A Study on the Application of Genetic Algorithms to the Optimization of Road Maintenance Strategies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Maintenance Strategy Optimization (Materials and Methods)
2.1. Problem Description
2.2. Model Construction
2.2.1. Parameters and Variables
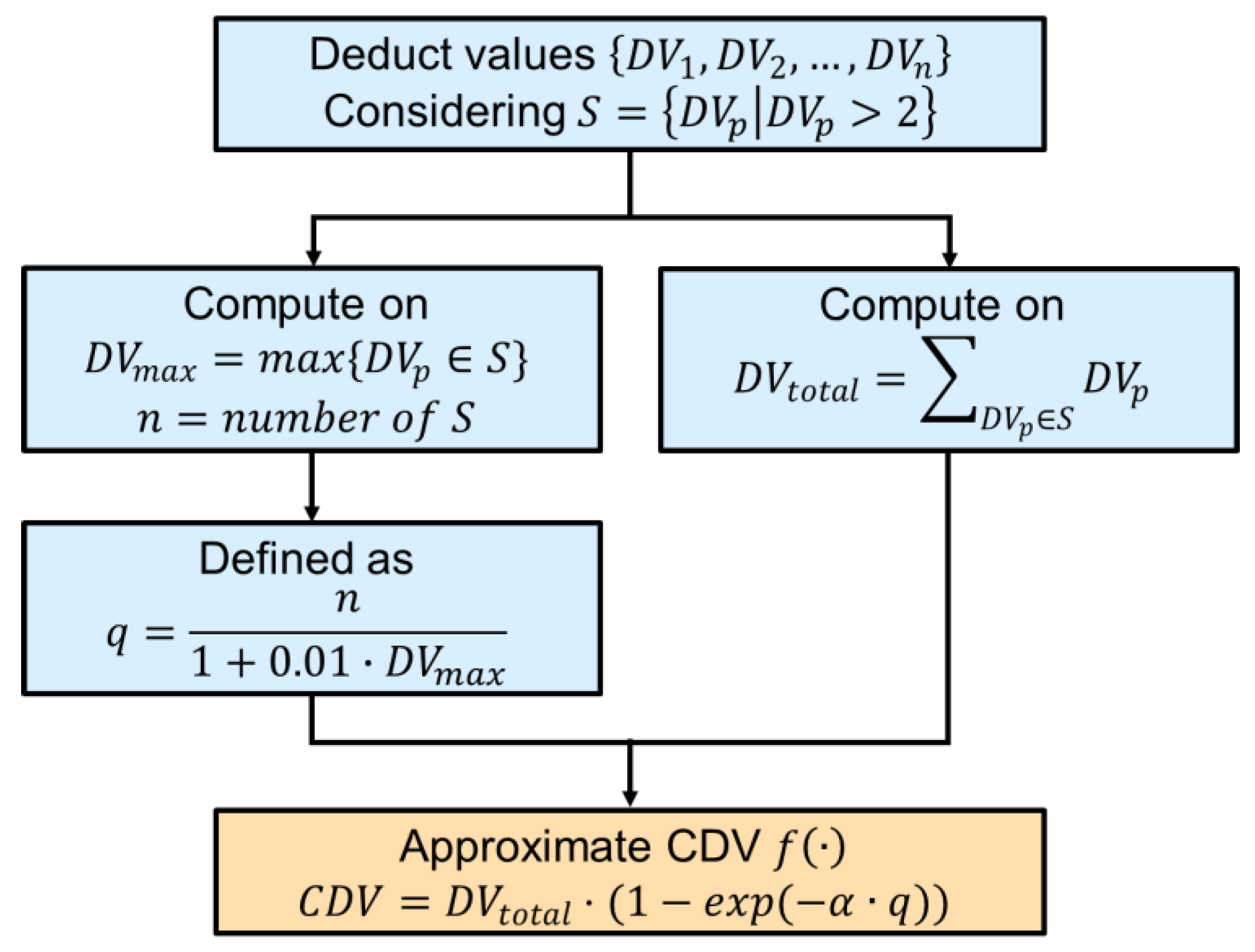
2.2.2. Objective Function
2.2.3. Constraints
- A.
- Non-overlapping constraint of resurfacing segments
- B.
- Constraint on marking all distresses within resurfacing segments
- C.
- Constraint of a unique maintenance method for a distress
- D.
- Budget constraint
2.3. Genetic Algorithm Design
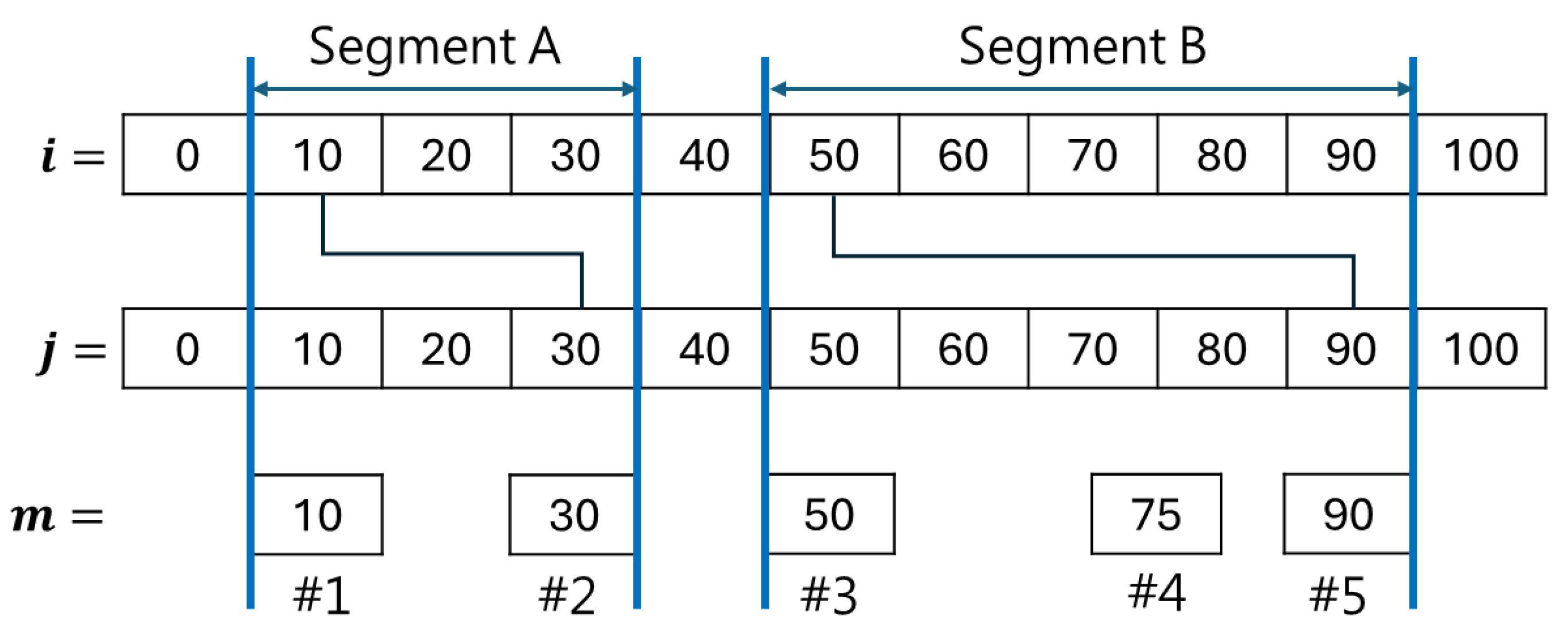
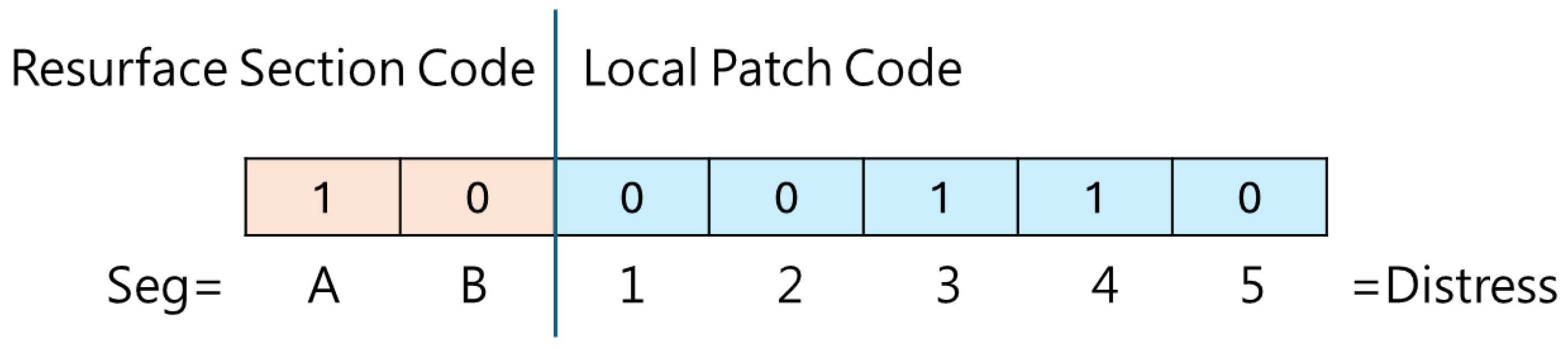
2.3.1. Chromosome Encoding Design
2.3.2. Fitness Function Design
3. Case Study
3.1. Data Sources
3.2. Scenario Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Margorínová, M.; Trojanová, M.; Decký, M.; Remišová, E. Noise costs from road transport. Civ. Environ. Eng. 2018, 14, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fwa, T.F.; Chan, W.T.; Hoque, K.Z. Analysis of pavement management activities programming by genetic algorithms. Transp. Res. Rec. 1998, 1643, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhadidy, A.A.; Elbeltagi, E.E.; Ammar, M.A. Optimum analysis of pavement maintenance using multi-objective genetic algorithms. HBRC J. 2015, 11, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.; Ferreira, A.; Flintsch, G. A multi-objective optimization approach for sustainable pavement management. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2018, 14, 854–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.; Ferreira, A.; Flintsch, G. An adaptive hybrid genetic algorithm for pavement management. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2019, 20, 266–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamany, M.S.; Abraham, D.M.; Ventresca, M.; Nantung, T.; Labi, S. Probabilistic optimization of pavement preventive maintenance using multi-objective genetic algorithm. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 2025, 10, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamany, M.S.; Cawley, L.; Reza, I.; Ksaibati, K. Network-level pavement maintenance and rehabilitation planning using genetic algorithm. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 2024, 9, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Remenyte-Prescott, R.; Andrews, J.D. Pavement maintenance scheduling using genetic algorithms. Int. J. Perform. Eng. 2015, 11, 135. [Google Scholar]
- Hamdi, H.; Hadiwardoyo, S.P.; Correia, A.G.; Pereira, P.A. Pavement maintenance optimization strategies for national road network in Indonesia applying genetic algorithm. Procedia Eng. 2017, 210, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Li, S.; Zhou, X. Preventive maintenance decision-making optimization method for airport runway composite pavements. Transp. Res. Rec. 2019, 2673, 227–237. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Luo, F. Integer search algorithm: A new discrete multi-objective algorithm for pavement maintenance management optimization. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 160, 113699. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, K.; Zhang, T.; Liu, M. Research on multi-Objective Pavement Maintenance Decision-Making Optimization Considering Uncertainty Factors. Master’s Thesis, Chang’an University, Xi’an, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, F.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Jin, M.; Chen, D. Optimizing rural highway maintenance scheme with mathematical programming. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 8253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Zhang, H.; Du, X.; Zhang, X.; Sun, M.; Bi, Y. Optimization for asphalt pavement maintenance plans at network level: Integrating maintenance funds, pavement performance, road users, and environment. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, F.; Zhao, X. MILP-based approach for high-altitude region pavement maintenance decision optimization. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Q.; Lin, T. A pavement crack detection and evaluation framework for a UAV inspection system based on deep learning. Autom. Constr. 2022, 138, 104273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, L.; Yu, P. A highway pavement crack identification method based on an improved U-Net model. J. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 25, 525–537. [Google Scholar]
- Bruno, S.; Colonnese, S.; Scarano, G.; Del Serrone, G.; Loprencipe, G. Pavement distress estimation via signal on graph processing. Sensors 2022, 22, 9183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loprencipe, G.; Pantuso, A. A specified procedure for distress identification and assessment for urban road surfaces based on PCI. Coatings 2017, 7, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New Taipei City Government. New Taipei City Smart Pavement Management Center and Road Maintenance Analysis; Municipal Infrastructure Report; New Taipei City Government: New Taipei City, China, 2023.
- Sun, W.; Lin, C.; Hou, J. Using an airport pavement management system to optimize the influence of maintenance alternatives on operating conditions. J. Transp. Eng. Part B Pavements 2018, 144, 04018017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Yi, W.; Song, Y.; Gao, Y.; Wu, P. Optimizing large-scale road maintenance plan in Western Australia. SSRN 2024, preprint. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.; Che, C. Optimizing urban road networks for resilience using genetic algorithms. Acad. J. Sociol. Manag. 2024, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Fard, A.; Yuan, A.X.X. Multi-year maintenance planning for large-scale infrastructure systems: A novel network deep Q-learning approach. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2507.18732. [Google Scholar]
- Indriastiwi, F.; Hadiwardoyo, S.P. Optimizing multimodal infrastructure development in Java: A budget-constrained planning approach. Civ. Eng. Archit. 2025, 13, 2735–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadifakhr, K.; Roy, S.; Han, F.; Bell, E. Flowing together: Synergistic road-stream crossing replacement prioritization for balanced stakeholder interests. In Proceedings of the AGU Fall Meeting 2024, Washington, DC, USA, 9–13 December 2024. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM D6433-18; Standard Practice for Roads and Parking Lots Pavement Condition Index Surveys. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2018.
- Kim, H.; Park, J.; Shin, Y. Pavement maintenance decision making based on optimization models. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2022, 28, 04022025. [Google Scholar]
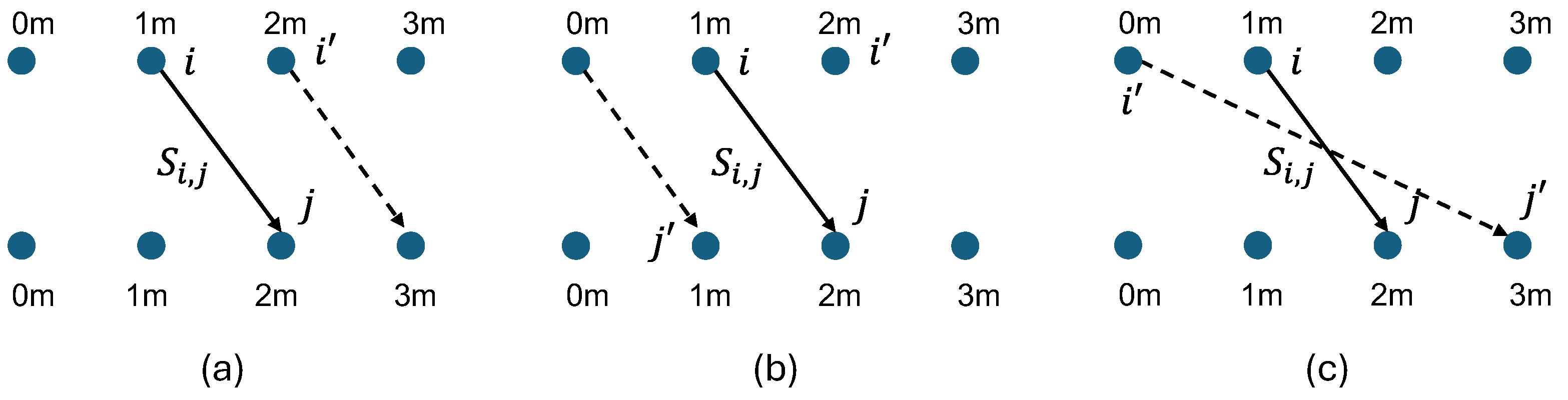

| Symbols | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Distress point index, . | |
| Resurfacing segment index, satisfying 0 ≤ i ≤ j ≤ L. | |
| Total road length (meters). | |
| Total number of distresses. | |
| The location of the m-th distress, in meters, indicating the specific location of the m-th distress on the road. | |
| The deduction value of the m-th distress, indicating the deduction incurred if that distress is not properly repaired. | |
| The repair cost of the m-th distress, expressed in monetary units, indicating the cost to repair that distress. | |
| The cost of resurfacing maintenance per meter, indicating the cost required to repair 1 m of road. | |
| The total maintenance budget, indicating the total amount of available funds in all maintenance activities. | |
| If the road segment from meter i to meter j undergoes resurfacing maintenance, then it is 1, otherwise it is 0. | |
| If the m-th distress is repaired by resurfacing, then it is 1, otherwise it is 0. | |
| If the m-th distress is repaired by local maintenance, then it is 1, otherwise it is 0. |
| ID | Location | Type | Method | Cost (USD) | Discovery |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3K+772 | Rutting | Local rehabilitation | 454 | Contractor patrol inspection |
| 2 | 10K+529 | Alligator cracking | Shallow pothole filling | 210 | Contractor patrol inspection |
| 3 | 9K+728 | Rutting | Local patching | 567 | Contractor patrol inspection |
| 4 | 1K+324 | Longitudinal and transverse cracks | Local thin overlay | 186 | Contractor patrol inspection |
| 5 | 7K+212 | Patching | Local rehabilitation | 435 | Contractor patrol inspection |
| 6 | 3K+595 | Patching | Local thin overlay | 163 | Contractor patrol inspection |
| 7 | 7K+595 | Rutting | Shallow pothole filling | 260 | Contractor patrol inspection |
| 8 | 1K+107 | Patching | Local rehabilitation | 589 | Contractor patrol inspection |
| 9 | 10K+692 | Potholes | Local rehabilitation | 635 | Contractor patrol inspection |
| 10 | 5K+349 | Patching | Shallow pothole filling | 366 | Contractor patrol inspection |
| 11 | 11K+516 | Alligator cracking | Local rehabilitation | 410 | Contractor patrol inspection |
| 12 | 3K+675 | Potholes | Local rehabilitation | 385 | Contractor patrol inspection |
| 13 | 2K+648 | Rutting | Local patching | 517 | Contractor patrol inspection |
| 14 | 6K+479 | Rutting | Shallow pothole filling | 210 | Contractor patrol inspection |
| 15 | 8K+295 | Longitudinal and transverse cracks | Local patching | 367 | Contractor patrol inspection |
| 16 | 6K+918 | Patching | Local thin overlay | 199 | Contractor patrol inspection |
| 17 | 11K+183 | Patching | Local patching | 594 | Contractor patrol inspection |
| 18 | 5K+903 | Rutting | Local patching | 436 | Contractor patrol inspection |
| 19 | 9K+296 | Patching | Local patching | 564 | Contractor patrol inspection |
| 20 | 10K+132 | Rutting | Shallow pothole filling | 200 | Contractor patrol inspection |
| Maintenance Method | Applicable Situation | Construction Method | Cost per Square Meter (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shallow pothole filling | Repair small-area and shallow potholes on the pavement. | Clean the pothole area, remove loose material or debris, then fill with appropriate repair material. | 200~400 |
| Local patching | A repair method for small-scale pavement damage, particularly suitable for cracks, potholes, or other local damage. | Clean the damaged area, remove loose material, then fill with repair materials such as asphalt or concrete, and compact. | 300~600 |
| Local rehabilitation | Repair pavement with larger-area or moderate-severity damage. | Lay a new layer of asphalt on the original pavement surface layer, and compact. | 350~700 |
| Local thin overlay | Applicable to situations where the pavement surface layer has slight wear, aging, or slight cracks. | Evenly apply asphalt emulsion on the original pavement surface, then spread crushed stone or aggregate, and compact. | 100~200 |
| Lane Length (Meters) | Resurfacing Cost (USD) |
|---|---|
| 5 | 6400 |
| 10 | 7700 |
| 15 | 9033 |
| 20 | 10,267 |
| 25 | 11,333 |
| 30 | 12,567 |
| 35 | 15,733 |
| 40 | 17,000 |
| 45 | 18,233 |
| 50 | 19,467 |
| 100 | 31,000 |
| 150 | 43,333 |
| 200 | 56,000 |
| 250 | 68,000 |
| 300 | 80,333 |
| 350 | 93,333 |
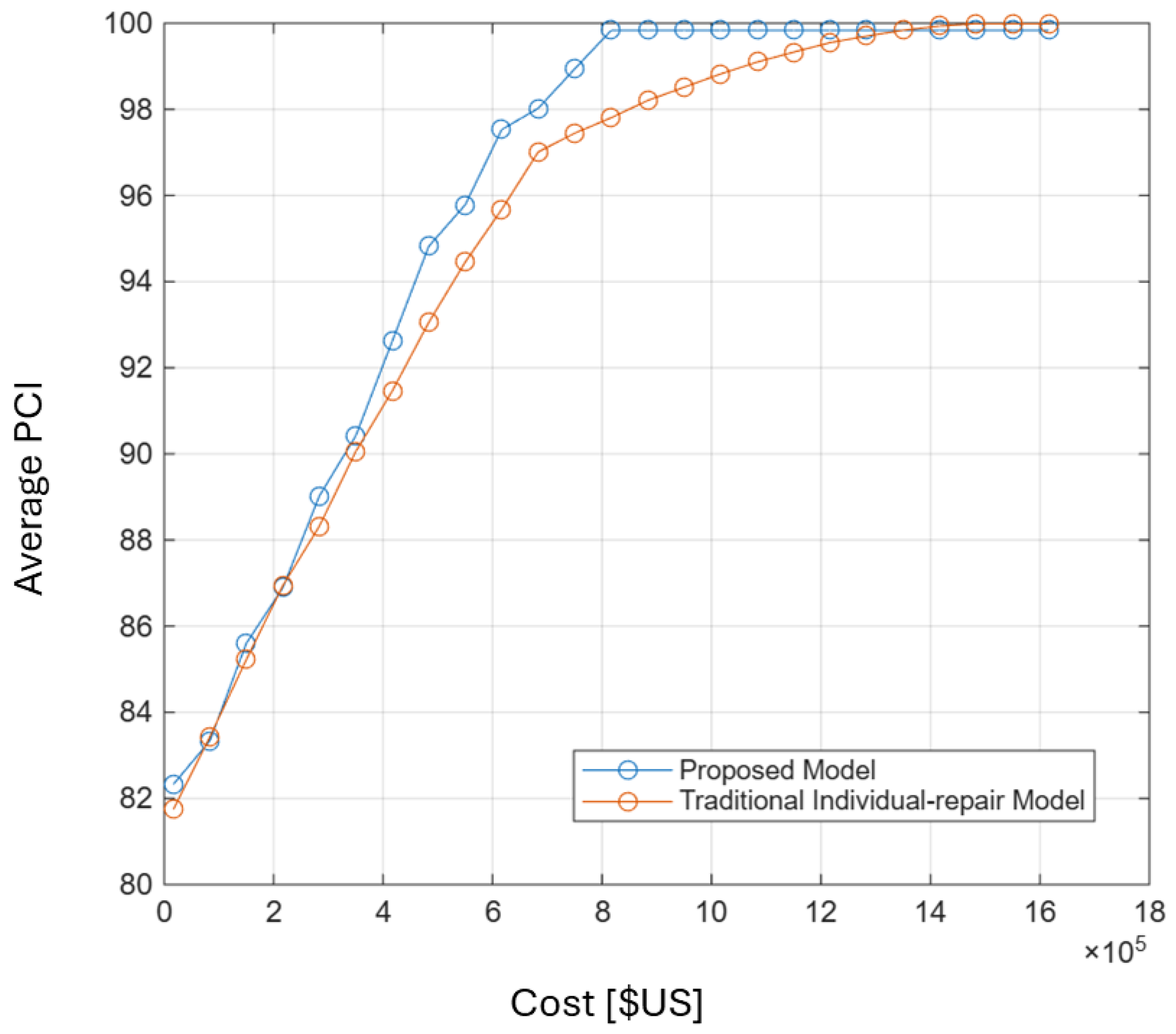
| Budget (USD) | Average PCI of Method | Average PCI of Individual Maintenance Method |
|---|---|---|
| USD 20,000 | 82.52 | 82.21 |
| USD 80,000 | 83.74 | 83.74 |
| USD 150,000 | 87.00 | 85.65 |
| USD 220,000 | 88.80 | 87.35 |
| USD 280,000 | 91.13 | 88.99 |
| USD 350,000 | 92.66 | 90.31 |
| USD 420,000 | 93.66 | 91.80 |
| USD 480,000 | 94.80 | 93.12 |
| USD 550,000 | 96.43 | 94.17 |
| USD 620,000 | 97.53 | 95.40 |
| USD 680,000 | 98.67 | 96.92 |
| USD 750,000 | 99.31 | 97.41 |
| USD 820,000 | 100.00 | 97.78 |
| USD 880,000 | 100.00 | 98.09 |
| USD 950,000 | 100.00 | 98.40 |
| USD 1,020,000 | 100.00 | 98.71 |
| USD 1,080,000 | 100.00 | 98.95 |
| USD 1,150,000 | 100.00 | 99.16 |
| USD 1,220,000 | 100.00 | 99.40 |
| USD 1,280,000 | 100.00 | 99.55 |
| USD 1,350,000 | 100.00 | 99.71 |
| USD 1,420,000 | 100.00 | 99.82 |
| USD 1,480,000 | 100.00 | 99.92 |
| USD 1,550,000 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| USD 1,620,000 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
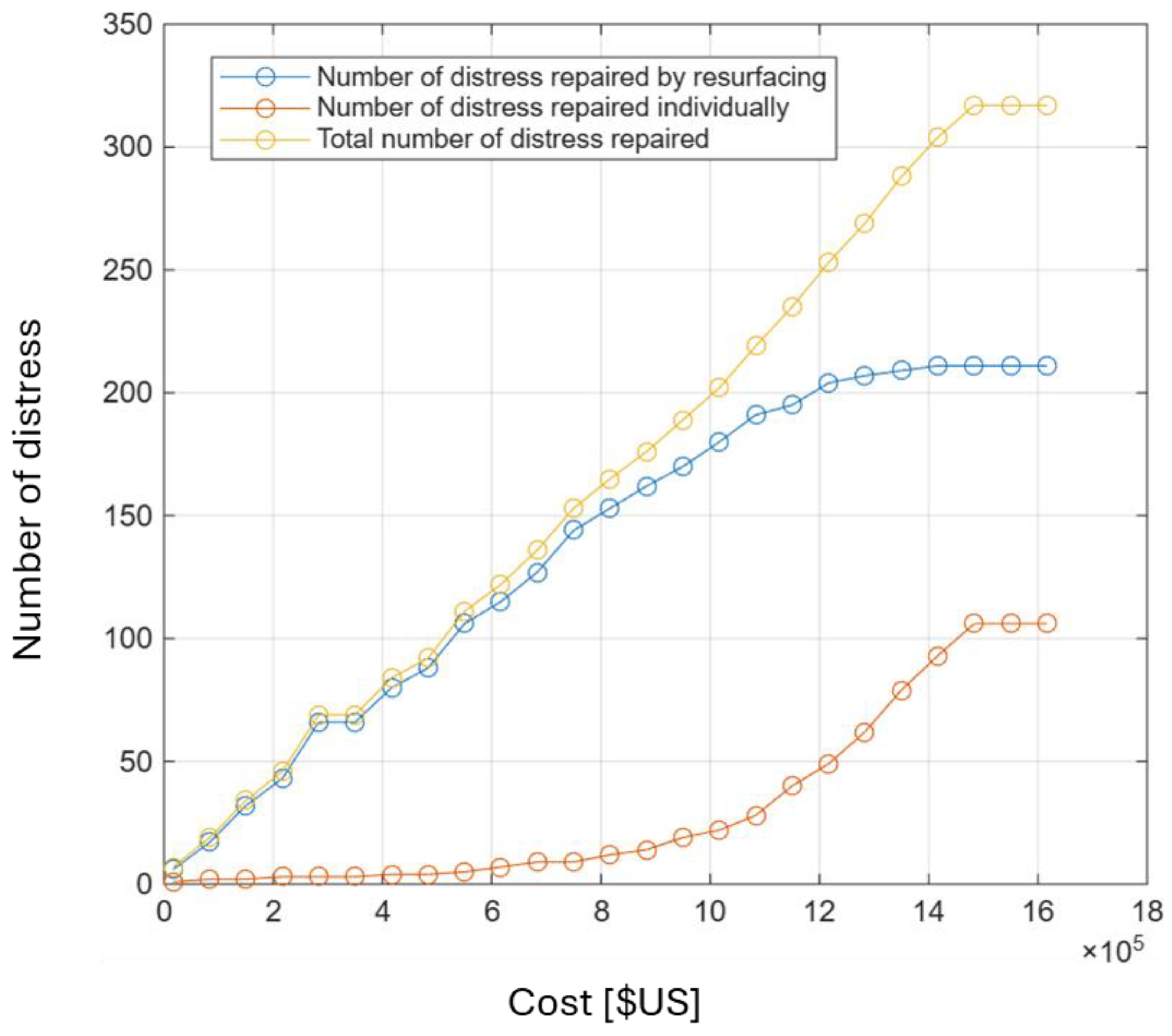
| Start (Meters) | End (Meters) | Number of Distresses | Average Deduction Value | Resurfacing Length (Meters) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 47 | 3 | 24.00 | 45 |
| 81 | 96 | 3 | 4.33 | 15 |
| 153 | 173 | 2 | 4.50 | 20 |
| 199 | 224 | 2 | 13.00 | 25 |
| 454 | 489 | 3 | 20.67 | 35 |
| 608 | 618 | 1 | 21.00 | 10 |
| 743 | 748 | 1 | 5.00 | 5 |
| 764 | 864 | 7 | 13.86 | 100 |
| 924 | 949 | 3 | 4.33 | 25 |
| 1018 | 1043 | 2 | 27.50 | 25 |
| 1463 | 1513 | 5 | 11.80 | 50 |
| 1628 | 1778 | 10 | 15.50 | 150 |
| 1847 | 1877 | 2 | 22.00 | 30 |
| 1923 | 1928 | 1 | 25.00 | 5 |
| 2049 | 2089 | 3 | 24.33 | 40 |
| 2176 | 2181 | 1 | 37.00 | 5 |
| 2294 | 2444 | 8 | 14.38 | 150 |
| 2608 | 2623 | 2 | 18.50 | 15 |
| 2955 | 3000 | 3 | 20.00 | 45 |
| 3227 | 3257 | 3 | 12.00 | 30 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chiou, Y.-S.; Ho, M.-C.; Song, P.-Y.; Lin, J.-D.; Lu, S.-H.; Ke, C.-y. A Study on the Application of Genetic Algorithms to the Optimization of Road Maintenance Strategies. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 10094. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151810094
Chiou Y-S, Ho M-C, Song P-Y, Lin J-D, Lu S-H, Ke C-y. A Study on the Application of Genetic Algorithms to the Optimization of Road Maintenance Strategies. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(18):10094. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151810094
Chicago/Turabian StyleChiou, Yi-Shian, Min-Che Ho, Pin-Yu Song, Jyh-Dong Lin, Szu-Han Lu, and Chi-yun Ke. 2025. "A Study on the Application of Genetic Algorithms to the Optimization of Road Maintenance Strategies" Applied Sciences 15, no. 18: 10094. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151810094
APA StyleChiou, Y.-S., Ho, M.-C., Song, P.-Y., Lin, J.-D., Lu, S.-H., & Ke, C.-y. (2025). A Study on the Application of Genetic Algorithms to the Optimization of Road Maintenance Strategies. Applied Sciences, 15(18), 10094. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151810094





