Innovative Green Strategy for the Regeneration of Spent Activated Carbon via Ionic Liquid-Based Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
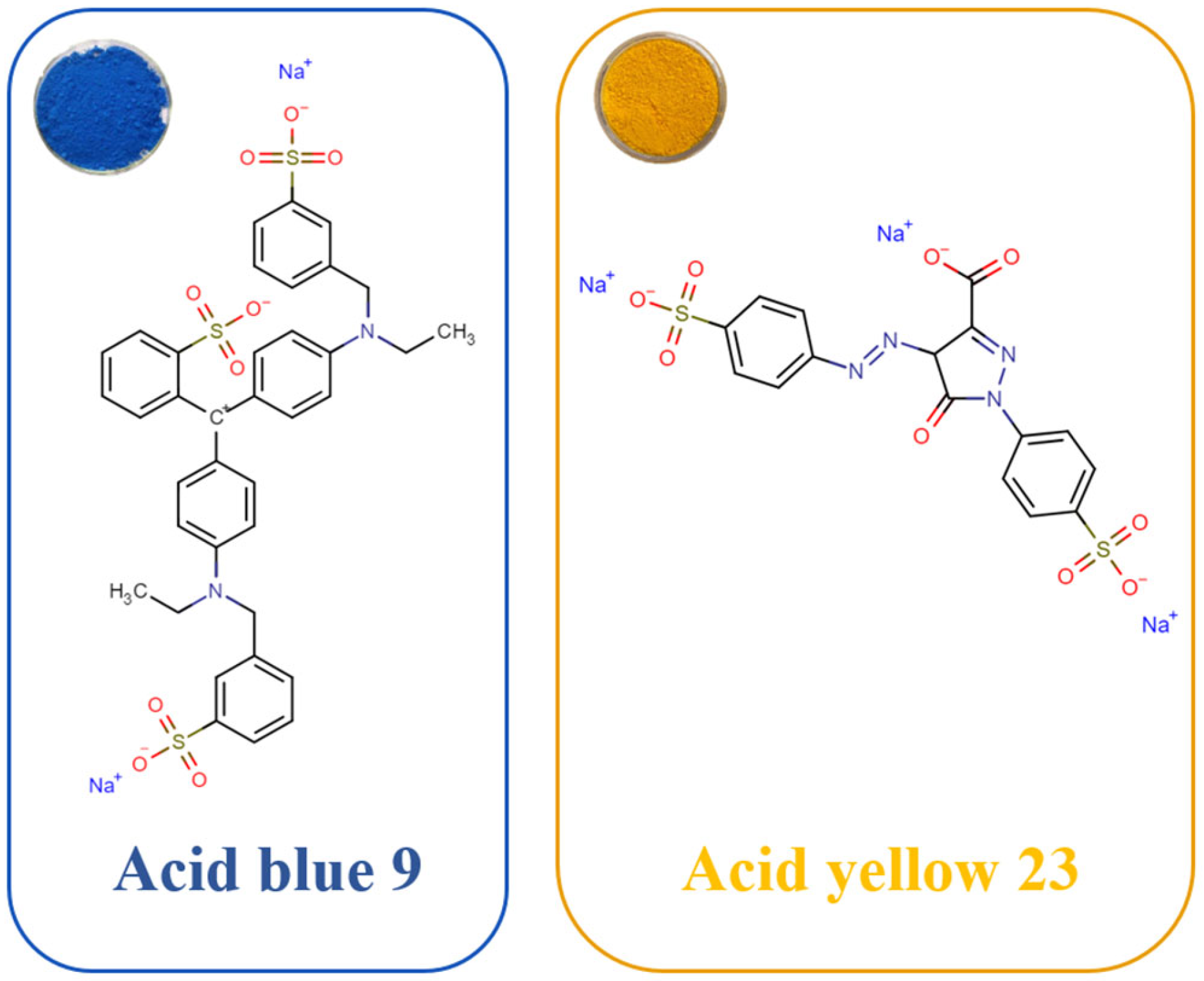
2.1. Materials
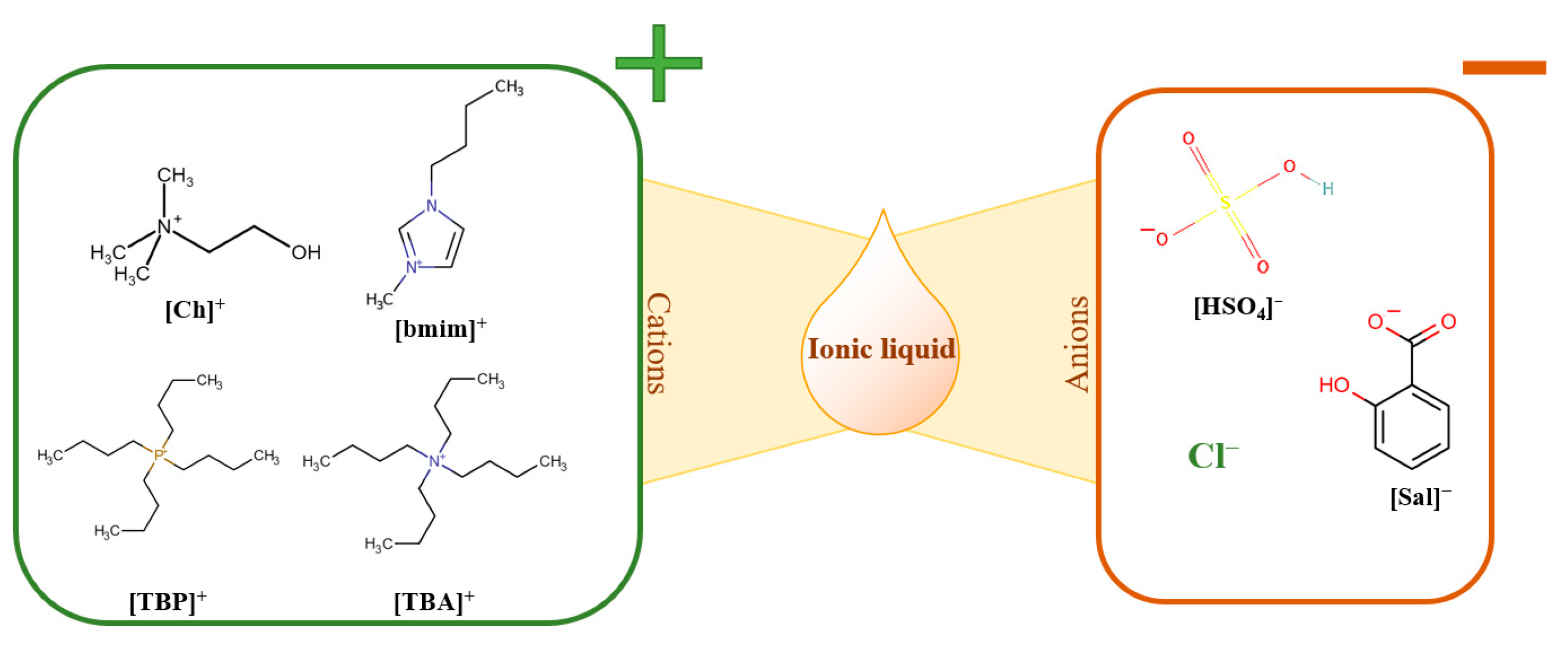
2.2. IL Synthesis
2.3. AC Properties
2.3.1. Zero Point Charge
2.3.2. Boehm Titration
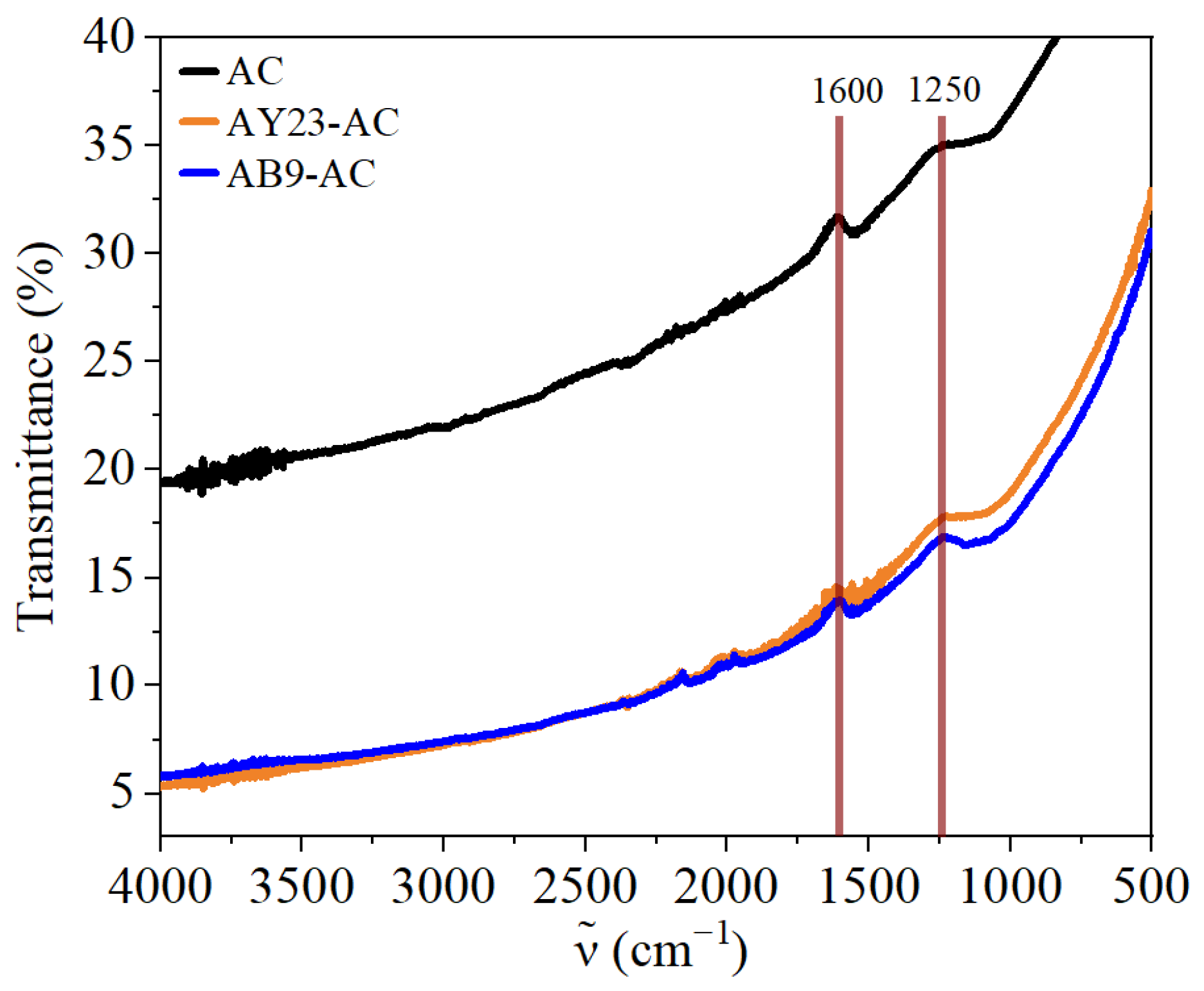
2.3.3. FTIR Analysis
2.3.4. Methylene Blue Number
2.4. Adsorption Experiments
2.4.1. Determination of the Optimal Initial Dye Concentration
2.4.2. Isotherm Determination
2.5. AC Regeneration
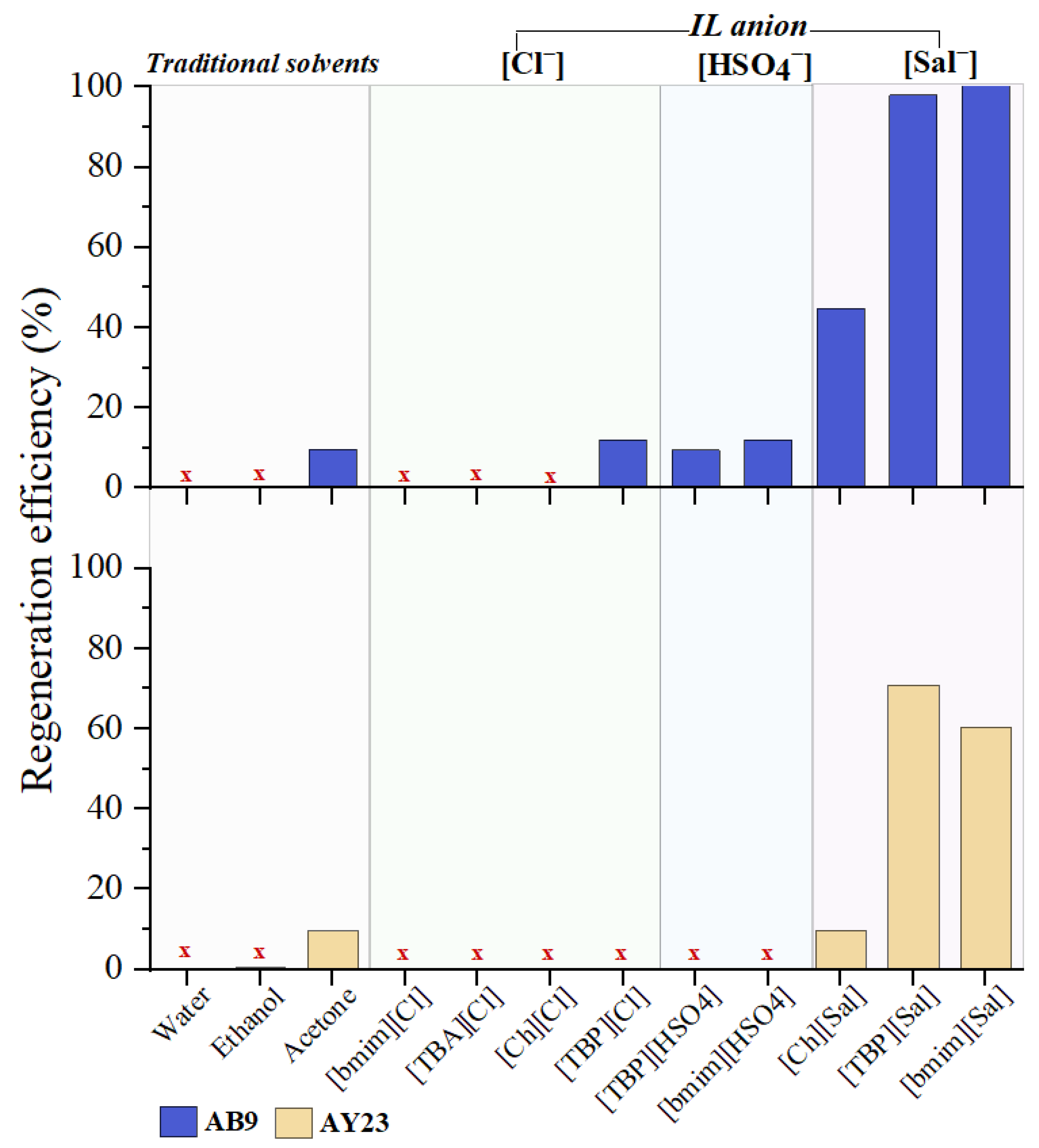
2.5.1. Screening Study
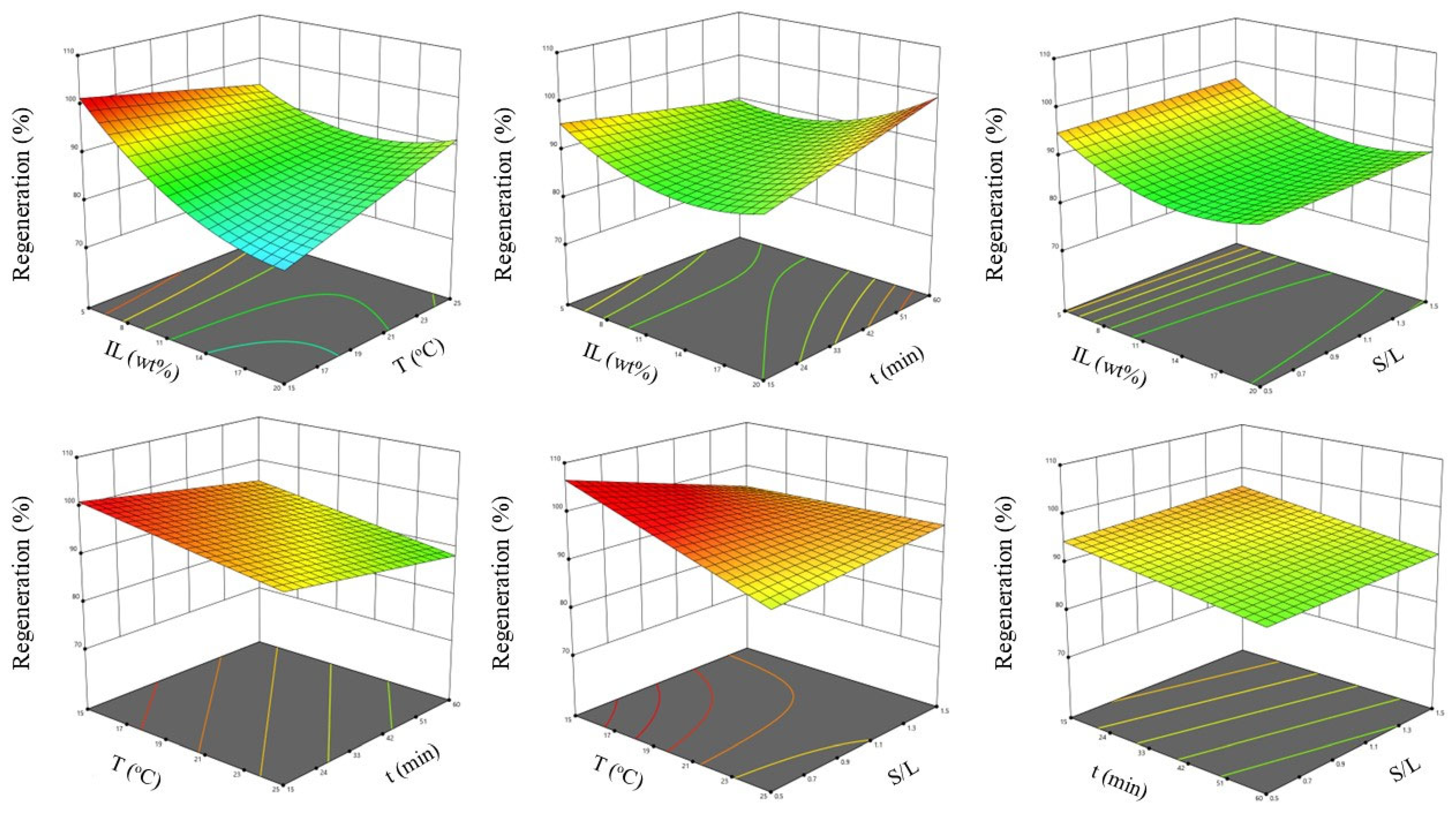
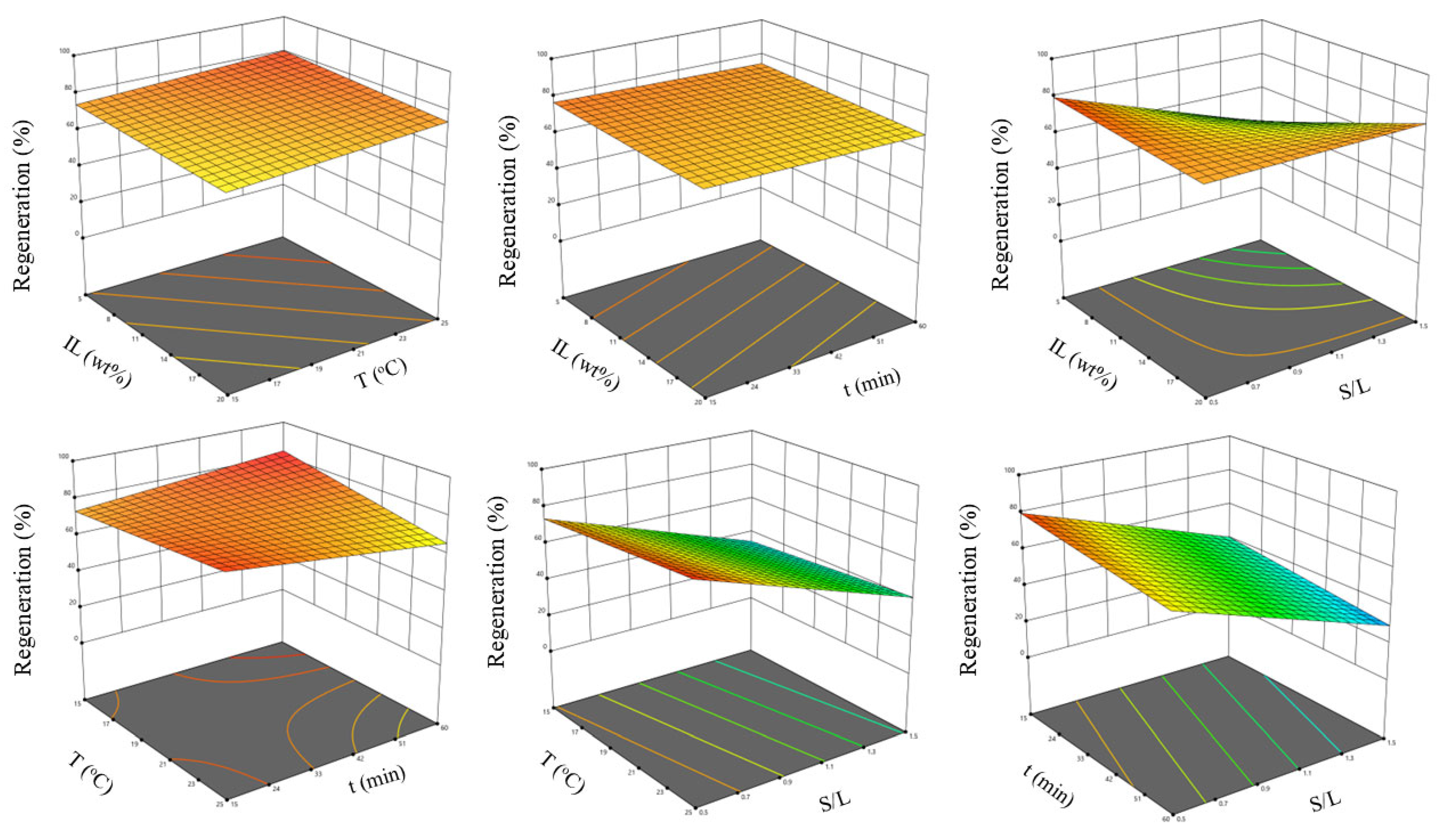
2.5.2. Optimization Study
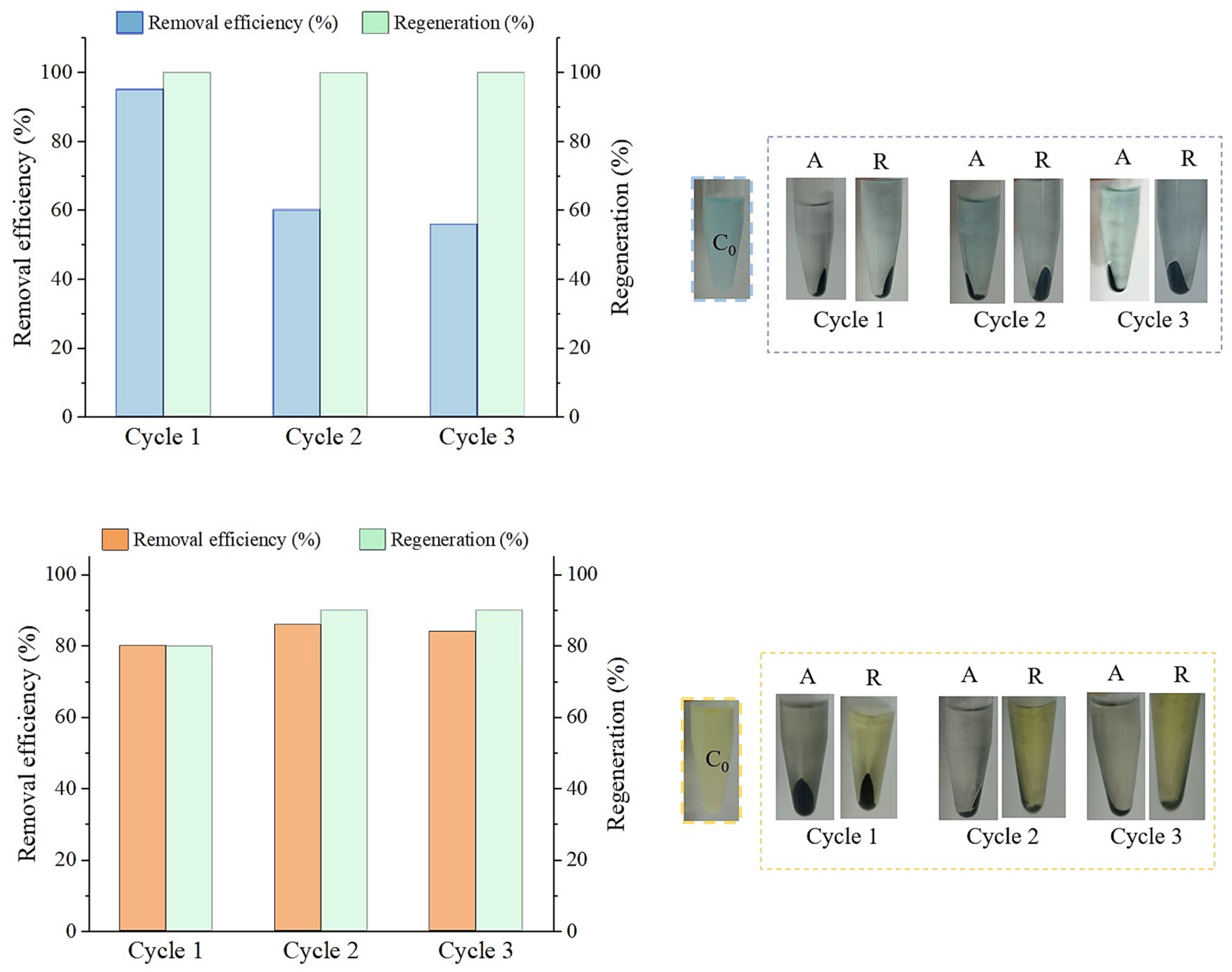
2.5.3. Multi-Cycle Adsorption and Regeneration Performance
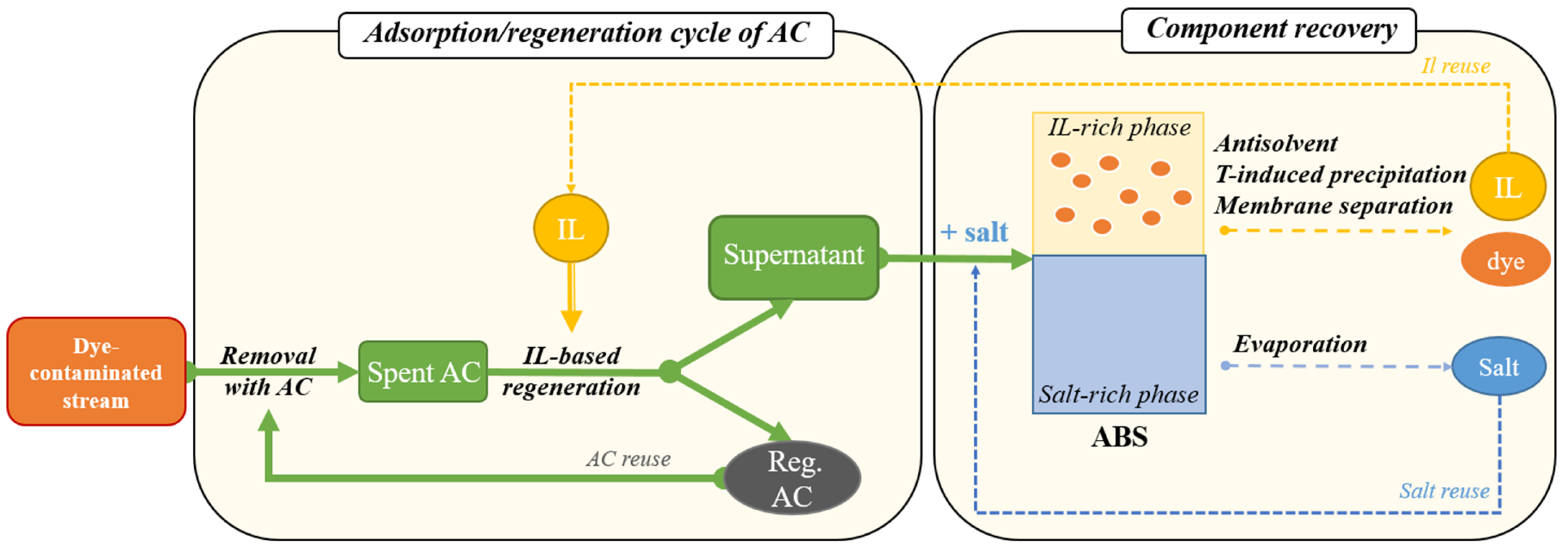
2.5.4. Preliminary Assessment of Component Recovery via Aqueous Biphasic Systems
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. AC Properties
3.2. Dye Adsorption Conditions
3.3. Dye Adsorption Isotherms
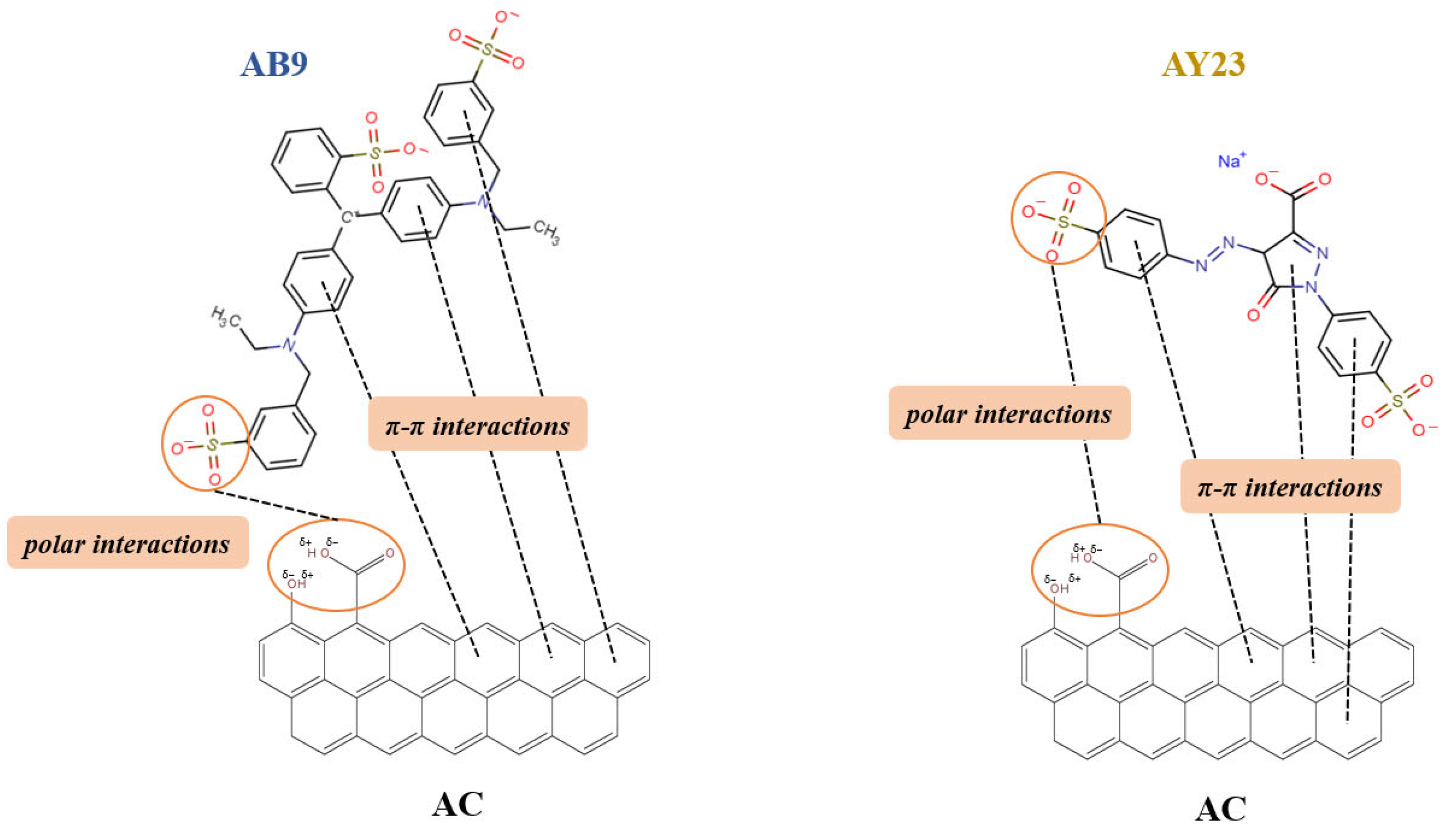
3.4. FTIR Analysis of Dye-AC Interactions
3.5. AC Regeneration
3.5.1. Screening Study
3.5.2. Optimization Study
3.6. Regenerated AC’s Adsorbent Performance and Reusability Assessment
3.6.1. Adsorption Using Regenerated AC
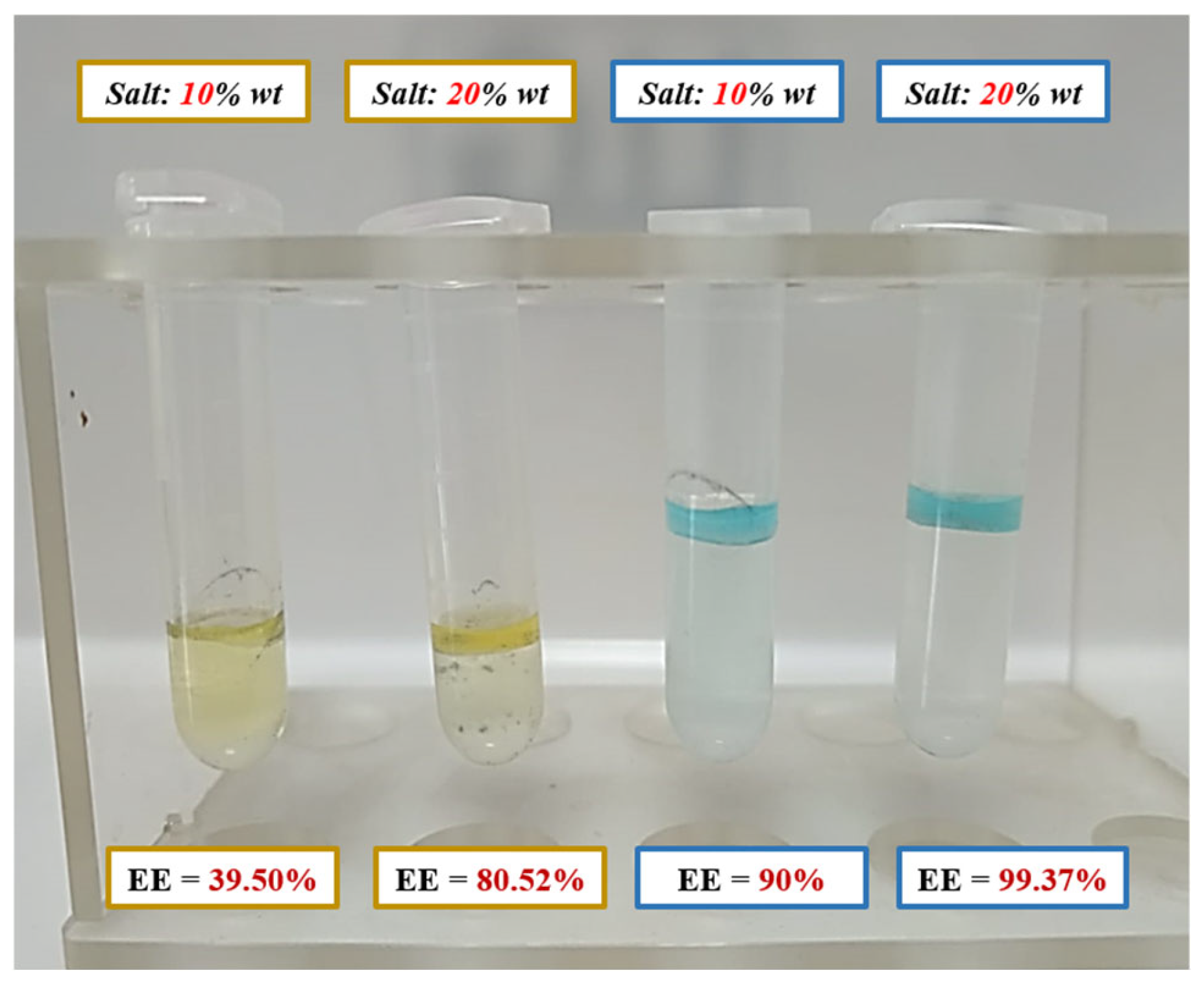
3.6.2. Preliminary Assessment of Component Recovery via Aqueous Biphasic Systems
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Zhang, T.; Zheng, L.; Yang, X.; Demeestere, K.; Van Hulle, S.W.H. Integrated spectral based monitoring, optimization and control of the combined ozonation and powdered activated carbon adsorption process to remove organic micropollutants from secondary effluent. Water Res. 2025, 268, 122588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, C.A.; Choi, Y.-L.; Lingamdinne, L.P.; Kulkarni, R.; Karri, R.R.; Koduru, J.R.; Chang, Y.-Y. Plasma-assisted MnO surface engineered activated carbon felt for enhanced heavy metal adsorption. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salatein, N.M.; Shaaban, M.; Fahim, I.S. Comparing low-cost activated carbon made from coffee waste and bagasse to remove heavy metals and methylene blue dye. Results Chem. 2025, 13, 102020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satyam, S.; Patra, S. Innovations and challenges in adsorption-based wastewater remediation: A comprehensive review. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Su, Y.; Zhang, H. The deactivation mechanisms, regeneration methods and devices of activated carbon in applications. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 476, 143751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladejo, J.; Shi, K.; Chen, Y.; Luo, X.; Gang, Y.; Wu, T. Closing the active carbon cycle: Regeneration of spent activated carbon from a wastewater treatment facility for resource optimization. Chem. Eng. Process.—Process Intensif. 2020, 150, 107878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathinam, K.; Mauer, V.; Bläker, C.; Pasel, C.; Landwehrkamp, L.; Bathen, D.; Panglisch, S. Eliminating Luck and Chance in the Reactivation Process: A Systematic and Quantitative Study of the Thermal Reactivation of Activated Carbons. C-J. Carbon Res. 2023, 9, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazigil, L.; Er, E.; Yonar, T. Determination of the optimum conditions for electrochemical regeneration of exhausted activated carbon. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2023, 133, 109741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrández-Gómez, B.; Ruiz-Rosas, R.; Beaumont, S.; Cazorla-Amorós, D.; Morallón, E. Electrochemical regeneration of spent activated carbon from drinking water treatment plant at different scale reactors. Chemosphere 2021, 264, 128399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, T.; Kim, T.; Vellingiri, K.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Shon, J.R.; Kim, K.H.; Kumar, S. Recycling and regeneration of carbonaceous and porous materials through thermal or solvent treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 364, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maliyekkal, S.M.; Sreeprasad, T.S.; Krishnan, D.; Kouser, S.; Mishra, A.K.; Waghmare, U.V.; Pradeep, T. Graphene: A Reusable Substrate for Unprecedented Adsorption of Pesticides. Small 2013, 9, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chern, J.M.; Wu, C.Y. Desorption of dye from activated carbon beds: Effects of temperature, pH, and alcohol. Water Res. 2001, 35, 4159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wei, X.; Zhang, R.; Wu, Y.; Farid, M.U.; Huang, H. Comparison of chemical, ultrasonic and thermal regeneration of carbon nanotubes for acetaminophen, ibuprofen, and triclosan adsorption. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 52719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemus, J.; Palomar, J.; Heras, F.; Gilarranz, M.A.; Rodriguez, J.J. Developing criteria for the recovery of ionic liquids from aqueous phase by adsorption with activated carbon. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 97, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakili, M.; Deng, S.; Shen, L.; Shan, D.; Liu, D.; Yu, G. Regeneration of Chitosan-Based Adsorbents for Eliminating Dyes from Aqueous Solutions. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2019, 48, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnuchamy, M.; Kapoor, A.; Kumar, P.S.; Vo, D.-V.N.; Balakrishnan, A.; Jacob, M.M.; Sivaraman, P. Sustainable adsorbents for the removal of pesticides from water: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hupsel, A.L.; Borges, C.P.; da Fonseca, F.V. Treatment of stabilized landfill leachate using powdered activated carbon: Adsorption behavior and chemical regeneration. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2025, 32, 15614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juturu, R.; Vinayagam, R.; Murugesan, G.; Selvaraj, R. Mesoporous phosphorus-doped activated carbon from Acacia falcata: Mechanistic insights into Cr (VI) removal, regeneration, and spiking studies. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2025, 153, 112015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuhara, S.; McKay, G. Single and binary pollutant adsorption of strontium and barium on waste-derived activated carbons: Modelling, regeneration and mechanistic insights. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2025, 39, 104220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larasati, A.; Fowler, G.D.; Graham, N.J.D. Insights into chemical regeneration of activated carbon for water treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Karre, A.V.; Valsaraj, K.T.; Sharma, S. Intensification of a Neutralization Process for Waste Generated from Ion Exchange Regeneration for Expansion of a Chemical Manufacturing Facility. Processes 2021, 9, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA. Initial List of Hazardous Air Pollutants with Modifications. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/haps/initial-list-hazardous-air-pollutants-modifications (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Stark, A.; Seddon, K.R. Ionic Liquids. In Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Mital, D.K.; Nancarrow, P.; Zeinab, S.; Jabbar, N.A.; Ibrahim, T.H.; Khamis, M.I.; Taha, A. Group contribution estimation of ionic liquid melting points: Critical evaluation and refinement of existing models. Molecules 2021, 26, 2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vekariya, R.L. A review of ionic liquids: Applications towards catalytic organic transformations. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 227, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Pei, Y.; Wang, J.; He, M. Design of environmentally friendly ionic liquid aqueous two-phase systems for the efficient and high activity extraction of proteins. Green Chem. 2012, 14, 2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llaver, M.; Fiorentini, E.F.; Quintas, P.Y.; Oviedo, M.N.; Arenas, M.B.B.; Wuilloud, R.G. Task-specific ionic liquids: Applications in sample preparation and the chemistry behind their selectivity. Adv. Sample Prep. 2022, 1, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, E.A.; Ijardar, S.P. Insights into the separation of metals, dyes and pesticides using ionic liquid based aqueous biphasic systems. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 334, 116027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivier-Bourbigou, H.; Magna, L.; Morvan, D. Ionic liquids and catalysis: Recent progress from knowledge to applications. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2010, 373, 1–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cláudio, A.F.M.; Neves, M.C.; Shimizu, K.; Lopes, J.N.C.; Freire, M.G.; Coutinho, J.A.P. The magic of aqueous solutions of ionic liquids: Ionic liquids as a powerful class of catanionic hydrotropes. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 3948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, Y.S.; Tjong, T.C.; Chew, J.W.; Hu, X. Techniques for recovery and recycling of ionic liquids: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 922, 171238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cláudio, A.F.M.; Marques, C.F.C.; Boal-Palheiros, I.; Freire, M.G.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Development of back-extraction and recyclability routes for ionic-liquid-based aqueous two-phase systems. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotto, G.L.; Pinto, L.A.A. Adsorption of food dyes acid blue 9 and food yellow 3 onto chitosan: Stirring rate effect in kinetics and mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 187, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tohamy, R.; Ali, S.S.; Li, F.; Okasha, K.M.; Mahmoud, Y.A.-G.; Elsamahy, T.; Jiao, H.; Fu, Y.; Sun, J. A critical review on the treatment of dye-containing wastewater: Ecotoxicological and health concerns of textile dyes and possible remediation approaches for environmental safety. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 231, 113160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, S.; Gupta, B.; Srivastava, S.K.; Gupta, A.K. Recent advances on the removal of dyes from wastewater using various adsorbents: A critical review. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 4497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Savoy, A.W. Ionic liquids synthesis and applications: An overview. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 297, 112038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Kaur, S.; Sapehiyia, V.; Singh, J.; Kad, G.L. Microwave accelerated preparation of [bmim][HSO4] ionic liquid: An acid catalyst for improved synthesis of coumarins. Catal. Commun. 2005, 6, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suprapto, S.; Wahyuningtyas, A.; Madurani, K.A.; Ni’mah, Y.L. Predicting ash content and water content in coal using full infrared spectra and machine learning models. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2025, 51, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hina, K.; Zou, H.; Qian, W.; Zuo, D.; Yi, C. Preparation and performance comparison of cellulose-based activated carbon fibres. Cellulose 2018, 25, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mopoung, S.; Moonsri, P.; Palas, W.; Khumpai, S. Characterization and Properties of Activated Carbon Prepared from Tamarind Seeds by KOH Activation for Fe(III) Adsorption from Aqueous Solution. Sci. World J. 2015, 2015, 415961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, C.A.; Guerreiro, M.C. Estimation of surface area and pore volume of activated carbons by methylene blue and iodine numbers. Quim. Nova 2011, 34, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, F.; De La Rubia, M.A.; Borja, R. Methylene blue number as useful indicator to evaluate the adsorptive capacity of granular activated carbon in batch mode: Influence of adsorbate/adsorbent mass ratio and particle size. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 165, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, C.A.; Lingamdinne, L.P.; Chang, Y.-Y.; Koduru, J.R. Carbon dots as adsorbents for removal of toxic chemicals. In Carbon Dots in Analytical Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 161–180. [Google Scholar]
- Majd, M.M.; Kordzadeh-Kermani, V.; Ghalandari, V.; Askari, A.; Sillanpää, M. Adsorption isotherm models: A comprehensive and systematic review (2010−2020). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 812, 151334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghouti, M.A.; Da’ana, D.A. Guidelines for the use and interpretation of adsorption isotherm models: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, D.; Zhou, H.; Xu, J.; Zhang, S. Studies on the interaction of salicylic acid and its monohydroxy substituted derivatives with bovine serum albumin. Chem. Phys. 2021, 546, 111182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huddleston, J.G.; Visser, A.E.; Reichert, W.M.; Willauer, H.D.; Broker, G.A.; Rogers, R.D. Characterization and comparison of hydrophilic and hydrophobic room temperature ionic liquids incorporating the imidazolium cation. Green Chem. 2001, 3, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhiman, D.; Bisht, M.; Tavares, A.P.M.; Freire, M.G.; Venkatesu, P. Cholinium-Based Ionic Liquids as Efficient Media for Improving the Structural and Thermal Stability of Immunoglobulin G Antibodies. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 5404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurnia, K.A.; Lima, F.; Cláudio, A.F.M.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Freire, M.G. Hydrogen-bond acidity of ionic liquids: An extended scale. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 18980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, M.; Simmons, B.A.; Sale, K.L.; Singh, S. Multiscale molecular simulations for the solvation of lignin in ionic liquids. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chemicalize Was Used for Dye Properties Discussion. Developed by ChemAxon. Available online: https://chemicalize.com/ (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Li, H.Y.; Chu, Y.H. Expeditious Discovery of Small-Molecule Thermoresponsive Ionic Liquid Materials: A Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 6817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellefqih, H.; Bilal, E.; Fakhreddine, R.; Mehdaoui, B.; Haneklaus, N.; Aatiq, A. Structural, vibrational, and optical studies of newly synthesized Yavapaiite-type phases BaSb2/3X1/3(PO4)2 (X = Mn, Co, Cu, Zn). Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2024, 163, 112347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jocić, A.; Marić, S.; Tekić, D.; Lazarević-Pašti, T.; Mušović, J.; Tričković, J.F.; Dimitrijević, A. Complete removal of organophosphate pesticides from wastewaters with sustainable ionic liquid-based aqueous two-phase strategy. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 64, 105621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, M.G. (Ed.) Ionic-Liquid-Based Aqueous Biphasic Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, A.M.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Fernandes, A.M.; Freire, M.G. Complete removal of textile dyes from aqueous media using ionic-liquid-based aqueous two-phase systems. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 128, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Ma, W.; Theyssen, N.; Chen, C.; Hou, Z. Temperature-Responsive Ionic Liquids: Fundamental Behaviors and Catalytic Applications. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 6881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Isotherm | AB9 | CI Limits (95%) | AY23 | CI Limits (95%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Langmuir | qm (mg/g) | 54.75 | 44.57 | 64.94 | −106.3 | −434.10 | 221.50 |
| b (L/mg) | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.03 | −8.82 | −2.59 × 10−3 | 8.25 × 10−4 | |
| R2 | 0.97 | 0.98 | |||||
| red.χ2 | 18.45 | 11.01 | |||||
| Freundlich | K (mg/g) | 2.02 | 0.14 | 3.89 | 0.04 | −0.11 | 0.18 |
| n | 1.71 | 1.19 | 2.23 | 0.81 | 0.38 | 1.25 | |
| R2 | 0.98 | 0.98 | |||||
| red.χ2 | 7.60 | 12.05 | |||||
| Langmuir–Freundlich | qm (mg/g) | 75.97 | 59.57 | 92.38 | 31,391.69 | −64,956.98 | 127,740.37 |
| b (L/mg) | 0.01 | 3.87 × 10−3 | 1.16 × 10−2 | 1.48 × 10−6 | −6.82 × 10−6 | 9.77 × 10−6 | |
| n | 1.01 | 0.59 | 1.41 | 1.19 | −8.02 | 10.41 | |
| R2 | 0.99 | 0.98 | |||||
| red.χ2 | 1.75 | 12.18 | |||||
| Temkin | B (J/mol) | 12.11 | −0.05 | 0.56 | 16.25 | −0.18 | 0.43 |
| A (L/g) | 0.25 | −7.71 | 31.94 | 0.13 | −3.57 | 36.07 | |
| R2 | 0.68 | 0.26 | |||||
| red.χ2 | 136.10 | 885.41 | |||||
| Dubinin–Radushkevich | qm (mg/g) | 47.04 | 36.90 | 57.18 | 58.2 | 57.41 | 58.98 |
| K (mol2 kJ−2) | 1.98 × 10−4 | −2.18 × 10−4 | 6.14 × 10−4 | 3.21 × 10−4 | 2.92 × 10−4 | 3.5 × 10−4 | |
| R2 | 0.94 | 0.86 | |||||
| red.χ2 | 24.59 | 35.23 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tekić, D.; Mušović, J.; Milojević-Rakić, M.; Jocić, A.; Dimitrijević, A. Innovative Green Strategy for the Regeneration of Spent Activated Carbon via Ionic Liquid-Based Systems. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9880. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15189880
Tekić D, Mušović J, Milojević-Rakić M, Jocić A, Dimitrijević A. Innovative Green Strategy for the Regeneration of Spent Activated Carbon via Ionic Liquid-Based Systems. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(18):9880. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15189880
Chicago/Turabian StyleTekić, Danijela, Jasmina Mušović, Maja Milojević-Rakić, Ana Jocić, and Aleksandra Dimitrijević. 2025. "Innovative Green Strategy for the Regeneration of Spent Activated Carbon via Ionic Liquid-Based Systems" Applied Sciences 15, no. 18: 9880. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15189880
APA StyleTekić, D., Mušović, J., Milojević-Rakić, M., Jocić, A., & Dimitrijević, A. (2025). Innovative Green Strategy for the Regeneration of Spent Activated Carbon via Ionic Liquid-Based Systems. Applied Sciences, 15(18), 9880. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15189880








