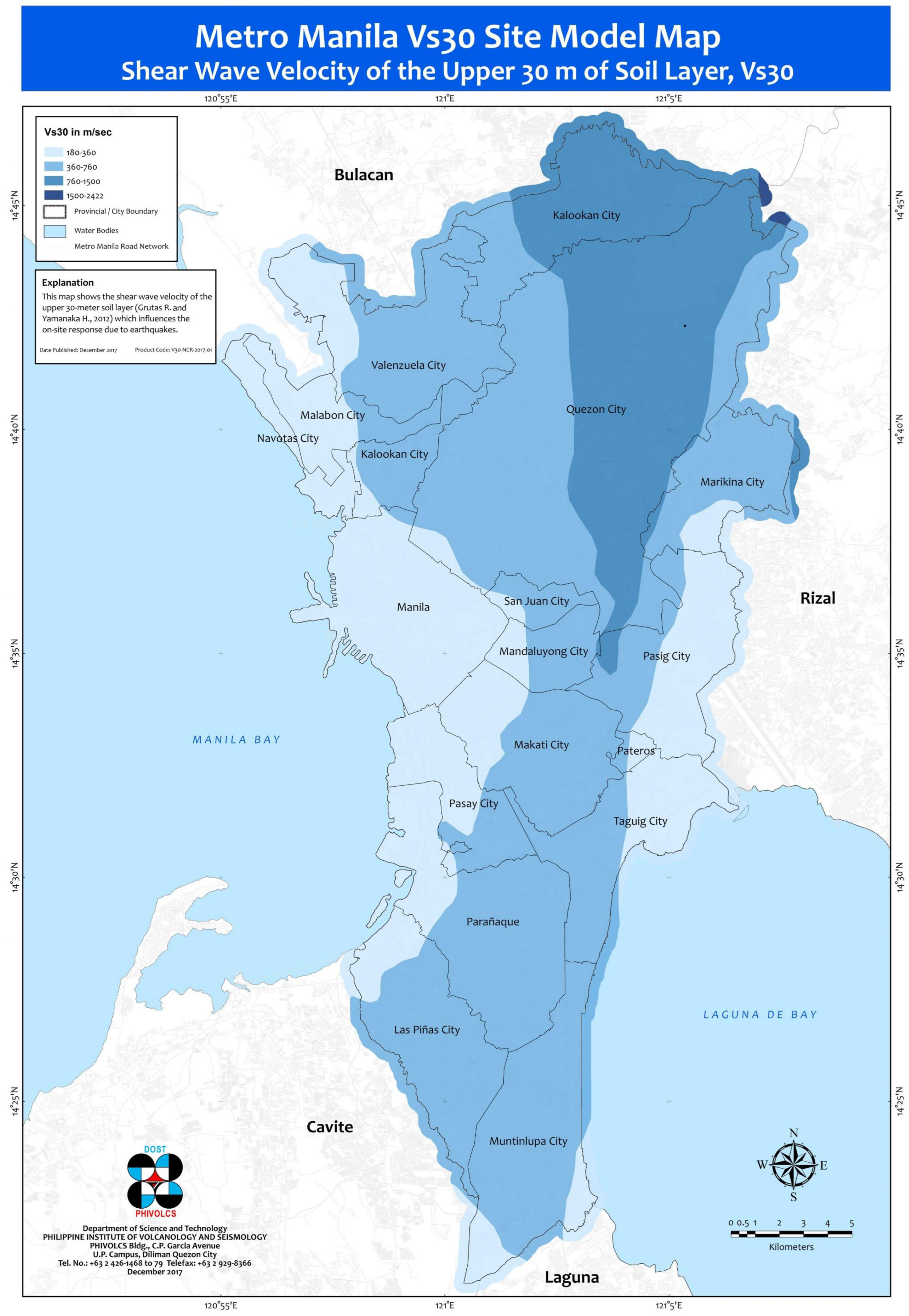
Deterministic Spatial Interpolation of Shear Wave Velocity Profiles with a Case of Metro Manila, Philippines
Abstract
1. Introduction
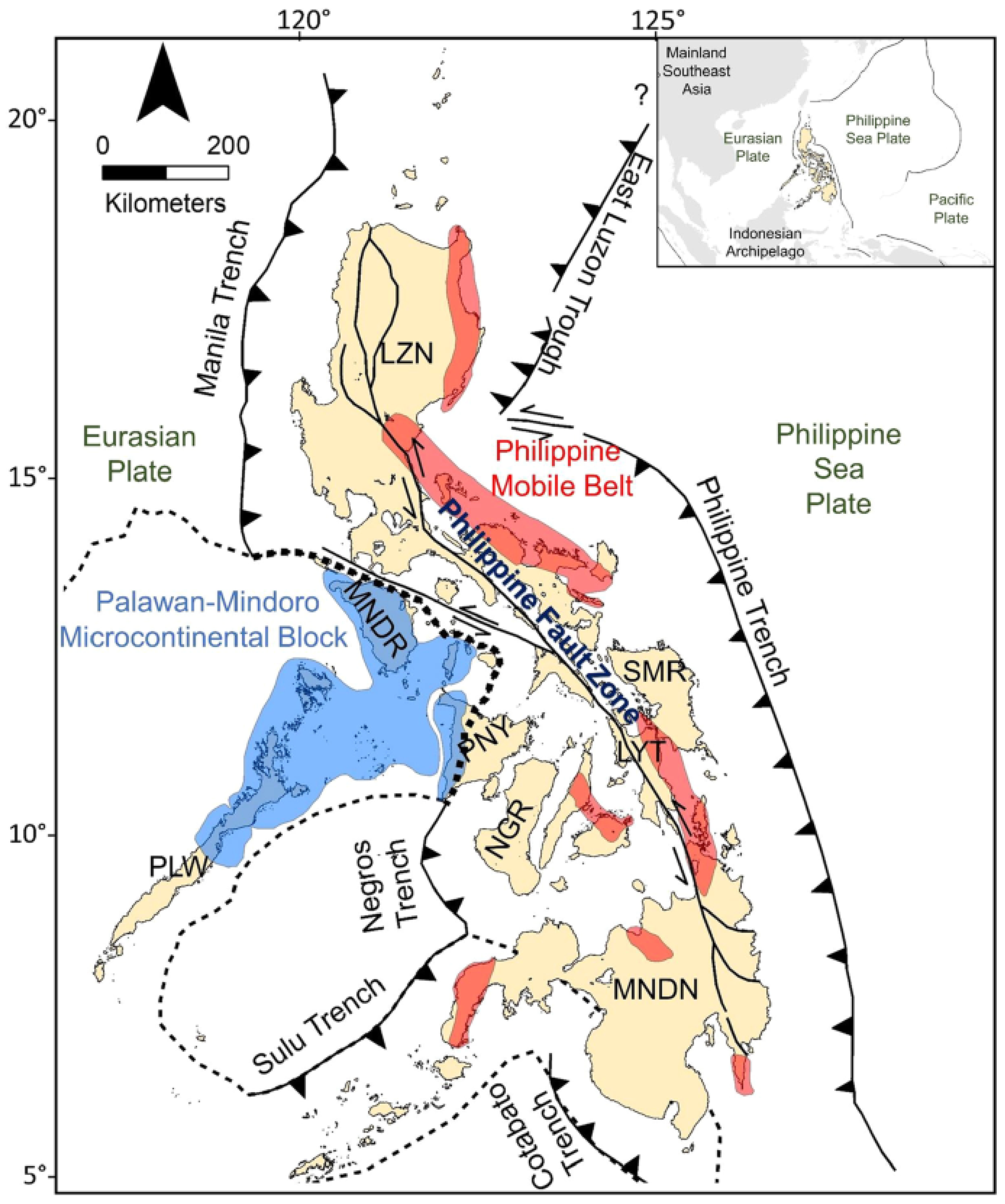
2. Literature Review
2.1. Measuring Shear Wave Velocities
2.2. Empirical Shear Wave Velocity Equations
3. Methodology
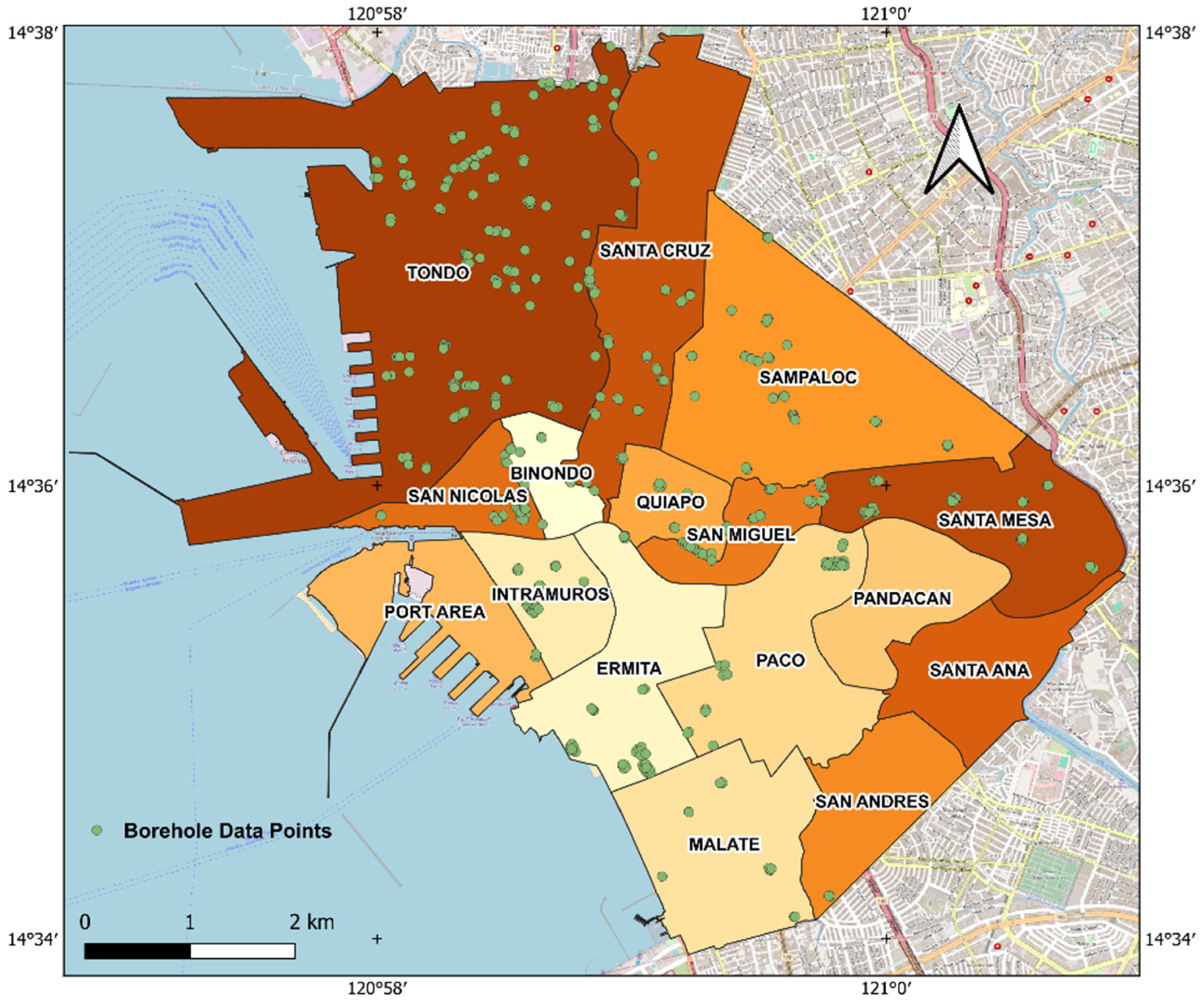
3.1. Research Locale
3.2. Shear Wave Velocity
3.3. Subsurface Data
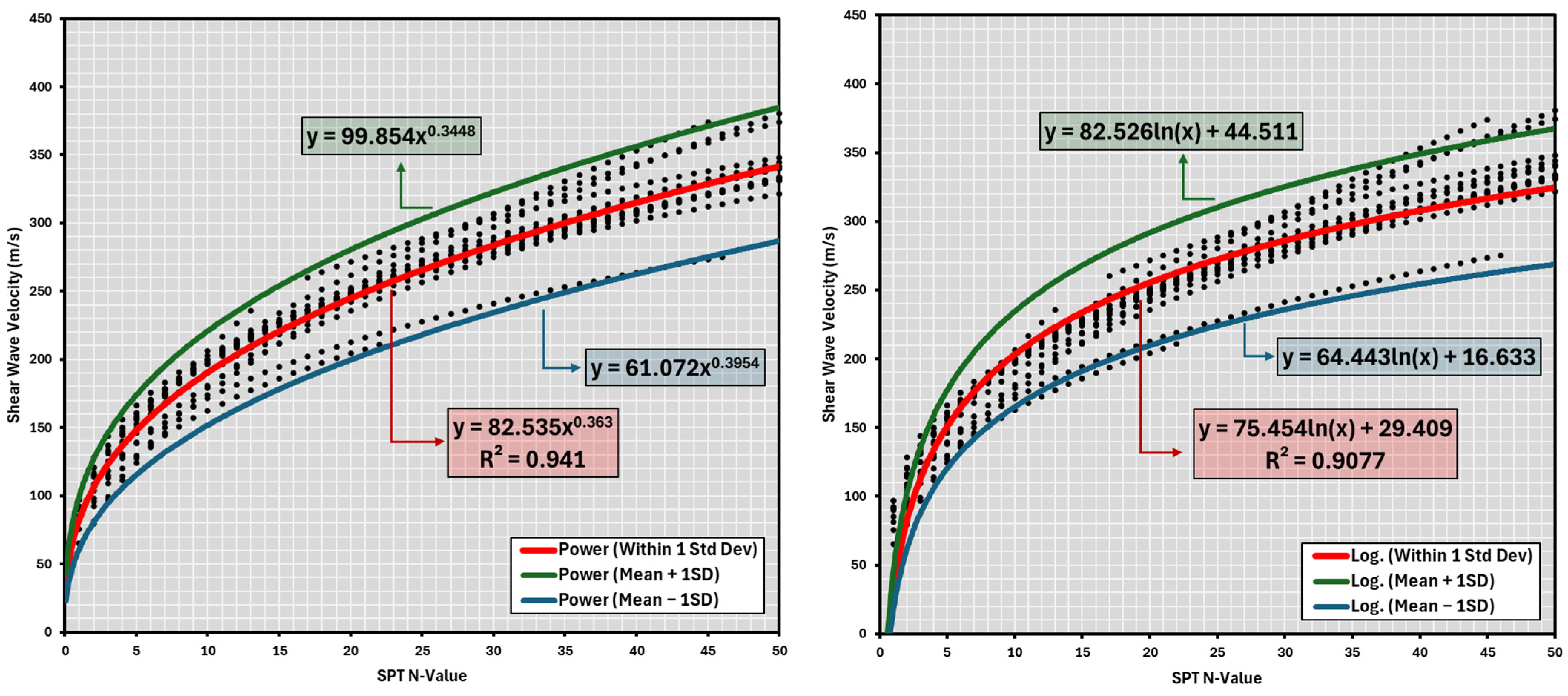
3.4. Selected Empirical Equations
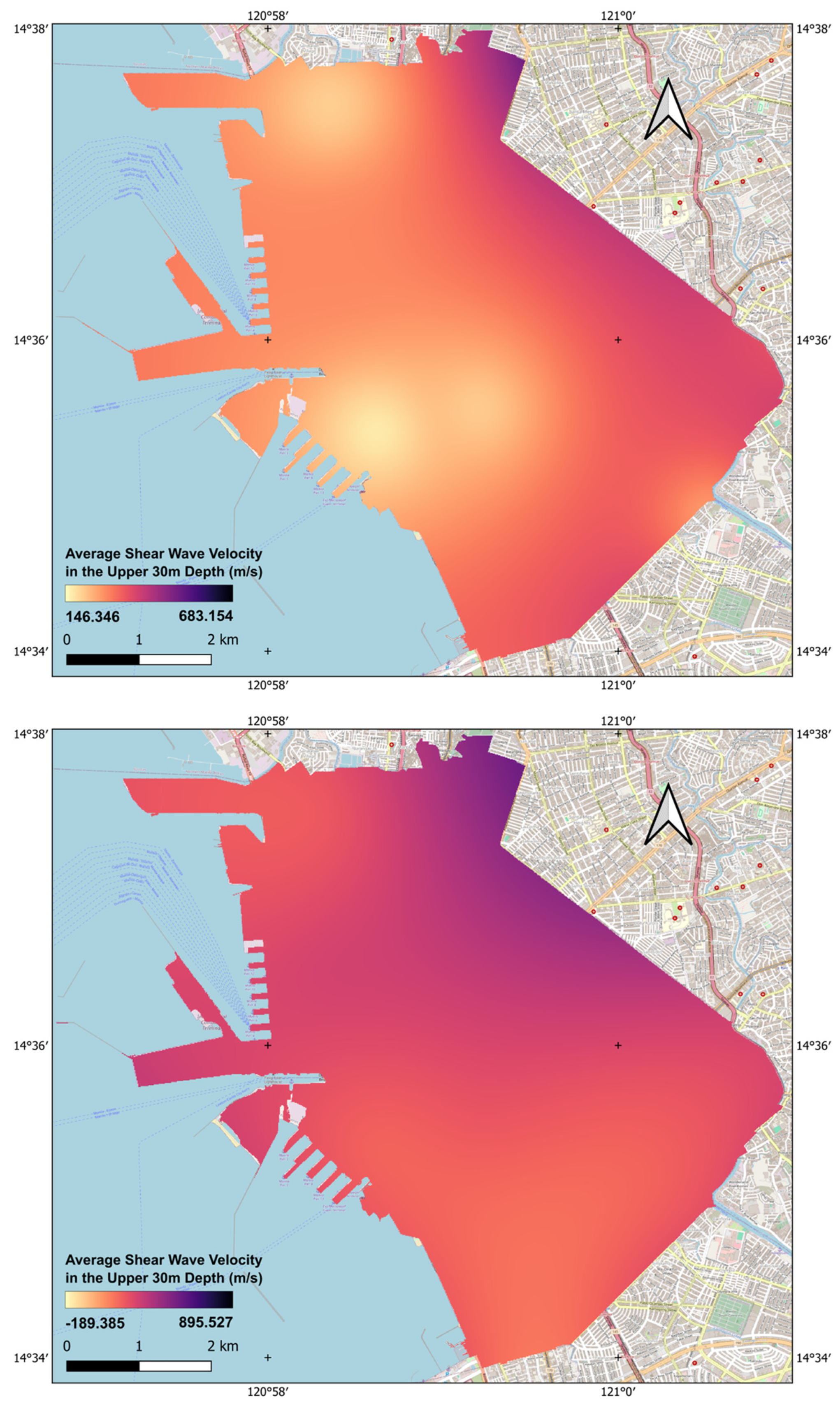
3.5. Average Shear Wave Velocity (Vs30) in the Upper 30 m Profile
3.6. Spatial Interpolation
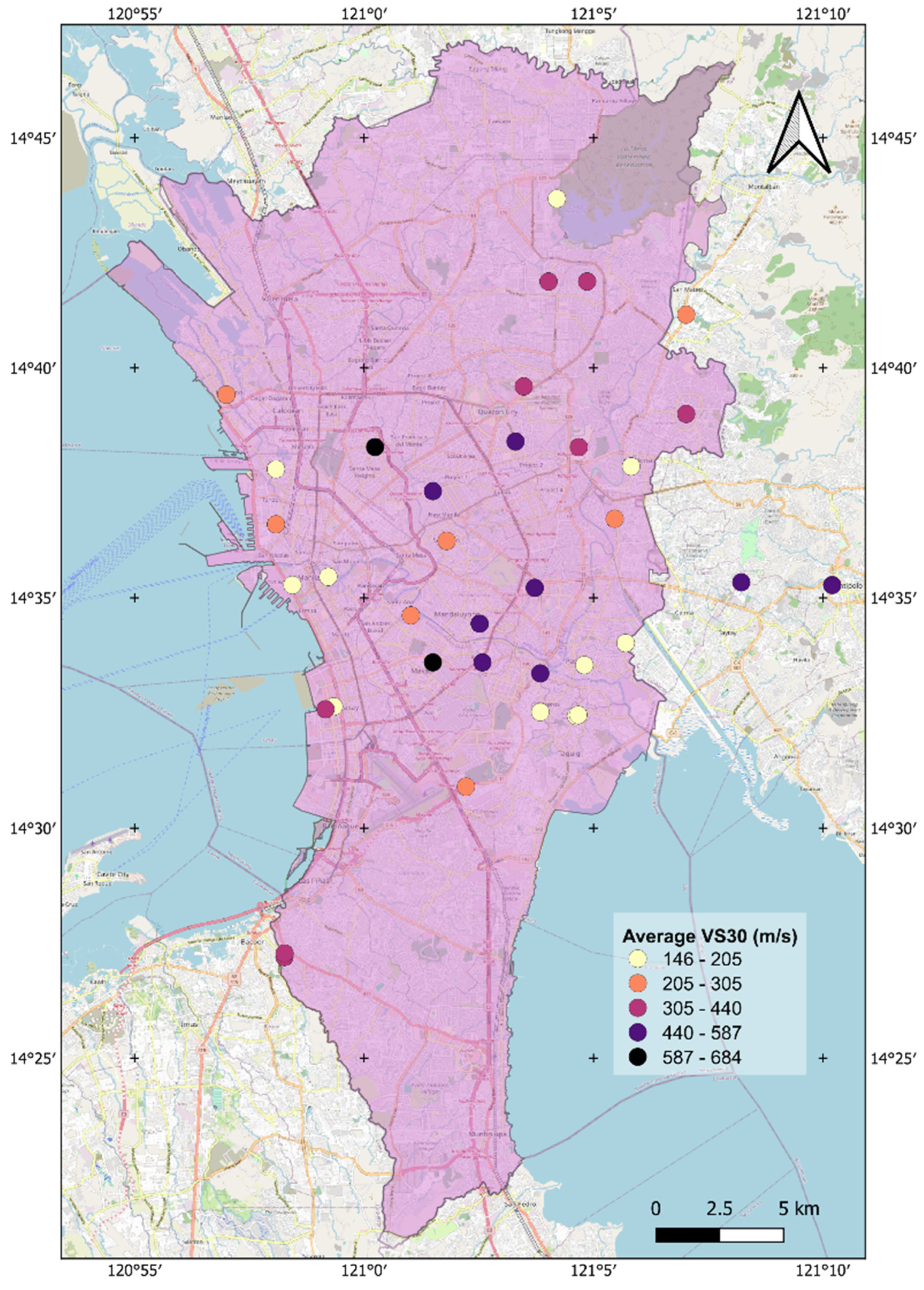
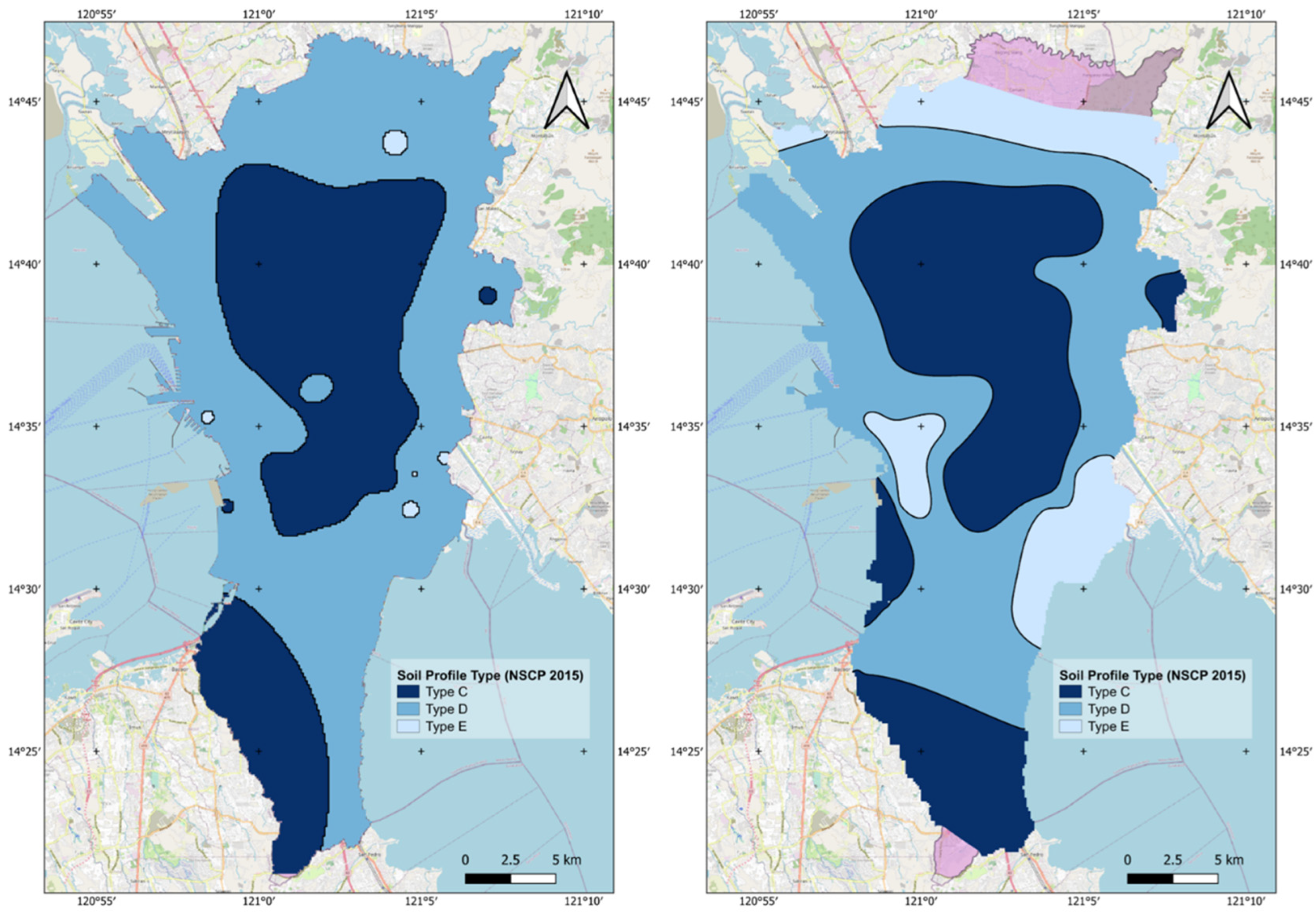
4. Results and Discussions
5. Conclusions and Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NSCP | National Structural Code of the Philippines |
| ASCE | American Society of Civil Engineers |
| SEI | Structural Engineering Institute |
| EN | European Norm (Eurocode) |
| NEHRP | National Earthquake Hazard Reduction Program |
| SPT | standard penetration test |
| GIS | geographic information system |
| OCR | over-consolidation ratio |
| ReMi | refraction microtremor |
| MASW | multichannel analysis of surface waves |
| SASW | spectral analysis of surface waves |
| ESAC | extended spatial autocorrelation |
| HVSR | horizontal to vertical spectral ratio |
| CPT | cone penetration test |
| DPWH | Department of Public Works and Highways |
| IDW | inverse distance weighted |
| SAGA | System for Automated Geoscientific Analyses |
| QGIS | quantum geographic information system |
| NMRSE | normalized root mean square error |
| ASTM | American Society for Testing and Materials |
| WGS | World Geodetic System |
| PHIVOLCS | Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology |
References
- Rimando, R.E.; Knuepfer, P.L.K. Neotectonics of the Marikina Valley Fault System (MVFS) and Tectonic Framework of Structures in Northern and Central Luzon, Philippines. Tectonophysics 2006, 415, 17–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monjardin, C.E.; Medina, A.B. Comparative Analysis of Geotechnical and Geophysical Investigations for Average Shear Wave Velocity in Metro Manila. Energy Rep. 2023, 9, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brecht, H.; Deichmann, U.; Wang, H.G. A Global Urban Risk Index; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Grutas, R.; Yamanaka, H. Shallow Shear-Wave Velocity Profiles and Site Response Characteristics from Microtremor Array Measurements in Metro Manila, the Philippines. Explor. Geophys. 2012, 43, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, K.; Choudhury, D. Variations in Shear Wave Velocity and Soil Site Class in Kolkata City Using Regression and Sensitivity Analysis. Nat. Hazards 2013, 69, 2057–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioncu, V.; Mazzolani, F.M. Earthquake Engineering for Structural Design; Spon Press/Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2011; ISBN 978-0-203-84889-0. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, H.A.; Al-Jeznawi, D.; Al-Janabi, M.A.Q.; Bernardo, L.F.A.; Jacinto, M.A.S.C. Exploring Shear Wave Velocity—NSPT Correlations for Geotechnical Site Characterization: A Review. CivilEng 2024, 5, 119–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunusluoglu, M.C. Determination of Empirical Correlations between Shear Wave Velocity and Penetration Resistance in the Canakkale Residential Area (Turkey). Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omote, S.; Osawa, Y.; Skinner, I.; Yoshima, Y. Luzon Earthquake of 2 August 1968; Series No. 977; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, C.G.; Majid, T.A.; Ariffin, K.S.; Bunnori, N.M. Seismic Microzonation for Penang Using Geospatial Contour Mapping. Nat. Hazards 2014, 73, 657–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguibao, K.J.L.; Takahashi, R. Whole-Rock Geochemistry of Host Rocks and K/Ar Age of Hydrothermal Mineral of the Co-O Epithermal Gold Deposit, Mindanao, Philippines. Open J. Geol. 2018, 8, 383–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dungca, J. A Reference for the Allowable Soil Bearing Capacities in Quezon City, Philippines. Int. J. GEOMATE 2020, 19, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dungca, J.; Concepcion, I.; Limyuen, M.C.M.; See, T.O.; Vicencio, M.R. Soil Bearing Capacity Reference for Metro Manila, Philippines. Int. J. GEOMATE 2017, 12, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galupino, J.; Dungca, J. Estimating Liquefaction Susceptibility Using Machine Learning Algorithms with a Case of Metro Manila, Philippines. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliquino, C.J.; Dungca, J. Probabilistic Liquefaction Potential Analysis of San Fernando Pampanga, Philippines Using Semi-Markov Chain. Int. J. GEOMATE 2021, 21, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dungca, J.; Montejo, M.F.G. Metropolitan Manila Seismic Hazard Map Using Midorikawa & Hori Site Amplification Model. GEOMATE J. 2022, 22, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wald, D.J.; Allen, T.I. Topographic Slope as a Proxy for Seismic Site Conditions and Amplification. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2007, 97, 1379–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macaraeg, C.J.; Dungca, J.R. Development of a Reference for Seismic Amplification: The Case of Metro Manila. In Proceedings of the 19th Congress of International Association for Bridge and Structural Engineering, Stockholm, Sweden, 21–23 September 2016; pp. 1015–1022. [Google Scholar]
- ASCE. Minimum Design Loads and Associated Criteria for Buildings and Other Structures (ASCE/SEI 7-22); ASCE: Reston, VA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 1998-1:2004; Eurocode 8: Design of Structures for Earthquake Resistance. CEN The European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2004.
- Bandyopadhyay, S.; Sengupta, A.; Reddy, G.R. Development of Correlation between SPT-N Value and Shear Wave Velocity and Estimation of Non-Linear Seismic Site Effects for Soft Deposits in Kolkata City. Geomech. Geoengin. 2021, 16, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfehanizadeh, M.; Nabizadeh, F.; Yazarloo, R. Correlation between Standard Penetration (N SPT) and Shear Wave Velocity (V S) for Young Coastal Sands of the Caspian Sea. Arab. J. Geosci. 2015, 8, 7333–7341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Orense, R.; Lombardi, D. Seismic Design of Foundations: Concepts and Applications; ICE Publishing: London, UK, 2019; ISBN 978-0-7277-6166-8. [Google Scholar]
- Sen, T.K. Fundamentals of Seismic Loading on Structures; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2009; ISBN 978-0-470-01755-5. [Google Scholar]
- Daag, A.S.; Halasan, O.P.C.; Magnaye, A.A.T.; Grutas, R.N.; Solidum, R.U. Empirical Correlation between Standard Penetration Resistance (SPT-N) and Shear Wave Velocity (Vs) for Soils in Metro Manila, Philippines. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansary, M.; Ansary, M. Use of SPT and Depth for Estimating Shear-Wave Velocity Using Optimised Machine Learning Models. J. Civ. Eng. 2023, 51, 99–119. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, J.; Lee, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Day, S. Control of Strong Motion by the Upper 30 Meters. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1996, 86, 1749–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.-H.; Wen, K.-L.; Hsieh, H.-H.; Chang, T.-M.; Lin, C.-M.; Chen, C.-T. Evaluating Empirical Regression Equations for Vs and Estimating Vs30 in Northeastern Taiwan. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2011, 31, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallipoli, M.R.; Mucciarelli, M. Comparison of Site Classification from VS30, VS10, and HVSR in Italy. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2009, 99, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo, M.; Benjumea, B.; Moratalla, J.M.; Lacoma, L.; Macau, A.; González, Á.; Gutiérrez, F.; Stafford, P. A Proxy-Based Model for Estimating VS30 in the Iberian Peninsula. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2022, 155, 107165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Satyannarayana, R.; Rajesh, B.G. Correlation between SPT-N and Shear Wave Velocity (V) and Seismic Site Classification for Amaravati City, India. J. Appl. Geophys. 2022, 205, 104757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motalleb Nejad, M.; Momeni, M.S.; Manahiloh, K.N. Shear Wave Velocity and Soil Type Microzonation Using Neural Networks and Geographic Information System. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2018, 104, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghanian, K.; Çaltili, E.; Koçak Dinç, B.; Soysal, H.M. Implementation of Shear Wave Velocity and Standard Penetration Test Correlation for Edirne District, Turkey. J. Sustain. Constr. Mater. Technol. 2022, 7, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslami, A.; Moshfeghi, S.; MolaAbasi, H.; Eslami, M.M. 4—Geotechnical Parameters from CPT Records. In Piezocone and Cone Penetration Test (CPTu and CPT) Applications in Foundation Engineering; Eslami, A., Moshfeghi, S., MolaAbasi, H., Eslami, M.M., Eds.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2020; pp. 81–110. ISBN 978-0-08-102766-0. [Google Scholar]
- Shooshpasha, I.; Molaabasi, H.; Jamalian, A.; Dikmen, Ü.; Salahi, M. Validation and Application of Empirical Shear Wave Velocity Models Based on Standard Penetration Test. Comput. Methods Civ. Eng. 2013, 4, 25–41. [Google Scholar]
- Heo, G.; Kim, J.; Jeong, S.; Kwak, D. Evaluation of Shear Wave Velocity Prediction Models from Standard Penetration Test N Values Depending on Geologic Attributes: A Case Study in Busan, South Korea. Geotechnics 2023, 3, 1004–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvasi, Y. Shear-Wave Velocity Measurements and Their Uncertainties at Six Industrial Sites. Earthq. Spectra 2021, 37, 2223–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiuly, A.; Roy, N. A Generalized VS–N Correlation Using Various Regression Analysis and Genetic Algorithm. Acta Geod. Geophys. 2018, 53, 479–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzel, Y. Correlating Measured SPT-N, Shear Wave Velocity and Liquid Limit Values in Melekli Region, Igdır (Türkiye). Çanakkale Onsekiz Mart Univ. J. Adv. Res. Nat. Appl. Sci. 2024, 2024, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataee, O.; Moghaddas, N.H.; Lashkaripour, G.R. Estimating Shear Wave Velocity of Soil Using Standard Penetration Test (SPT) Blow Counts in Mashhad City. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 128, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazi, A.; Moghadas, N.H.; Sadeghi, H.; Ghafoori, M.; Lashkaripur, G.R. Empirical Relationships of Shear Wave Velocity, SPT_N Value and Vertical Effective Stress for Different Soils in Mashhad, Iran. Ann. Geophys. 2015, 58, S0325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasancebi, N.; Ulusay, R. Empirical Correlations between Shear Wave Velocity and Penetration Resistance for Ground Shaking Assessments. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2007, 66, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeel, M.B.; Nizamani, Z.A.; Aaqib, M.; Khan, S.; Rehman, J.U.; Bhusal, B.; Park, D. Estimation of VS30 Using Shallow Depth Time-Averaged Shear Wave Velocity of Rawalpindi–Islamabad, Pakistan. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2023, 14, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marto, A.; Soon, T.C.; Kasim, F.; Suhatril, M. A Correlation of Shear Wave Velocity and Standard Penetration Resistance. Electron. J. Geotech. Eng. 2013, 18, 463–471. [Google Scholar]
- Darzi, A.; Halldorsson, B.; Cotton, F.; Rahpeyma, S. Nationwide Frequency-Dependent Seismic Site Amplification Models for Iceland. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2024, 183, 108798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirar, B.; Maheshwari, B.K.; Muley, P. Correlation Between Shear Wave Velocity (Vs) and SPT Resistance (N) for Roorkee Region. Int. J. Geosynth. Ground Eng. 2016, 2, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-C.; Kishida, T.; Kuo, C.-H. Unified Correlation between SPT–N and Shear Wave Velocity for a Wide Range of Soil Types Considering Strain-Dependent Behavior. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2019, 126, 105783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussien, M.N.; Karray, M. Shear Wave Velocity as a Geotechnical Parameter: An Overview. Can. Geotech. J. 2016, 53, 252–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Liu, J.; Guo, L.; Deng, Z. Methodology and Assessment of Proxy-Based Vs30 Estimation in Sichuan Province, China. Int. J. Disaster Risk Sci. 2020, 11, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatrayi, H.; Hajizadeh, F.; Taghavi, B. Shear Wave Velocity (Vs) and SPT Resistance (N) Correlation for the Isfahan Metro, Iran. Acta Geophys. 2023, 72, 1749–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhuay-León, C.G.; Trejo-Noreña, P.C. The Empirical Correlation between Shear Wave Velocity and Penetration Resistance for the Eolian Sand Deposits in the City of Olmos-Peru. DYNA 2021, 88, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbazhagan, P.; Parihar, A.; Rashmi, H.N. Review of Correlations between SPT N and Shear Modulus: A New Correlation Applicable to Any Region. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2012, 36, 52–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashikuzzaman, M.; Hossain, A.; Shakil Ar Salan, M.; Ashikur Rahman, M.; Mahmudul Hasan, M. Development of Empirical Correlations Between Shear Wave Velocity and Standard Penetration Value: A Case Study of Rajshahi District, Bangladesh. Am. J. Mech. Ind. Eng. 2021, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauzi, A.; Irsyam, M.; Fauzi, U.J. Empirical Correlation of Shear Wave Velocity and N-Spt Value For Jakarta. GEOMATE J. 2014, 7, 980–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uma Maheswari, R.; Boominathan, A.; Dodagoudar, G.R. Use of Surface Waves in Statistical Correlations of Shear Wave Velocity and Penetration Resistance of Chennai Soils. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2010, 28, 119–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanai, K. Conference on Cone Penetrometer; The Ministry of Public Works and Settlement: Ankara, Turkey, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Imai, T.; Yoshimura, Y. Elastic Wave Velocity and Soil Properties in Soft Soil (in Japanese). Tsuchito-kiso 1970, 18, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Ohba, S.; Toriumi, I. Dynamic Response Characteristics of Osaka Plain. In Proceedings of the Annual Meeting AIJ; AIJ: Tokyo, Japan, 1970; Volume 12. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara, T. Estimation of Ground Movements in Actual Destructive Earthquakes. In Proceedings of the Fourth European Symposium on Earthquake Engineering, London, UK, 5–7 September 1972; pp. 125–132. [Google Scholar]
- Ohsaki, Y.; Iwasaki, R. On Dynamic Shear Moduli and Poisson’s Ratios of Soil Deposits. Soils Found. 1973, 13, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, T.; Yoshimura, Y. The Relation of Mechanical Properties of Soils to P and S-Wave Velocities for Ground in Japan; Technical note OYO Corporation: Tokyo, Japan, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Imai, T.; Fumoto, H.; Yokota, K. The Relation of Mechanical Properties of Soil to P-and S-Wave Velocities in Japan. In Proceedings of the 4th Japan Earthquake Engineering Symposium, Tokyo, Japan, 26–28 November 1975; pp. 89–96. [Google Scholar]
- Imai, T. P and S Wave Velocities of the Ground in Japan. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering, Tokyo, Japan, 10–15 July 1977; Volume 2, pp. 257–260. [Google Scholar]
- Ohta, Y.; Goto, N. Empirical Shear Wave Velocity Equations in Terms of Characteristic Soil Indexes. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 1978, 6, 167–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seed, H.B.; Idriss, I. Evaluation of Liquefaction Potential Sand Deposits Based on Observation of Performance in Previous Earthquakes. In Proceedings of the ASCE National Convention (MO), St. Louis, MO, USA, 26–30 October 1981; pp. 481–544. [Google Scholar]
- Yokota, K.; Imai, T.; Konno, M. Dynamic Deformation Characteristics of Soils Determined by Laboratory Tests. OYO Tec. Rep. 1981, 3, 13–37. [Google Scholar]
- Imai, T.; Tonouchi, K. Correlation of N Value with S-Wave Velocity and Shear Modulus. In Proceedings of the 2nd European Symposium on Penetration Testing, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 24–27 May 1982; pp. 67–72. [Google Scholar]
- Tonouchi, K.; Sakayama, T.; Imai, T. S Wave Velocity in the Ground and the Damping Factor. In Proceedings of the Bulletin of the International Association of Engineering Geology; 1983; pp. 327–333. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S. Analysis of the Multicollinearity of Regression Equations of Shear Wave Velocities. Soils Found. 1992, 32, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J. Correlation between Seismic Wave Velocity and the Number of Blow of SPT and Depth. Sel. Pap. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 1987, 12, 92–100. [Google Scholar]
- Kalteziotis, N.; Sabatakakis, N.; Vassiliou, J. Evaluation of Dynamic Characteristics of Greek Soil Formations. In Proceedings of the Second Hellenic Conference on Geotechnical Engineering, Thessaloniki, Greece, 21–23 October 1992; Volume 2, pp. 239–246. [Google Scholar]
- Athanasopoulos, G. Empirical Correlations Vso-NSPT for Soils of Greece: A Comparative Study of Reliability. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, Seville, Spain, 23–25 September 2024; WIT Press: Crete, Greece, 1995; Volume 15. [Google Scholar]
- Sisman, H. An Investigation on Relationships Between Shear Wave Velocity, and SPT and Pressuremeter Test Results. Master’s Thesis, Ankara University, Ankara, Turkey, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Iyisan, R. Correlations between Shear Wave Velocity and In-Situ Penetration Test Results. Tek. Dergi-Tmmob Insa. Muhendisleri Odasi 1996, 7, 371–374. [Google Scholar]
- Jafari, M.; Asghari, A.; Rahmani, I. Empirical Correlation between Shear Wave Velocity (Vs) and SPT-N Value for South of Tehran Soils. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Civil Engineering, Tehran, Iran, 4–6 May 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Kiku, H. In-Situ Penetration Tests and Soil Profiling in Adapazari, Turkey. In Proceedings of the 15th ICSMGE TC4 Satellite Conference on Lessons Learned from Recent Strong Earthquakes, Istanbul, Turkey, 25 August 2001; pp. 259–265. [Google Scholar]
- Ulugergerli, E.; Uyanik, O. Statistical Correlations Between Seismic Wave Velocities and SPT Blow Counts and the Relative Density of Soils. J. Test. Eval. 2007, 35, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanumantharao, C.; Ramana, G.V. Dynamic Soil Properties for Microzonation of Delhi, India. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2008, 117, 719–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.-G.; Kim, H.-J.; Chung, C.-K. Deduction of Correlations between Shear Wave Velocity and Geotechnical In-Situ Penetration Test Data. J. Earthq. Eng. Soc. Korea 2008, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikmen, Ü. Statistical Correlations of Shear Wave Velocity and Penetration Resistance for Soils. J. Geophys. Eng. 2009, 6, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafezi Moghaddas, N.; Azadi, A.; Amanian, M. Assessment of Shear Wave Velocity Based on Standard Penetration and Accuracy of the Results in the Range of Mashhad City. In Proceedings of the Fourteenth Geophysics Conference of Iran, Tehran, Iran, 13 May 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Mhaske, S.Y.; Choudhury, D. Geospatial Contour Mapping of Shear Wave Velocity for Mumbai City. Nat. Hazards 2011, 59, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sil, A.; Haloi, J. Empirical Correlations with Standard Penetration Test (SPT)-N for Estimating Shear Wave Velocity Applicable to Any Region. Int. J. Geosynth. Ground Eng. 2017, 3, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, T. The Relationship Between the N-Value and S-Wave Velocity in the Soil Layer; Disaster Prevention Research Laboratory, Kyoto University: Kyoto, Japan, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Ohta, T.; Hara, A.; Niwa, M.; Sakano, T. Elastic Shear Moduli as Estimated from N-Value. In Proceedings of the 7th Annual Convention of Japan Society of Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering, Tokyo, Japan, 10–15 July 1972; pp. 265–268. [Google Scholar]
- Seed, H.B.; Idriss, I.M.; Arango, I. Evaluation of Liquefaction Potential Using Field Performance Data. J. Geotech. Eng. 1983, 109, 458–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykora, D.W. Correlations of in Situ Measurements in Sands of Shear Wave Velocity, Soil Characteristics, and Site Conditions. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Texas at Austin, Austin, TX, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Fumal, T.; Tinsley, J.; Ziony, J. Mapping Shear-Wave Velocities of near-Surface Geologic Materials. US Geol. Surv. Prof. Pap. 1985, 1360, 127–150. [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto, T.; Kokusho, T.; Yoshida, Y.; Kusuonoki, K. Comparison of Surface versus Subsurface Wave Source for P–S Logging in Sand Layer. In Proceedings of the 44th Annual Conference of the Japan Society of Civil Engineers (JSCE), Tokyo, Japan, 4–6 October 1989; Volume 3, pp. 996–997. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.H.-H. Regression Models of Shear Wave Velocities in Taipei Basin. J. Chin. Inst. Eng. 1990, 13, 519–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitilakis, K.; Anastasiadis, A.; Raptakis, D. Field and Laboratory Determination of Dynamic Properties of Natural Soil Deposits. In Proceedings of the 10th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering, Madrid, Spain, 19–24 July 1992; Volume 5, pp. 1275–1280. [Google Scholar]
- Raptakis, D.; Anastasiadis, S.; Pitilakis, K.; Lontzetidis, K. Shear Wave Velocities and Damping of Greek Natural Soils. In Proceedings of the 10th European Conference on Earthquake Engineering, Vienna, Austria, 28 August–2 September 1994; Volume 477482. [Google Scholar]
- Kayabali, K. Soil Liquefaction Evaluation Using Shear Wave Velocity. Eng. Geol. 1996, 44, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitilakis, K.; Raptakis, D.; Lontzetidis, K.; Tika-Vassilikou, T.; Jongmans, D. Geotechnical and Geophysical Description of EURO-SEISTEST, Using Field, Laboratory Tests and Moderate Strong Motion Recordings. J. Earthq. Eng. 1999, 3, 381–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, L.; Oh, E. Laboratory and Field Shear Wave Measurement at a Reclaimed Site in West Taiwan. Geotech. Test. J. 2000, 23, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, M.K.; Shafiei, A.; Razmkhah, A. Dynamic Properties of Fine Grained Soils in South of Tehran. J. Seismol. Earthq. Eng. 2002, 4, 25–35. [Google Scholar]
- Tsiambaos, G.; Sabatakakis, N. Empirical Estimation of Shear Wave Velocity from in Situ Tests on Soil Formations in Greece. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2011, 70, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatehnia, M.; Hayden, M.; Landschoot, M. Correlation between Shear Wave Velocity and SPT-N Values for North Florida Soils. Electron. J. Geotech. Eng. 2015, 20, 12421–12430. [Google Scholar]
- Boore, D.; Thompson, E.; Cadet, H. Regional Correlations of VS30 and Velocities Averaged Over Depths Less Than and Greater Than 30 Meters. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2011, 101, 3046–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boore, D. Estimating V ¢ s (30) (or NEHRP Site Classes) from Shallow Velocity Models (Depths 30 m). Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 2004, 94, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PHIVOLCS. The Philippine Earthquake Model: A Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Assessment of the Philippines and of Metro Manila 2017; Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology: Quezon City, Philippines, 2017.
- Midorikawa, S.; Fujimoto, K.; Yamanaka, H.; Miura, H.; Pacheco, B.M.; Bautista, B.C. GIS-Based Earthquake Damage Assessment Considering Seismic Capacity of Existing Buildings in Metro Manila, Philippines; Association of Structural Engineers of the Philippines: Manila, Philippines, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Adajar, M.A.; Tan, J.; Adriano, A.; Vera, S.B.D.; Manabat, J.V.; Navarro, H. Agar Biopolymer as a Sustainable Alternative Binder to Enhance the Strength of Low-Plasticity Soil. Polymers 2025, 17, 1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galupino, J.; Dungca, J. Estimating Ground Elevation Using Borehole Information: A Case of Metro Manila, Philippines. In Proceedings of the International Exchange and Innovation Conference on Engineering & Sciences (IEICES); Interdisciplinary Graduate School of Engineering Sciences, Kyushu University: Fukuoka, Japan, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM D1586; Test Method for Standard Penetration Test (SPT) and Split-Barrel Sampling of Soils. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2018. [CrossRef]
- ASEP. National Structural Code of the Philippines, 2015. Volume 1, Buildings, Towers, and Other Vertical Structures; Association of Structural Engineers of the Philippines: Quezon City, Philippines, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hengl, T. A Practical Guide to Geostatistical Mapping of Environmental Variables. Available online: https://publications.jrc.ec.europa.eu/repository/handle/JRC38153 (accessed on 5 August 2024).
- Tan, J.; Aniñon, M.J. Review of GIS-Based Approaches in Earthquake Disaster Management. In Proceedings of the International Exchange and Innovation Conference on Engineering & Sciences (IEICES); Interdisciplinary Graduate School of Engineering Sciences, Kyushu University: Fukuoka, Japan, 2024. [Google Scholar]




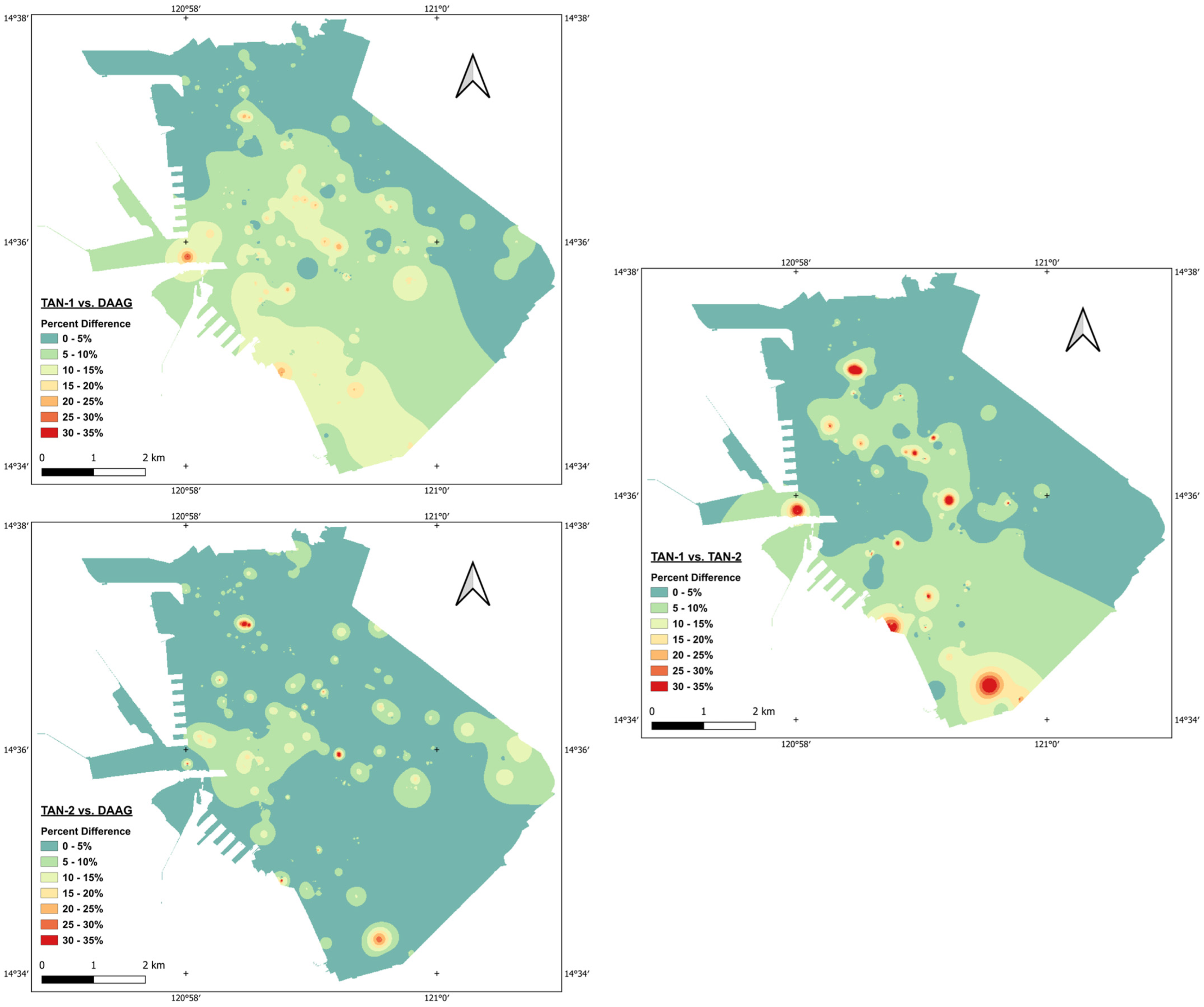
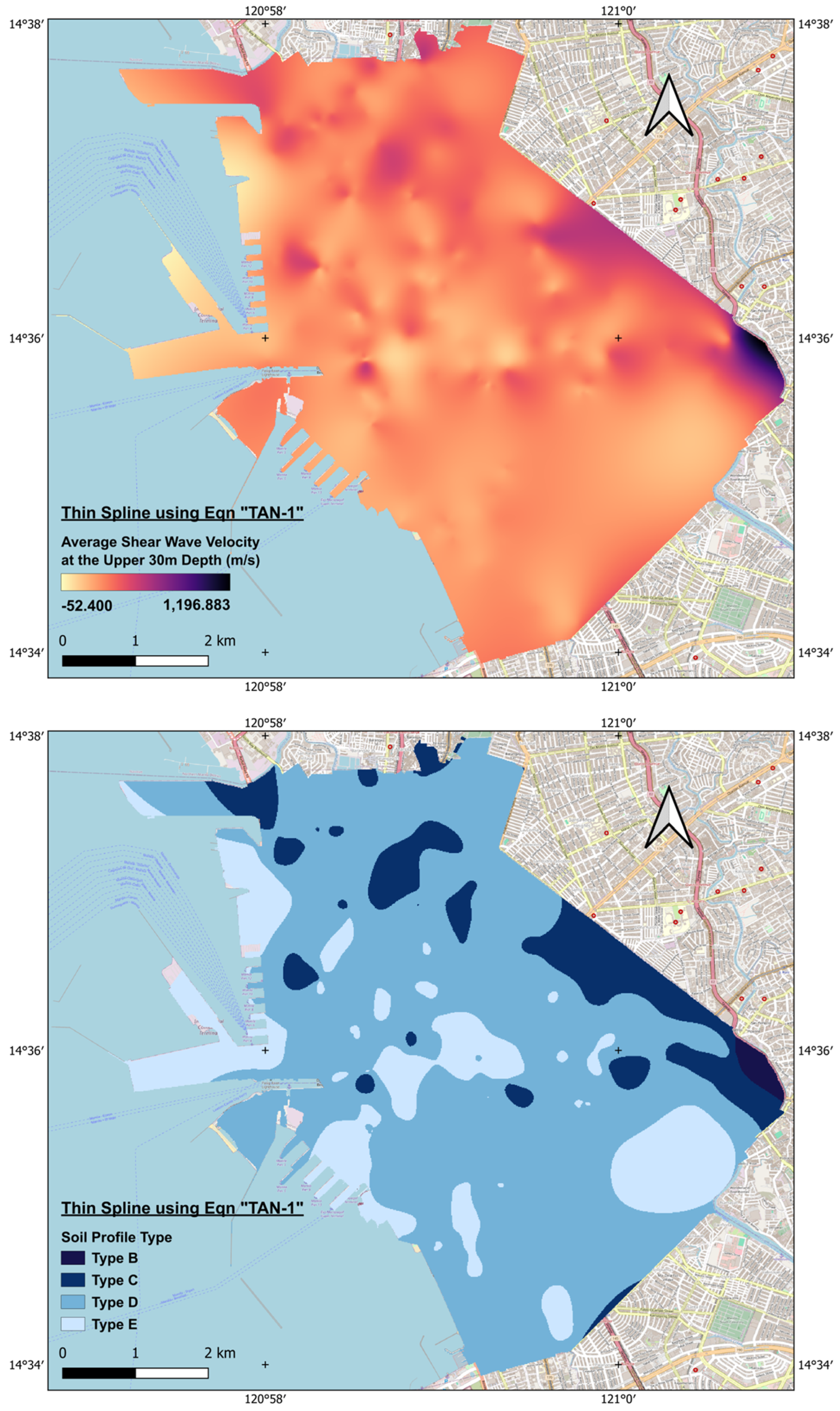
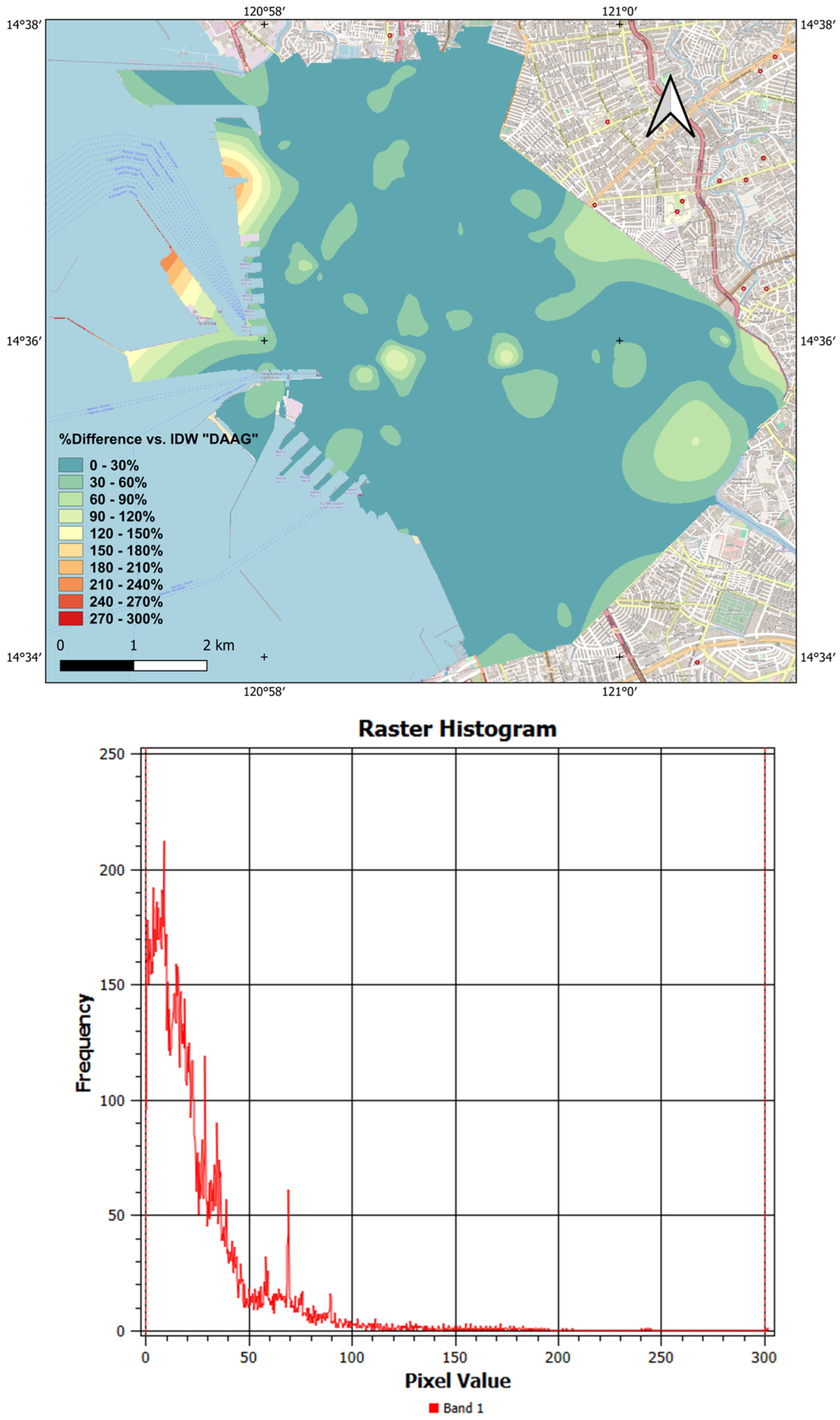

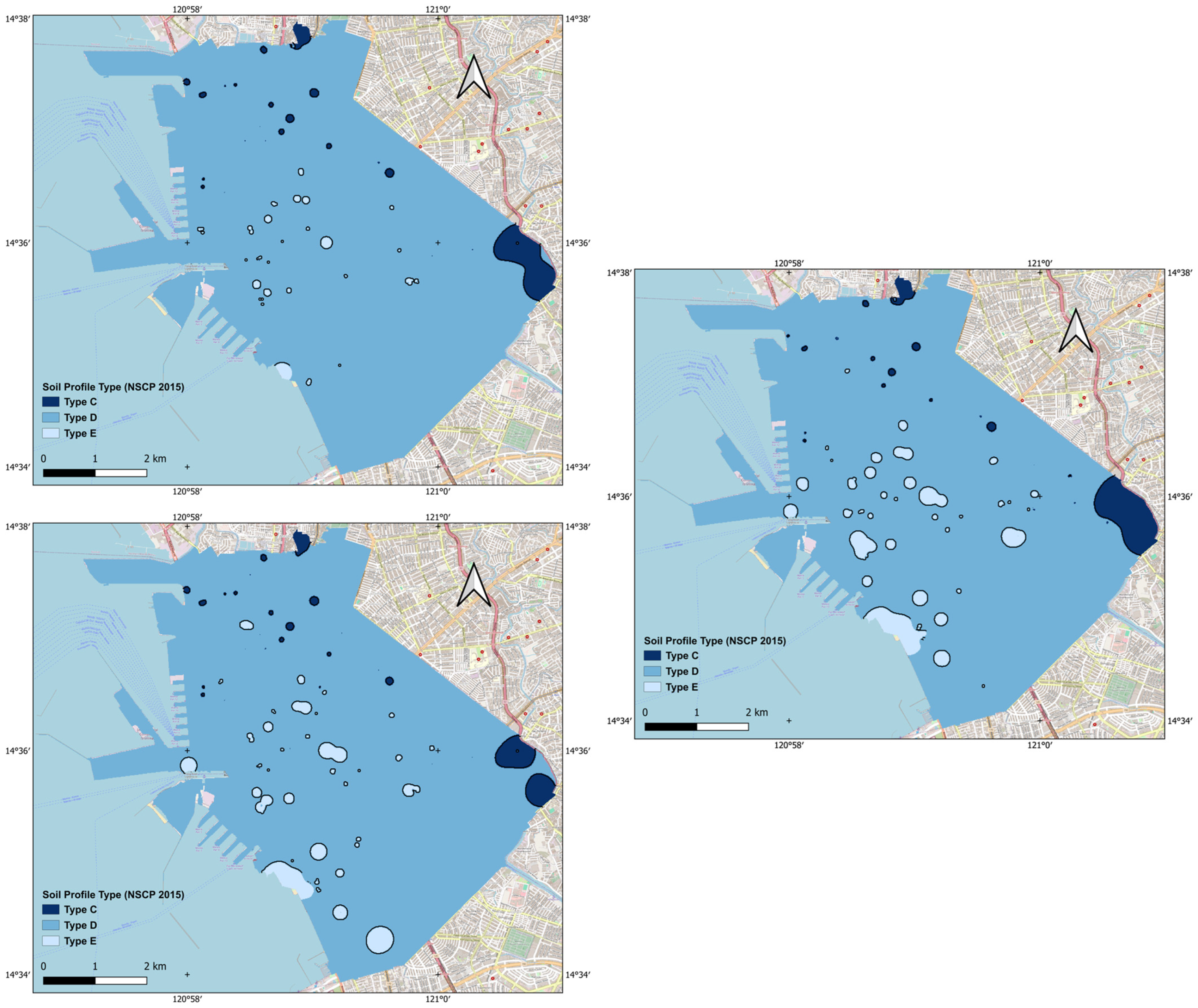
| Parameter | Effect of Gmax on Vs |
|---|---|
| Confining stress | Increases with confining stress |
| Void ratio | Decreases with increase in void ratio |
| Over-consolidation ratio (OCR) | Increases |
| Cementation | Increases |
| Author | Country | All Soils |
|---|---|---|
| Kanai [56] | Japan | Vs = 19N0.6 |
| Imai and Yoshimura [57] | Japan | Vs = 76N0.33 |
| Ohba and Toriumi [58] | Japan | Vs = 84N0.31 |
| Fujiwara [59] | Japan | Vs = 92.1N0.337 |
| Ohsaki and Iwasaki [60] | Japan | Vs = 81.38N0.39 |
| Imai and Yoshimura [61] | Japan | Vs = 92.05N0.329 |
| Imai, Fumoto, and Yokota [62] | Japan | Vs = 89.92N0.341 |
| Imai [63] | Japan | Vs = 91N0.337 |
| Ohta and Goto [64] | Japan | Vs = 85.35N0.348 |
| Seed and Idriss [65] | USA | Vs = 61.4N0.5 |
| Yokota et al. [66] | Japan | Vs = 121N0.27 |
| Imai and Tonouchi [67] | Japan | Vs = 96.9N0.314 |
| Tonouchi et al. [68] | Japan | Vs = 97N0.314 |
| Lin et al. [69] | Taiwan | Vs = 65N0.502 |
| Zheng [70] | China | Vs = 116.1(N + 0.3185)0.6 |
| Lee [69] | Taiwan | Vs = 57.4N0.49 |
| Kalteziotis et al. [71] | Greece | Vs = 76.2N0.24 |
| Athanasopoulos [72] | Greece | Vs = 107.6N0.36 |
| Sisman [73] | Turkey | Vs = 32.8N0.51 |
| Iyisan [74] | Turkey | Vs = 51.5N0.516 |
| Jafari et al. [75] | Iran | Vs = 22N0.85 |
| Kiku et al. [76] | Turkey | Vs = 68.3N0.292 |
| Hasancebi and Ulusay [42] | Turkey | Vs = 90N0.309 and Vs = 104.79(N60)0.26 |
| Ulugergerli and Uyanik [77] | Turkey | Vs = 23.29ln(N) + 405.61 (upper bound) Vs = 52.9e−0.01N (lower bound) |
| Hanumantharao and Ramana [78] | India | Vs = 86.2N0.43 |
| Sun et al. [79] | South Korea | Vs = 65.64N0.407 |
| Dikmen [80] | Turkey | Vs = 58N0.39 |
| Hafezi Moghaddas et al. [81] | Iran | Vs = 99N0.53 |
| Uma Maheswari et al. [55] | India | Vs = 95.64N0.301 |
| Mhaske and Choudhury [82] | India | Vs = 72N0.40 |
| Chatterjee and Choudhury [5] | India | Vs = 78.21N0.38 |
| Marto et al. [44] | Global | Vs = 77.13N0.377 |
| Fauzi [54] | Indonesia | Vs = 105.03N0.286 |
| Kirar [46] | India | Vs = 99.5N0.345 and Vs = 90.6(N60)0.341 |
| Sil and Haloi [83] | Global | Vs = 75.478N0.3799 |
| Daag et al. [25] | Philippines | Vs = 56.82N0.4861 |
| Chatrayi et al. [50] | India | Vs = 141.84N0.5853 |
| Author | Country | Sand | Silt | Clay |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shibata [84] | Japan | Vs = 31.7N0.54 | - | - |
| Ohta et al. [85] | Japan | Vs = 87.2N0.36 | - | - |
| Ohsaki and Iwasaki [60] | Japan | Vs = 59.4N0.47 | - | - |
| Imai [62] | Japan | Vs = 80.6N0.331 | - | Vs = 102N0.292 |
| Yokota et al. [66] | Japan | - | - | Vs = 114N0.31 |
| Seed et al. [86] | Japan | Vs = 56.4N0.5 | - | - |
| Sykora and Stokoe [87] | USA | Vs = 100.5N0.29 | - | - |
| Fumal and Tinsley [88] | USA | Vs = 152 + 51N0.27 | - | - |
| Okamoto et al. [89] | Japan | Vs = 125N0.3 | - | - |
| Lee [90] | Taiwan | Vs = 57.4N0.49 | Vs = 105.64N0.319 | Vs = 114.43N0.31 |
| Lee [69] | Taiwan | - | - | Vs = 138.4(N + 1)0.242 |
| Pitilakis et al. [91] | Greece | Vs = 162N0.17 | Vs = 165.7N0.19 | - |
| Athanasopoulos [72] | Greece | - | - | Vs = 76.55N0.445 |
| Raptakis et al. [92] | Greece | Vs = 100.7N0.24 | - | Vs = 184.2N0.17 |
| Kayabali [93] | Turkey | Vs = 175 + 3.75N | - | - |
| Pitilakis et al. [94] | Turkey | Vs = 145(N60)0.178 | - | Vs = 132(N60)0.271 |
| Chien and Oh [95] | Taiwan | Vs = 22N0.76 | - | - |
| Jafari et al. [96] | Iran | Vs = 19N0.85 | Vs = 22N0.77 | Vs = 27N0.73 |
| Hasancebi and Ulusay [42] | Turkey | Vs = 90.82N0.319 Vs = 131(N60)0.205 | - | Vs = 97.89N0.269 Vs = 107.6(N60)0.237 |
| Hanumantharao and Ramana [78] | India | Vs = 79.0N0.434 | Vs = 86N0.42 | - |
| Sun et al. [79] | South Korea | Vs = 82.01N0.319 | Vs = 82.01N0.319 | - |
| Dikmen [80] | Turkey | Vs = 73N0.33 | Vs = 60N0.36 | Vs = 44N0.48 |
| Hafezi Moghaddas et al. [81] | Iran | Vs = 80N0.58 | - | Vs = 45N0.72 |
| Tsiambaos and Sabatakakis [97] | Greece | - | Vs = 99.45N0.364 | - |
| Uma Maheswari et al. [55] | India | Vs = 100.53N0.265 | - | Vs = 89.3N0.358 |
| Chatterjee and Choudhury [5] | India | - | Vs = 54.82N0.53 | Vs = 77.11N0.39 |
| Esfehanizadeh et al. [22] | Iran | Vs = 107.3N0.34 | - | - |
| Fatehnia et al. [98] | USA | Vs = 77.1N0.355 | - | Vs = 77.1N0.355 |
| Kirar [46] | India | Vs = 100.3N0.338 | - | Vs = 94.4N0.379 |
| Daag et al. [25] | Philippines | Vs = 45.07N0.5534 | - | Vs = 70.26N0.4420 |
| Chatrayi et al. [50] | India | Vs = 140.85N05872 | - | Vs = 143.2N0.5815 |
| Tunusluoglu [8] | Turkey | Vs = 59N0.42 Vs = 83(N60)0.343 | - | - |
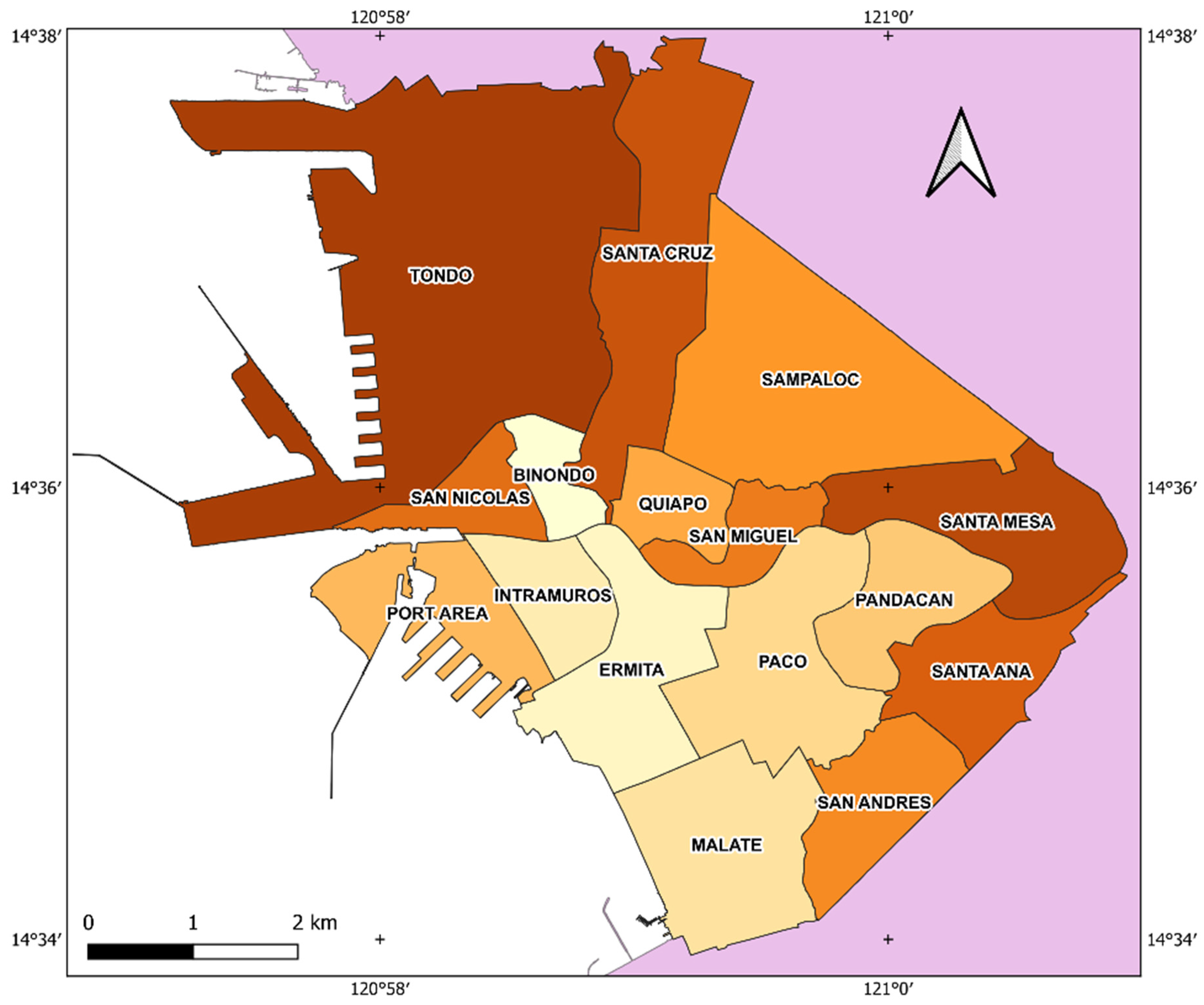
| District | Borehole Points | Borehole Density (per km2) | District | Borehole Points | Borehole Density (per km2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Binondo | 4 | 6 | Sampaloc | 32 | 16 |
| Ermita | 40 | 16 | San Andres | 2 | 1 |
| Intramuros | 26 | 22 | San Miguel | 22 | 24 |
| Malate | 11 | 4 | San Nicolas | 32 | 34 |
| Paco | 26 | 9 | Santa Ana | 0 | 0 |
| Pandacan | 0 | 0 | Santa Cruz | 48 | 13 |
| Port Area | 2 | 1 | Santa Mesa | 34 | 13 |
| Quiapo | 17 | 19 | Tondo | 175 | 15 |
| Author | Equation | Author | Equation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kanai [56] | Vs = 19N0.6 | Yokota et al. [66] | Vs = 121N0.27 |
| Imai and Yoshimura [57] | Vs = 76N0.33 | Imai and Tonouchi [67] | Vs = 96.9N0.314 |
| Ohba and Toriumi [58] | Vs = 84N0.31 | Tonouchi et al. [68] | Vs = 97N0.314 |
| Fujiwara [59] | Vs = 92.1N0.337 | Lin et al. [69] | Vs = 65N0.502 |
| Ohsaki and Iwasaki [60] | Vs = 81.38N0.39 | Lee [69] | Vs = 57.4N0.49 |
| Imai and Yoshimura [61] | Vs = 92.05N0.329 | Fauzi [54] | Vs = 105.03N0.286 |
| Imai, Fumoto, and Yokota [62] | Vs = 89.92N0.341 | Sil and Haloi [83] | Vs = 75.478N0.3799 |
| Imai [63] | Vs = 91N0.337 | Daag et al. [25] | Vs = 56.82N0.4861 |
| Ohta and Goto [64] | Vs = 85.35N0.348 |
| Soil Profile Type | Description | Average Values for Top 30 m of Soil Profile | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shear Wave Velocity Vs (m/s) | SPT, N (Blows/300 mm) | Undrained Shear Strength, Su (kPa) | ||
| SA | Hard Rock | >1500 | ||
| SB | Rock | 760 to 1500 | ||
| SC | Very Dense Soil and Soft Rock | 360 to 760 | >50 | >100 |
| SD | Stiff Soil Profile | 180 to 360 | 15 to 50 | 50 to 100 |
| SE | Soft Soil Profile 1 | <180 | <15 | <50 |
| SF | Soil requiring site-specific evaluation 2 | |||
| Model | RMSE | Range | NMRSE |
|---|---|---|---|
| IDW—TAN-1 | 21.208 | 397.148 | 0.0534 |
| IDW—TAN-2 | 22.814 | 439.317 | 0.0519 |
| IDW—DAAG | 23.916 | 467.130 | 0.0512 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, J.; Galupino, J.; Dungca, J. Deterministic Spatial Interpolation of Shear Wave Velocity Profiles with a Case of Metro Manila, Philippines. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9596. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179596
Tan J, Galupino J, Dungca J. Deterministic Spatial Interpolation of Shear Wave Velocity Profiles with a Case of Metro Manila, Philippines. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(17):9596. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179596
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Jomari, Joenel Galupino, and Jonathan Dungca. 2025. "Deterministic Spatial Interpolation of Shear Wave Velocity Profiles with a Case of Metro Manila, Philippines" Applied Sciences 15, no. 17: 9596. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179596
APA StyleTan, J., Galupino, J., & Dungca, J. (2025). Deterministic Spatial Interpolation of Shear Wave Velocity Profiles with a Case of Metro Manila, Philippines. Applied Sciences, 15(17), 9596. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179596