The Effect of Applying Model Nanoplastic Particles to Soil on the Composition of Its Microbial Community
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
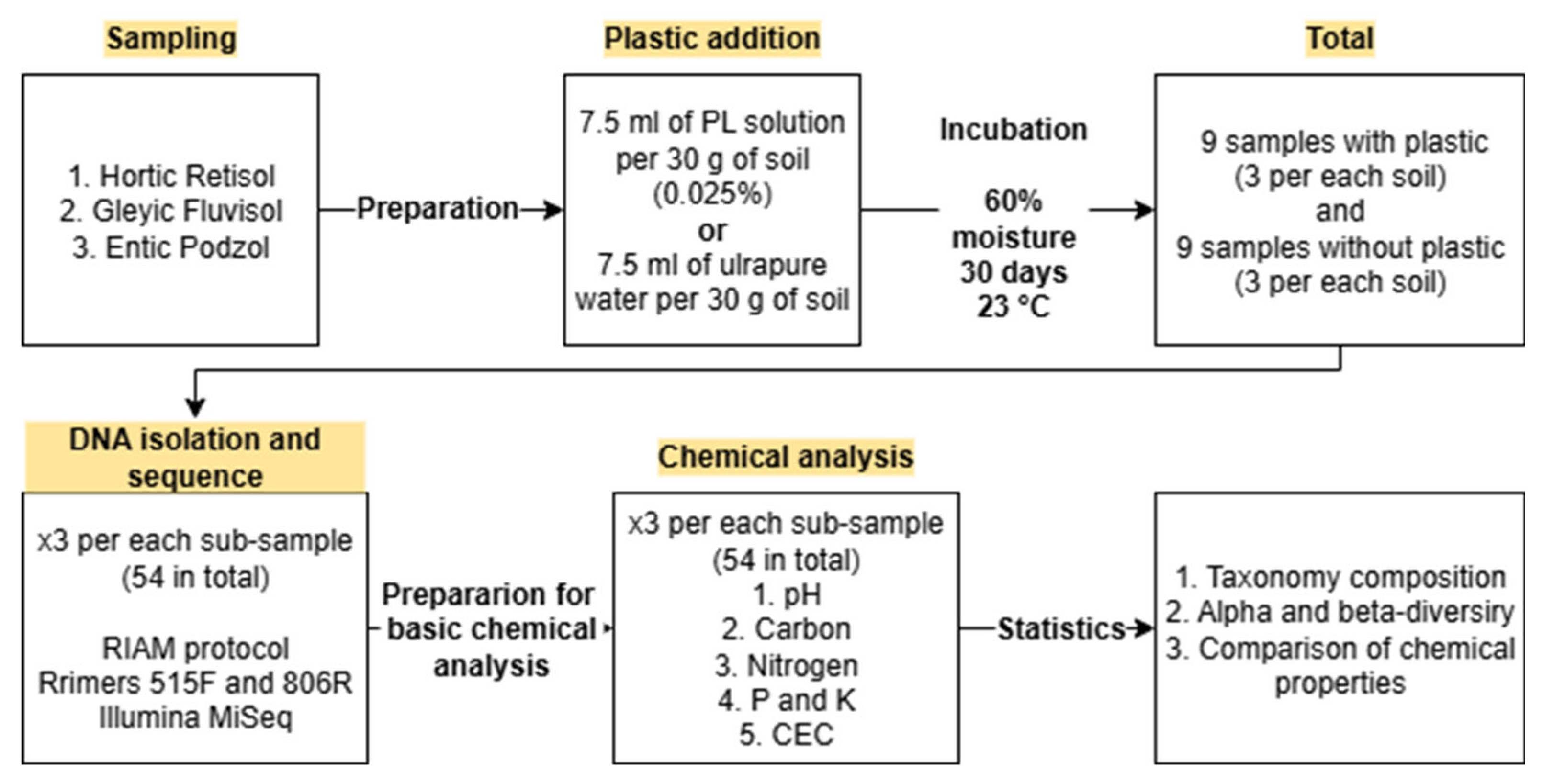
2.1. General Design of Experiment
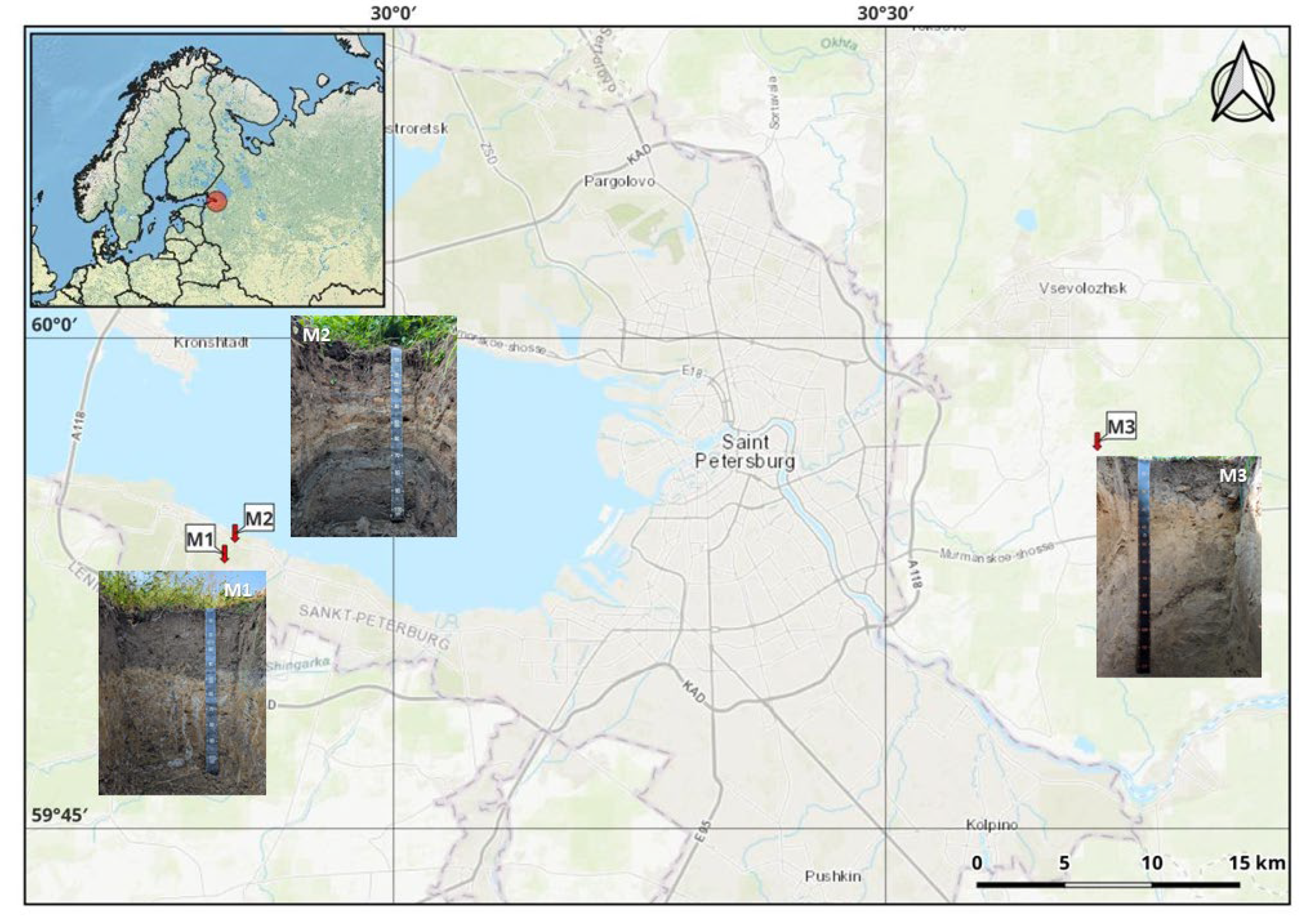
2.2. Soil Sample Characterization and Preparation
2.3. Soil Preparation for Incubation Experiment
2.4. Microplastic Preparation and Application
2.5. Chemical Analysis of Soil Samples
2.6. DNA Processing
2.7. Statistics
3. Results and Discussion
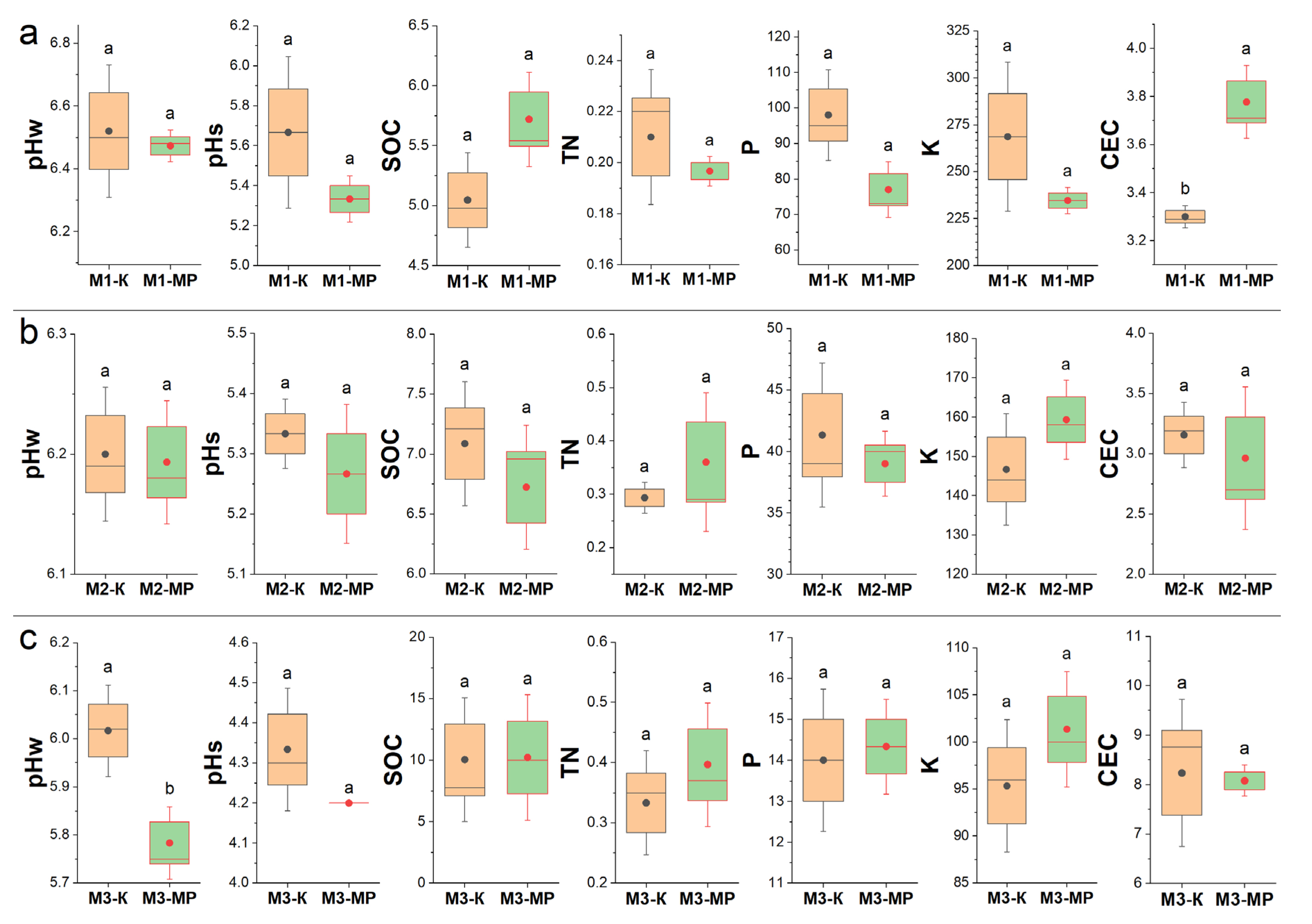
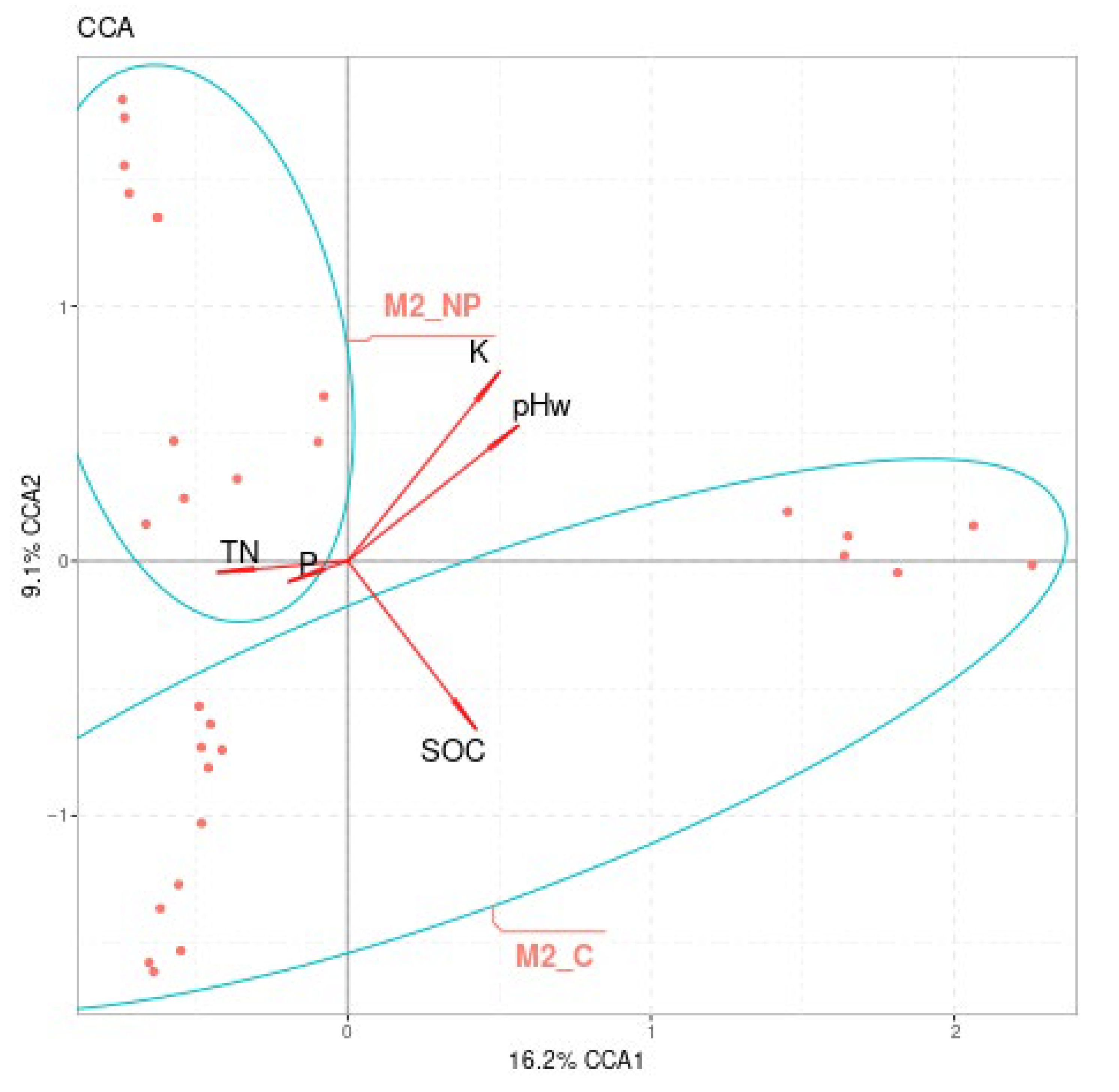
3.1. Soil Chemical Properties
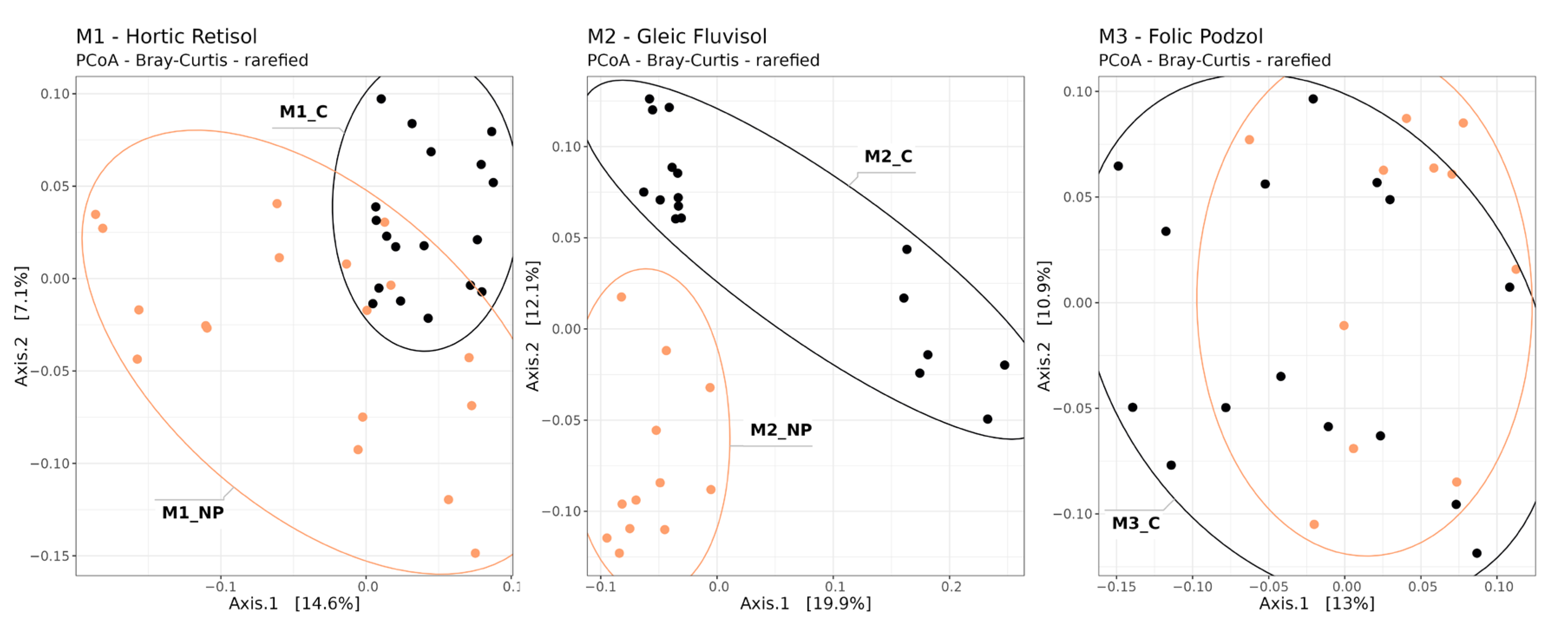
3.2. Soil Microbiome
- Altered biogeochemical cycles: shifts in microbial communities responsible for carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus cycling could create nutrient availability imbalances, affecting plant growth and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Reduced functional redundancy: loss of microbial diversity may weaken soil’s capacity to withstand additional disturbances like drought or pathogen outbreaks.
- Trophic cascades: as soil microorganisms form the foundation of detrital food webs, compositional changes could propagate to higher trophic levels, impacting invertebrates, fungi, and plant-microbe symbiotic relationships.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koutnik, V.S.; Leonard, J.; Alkidim, S.; DePrima, F.J.; Ravi, S.; Hoek, E.M.V.; Mohanty, S.K. Distribution of microplastics in soil and freshwater environments: Global analysis and framework for transport modeling. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 274, 116552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, A.; Deepo, D.M.; Nandi, R.; Rana, J.; Islam, S.; Rahman, S.; Hossain, M.N.; Islam, M.S.; Baroi, A.; Kim, J.-E. A review of microplastics pollution in the soil and terrestrial ecosystems: A global and Bangladesh perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 139296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nizzetto, L.; Futter, M.; Langaas, S. Are agricultural soils dumps for microplastics of urban origin? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 10777–10779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petroody, S.S.A.; Hashemi, S.H.; van Gestel, C.A. Transport and accumulation of microplastics through wastewater treatment sludge processes. Chemosphere 2021, 278, 130471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monkul, M.M.; Özhan, H.O. Microplastic Contamination in Soils: A Review from Geotechnical Engineering View. Polymers 2021, 13, 4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Qin, W. Soil microplastic characteristics and the effects on soil properties and biota: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 313, 120183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.-K.; Rakib, M.R.J.; Hwangbo, M.; Kim, J. Microplastic accumulation in soils: Unlocking the mechanism and biodegradation pathway. J. Hazard. Mat. Adv. 2025, 17, 100629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Tang, J.; Yu, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Xu, S.; Li, G.; Zhou, Q. Microplastic Pollution in the Soil Environment: Characteristics, Influencing Factors, and Risks. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta Lwanga, E.; Gertsen, H.; Gooren, H.; Peters, P.; Salánki, T.; van der Ploeg, M.; Besseling, E.; Koelmans, A.A.; Geissen, V. Microplastics in the Terrestrial Ecosystem: Implications for Lumbricus terrestris (Oligochaeta, Lumbricidae). Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Xu, M.; Zhao, W.; Yang, X.; Xin, F.; Dong, W.; Jia, H.; Wu, X. Microbial Degradation of (Micro)plastics: Mechanisms, Enhancements, and Future Directions. Fermentation 2024, 10, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Wang, L.; Cao, T.; Chen, J.; Lv, M.; Wei, S.; Lu, S.; Tian, X. Microplastics are transferred by soil fauna and regulate soil function as material carriers. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Yang, G.; Dou, P.; Qian, S.; Zhao, L.; Yang, Y.; Fanin, N. Microplastics negatively affect soil fauna but stimulate microbial activity: Insights from a field-based microplastic addition experiment. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2020, 287, 20201268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Yao, H.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Y. Microplastic Addition Alters the Microbial Community Structure and Stimulates Soil Carbon Dioxide Emissions in Vegetable-Growing Soil. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 352–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Duan, C.; Cao, N.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, J. Effects of microplastics on soil microbiome: The impacts of polymer type, shape, and concentration. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Tang, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, Q. Effects of microplastics on greenhouse gas emissions and the microbial community in fertilized soil. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 256, 113347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, Y.; Huang, S.; Zhang, H.; Tong, Y.; Wen, D.; Xia, X.; Wang, H.; Luo, Y.; Barceló, D. Response of soil enzyme activities and bacterial communities to the accumulation of microplastics in an acid cropped soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 707, 135634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, J. Microplastics reduce soil microbial network complexity and ecological deterministic selection. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 24, 2157–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, S.; Fan, C.; Yang, P.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Jian, M.; Dai, G.; Liu, J.; Yang, H.; Shen, L. Effects of different microplastics on the physicochemical properties and microbial diversity of rice rhizosphere soil. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 15, 1513890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Z.; Zhu, D.; Lindhardt, J.H.; Lin, S.M.; Ke, X.; Cui, L. Long-Term Fertilization History Alters Effects of Microplastics on Soil Properties, Microbial Communities, and Functions in Diverse Farmland Ecosystem. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 4658–4668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeley, M.E.; Song, B.; Passie, R.; Hale, R.C. Microplastics affect sedimentary microbial communities and nitrogen cycling. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.F.; Sikder, A.H.F. Microplastic can decrease enzyme activities and microbes in soil. Open J. Soil. Sci. 2024, 14, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, M.; Gutow, L.; Klages, M. Marine Anthropogenic Litter; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Griffin-LaHue, D.; Ghimire, S.; Yu, Y.; Scheenstra, E.J.; Miles, C.A.; Flury, M. In-field degradation of soil-biodegradable plastic mulch films in a Mediterranean climate. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO. Standard Operating Procedure for Soil pH Determination; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kreyer, K.G.; Bankina, T.A.; Orlova, N.E.; Yur’eva, G.M. Practical tasks on agrochemical soil analysis. In Textbook, 3rd ed.; Revision and Addendum; St. Petersburg University Press: St. Petersburg, Russia, 2005; 88p. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Maskalchuk, L.N.; Baklai, A.A.; Leont’eva, T.G.; Makovskaya, N.A. Removal of Cesium Radionuclides from Aqueous Media with an Aluminosilicate Sorbent Prepared from Belaruskalii Production Waste. Radiochemistry 2019, 61, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinaev, A.G.; Kichko, A.A.; Aksenova, T.S.; Safronova, V.I.; Kozhenkova, E.V.; Andronov, E.E. RIAM: A universal accessible protocol for the isolation of high purity DNA from various soils and other humic substances. Methods Protoc. 2022, 5, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 27 June 2025).
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Lozupone, C.A.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Fierer, N.; Knight, R. Global Patterns of 16S rRNA Diversity at a Depth of Millions of Sequences per Sample. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4516–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladkov, G.; Kimeklis, A.; Zverev, A.; Pershina, E.; Ivanova, E.; Kichko, A.; Andronov, E.; Abakumov, E. Soil Microbiome of the Postmining Areas in Polar Ecosystems in Surroundings of Nadym, Western Siberia, Russia. Open Agric. 2019, 4, 684–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladkov, G.V.; Kimeklis, A.K.; Tembotov, R.K.; Ivanov, M.N.; Andronov, E.E.; Abakumov, E.V. Linking the Composition of Cryoconite Prokaryotic Communities in the Arctic, Antarctic, and Central Caucasus with Their Chemical Characteristics. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 15838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-Resolution Sample Inference from Illumina Amplicon Data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posit Team. RStudio: Integrated Development Environment for R. 2025. Available online: http://www.posit.co/ (accessed on 27 June 2025).
- Shannon, C.E. A Mathematical Theory of Communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, E.H. Measurement of Diversity. Nature 1949, 163, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, J.R.; Curtis, J.T. An Ordination of the Upland Forest Communities of Southern Wisconsin. Ecol. Monogr. 1957, 27, 325–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ter Braak, C.J.F.; Verdonschot, P.F.M. Canonical Correspondence Analysis and Related Multivariate Methods in Aquatic Ecology. Aquat. Sci. 1995, 57, 255–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Peddada, S.D. Analysis of Compositions of Microbiomes with Bias Correction. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oksanen, J.; Simpson, G.L.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.H.H.; Szoecs, E.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. Version 2.7-1. The R Foundation: Vienna, Austria, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. Phyloseq: An R Package for Reproducible Interactive Analysis and Graphics of Microbiome Census Data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, K.S.; Kirkegaard, R.H.; Karst, S.M.; Albertsen, M. Ampvis2: An R Package to Analyse and Visualise 16S rRNA Amplicon Data. BioRxiv 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J. Microplastic effects on soil system parameters: A meta-analysis study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 11027–11038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, A.; Fitschen, K.; Rillig, M.C. Abiotic and biotic factors influencing the effect of microplastic on soil aggregation. Soil Syst. 2019, 3, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vainberg, A.; Abakumov, E.; Nizamutdinov, T. Recent Insights into Microplastic Pollution and Its Effects on Soil Carbon: A Five-Year Ecosystem Review. Microplastics 2025, 4, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isakov, V.; Vlasova, E.; Forer, V.; Kenny, J.; Lyulin, S. Analysis of Slow-Released Fertilisers as a Source of Microplastics. Land 2024, 14, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evdokimova, E.; Ivanova, E.; Gladkov, G.; Zverev, A.; Kimeklis, A.; Serikova, E.; Pinaev, A.; Kichko, A.; Aksenova, T.; Andronov, E. Structural Shifts in the Soil Prokaryotic Communities Marking the Podzol-Forming Process on Sand Dumps. Soil Syst. 2024, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, S.S.; González, S.S.; Suravajhala, P.; Jain, S.K.; Yadav, S.; Narayan, K.S.; Esack, E.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Ratnasari, A. Metagenomic insights of microbial functions under conventional and conservation agriculture. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2025, 41, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Li, Y.; Zhao, S.; Shao, Z. Biodegradation of Typical Plastics: From Microbial Diversity to Metabolic Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olabemiwo, A.; Hagan, A.; Cham, M.; Cohan, F.M. Two plant-growth-promoting Bacillus species can utilize NPs. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 907, 167972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abakumov, E.; Kimeklis, A.; Gladkov, G.; Nizamutdinov, T.; Kushnov, I.; Vainberg, A.; Andronov, E. The Effect of Applying Model Nanoplastic Particles to Soil on the Composition of Its Microbial Community. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9937. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15189937
Abakumov E, Kimeklis A, Gladkov G, Nizamutdinov T, Kushnov I, Vainberg A, Andronov E. The Effect of Applying Model Nanoplastic Particles to Soil on the Composition of Its Microbial Community. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(18):9937. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15189937
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbakumov, Evgeny, Anastasiia Kimeklis, Grigory Gladkov, Timur Nizamutdinov, Ivan Kushnov, Anastasia Vainberg, and Evgeny Andronov. 2025. "The Effect of Applying Model Nanoplastic Particles to Soil on the Composition of Its Microbial Community" Applied Sciences 15, no. 18: 9937. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15189937
APA StyleAbakumov, E., Kimeklis, A., Gladkov, G., Nizamutdinov, T., Kushnov, I., Vainberg, A., & Andronov, E. (2025). The Effect of Applying Model Nanoplastic Particles to Soil on the Composition of Its Microbial Community. Applied Sciences, 15(18), 9937. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15189937









