Abstract
Cotton is one of the most important crops worldwide, having considerable economic importance in Greece. This study aimed to evaluate the fiber quality traits of partially interspecific cotton lines under contrasting irrigation and nitrogen environments within a strip-split block field design. Experiments conducted over two consecutive years include a control (commercial cultivar Celia) and four partially interspecific lines of the Pa7 generation (Gossypium hirsutum × G. barbadense). Three irrigation and two nitrogen fertilization levels were applied. Significant differences were observed among genotypes and environments for all fiber quality traits, with some year-to-year variation. Genotypic response for yellowness was influenced by fertilization. Across the two experimental years, a strong Fertilization × Environment interaction was observed, and in the second year, a Genotype × Fertilization × Environment interaction was detected for the uniformity index. Pa7 lines consistently outperformed Celia in fiber length (≈33 vs. 30 mm) and elongation (≈7.0 vs. 5.5%), while exhibiting higher yellowness values. Fiber strength, micronaire, uniformity, and reflectance varied between years but remained within acceptable ranges. Overall, Pa7 lines demonstrated superior fiber quality and stability under variable conditions, highlighting their potential for breeding programs. These findings support the importance of integrating interspecific germplasm with suitable irrigation–nitrogen management to improve cotton fiber performance and resilience under diverse cultivation environments.
1. Introduction
Cotton is one of the most important crops cultivated worldwide [1] and plays a critical role in global textile production. In Greece, cotton holds substantial economic significance [2], with the country recognized as one of Europe’s leading producers. Cotton farming provides a primary source of income for over 100,000 households [2], while the cotton-based textile industry represents a major industrial sector in terms of employment. Greece accounts for the largest share of Europe’s cotton cultivation, covering approximately 80% of the continent’s cotton-growing area and contributing more than 8% to the nation’s total agricultural output [3]. With a planted surface reaching 224,000 hectares, Greece plays a dominant role in European cotton production, which in turn underlines the importance of producing a high-quality fiber to retain market advantages [3]. Both the quantity and quality of cotton affect the earnings of farmers [4]. Improving fiber quality and its stability is therefore a priority not only for breeders but also for growers and industry stakeholders.
Fiber quality is a combination of characteristics, including fiber length, fiber strength, fiber elongation, uniformity index, micronaire, yellowness, and reflectance index, which are considered crucial for the textile industry, improving the quality of the final product [5,6,7].
Interspecific hybridization, particularly between G. hirsutum and G. barbadense, is a promising strategy for improving fiber properties [8]. G. barbadense is used for its longer, stronger, and finer fibers in comparison to G. hirsutum, which is commonly cultivated for better yielding performance [9]. Interspecific hybrids have been proven to be vigorous [10] and thus many studies have been conducted to analyze the yield performance and fiber quality of these hybrids [11,12,13,14]. Methods for developing interspecific hybrids were described by Endrizzi [15] and Kohel et al. [16]. Mavromatis and Roupakias [17] consider that cotton partial interspecific hybrids are homozygous plants that include (in the nucleus) chromosomes or parts of them that exist in homozygous condition and belong to the respective species. The first interspecific lines in cotton were developed after the pollination of F1 hybrids (G. hirsutum and G. barbadense) with pollen from Hibiscus cannabinus [18] and in successive generations, with pollen from Abelmoschus esculentus [19,20].
Plant breeders can improve stability by identifying the factors responsible for genotype stability or the genotype × environment interaction. Resistance or tolerance to biotic and abiotic stresses is critical for its stable performance, and thus, it is necessary to identify the various factors responsible for such interactions [21]. The impact of different abiotic factors on cultivated plants varies depending on the location and season. Thus, testing different genetic materials for a specific area is necessary to cope with abiotic stresses [22,23].
Many researchers [24,25] report that cotton yield and fiber quality are affected across environments. Among the key agronomic factors, water availability and nitrogen fertilization play a critical role in determining cotton fiber quality. Recent research reveals that both irrigation depth and nitrogen application rates significantly influence fiber traits, emphasizing the importance of optimized resource management for achieving stable and high-quality fibers [26]. Moreover, the strategic application of additional N, P, and K fertilizers contributes to maintaining productive, profitable, and sustainable cotton cultivation systems [27,28]. Generally, fertilizer, along with irrigation, supports both the quantity and quality of cotton [4]. Fiber length is mostly not affected by nitrogen fertilization [29,30]. Only in extremely deficient field conditions, nitrogen may affect fiber length [31]. According to reports, nitrogen has little impact on the fiber’s micronaire and strength [29,32]. Shorter fibers may occur from insufficient cell expansion in the case of a water deficit shortly after flowering [33,34,35,36]. Fiber length was increased after increasing irrigation according to Lascano and Hicks [37] and Balkcom et al. [38], but Campbell and Bauer [39] reported a decreased fiber length (according to irrigation level), micronaire, fiber uniformity, and fiber strength. According to Basal et al. [40], fiber strength is negatively affected by a water deficit, indicating a sensitivity of this trait to limited water availability. Micronaire was not affected by water [40,41], but in some cases, water stress may reduce micronaire [36,42] or even increase it [43]. Increased irrigation may reduce or increase micronaire units [44], but generally, increased irrigation resulted in decreased micronaire [37,38,45].
The objective of this study was to estimate fiber quality traits in partially interspecific Pa7 lines across environments defined by irrigation and nitrogen combinations. We aimed to quantify genetic differences, assess trait stability, and identify promising genotypes for cotton breeding programs under variable management conditions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Conditions
The experiments of this study were conducted at the experimental farm of the Aristotle University of Thessaloniki [46], located in Northern Greece (22°59′6.17″ E, 40°32′9.32″ N, elevation 10 m) for two consecutive years. These two years were deliberately selected because they represented contrasting climatic conditions in terms of rainfall and temperature distribution. The year 2006 had average rainfall and temperature, while 2007 had a hot, dry summer. Such variation provided distinct environments to test genotype × environment interactions. Although the experiment was performed nearly two decades ago, its findings remain relevant and applicable regarding evaluating fiber quality stability in the Mediterranean region, which faces an immediate climate change issue.
Each year, to guide fertilization practices, pre-planting soil chemical analyses are conducted to assess baseline fertility. The soil type was a calcareous loam (Typic Xerorthent); in 2006 the pH was 7.71, organic matter content was 1.15%, N-NO3 was 8.4 ppm, P (Olsen) was 9.8 ppm, and K was 135 ppm, whereas in 2007, pH was 8, organic matter content was 2.63%, N-NO3 was 53.2 ppm, P (Olsen) was 16.2 ppm, and K was 189 ppm (at 0–30 cm depth).
Table 1 shows daily recorded environmental data (maximum and minimum temperatures, and rainfall).

Table 1.
Monthly means of maximum (Max), minimum (Min) air temperatures (in °C) and rainfall (in mm) for 2006 and 2007 in Thessaloniki, Greece.
2.2. Genetic Materials
The genetic material comprised four partially interspecific cotton lines from the Pa7 generation (G. hirsutum × G. barbadense). These lines were developed by pollinating F1 hybrids between G. hirsutum (4S, Coker 310) and G. barbadense (B403, Carnak) with pollen from Hibiscus cannabinus L. [18]. The commercial cultivar Celia was included as a control because of its proven adaptation to local conditions and its frequent use in comparative fiber quality studies, providing a reliable benchmark for evaluating the performance of the Pa7 lines (Table 2). The interspecific lines were selected to capture complementary characteristics of the parental species.

Table 2.
Pedigree of plant material assessed and codified in 2006, 2007 (M1–M4 are Pa7 partially interspecific lines).
2.3. Experimental Design
A strip-split factorial design with three replications was employed to investigate the combined effects of irrigation, nitrogen fertilization, and genotype performance. Irrigation treatments were applied in strips (three levels in 2006; adjusted in 2007 due to water limitations), while nitrogen fertilization rates (40 and 80 kg ha−1) were imposed perpendicularly. Genotypes were randomized within each irrigation × nitrogen combination, ensuring a complete factorial structure. This layout allowed every combination of irrigation and nitrogen regime to be treated as a distinct experimental condition.
Although irrigation scheduling was modified in 2007 due to environmental constraints, the same strip-split factorial framework was maintained across both years, allowing valid comparisons. For the purposes of combined analysis, we considered environments as the combinations of year and irrigation level, resulting in six environments across the two growing seasons. Within each irrigation block, nitrogen treatments and genotypes were randomized independently, minimizing systematic bias and maintaining the validity of treatment contrasts.
This experimental arrangement facilitated the estimation of main effects and interactions among genotypes, irrigation, and nitrogen fertilization. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) was applied to partition the total variation into its respective sources. Defining “environments” as year × irrigation combinations follows the framework of Stratilakis and Goulas [47], which helps to reduce uncontrolled interactions and enables a clearer interpretation of variance components under contrasting water and nutrient regimes. We treat Year × Irrigation as the environment because irrigation defines moisture regimes while Year captures the seasonal climatic backdrop; nitrogen is an experimental factor within these environments.
Each experimental plot consisted of seven rows, 8.0 m in length, with 1.0 m spacing between rows. For statistical analysis, data were collected only from the five central rows, while the two outer rows, sown with the commercial cultivar Celia, served as border rows to minimize edge effects. Genotypes were randomly assigned within the established strips to ensure unbiased comparisons.
2.4. Fertilizer and Irrigation Application
Three irrigation levels were applied each year, corresponding to 233, 333, and 433 mm in 2006 and 321, 421, and 521 mm in 2007, maintaining a consistent 100 mm spacing between levels despite the higher summer temperatures in 2007 (Table 3). Two nitrogen rates, 40 and 80 kg N ha−1, were applied in accordance with locally relevant agronomic practices. To ensure sufficient soil moisture for germination, the first two irrigations after sowing were applied as artificial rainfall, whereas subsequent irrigations were delivered via drip irrigation (Table 3). Irrigation scheduling was guided by continuous soil water monitoring, ensuring that full, moderate, and deficit irrigation levels accurately reflected target soil water availability and agronomic recommendations. These treatments established management-defined water regimes that simulated field conditions and accounted for inter-annual climatic variability.

Table 3.
Dates and level of irrigation (in mm) applied and rainfall at the experimental field in 2006 and 2007.
Pre-sowing soil analyses indicated differences in nutrient availability between the two years. In 2007, boron (20 kg ha−1) and a zinc-based foliar fertilizer were applied to correct micronutrient deficiencies identified in the soil, whereas these amendments were unnecessary in 2006. Nitrogen treatments were selected to reflect local management practices and experimental objectives. This experimental framework enabled a controlled assessment of genotype performance under variable water and nitrogen conditions while maintaining consistent irrigation spacing, timing, and nutrient application across years.
The plant growth regulator mepiquat chloride was applied at a rate of 150 mL and 300 mL per 100 L of water in 2006 and 2007, respectively.
2.5. Crop Management
For the 2007 sowing, seeds were pre-screened to remove damaged and/or infertile seeds, whilst in 2006, they were not. Sowing was conducted on 25 April 2006 and 4 May 2007. Seed cotton was harvested manually in two stages in both years: 4–6 October and 16 November. Throughout the growing seasons, the standard agronomic procedures, determined by official cotton yield evaluation trials, were implemented.
Weed control was achieved using pre- and post-emergence herbicides, including trifluralin, fluometuron, and fluazifop-p-butyl, supplemented by hand-weeding and mechanical methods to maintain weed-free plots. Pest management included applications of insecticides targeting Lygus spp. and green and pink bollworm, such as dimethoate, endosulfan, chlorpyrifos, deltamethrin, methomyl, and lambda-cyhalothrin. Acaricides, including propargite, dicofol, and fenbutatin oxide, were applied to control mite populations, while imidacloprid was used against aphids. Fungal diseases caused by Alternaria were managed using copper hydroxide, captan, and mancozeb. At crop maturity, chemical defoliation was performed using a combination of ethephon and cyclanilide.
2.6. Measurements
At crop maturity, fiber samples were collected and analyzed using a High Volume Instrument (HVI) system (Zellweger Uster Inc., Uster, Switzerland) to assess technological properties relevant to textile performance. Measured traits included fiber length (mm), fiber strength (g tex−1), fiber elongation (%), uniformity index (%), micronaire units (fiber fineness), yellowness (+b), and reflectance index (%). HVI equipment was calibrated daily using USDA calibration cottons; the maintenance followed the manufacturer’s guidelines, ensuring reproducibility.
Fiber length was reported as the 2.5% span length, and the uniformity index was calculated as the ratio of the 50% span length to the 2.5% span length (50/2.5), expressed as a percentage. Fiber strength was determined by clamping bundles of fibers between two sets of clamps at a defined distance and measuring the force required to break them. Elongation was calculated as the percentage increase in fiber bundle length before breakage. Micronaire values provided an indirect measurement of fiber fineness by relating airflow resistance to fiber surface area; finer fibers yielded lower micronaire readings. Cotton color was evaluated by reflectance index (Rd) and yellowness (+b), which together quantify the degree of fiber pigmentation and overall whiteness [48].
2.7. Statistical Analysis
In the combined analysis, environments were defined as the interaction of year and irrigation level (Year × Irrigation), with each combination treated as a distinct environment. This approach allowed the evaluation of genotype performance under varying water regimes and inter-annual climatic conditions. Combined analysis of variance (ANOVA) was conducted using a fixed-effects model, following the methodology described by Steel et al. [49]. Separate ANOVAs were also performed for individual years and irrigation levels to further examine the contributions that specific factors have. In all ANOVAs, fertilization (F; 40 vs. 80 kg N ha−1) was explicitly included as a fixed factor together with genotype (G) and environment (E = Year × Irrigation). The factorial model therefore examined the main effects of G, F, and E, as well as their two- and three-way interactions (G × E, F × E, G × F, G × F × E). Replications were nested within environments and used as the error term for environment effects.
Means were compared using Duncan’s multiple range test as implemented in MSTAT-C (Michigan State University).
Genotype stability across environments was evaluated using a stability index [50], calculated as where represents the entry mean yield and s the standard deviation. ANOVA was used to analyze the data across environments to reveal significant differences for all the variables examined in this study. These analyses allowed the quantification of both average performance and consistency of genotypes across environments.
For each irrigation regime and experimental year, data were collected on fiber quality traits and subsequently summarized as mean values and standard deviations (SD). These statistics were used to characterize both the central tendency and the variability of each parameter under the different water regimes. To evaluate adaptability, a mean–stability (balance) approach was applied, in which the across-irrigation mean of each trait was plotted against its respective SD. This visualization provided a direct assessment of the relationship between performance and stability, allowing traits with high means and low variability to be identified as more desirable under variable irrigation conditions. The graphical representation of this analysis is shown in Figure 1.
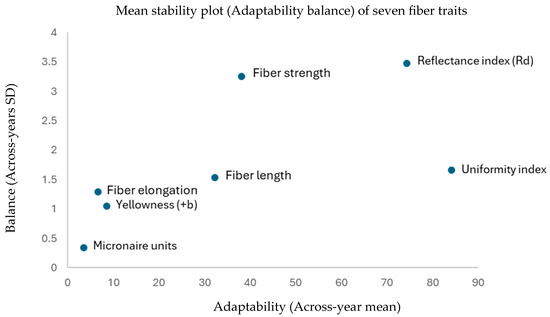
Figure 1.
Mean–stability (adaptability balance) plot of seven fiber quality traits: fiber length (mm), fiber strength (g tex−1), fiber elongation (%), uniformity index (%), micronaire units, yellowness (+b), and reflectance index (%). The x-axis represents the mean value of each trait averaged across irrigation levels and years, while the y-axis represents the corresponding standard deviation (SD), indicating stability. Traits located towards the right and lower regions of the plot reflect higher performance combined with greater stability, thereby illustrating adaptability under different irrigation conditions.
Pearson correlation coefficients among the seven fiber traits were calculated using all plot-level observations (3 replications × 3 irrigation levels × 2 nitrogen rates × 5 genotypes × 2 years), ensuring adequate statistical power. Diagnostic assessments confirmed the approximate normality of residuals.
Principal component analysis (PCA) was conducted on standardized genotype-by-year mean values for the seven traits. Variables were centered and scaled (z-scores), and principal components were extracted from the correlation matrix. The resulting PC1 versus PC2 score plot illustrates genotype–year distributions, while the loading plot depicts trait contributions and relationships. Pearson’s correlation among the parameters studied and the PCA (Principal Components Analysis) are performed using JMP 18 statistical software (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA). Significance is given at α = 0.05.
3. Results
Table 4 presents ANOVA for quality characteristics. As specified in the statistical model, fertilization (F) was analyzed together with genotype (G) and environment (E). Although its direct effects were limited, fertilization significantly affected yellowness and contributed through F × E and G × F × E interactions to variation in the uniformity index. These findings highlight that nitrogen fertilization, while not the dominant source of variation, influenced specific fiber quality traits directly and in combination with other factors (Table 4 and Tables S1–S3). There were statistically significant differences between environments (irrigation levels) and genotypes for all quality characteristics. For fiber strength, a diversified behavior of genotypes across environments was found, with a significant G × E interaction. A novelty in our approach is that we consider irrigation and thus water efficiency in different environments. CV coefficients were generally low for fiber length (3.8%), fiber elongation (3.8%), uniformity index (1.7%), and reflectance index (2.6%). Micronaire units and yellowness exhibited CVs over 9%.

Table 4.
Combined analysis ANOVA for fiber length (mm), fiber strength (g tex−1), fiber elongation (%), uniformity index (%), micronaire units, yellowness (+b), and reflectance index (%) across artificial/considered environments over two years within each of the three irrigation levels.
ANOVA results for the two years of experimentation are shown in Table S1. In both years of the trial, there were genotype-to-genotype variations for all quality characteristics, which were statistically significant (except for micronaire units in 2007). The environment affected the uniformity index, micronaire, and yellowness in 2007. Fertilization again affected genotype behavior for yellowness for each year. For the uniformity index, a significant Fertilization × Environments (F × E) and Genotypes × Fertilization × Environments (G × F × E) interaction only for the years 2006 and 2007, respectively, was found.
ANOVA results for the three levels of irrigation are shown in Table S2. With the exception of the uniformity index and micronaire at the low irrigation level, numerous quality parameters showed statistically significant variations between genotypes. The uniformity index showed G × Y and F × G interactions at the I2 level, and these interactions were present in some micronaire and fiber elongation cases. The year had no effect on fiber length, while it did not affect micronaire at specific irrigation levels. The year effect was found to be significant for all other characteristics.
Similar results are presented in Table S3, where ANOVA was performed separately for each experimentation year. In most cases and almost for all quality traits, genotypes showed significant differences, with a few fertilization effects being present.
Table 5 presents data for all fiber quality traits. Cultivar Celia was inferior to interspecific lines for fiber length (values close to 30 mm instead of 33 mm for lines) and fiber elongation (values close to 5.5% instead of 7% for lines). Interspecific lines were also better for trait yellowness (over 1.5), while for all the rest of the quality traits, there was no clear advantage for a specific genotype. Almost all the genotypes showed the same measurements for micronaire, but in combination with the year factor, statistically significant differences were found.

Table 5.
Mean performance for fiber quality traits: fiber length (mm), fiber strength (g tex−1), fiber elongation (%), uniformity index (%), micronaire units, yellowness (+b), and reflectance index (%) of each cultivar in each environment-irrigation level (I1, I2, I3), across irrigation levels (Across I) in each year (Y1, Y2), over years in each irrigation level (I1, I2, I3) and across years.
Fluctuations across years were observed. For fiber length, values ranged from 29.88 to 33.44 mm; for fiber strength, from 35.86 to 39.95 g tex−1; for fiber elongation, from 5.42 to 7.20%; for uniformity index, from 83.19 to 85.55%; for micronaire, from 3.37 to 3.72; for yellowness (+b), from 7.28 to 9.56; and finally, for reflectance (Rd), from 73.29 to 77.34%.
There were no variations in genotype behavior for fiber length across irrigation levels or years, as evidenced by Table 6’s mean performance for each fiber quality characteristic in each irrigation level, across irrigation in each year, over years in each irrigation level, and across years. There were some significant differences for various quality parameters within years and across irrigation levels, such as fiber strength (36.52–39.73 g tex−1) and fiber elongation (5.53–7.57%).

Table 6.
Mean performance of fiber quality traits: fiber length (mm), fiber strength (g tex−1), fiber elongation (%), uniformity index (%), micronaire units, yellowness (+b), and reflectance index (%) for all genotypes in each environment-irrigation level (I1, I2, I3), across the irrigation level (Across I) in each year (Y1, Y2), over years in each irrigation level (I1, I2, I3) and across years.
As illustrated in Figure 1, the seven fiber quality traits—fiber length, fiber strength, fiber elongation, uniformity index, micronaire, yellowness (+b), and reflectance index—displayed consistently low variability across irrigation levels, with narrow ranges of mean values and small balance (SD) estimates. This overall uniformity across years and irrigation regimes highlights the stable performance of fiber quality characteristics and demonstrates a clear adaptability of the evaluated genotypes under contrasting water conditions.
In Table 7, comparisons between genetic materials revealed that M1 and M3 showed increased stability in fiber length (107 and 114, respectively) and M5 (over 5000), followed by M2, M3 (over 2500), for fiber elongation. M5 for fiber strength, micronaire units, yellowness, and reflectance index (149, 1381, 851, and 171, respectively).

Table 7.
Trait stability index across cotton genotypes.
Table S4 and Figure 2 summarize the correlation patterns among all fiber quality traits across the genetic materials evaluated. In addition, Figure 2 provides the corresponding scatterplot matrix, illustrating pairwise relationships among traits and highlighting key associations between fiber characteristics. Fiber elongation was positively correlated with fiber strength (r = 0.41), fiber length (r = 0.24), and yellowness (r = 0.55), while showing negative correlations with micronaire (r = −0.57), reflectance index (r = −0.78), and uniformity (r = −0.43). Moreover, micronaire was positively correlated with uniformity (r = 0.44). These relationships emphasize the complex interdependence among cotton fiber traits and their potential implications for breeding strategies.
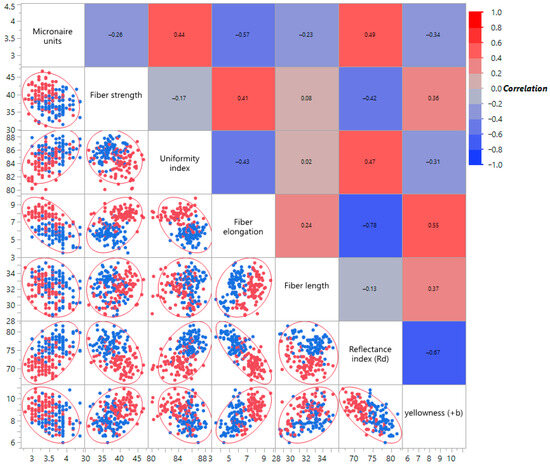
Figure 2.
Correlation matrix with pairwise scatterplots between parameters studied. The upper triangle shows the correlation coefficients, and the lower triangle shows scatterplots with 95% density ellipses that indicate the concentration of data points. The first-year data points in scatterplot are shown in red, while those of the second year in blue.
Figure 3 presents the results of principal component analysis (PCA) based on fiber-related traits across five genotypes. Component 1 explains 48.1% of the total variability, while Component 2 accounts for 15.5%, resulting in a combined explanation of 63.6% of the overall variance. Principal component analysis (PCA) clearly distinguished the Pa7 lines from Celia (pink color markers), which are located in the negative part of both Components (1 and 2) (Figure 3a). In the PCA score plot (Figure 3a), each genotype is represented using a consistent color, while the marker shape distinguishes the year: rhombs correspond to year 2006 and circles to year 2007, allowing visual comparison of year-to-year variation within the same genotype. The PCA score plot displays a clear distribution pattern among the genotypes, with separation along Component 1 mainly driven by differences in fiber elongation, strength, length, and yellowness, as highlighted in the loading plot (Figure 3b). On the contrary, micronaire units and the reflectance index contributed negatively to Component 1. Some genotypes exhibit noticeable shifts between years—e.g., the pink genotype (Μ5) shows a visible separation between year 2006 (rhombs) and year 2007 (circles), suggesting a year effect on trait expression for this genotype. This fact suggests that while genotype contributes strongly to trait clustering, environmental effects (year) also influence certain traits in specific genotypes.
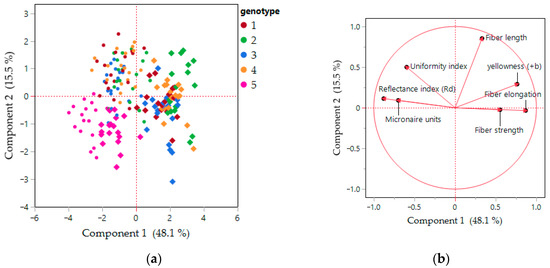
Figure 3.
Principal component analysis (PCA) for the traits of the five genotypes. (a) Score plot: year for each cultivar is shown with a different marker (filled rhombs—year 2006 and filled circles—year 2007), (b) loading plot. (Genotype 1: M1, Genotype 2: M2, Genotype 3: M3, Genotype 4: M4, Genotype 5: M5).
The loading plot (Figure 3b) further reveals that samples positioned on the right side of the horizontal axis are associated with higher fiber strength and elongation, while those on the left tend to exhibit higher micronaire values and reflectance index. Similarly, Component 2, influenced by the uniformity index and fiber length, contributes to the vertical separation of genotypes. These results suggest distinct trait profiles among the genotypes, although some overlap is observed, particularly for genetic materials Μ3 and Μ4. The PCA supports prior findings, indicating both trait contribution and genotypic differentiation across years. Some genotypes are stable across years, while others are more sensitive to year-to-year environmental variation, possibly due to differences in climate, soil, or growing conditions affecting fiber traits such as elongation, strength, and reflectance.
4. Discussion
Good fiber quality is necessary for the textile business because it affects processing performance, which impacts processing cost and branding/marketing, and final product quality [40]. Cotton fiber quality traits are influenced by genotype, environmental conditions such as irrigation, fertilization, and culture practices, and, of course, G × E interactions [34,40,51]. Environmental fluctuations affect cotton fiber quality traits differently, based on the kind of inheritance of each trait and genotype background [52].
Our results depicted statistically significant differences between environments and genotypes for all quality characteristics, with some differentiations between years.
Fiber length is possibly a genetically dependent characteristic because of the significant differences found. This is in agreement with Bradow et al. [53,54]. Environmental differentiation based on irrigation levels had an impact on all quality traits, but this was not always the case (in both years) or obvious within the different irrigation levels. Indeed, regardless of irrigation level or year, results were almost the same for each genotype’s fiber length. This was in agreement with some of Campbell and Bauer’s [39] findings but in contrast to Lascano and Hicks’ [37] and Balkcom et al.’s [38] findings. Regular irrigation (at specified periods) had no discernible impact on fiber cells in our investigation, which means that it had no immediate impact on genotype behavior across environments, as shown by Marani and Amirav [55] and Basal et al. [40]. The cultivar Celia was inferior to interspecific lines for fiber length and fiber elongation. Celia showed the profile of fibers observed in varieties of G. hirsutum, while partial interspecific lines exhibited behavior similar to that of G. barbadense [56,57]. Our results demonstrate that partially interspecific Pa7 lines outperform the commercial cultivar Celia in fiber length and elongation, maintaining stable performance across different environments. This is consistent with the known contribution of the G. barbadense genetic background to fiber quality, as cultivars carrying its alleles exhibit greater elongation and improved color properties, including yellowness, compared to G. hirsutum lines [58,59]. Quantitative trait locus (QTL) analyses have further demonstrated that these alleles positively affect key technological traits of cotton fibers, supporting their use in breeding programs aimed at enhancing fiber performance [60]. Accordingly, the presence of G. barbadense characteristics in interspecific lines may explain the significant differences observed between Celia and the Pa7 materials in this study.
Fiber strength varied with environment, consistent with the findings of Sasser and Shane [61], May [62], and Bednarz et al. [63]. Basal et al. [40] reported that fiber quality response, averaged across years, varies significantly among irrigation levels, with fiber length typically reduced under soil moisture deficits. Genotype × irrigation interactions were occasionally reported for fiber length and strength [40]. According to Pettigrew [36], irrigation can also have a considerable impact on fiber strength, fiber elongation in some years, length uniformity, and micronaire in certain cases.
Across the three irrigation levels, genotypes differed significantly for many quality traits. However, statistically significant differences between genotypes were not observed for uniformity index, yellowness, reflectance index, and micronaire under low irrigation. The uniformity index exhibited G × Y and F × G interactions at the I2 level, and similar interactions were noted for certain cases of micronaire and fiber elongation.
The effect of year on fiber length was not significant, and it was also non-significant for micronaire at specific irrigation levels; for all other traits, year effects were significant. Overall, environment (irrigation levels) influenced the uniformity index and micronaire, as well as yellowness in 2007. Fertilization, included both in the experimental design and the statistical model, directly affected fiber yellowness and contributed to significant Fertilization × Environment (F × E) and Genotype × Fertilization × Environment (G × F × E) interactions for the uniformity index.
These results highlight that nitrogen management plays a measurable role in fiber quality stability and should be considered together with irrigation when evaluating breeding material and designing agronomic strategies. Fertilization affected the genotype behavior of yellowness, as found by Tewolde and Fernandez [64]. Contrary to the findings of Saleem et al. [65], a strong F × E and G × F × E interaction was detected for the uniformity index during the course of the two years of experimentation, respectively.
According to some studies, mepiquat chloride and increasing fertilization reduce the reflection index, with some undesired yellowness only developing in the absence of mepiquat treatment [30]. Papastylianou and Argyrokastritis [66] reported that there were no significant differences in the uniformity index across irrigation treatments and genotypes; however, Basal et al. [40] reported that a water shortage resulted in decreased fiber uniformity. According to Ünlü et al. [67], irrigation enhances fiber uniformity under conditions of water deficit.
With regard to micronaire, Bauer and Frederick [68] concluded that water availability may influence its measurement, whereas Campbell and Bauer [39] reported a decrease when supplemental irrigation was applied. Witt et al. [69] provided a detailed description of the effects of different irrigation levels on multiple traits, particularly fiber properties. In terms of trait stability across environments, Greveniotis et al. [70] indicated that maturity and fiber uniformity indices were the most stable among qualitatively inherited traits. Fiber length may also be considered qualitatively inherited under favorable environmental conditions. Moreover, the estimation of stability in multi-location trials was found to be comparable to that obtained from multi-genotype evaluations. Among Greek cultivation environments, the cultivars Elsa and Celia were identified as the most stable [70]. Overall, Greveniotis et al. [70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78] concluded that stability is strongly associated with high stability indices and traits governed by more qualitative inheritance.
For yellowness, interspecific lines were superior and more stable than Celia. Micronaire showed no consistent differences among genotypes, reflecting limited genetic variability for this trait under the tested conditions. Comparisons among genetic materials showed M1 and M3 had increased stability in fiber length, M5 (followed by M2, M3) for elongation, M1 and M5 for strength, and M5 (Celia) for micronaire, yellowness, and reflectance index—all critical for commercial cultivars.
In terms of fiber length, the interspecific lines consistently demonstrated increased stability. These findings are in agreement with Lacape et al. [9] and Saha et al. [7]. Similarly, Bradow et al. [32] reported that fiber length is primarily under genetic control with limited environmental influence, which supports our observation of stable fiber length across years and irrigation levels.
Regarding fiber strength, Campbell and Bauer [39], Marani [11], and Meredith [12] documented irrigation-dependent variation. In contrast, our results showed increased stability for this trait, likely due to the specific genetic composition of our materials.
For micronaire and uniformity, Papastylianou and Argyrokastritis [66] reported no significant genotype-related differences under Mediterranean conditions, which contrasts with our findings of genotype effects under certain irrigation regimes. Greveniotis and Sioki [52], as well as Greveniotis et al. [70] have highlighted the importance of stability analysis for cotton fiber traits, particularly micronaire and uniformity, emphasizing their relevance in breeding programs.
From an agronomic perspective, fiber elongation and uniformity index are crucial for spinning performance, influencing yarn strength and consistency. Micronaire, indicative of fiber maturity and fineness, significantly affects dye uptake and fabric quality. Delhom et al. [79] emphasized that fiber length, uniformity, strength, and fineness are pivotal for yarn quality and processing efficiency. Valco et al. [80] noted that micronaire readings correlate with fiber maturity, impacting dye uptake and fabric appearance. Furthermore, Bradow and Davidonis [35] highlighted that variations in fiber properties, including micronaire, can lead to inconsistencies in yarn and fabric quality. Economically, the superior fiber properties of Pa7 lines can enhance the competitiveness of Greek cotton in international markets. Greece is Europe’s leading cotton producer, with an annual output of over 1 million bales, much of which is exported [3]. Cultivars with stable fiber quality are essential for maintaining export value under climate variability.
Multivariate analyses have highlighted trait associations, showing that fiber length and strength cluster together along the first principal component, reflecting their strong genetic correlation and importance as stable breeding targets. In contrast, elongation and yellowness were grouped along the second component, indicating greater environmental sensitivity. These findings suggest that breeding strategies can focus on length and strength as stable traits, while elongation and color traits should be evaluated across multiple environments to ensure consistent fiber quality.
The correlations among the main fiber quality traits observed in our study are consistent with previous reports by Greveniotis and Sioki [52] and Greveniotis et al. [70], as well as with Davidonis et al. [45]. These results highlight the complex interrelationships among fiber characteristics, indicating that improvement in one trait may positively or negatively influence others. In particular, fiber elongation demonstrated both positive and negative correlations with key traits, such as fiber strength, length, micronaire, and uniformity. Understanding these relationships is crucial for breeding programs, as it allows for the selection of genotypes that optimize multiple fiber quality traits simultaneously, while minimizing undesirable trade-offs. Consequently, these findings provide valuable guidance for the genetic improvement of cotton, emphasizing the importance of considering trait interdependence in selection strategies.
According to Fasoulas [81], traits with low CV% exhibit a rather qualitative gene expression, and in this case, fiber length and elongation, uniformity, and reflectance index must be considered as qualitative gene traits. Correlations presented here encourage breeders to replace mostly quantitative traits with qualitative ones in order to simplify successful breeding by indirect selection [70].
Strong negative correlations are observed between fiber elongation and reflectance index, as well as between reflectance index and yellowness (+b), suggesting that as fiber elongates, the reflectance (brightness or whiteness) decreases, and whiter cotton reflects less yellow coloration. A strong negative correlation also exists between micronaire units and fiber length, indicating that finer fibers tend to be longer. On the positive side, fiber elongation shows a moderate positive correlation with yellowness, while micronaire units correlate positively with reflectance index, implying that longer fibers appear more yellowish and denser fibers appear whiter. Kadam et al. [82] also showed a significant moderate negative correlation of fiber strength to fiber fineness, and significant moderate negative correlations of uniformity ratio to fiber strength and fiber fineness. Chapepa et al. [83] reported a strong positive correlation between micronaire and fiber strength (r = 0.71), a moderate positive correlation with elongation percentage (r = 0.43), and a moderate positive correlation between fiber strength and elongation (r = 0.55). These findings provide significant insights for breeders selecting cotton varieties with desirable fiber quality characteristics. Scatterplots in the lower triangle of the correlation matrix visually support these relationships, displaying linear trends (elliptical distributions), some outliers, and density differences across traits.
Davidonis et al. [45] highlighted the influence of genotype on fiber color traits. In addition, Ünlü et al. [67] observed improved reflectance under optimal irrigation conditions, which aligns with our results in high-irrigation environments. Notably, our study further demonstrates that interspecific lines exhibit increased stability in reflectance, reinforcing their potential for breeding programs targeting both fiber quality and consistency.
The evaluation of partially interspecific Pa7 cotton lines under contrasting irrigation and nitrogen environments confirmed the potential of G. barbadense introgressions to enhance fiber quality traits while maintaining stability. The superiority of Pa7 lines over the control cultivar Celia in fiber length and elongation highlights the genetic contribution of G. barbadense, which is well known for its longer and finer fibers. These improvements are consistent with previous studies demonstrating that introgression from G. barbadense increases fiber length and flexibility in G. hirsutum-based backgrounds [84].
The practical implications of these findings for Greek cotton cultivation are substantial. Greece accounts for the largest share of Europe’s cotton-growing area, representing approximately 80% of the continent’s production and contributing over 8% to the national agricultural output [3]. Maintaining stable and high-quality fiber production is therefore essential to ensure competitiveness in global markets, highlighting the importance of integrating genetic improvement with optimized irrigation and fertilization management. The results indicate that Pa7 lines provide superior fiber quality compared with Celia, while showing stability across diverse management regimes, thereby reducing risk for growers under variable environmental conditions.
5. Conclusions
Partially interspecific Pa7 cotton lines consistently outperformed the commercial cultivar Celia in fiber length and elongation across contrasting irrigation and nitrogen environments. Fiber length exhibited high genetic stability, whereas elongation and yellowness were more influenced by environmental variation. Genotypic response for yellowness was affected by fertilization. Across the two experimental years, a strong Fertilization × Environment interaction was observed, and in the second year, a Genotype × Fertilization × Environment interaction was detected for the uniformity index, highlighting the impact of combined management practices on this trait. Micronaire remained largely consistent across genotypes, with minor variations related to environmental conditions.
These findings indicate that Pa7 lines combine superior fiber quality with stability under variable agronomic conditions. Enhanced fiber properties, including length and elongation, directly translate into improved spinning performance and textile quality, which are critical for industrial applications. From an agronomic perspective, the robustness of Pa7 lines under different water and nutrient regimes supports their potential adoption in Mediterranean cotton systems, contributing to consistent yield and fiber quality.
Overall, Pa7 lines represent promising breeding material for the development of commercial cultivars that balance high fiber quality with environmental resilience. These results underscore the value of integrating interspecific germplasm into breeding programs to achieve stable, industrially relevant fiber traits while maintaining adaptability to local management practices. The study further highlights the importance of combining genetic improvement with irrigation–nitrogen management strategies to optimize cotton fiber quality and consistency, providing valuable insights for future breeding programs aiming at enhanced fiber performance under variable cultivation conditions.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/app15179684/s1, Table S1: ANOVA for fiber length (mm), fiber strength (g tex−1), fiber elongation (%), uniformity index (%), micronaire units, yellowness (+b) and reflectance index (Rd) within each artificial/considered environment in each year for the factors: irrigation levels (environments), genotype and fertilization; Table S2. ANOVA for fiber length (mm), fiber strength (g tex−1), fiber elongation (%), uniformity index (%), micronaire units, yellowness (+b) and reflectance index (Rd) at each of the three irrigation levels (I1, I2, I3) over years; Table S3. ANOVA for fiber length (mm), fiber strength (g tex−1), fiber elongation (%), uniformity index (%), micronaire units, yellowness (+b) and reflectance index (Rd) at each of the three irrigation levels (I1, I2, I3) for each of the two years (Y1, Y2), for factors genotypes and fertilizer; Table S4. Correlations between all the quality traits measured: fiber length (mm), fiber strength (g tex−1), fiber elongation (%), uniformity index (%), micronaire units, yellowness (+b) and reflectance index (Rd).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.G.; methodology, V.G.; validation, V.G.; investigation, V.G., E.B. and C.G.I.; statistical analysis, A.S. and V.G.; data curation, V.G.; writing—original draft preparation, V.G., E.B. and C.G.I.; writing—review and editing, E.B. and C.G.I.; visualization, A.S. and V.G.; supervision, V.G.; project administration, V.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data sets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Zaidi, S.S.E.A.; Mansoor, S.; Paterson, A. The rise of cotton genomics. Trends Plant Sci. 2018, 23, 953–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engonopoulos, V.; Kouneli, V.; Mavroeidis, A.; Karydogianni, S.; Beslemes, D.; Kakabouki, I.; Papastylianou, P.; Bilalis, D. Cotton versus climate change: The case of Greek cotton production. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. Cluj-Napoca 2021, 49, 12547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA Foreign Agricultural Service. Cotton and Products Annual—Greece; Report No. GR2025-0001; USDA FAS: Washington, DC, USA, 2025. Available online: https://apps.fas.usda.gov/newgainapi/api/Report/DownloadReportByFileName?fileName=Cotton+and+Products+Annual_Rome_Greece_GR2025-0001.pdf (accessed on 24 August 2025).
- Van Der Sluijs, M.H.J. Effect of nitrogen application level on cotton fibre quality. J. Cotton Res. 2022, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieg, D.R.; Hequet, E.F. Fiber Quality Variation within a Cotton Plant as Affected by Genetics and Environment. In Proceedings of the Beltwide Cotton Conferences, New Orleans, LA, USA, 4–7 January 2005; National Cotton Council: New Orleans, LA, USA, 2005; pp. 2380–2385. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.A.; Khan, I.A.; Awan, S.I.; Ali, S.; Niaz, S. Genetic of fiber quality traits in Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2008, 2, 10–17. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, S.; Jenkins, J.N.; Wu, J.; McCarty, J.C.; Stelly, D.M. Genetic analysis of agronomic and fiber traits using four interspecific chromos substitution lines in cotton. Plant Breed. 2008, 127, 612–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Percy, R.G.; McCarty, J.C. Introgression genetics and breeding between Upland and Pima cotton: A review. Euphytica 2014, 198, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacape, J.M.; Nguyen, T.B.; Courtois, B.; Belot, J.T.; Giband, M.; Gourlot, J.P.; Gawryziak, G.; Roques, S.; Hau, B. QTL analysis of cotton fiber quality using multiple Gossypium hirsutum × Gossypium barbadense backcross generations. Crop Sci. 2005, 45, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loden, H.D.; Richmond, T.R. Hybrid vigor in cotton-cytogenetic aspects and practical application. Econ. Bot. 1951, 5, 387–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marani, A. Heterosis and inheritance of quantitative characters in interspecific crosses of cotton. Crop Sci. 1968, 8, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meredith, W.R., Jr. Yield and fiber quality potential for second generation cotton hybrids. Crop Sci. 1990, 30, 1045–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanopoulou-Sendouca, S.; Roupakias, D. Performance of cotton F1 Hybrids and its relation to the mean yield of advanced bulk generations. Eur. J. Agron. 1999, 1, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettigrew, W.T. Environment effects on cotton fiber carbohydrate concentration and quality. Crop Sci. 2001, 41, 1108–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endrizzi, J.E. Genetic analysis of six primary monosomes and one tertiary monosome in Gossypium hirsutum. Genetics 1963, 48, 1625–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohel, R.J.; Endrizzi, J.E.; White, T.G. An evaluation of Gossypium barbadense L. chromosome 6 and 17 in the G. hirsutum L. genome. Crop Sci. 1977, 17, 404–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavromatis, A.G.; Roupakias, D.G. Biotechnology: A hope for partial interspecific hybrid in cotton (Gossypium spp). In Cotton Biotechnology, Proceedings of the first Meeting of the Working Group on Cotton Biotechnology, Leuven, Belgium, 22–23 October 1993; Peeters, M.C., Ed.; FAO-Technical Series No.32; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1994; pp. 29–36. [Google Scholar]
- Mavromatis, A.G.; Kantartzi, S.K.; Vlachostergios, D.N.; Xynias, I.N.; Skarakis, G.N.; Roupakias, D.G. Induction of embryo development and fixation of partial interspecific lines after pollination of F1 cotton interspecific hybrids (G. barbadense × G. hirsutum) with pollen from Hibiscus cannabinus. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 2005, 56, 1101–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachostergios, D.N.; Mavromatis, A.G.; Kantartzi, S.K.; Roupakias, D.G. In-vitro development of obtained after pollination of cotton (G. hirsutum spp) flowers with pollen from okra Abelmoschus esculentus L. Moench. Plant Cell Tiss. Organ Cult. 2006, 88, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantarzi, S.; Roupakias, D.G. Production of aneuploids of the cotton hybrid G. barbadense × G. hirsutum L. via intergeneric pollination with Abelmoschus esculentus. Euphytica 2008, 161, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahtabi, E.; Farshadfar, E.; Jowkar, M.M. Stability Analysis of Yield and Yield Components in Chickpea Genotypes. Agri. Commun. 2014, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Gul, S. Genotype by Environment Interaction for Morphoyield Traits in Upland Cotton. Master’s Thesis, University of Agriculture, Peshawar, Pakistan, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Riaz, M.; Farooq, J.; Ahmed, S.; Amin, M.; Chattha, W.S.; Ayoub, M.; Kainth, R.A. Stability analysis of different cotton genotypes under normal and water-deficit conditions. J. Integr. Agric. 2019, 18, 1257–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, G.I.A.; Abd-El-Halem, S.H.M.; Ibrahim, E.M.A. A genetic analysis of yield and its components of Egyptian cotton (Gossypium barbadense L.) under divergent environments. Am.-Eurasian J. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2009, 5, 5–13. [Google Scholar]
- Jawdad, D.; Hilali, M.A.; Ayyoubi, Z.; Elias, R.; Al-Rayan, R.; Al-Salti, M.N.; Al-Safadi, B. Response of cotton varieties to different environments: Flowering behavior and fiber quality. Pak. J. Agric. Sci. 2012, 49, 289–298. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Z.; Bai, W.; Xie, C.; Yu, J.; Dai, Y.; Pei, S.; Zhang, F.; Li, Y.; Fan, J.; Yin, F. Irrigation depth and nitrogen rate effects on seed cotton yield, fiber quality and water-nitrogen utilization efficiency in southern Xinjiang, China. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 290, 108583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, M.R. Essential Plant Nutrients: Their Presence in North Carolina Soils and Role in Plant Nutrition; Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services, Agronomic Division: Raleigh, NC, USA, 1999; p. 9. Available online: https://digital.ncdcr.gov/Documents/Detail/essential-plant-nutrients-their-presence-in-north-carolina-soils-and-role-in-plant-nutrition/2558624?item=2567833 (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- Khan, A.; Tan, D.K.Y.; Afridi, M.Z.; Luo, H.H.; Tung, S.A.; Ajab, M. Nitrogen fertility and abiotic stresses management in cotton crop: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 14551–14566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kechagia, U.; Mitsios, J.; Paschalidis, C.; Katranis, N. Effect of nitrogen levels on cotton quality parameters. In Proceedings of the 2nd FAO Consultation of the Interregional Cooperative Research Network on Cotton, Thessaloniki, Greece, 16–19 June 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Boman, R.K.; Westerman, R.L. Nitrogen and mepiquat chloride effects on the production of nonrank, irrigated, short-season cotton. J. Prod. Agric. 1994, 7, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xanthopoulos, F.P.; Kechagia, O.E.; Batzios, B.P. The effect of nitrogen on characteristic of folliage, yield and quality of cotton. Agric. Res. 1996, 20, 1–8. (In Greek) [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, P.J.; Camerato, J.J.; Roach, S.H. Cotton yield and fiber response to green manures and nitrogen. Agron. J. 1993, 85, 1019–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hearn, A.B. Response of cotton to nitrogen and water in a tropical environment III, fibre quality. J. Agric. Sci. 1976, 86, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hearn, A.B. The principles of cotton water relations and their application in management. In Challenging the Future, Proceedings of the World Cotton Conference, Brisbane, Australia, 14–17 February 1994; Constable, G.A., Forrester, N.W., Eds.; CSIRO: Brisbane, Australia, 1994; pp. 66–92. [Google Scholar]
- Bradow, J.M.; Davidonis, G.H. Quantitation of fiber quality and the cotton production-processing interface: Physiologist’s perspective. J. Cotton Sci. 2000, 4, 34–36. [Google Scholar]
- Pettigrew, W.T. Moisture deficit effects on cotton lint yield, yield components, and boll distribution. Agron. J. 2004, 96, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lascano, R.J.; Hicks, S.K. Cotton lint yield and fiber quality as a function of irrigation level and termination dates in the Texas high plains: 1996–1998. In Proceedings of the Beltwide Cotton Conference, Orlando, FL, USA, 3–7 January 1999; National Cotton Council of America: Memphis, TN, USA, 1999; pp. 570–571. [Google Scholar]
- Balkcom, K.S.; Reeves, D.W.; Shaw, J.N.; Burmester, C.H.; Curtis, L.M. Cotton yield and fiber quality from irrigated tillage systems in the Tennessee Valley. Agron. J. 2006, 98, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, B.T.; Bauer, P.J. Genetic variation for yield and fiber quality response to supplemental irrigation within the Pee Dee Upland cotton germplasm collection. Crop Sci. 2007, 47, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basal, H.; Dagdelen, N.; Unay, A.; Yilmaz, E. Effects of deficit drip irrigation ratios on cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) yield and fibre quality. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2009, 195, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booker, J.D.; Bordovsky, J.R.; Lascano, J.; Segarra, E. Variable rate irrigation on cotton lint yield and fiber quality. In Proceedings of the Beltwide Cotton Conference, San Antonio, TX, USA, 3–6 January 2006; pp. 1768–1776. [Google Scholar]
- Ramey, H.H., Jr. Stress influences on fiber development. In Cotton Physiology; Mauney, J.R., Stewart, J., Eds.; The Cotton Foundation: Memphis, TN, USA, 1986; pp. 315–359. [Google Scholar]
- McWilliams, D. Drought Strategies for Cotton, Cooperative Extension Service Circular 582; College of Agriculture and Home Economics, New Mexico State University: Las Cruces, NM, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Snowden, C.; Ritchie, G.; Cave, J.; Keeling, W.; Rajan, N. Multiple irrigation levels affect boll distribution, yield, and fiber micronaire in cotton. Agron. J. 2013, 105, 1536–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidonis, G.H.; Johnson, A.; Landivar, J.; Hinojosa, O. Influence of low-weight seeds and motes on the fiber properties of other cotton seeds. Field Crops Res. 1996, 48, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greveniotis, V. Impact of the Inputs Level on Yielding Performance and Fiber Quality of Pa7 Partially Interspecific Lines of Cotton. Master’s Thesis, Department of Plant Breeding, Faculty of Agriculture Science, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Thessaloniki, Greece, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Stratilakis, S.N.; Goulas, C.K. Yield performance at three nitrogen rates of a set of honeycomb vs. traditional pedigree selected bread wheat varieties. Eur. J. Agron. 2003, 19, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darawsheh, M.K.; Beslemes, D.; Kouneli, V.; Tigka, E.; Bilalis, D.; Roussis, I.; Karydogianni, S.; Mavroeidis, A.; Triantafyllidis, V.; Kosma, C.; et al. Environmental and Regional Effects on Fiber Quality of Cotton Cultivated in Greece. Agronomy 2022, 12, 943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steel, R.G.D.; Torrie, H.; Dickey, D.A. Principles and Procedures of Statistics. A Biometrical Approach, 3rd ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1997; p. 666. [Google Scholar]
- Fasoula, V.A. Prognostic breeding: A new paradigm for crop improvement. Plant Breed. Rev. 2013, 37, 297–347. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, B.T.; Jones, M.A. Assessment of genotype × environment interactions for yield and fiber quality in cotton performance trials. Euphytica 2005, 144, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greveniotis, V.; Sioki, E. Genotype by environment interactions on cotton fiber traits and their implications on variety recommendation. J. Agric. Stud. 2017, 5, 86–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bradow, J.M.; Bauer, P.J.; Hinojosa, O.; Sassenrath-Cole, G.F. Quantitation of cotton fibre-quality variations arising from boll and plant growth environments. Eur. J. Agron. 1997, 6, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradow, J.M.; Bauer, P.J.; Sassenrath-Cole, G.F.; Johnson, R.M. Modulations of fiber properties by growth environment that persist as variations of fiber and yarn quality. In Proceedings of the Beltwide Cotton Conferences, New Orleans, LA, USA, 6–10 January 1997; National Cotton Council: Memphis, TN, USA, 1977; pp. 1351–1360. [Google Scholar]
- Marani, A.; Amirav, A. Effects of Soil Moisture Stress on Two Varieties of Upland Cotton in Israel. The Coastal Plain Region. Exp. Agric. 1971, 7, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christidis, G.V. The Cotton; University of Thessalaniki: Thessalaniki, Greece, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Bradow, J.M.; Davidonis, G.H. Effects of environment on fiber quality. In Physiology of Cotton; Stewart, J.M., Oosterhuis, D.M., Heitholt, J.J., Mauney, J.R., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 229–245. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Geng, Y.; Pei, W.; Wu, M.; Li, X.; Liu, G.; Li, D.; Ma, Q.; Zang, Y.; Yu, S.; et al. Genetic variation of dynamic fiber elongation and its association with fiber quality traits in cotton. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Wang, W.; Grover, C.E.; Jiang, K.; Pan, Z.; Guo, B.; Zhu, J.; Su, Y.; Wang, M.; Nie, H.; et al. Genomic and GWAS analyses demonstrate phylogenomic relationships of Gossypium barbadense in China and selection for fibre length, lint percentage and Fusarium wilt resistance. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 691–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Guo, J.; Gao, W.; Geng, H.; Chen, Q.; Qu, Y. A high-density genetic map of extra-long staple cotton (Gossypium barbadense) constructed using genotyping-by-sequencing based single nucleotide polymorphic markers and identification of fiber traits-related QTL in a recombinant inbred line population. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasser, P.; Shane, J.L. Crop quality—A decade of improvement. In Proceedings of the Beltwide Cotton Conference, Nashville, TN, USA, 12 January 1996; National Cotton Council of America: Memphis, TN, USA, 1996; pp. 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- May, O.L. Genetic variation in fiber quality. In Cotton Fibers: Developmental Biology, Quality Improvement, and Textile Processing; Basra, A.S., Ed.; Food Products Press: Binghamton, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 183–230. [Google Scholar]
- Bednarz, C.W.; Shurley, W.D.; Anthony, W.S.; Nichols, R.L. Yield, quality, and profitability of cotton produced at varying plant densities. Agron. J. 2005, 97, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewolde, H.; Fernandez, C.J. Fiber quality response of Pima cotton to nitrogen and phosphorus deficiency. J. Plant Nutr. 2003, 26, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.F.; Bilal, M.F.; Awais, M.; Shahid, M.Q.; Anjum, S.A. Effect of nitrogen on seed cotton yield and fiber qualities of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) cultivars. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2010, 20, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Papastylianou, P.T.; Argyrokastritis, I.G. Effect of limited drip irrigation regime on yield, yield components, and fiber quality of cotton under Mediterranean conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 142, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ünlü, M.; Kanber, R.; Koç, D.L.; Tekin, S.; Kapur, B. Effects of deficit irrigation on the yield and yield components of drip irrigated cotton in a Mediterranean environment. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 98, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, P.J.; Frederick, J.R. Tillage effects on canopy position specific cotton fiber properties on two soils. Crop Sci. 2005, 45, 698–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witt, T.W.; Ulloa, M.; Schwartz, R.C.; Ritchie, G.L. Response to deficit irrigation of morphological, yield and fiber quality traits of upland (Gossypium hirsutum L.) and Pima (G. barbadense L.) cotton in the Texas High Plains. Field Crops Res. 2020, 249, 107759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greveniotis, V.; Sioki, E.; Ipsilandis, C.G. Estimations of fibre trait stability and type of inheritance in cotton. Czech J. Genet. Plant Breed. 2018, 54, 190–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greveniotis, V.; Bouloumpasi, E.; Zotis, S.; Korkovelos, A.; Ipsilandis, C.G. A Stability Analysis Using AMMI and GGE Biplot Approach on Forage Yield Assessment of Common Vetch in Both Conventional and Low-Input Cultivation Systems. Agriculture 2021, 11, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greveniotis, V.; Bouloumpasi, E.; Zotis, S.; Korkovelos, A.; Ipsilandis, C.G. Estimations on Trait Stability of Maize Genotypes. Agriculture 2021, 11, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greveniotis, V.; Bouloumpasi, E.; Zotis, S.; Korkovelos, A.; Ipsilandis, C.G. Stability, the Last Frontier: Forage Yield Dynamics of Peas under Two Cultivation Systems. Plants 2022, 11, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greveniotis, V.; Bouloumpasi, E.; Zotis, S.; Korkovelos, A.; Kantas, D.; Ipsilandis, C.G. Genotype-by-Environment Interaction Analysis for Quantity and Quality Traits in Faba Beans Using AMMI, GGE Models, and Stability Indices. Plants 2023, 12, 3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greveniotis, V.; Bouloumpasi, E.; Zotis, S.; Korkovelos, A.; Kantas, D.; Ipsilandis, C.G. Stability Dynamics of Main Qualitative Traits in Maize Cultivations across Diverse Environments regarding Soil Characteristics and Climate. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greveniotis, V.; Bouloumpasi, E.; Zotis, S.; Korkovelos, A.; Kantas, D.; Ipsilandis, C.G. A Comparative Study on Stability of Seed Characteristics in Vetch and Pea Cultivations. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greveniotis, V.; Bouloumpasi, E.; Skendi, A.; Korkovelos, A.; Kantas, D.; Zotis, S.; Ipsilandis, C.G. Modeling Stability of Alfalfa Yield and Main Quality Traits. Agriculture 2024, 14, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greveniotis, V.; Bouloumpasi, E.; Skendi, A.; Korkovelos, A.; Kantas, D.; Ipsilandis, C.G. Evaluation and Stability of Red and White Trifolium Species for Nutritional Quality in a Mediterranean Environment. Agriculture 2025, 15, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delhom, C.D.; Martin, V.B.; Schreiner, M.K. Textile industry needs. J. Cotton Sci. 2017, 21, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valco, T.D. Fiber Quality Aspects of Cotton Ginning. Handout in Level III Cotton Ginners Short Course Text 2002. Available online: https://cotton.tamu.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/27/legacy-files/Harvest/Ginning%20Quality%20Aspects.pdf (accessed on 24 August 2025).
- Fasoulas, A.C. The Honeycomb Methodology of Plant Breeding; Department of Genetics and Plant Breeding, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki: Thessaloniki, Greece, 1988; p. 168. [Google Scholar]
- Kadam, K.; Chinchane, V.N.; Deshmukh, S.; Rani, R. Correlation and path analysis of yield and fiber quality traits in upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Int. J. Adv. Biol. Chem. Res. 2024, 8, 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Chapepa, B.; Mubvekeri, W.; Mare, M.; Kutywayo, D. Correlation and path coefficient analysis of polygenic traits of upland cotton genotypes grown in Zimbabwe. Cogent Food Agric. 2020, 6, 1823594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Kong, L.; Xiao, X.; Li, P.; Liu, A.; Li, J.; Gong, J.; Gong, W.; Ge, Q.; Shang, H. Genome-wide artificial introgressions of Gossypium barbadense into G. hirsutum reveal superior loci for simultaneous improvement of cotton fiber quality and yield traits. J. Adv. Res. 2023, 53, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).