1. Introduction
Modern manufacturing enterprises operate in conditions of fierce competition and increasing demands for efficiency and reliability. One of the key problems in such conditions is managing risks associated with delays in order fulfillment and interruptions in technological operations, which also significantly affect internal logistics processes and material flow stability. To improve the sustainability of production processes and logistics efficiency, more and more companies, both large and small, are seeking to implement systematic approaches to assessing and minimizing production- and logistics-related risks [
1,
2,
3]. A distinctive feature of production lines oriented toward serial and mass production of products is the presence of inter-operational reserves—time and material buffers formed between technological operations to ensure uninterrupted and synchronized operation of the production system [
4,
5]. Accurate risk assessment has a critical role in maintaining production flow and operational efficiency. Inaccurate or simplistic estimations may lead to underestimated safety buffers or excessive reserves, both of which negatively impact productivity and costs [
6,
7].
Manufacturing systems, even in their basic linear configurations, are complex dynamic structures with many interconnected processes and possible delays in the processing of products at process operations along the process route. Equipment failures, variability in raw material supplies, human factors and external conditions can cause stochastic deviations that spread throughout the entire technological route [
8]. At the same time, a stop or failure in one operation does not necessarily lead to a complete stop of the production line but can cause an accumulation of inter-operational backlogs and uneven loading of equipment, which in turn can generate disruptions in the internal logistics flow [
9]. A special feature of production lines oriented towards serial and mass production of products is the presence of inter-operational reserves—time and material buffers formed between technological operations in order to ensure uninterrupted and synchronized operation of the production system [
4,
10]. Inter-operational backlogs play a key role in maintaining the production rate when deviations and failures occur while also supporting the stability and continuity of material flows and logistics processes. In risk analysis, particular attention is paid to the probability of exceeding the agreed production deadlines, which directly affects the fulfillment of contractual obligations, logistics, and service levels, and can lead to significant financial losses. Methods for quantitative assessment of such risks are being developed but remain difficult to implement in practical application due to the complexity of the relationships and heterogeneity of factors [
11]. Traditional approaches often rely on the assumption that risk (R) and reliability (N) are related through the simplistic formula R + N = 1. While useful in basic systems, such models do not capture the stochastic and interdependent nature of modern manufacturing environments [
12,
13]. Therefore, more sophisticated models that incorporate time-dependent behaviors and multi-state processes are necessary. Several attempts have been made to enhance the classical risk formulation by introducing dynamic factors, reliability distributions, or process interdependencies [
14,
15,
16]. However, most of these models are either too complex for real-time applications or lack integration with internal logistics structures, which are vital for modern production lines [
17].
This paper proposes a method for stochastic modeling of a production line that takes into account the probabilistic characteristics of process operations and the influence of production risks with special consideration for the impact on production logistics and material flow continuity. As a demonstration example, a line for the production of wooden single-leaf windows is considered, where the sequence of technological operations is strictly regulated. Using the subject-technological description of the system [
18], random delays, changes in equipment states and variations in the flow of parts are displayed in the production line model. The proposed method goes beyond traditional queueing network models and PERT/CPM-based approaches. Unlike queueing models, which analyze system performance but often overlook the stabilizing effect of buffers, and unlike PERT/CPM methods, which focus on critical paths and schedules without fully accounting for stochastic variability, the proposed method simultaneously considers the process structure and statistical parameters of operations, including the probability and duration of process interruptions. This allows for a comprehensive, logistics-oriented evaluation of operational stability, identification of bottlenecks, and quantitative assessment of production losses.
The aim of the paper is to develop an analytical tool for assessing the risk of violation of production deadlines for a batch of products while taking into account the internal logistics structure of the production process, as well as to provide a quantitative assessment of potential production losses. The presented results are useful for developing practical solutions for risk management adapted to the specifics of discrete manufacturing systems. This enables a more realistic and logistics-oriented assessment of buffer systems and their effectiveness in reducing production risks.
4. Results
To demonstrate the application of the proposed stochastic model of the production line, the process of manufacturing a single-leaf wooden window in an industrial production environment is considered. The case study examines a linear production line, where a detail sequentially passes through a series of technological operations before turning into a finished product. The technological route consists of
M consecutive operations, each of which is performed at a dedicated workstation. For each operation, standard processing times were defined in accordance with the technical documentation of the enterprise. These values do not include non-production downtime and are used as input parameters for the model.
Table 2 summarizes the technological key parameters for each technological operation, including mean processing time, standard deviation of processing time and identified main risk factors. The production line operates in a serial-batch mode, where batches of details are processed in sequence. Inter-operational buffers between operations are used to compensate for variability in operation times. The capacity of these buffers and their utilization rate are important factors in ensuring an uninterrupted flow of details. The enterprise aims to meet daily production targets while minimizing downtime and production losses. Variability in processing times arises from technological and risk factors (
Table 1). These factors influence the probability of downtime at each operation and are incorporated into the stochastic model. The production line operates in steady-state conditions once the first part reaches the last workstation. Inter-operational buffer capacities remain constant during the observation period. The model parameters (mean, standard deviation, probability of downtime) are estimated from recorded production data over a representative period of time. The technological process of producing a batch of 60 single-leaf windows, including seven consecutive processing operations presented in
Table 2, is analyzed [
11]. The average time during which a detail is in the
-th state during processing at the
-th technological operation is designated as
. The values of the standard deviation of the execution time of a technological operation are determined on the basis of statistical processing of data and are equal to
for
and
for
. In order to simplify the analysis, we will assume that the distribution function
(3) of random variables corresponds to the normal distribution law.
During the process of performing a technological operation, the equipment may be in one of the states (see
Table 1) with the probability
indicated in
Table 3. These values were obtained as a result of processing experimental data in [
11]. The total time that a part spends in technological processing consists of the time of the technological processing itself
and the time required to solve production problems by taking the equipment out of the
-th state. At this time, the object is at the level of technological processing and does not allow other objects to start this technological processing operation. All other objects are awaiting their processing time in this technological operation, being in the inter-operational backlog.
Using the introduced dimensionless parameters (1), the parameters of technological operations can be presented in dimensionless form (
Table 4). In the limiting case, when production risk
for factors
and the process of performing technological operations is deterministic, the time required to produce a serial batch of 60 windows can be calculated using the formula
This formula assumes that there are no inter-operational reserves for the technological operations. This is a limiting case of the technological process. The value of time required for the production of a batch of 60 windows will be used in this work for a comparative analysis of different technological routes and modes of operation of the technological equipment. Note that the obtained value (32) corresponds to the operating time interval of a manufacturing enterprise during one calendar month , during which a batch of 60 windows is manufactured on a production line that does not provide for technological reserves.
If the distribution density function
of a random variable
is known for each technological operation, the distribution density
of the random variable
can be calculated according to Formula (3).
Figure 2 shows the calculated distribution densities
of the random variable
for the
-th technological operation. The multimodal distribution density function
of a random variable
reflects the presence of a risk
of occurrence of the
-th state for the
-th technological operation. The prevailing mode corresponds to the state
with the probability of occurrence
, in which the product is directly processed during the technological operation.
Technological trajectories (implementation of a stochastic process for manufacturing a batch of products), formed using the distribution densities
of the processing time of a part at the
-th technological operation for the limiting case of a production line for which no inter-operational backlogs are provided, are presented in
Figure 3.
Figure 3a illustrates the process paths of the first five details (details 1–5) in a production batch, while subfigure
Figure 3b illustrates the process paths of the last five details (details 55–60). This difference highlights how stochastic variability and risk-related delays affect parts differently depending on their position in the production sequence. The solution to the problem regarding technological trajectories allows us to estimate the manufacturing time of a batch of details, which is correspondingly equal to the time interval between the start of processing the first detail in the first operation and the end of processing the last detail in the last operation.
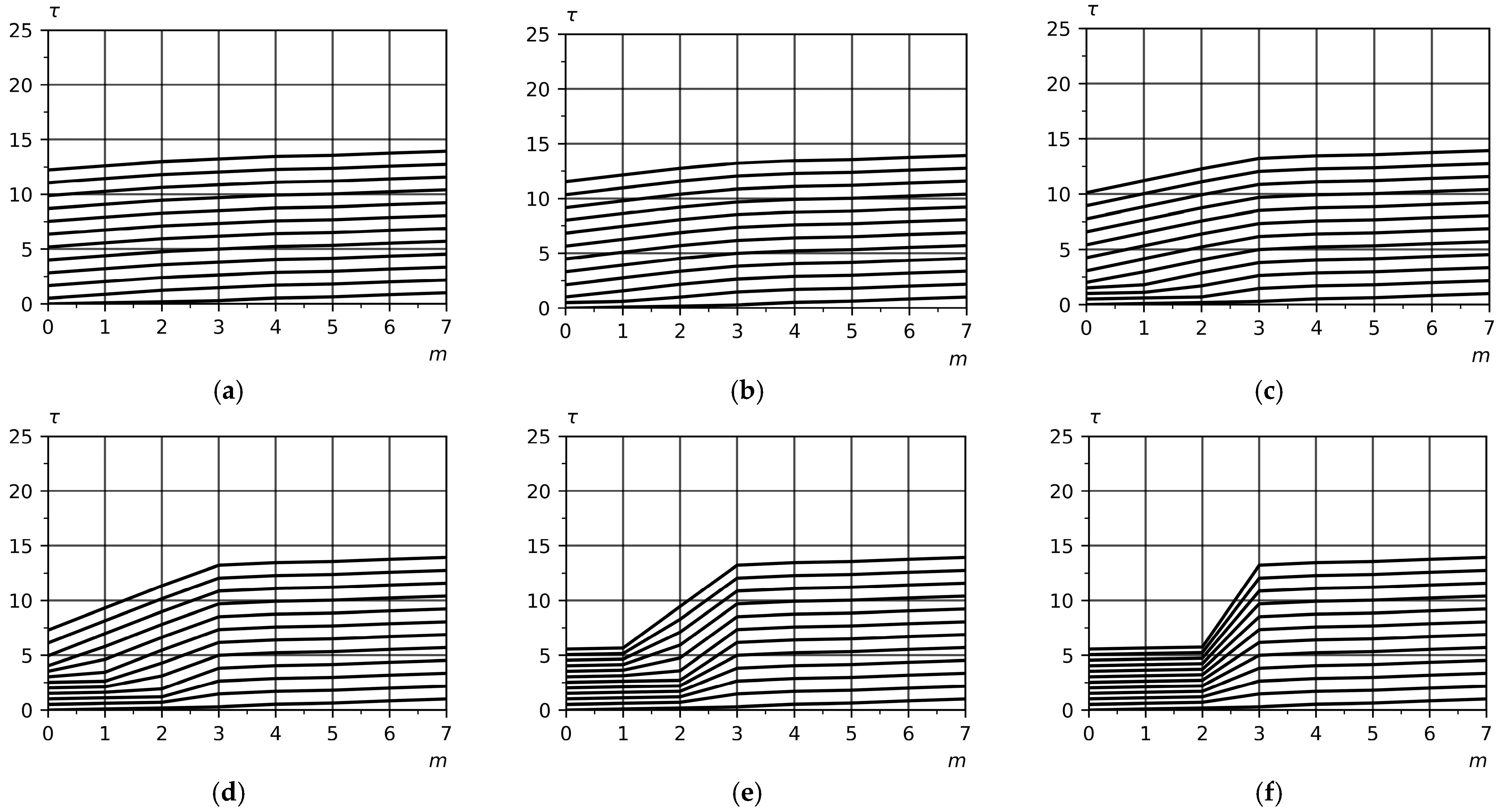
Before moving on to assessing the risk of the production system exceeding the agreed production time for a batch of details, the effect of the size of the inter-operational backlog on the production time for a batch of 60 single-leaf windows for a deterministic model of the production line in the absence of production risks was considered:
for factors
. The process trajectories of a batch of 60 wooden single-leaf windows for production line variants that provide different sizes
of the inter-operational buffers are shown in
Figure 4. For clarity of demonstration, the graphs contain technological trajectories, the product number of which is a multiple of five. The size
of the inter-operational buffer is understood as the maximum number of details that are undergoing or have undergone processing at the
-th technological operation and are awaiting the start of processing at the
-th technological operation. In the qualitative analysis, it is assumed that the size
of the inter-operational buffer is the same for each technological operation.
Figure 4a shows process trajectories where no more than one detail is allowed to be present in a process operation. This option corresponds to Equation (15) for calculating the production risk
of the production system exceeding the agreed production time of a batch of details. When the size of the inter-operational buffer increases, the process trajectories are deformed in the interval from the first to the third process operation. This is explained by the fact that the fourth operation has the maximum processing time for the detail
(
Table 4). The fourth operation is the bottleneck of the production line and sets the overall pace of production of single-leaf wooden windows. Increasing the size
of the inter-operation buffer results in more parts being shifted to the fourth process operation.
It is worth paying attention to the fact that the technological trajectories for
and
are the same. The explanation for this is quite simple. The number of details in the inter-operational buffer
before the fourth technological operation is determined by solving the system of Equation (9). From the graphical analysis of
Figure 4f, it follows that in the third technological operation for cases
and
, the limitation, defined by
, for
is not achieved for two variants. The next step is to analyze the process trajectories for the stochastic model of the production line taking into account production risks
. The process trajectories of a batch of 60 single-leaf windows for a stochastic model of a production line in the presence of production risks
are shown in
Figure 5. The process trajectories for the stochastic model are qualitatively consistent with the picture observed for the deterministic production line model. The fourth operation, as in the previous case, is a bottleneck in the technological route of manufacturing a batch of 60 wooden single-leaf windows. As the size
of the inter-operational buffer increases, the process trajectories shift to the process operation that is identified as the bottleneck in the process route. Since process trajectories are implementations of a stochastic process of processing a batch of details taking into account the risk of the production system exceeding the agreed time for manufacturing a batch of details, the bottleneck in the process route can migrate from operation to operation depending on the probability of occurrence of a production risk and the duration of the time interval for eliminating the consequences associated with this risk. Obviously, the minimum production time for a batch of 60 single-leaf wooden windows will be in the case where, with equal processing time for the part in the technological operation, the bottleneck corresponds to the last technological operation.
In this case, the technological trajectories of a batch of details are gradually deformed towards the last production operation, creating a high level of inter-operational backlogs at these technological operations. This leads to the fact that the risk of the production system exceeding the agreed time for the production of a batch of details is reduced for two reasons, the first of which is the high level of inter-operational backlogs, and the second is that products accumulate at the last technological operations and the contribution of the occurrence of conditions associated with the presence of risks during the first technological operations is significantly reduced.
5. Discussion
We take into consideration the distribution function
, which determines the probability that the production time
of a batch of 60 wooden single-leaf windows will not exceed the time
.
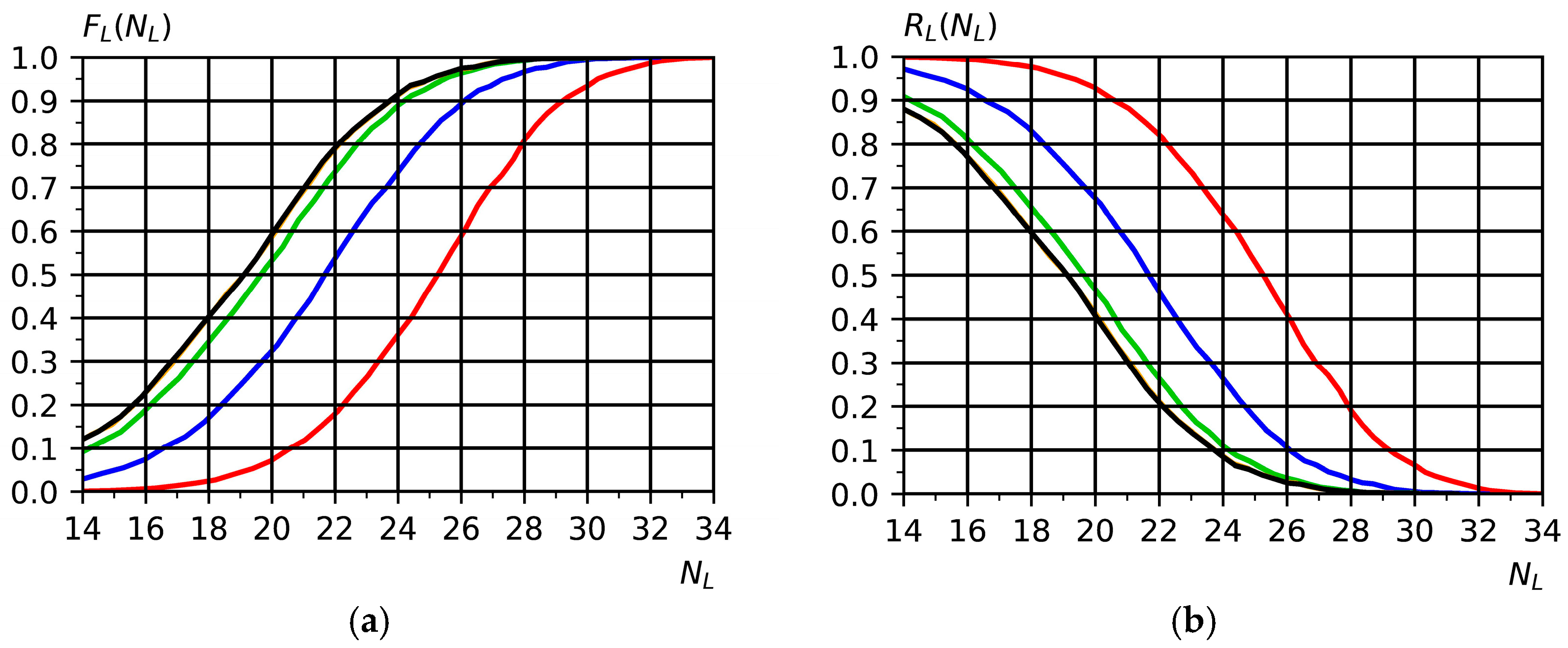
Figure 6a shows the curves for the distribution function
for different values of the buffer size for inter-operational backlogs:
(red curve),
(blue curve),
(green curve),
(black curve). Increasing the size of the buffer for inter-operational backlogs leads to a decrease in the batch time of details.
Then the probability that the production time
of a batch of details will exceed the time
can be determined as follows:
. The function
represents the risk of the production system exceeding the agreed time for manufacturing a batch of products, that is, the probability that a batch of products cannot be manufactured within the specified time
.
Figure 6b shows the risk function
of exceeding the manufacturing time
of a batch of 60 single-leaf wooden windows for different values of the buffer size for inter-operational backlogs.
Figure 6b shows the curves
corresponding to the results
(red curve),
(blue curve),
(green curve),
(black curve). The first curve on the right (shown in red) is for a production line that does not provide inter-operational backlogs,
. To build this curve, the calculation method for
, corresponding to Formulas (15) and (21), was used. For example, with a probability of 0.75, it can be stated that the production time
for a batch of 60 wooden single-leaf windows will exceed the value for a production line that does not provide inter-operational backlogs (
, red curve). For the case when the value is
, the probability is already ~0.35 (
Figure 6a, blue curve). A further increase in the value of
reduces the probability to ~0.15 (the black curve corresponds to
;
Figure 6b).
Thus, the use of inter-operational buffers allows us to significantly reduce the probability of occurrence of production risks in accordance with Formula (27). Depending on the buffer configuration and the specifics of the process operations, the total processing time of the pilot batches was reduced by approximately 18–25% compared to the baseline without a buffer. At the same time, the estimated probability of failure to meet production deadlines was reduced several times, indicating a significant reduction in operational risks. This result is achieved due to the ability of interoperational buffers to compensate for random fluctuations in the duration of operations and localize their impact, preventing the cascading spread of failures along the process route. The results obtained confirm not only the theoretical but also the practical significance of the proposed approach to increasing the stability of discrete production systems. Each moment in time
corresponds to a quantitative assessment of work in progress (WIP) within the production system
. Production losses can be characterized as the difference between the potential volume
of production for the reporting period
and the actual volume,
, taking into account the absence of risks. A visual representation of losses due to production risks is shown in
Figure 7. This graph represents the transformation of
,
into
,
by moving from variable
to variable
. The transformation simplifies the interpretation of the obtained results, allowing the manufacturer to estimate losses in natural units, as well as the probability of these losses.
The quantitative and qualitative analysis performed demonstrates the significant influence of inter-operational reserves on the volume of losses arising from production risks. The losses calculated in accordance with Formula (15) are units with a probability of ~0.65, while with the same probability, the estimate of production losses can be reduced to units in the presence of inter-operational buffers of the required capacity.
The proposed method, although demonstrated using a wooden single-leaf window production line, has a general structure that makes it applicable to a wide variety of manufacturing systems characterized by sequential operations. It can be used in assembly lines in the automotive or electronics industries, where inter-operational buffers help mitigate disruptions caused by component delays, tooling changes, or rework. Similarly, the method is suitable for flexible manufacturing systems, where production times are highly variable due to customization and frequent equipment reconfigurations, as well as in metalworking and machining operations, where tool wear and operator variability significantly impact lead times. The use of dimensionless parameters in the model enables its application across production systems with varying scales, process structures, and technological settings.
The proposed method of analyzing production risks is not limited to strictly sequential technological operations. The use of an example with a linear production system in the article is due to the desire to simplify the mathematical transformations associated with parallel–sequential execution of technological operations, and thereby clearly demonstrate the key features of the developed approach. In this case, two parallel technological operations can be formally represented as one generalized operation, for which the statistical characteristics of the processing time are determined through the convolution of the distributions of random variables describing the execution time of each of the parallel operations. Issues of expanding the model to cases of flexible routing and parallel processing are planned to be considered in subsequent studies.
6. Conclusions
This paper is devoted to the justification of the use of the risk assessment method based on the assumption that risk (R), understood as the probability of occurrence of production losses, is synonymous with unreliability (Z) (15) [
6] for production systems engaged in serial or mass production of products. The conditions for applying this approach have been defined. It is shown that calculation methods (15) and (21) assume that production lines do not provide buffers for inter-operational backlogs. A model of a production line based on the subject’s technological description of the production system was constructed and used to justify the applicability conditions of the proposed risk assessment concept, which assumes that risk (R) is equivalent to unreliability (Z) (15) [
6] in production systems with serial or mass production of products. A new concept of the risk assessment method has been developed, based on the technological model of the production line. Analytical expressions for calculating production losses in serial and mass production conditions of a production line have been obtained. The risk assessment includes not only the probability that a process operation will remain in this state (for example, a stop due to a breakdown or reconfiguration of equipment), but also the distribution of the time the product will be in this state, described by the mathematical expectation and standard deviation. This approach allows for a more comprehensive and logistics-oriented evaluation of the operational stability of the production system. The key advantage of the proposed risk assessment method is its ability to simultaneously account for both the structure of the process route and the statistical parameters of operations. Importantly, the method demonstrates that when using the traditional risk formula, the result R is not zero; however, with the new formula, the risk R can approach zero as inter-operational reserves increase, which provides a more realistic tool for planning production buffers in logistics-intensive environments.
From a production management standpoint, the proposed model constitutes an analytically grounded instrument for supporting decision-making in the domains of production planning, scheduling, and capacity management within discrete manufacturing systems. By providing a quantitative framework for evaluating the effects of stochastic perturbations—such as variable operation durations and equipment downtimes—on lead time distribution and throughput performance, the model enables identification of bottleneck operations and estimation of the probability of schedule deviations. This facilitates evidence-based decisions regarding the configuration of inter-operational buffers, optimization of resource utilization, and adjustment of production schedules under uncertainty. Furthermore, the model functions as a decision-support tool for evaluating trade-offs between buffer sizing and operational reliability, thereby contributing to the formulation of robust production control strategies. In doing so, it establishes a methodological link between stochastic process modeling and practical applications in industrial operations management. The obtained results show that the presence of inter-operational buffers not only reduces the probability of violation of production batch deadlines but also stabilizes the production flow under stochastic disturbances. From the point of view of production risk management, this means that the size of the buffers should be considered as a control parameter that allows the level of production risks to be reduced to the required value. In practice, the proposed approach can be used to identify critical operations, assess possible production losses and make informed decisions on resource allocation, planning and configuration of production lines.
The vector of further research includes the following areas: (1) analysis of the risk of exceeding the established time for manufacturing a batch of details on a production line with sequential- and parallel-type technological routes; (2) development of a risk assessment model for a line that simultaneously processes several batches of details; (3) simulation modeling of batch processing in the presence of a stochastic incoming flow of orders; (4) analysis of the relationship between the size of the production batch and the parameters of production risk in order to identify optimal modes of organizing production; (5) comparative evaluation of the proposed approach with other established methods of production risk assessment, with an emphasis on validation using experimental data.
Although the model was validated on a specific example of wooden window manufacturing, its general structure based on dimensionless variables and stochastic characteristics of operation times makes it applicable to a wide range of manufacturing environments. Future research will focus on empirical validation in other industries, such as automotive, electronics, and mechanical engineering, using real production data. These comparative studies should assess the robustness of the model, provide empirical calibration, and contribute to the development of industry-specific guidelines for manufacturing risk management and buffer stock optimization.