Research on Estimation of State of Charge for Lithium-Ion Batteries Based on TRNN-CTA
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the SOC Dataset
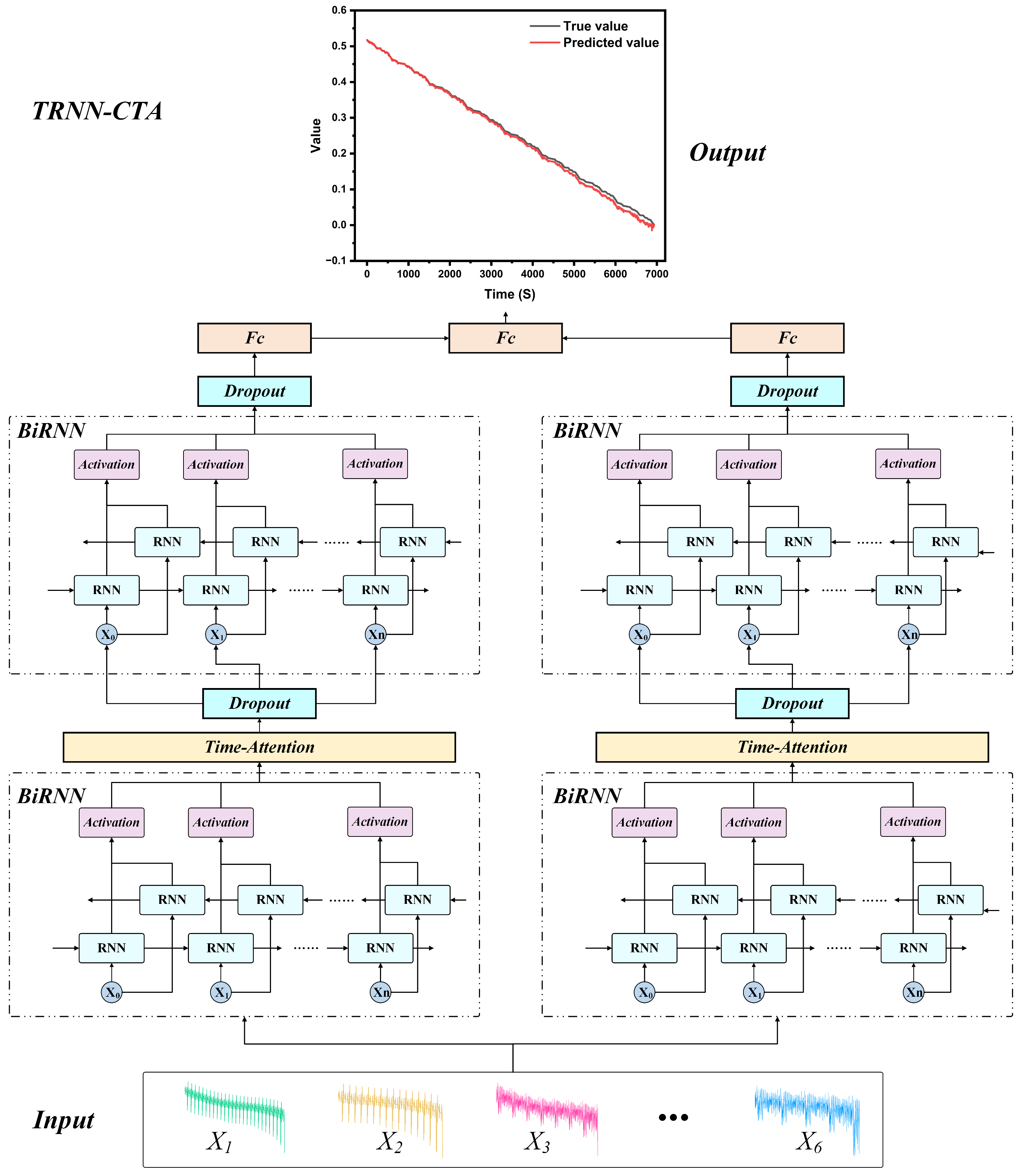
2.2. TRNN-CTA
2.2.1. Overall Framework
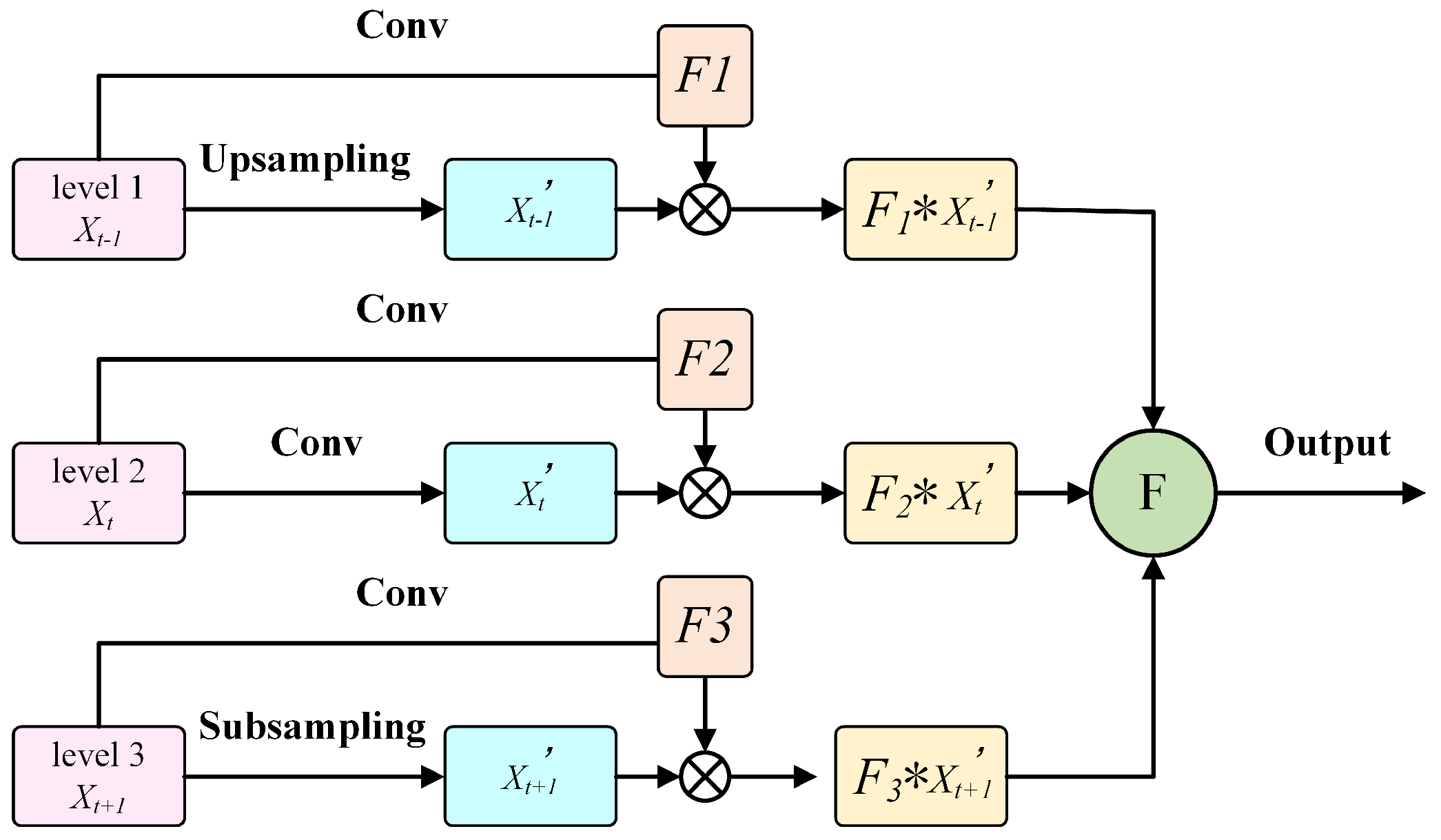
2.2.2. CTA Mechanism
2.3. Experimental Environment and Evaluation Iindicators
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Feature Expansion Experiment
3.2. Ablation Experiment
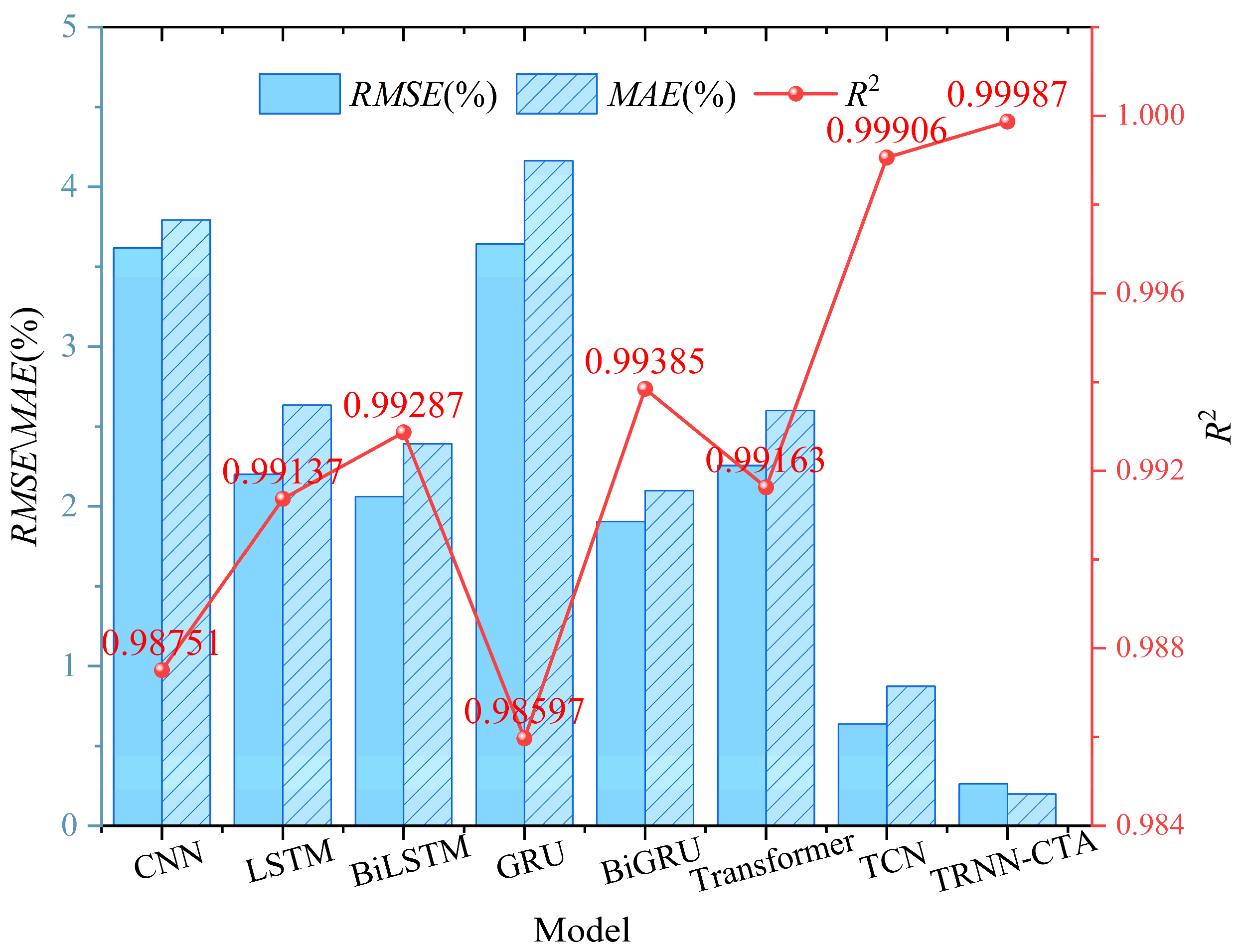
3.3. Model Comparison Experiment
3.4. Model Generalization Experiment
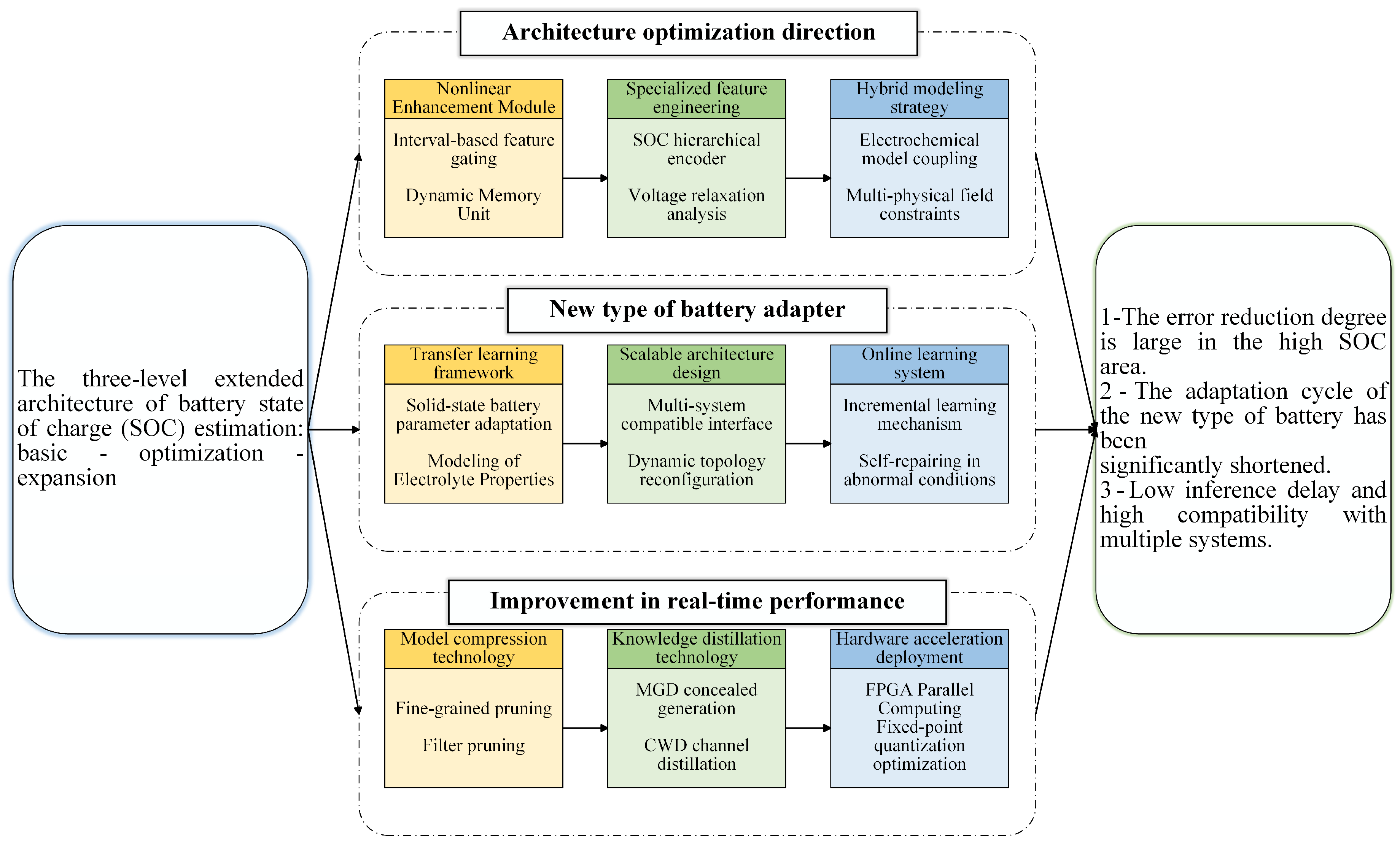
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, L.; Li, S.; Jain, A.; Sun, G.; Chen, G.; Guo, D.; Kang, J.; Zhao, Y. Optimization of Thermal Non-Uniformity Challenges in Liquid-Cooled Lithium-Ion Battery Packs Using NSGA-II. J. Electrochem. Energy Convers. Storage 2024, 22, 041002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.T.J.; Rubeša-Zrim, J.; Pichler, F.; Salihi, A.; Mourad, A.; Šimić, I.; Časni, K.; Veas, E. Explainable Artificial Intelligence for State of Charge Estimation of Lithium-Ion Batteries. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 5078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Won, J. Enhanced Coulomb Counting Method for SoC and SoH Estimation Based on Coulombic Efficiency. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 15449–15459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, F. Lithium-ion battery State-of-Charge estimation based on an improved Coulomb-Counting algorithm and uncertainty evaluation. J. Energy Storage 2022, 48, 104061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, Y.; Cho, K.; Kim, M.; Choi, W. A Novel Capacity Estimation Method for the Lithium Batteries Using the Enhanced Coulomb Counting Method With Kalman Filtering. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 38793–38801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Sun, J.; Cai, Y.; Lian, Y.; Jin, M.; Zhao, X.; Wang, R.; Chen, L.; Chen, J. A novel OCV curve reconstruction and update method of lithium-ion batteries at different temperatures based on cloud data. Energy 2023, 268, 126773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Cui, N.; Li, Y.; Duan, B.; Zhang, C. Fractional calculus based modeling of open circuit voltage of lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles. J. Energy Storage 2020, 27, 100945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Fang, J.; Wen, C.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Peng, B.; Yang, F.; Zhang, J.; et al. A combined method for state-of-charge estimation for lithium-ion batteries based on IGWO-ASRCKF and ELM under various aging levels. J. Energy Storage 2025, 124, 116843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Q.; Jiang, L.; Shi, Y.; Lyu, L.; Cai, G. Fault diagnosis of energy storage batteries based on dual driving of data and models. J. Energy Storage 2025, 112, 115485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Xiong, R.; Shen, W.; Lu, J. State-of-charge estimation of LiFePO4 batteries in electric vehicles: A deep-learning enabled approach. Appl. Energy 2021, 291, 116812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Sadoughi, M.; Li, M.; Wang, Z.; Hu, C. Deep convolutional neural networks with ensemble learning and transfer learning for capacity estimation of lithium-ion batteries. Appl. Energy 2020, 260, 114296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Ye, M.; Wei, M.; Lian, G.; Li, Y. Deep convolutional neural network based closed-loop SOC estimation for lithium-ion batteries in hierarchical scenarios. Energy 2023, 263, 125718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Cheng, F.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, S.; Ma, L. State of charge estimation for lithium-ion batteries based on data augmentation with generative adversarial network. J. Energy Storage 2024, 80, 110004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chunli, L.; Jianrui, S.; Kun, Z.; Kai, W. Bidirectional LSTM RNN for precise predict remaining useful life of supercapacitors. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Mechatronics Technology (ICEEMT), Qingdao, China, 2–4 July 2021; pp. 56–59. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, C.; Chen, A.; An, F. SOC estimation of Li-ion battery using convolutional neural network with U-Net architecture. Energy 2022, 256, 124612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Cheng, W.; Zhu, Q. SOC estimation for lithium-ion battery using the LSTM-RNN with extended input and constrained output. Energy 2022, 262, 125375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, M.; Wang, D.; Qiu, J. A GRU-RNN based momentum optimized algorithm for SOC estimation. J. Power Sources 2020, 459, 228051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasib, S.A.; Islam, S.; Chakrabortty, R.K.; Ryan, M.J.; Saha, D.K.; Ahamed, H.; Moyeen, S.I.; Das, S.K.; Ali, F.; Islam, R.; et al. A comprehensive review of available battery datasets, RUL prediction approaches, and advanced battery management. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 86166–86193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avola, D.; Cascio, M.; Cinque, L.; Foresti, G.L.; Massaroni, C.; Rodola, E. 2-D skeleton-based action recognition via two-branch stacked LSTM-RNNs. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2019, 22, 2481–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, C.; Wei, J.; Chen, Z.; Lei, G.; Wu, L. State of Health (SOH) Estimation of Lithium-Ion Batteries Based on ABC-BiGRU. Electronics 2024, 13, 1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Li, L.; Chang, C.; Tang, R.; Zheng, G.; Wan, M.; Jiang, J.; Zhou, S.; Tian, Z.; Liu, Z. Dual-Branch Luminance–Chrominance Attention Network for Hydraulic Concrete Image Enhancement. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 7762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, P.; Deng, Y.; Li, B. The Lithium-Ion Battery Temperature Field Prediction Model Based on CNN-Bi-LSTM-AM. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Sun, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, W.; Liu, C.; Lu, H. A Joint Estimation Method for the SOC and SOH of Lithium-Ion Batteries Based on AR-ECM and Data-Driven Model Fusion. Electronics 2025, 14, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Luo, X. Joint estimation of state of charge (SOC) and state of health (SOH) for lithium ion batteries using support vector machine (SVM), convolutional neural network (CNN) and long sort term memory network (LSTM) models. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2024, 19, 100747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Yang, F.; Wang, D.; Tsui, K.-L. Combined CNN-LSTM network for state-of-charge estimation of lithium-ion batteries. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 88894–88902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wei, X.; Lin, C.; Huang, Z.; Fan, Y.; Liu, C.; Fang, S. Battery SOC estimation with physics-constrained BiLSTM under different external pressures and temperatures. J. Energy Storage 2025, 117, 116205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, C.; Zhu, R.; Buticchi, G.; Liserre, M. Sizing and SOC management of a smart-transformer-based energy storage system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 65, 6709–6718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Cheng, F.; Ma, L.; Li, B. State of charge estimation for lithium-ion batteries based on TCN-LSTM neural networks. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2022, 169, 030544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.-Z.; Wang, X.-Y.; Yuan, H.-M. Estimation for SOC of Li-ion battery based on two-order RC temperature model. In Proceedings of the 2018 13th IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications (ICIEA), Wuhan, China, 31 May–2 June 2018; pp. 2601–2606. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Y.; Ma, J.; Sun, G. A structural pruning method for lithium-ion batteries remaining useful life prediction model with multi-head attention mechanism. J. Energy Storage 2024, 86, 111396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.H.; Jang, H.-D.; Chang, D.E. Optimized Network Pruning Method for Li-ion Batteries State-of-charge Estimation on Robot Embedded System. J. Korea Robot. Soc. 2023, 18, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nampeera, J.; Recepoğlu, Y.K.; Yuksel, A. Valorization of olive tree pruning waste for potential utilization in lithium recovery from aqueous solutions. Biomass-Convers. Biorefin. 2024, 14, 4975–4987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Gao, H.; Cao, A. Battery capacity correction method for electric vehicles based on knowledge distillation and multi-feature coupling. J. Power Sources 2025, 643, 236909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Qu, J. Capacity estimation of lithium-ion battery based on soft dynamic time warping, stratified random sampling and pruned residual neural networks. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 138, 109278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
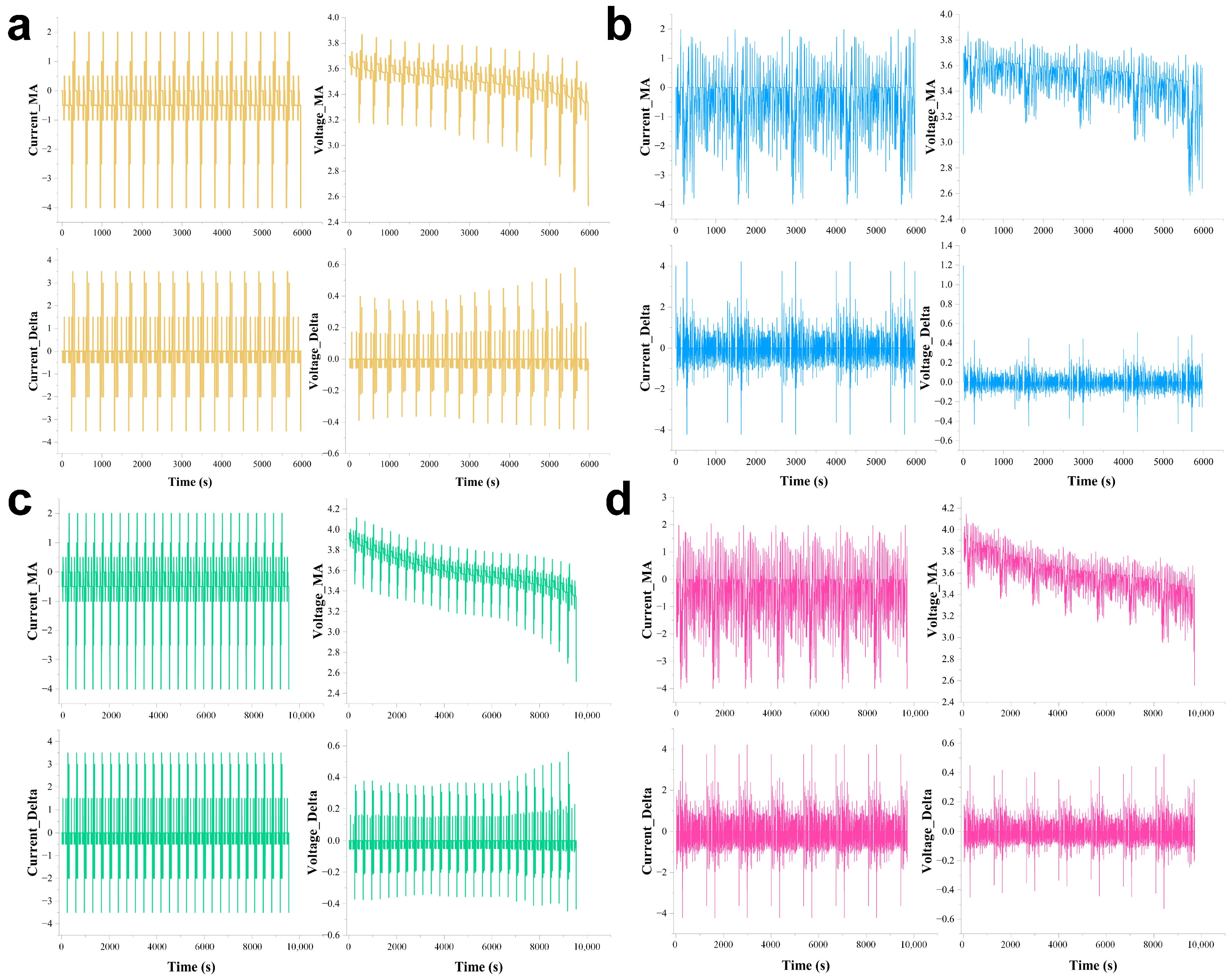
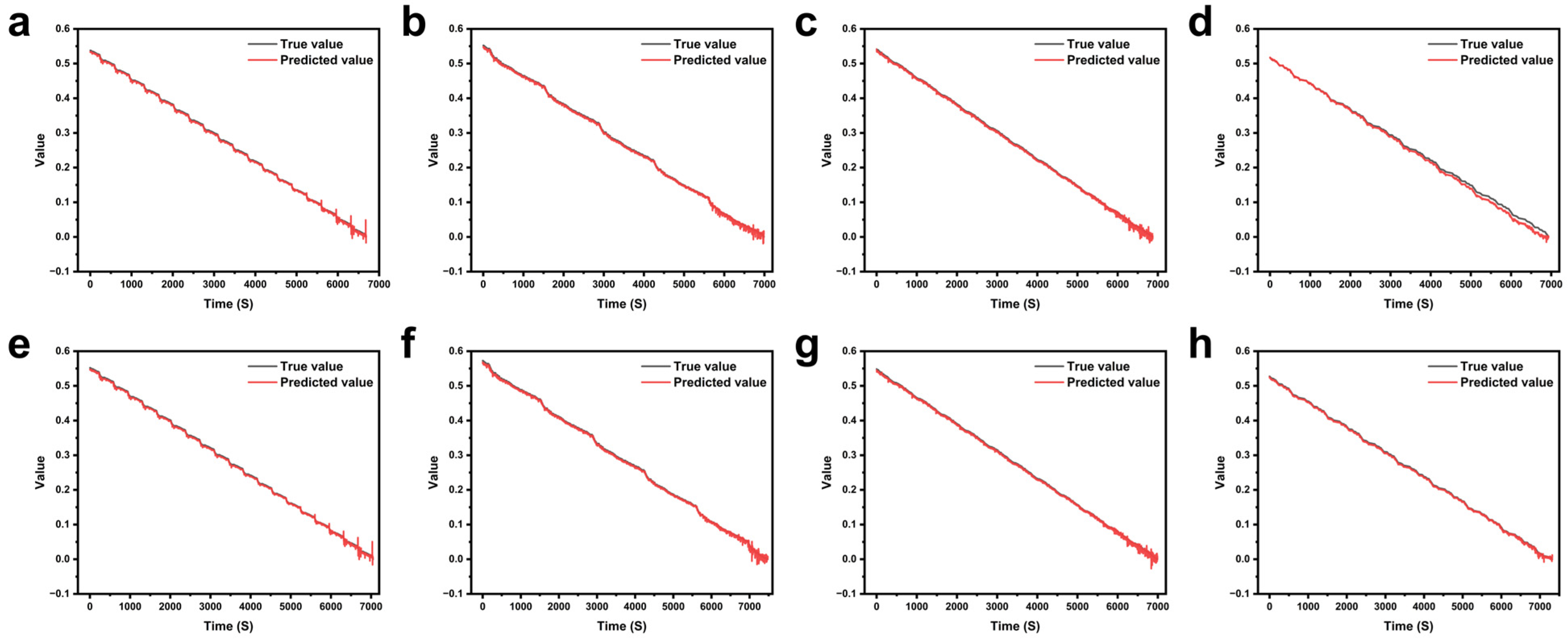
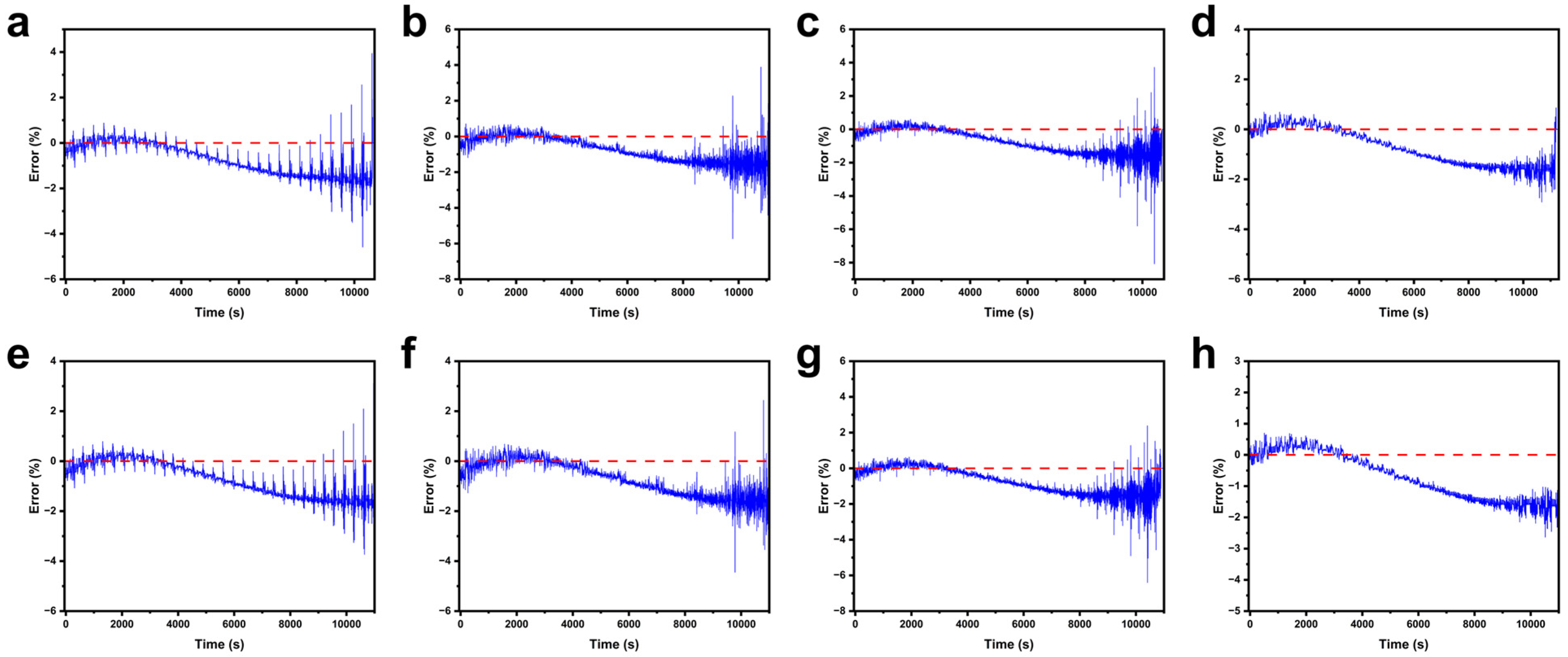
| Operating Condition Name | Temperature (°C) | Initial/Maximum Capacity (%) | Description of Operating Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|
| BJDST | 0, 25, 45 | 50/0, 80/0 | The Beijing Dynamic Stress Test Condition is a dynamic condition that simulates the driving of a vehicle in the Beijing area. |
| FUDS | 0, 25, 45 | 50/0, 80/0 | The US Federal Urban Driving Condition is used to simulate the driving condition on urban roads. |
| US06 | 0, 25, 45 | 50/0, 80/0 | One of the conditions used in the testing standards of the US Environmental Protection Agency, used to supplement and reflect the motivating driving condition. |
| DST | 0, 25, 45 | 50/0, 80/0 | The Dynamic Stress Test Condition is used to evaluate the comprehensive performance of the battery under actual usage conditions. |
| Parameter Type | Name | Calculation Formula |
|---|---|---|
| Input parameters | Voltage, U | - |
| Current, I | - | |
| Voltage_MA, VMA | ||
| Current_MA, CMA | ||
| Voltage_Delta, VD | ||
| Current_Delta, CD | ||
| Output parameters | State of Charge, SOC | - |
| Feature | Training Set | Testing Set | R2 ↑ | RMSE (%) ↓ | MAE (%) ↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw (2 features) | DST+FUDS (0 °C-50%soc) | BJDST | 0.99816 | 1.167 | 0.878 |
| US06 | 0.99588 | 1.482 | 4.360 | ||
| DST+FUDS (0 °C-80%soc) | BJDST | 0.99762 | 1.128 | 0.828 | |
| US06 | 0.99983 | 0.299 | 0.216 | ||
| Raw (6 features) | DST+FUDS (0 °C-50%soc) | BJDST | 0.99798 | 1.192 | 2.182 |
| US06 | 0.99693 | 1.274 | 0.951 | ||
| DST+FUDS (0 °C-80%soc) | BJDST | 0.99984 | 0.287 | 0.219 | |
| US06 | 0.99987 | 0.263 | 0.199 |
| Model Type | Model | R2 ↑ | RMSE (%) ↓ | MAE (%) ↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single branch | BiLSTM | 0.99287 | 2.062 | 2.392 |
| BiGRU | 0.99385 | 1.905 | 2.099 | |
| BiLSTM-CTA | 0.99578 | 1.591 | 1.800 | |
| BiGRU-CTA | 0.99655 | 1.257 | 1.658 | |
| Double branch | BiLSTM-BiGRU | 0.99621 | 1.226 | 1.726 |
| BiLSTM-BiLSTM | 0.99481 | 1.495 | 1.979 | |
| BiGRU-BiGRU | 0.99244 | 1.880 | 2.253 | |
| Ours (TRNN-CTA) | BiGRU-BiGRU-CTA | 0.99835 | 0.820 | 1.024 |
| BiLSTM-BiLSTM-CTA | 0.99837 | 0.888 | 1.138 | |
| BiLSTM-BiGRU-CTA | 0.99987 | 0.263 | 0.199 |
| Model | R2 ↑ | RMSE (%) ↓ | MAE (%) ↓ |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNN | 0.98751 | 3.617 | 3.792 |
| LSTM | 0.99137 | 2.201 | 2.634 |
| BiLSTM | 0.99287 | 2.062 | 2.392 |
| GRU | 0.98597 | 3.641 | 4.162 |
| BiGRU | 0.99385 | 1.905 | 2.099 |
| Transformer | 0.99163 | 2.256 | 2.601 |
| TCN | 0.99906 | 0.637 | 0.873 |
| TRNN-CTA (Ours) | 0.99987 | 0.263 | 0.199 |
| Operating Conditions | Temperature (°C) | R2 ↑ | RMSE (%) ↓ | MAE (%) ↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DST | 25 | 0.99948 | 0.354 | 0.323 |
| 45 | 0.99947 | 0.366 | 0.335 | |
| FUDS | 25 | 0.99942 | 0.375 | 0.330 |
| 45 | 0.99944 | 0.385 | 0.336 | |
| US06 | 25 | 0.99938 | 0.372 | 0.327 |
| 45 | 0.99940 | 0.373 | 0.329 | |
| BJDST | 25 | 0.99951 | 0.348 | 0.316 |
| 45 | 0.99953 | 0.329 | 0.314 |
| Operating Condition | Temperature (°C) | R 2 ↑ | RMSE (%) ↓ | MAE (%) ↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DST | 25 | 0.99817 | 1.013 | 0.811 |
| 45 | 0.99821 | 1.021 | 0.821 | |
| FUDS | 25 | 0.99815 | 1.023 | 0.815 |
| 45 | 0.99817 | 1.023 | 0.813 | |
| US06 | 25 | 0.99800 | 1.058 | 0.830 |
| 45 | 0.99806 | 1.047 | 0.826 | |
| BJDST | 25 | 0.99796 | 1.050 | 0.851 |
| 45 | 0.99801 | 1.046 | 0.851 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.; Zhuang, J.; Liu, L.; Zeng, F.; Li, P.; Cheng, X. Research on Estimation of State of Charge for Lithium-Ion Batteries Based on TRNN-CTA. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9653. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179653
Wu Y, Zhuang J, Liu L, Zeng F, Li P, Cheng X. Research on Estimation of State of Charge for Lithium-Ion Batteries Based on TRNN-CTA. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(17):9653. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179653
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yanfeng, Jihui Zhuang, Ling Liu, Fan Zeng, Pei Li, and Xiaoming Cheng. 2025. "Research on Estimation of State of Charge for Lithium-Ion Batteries Based on TRNN-CTA" Applied Sciences 15, no. 17: 9653. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179653
APA StyleWu, Y., Zhuang, J., Liu, L., Zeng, F., Li, P., & Cheng, X. (2025). Research on Estimation of State of Charge for Lithium-Ion Batteries Based on TRNN-CTA. Applied Sciences, 15(17), 9653. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179653





