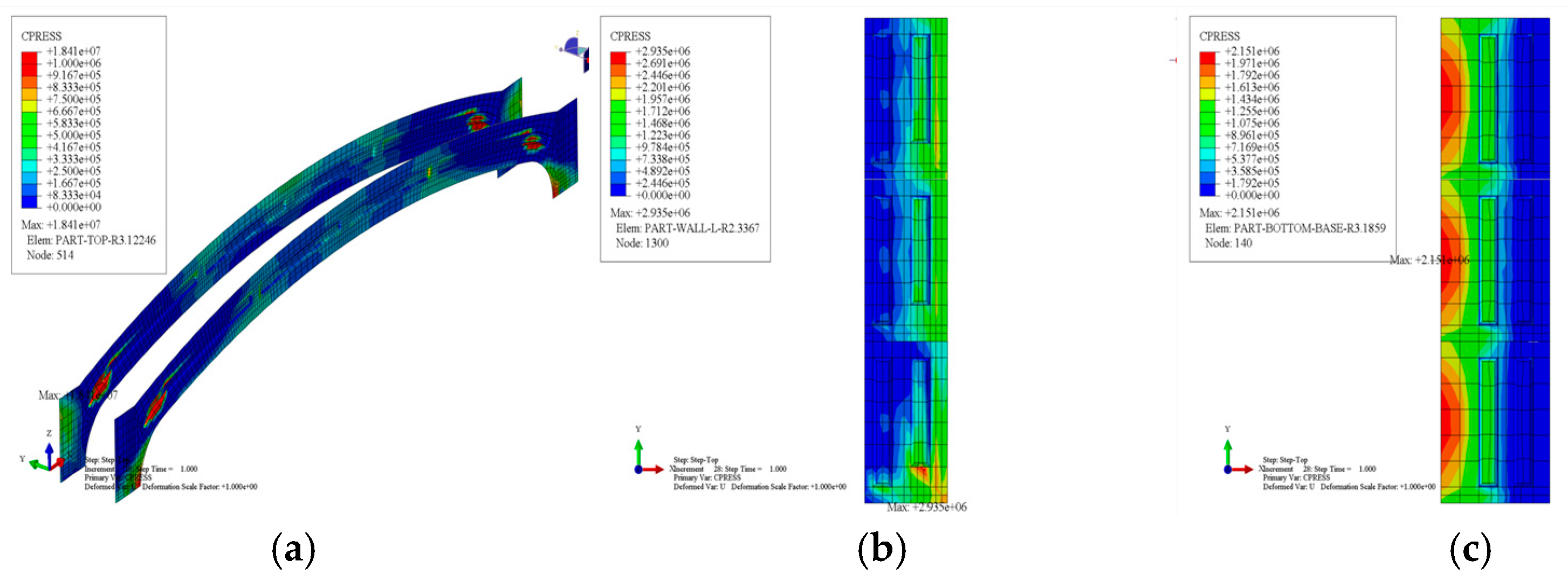
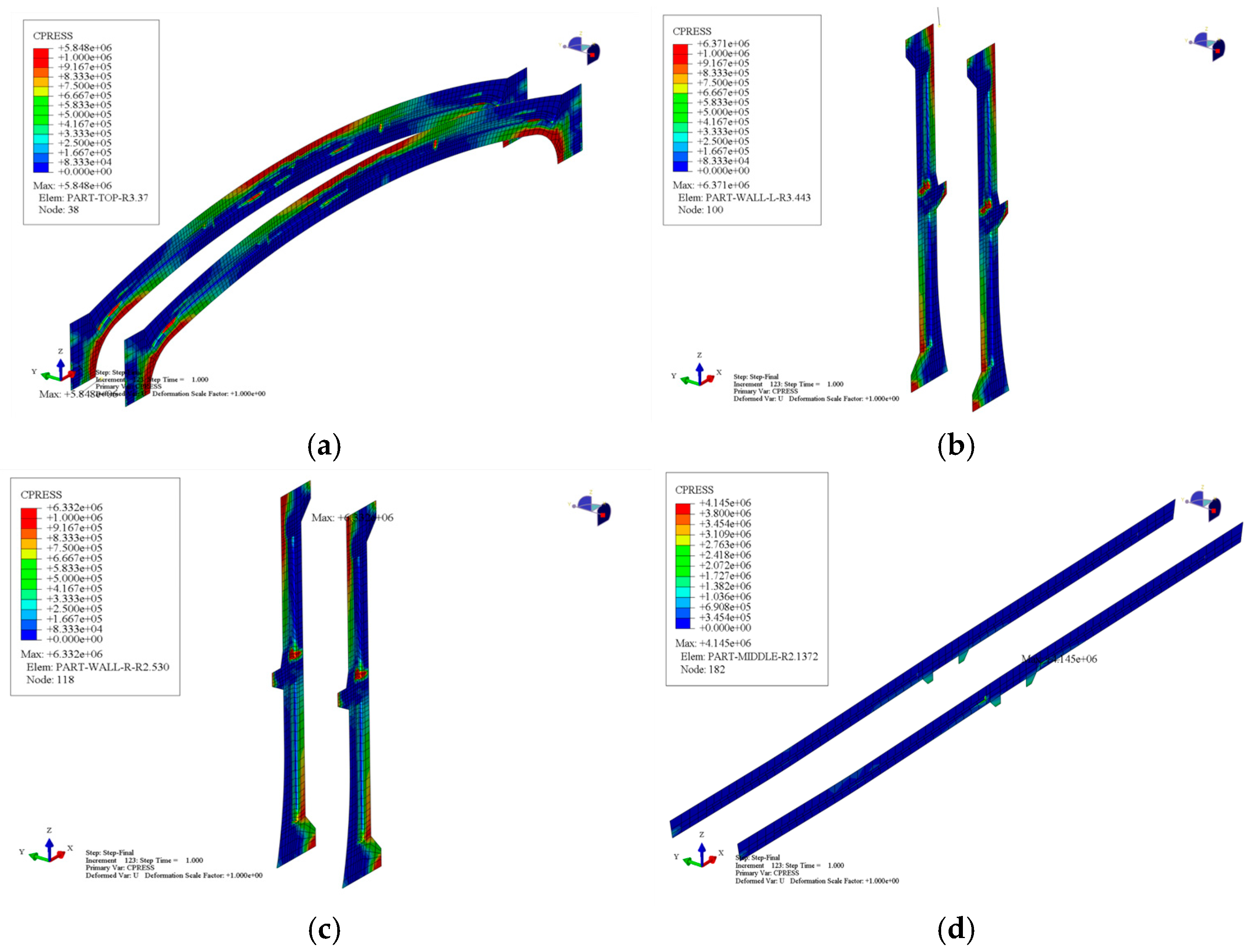
3.2.3. Stress Analysis of Contact Surfaces in Different Processes
3.2.4. Process Analysis of Key Mechanical Indicators
- (1)
- Displacement of the underground continuous wall
- (2)
- Contact stress between structural rings
- (3)
- The connection between the middle plate, the middle column, and other parts of the structure
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Q.; Luo, X.; Zheng, X.; Deng, C. Shear behavior of the horizontal joint with tooth groove connection and large-diameter steel bar grout lapping in reserved hole. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 470, 140593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Guo, Z.; Guan, D.; Li, X. Tensile anchorage and seismic performance of U-bar connections between sidewall and bottom slabs for prefabricated subway station structures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 472, 140825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, L.; Deng, B.; Zhang, Z.; Jia, L. Experimental study on seismic behavior of prefabricated RC frame joints with T-shaped columns. Eng. Struct. 2021, 233, 111912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, M.; Abdelaty, A. BIM-based framework for managing performance of subway stations. Autom. Constr. 2014, 41, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, P.; Tao, L.; Yang, X.; Zhao, J.; Shi, C. Three-dimensional dynamic response analysis of a single-ring structure in a prefabricated subway station. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 45, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Yang, W.; Qiu, T.; Su, D.; Wu, H. Low-carbon effects of constructing a prefabricated subway station with temporary internal supports: An innovative case of Shenzhen, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 426, 139023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, G.; Wang, S.; Xie, K. Numerical study on seismic performance of a prefabricated subway station considering the influence of the construction process. Structures 2024, 69, 107218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Ma, S.; Wang, R.; Ou, F.; Liang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Xie, K.; Wang, S. A novel technique for constructing prefabricated subway stations under open excavation Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers-Engineering Sustainability. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Eng. Sustain. 2023, 177, 299–308. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Lu, D.; Ma, C.; El Naggar, M.H.; Du, X. Structural design and seismic performance analysis of partially prefabricated subway station structure. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2023, 140, 105264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xu, C.; El Naggar, H.M.; Du, X. Seismic response analysis of rectangular prefabricated subway station structure. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2023, 131, 104795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.; Shi, C.; Ding, P.; Li, S.; Wu, S.; Bao, Y. A study on bearing characteristic and failure mechanism of thin-walled structure of a prefabricated subway station. Front. Struct. Civ. Eng. 2022, 16, 359–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejat, P.; Jomehzadeh, F.; Taheri, M.M.; Gohari, M.; Majid, M.Z.A. A global review of energy consumption, CO2 emissions and policy in the residential sector (with an overview of the top ten CO2 emitting countries). Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 43, 843–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Association of Building Energy Efficiency. China Building Energy Consumption Annual Report 2020; China Association of Building Energy Efficiency: Shanghai, China, 2020. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Q.; Hua, T.; Xue, H.; Yao, H. A review and scientometric analysis of global research on prefabricated buildings. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2021, 2021, 8869315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, D.; Bahaj, A.S.; Wu, Y.; Liu, J. Review of thermal and environmental performance of prefabricated buildings: Implications to emission reductions in China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 137, 110472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Chen, J.; Shan, K.; Wu, Y.-F. Seismic performance of corroded prefabricated column-footing joint with grouted splice sleeve connection: Experiment and simulation. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 80, 108112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, C.L.; Meng, S.; Zeng, B. Experimental study of precast columns with a hybrid joint incorporating bolted couplers and grouted sleeves. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 74, 106878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, Z.; Ge, J.; Yan, X.; Liu, S. Full-scale experimental study on precast bridge column with grouted sleeve connections and large-diameter reinforcing bars. Eng. Struct. 2023, 294, 116747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.L.; Ma, C.; Lu, D.C.; Xu, C.S.; Xu, Z.G. Collapse simulation and failure mechanism analysis of the Daikai subway station under seismic loads. China Civ. Eng. J. 2017, 50, 53–62. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, V.Q.; Nizamani, Z.A.; Park, D.; Kwon, O.-S. Numerical simulation of damage evolution of Daikai station during the 1995 Kobe earthquake. Eng. Struct. 2020, 206, 110180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, Z.; Du, X.; Shen, G.Q. The seismic behaviour of precast concrete interior joints with different connection methods in assembled monolithic subway station. Eng. Struct. 2021, 232, 111799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB50010-2010; Code for Design of Concrete Structures. China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2010.
- GB/T 228.1-2021; Metallic Materials—Tensile Testing—Part 1: Method of Test at Room Temperature. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2021.

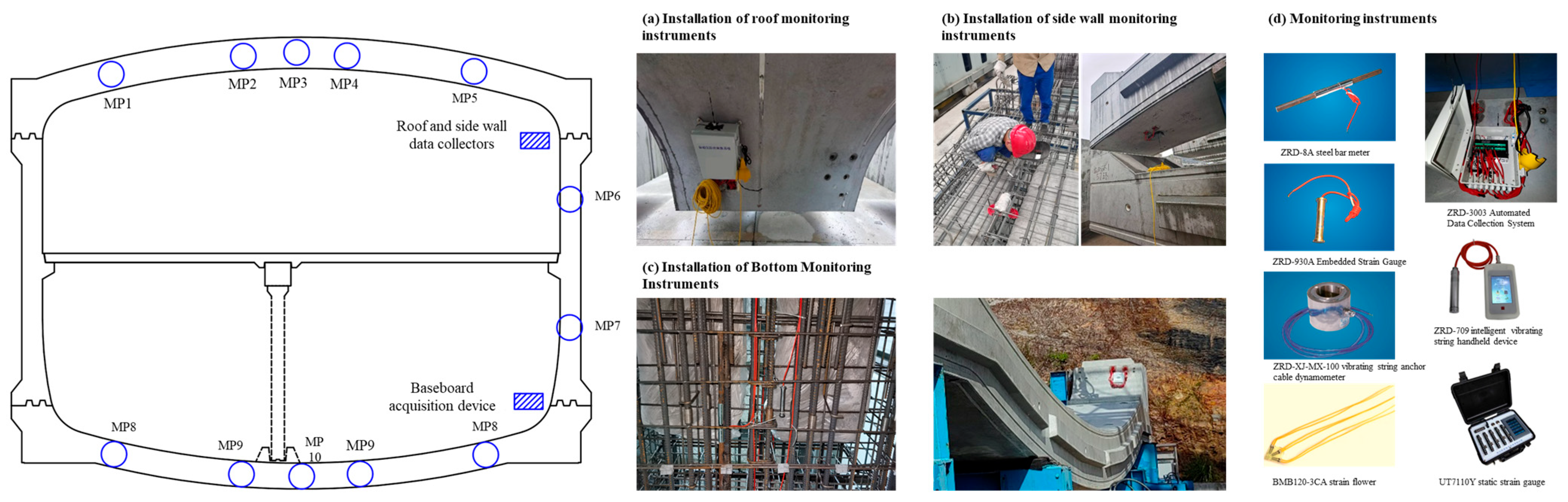
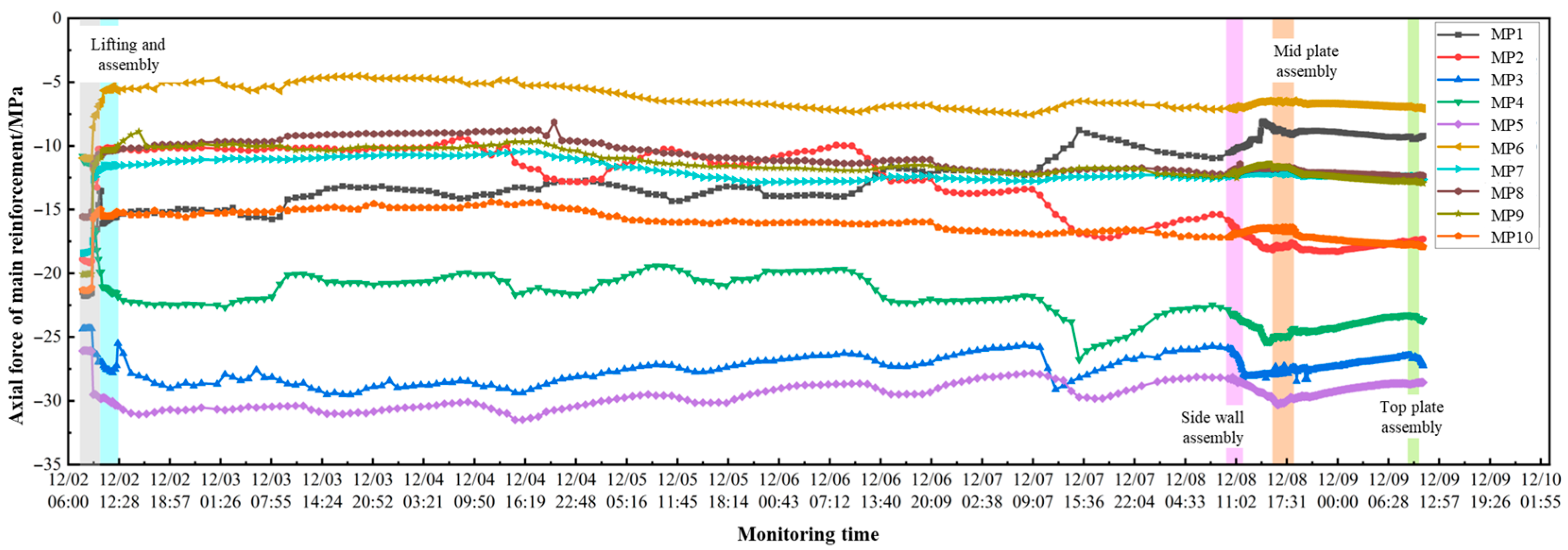
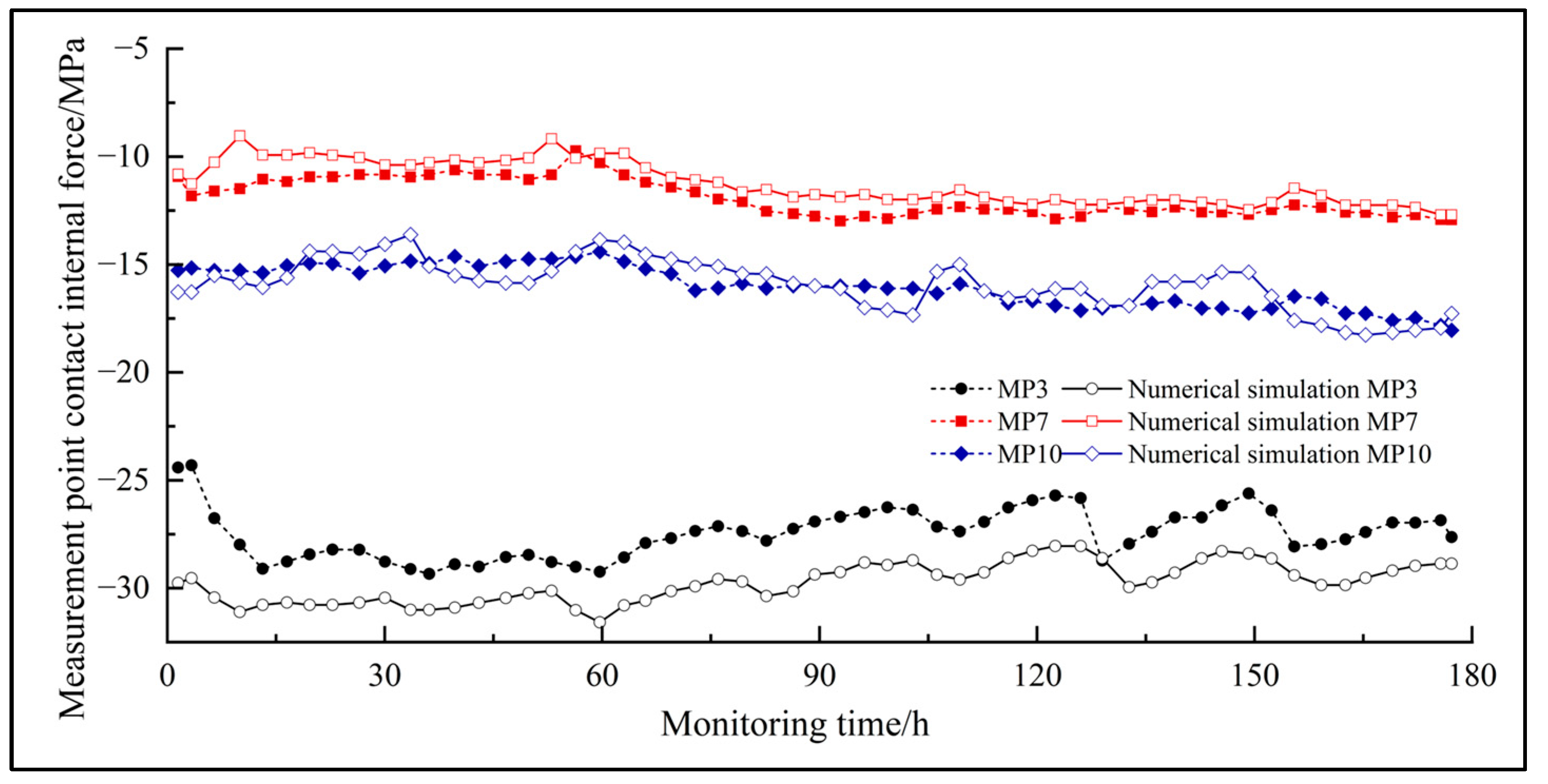










| Overburden Type | Soil Layer Name | Primary Composition | Characteristics | Layer Thickness | Top Depth |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Holocene Anthropogenic Fill (Q4ml) | Plain Fill | Silty Clay | Low strength, High compressibility, Load-sensitive | 0.80~10.00 m | 28.63~36.21 m |
| Fluvial–Pluvial Deposits (Q4al+pl) | Mucky Clay | Silty Clay | Low strength, High compressibility | 0.50~3.40 m | 6.50~9.00 m |
| Silty Clay | Silty Clay | Medium compressibility | 1.00~6.70 m | 2.10~3.00 m | |
| Medium-Coarse Sand | Quartz, Feldspar | Poorly sorted | 1.40~3.00 m | 4.00~8.80 m | |
| Residual Deposits (Qel) | Sandy Clayey Soil | Sand Particles | Water-softening susceptibility | 0.90~29.80 m | 0.80~12.40 m |
| Late Ordovician Caledonian (ηγO1) | Completely Weathered Granite | Granite | Relatively intact | 2.70~22.90 m | 7.30~35.30 m |
| Earthy Completely Weathered Granite | Granite Fragments | Sandy texture | 0.90~19.30 m | 10.10~39.80 m | |
| Highly Weathered Granite | Fractured Granite | Intensely jointed/fissured | 0.30~7.50 m | 27.00~47.60 m | |
| Moderately Weathered Granite | Medium–Fine-Grained Granite | Massive structure | 0.80~7.74 m | 28.20~48.60 m | |
| Slightly Weathered Granite | Medium–Fine–Grained Granite | Moderately jointed | 3.09~8.30 m | 27.60~47.40 m |
| E0 (GPa) | fc,r (MPa) | εc,r (με) | αc | ft,r (MPa) | εt,r (με) | αt |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 34.5 | 32.4 | 1678.4 | 1.4992 | 2.64 | 110.08 | 2.1908 |
| εc (με) | εcin (με) | dc | εt (με) | εtin (με) | dt |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 737.35 | 0 | 0 | 110.08 | 0 | 0 |
| 1000 | 69.29377 | 0.0543 | 133 | 31.47494 | 0.04426 |
| 1333 | 206.4597 | 0.131514 | 167 | 81.40694 | 0.135283 |
| 1678.4 | 395.5848 | 0.219248 | 200 | 125.1887 | 0.232814 |
| 1840 | 495.5807 | 0.261288 | 233 | 165.4103 | 0.327076 |
| 2000 | 599.5378 | 0.302682 | 267 | 204.5683 | 0.414691 |
| 2333 | 826.0909 | 0.385948 | 300 | 241.2011 | 0.488649 |
| 2667 | 1060.265 | 0.462966 | 333 | 276.9575 | 0.551928 |
| 3000 | 1295.461 | 0.531609 | 367 | 313.1757 | 0.607122 |
| 3333 | 1529.643 | 0.591717 | 400 | 347.903 | 0.65237 |
| 3667 | 1762.228 | 0.643803 | 433 | 382.3243 | 0.690742 |
| 4000 | 1991.349 | 0.688326 | 467 | 417.5484 | 0.724304 |
| 4333 | 2217.651 | 0.726365 | 500 | 451.5569 | 0.752086 |
| 4667 | 2441.945 | 0.758924 | 533 | 485.4263 | 0.775962 |
| 5000 | 2663.119 | 0.786653 | 567 | 520.2058 | 0.797171 |
| 5333 | 2882.102 | 0.810398 | 600 | 553.8706 | 0.815016 |
| 5667 | 3099.792 | 0.83085 | 633 | 587.4608 | 0.830603 |
| 6000 | 3315.116 | 0.848423 | 667 | 622.0039 | 0.844675 |
| 6333 | 3528.934 | 0.863632 | 700 | 655.4778 | 0.856702 |
| 6667 | 3742.064 | 0.876883 | 733 | 688.9071 | 0.867364 |
| 7000 | 3953.388 | 0.888407 | 767 | 723.3093 | 0.877128 |
| 7333 | 4163.685 | 0.898502 | 800 | 756.666 | 0.885587 |
| 7667 | 4373.701 | 0.907406 | 833 | 789.9938 | 0.89318 |
| 8000 | 4582.281 | 0.915241 | 867 | 824.305 | 0.900218 |
| − | − | − | 900 | 857.5844 | 0.906386 |
| Component | Model | Label | E0 (GPa) | fc,r (MPa) | εc,r (με) | αc | ft,r (MPa) | εt,r (με) | αt |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prefabricated component | CDP | C50 | 34.5 | 32.4 | 1678.4 | 1.4992 | 2.64 | 110.08 | 2.1908 |
| Underground continuous wall | Elasticity | C30 | 30 | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| Concrete support | CDP | C30 | 30 | 20.1 | 1471.8 | 0.7464 | 2.01 | 95.24 | 1.264 |
| Fertilizer tank backfilling | Elasticity | C20 | 25.5 | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| Label | Es (GPa) | ν | ρ (t/m3) | fy (MPa) | fu (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q235 | 206 | 0.31 | 7.85 | 279 | 450 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, Z.; Li, Y.; Fan, X.; Wang, J. Study on the Mechanical Behavior of a Large-Segment Fully Prefabricated Subway Station During the Construction Process. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9941. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15189941
Tan Z, Li Y, Fan X, Wang J. Study on the Mechanical Behavior of a Large-Segment Fully Prefabricated Subway Station During the Construction Process. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(18):9941. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15189941
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Zhongsheng, Yuanzhuo Li, Xiaomin Fan, and Jian Wang. 2025. "Study on the Mechanical Behavior of a Large-Segment Fully Prefabricated Subway Station During the Construction Process" Applied Sciences 15, no. 18: 9941. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15189941
APA StyleTan, Z., Li, Y., Fan, X., & Wang, J. (2025). Study on the Mechanical Behavior of a Large-Segment Fully Prefabricated Subway Station During the Construction Process. Applied Sciences, 15(18), 9941. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15189941






