1. Introduction
The Hybrid Aerial Underwater Vehicle (HAUV) is an emerging marine unmanned equipment capable of autonomous underwater navigation, aerial flight, and repeated transitions between water and air media [
1]. It holds broad application prospects in fields such as rapid cross-water sampling, maritime emergency search and rescue, water–air communication relay, reconnaissance and surveillance, and time-sensitive strikes. Against the backdrop of continuous development in HAUV technology, its Variable Buoyancy System (VBS), as a key component, plays a decisive role in the performance of the unmanned vehicle in both water and air media [
2,
3].
The variable buoyancy system can actively or passively adjust buoyancy, enabling precise and complex underwater depth control with low power consumption without relying on thrusters [
4,
5]. Therefore, it has been widely applied in various underwater robots. In the fields of marine exploration and cross-domain robotics, these systems are core components for depth control and attitude adjustment of underwater robots, and their technological evolution is closely linked to application requirements. Due to the limited energy capacity of HAUV, achieving long endurance in both air and water requires an optimized airframe structure combined with a small and lightweight buoyancy adjustment system to reduce underwater energy consumption and control the total flight weight [
6].
According to the implementation principle of VBS, they can be divided into variable volume VBS and variable ballast VBS. Among them, variable volume VBS is generally equipped with a volume-variable device on the underwater vehicle and realizes buoyancy adjustment by changing its displaced liquid volume [
7,
8]. Variable ballast VBS changes the buoyancy state of the underwater vehicle by adjusting the weight and position of the ballast to change the gravity and center of gravity of the underwater vehicle. The variable volume VBS is a closed system with constant total mass, which has the advantage of a compact structure, can achieve precise control of buoyancy, and has a simple structure and small volume, making it more suitable for the HAUV platform in this paper.
Traditional variable volume buoyancy systems mainly achieve buoyancy control through two typical methods: one is volume change technology based on oil bladders, which change the volume of the oil bladder through hydraulic drive, thereby adjusting the displacement volume to achieve buoyancy change. Autosub AUV is equipped with a passive buoyancy compensation system, which consists of three parts: a low-pressure air compensator, an oil bladder, and a high-pressure air compensator. It can use the pressure of seawater to achieve passive compensation of buoyancy when the depth changes and allows the AUV to have a certain positive buoyancy when sailing on the water surface to ensure communication quality [
9]. B.K. Tiwari et al. designed a hydraulic-oil bladder-type variable buoyancy system based on demand and realized pitch and hover control through a symmetric arrangement [
4]. The electro-hydraulic scheme has significant advantages in environments with large buoyancy changes or large working depths, but the structure is complex, requiring a large installation space, which is difficult to integrate into small underwater robots.
Another approach involves integrating airbags with high-pressure gas cylinders, where gas release or retraction fills the airbag to adjust buoyancy by altering displaced volume. These technologies demonstrated basic control capabilities in early underwater robot applications, as shown in
Figure 1. The variable buoyancy system combining airbags and high-pressure cylinders offers distinct advantages for compact underwater vehicles, featuring simple structures, small size, and straightforward control design. However, when addressing emerging cross-domain platforms like hybrid aerial underwater vehicles, their inherent limitations have become increasingly apparent.
The main shortcomings of existing technologies are concentrated in three aspects: First, the airbag system relying on high-pressure gas cylinders requires frequent gas replenishment, which not only interrupts the continuity of cross-domain tasks of amphibious unmanned vehicles but also increases logistics support and maintenance costs [
12]. Second, the traditional hydraulic or pneumatic drive systems have complex structures, and the design of multi-stage valve groups and pipelines makes it difficult to reduce weight and miniaturize the device, which cannot meet the strict requirements of HAUV for “lightweight and compact”. Third, the nonlinear deformation characteristics of oil bladders or airbags, coupled with the influence of fluid resistance, make it difficult to balance the accuracy and response speed of buoyancy adjustment [
13,
14]. This problem is particularly prominent in scenarios requiring high-frequency cross-domain conversion, and the control stability of traditional devices faces greater challenges.
This study proposes a variable buoyancy system applicable to HAUV and analyzes its stability, with three core innovations that distinguish it from existing solutions. Firstly, the VBS achieves internal gas recycling through a redesigned pipeline structure, eliminating the need for high-pressure gas cylinder replacement and external gas replenishment. This addresses the frequent gas replenishment issue of traditional airbag systems, ensuring uninterrupted cross-domain task execution and reducing logistics and maintenance costs—a critical advantage for HAUVs operating in remote or extended missions. Secondly, the system features a simplified structure with minimal components (a cylindrical gas storage tank, two elastic airbags, a one-way vacuum pump, and multiple solenoid valves), enabling lightweightness and miniaturization. This directly meets HAUV’s strict “lightweight and compact” requirements, which traditional complex hydraulic/pneumatic systems fail to satisfy. Thirdly, a PID-based dual-loop control strategy is developed, where the outer loop regulates depth through buoyancy adjustment and the inner loop controls attitude via symmetric airbag inflation/deflation. This hierarchical regulation mechanism achieves both rapid response and precise control (maintaining depth accuracy within ±5 cm), effectively resolving the trade-off between accuracy and response speed in traditional systems.
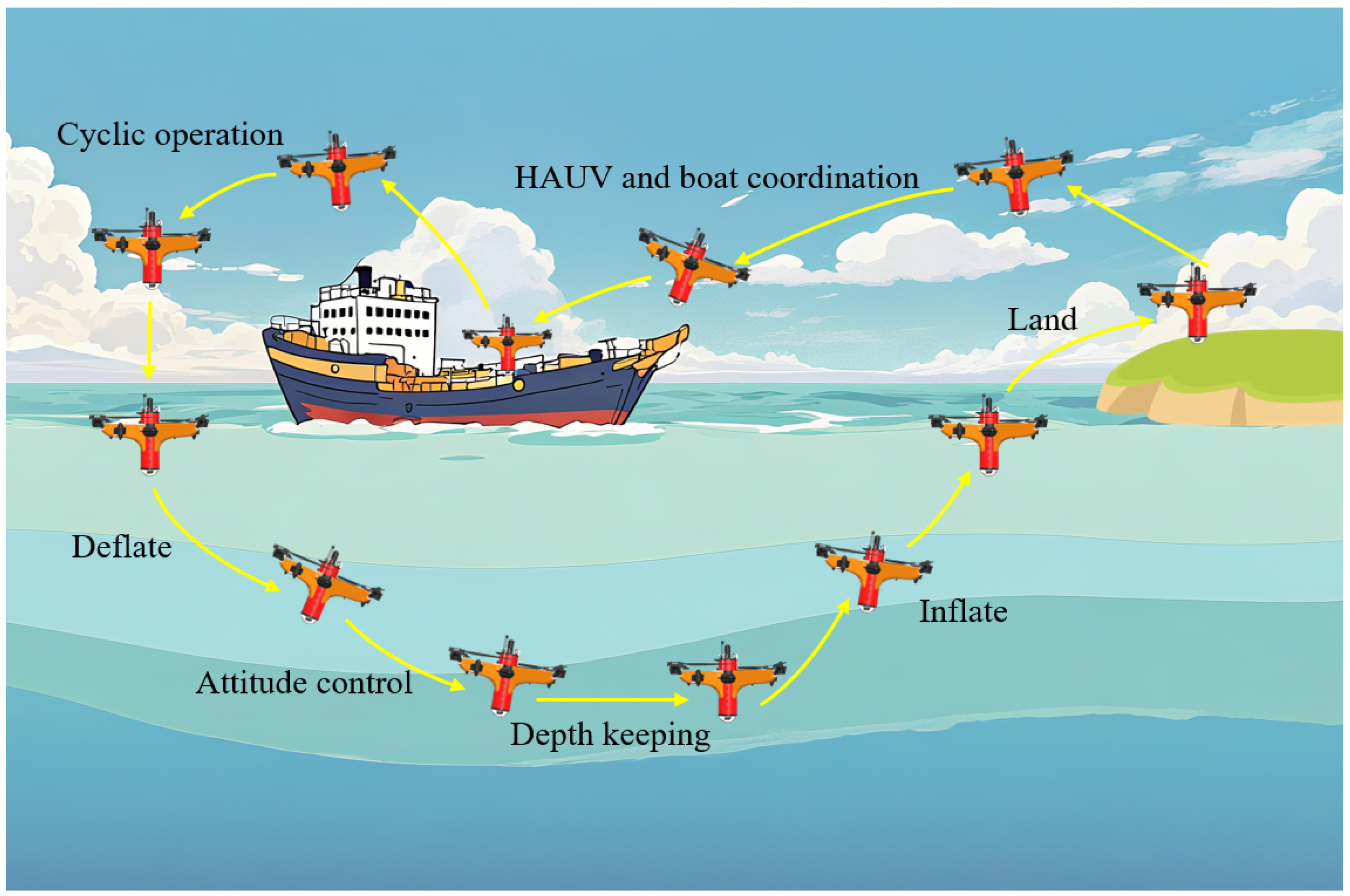
The VBS-enabled HAUV leverages its high-speed aerial maneuverability to swiftly reach designated monitoring areas and execute full-cycle cross-domain hydrographic profile monitoring tasks: underwater descent, observation, surfacing, data transmission, and return. As shown in
Figure 2, by controlling airbag inflation and deflation, the HAUV can regulate ascending, descending, and underwater posture, enabling stable cross-domain cyclic operations.
Recent relevant studies have provided diverse insights for the low-cost design and performance optimization of HAUVs: In terms of the lightweight design of control systems, optimizing data transmission frequency through event thresholds avoids the use of high-cost, high-frequency sensors [
15], which is consistent with the “on-demand triggering” logic adopted by the VBS in this paper, effectively reducing the cost of the electronic control module and ensuring the real-time performance of buoyancy adjustment. In the field of environmental perception, the approach of improving perception accuracy by combining low-cost hardware with algorithm optimization [
16] enables underwater obstacle monitoring without relying on expensive equipment; for nonlinear systems such as VBS, advanced sampled-data control methods have shown the potential to reduce complexity while improving performance [
17]. When designing the dual-loop PID control in this paper, the sampling interval and parameters are optimized based on the nonlinear characteristics of the VBS, which simplifies the algorithm while achieving real-time suppression of nonlinear disturbances, verifying the feasibility of low-cost control strategies.
Notably, the low-cost nature of this VBS addresses critical cost constraints in HAUV large-scale applications. For instance, academic research projects often face tight budgets, making expensive traditional VBS (with high-pressure cylinder maintenance and complex manufacturing costs) prohibitive. Similarly, multi-device collaborative monitoring missions—essential for large-area marine surveys—require cost-effective solutions to deploy sufficient units, a need unmet by existing high-cost systems. This study’s VBS, with its simplified structure and reduced maintenance needs, significantly lowers entry barriers for HAUV deployment across scientific, commercial, and emergency response sectors.
Table 1 presents several existing studies on HAUV. As a representative of early cross-medium unmanned systems, the LoonCopter adopts a quadcopter structure to achieve amphibious functionality, and it is equipped with VBS that changes buoyancy by inhaling and expelling water. The VBS of Nezha III alters buoyancy by displacing water volume. In contrast, the VBS proposed in this paper changes buoyancy by controlling airbags.
The remaining sections of this paper are structured as follows.
Section 2 introduces the system design and overall architecture of the VBS, including core components such as the sealed chamber and pressure regulation mechanism along with their relevant design parameters and
Section 3 elaborates on the electronic architecture of the electrical control system, the PID-based dual-loop control system, and specific control strategies for buoyancy regulation;
Section 4 details the pipeline design specifications and experimental procedures, covering closed-loop gas circuit design, inflation/exhaust workflows, and performance testing;
Section 5 validates the practical application performance of the VBS through indoor and outdoor experiments conducted in HAUV prototype.
2. System Design
The VBS achieves motion control of the vehicle by regulating the volume of water displaced by bladders. Based on this premise, the design of the air pressure regulating mechanism in the VBS becomes the technical core [
20], which requires that the execution system not only have rapid response characteristics but also maximize the overall range of change in buoyancy of the VBS [
21]. Based on this, we selected existing commercial components and successfully designed a low-cost, sustainable VBS system.
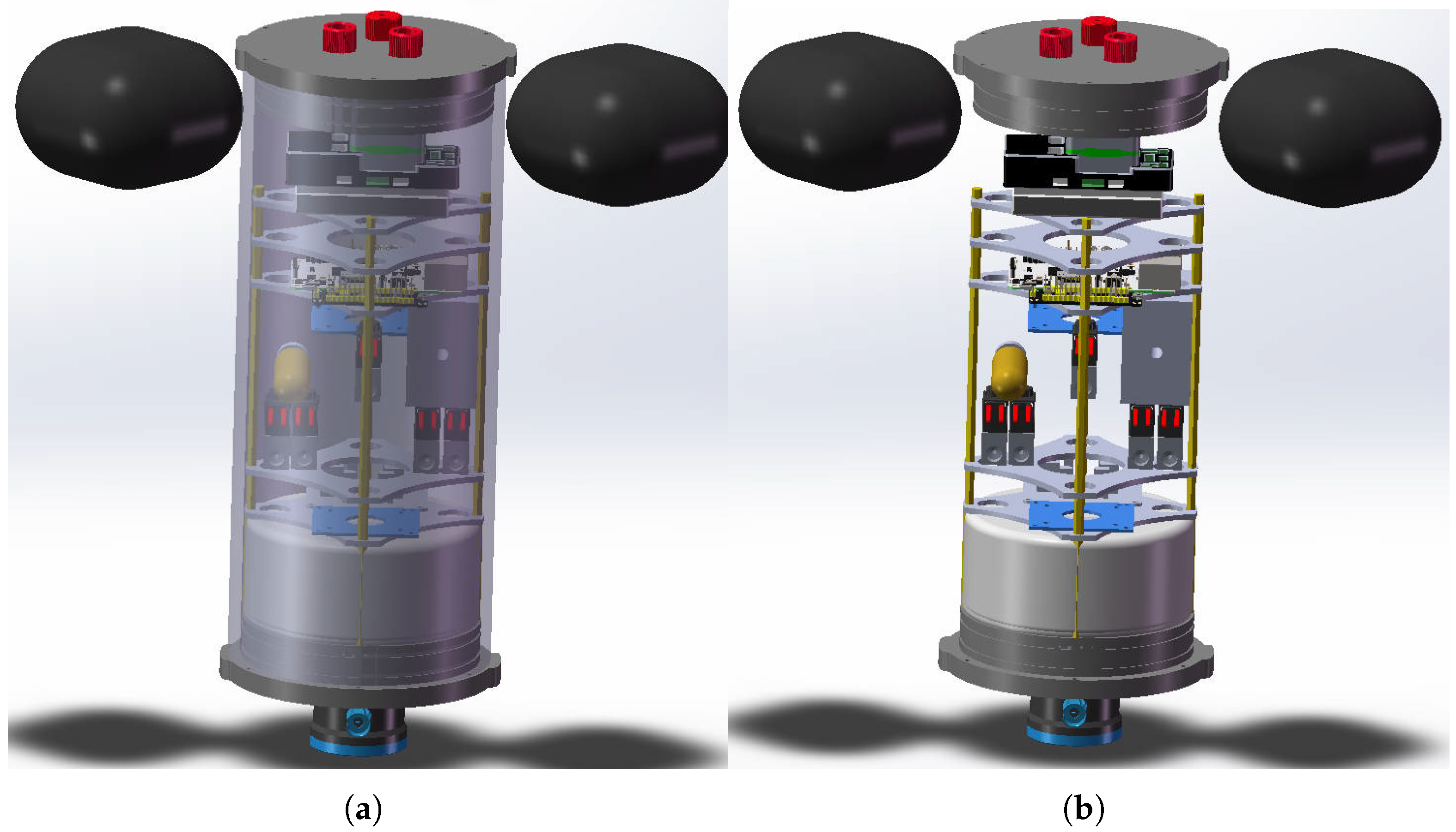
As shown in
Figure 3. The main structure of the VBS is a sealed cabin. Two bladders were placed outside the sealed cabin, and an air pressure regulating mechanism and an electrical control mechanism were placed inside the sealed cabin [
12,
22]. The air pressure regulating mechanism is connected to each bladder through gas conduits. Attitude sensors, depth sensors, and sonar were arranged inside and outside the sealed cabin. The electrical control mechanism drives the air pressure-regulating mechanism to adjust the buoyancy through the bladders according to the body attitude and sensor detection data.
The maximum operating depth of this design is 10 m, a parameter optimized for the requirements of shallow water and nearshore operations. It is suitable for shallow-water tasks such as estuary monitoring, nearshore ecological surveys, and port security. In these scenarios, water flow disturbances are minor, and the water pressure environment is relatively mild. The 10 m depth range can meet most operational needs, and the low-cost and lightweight characteristics of this design can significantly enhance deployment flexibility and economy in such scenarios.
2.1. Sealed Cabin
The sealed cabin has a cylindrical body. When a cylindrical structure is subjected to external water pressure, the pressure is evenly distributed over the entire cabin surface. Compared with other shapes, it can resist water pressure more effectively, reduce stress concentration, and improve the pressure resistance of the cabin [
23]. The inner cavity of the cabin is equipped with a support frame that includes multiple vertical support columns and multiple layers of horizontal support plates [
24]. A plurality of support columns are arranged along the circumferential direction in the inner cavity of the cabin near the inner wall, the lower ends of which are fixedly supported on the lower sealing seat, and multilayer support plates are fixedly connected to the support columns. The air pressure-regulating and electrical control mechanisms are supported and arranged in the inner cavity of the cabin through multilayer support plates [
25]. The arrangement of the support frame provides stable support for various components in the cabin, prevents shaking or damage caused by water pressure and movement during underwater work, and is conducive to the layout and heat dissipation of various components.
2.2. Pressure Regulating Mechanism
The air pressure-regulating mechanism mainly comprises a pressure-resistant gas storage tank, a diaphragm vacuum pump, solenoid valves, and high-pressure gas pipes. The pressure-resistant gas storage tank is connected to the bladder through a diaphragm vacuum pump, which can deliver the gas in the pressure-resistant gas storage tank to the bladder to increase buoyancy or suck the gas in the bladder back into the pressure-resistant gas storage tank to reduce buoyancy [
26,
27].
The pressure-resistant gas storage tank is the core component for storing high-pressure gas in the sealed cabin, with a capacity of 0.5 L, which can withstand approximately 5 atmospheres (0.5 MPa). It can support a volume change of 1 L in the bladder, corresponding to a buoyancy change, adapting to the maximum diving depth of an unmanned aerial vehicle (such as 10 m, corresponding to a water pressure of approximately 1 atm). Combined with the ideal gas law and the underwater pressure environment, the calculation process is as follows: It is assumed that the gas temperature is constant, and the influence of temperature change on the gas state is ignored.
When the gas in the gas storage tank is delivered to the bladder through the air pump, it follows the ideal gas law of an isothermal process:
where
(initial pressure of the gas storage tank);
(volume of the gas storage tank);
(ambient pressure at 10 m underwater, the final pressure of the gas in the bladder, which needs to balance the external water pressure);
is the volume of the gas in the bladder (final volume).
therefore,
.
The vacuum pump cannot completely pump to an absolute vacuum; therefore, the actual pumping volume is slightly reduced, and the volume change is approximately 1.1 L. Air path leakage, such as solenoid valves and gas pipe interfaces, leads to 5–10 percent loss, and the final effective volume change is approximately 0.99–1.05 L.
The delivery efficiency of the diaphragm vacuum pump determined the speed of bladder inflation and deflation. If the efficiency is low, the inflation and deflation process will take a long time, and the response speed of the device’s depth control will be slow, affecting the flexibility of underwater operations. The VBS used a rated flow rate of 5.5 L/min.
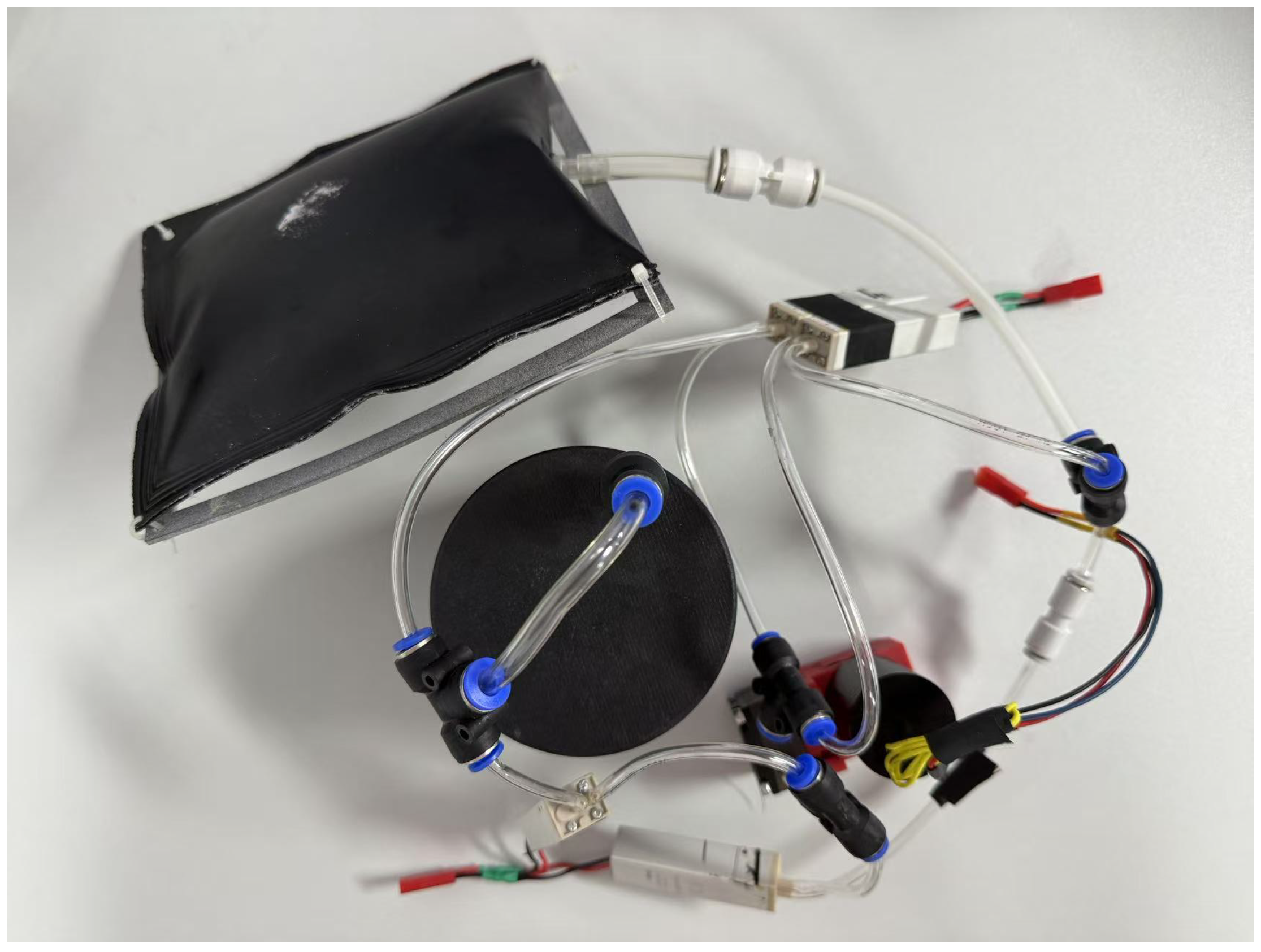
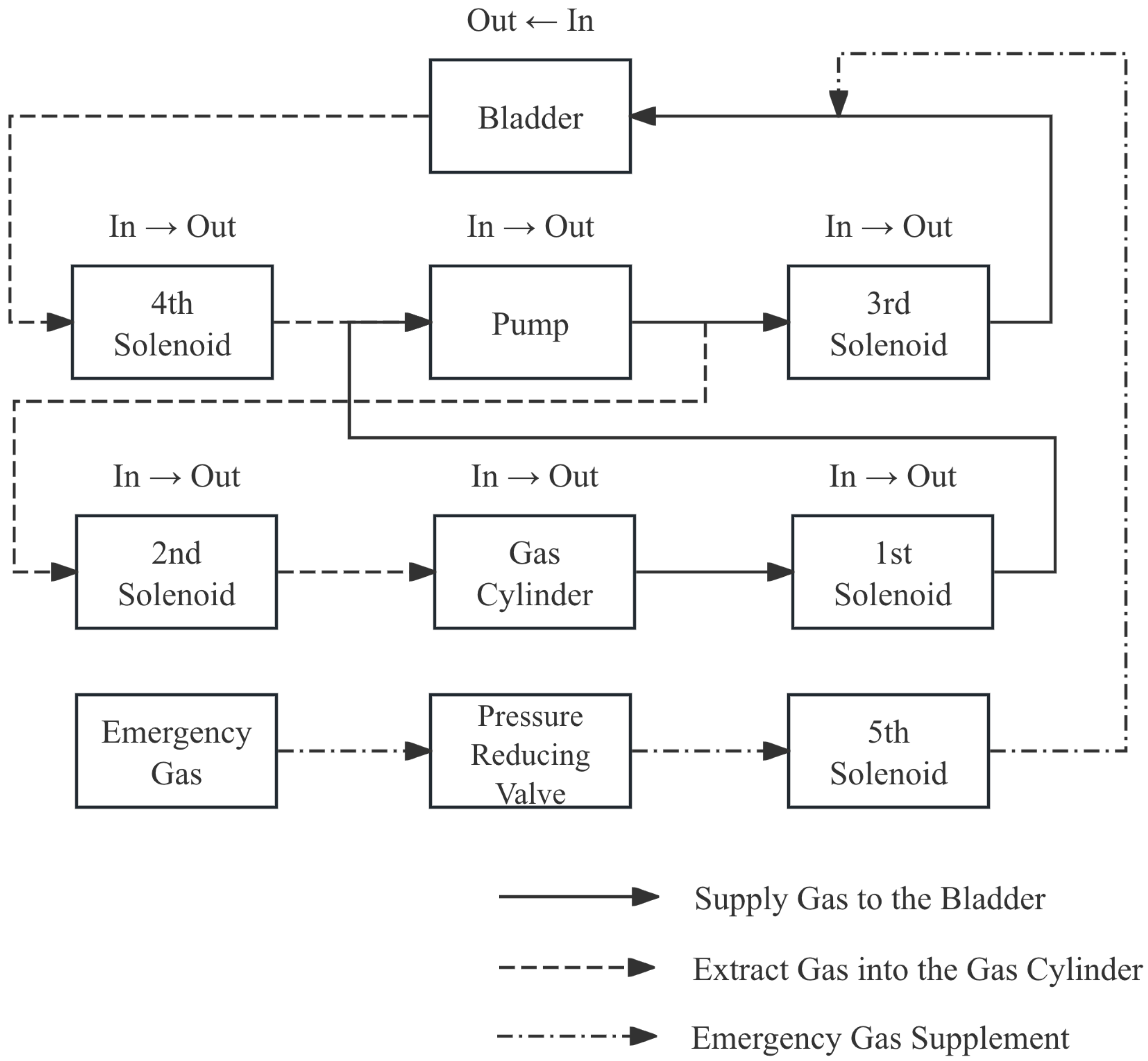
The air pressure-regulating mechanism includes four solenoid valves that form a closed-loop air path through high-pressure gas pipes, and the specific connection method is shown in
Figure 4.
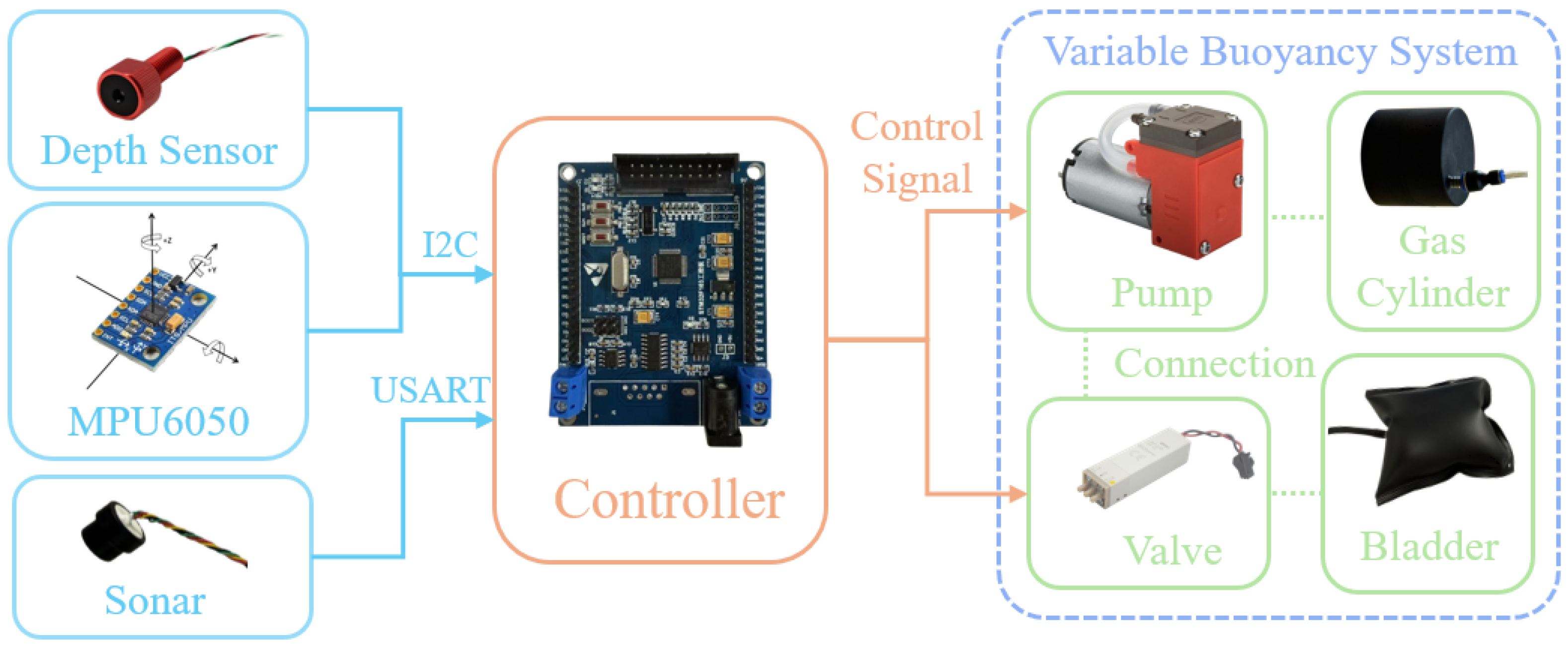
3. Electrical Control Mechanism
3.1. Control Mechanism Electronic Architecture
The electrical control mechanism, functioning as the “central nervous system” of the variable buoyancy adjustment device, undertakes core tasks such as receiving sensor data, executing logical operations, driving the air pressure adjustment mechanism, and managing energy distribution [
28,
29]. The architecture of its core components and functions is illustrated in
Figure 5.
As the direct executive controller for buoyancy adjustment, the single-chip microcomputer is connected to the diaphragm vacuum pump, waterproof sonar module, and depth sensor and drives the action of the air pressure adjustment mechanism based on the detected data [
7]. During operation, the single-chip microcomputer continuously collects the current depth data from the depth sensor—specifically the MS5837-30BA model, which features a measurement range of 0–30 m, an accuracy of ±0.02 m, and a sampling frequency of 10 Hz—and the obstacle distance information from the waterproof sonar module—the JQ-US1M-TTL model, with a detection range of 0.3–4 m, an accuracy of ±0.01 m, and a sampling frequency of 5 Hz. According to preset logic (such as the difference between the target and actual depth), it sends instructions to the electromagnetic relay, thereby controlling the start–stop of the diaphragm vacuum pump, inflation–deflation operations, and the switching of solenoid valves. It also records real-time status parameters, including current buoyancy adjustment progress and sensor abnormality information.
In addition, the electrical control mechanism includes a voltage-dividing distribution board module [
30]. This module distributes the electrical energy, such as the 24 V voltage output by the battery module, and generates adaptive voltages according to the requirements of various components (for example, the one-way vacuum pump requires 5 V, and the solenoid valve requires 12 V), ensuring the stable operation of various electrical equipment. After being connected to the power module through the electromagnetic relay, it can precisely control the on–off status of key components such as the diaphragm vacuum pump and solenoid valve.
A water leakage detection sensor is installed inside the sealed cabin to monitor in real-time whether the cabin is leaking. This sensor operates on the principle of conductivity detection: when water enters the cabin, the system first cuts off power to non-essential components to prevent short circuits, then activates the diaphragm vacuum pump at maximum power to rapidly inflate the airbags, initiating an emergency ascent to the water surface. Simultaneously, it records the leakage event and current position data (via integrated positioning modules) for post-recovery analysis. Once a leak is detected, the data is immediately transmitted to the air pressure control module, triggering an emergency response and initiating an emergency rapid ascent.
3.2. Comparison and Evaluation of Control Methods
In existing VBS buoyancy regulation solutions, open-loop control systems, while structurally simple and easy to implement, rely entirely on preset air pump operating curves. This makes them unable to handle parameter drift, external disturbances, or load fluctuations in real-world operations, leading to cumulative errors that cause depth deviations beyond permissible limits [
31]. Single-loop control systems, though incorporating depth feedback mechanisms to improve steady-state accuracy through error correction, fail to account for dynamic hysteresis characteristics of air pump actuators, such as dead time between command input and actual flow rate output, or nonlinear flow-voltage relationships [
32]. When depth deviations change rapidly, the delayed response of air pumps results in buoyancy regulation lag, causing system overshoot or oscillation that cannot meet high-dynamic control requirements.
Model Predictive Control (MPC) can handle constraints through rolling optimization, but it has high computational complexity and requires high computing power for the embedded hardware of HAUV. This may increase system costs, which conflicts with the low-cost design goal of this paper.
Fuzzy Control does not require an accurate mathematical model and is suitable for scenarios with nonlinear deformation of airbags. However, its control accuracy depends on the design of empirical rules, and its dynamic response speed is not as good as that of PID dual-loop control.
Sliding Mode Control has strong robustness against parameter perturbations, but it has chattering phenomena, which may cause frequent actions of solenoid valves, increase energy consumption and equipment wear, and thus does not meet the low-power consumption requirements of HAUV.
3.3. Floating Control System PID Double Closed-Loop Control
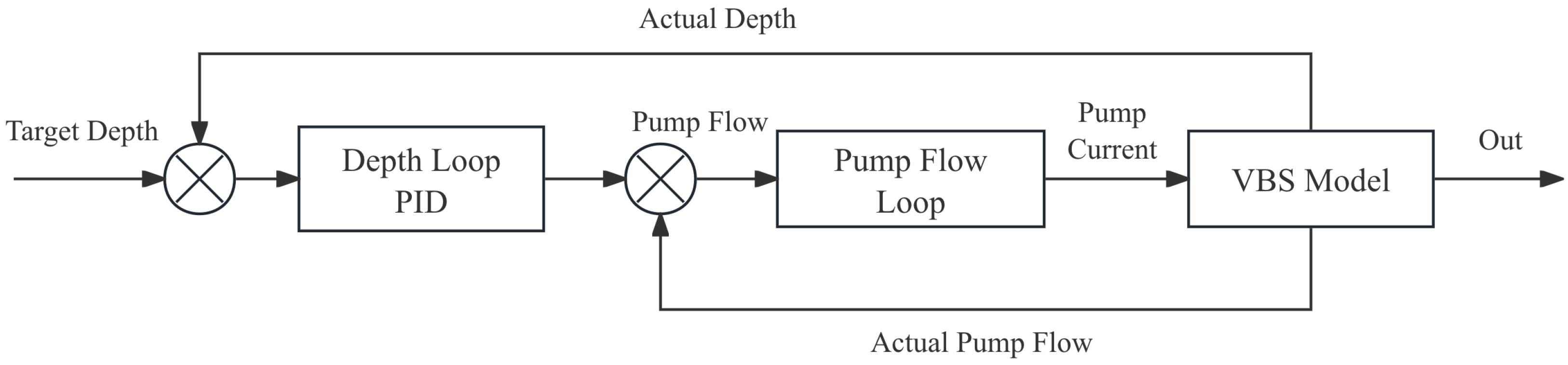
This paper designs a dual-loop control structure integrating depth and air pump flow rates, as shown in
Figure 6 above, enhancing system performance through coordinated inner and outer loops. The outer loop serves as the depth control loop, using the deviation between desired and actual depths as input to calculate target buoyancy change rates via PID controllers, which are then converted into air pump flow rate commands. The inner loop functions as the air pump flow rate control loop, continuously monitoring actual air pump flow rates [
33,
34]. By comparing these with the flow rate commands from the outer loop, it adjusts air pump drive signals (e.g., voltage or PWM duty cycle) through another PID controller. The dual-loop design delivers core advantages through its architecture: The inner loop directly suppresses the pump’s inherent nonlinearity and dynamic hysteresis, ensuring rapid flow rate tracking of control commands while providing a “rigid” execution foundation for depth adjustment in the outer loop. The outer loop leverages precise inner-loop performance to achieve global optimization of depth control. This synergy between “rapid response” and “precision regulation” significantly enhances the system’s capability to mitigate complex disturbances and improve dynamic tracking performance.
The PID controller is selected as the core algorithm for dual-loop control based on two key considerations: Firstly, its simple structure and mature parameter tuning methods facilitate engineering implementation and debugging, reducing system complexity. Secondly, adopting a unified PID framework allows unbiased evaluation of performance differences among control algorithms, enabling precise validation of how dual-loop architecture enhances depth control performance.
The mathematical model of the PID dual-loop controller is explicitly defined as follows: For the depth-loop PID controller, the mathematical expression is
where
, and
,
,
are the proportional, integral, and derivative coefficients of the depth loop, respectively.
For the pump flow loop PID controller, the mathematical expression is
where
, and
,
,
are the proportional, integral, and derivative coefficients of the depth loop, respectively.
Based on Newton’s second law, the correlation between net buoyancy and depth variation can be established.
where
is the total mass of the HAUV (including VBS),
is the vertical acceleration (m/s
2),
h is the depth (m), and
is the water flow resistance,
, where
is the drag coefficient,
A is the frontal area, and
v is the vertical velocity.
This equation directly correlates the buoyancy output of the VBS () with the depth response of the HAUV (h), explaining the physical essence of “low overshoot in depth control” and “small errors under water flow disturbances” mentioned in the paper. Specifically, the dual-loop control offsets the fluctuations of by adjusting , ensuring that the depth dynamic response meets expectations. Meanwhile, it also provides a physical reference for the tuning of control parameters (such as PID proportional gain). For instance, when the water flow resistance increases, the proportional gain needs to be increased to enhance the adjustment range of .
In this study, the empirical tuning method (trial-and-error method) is adopted to determine the PID gain values. Firstly, the integral coefficient and derivative coefficient are set to 0, and the proportional coefficient is gradually increased until the system exhibits slight oscillations. Then, the integral coefficient is introduced to eliminate the steady-state error, starting from 0.01 and increasing gradually until the depth deviation stabilizes within ±0.05 m. Finally, the derivative coefficient is added to suppress overshoot, and the optimal dynamic response of the system is achieved by testing different values.
The dual-loop PID control adopted in this paper is characterized by a simple structure and mature parameter tuning. The outer loop achieves steady-state accuracy control through depth feedback, and the inner loop suppresses the dynamic lag of the air pump based on flow feedback. The synergistic effect of the two loops has achieved centimeter-level depth control accuracy in experiments, fully meeting the accuracy requirements of shallow water operations. At the same time, its low computational complexity can be adapted to low-cost embedded hardware, avoiding additional computing power costs. In addition, there is no risk of chattering, which can effectively reduce equipment energy consumption and wear. It is highly consistent with the lightweight, low-cost, and long-endurance design goals of HAUV, making it the optimal choice in the current application scenario.
3.4. Control Strategy and Task of Buoyancy System
The control program of the buoyancy adjustment system performs three core tasks: comparison between the target depth command and the current depth, calculation of the piston displacement, and realization of piston position control according to the command. The controller of the system first receives the target depth command that needs to be reached, compares it with the current depth to determine whether it is necessary to output buoyancy immediately, and then realizes the buoyancy adjustment function based on the results output by the control system [
35]. The specific adjustment steps are as follows:
- 1.
When the HAUV does not need to adjust the buoyancy, the controller will cut off the power supply of the external sensors and enter the energy-saving mode. If it is necessary to change the water depth by adjusting the buoyancy, the control system exits sleep mode to receive the command and executes the buoyancy adjustment accordingly [
36]. If no buoyancy adjustment command is received within the specified time, the buoyancy control system will enter the dormant state again.
- 2.
When it is necessary to increase buoyancy to achieve upward movement, after receiving the buoyancy output command, the control system determines the required displacement variation and drives the electrical control module to increase the buoyancy. When the buoyancy reaches the target value, the buoyancy adjustment process stops.
- 3.
When it is necessary to reduce buoyancy to achieve diving, after receiving the command to reduce buoyancy, the depth controller determines the required displacement reduction and executes the electrical control command. When the target displacement is reached, the buoyancy adjustment process terminates.
During underwater operations, the system’s energy consumption is mainly concentrated in two parts: pump driving and sensor operation. In long-term operations, the dynamic adjustment characteristics of the dual-loop control can realize on-demand distribution of energy consumption: when the system is working at a fixed depth, the pump only needs to maintain low-power operation, while in the stage of depth switching or disturbance adjustment, the pump power dynamically increases with the increase of deviation but quickly drops back to the low-power range after the adjustment is completed. This mode of “high-power instantaneous response and low-power steady-state maintenance” logically avoids the continuous high consumption of energy.
Through the Algorithm 1, the buoyancy adjustment system can perform corresponding buoyancy adjustments according to commands under different conditions, thereby achieving precise control of the underwater vehicle.
| Algorithm 1 Buoyancy Adjustment Control Logic |
- 1:
Start: System Initialization (Sensor self-check, parameter loading) - 2:
Check water leakage sensor status - 3:
if Water leakage detected then - 4:
Execute emergency ascent - 5:
Go to Step 12 - 6:
end if - 7:
Check if target depth command is received - 8:
if No command received then - 9:
Enter sleep mode after 30 s - 10:
Go to Step 13 - 11:
else - 12:
Enter active state - 13:
end if - 14:
loop - 15:
Calculate depth deviation (current depth - target depth) - 16:
if Deviation m then - 17:
Maintain current state - 18:
else - 19:
if Need ascent (current depth < target depth) then - 20:
Open solenoid valves 1 and 3 - 21:
Start vacuum pump to inflate airbag - 22:
Real-time feedback via depth sensor - 23:
if Deviation m then - 24:
Stop inflation - 25:
Break loop - 26:
end if - 27:
else Need descent - 28:
Open solenoid valves 2 and 4 - 29:
Start vacuum pump to pump air to storage tank - 30:
Adjust with depth feedback - 31:
if Deviation m then - 32:
Stop deflation - 33:
Break loop - 34:
end if - 35:
end if - 36:
end if - 37:
end loop - 38:
Task completed or command interrupted - 39:
System reset - 40:
End
|
4. Pipeline Design and Experiment
4.1. Pipeline Design
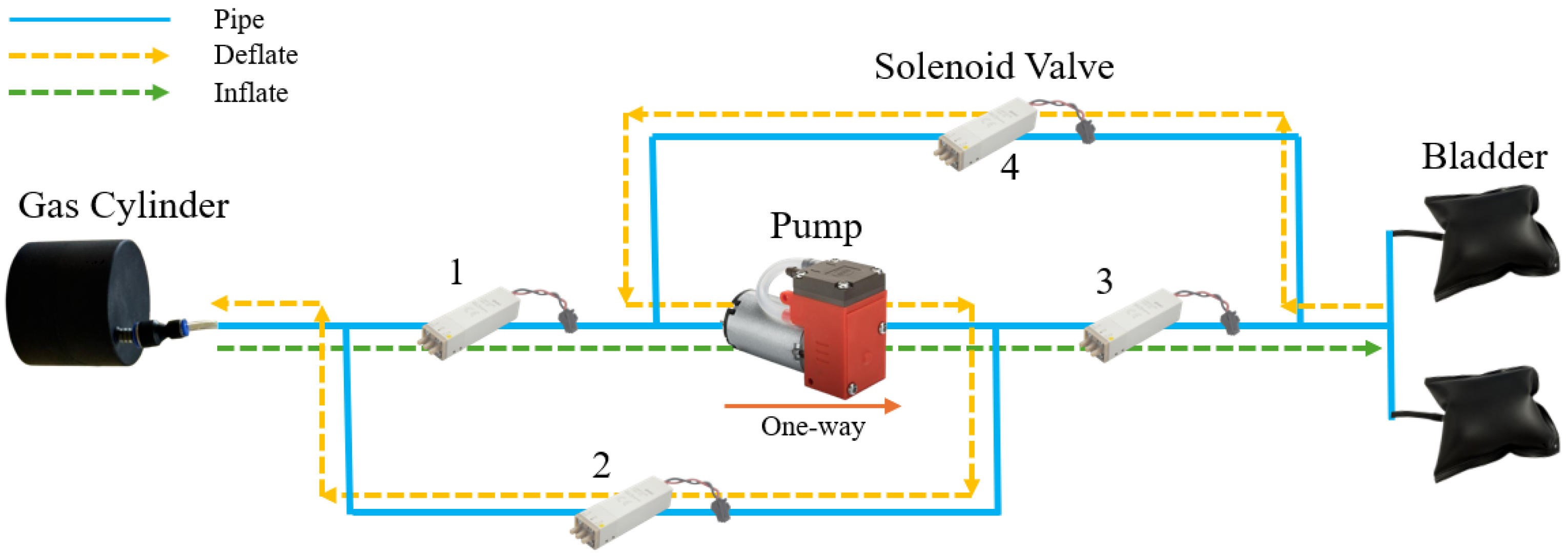
To realize the function of no external gas replenishment for the variable buoyancy adjustment device of cross-sea-air medium amphibious unmanned aerial vehicles, the device was built with a closed gas circulation system through improvements such as air path circulation design, efficient gas management, and structural optimization, as shown in
Figure 7.
In the design shown in
Figure 7, the symmetrical distribution of the main pipeline and the circulation pipeline can reduce the path difference in gas circulation. During the system’s buoyancy adjustment, this layout improves the efficiency of gas distribution between the two airbags, thereby shortening the response cycle of airbag inflation and deflation. Its efficiency advantage lies in the fact that gas can realize bidirectional adjustment without backflow.
A closed-loop air path of a pressure-resistant gas storage tank, bladder, and diaphragm vacuum pump was adopted to perform the gas recycling within the system without external replenishment [
37]. When the HAUV needs to ascend, the diaphragm vacuum pump delivers high-pressure gas from the pressure-resistant gas storage tank into the bladder, increasing the volume of the bladder to enhance buoyancy. When it needs to descend, the solenoid valve is controlled to switch the pipeline structure, and the gas in the bladder is pumped back to the pressure-resistant gas storage tank for storage, thereby reducing the volume of the bladder and reducing buoyancy [
38]. The specific working process is shown in
Figure 8.
When the device needs to ascend, the 1st and 3rd solenoid valves are opened, and the diaphragm pump presses the high-pressure gas in the gas storage tank into the bladder through the 1st solenoid valve, the pump, and the 3rd solenoid valve. The inflation amount of the bladder can be precisely adjusted by controlling the running time of the pump and the opening and closing frequencies of the solenoid valves. For example, the pump can pump 0.45 L of gas in 5 s, corresponding to a buoyancy increase of approximately 4.5 N, realizing fixed-depth control. The depth sensor and waterproof sonar module monitored the depth and surrounding environment of the device in real time, and the electrical control mechanism adjusted the opening and closing times of the solenoid valves according to the data. When approaching the target depth, the running time of the pump was reduced to avoid excessive inflation, leading to excessive buoyancy and achieving millimeter-level depth accuracy.
During descent, the 2nd and 4th solenoid valves were opened, and the pump pumped gas from the bladder to the gas storage tank. The gas is pressed into the gas storage tank through the 4th solenoid valve, pump, and 2nd solenoid valve. At this time, the air pressure in the gas storage tank increases, and the pumping efficiency of the pump is affected by the pressure difference. The 1st solenoid valve was used to adjust the air intake of the gas storage tank to maintain a stable pressure difference between the two ends of the pump, ensuring a uniform pumping flow and avoiding attitude fluctuations of the device caused by sudden changes in the bladder volume. When a rapid descent is required, the pump operates at the maximum flow rate. When approaching the target depth, the pump speed and solenoid valve opening time are reduced to realize the hierarchical control of ‘fast pumping–slow stopping’, preventing excessive downtime of the device caused by excessive pumping.
In addition to the conventional gas pipeline design, an emergency gas cylinder is added as an internal backup gas source, which is pre-charged with high-pressure gas (50 mL at 10 atm). It is only activated in the event of gas pipeline failures (such as vacuum pump malfunction or gas leakage) and supplies gas to the bladder through a pressure-reducing valve and the fifth solenoid valve. This design belongs to the category of “internally stored emergency gas” rather than an external gas supply, ensuring that basic buoyancy adjustment functions can still be maintained under extreme conditions. Moreover, the emergency gas can be refilled during subsequent maintenance without affecting the regular closed-loop cycle.
4.2. Pipeline Experiment
After the construction of the gas pipeline, a series of systematic tests were conducted in a targeted manner to verify the stability and reliability of its overall performance. As the core power component of the entire VBS, the operating efficiency of the vacuum pump directly determines the response speed and flow accuracy of the inflation and deflation of the bladder, which in turn affects the depth control capability and attitude stability of the device [
39]. Therefore, the performance test of the pump was taken as the primary link in the entire testing process.
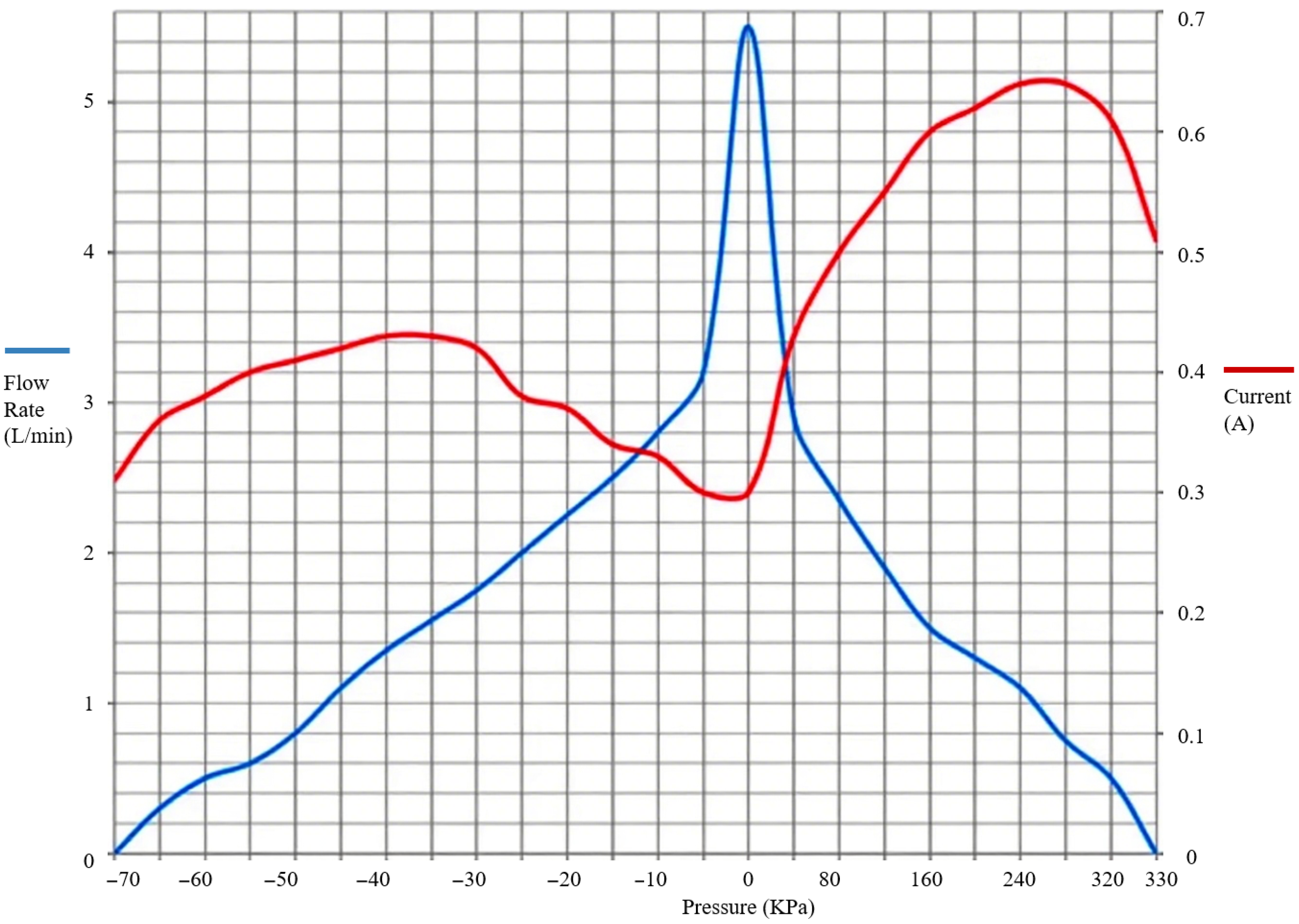
As shown in
Figure 9, we focused on monitoring the gas delivery efficiency of the pump under different pressure difference conditions, including the exhaust volume when inflating the bladder from the gas tank (such as the flow change in the range of 0–4 atm) and the suction rate when pumping gas from the bladder to the gas tank (with special attention to the attenuation curve of the pump’s pumping performance during the process of pressure increase in the gas tank). Data were recorded in real-time by high-precision flowmeters and pressure sensors, and the flow-pressure characteristic curve of the pump was plotted to determine its stable output range under conventional working conditions (such as maintaining a pressure difference of 1 atm) and the operating threshold under extreme working conditions (such as the maximum flow during rapid sinking).
After completing the performance test of the vacuum pump and clarifying its characteristic parameters, we further conducted a special test on the inflation and deflation speed of the bladder. This test link aims to combine the performance data of the pump with the actual response characteristics of the bladder so as to verify the cooperative working efficiency of the gas circuit system in the integrated state [
40].
In the test, based on the pump flow-pressure characteristic curve obtained in the early stage, we set multiple groups of typical working conditions: simulating conventional depth keeping, rapid descent, and rapid ascent (the pump outputs at the maximum flow rate), respectively. The volume expansion of the bladder per unit time was monitored in real time by a high-precision displacement sensor.
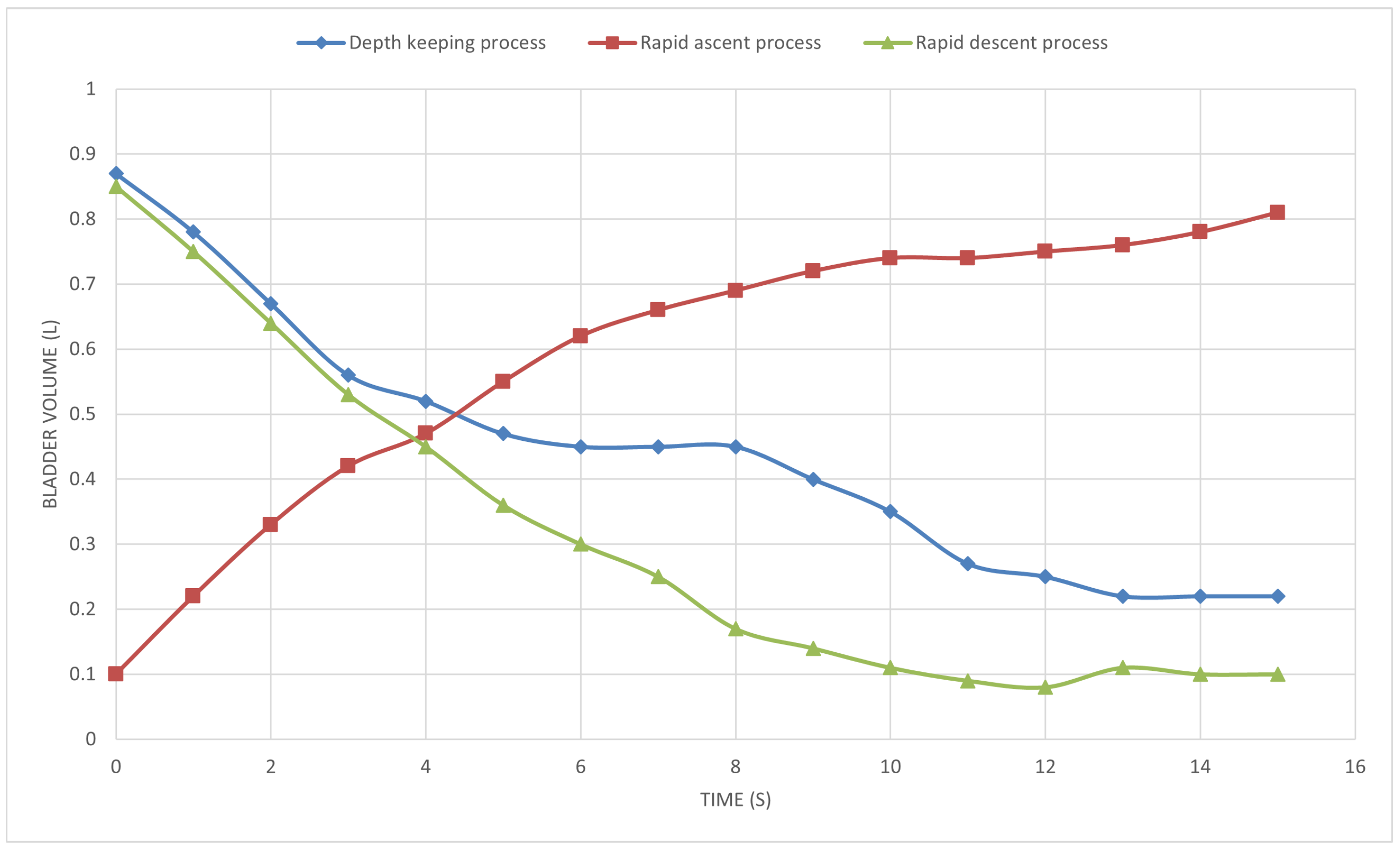
The test results are shown in
Figure 10. During the depth-keeping process, the initial volume of the bladder is approximately 0.9 L. It decreases rapidly in the first 4 s or so and remains basically stable in the range of about 0.45 L from 4 to 9 s. At this stage, the system achieves depth keeping by regulating the bladder volume to be stable. Then, as the depth-keeping state is updated, it decreases gradually after 9 s and tends to stabilize at around 0.2 L after 12 s. During the depth-keeping phase, the error margin between the actual volume and the target volume is stabilized within ±0.05 m.
In both the rapid ascent process and the rapid descent process, the pump operates at maximum power at the beginning to achieve rapid buoyancy changes. After 4 s, affected by internal pressure and external water pressure, the rate of change decreases gradually until the inflation and deflation processes are completed.
These test data can not only verify the deviation between the inflation and deflation speed of the bladder and the theoretical calculation value but also provide a key basis for the subsequent optimization of control parameters such as the opening and closing frequency of solenoid valves and the running time of the pump, ensuring that the device can accurately respond to the depth adjustment command according to the preset lifting rate in actual operation.
5. Prototype Experiment
The proposed low-cost variable buoyancy system (VBS) was manufactured and integrated into a new type of hybrid aerial underwater vehicle prototype. The total mass of the VBS was 4.2 kg, which meets the low-weight requirements of the HAUV. Various sensors were used in the experiment to obtain underwater motion information. A depth sensor was used to obtain the depth data. To reduce wave interference, the heave speed was calculated through depth changes every 3 s, and GPS was used as a supplement to obtain position data when the vehicle dived and ascended. The sonar monitors obstacle information in real time under the body to avoid touching the bottom.
The HAUV provides basic static buoyancy for the body by carrying buoyancy materials with specific densities, such as lightweight foam or hollow composite materials, as shown in
Figure 11, thereby enabling it to maintain a relatively stable, slow sinking state in water. The arrangement of the airbags and buoyancy materials directly affects the spatial coordinates of the center of buoyancy. When the airbags and buoyancy materials are distributed symmetrically along the longitudinal axis of the HAUV, the additional buoyancy generated by them forms a balanced moment on both sides of the center of gravity, and the lateral offset between the center of buoyancy and the center of gravity can be controlled within a minimum range. This symmetrical layout plays a role in ensuring the stability of the center of buoyancy.
The VBS adjusts the vehicle’s buoyancy dynamically by inflating or deflating the bladder. When the VBS drives the bladder to inflate and expand, the additionally generated incremental buoyancy can be superimposed on the basic buoyancy, pushing the HAUV to overcome its gravity and water flow resistance to ascend. When the bladder deflates and contracts, the dynamic buoyancy decreases, and the HAUV sinks because of the balance offset between the basic buoyancy and gravity. This collaborative design of basic buoyancy and dynamically adjusted buoyancy not only reduces the continuous power consumption of the VBS through the buoyancy materials carried on the arm (without the need to maintain basic suspension at all times) but also realizes the rapid switching and stable hovering of the HAUV at any underwater depth with the precise control capability of the VBS, which is especially suitable for the multi-scenario requirements of “underwater fine operation-rapid ascent to the water surface-air flight switching” in cross-medium operations.
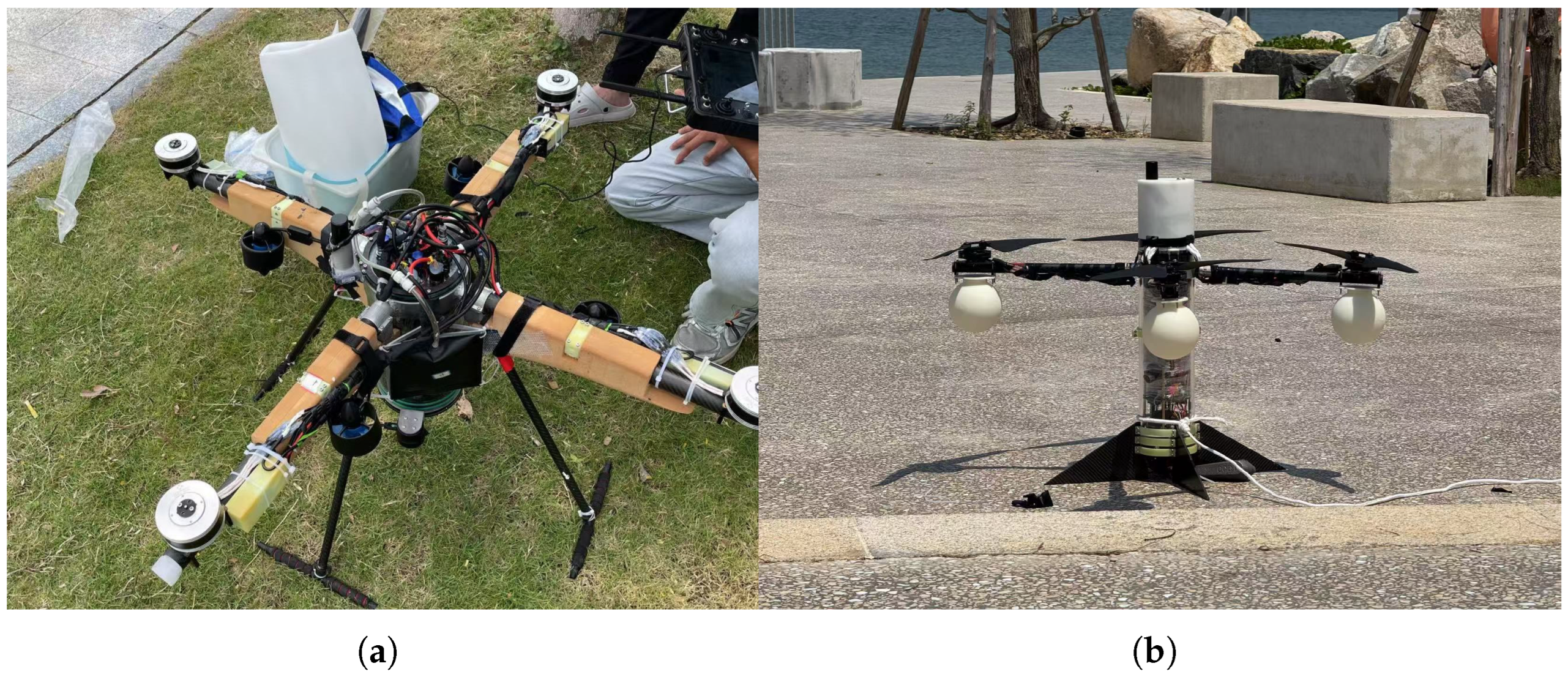
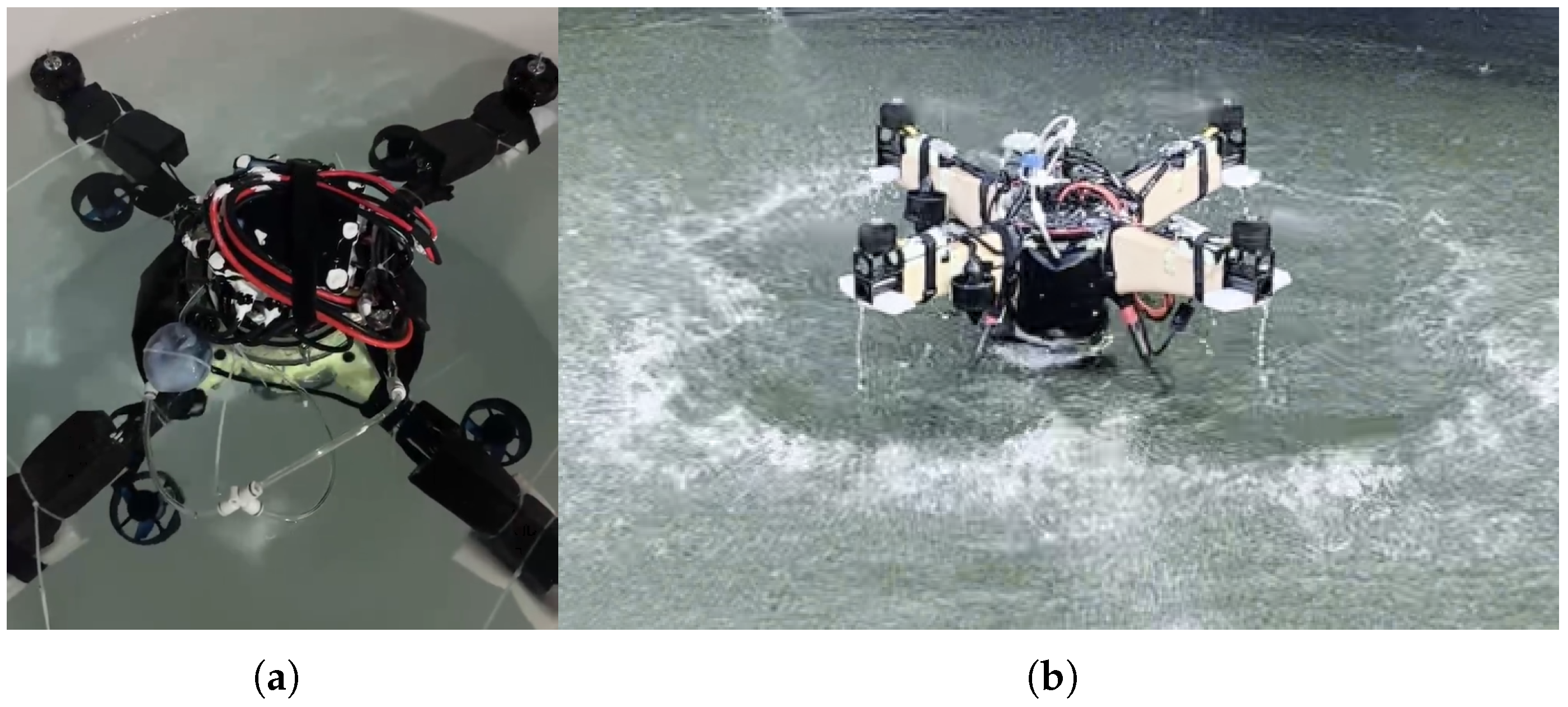
First, we set up an indoor test environment and conducted preliminary tests to verify the functional integrity of the HAUV and VBS. In
Figure 12a, we tested the underwater stability and inflation/deflation speed of the VBS in a bucket. Equipped with foam material on the arm, the VBS showed good stability in the test. When the HAUV tilted, it could spontaneously return to a stable state, ensuring that the HAUV propellers were not submerged in water during take-off on the water surface, as shown in
Figure 12b.
Subsequently, we conducted field tests on the HAUV and VBS in the waters off Dongshan Island, Dapeng, Shenzhen. This sea area is located in the eastern part of the Dapeng Peninsula, with a superior surrounding ecological environment and relatively little interference from human activities. Its water depth is usually between 3 and 12 m, which is somewhat similar to the indoor simulation environment, while also having the complex characteristics of natural waters, making it suitable for cross-domain testing. The seawater salinity is stable at 25–28‰, ensuring the consistency of buoyancy conditions, which helps to accurately evaluate the inflation and deflation efficiency of the VBS in the actual salinity environment. The turbidity is 15–20 NTU, with good light transmittance, facilitating the observation of the underwater attitude of the HAUV and the operating status of the VBS.
During the test, the single duration of the HAUV’s underwater hovering can reach 20–25 min, and the single duration of aerial cruising is 10–15 min. Without any external supply, the system can operate continuously for 4 times (limited by battery power), with a cumulative number of cross-domain transitions reaching 8–10 times.
In multiple flight and cross-domain tests, the VBS showed good adaptability throughout the entire process of the HAUV taking off from the sea surface, entering the water, hovering underwater, and then taking off from the water. At different water depths, the VBS can quickly respond to commands, adjust the inflation and deflation of the airbag, maintain the stable underwater attitude of the HAUV, and ensure its stability during cross-medium transitions. The test results show that the designed VBS system can complete cross-domain tasks multiple times without an external gas supply, fully verifying its reliability and independence in the complex natural marine environment and laying a solid foundation for subsequent practical applications.