Local Contextual Attention for Enhancing Kernel Point Convolution in 3D Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
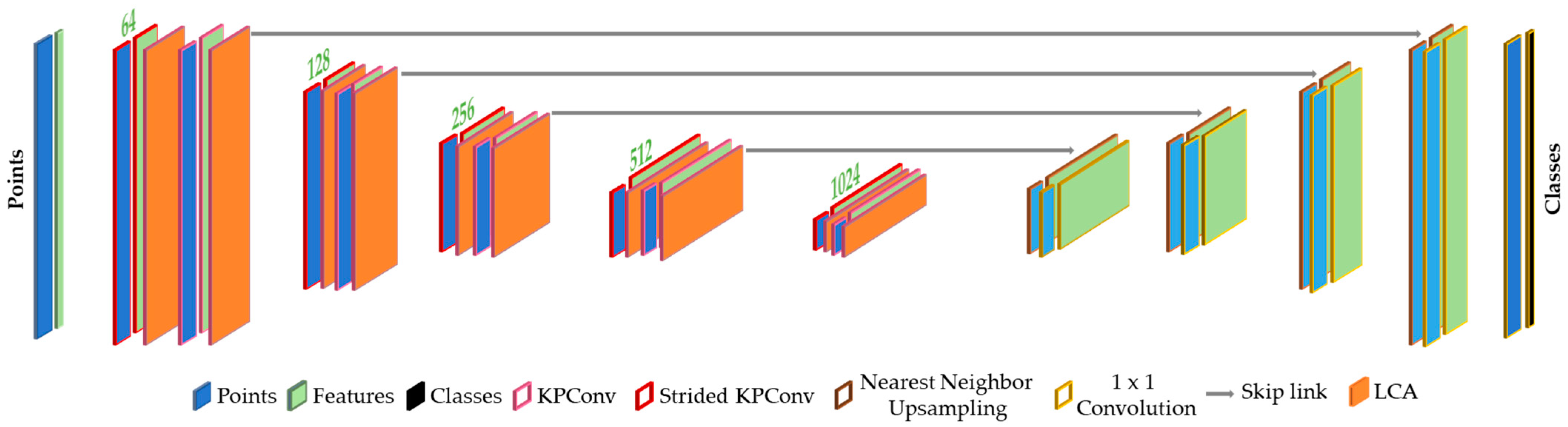
3. Local Contextual Attention Module
4. Experiments: Setup, Metrics, and Comparison
4.1. Datasets and Implementation Details
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
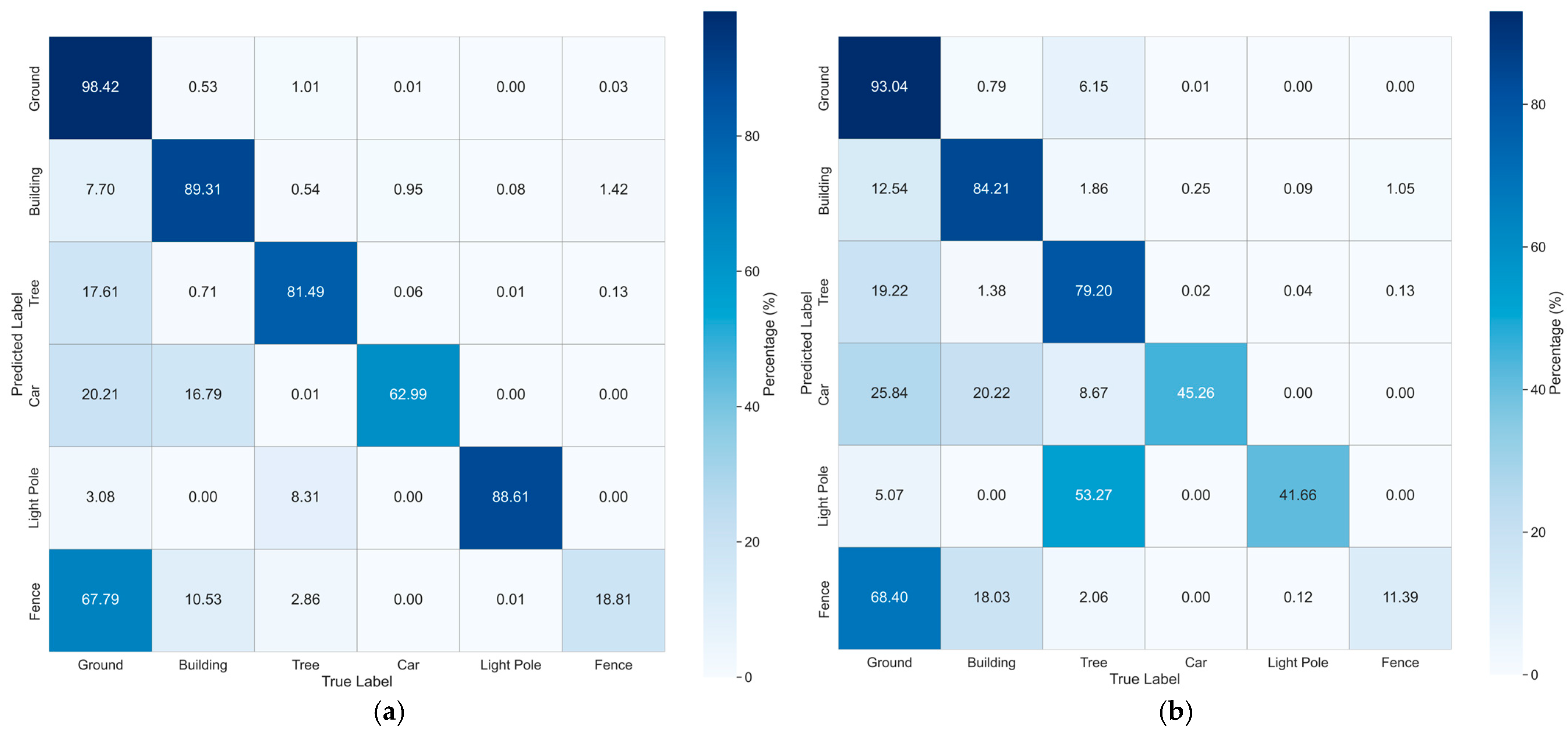
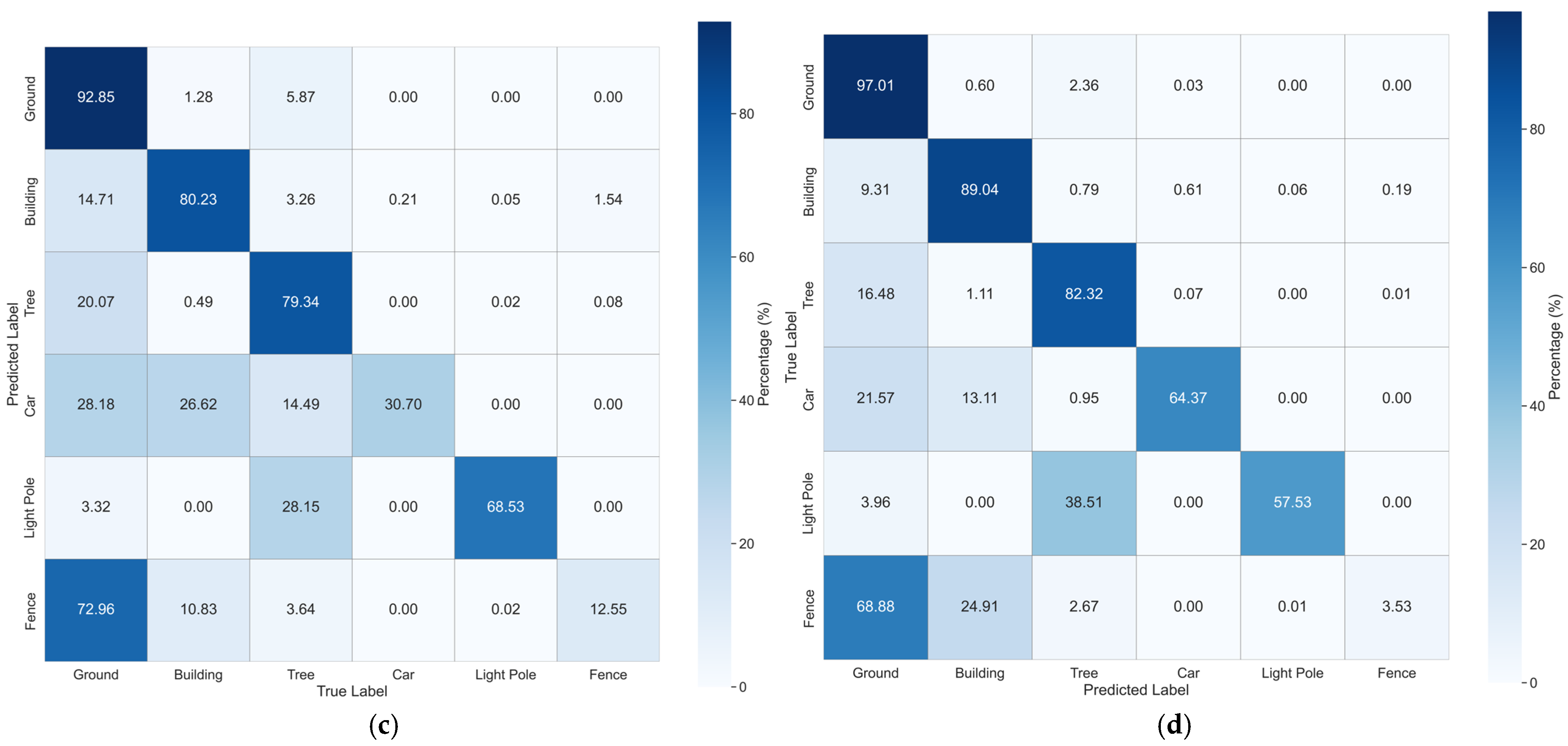
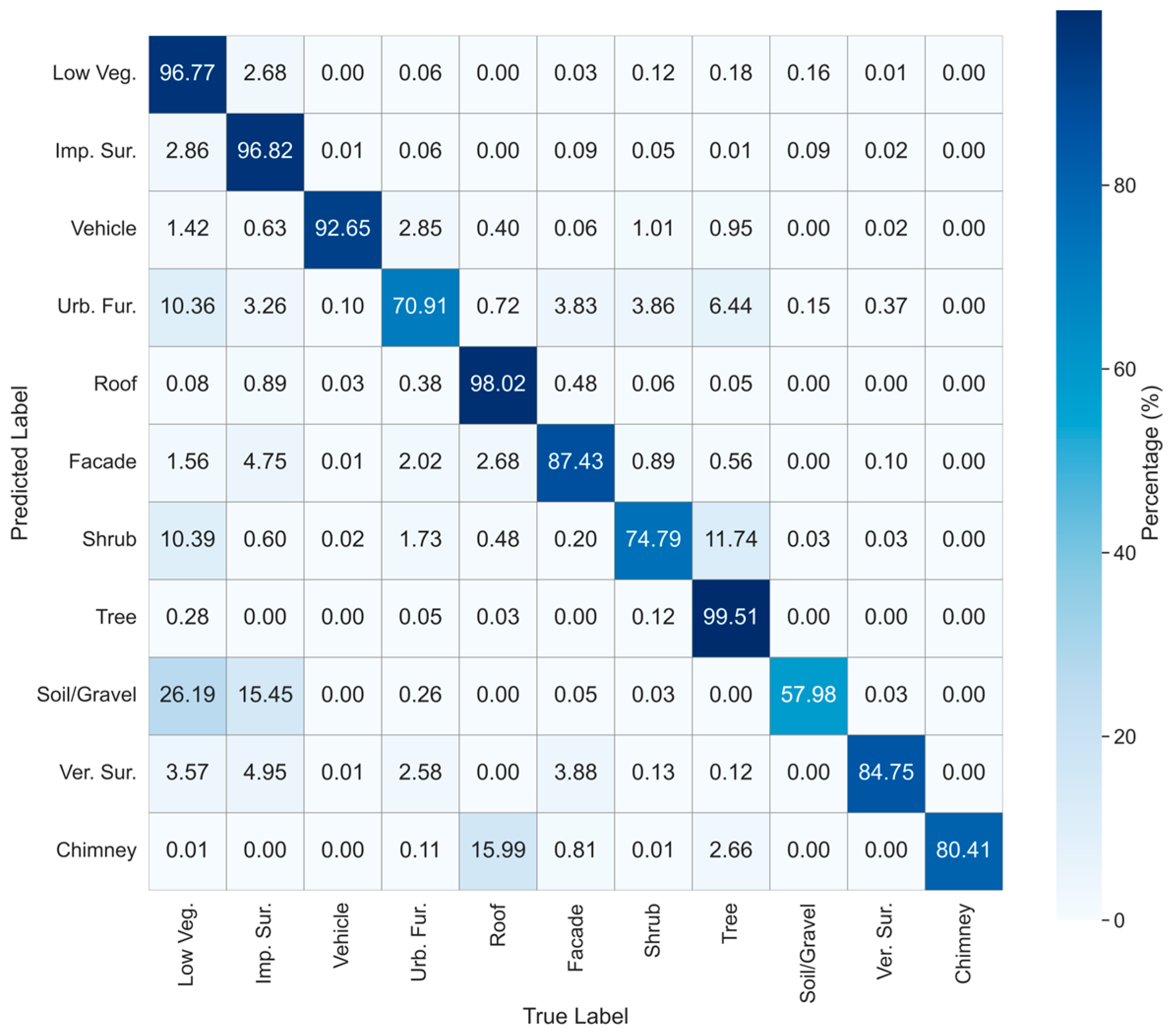
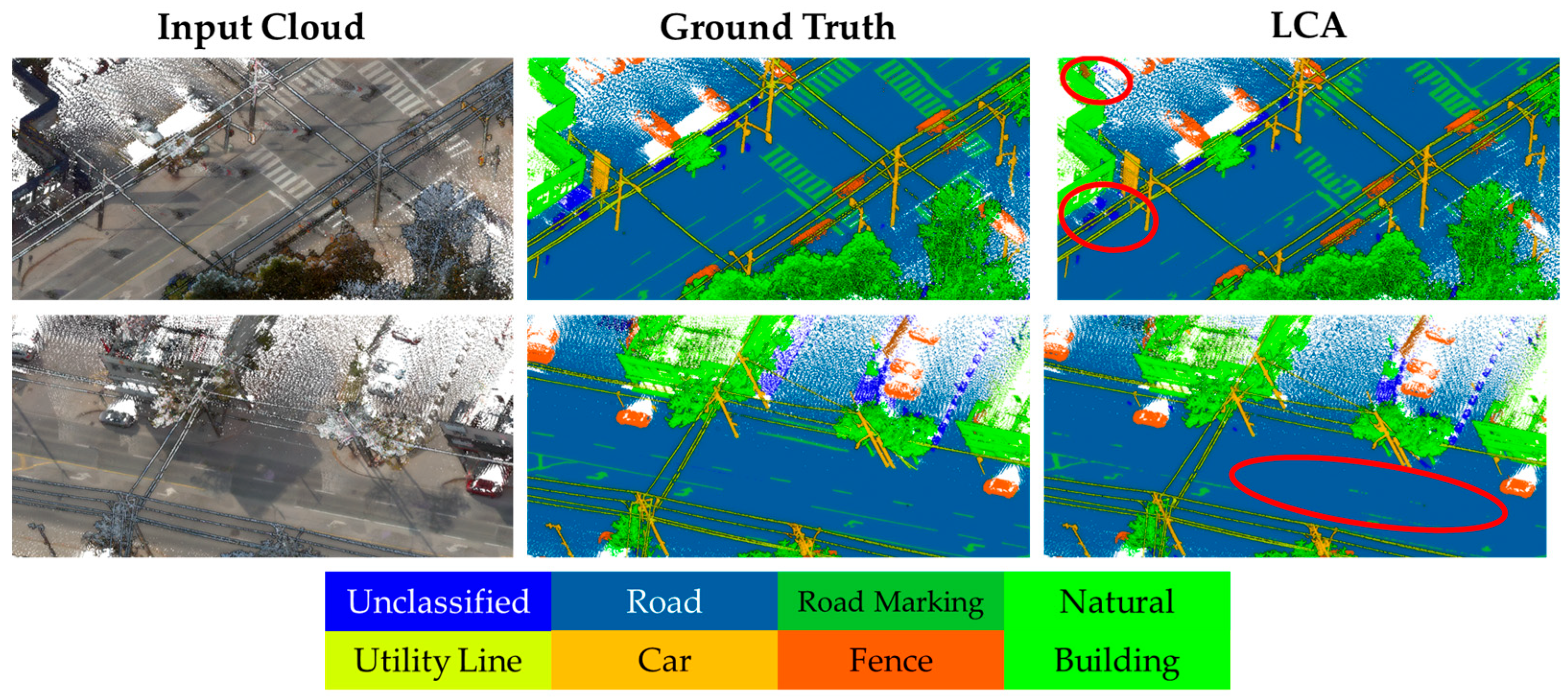
4.3. Performance Comparison
| Training Sets | Methods | mIoU (%) | oAcc (%) | Per-Class IoU (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ground | Building | Tree | Car | Light Pole | Fence | ||||
| Real | PT [32] | 36.27 | 54.31 | 39.95 | 20.88 | 62.57 | 36.13 | 49.32 | 8.76 |
| PT (Ours, retrained) | 35.58 | 53.94 | 33.50 | 23.11 | 64.98 | 35.11 | 51.26 | 5.54 | |
| RandLA-Net [11] | 42.33 | 60.19 | 46.13 | 24.23 | 72.46 | 53.37 | 44.82 | 12.95 | |
| SCF-Net [67] | 45.93 | 75.75 | 68.77 | 37.27 | 65.49 | 51.50 | 31.22 | 21.34 | |
| MinkowskiNet [29] | 46.52 | 70.44 | 64.22 | 29.95 | 61.33 | 45.96 | 65.25 | 12.43 | |
| KPConv [16] | 45.22 | 70.67 | 60.87 | 32.13 | 69.05 | 53.80 | 52.08 | 3.40 | |
| KPConv (Ours, retrained) | 43.42 | 69.21 | 62.03 | 29.22 | 68.44 | 51.36 | 48.44 | 1.07 | |
| VGM [68] | 52.93 | 82.52 | 77.76 | 63.16 | 60.17 | 39.86 | 64.13 | 12.53 | |
| LGFF-Net [69] | 49.1 | 78.8 | 70.7 | 55.0 | 57.3 | 59.1 | 38.8 | 13.6 | |
| PointRAS [70] | 47.4 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| DR-Net [71] | 48.6 | 76.2 | 69.5 | 37.4 | 67.0 | 51.3 | 54.5 | 11.9 | |
| LCA (Ours) | 65.32 | 93.08 | 91.33 | 84.47 | 78.63 | 48.46 | 74.20 | 14.78 | |
| Synthetic | PT [32] | 45.73 | 86.76 | 84.12 | 73.37 | 60.60 | 16.96 | 27.23 | 12.10 |
| PT (Ours, retrained) | 46.5 | 87.18 | 82.79 | 75.66 | 57.98 | 19.22 | 29.27 | 14.08 | |
| RandLA-Net [11] | 45.03 | 81.30 | 76.78 | 57.74 | 56.08 | 28.44 | 40.36 | 10.78 | |
| SCF-Net [67] | 47.82 | 82.69 | 77.51 | 68.68 | 56.81 | 29.87 | 42.53 | 11.52 | |
| MinkowskiNet [29] | 50.78 | 87.64 | 85.23 | 72.66 | 64.80 | 31.31 | 36.85 | 13.83 | |
| KPConv [16] | 49.16 | 88.08 | 85.50 | 70.65 | 63.84 | 28.75 | 32.97 | 13.22 | |
| KPConv (Ours, retrained) | 45.60 | 85.89 | 81.34 | 64.32 | 59.13 | 25.61 | 34.83 | 8.36 | |
| LCA (Ours) | 51.77 | 88.29 | 85.25 | 77.14 | 65.47 | 41.57 | 31.62 | 9.54 | |
| Real + Synthetic | PT [32] | 47.64 | 84.37 | 80.19 | 76.35 | 57.13 | 36.35 | 23.72 | 12.10 |
| PT (Ours, retrained) | 47.46 | 83.86 | 79.35 | 77.4 | 56.61 | 31.14 | 26.31 | 13.97 | |
| RandLA-Net [11] | 50.53 | 86.25 | 82.90 | 66.59 | 63.77 | 33.91 | 41.84 | 14.19 | |
| SCF-Net [67] | 50.65 | 83.32 | 77.80 | 58.98 | 64.86 | 46.37 | 40.50 | 15.41 | |
| MinkowskiNet [29] | 51.35 | 84.90 | 80.86 | 74.03 | 59.21 | 31.72 | 45.51 | 16.79 | |
| KPConv [16] | 53.73 | 89.87 | 87.40 | 78.51 | 66.18 | 39.63 | 41.30 | 9.34 | |
| KPConv (Ours, retrained) | 47.93 | 86.71 | 77.15 | 71.20 | 64.73 | 32.34 | 37.8 | 4.34 | |
| PointCT [72] | 53.2 | N/A | 84.1 | 74.9 | 62.4 | 30.4 | 28.1 | 15.2 | |
| LCA (Ours) | 53.32 | 87.70 | 84.53 | 72.85 | 65.60 | 28.87 | 58.04 | 10.03 | |
| LCA w/normalization | 59.1 | 92.15 | 90.07 | 82.62 | 76.12 | 51.38 | 50.99 | 3.43 | |
4.4. Ablation Study
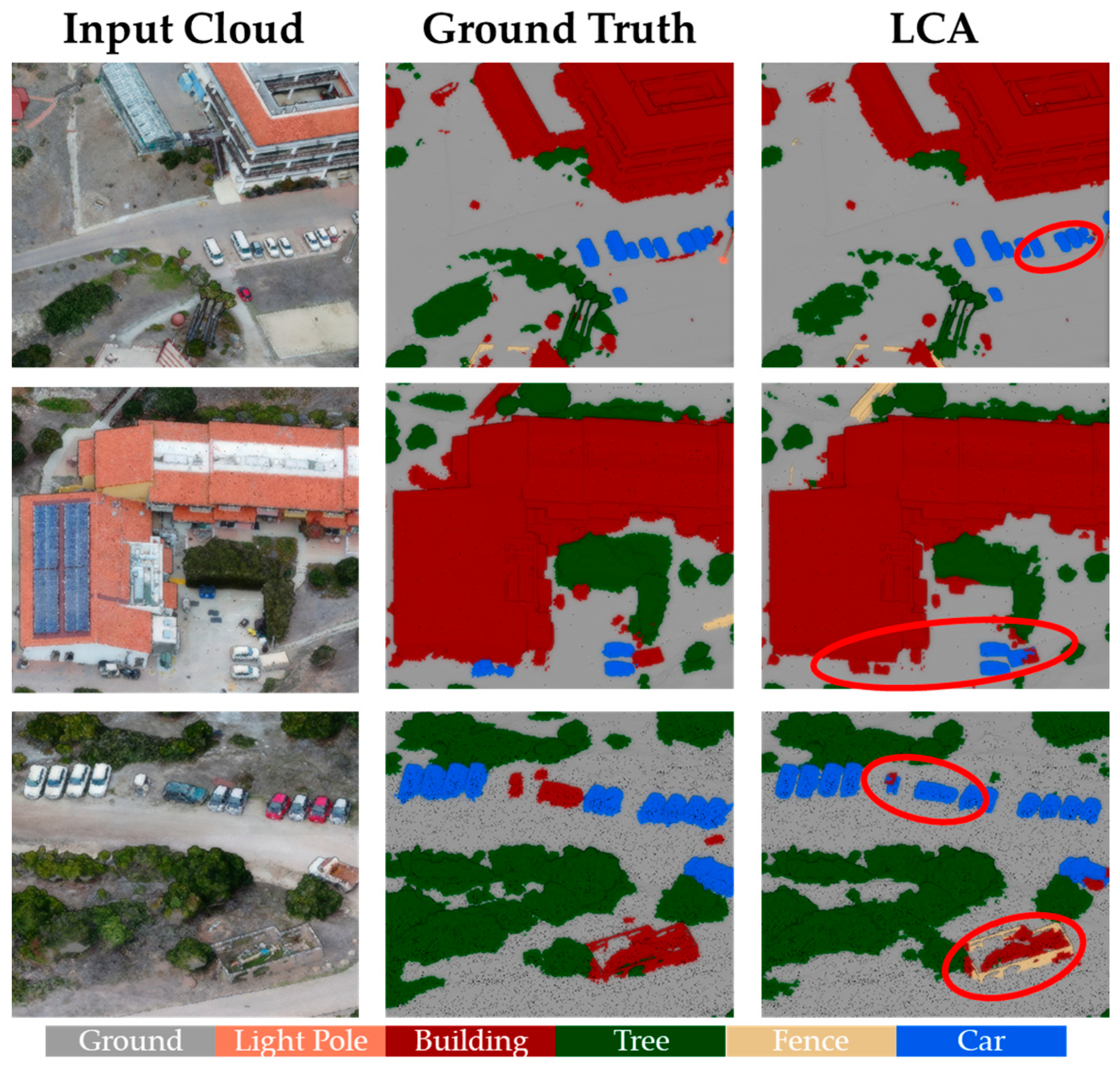
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liamis, T.; Mimis, A. Establishing Semantic 3D City Models by GRextADE: The Case of the Greece. J. Geovis. Spat. Anal. 2022, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iman Zolanvari, S.M.; Ruano, S.; Rana, A.; Cummins, A.; Da Silva, R.E.; Rahbar, M.; Smolic, A. DublinCity: Annotated LiDAR Point Cloud and Its Applications. In Proceedings of the 30th British Machine Vision Conference 2019, BMVC 2019, Cardiff, UK, 9–12 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Z.; He, Y.; Du, X.; Yu, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y. YCANet: Target Detection for Complex Traffic Scenes Based on Camera-LiDAR Fusion. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 8379–8389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, Y.; Alarfaj, A.A.; Alabdulqader, E.A.; Algarni, A.; Jalal, A.; Liu, H. Drone-Based Public Surveillance Using 3D Point Clouds and Neuro-Fuzzy Classifier. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2025, 82, 4759–4776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Q.; Lindenbergh, R.C.; Vijverberg, J.; Guelen, J.A.P. Road Type Classification of MLS Point Clouds Using Deep Learning. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci.–ISPRS Arch. 2021, 43, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Shu, J.; Yang, Z.; Ding, H.; Zeng, W.; Bai, Y. Deep Learning-Based Pipe Segmentation and Geometric Reconstruction from Poorly Scanned Point Clouds Using BIM-Driven Data Alignment. Autom. Constr. 2025, 173, 106071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, G.; Meng, Q.; Finley, T.; Wang, T.; Chen, W.; Ma, W.; Ye, Q.; Liu, T.-Y. LightGBM: A Highly Efficient Gradient Boosting Decision Tree. Adv. Neural Inf. Process Syst. 2017, 30, 52. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinmann, M.; Jutzi, B.; Hinz, S.; Mallet, C. Semantic Point Cloud Interpretation Based on Optimal Neighborhoods, Relevant Features and Efficient Classifiers. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 105, 286–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Yang, B.; Xie, L.; Rosa, S.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Z.; Trigoni, N.; Markham, A. Randla-Net: Efficient Semantic Segmentation of Large-Scale Point Clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Q.; Yang, B.; Khalid, S.; Xiao, W.; Trigoni, N.; Markham, A. Towards Semantic Segmentation of Urban-Scale 3D Point Clouds: A Dataset, Benchmarks and Challenges. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, Y.; Chen, K.; Diao, W.; Sun, X.; Lu, X.; Fu, K.; Weinmann, M. Beyond Single Receptive Field: A Receptive Field Fusion-and-Stratification Network for Airborne Laser Scanning Point Cloud Classification. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 188, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, P.; Xia, Q. Classification Method for Imbalanced LiDAR Point Cloud Based on Stack Autoencoder. Electron. Res. Arch. 2023, 31, 3453–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benchmark on High Density Aerial Image Matching. Available online: https://ifpwww.ifp.uni-stuttgart.de/benchmark/hessigheim/results.aspx (accessed on 4 August 2025).
- Thomas, H.; Qi, C.R.; Deschaud, J.E.; Marcotegui, B.; Goulette, F.; Guibas, L. KPConv: Flexible and Deformable Convolution for Point Clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Tian, S.; Lu, B.; Zhang, L.; Ning, X.; Bai, X. Deep Learning-Based 3D Point Cloud Classification: A Systematic Survey and Outlook. Displays 2023, 79, 102456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Maji, S.; Kalogerakis, E.; Learned-Miller, E. Multi-View Convolutional Neural Networks for 3D Shape Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, T.; Meng, J.; Yuan, J. Multi-View Harmonized Bilinear Network for 3D Object Recognition. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, H.; Wang, J.; Yang, M.; Velipasalar, S. PointOfView: A Multi-Modal Network for Few-Shot 3D Point Cloud Classification Fusing Point and Multi-View Image Features. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) Workshops, Seattle, WA, USA, 17–18 June 2024; pp. 784–793. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.; Cho, B.; Ryoo, S.; Lee, S. Multi-View Structural Convolution Network for Domain-Invariant Point Cloud Recognition of Autonomous Vehicles. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2501.16289. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Wang, H.; Hu, Q.; Liu, H.; Liu, L.; Bennamoun, M. Deep Learning for 3D Point Clouds: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 43, 4338–4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maturana, D.; Scherer, S. VoxNet: A 3D Convolutional Neural Network for Real-Time Object Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–2 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhai, D.; Li, W.; Li, J. Toward Better Boundary Preserved Supervoxel Segmentation for 3D Point Clouds. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 143, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Cai, R.; Wu, X.; Zhao, J.; Qin, P. IBALR3D: ImBalanced-Aware Long-Range 3D Semantic Segmentation. Comput. Sci. Math. Forum 2024, 9, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Bie, L.; Xiao, G.; Li, Y.; Gao, Y. HyperG-PS: Voxel Correlation Modeling via Hypergraph for LiDAR Panoptic Segmentation. Fundam. Res. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.R.; Su, H.; Mo, K.; Guibas, L.J. PointNet: Deep Learning on Point Sets for 3D Classification and Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 30th IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2017, Honolulu, HI, USA, 22–25 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, C.R.; Yi, L.; Su, H.; Guibas, L.J. PointNet++: Deep Hierarchical Feature Learning on Point Sets in a Metric Space. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Choy, C.; Gwak, J.; Savarese, S. 4D Spatio-Temporal Convnets: Minkowski Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Yu, L.; Tian, S.; Ning, X.; Rodrigues, J. PointGT: A Method for Point-Cloud Classification and Segmentation Based on Local Geometric Transformation. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2024, 26, 8052–8062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.Q.; Bi, H.; Li, X.; Chen, K.; Wang, Z.; Sun, X.; Fu, K. Twin Deformable Point Convolutions for Airborne Laser Scanning Point Cloud Classification. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2025, 221, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Jiang, L.; Jia, J.; Torr, P.H.S.; Koltun, V. Point Transformer. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW), Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 16259–16268. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Jia, J.; Koltun, V. Exploring Self-Attention for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 10073–10082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Lao, Y.; Jiang, L.; Liu, X.; Zhao, H. Point Transformer V2: Grouped Vector Attention and Partition-Based Pooling. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 33330–33342. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Jiang, L.; Wang, P.-S.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X.; Qiao, Y.; Ouyang, W.; He, T.; Zhao, H. Point Transformer V3: Simpler, Faster, Stronger. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, G.; Ge, S.; Zhong, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Song, J.; Lu, J. SAPFormer: Shape-Aware Propagation Transformer for Point Clouds. Pattern Recognit. 2025, 164, 111578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanian, V.; Zamanakos, G.; Pratikakis, I. Improving Performance of Deep Learning Models for 3D Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation via Attention Mechanisms. Comput. Graph. 2022, 106, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Xu, S.; Liu, L.; Ming, D.; Tao, W. SVASeg: Sparse Voxel-Based Attention for 3D LiDAR Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Tang, L.; Rao, Y.; Huang, T.; Zhou, J.; Lu, J. Point-BERT: Pre-Training 3D Point Cloud Transformers with Masked Point Modeling. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Wang, M.; Yang, Y.; Yu, K.; Yuan, L.; Yue, Y. PointGPT: Auto-Regressively Generative Pre-Training from Point Clouds. Adv. Neural Inf. Process Syst. 2023, 36, 29667–29679. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, D.; Wu, Z.; Li, J.; Yu, P.; Guo, J.; Wei, M.; Guo, Y. Point Attention Network for Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2022, 65, 192104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wan, H.; Shen, X.; Wu, Z. PatchFormer: An Efficient Point Transformer with Patch Attention. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 11789–11798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, Z.; Han, F. LWSNet: A Lightweight Network for Automated Welding Point Cloud Segmentation. Measurement 2025, 243, 116290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Cai, L.; Kang, R.; Wu, Y.; Wang, C. Efficient and Lightweight Semantic Segmentation Network for Land Cover Point Cloud with Local-Global Feature Fusion. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 4408113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.; Qu, X.; Lu, K.; Wan, J.; He, S.; Wang, J. BAGNet: A Boundary-Aware Graph Attention Network for 3D Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2506.00475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.; Duan, Y. PointGrid: A Deep Network for 3D Shape Understanding. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, W.; Li, K.; Miao, X.; Cui, B.; Qiao, Y.; Gao, P.; Li, H. PointCLIP: Point Cloud Understanding by CLIP. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Afham, M.; Dissanayake, I.; Dissanayake, D.; Dharmasiri, A.; Thilakarathna, K.; Rodrigo, R. CrossPoint: Self-Supervised Cross-Modal Contrastive Learning for 3D Point Cloud Understanding. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- El Mendili, L.; Daniel, S.; Badard, T. Distribution-Aware Contrastive Learning for Domain Adaptation in 3D LiDAR Segmentation. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2025, 259, 104438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.L.; Wang, H.P.; Peng, W.H.; Chiu, W.C. All about Structure: Adapting Structural Information across Domains for Boosting Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 1900–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, N.; Shi, J.; Hou, X.; Liu, J. Adaptive Batch Normalization for Practical Domain Adaptation. Pattern Recognit. 2018, 80, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, S.; Tao, D. UniMix: Towards Domain Adaptive and Generalizable LiDAR Semantic Segmentation in Adverse Weather. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 14781–14791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, M.; Huang, J.; Liu, T.; Shen, T.; Gu, Y. Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Cross-Scene Multispectral Point Cloud Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5705115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, G.; Shen, Y.; Zou, X.; Chen, D.; Zang, Y. PGFormer: A Point Cloud Segmentation Network for Urban Scenes Combining Grouped Transformer and KPConv. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 5704318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Li, P.; Zhang, H. Hybrid Cross-Transformer-KPConv for Point Cloud Segmentation. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2024, 31, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhou, H.; Pan, F. A Dual Attention KPConv Network Combined with Attention Gates for Semantic Segmentation of ALS Point Clouds. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5107914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Chen, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y. IPCONV: Convolution with Multiple Different Kernels for Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Hu, Q.; Yu, Z.; Thomas, H.; Feng, A.; Hou, Y.; McCullough, K.; Ren, F.; Soibelman, L. STPLS3D: A Large-Scale Synthetic and Real Aerial Photogrammetry 3D Point Cloud Dataset. In Proceedings of the BMVC 2022—33rd British Machine Vision Conference Proceedings, London, UK, 21–24 November 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kölle, M.; Laupheimer, D.; Schmohl, S.; Haala, N.; Rottensteiner, F.; Wegner, J.D.; Ledoux, H. The Hessigheim 3D (H3D) Benchmark on Semantic Segmentation of High-Resolution 3D Point Clouds and Textured Meshes from UAV LiDAR and Multi-View-Stereo. ISPRS Open J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 1, 100001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Qin, N.; Ma, L.; Li, Y.; Du, J.; Cai, G.; Yang, K.; Li, J. Toronto-3D: A Large-Scale Mobile LiDAR Dataset for Semantic Segmentation of Urban Roadways. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 202–203. [Google Scholar]
- HuguesTHOMAS/KPConv-PyTorch: Kernel Point Convolution Implemented in PyTorch. Available online: https://github.com/HuguesTHOMAS/KPConv-PyTorch (accessed on 4 August 2025).
- STPLS3D/KPConv-PyTorch at Main Meidachen/STPLS3D. Available online: https://github.com/meidachen/STPLS3D/tree/main/KPConv-PyTorch (accessed on 4 August 2025).
- Zhao, W.; Jia, L.; Zhai, H.; Chai, S.; Li, P. PointSGLN: A Novel Point Cloud Classification Network Based on Sampling Grouping and Local Point Normalization. Multimed. Syst. 2024, 30, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; You, Y.; Liu, W.; Lu, C. Point Cloud Classification with Deep Normalized Reeb Graph Convolution. Image Vis. Comput. 2021, 106, 104092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- STPLS3D|LEADERBOARD. Available online: https://www.stpls3d.com/leaderboard (accessed on 4 August 2025).
- Fan, S.; Dong, Q.; Zhu, F.; Lv, Y.; Ye, P.; Wang, F.Y. SCF-Net: Learning Spatial Contextual Features for Large-Scale Point Cloud Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Virtual, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 14499–14508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Shu, Y.; Qiao, L.; Wu, Z.; Ling, J.; Wu, J.; Li, W. 3D Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation Based on Visual Guidance and Feature Enhancement. Multimed. Syst. 2025, 31, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Liu, H. A Local-Global Feature Fusing Method for Point Clouds Semantic Segmentation. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 68776–68790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhou, J.; Lu, J. PointRas: Uncertainty-Aware Multi-Resolution Learning for Point Cloud Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 31, 6002–6016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Bi, Y. Weakly-Supervised Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation Based on Dilated Region. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5105020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, A.T.; Le, H.S.; Lee, S.H.; Kwon, K.R. PointCT: Point Central Transformer Network for Weakly-Supervised Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, WACV 2024, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2024; pp. 3544–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Yan, Y.; Lin, H.; Shi, R. PIIE-DSA-Net for 3D Semantic Segmentation of Urban Indoor and Outdoor Datasets. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grilli, E.; Daniele, A.; Bassier, M.; Remondino, F.; Serafini, L. Knowledge Enhanced Neural Networks for Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevgen, E.; Abdikan, S. Point-Wise Classification of High-Density UAV-LiDAR Data Using Gradient Boosting Machines. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci.–ISPRS Arch. 2023, 48, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GitHub—WeikaiTan/Toronto-3D: A Large-Scale Mobile LiDAR Dataset for Semantic Segmentation of Urban Roadways. Available online: https://github.com/WeikaiTan/Toronto-3D (accessed on 4 August 2025).
- Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Z.; Sarma, S.E.; Bronstein, M.M.; Solomon, J.M. Dynamic Graph Cnn for Learning on Point Clouds. ACM Trans. Graph. 2019, 38, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Tan, W.; Yu, Y.; Chapman, M.A. Multi-Scale Point-Wise Convolutional Neural Networks for 3D Object Segmentation from LiDAR Point Clouds in Large-Scale Environments. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 22, 821–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ma, L.; Zhong, Z.; Cao, D.; Li, J. TGNet: Geometric Graph CNN on 3-D Point Cloud Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 3588–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Feragen, A. DiffConv: Analyzing Irregular Point Clouds with an Irregular View. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2022 17th European Conference, Tel Aviv, Israel, October 23–27, 2022, Proceedings, Part III; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 380–397. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, S.; Jeong, Y.; Jameela, M.; Sohn, G. Human Vision Based 3D Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation of Large-Scale Outdoor. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 6577–6586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Zhou, J.; Gao, K.; Du, J.; Xu, L.; Li, J. Dynamic Clustering Transformer Network for Point Cloud Segmentation. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2024, 128, 103791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rim, B.; Lee, A.; Hong, M. Semantic Segmentation of Large-Scale Outdoor Point Clouds by Encoder–Decoder Shared MLPs with Multiple Losses. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Hu, Q.; Wang, H.; Huang, X.; Li, L.; Ji, S. Continuous Mapping Convolution for Large-Scale Point Clouds Semantic Segmentation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 6502505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Cai, G.; Wang, Z.; Huang, S.; Su, J.; Marcato Junior, J.; Smit, J.; Li, J. ResDLPS-Net: Joint Residual-Dense Optimization for Large-Scale Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 182, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Xu, Y.; Xie, Z.; Tang, W.; Wan, J.; Wu, W. Large-Scale Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation via Local Perception and Global Descriptor Vector. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 246, 123269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Dong, Z.; Yang, B. A Point-Based Deep Learning Network for Semantic Segmentation of MLS Point Clouds. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 175, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Shojaei, D.; Khoshelham, K. Finding the Optimal Convolutional Kernel Size for Semantic Segmentation of Pole-like Objects in Lidar Point Clouds. Proc. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2025, 48, 1747–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Ma, J.; Zhou, H.; Shangguan, B.; Xiao, H.; Chen, Z. Large-Scale Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation with Density-Based Grid Decimation. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2025, 14, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, R.; Lai, X.; Li, X. BADet: Boundary-Aware 3D Object Detection from Point Clouds. Pattern Recognit. 2022, 125, 108524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Q.; Cheng, G.; Huang, K. BFANet: Revisiting 3D Semantic Segmentation with Boundary Feature Analysis. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Conference, Nashville, TN, USA, 10–17 June 2025; pp. 29395–29405. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Shi, G.; Wu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, M. Multi-Scale Neighborhood Feature Extraction and Aggregation for Point Cloud Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2021, 31, 2175–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Gao, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, R.; Li, Z.; Huang, R.; Cui, S. Sparse Single Sweep LiDAR Point Cloud Segmentation via Learning Contextual Shape Priors from Scene Completion. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2021, 35, 3101–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Dataset | Hessigheim3D | STPLS3D | Toronto3D |
|---|---|---|---|
| Input Radius (m) | 5 | 18 | 3 |
| Number of Kernel Points | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| First Subsampling (m) | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.08 |
| Deformable Convolution Radius (m) | 6 | 6 | 5 |
| Kernel Type | Rigid | Rigid | Rigid |
| Influence of Each Kernel Point | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.0 |
| Aggregation Mode | Sum | Sum | Closest |
| Minimum Scale | 0.8 | 0.95 | 0.9 |
| Maximum Scale | 1.2 | 1.05 | 1.1 |
| Batch Size | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| Optimizer | SGD | SGD | SGD |
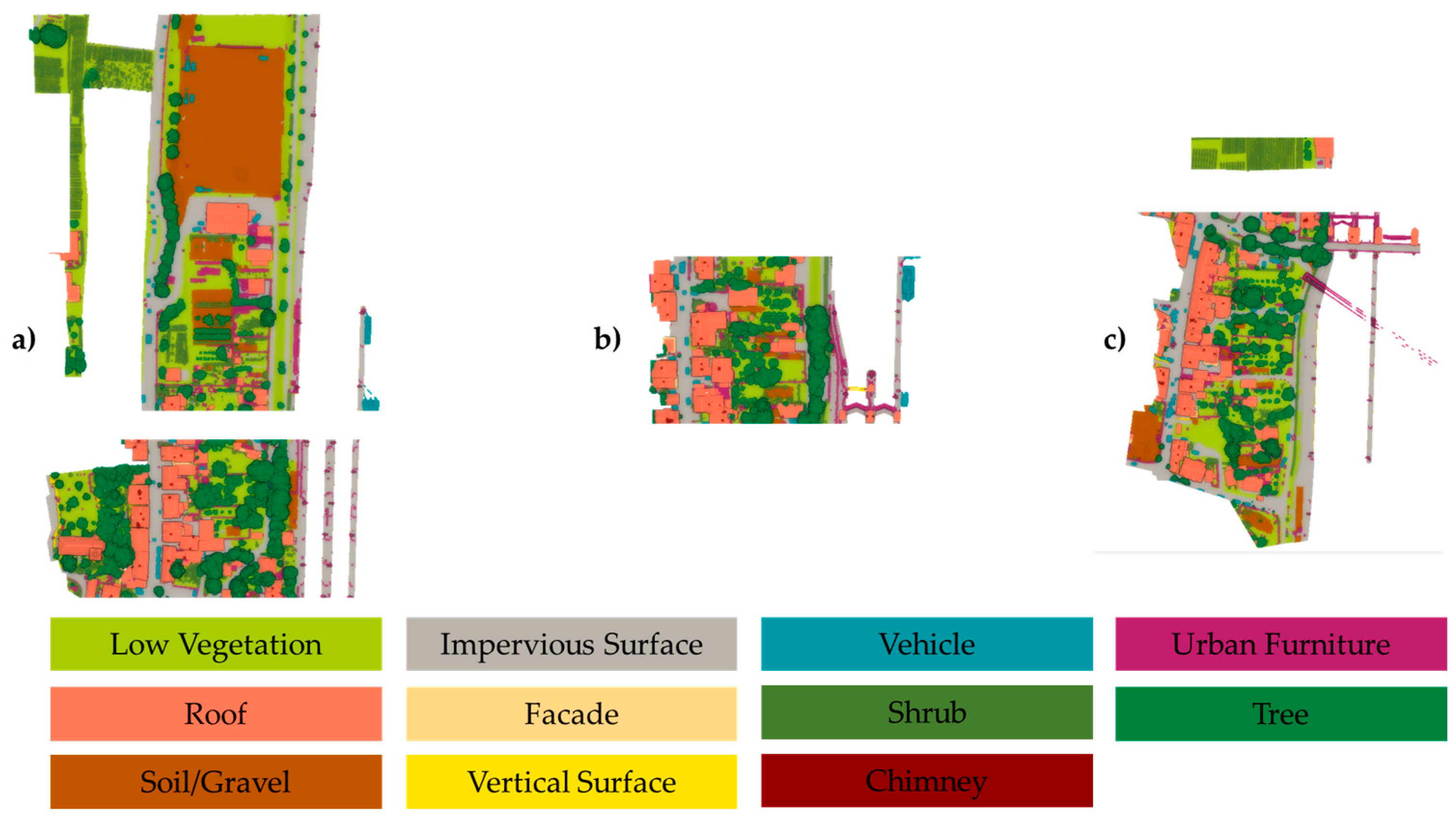
| Method | Low Vegetat. | Impervious Surface | Vehicle | Urban Furniture | Roof | Façade | Shrub | Tree | Soil/Gravel | Vertical Surface | Chimney | mF1 | OA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhan221112 | 58.74 | 22.06 | 0.32 | 16.65 | 57.06 | 30.02 | 5.07 | 69.34 | 0.11 | 28.59 | 2.22 | 26.38 | 46.1 |
| PN++ [28] | 78.11 | 72.07 | 31.78 | 13.65 | 73.98 | 47.79 | 28.34 | 71.8 | 9.65 | 21.67 | 4.39 | 41.2 | 68.5 |
| Jiabin221114 | 66.21 | 18.02 | 34.18 | 38.03 | 72.0 | 68.99 | 47.7 | 78.65 | 9.84 | 35.93 | 8.32 | 43.44 | 58.29 |
| Esmoris230208 | 71.13 | 55.83 | 2.73 | 25.85 | 93.74 | 73.28 | 38.95 | 93.21 | 20.68 | 70.4 | 49.84 | 54.15 | 68.84 |
| Letard230213 | 68.48 | 65.4 | 32.95 | 42.06 | 93.61 | 80.39 | 43.72 | 94.17 | 14.33 | 72.84 | 42.45 | 59.13 | 66.7 |
| Shi220705 [73] | 87.62 | 85.62 | 52.4 | 36.71 | 95.48 | 69.3 | 47.39 | 94.28 | 25.08 | 65.94 | 38.59 | 63.49 | 84.2 |
| Esmoris230207 | 84.83 | 81.95 | 19.45 | 42.38 | 94.83 | 77.77 | 59.06 | 94.53 | 3.55 | 73.8 | 69.18 | 63.76 | 81.67 |
| Zhan221025 | 84.33 | 77.86 | 58.11 | 42.32 | 93.25 | 65.41 | 53.53 | 95.29 | 23.66 | 59.85 | 64.66 | 65.3 | 79.69 |
| Sevgen220117 | 83.86 | 77.21 | 66.95 | 42.64 | 95.6 | 80.09 | 59.53 | 96.06 | 25.68 | 81.51 | 73.85 | 71.18 | 79.25 |
| KPConv [16] | 88.57 | 88.93 | 82.1 | 63.89 | 97.13 | 85.13 | 75.24 | 97.38 | 42.68 | 80.87 | 0.00 | 72.9 | 87.69 |
| KPConv (Ours, retr.) | 84.43 | 81.16 | 79.68 | 41.80 | 84.48 | 78.93 | 77.34 | 96.6 | 34.12 | 73.57 | 0.00 | 66.56 | 82.41 |
| Grilli220725 [74] | 88.91 | 87.74 | 74.89 | 54.27 | 96.83 | 78.85 | 53.21 | 93.28 | 43.73 | 75.89 | 58.22 | 73.26 | 85.33 |
| ifp-RF [60] | 90.36 | 88.55 | 66.89 | 51.55 | 96.06 | 78.47 | 67.25 | 95.91 | 47.91 | 59.73 | 80.65 | 74.85 | 87.43 |
| Sevgen220725 [75] | 90.88 | 89.4 | 77.28 | 55.76 | 97.05 | 81.88 | 62.06 | 97.1 | 23.17 | 80.27 | 80.28 | 75.92 | 87.59 |
| Qiu230831 | 91.81 | 84.74 | 64.6 | 52.24 | 95.04 | 80.59 | 68.02 | 97.35 | 42.11 | 74.76 | 85.1 | 76.03 | 86.81 |
| ifp-SCN [60] | 92.31 | 88.14 | 63.51 | 57.17 | 96.86 | 83.19 | 68.59 | 96.98 | 44.81 | 78.2 | 73.61 | 76.67 | 88.42 |
| WHU221118 | 92.9 | 90.23 | 78.51 | 57.89 | 95.71 | 80.43 | 68.46 | 97.21 | 62.37 | 73.08 | 72.45 | 79.02 | 89.75 |
| WHU220322 | 94.11 | 91.92 | 79.42 | 59.16 | 97.2 | 81.86 | 68.31 | 96.96 | 78.94 | 78.42 | 84.58 | 82.81 | 91.77 |
| PGFormer [54] | 89.4 | 85.2 | 61.0 | 48.5 | 95.7 | 75.0 | 61.9 | 95.4 | 38.7 | 76.9 | 74.1 | 72.9 | 85.8 |
| Zhang231204 | 91.89 | 90.56 | 84.12 | 64.75 | 97.98 | 84.21 | 71.07 | 97.15 | 70.66 | 85.13 | 84.72 | 83.84 | 90.45 |
| PT [74] | 90.91 | 84.5 | 38.54 | 43.54 | 89.06 | 75.15 | 58.33 | 96.18 | 48.46 | 64.8 | 48.86 | 67.12 | 84.06 |
| PT (Ours, retrained) | 89.15 | 83.7 | 41.21 | 45.69 | 88.21 | 78.09 | 60.11 | 93.22 | 48.04 | 63.54 | 44.15 | 66.83 | 83.89 |
| LCA (Ours) | 94.20 | 93.68 | 95.38 | 77.72 | 98.65 | 89.48 | 80.04 | 97.66 | 72.87 | 90.29 | 88.76 | 88.98 | 93.33 |
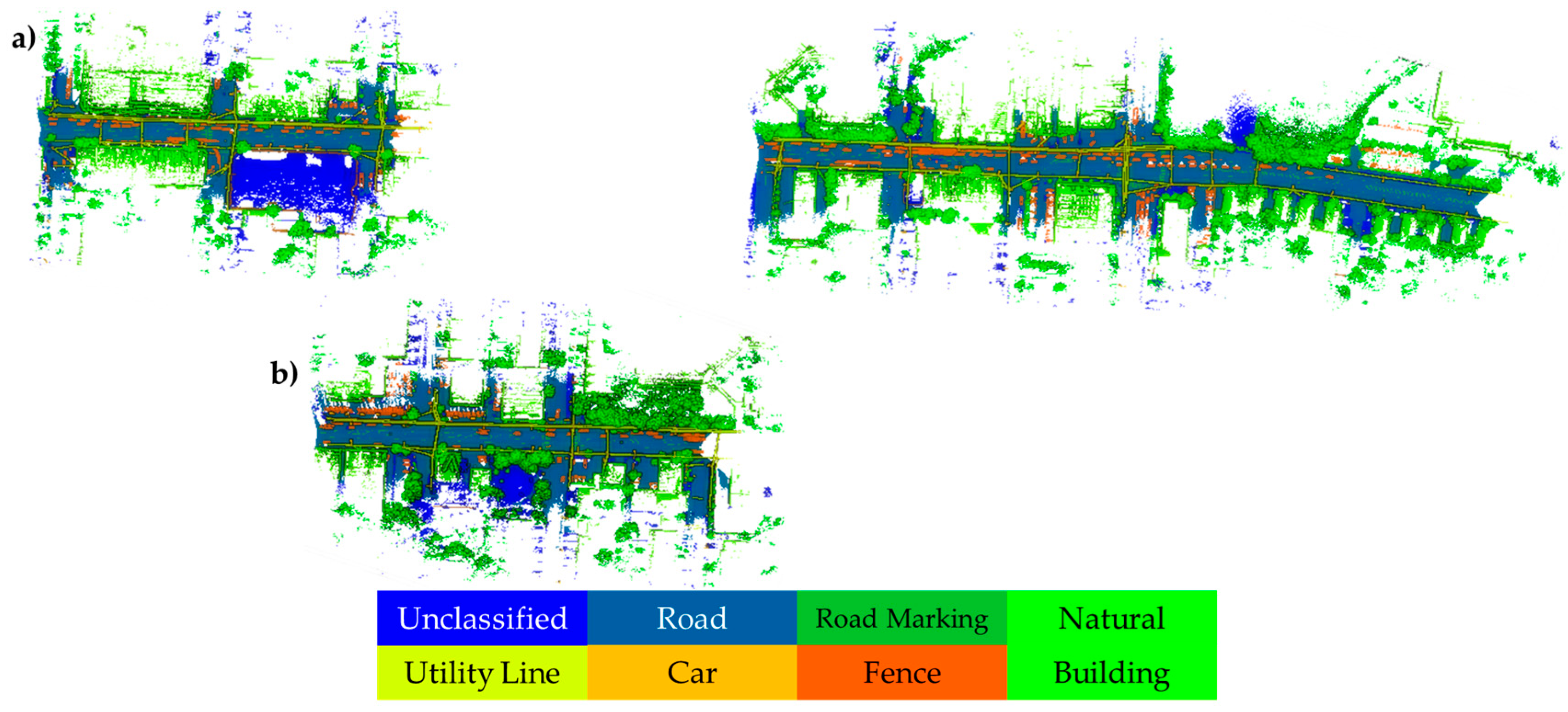
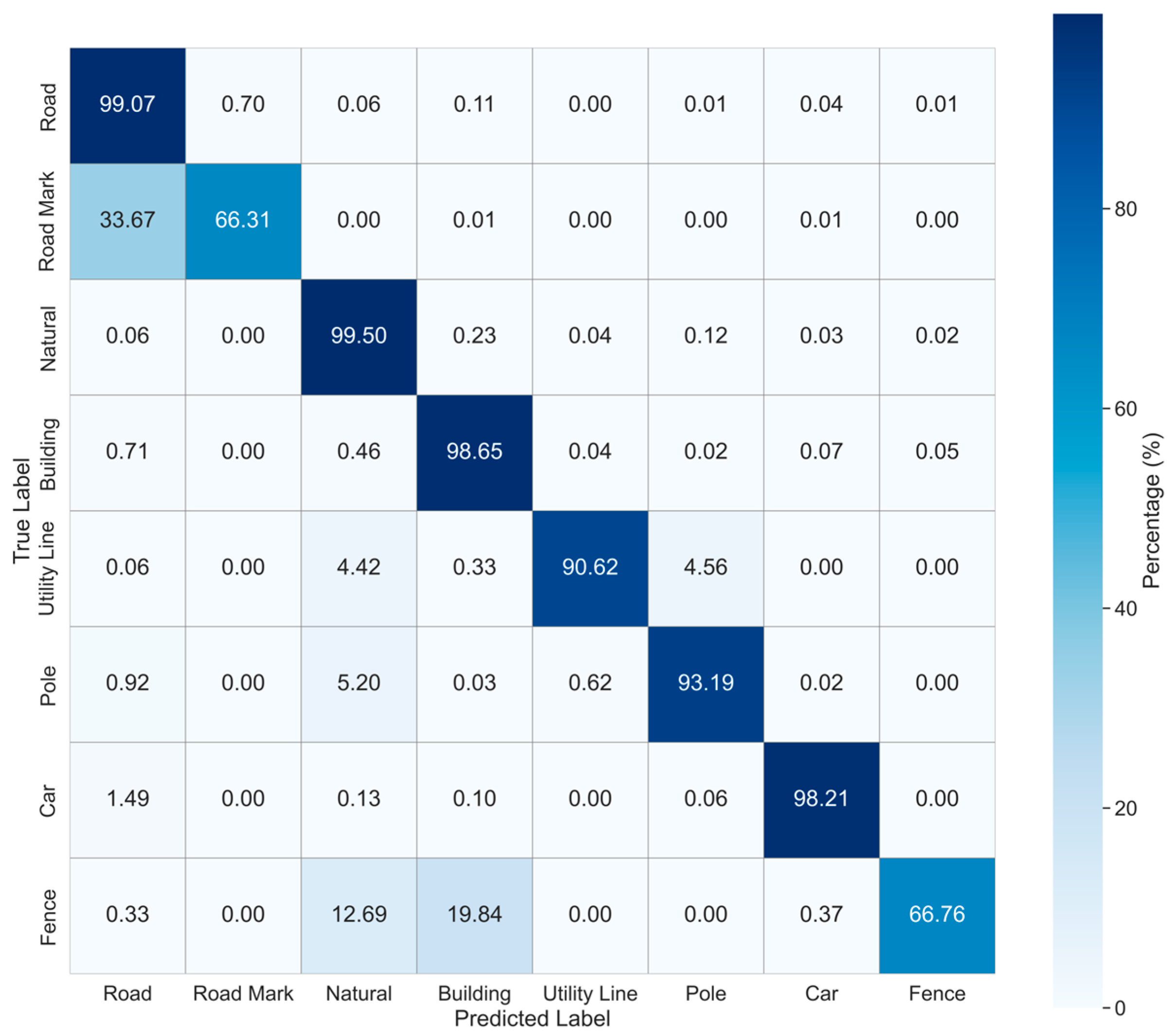
| Method | OA | mIoU | Road | Road Mark | Natural | Building | Utility Line | Pole | Car | Fence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PointNet++ [28] | 92.56 | 59.47 | 92.90 | 0.00 | 86.13 | 82.15 | 60.96 | 62.81 | 76.41 | 14.43 |
| DGCNN [77] | 94.24 | 61.79 | 93.88 | 0.00 | 91.25 | 80.39 | 62.40 | 62.32 | 88.26 | 15.81 |
| KPConv [16] | 95.39 | 69.11 | 94.62 | 0.06 | 96.07 | 91.51 | 87.68 | 81.56 | 85.66 | 15.72 |
| KPConv (Ours, retr.) | 91.07 | 64.63 | 92.11 | 0.00 | 89.53 | 85.12 | 81.28 | 71.59 | 83.76 | 13.59 |
| MS-PCNN [78] | 90.03 | 65.89 | 93.84 | 3.83 | 93.46 | 82.59 | 67.80 | 71.95 | 91.12 | 22.50 |
| TGNet [79] | 94.08 | 61.34 | 93.54 | 0.00 | 90.83 | 81.57 | 65.26 | 62.98 | 88.73 | 7.85 |
| MS-TGNet [61] | 95.71 | 70.50 | 94.41 | 17.19 | 95.72 | 88.83 | 76.01 | 73.97 | 94.24 | 23.64 |
| DiffConv [80] | - | 76.73 | 83.31 | 51.06 | 69.04 | 79.55 | 80.48 | 84.41 | 76.19 | 89.83 |
| EyeNet [81] | 94.63 | 81.13 | 96.98 | 65.02 | 97.83 | 93.51 | 86.77 | 84.86 | 94.02 | 30.01 |
| DCTNet [82] | - | 81.84 | 82.77 | 59.53 | 85.51 | 86.47 | 81.79 | 84.03 | 79.55 | 96.21 |
| RandLA-Net [11] | 94.37 | 81.77 | 96.69 | 64.21 | 96.92 | 94.24 | 88.06 | 77.84 | 93.37 | 42.86 |
| Rim et al. [83] | 83.60 | 71.03 | 92.84 | 27.43 | 89.90 | 95.27 | 85.59 | 74.50 | 44.41 | 58.30 |
| MappingConvSeg [84] | 94.72 | 82.89 | 97.15 | 67.87 | 97.55 | 93.75 | 86.88 | 82.12 | 93.72 | 44.11 |
| ResDLPS-Net [85] | 96.49 | 80.27 | 95.82 | 59.80 | 96.10 | 90.96 | 86.82 | 79.95 | 89.41 | 43.31 |
| LACV-Net [86] | 97.4 | 82.7 | 97.1 | 66.9 | 97.3 | 93.0 | 87.3 | 83.4 | 93.4 | 43.1 |
| PGFormer [54] | 96.5 | 81.1 | 95.9 | 50.5 | 95.9 | 91.5 | 79.7 | 72.8 | 93.0 | 39.9 |
| LGFF-Net | 97.2 | 81.4 | 96.9 | 65.5 | 96.1 | 92.7 | 86.0 | 78.8 | 93.6 | 41.4 |
| PT [32] | 96.8 | 79.9 | 96.7 | 64.6 | 95.9 | 91.0 | 87.6 | 79.0 | 87.5 | 36.9 |
| PT (Ours, retrained) | 93.11 | 74.69 | 84.23 | 59.14 | 87.01 | 90.18 | 81.92 | 74.43 | 82.17 | 38.46 |
| Han et al. [87] | 93.60 | 70.80 | 92.20 | 53.80 | 92.80 | 86.00 | 72.20 | 72.50 | 75.70 | 21.20 |
| LCA (Ours) | 96.62 | 84.06 | 95.99 | 57.66 | 96.86 | 95.76 | 88.14 | 88.07 | 96.06 | 53.91 |
| Dataset | Method | OA | mIoU | mF1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| STPLS3D Real | KPConv | 70.67 | 45.22 | - |
| KPConv (Ours, retrained) | 69.21 | 43.42 | ||
| LCA (Ours) | 93.08 | 65.32 | - | |
| STPLS3D Synthetic | KPConv | 88.08 | 49.16 | - |
| KPConv (Ours, retrained) | 85.89 | 45.60 | ||
| LCA (Ours) | 88.29 | 51.77 | - | |
| STPLS3D Real+Synthetic | KPConv | 88.08 | 53.73 | - |
| KPConv (Ours, retrained) | 86.71 | 47.93 | ||
| LCA (Ours) | 88.29 | 53.32 | - | |
| LCA w/normalization | 90.60 | 57.55 | ||
| Hessigheim3D | KPConv | 87.69 | - | 72.9 |
| KPConv (Ours, retrained) | 82.41 | 66.56 | ||
| LCA (Ours) | 93.33 | - | 88.98 | |
| Toronto3D | KPConv | 95.39 | 69.11 | - |
| KPConv (Ours, retrained) | 91.07 | 64.63 | ||
| LCA (Ours) | 96.62 | 84.06 | - |
| LCA | Input Radius (m) | Number of Kernel Points | D_Hidden | OA | mIoU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| w/o norm. | 15 | 18 | 88.29 | 53.32 | |
| 15 | 15 | 87.06 | 53.16 | ||
| 15 | 21 | 88.40 | 53.68 | ||
| 18 | 18 | 89.49 | 54.26 | ||
| 18 | 15 | 89.34 | 53.97 | ||
| 18 | 21 | 90.11 | 54.49 | ||
| 12 | 18 | 85.20 | 50.09 | ||
| 12 | 15 | 84.72 | 49.82 | ||
| 12 | 21 | 85.84 | 50.23 | ||
| 15 | 18 | 90.43 | 55.17 | ||
| 15 | 15 | 89.11 | 54.66 | ||
| 15 | 21 | 91.53 | 55.38 | ||
| 18 | 18 | 91.61 | 55.41 | ||
| 18 | 15 | 89.50 | 54.27 | ||
| 18 | 21 | 92.84 | 57.74 | ||
| 12 | 18 | 87.39 | 53.29 | ||
| 12 | 15 | 87.30 | 53.11 | ||
| 12 | 21 | 87.51 | 53.34 | ||
| w/norm. | 15 | 18 | 90.60 | 57.55 | |
| 15 | 15 | 89.13 | 56.1 | ||
| 15 | 21 | 91.16 | 57.93 | ||
| 18 | 18 | 91.97 | 58.36 | ||
| 18 | 15 | 90.13 | 56.72 | ||
| 18 | 21 | 92.44 | 59.06 | ||
| 12 | 18 | 87.14 | 54.33 | ||
| 12 | 15 | 85.66 | 53.09 | ||
| 12 | 21 | 88.31 | 54.79 | ||
| 15 | 18 | 91.67 | 58.16 | ||
| 15 | 15 | 90.32 | 56.83 | ||
| 15 | 21 | 92.08 | 58.84 | ||
| 18 | 18 | 93.15 | 59.77 | ||
| 18 | 15 | 92.56 | 58.13 | ||
| 18 | 21 | 93.47 | 59.96 | ||
| 12 | 18 | 89.04 | 56.0 | ||
| 12 | 15 | 88.73 | 54.94 | ||
| 12 | 21 | 89.51 | 55.58 |
| Method | FLOPs | Parameters (M) | Maximum VRAM Usage (GB) | Latency (Second/Epoch) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| STPLS3D | Hessigheim3D | Toronto3D | ||||
| KPConv | 6.5 | 14.93 | ~6.7 | 7.43 | 10.24 | 3.87 |
| Point Transformer | 5.05 | 21.1 | ~12.4 | 12.27 | 18.40 | 6.28 |
| LCA (Ours) | 6.9 | 24.61 | ~8.9 | 9.69 | 13.04 | 5.84 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bayrak, O.C.; Uzar, M. Local Contextual Attention for Enhancing Kernel Point Convolution in 3D Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9503. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179503
Bayrak OC, Uzar M. Local Contextual Attention for Enhancing Kernel Point Convolution in 3D Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(17):9503. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179503
Chicago/Turabian StyleBayrak, Onur Can, and Melis Uzar. 2025. "Local Contextual Attention for Enhancing Kernel Point Convolution in 3D Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation" Applied Sciences 15, no. 17: 9503. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179503
APA StyleBayrak, O. C., & Uzar, M. (2025). Local Contextual Attention for Enhancing Kernel Point Convolution in 3D Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation. Applied Sciences, 15(17), 9503. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179503






