Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Methane Adsorption and Diffusion in Limestone Pores in the Taiyuan Formation of the Ordos Basin, China: Effects of Pore Shapes, Apertures, and Formation Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Pore Morphology
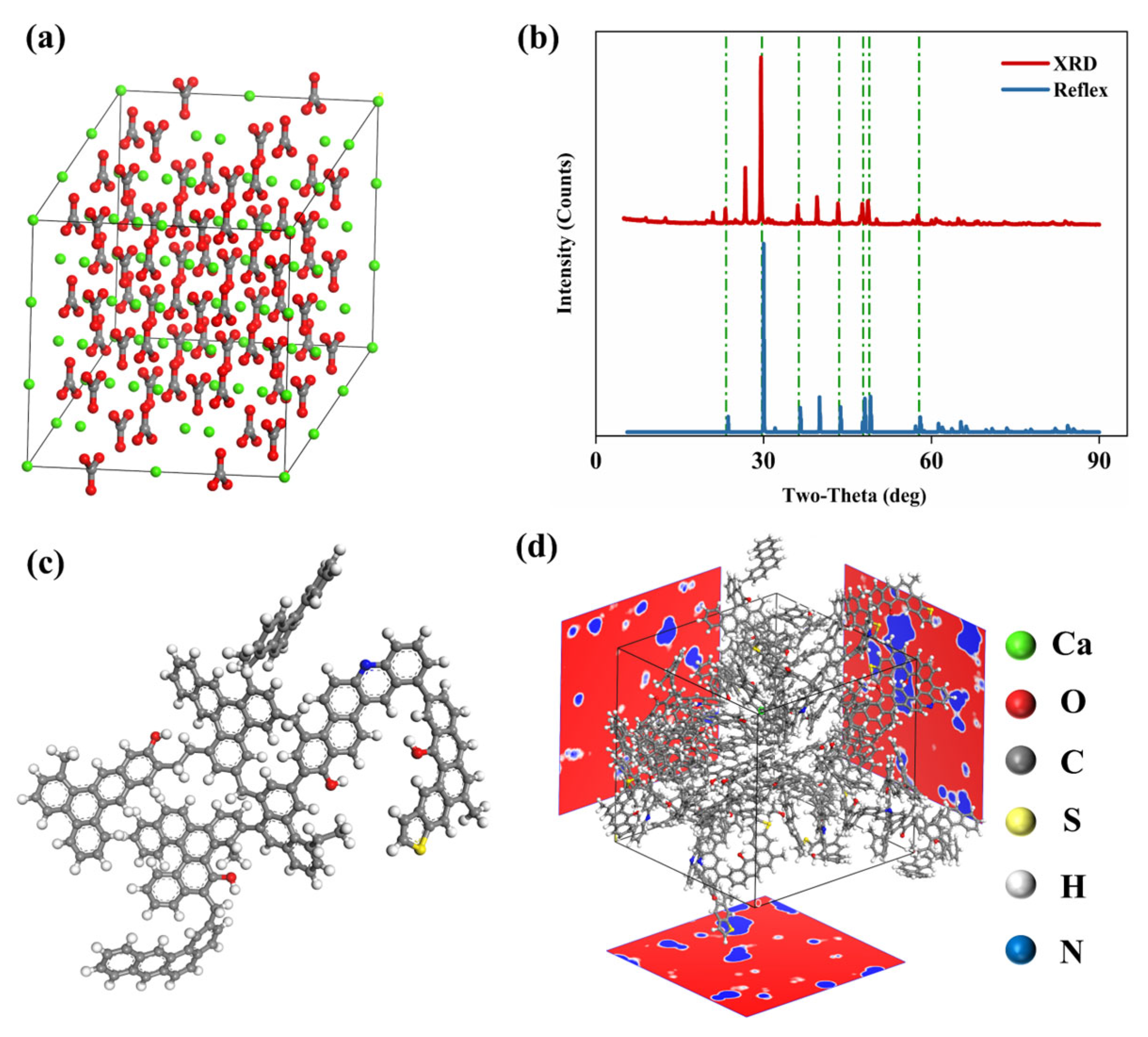
2.2. Molecular Model Construction
2.2.1. Calcite Model
2.2.2. Kerogen Model
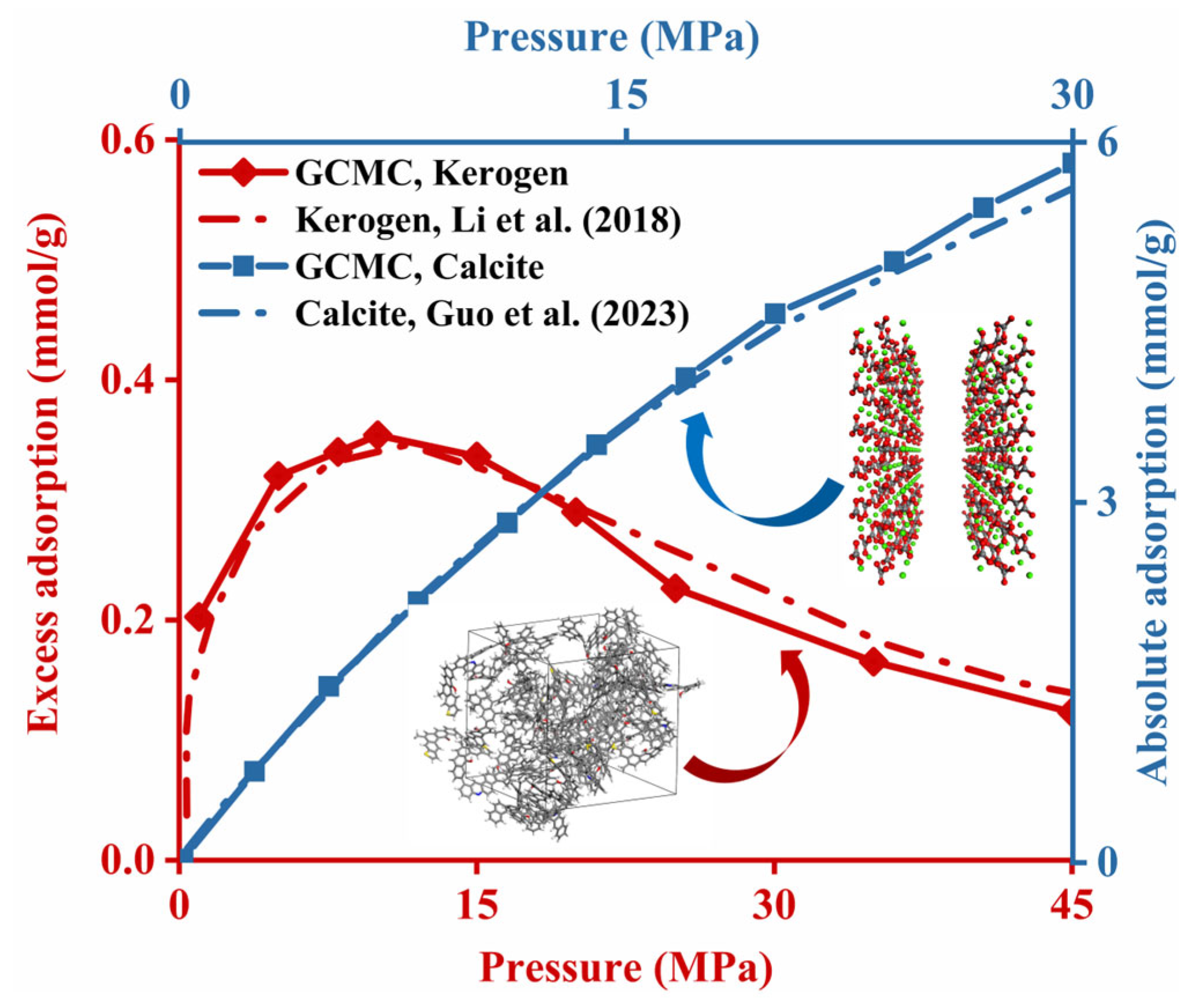
2.2.3. Model Validation
2.3. Simulation Methods and Details
2.4. Pore Structure Characterization
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Effect of Pore Shape
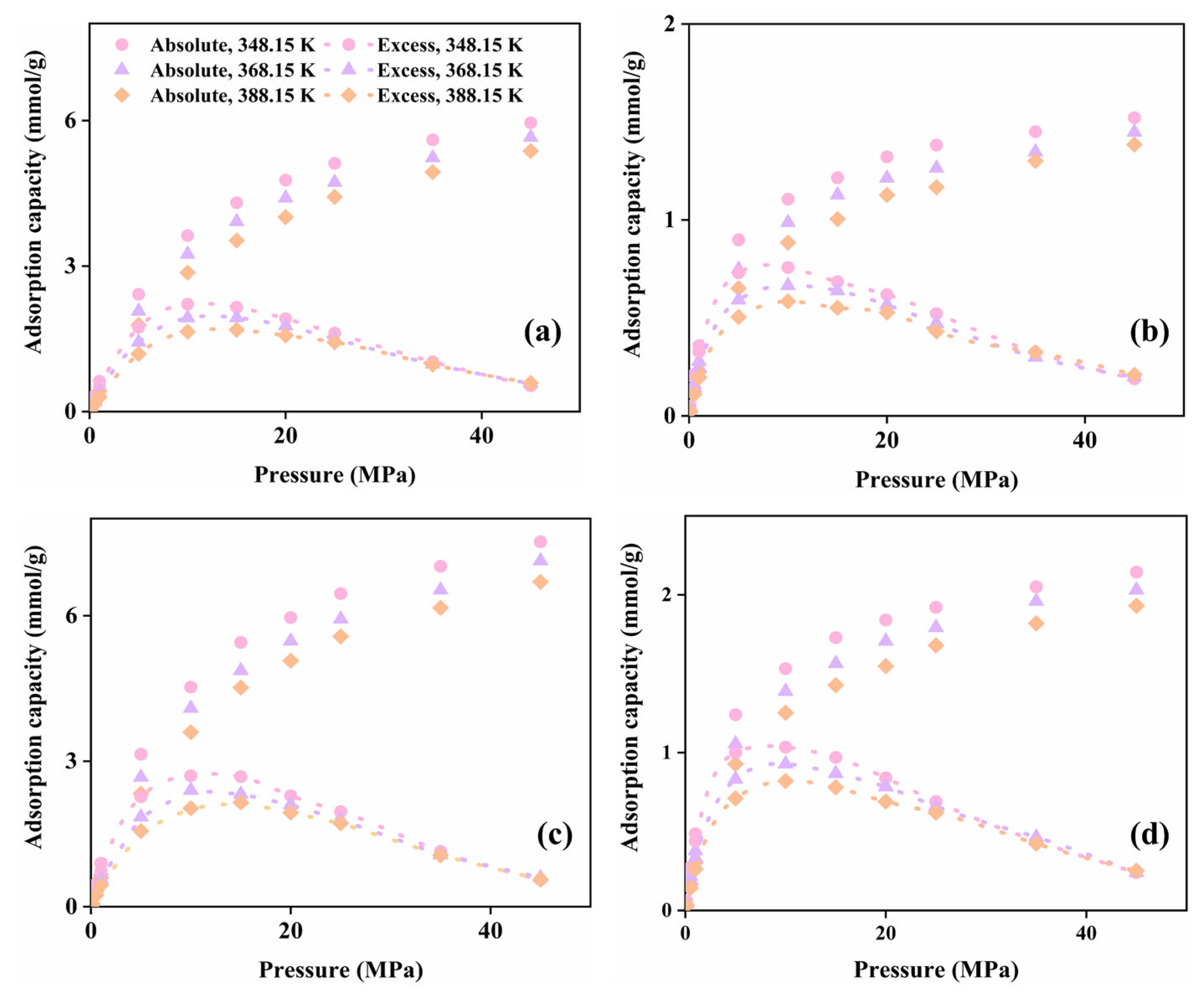
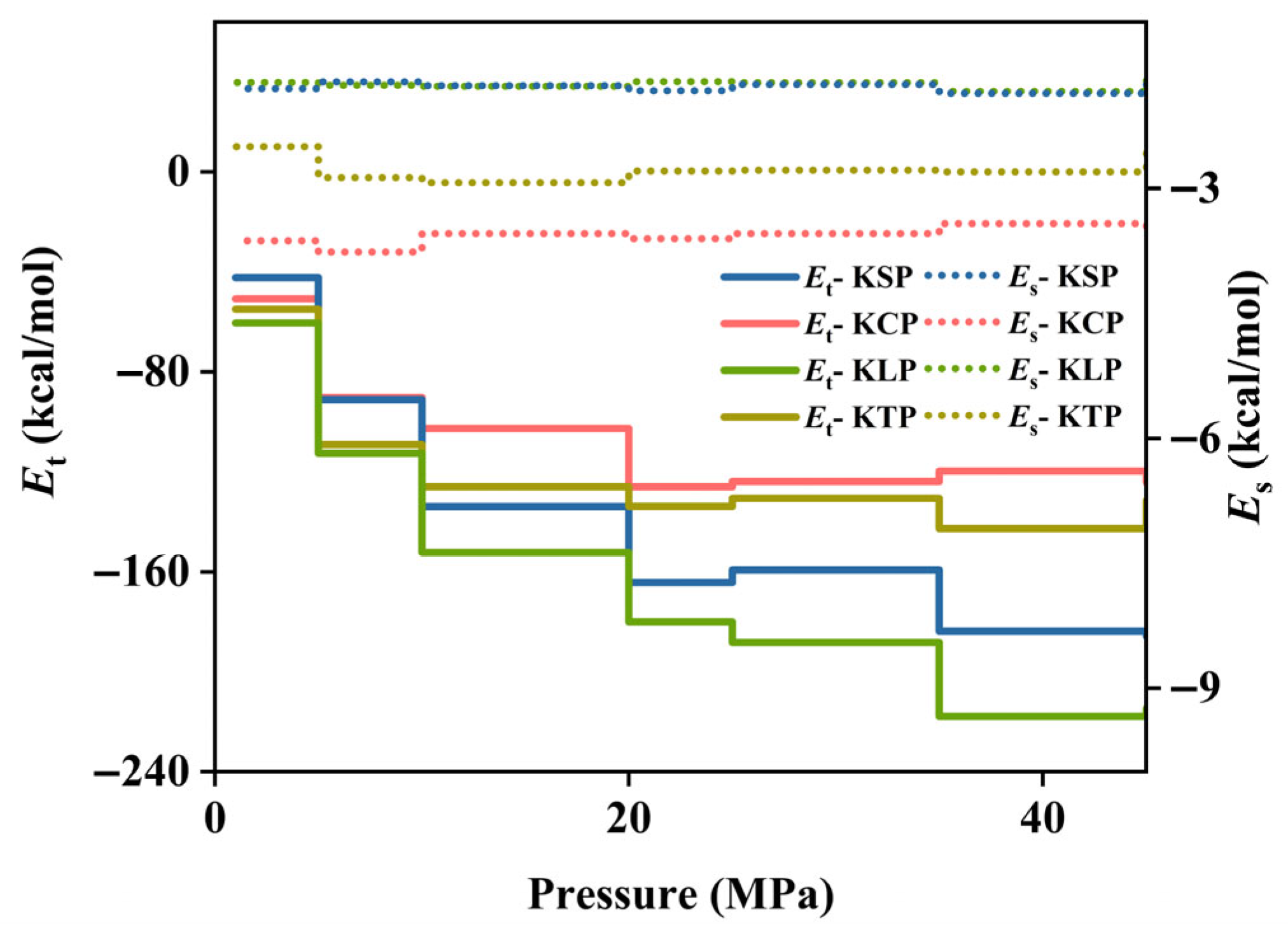
3.1.1. Effect of Pore Shape on CH4 Adsorption Capacity
3.1.2. Effect of Pore Shape on CH4 Adsorption Density
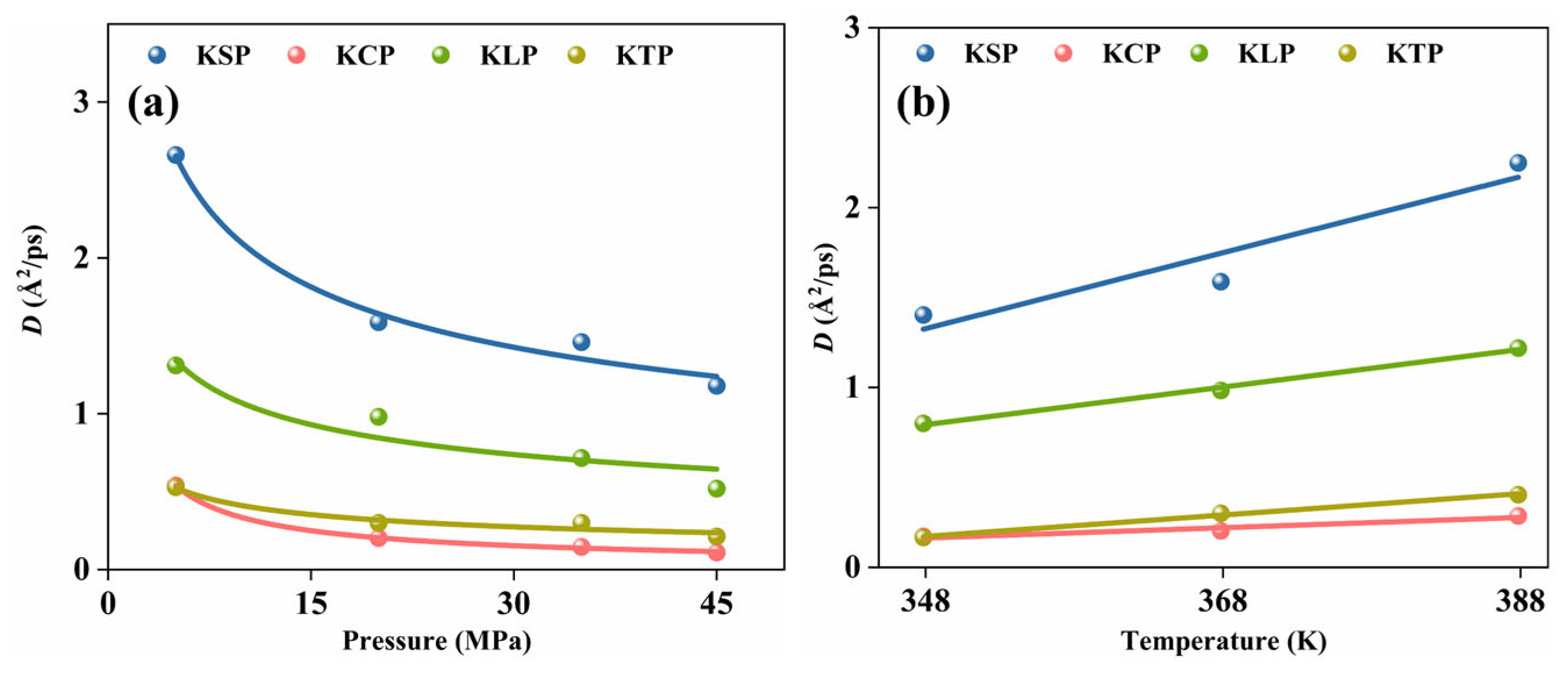
3.1.3. Effect of Pore Shape on CH4 Diffusion
3.2. Effect of Pore Aperture
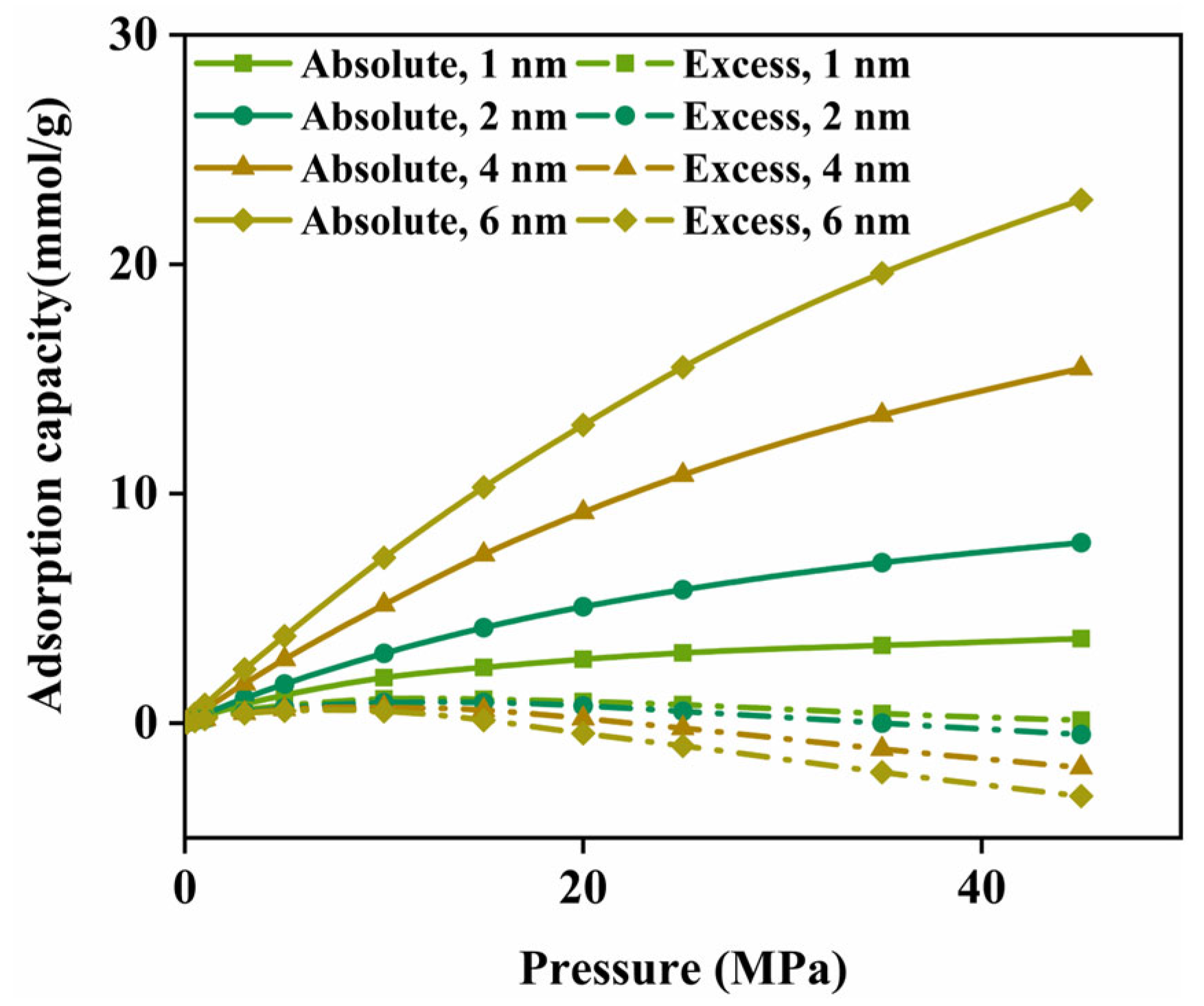
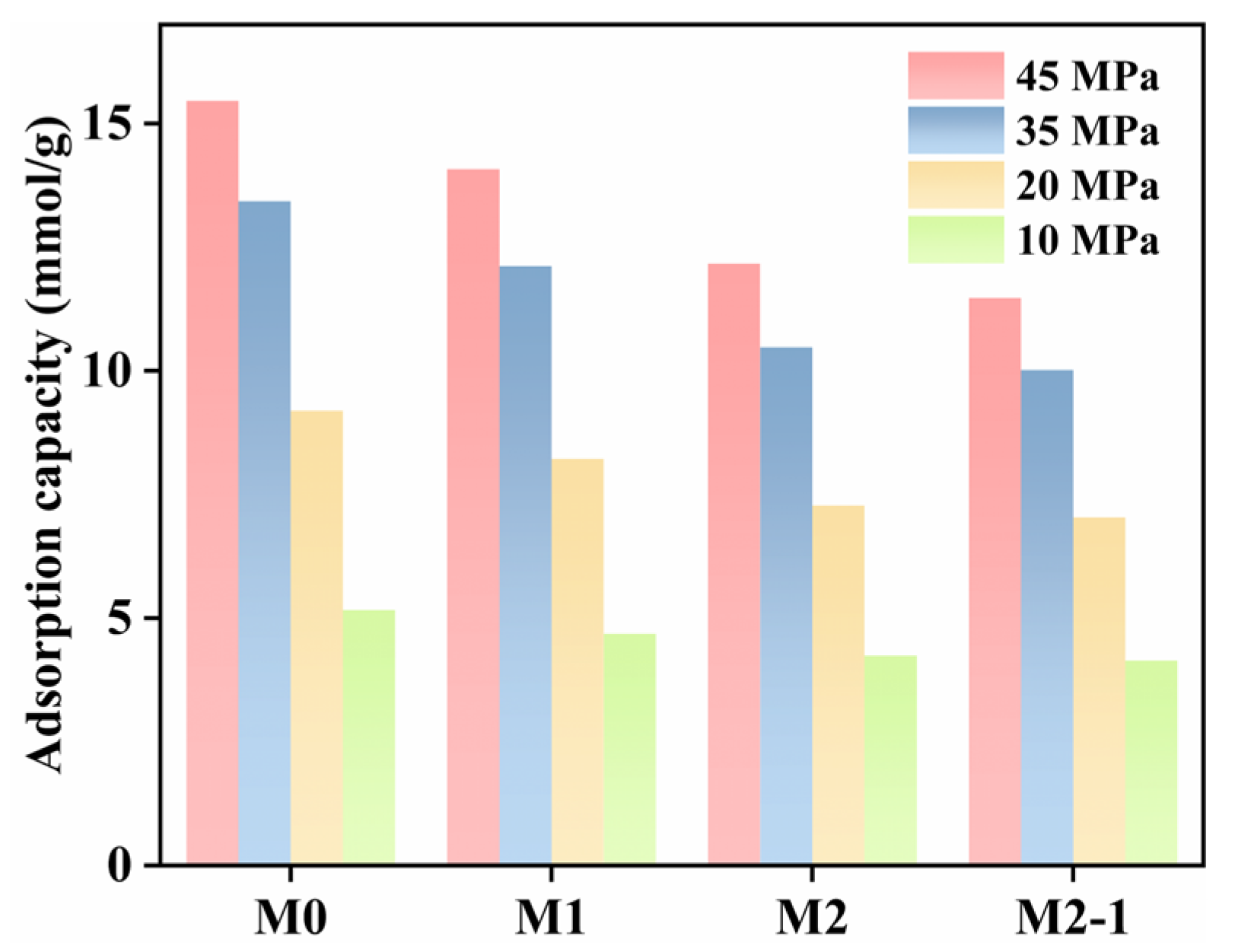
3.2.1. Effect of Pore Aperture on CH4 Adsorption Capacity
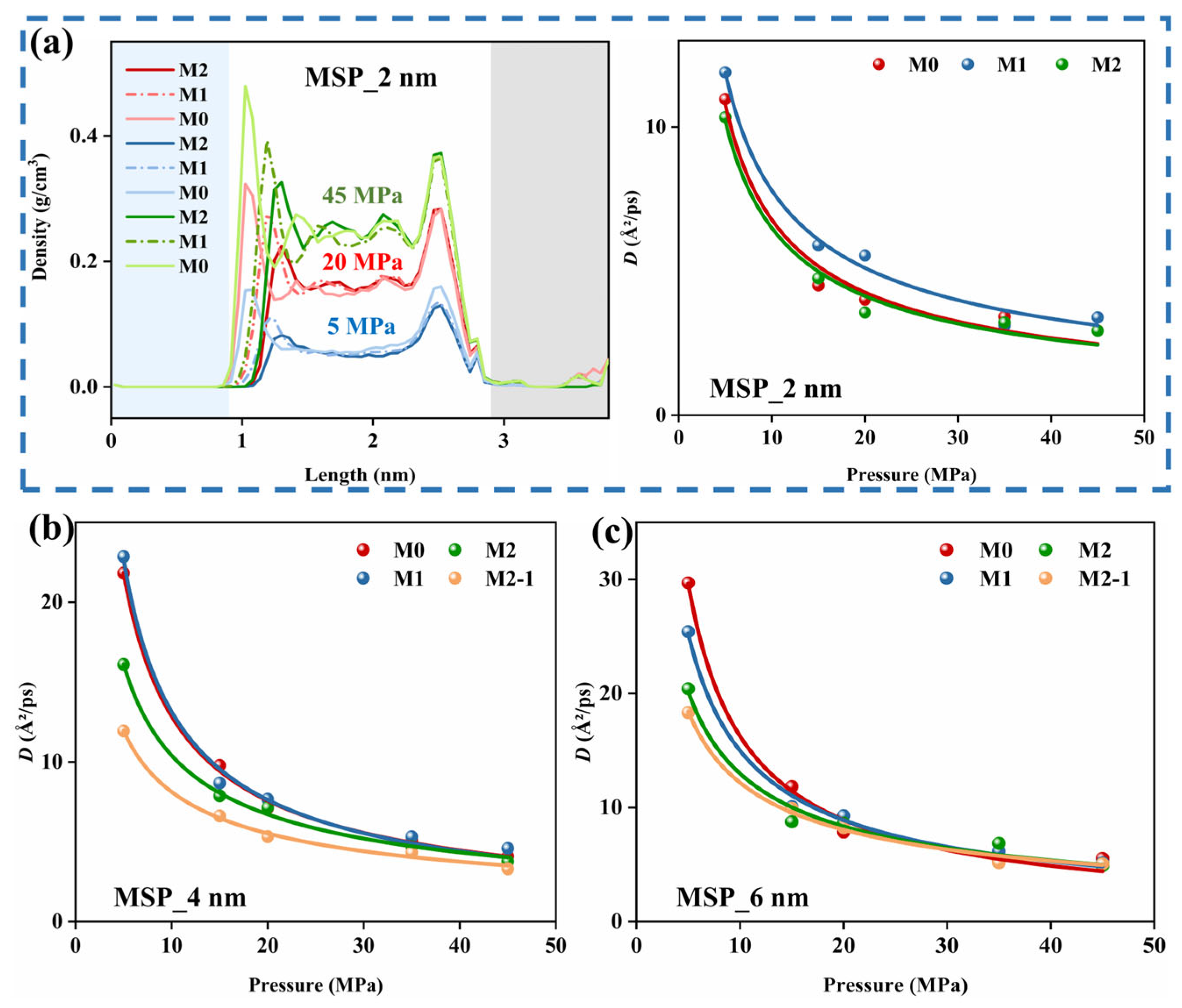
3.2.2. Effect of Pore Aperture on CH4 Adsorption Density
3.2.3. Effect of Pore Aperture on CH4 Diffusion
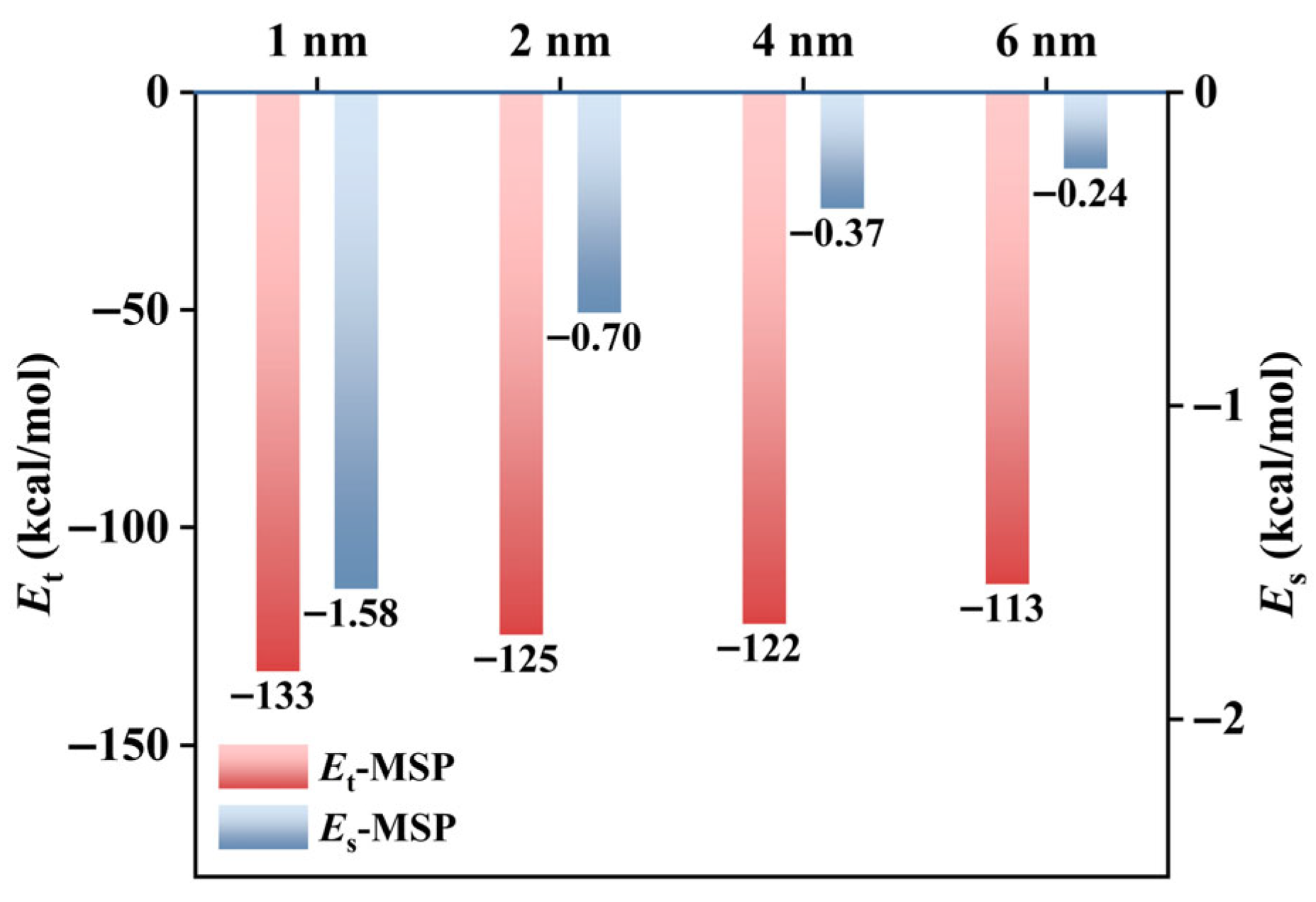
3.3. Effect of Formation Water
3.3.1. Effect of Formation Water on CH4 Adsorption Capacity
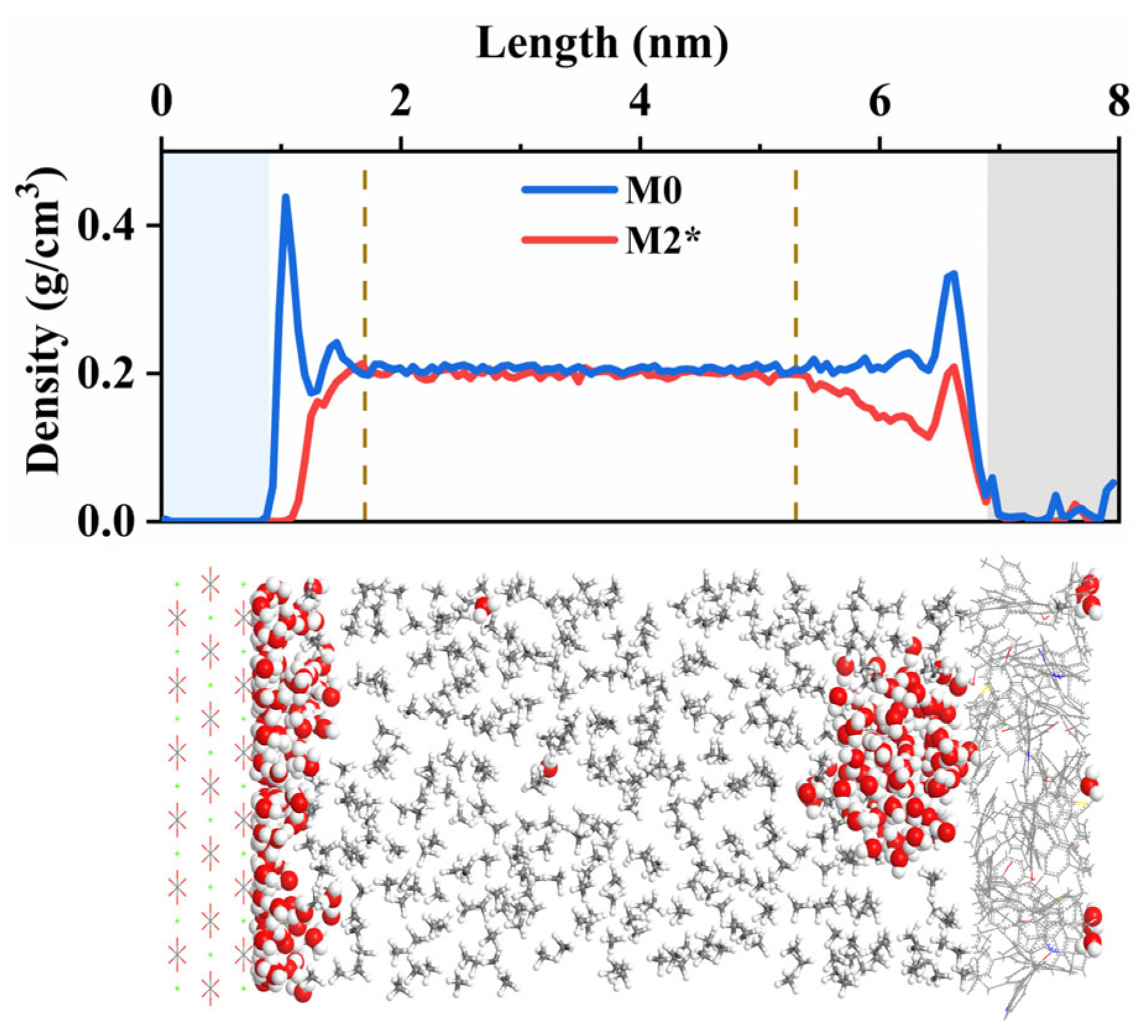
3.3.2. Effect of Formation Water on CH4 Adsorption Density
3.3.3. Effect of Formation Water on CH4 Diffusion
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Organic pore shape significantly influences CH4 adsorption–diffusion. Adsorption capacity mainly depends on specific surface area and potential energy strength. Pore space, tortuosity, and interaction energy synergistically influence diffusion. Diffusion is influenced by the combined effects of pore space, tortuosity, and interaction energy. KSP (slit) exhibits the highest diffusion coefficient—2.3, 3.4, and 10.7 times that of KLP (L-shaped), KTP (triangular), and KCP (circular), respectively—due to its larger pore space, low interaction strength, and minimal tortuosity.
- (2)
- The expansion of pore diameter increases CH4 absolute adsorption capacity, reduces excess adsorption, and enhances diffusion. Compared to 1 nm pores, 6 nm pores exhibit a 6.2 times increase in absolute adsorption, a 3.4 mmol/g decrease in excess adsorption, and a 67% improvement in diffusion coefficient (T = 368.15 K; P = 45 MPa). Pore size also affects the H2O aggregation behavior. At equivalent moisture content, a 4 nm pore forms a continuous water film, while a 6 nm pore exhibits both water films and clusters, reducing kerogen side adsorption density.
- (3)
- In organic–inorganic composite slit pores (MSPs), formation water readily forms films on calcite and clusters on kerogen, weakening CH4 adsorption and its interaction with the pore walls. For methane diffusion, 2 nm and 4 nm MSPs may exhibit a promoting trend under low moisture water conditions but show inhibition with increasing moisture content or the introduction of ions. In contrast, 6 nm pores exhibit inhibition under water-containing conditions. Ions further enhance cluster formation, significantly hindering gas diffusion.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, L.; Ye, W.; Wan, Y.X.; Feng, H.S.; Chen, B.X.; Liang, D.Z. Using knowledge graph and RippleNet algorithms to fulfill smart recommendation of water use policies during shale resources development. J. Hydrol. 2023, 617, 128970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Liu, X.; Yin, L.; Fu, X.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Pei, W. Development characteristics and genetic analysis of dense limestone reservoirs in the Taiyuan Formation of the Ordos Basin, China. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2023, 8, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Zhao, H.; Dong, G.; Han, T.; Ren, J.; Huang, Z.; Lu, Z.; Zhu, B.; Zhu, J.; Yin, L.; et al. Discovery and prospect of oil and gas exploration in new areas of Ordos Basin. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2023, 34, 1289–1304. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Xiong, W.; Li, X.; Feng, C.; Qiu, Z.; Liu, W.; Li, X.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, D.; Yang, H. Discussion on Transitional Shale Gas Accumulation Conditions from the Perspective of Source-Reservoir-Caprock Controlling Hydrocarbon: Examples from Permian Shanxi Formation and Taiyuan Formation in the Eastern Margin of Ordos Basin, NW China. Energies 2023, 16, 3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Z.; Gao, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, D.; Liang, Y. Role of overlying and underlying limestones in the natural hydraulic fracturing of shale sections: The case of marine–continental transitional facies in the Southern North China Basin. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 8711–8729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Gan, H.; Chen, C.; Vandeginsteet, V.; Chen, S.; Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Yu, Z. A model for superimposed coalbed methane, shale gas and tight sandstone reservoirs, Taiyuan Formation, Yushe-Wuxiang Block, eastern Qinshui Basin. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Liu, T.; Zhang, X.; Huang, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, S. Origin type and generating mechanism of coal measure limestone gas: A case study of L1 limestone gas in the Taiyuan formation of the Shenzhou coal mine, Eastern edge of the Ordos Basin, China. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 10904–10914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, Q.; Wu, C.; Qiu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Liu, D.; Dong, D.; Zhou, S. Pore structures of the lower Permian Taiyuan shale and limestone in the Ordos Basin and the significance to unconventional natural gas generation and storage. Geofluids 2022, 2022, 3156547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Hu, P.; Guo, Y.; Li, Y.; Luo, S. Petrological Characteristics and Hydrocarbon Generation of Carbonate Source Rocks of the Permian Taiyuan Formation in Central and Eastern Ordos Basin, China. Minerals 2023, 13, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, D.; Fan, W.; Ejembi, J.I.; Wu, D.; Wang, D.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Li, P. Depositional environments of limestones from the Taiyuan Formation in the North China Block interpreted from REE proxies. Carbonates Evaporites 2020, 35, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Fu, X.; Zhang, B.; Feng, J.; Li, W. Preliminary study on exploration prospect of carbonate gas in coal measures: A case study of Taiyuan Formation in North China. Int. J. Coal. Sci. Technol. 2021, 49, 138–149. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, J.; Liu, X.; Liang, L. Experimental study on the pore structure characteristics of the Upper Ordovician Wufeng Formation shale in the southwest portion of the Sichuan Basin, China. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2015, 22, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, Q.; Cheng, H.; Li, X.; Zeng, F.; Frost, R.L. Intercalation of dodecylamine into kaolinite and its layering structure investigated by molecular dynamics simulation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 430, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Tian, S.; Li, G.; Zhang, L.; Sheng, M.; Ren, W. Molecular simulation of gas adsorption in shale nanopores: A critical review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 149, 111391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.; Yuan, Q.; Zhao, Y.P. Using graphene to simplify the adsorption of methane on shale in MD simulations. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2017, 133, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Yao, J.; Ma, J.; Li, A.; Li, Y.; Sun, H.; Zhang, L. Grand canonical Monte Carlo simulations of pore structure influence on methane adsorption in micro-porous carbons with applications to coal and shale systems. Fuel 2018, 215, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Tian, S.; Li, G.; Sheng, M.; Ren, W.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, S. Molecular simulation of CO2/CH4 competitive adsorption on shale kerogen for CO2 sequestration and enhanced gas recovery. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 17009–17018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Ning, Z.; Wang, Q.; Huang, L.; Meng, H.; Yu, X.; Qin, H. Molecular simulation of methane adsorption behavior on clay minerals. CCS 2019, 44, 3117–3124. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Mu, J.; Li, W.; Song, Y. Adsorption characteristics of CH4 and CO2 in organic-inorganic slit pores. Fuel 2020, 265, 116969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, M.; Takbiri-Borujeni, A. Modeling and simulation of gas transport in carbon-based organic nano-capillaries. Fuel 2017, 206, 724–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Jang, H.; Lee, J. Experimental investigation on the characteristics of gas diffusion in shale gas reservoir using porosity and permeability of nanopore scale. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2015, 133, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, S.K.; Nicholson, D. Adsorption and diffusion of methane in silica nanopores: A comparison of single-site and five-site models. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 2344–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, W.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, F.; Tao, J.; Wei, X.; Tang, X.; Wang, C.; Chen, Q. Experimental and modeling study on the effect of shale composition and pressure on methane diffusivity. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 714–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Chang, S.; Yan, X.; Meng, Y.; Zhao, D. Study on Hydrogeological Conditions and Water Source Identification of 8+9# Coalbed Methane Reservoir in Sanjiao Block. J. Taiyuan Univ. Technol. 2023, 54, 673–683. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X. Study on Chemical Composition of Mine Water in Shaqu No.1 Coal Mine. Shanxi Coking Coal Sci. Technol. 2023, 47, 33–36+47. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Z.; Liu, G.; Sun, R.; Tang, Q.; Wu, D.; Wu, B.; Zhou, C. Geochemistry of rare earth elements in groundwater from the Taiyuan Formation limestone aquifer in the Wolonghu Coal Mine, Anhui province, China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2013, 135, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Gui, H.; Wei, J.; Pang, Y.; Hu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Nie, F.; Hong, H.; Cui, Y.; Zhao, J. Hydrogeochemical evolution of Taiyuan formation limestone water under the disturbance of water inrush from karst collapse column in Taoyuan coal mine, China. Water Supply 2022, 22, 8196–8210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Gui, H.; Hu, R.; Zhao, H.; Li, J.; Yu, H.; Fang, H. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and water quality evaluation of carboniferous Taiyuan formation limestone water in Sulin mining area in Northern Anhui, China. Int. J. Env. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Jin, D.; Xu, F.; Zhao, C. Hydrochemical characteristics and evolution processes of karst groundwater in Carboniferous Taiyuan formation in the Pingdingshan coalfield. Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Fi, Y.; Yin, J.; Dai, R. Lithofacies types and geochemical characteristics of carbonate source rocks in Taiyuan Formation of middle and eastern Ordos Basin. J. Yangtze Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2024, 21, 19–31. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, T.; Zhan, Z.W.; Zou, Y.R.; Lin, X.H.; Shan, Y.; Peng, P. Research on type I kerogen molecular simulation and docking between kerogen and saturated hydrocarbon molecule during oil generation. Chem. Geol. 2023, 617, 121263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Ma, X.; Yang, H.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, D.; Ren, C.; Huang, L. Experimental characterization and molecular modeling of kerogen in Silurian deep gas shale from southern Sichuan Basin, China. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 1497–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerisit, S.; Parker, S.C. Free energy of adsorption of water and metal ions on the {1014} calcite surface. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 10152–10161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán-Álvarez, A.; Maldonado-Domínguez, M.; González-Antonio, O.; Durán-Valencia, C.; Romero-Ávila, M.; Barragán-Aroche, F.; López-Ramírez, S. Experimental–theoretical approach to the adsorption mechanisms for anionic, cationic, and zwitterionic surfactants at the calcite–water interface. Langmuir 2016, 32, 2608–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Leeuw, N.H.; Parker, S.C. Surface–water interactions in the dolomite problem. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2001, 3, 3217–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Zhang, L.H.; Li, X.G.; Yang, X.; Zhao, Y.L.; Chen, X. Effect of the Water Content on the Adsorption of CO2 and CH4 in Calcite Slit Nanopores: Insights from GCMC, MD, and DFT. Langmuir 2023, 40, 818–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H. COMPASS: An ab initio force-field optimized for condensed-phase applications overview with details on alkane and benzene compounds. J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 7338–7364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, H.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y. Effect of kerogen maturity, water content for carbon dioxide, methane, and their mixture adsorption and diffusion in kerogen: A computational investigation. Langmuir 2020, 36, 9756–9769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Li, X.; Fang, Z.; Wei, N.; Li, Q. Small-molecule gas sorption and diffusion in coal: Molecular simulation. Energy 2010, 35, 2939–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McQuaid, M.J.; Sun, H.; Rigby, D. Development and validation of COMPASS force field parameters for molecules with aliphatic azide chains. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, S.; Gaus, G.; Li, Y.; Ma, Y.; Chen, K.; Zhang, Y. Characterization of methane adsorption on shale and isolated kerogen from the Sichuan Basin under pressure up to 60 MPa: Experimental results and geological implications. Int. J. Coal. Geol. 2018, 189, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Feng, X.; Yang, Q.; Wu, J.; Yang, X.; Huang, S. Microscopic Occurrence Characteristics of Methane in Kerogen Nanopores of Deep Shale Reservoirs. Pet. Drill. Tech. 2023, 51, 112–120. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.; Xu, R.; Jiang, P. Novel molecular simulation process design of adsorption in realistic shale kerogen spherical pores. Fuel 2016, 180, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Jiang, F.; Cong, Q.; Pang, X.; Ma, K.; Shi, K.; Pang, B.; Chen, D.; Pang, H.; Yang, X.; et al. Adsorption characteristics of shale gas in organic-inorganic slit pores. Energy 2023, 278, 127788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Wei, Q.; Huang, H.; Wang, T.; Xiong, H.; Wang, J.; Ren, Y.; Cui, X. Insight into adsorption behaviors of shale oil in kerogen slit by molecular dynamics. Fuel 2024, 374, 132432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Su, H.; Jing, Y.; Guo, J.; Tang, J. Methane adsorption on the surface of a model of shale: A density functional theory study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 387, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deible, M.J.; Tuguldur, O.; Jordan, K.D. Theoretical study of the binding energy of a methane molecule in a (H2O)20 dodecahedral cage. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 8257–8263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Tian, S.; Li, G.; Sheng, M. Selective adsorption of supercritical carbon dioxide and methane binary mixture in shale kerogen nanopores. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2018, 50, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Feng, Q.; Javadpour, F.; Hu, Q.; Wu, K. Competitive adsorption of methane and ethane in montmorillonite nanopores of shale at supercritical conditions: A grand canonical Monte Carlo simulation study. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 355, 76–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, S.; Gadikota, G. Exploring the role of inorganic and organic interfaces on CO2 and CH4 partitioning: Case study of silica, illite, calcite, and kerogen nanopores on gas adsorption and nanoscale transport behaviors. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 3578–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, S.; Ghasemzadeh, H.; Tesson, S. Methane adsorption of nanocomposite shale in the presence of water: Insights from molecular simulations. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 475, 146196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Xu, H.Y.; Fan, J.C.; Zhu, Y.B.; Wang, F.C.; Wu, H.A. Transport of shale gas in microporous/nanoporous media: Molecular to pore-scale simulations. Energy Fuels 2020, 35, 911–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Namsani, S.; Singh, J.K. Molecular simulation of shale gas adsorption and diffusion in inorganic nanopores. Mol. Simulat. 2015, 41, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, S.; Gadikota, G. The effect of hydration on the structure and transport properties of confined carbon dioxide and methane in calcite nanopores. Front. Energy Res. 2018, 6, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zhou, W.; Xu, H.; Wang, L.; Zou, J.; Zhou, Q. Dynamic fluid states in organic-inorganic nanocomposite: Implications for shale gas recovery and CO2 sequestration. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 411, 128423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Feng, Q.; Zha, M.; Javadpour, F.; Hu, Q. Supercritical methane diffusion in shale nanopores: Effects of pressure, mineral types, and moisture content. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Kang, Y.; Chen, M.; Liang, L.; You, L.; Li, X. Investigation of multi-gas transport behavior in shales via a pressure pulse method. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 360, 1667–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Kang, Y.; Chen, M.; Li, X.; You, L.; Chen, Z.; Fang, D. Impact of water film on methane surface diffusion in gas shale organic nanopores. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 196, 108045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
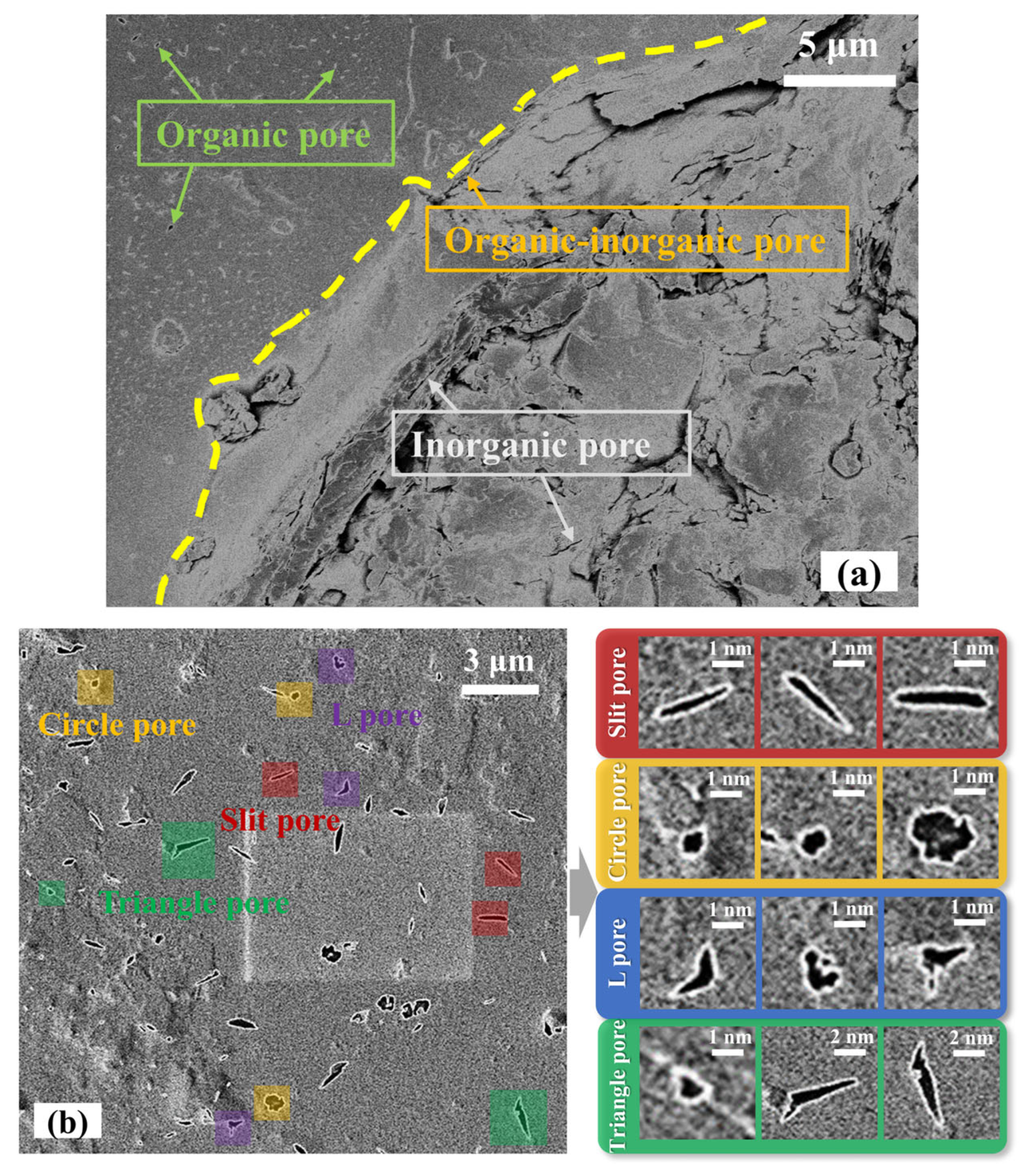
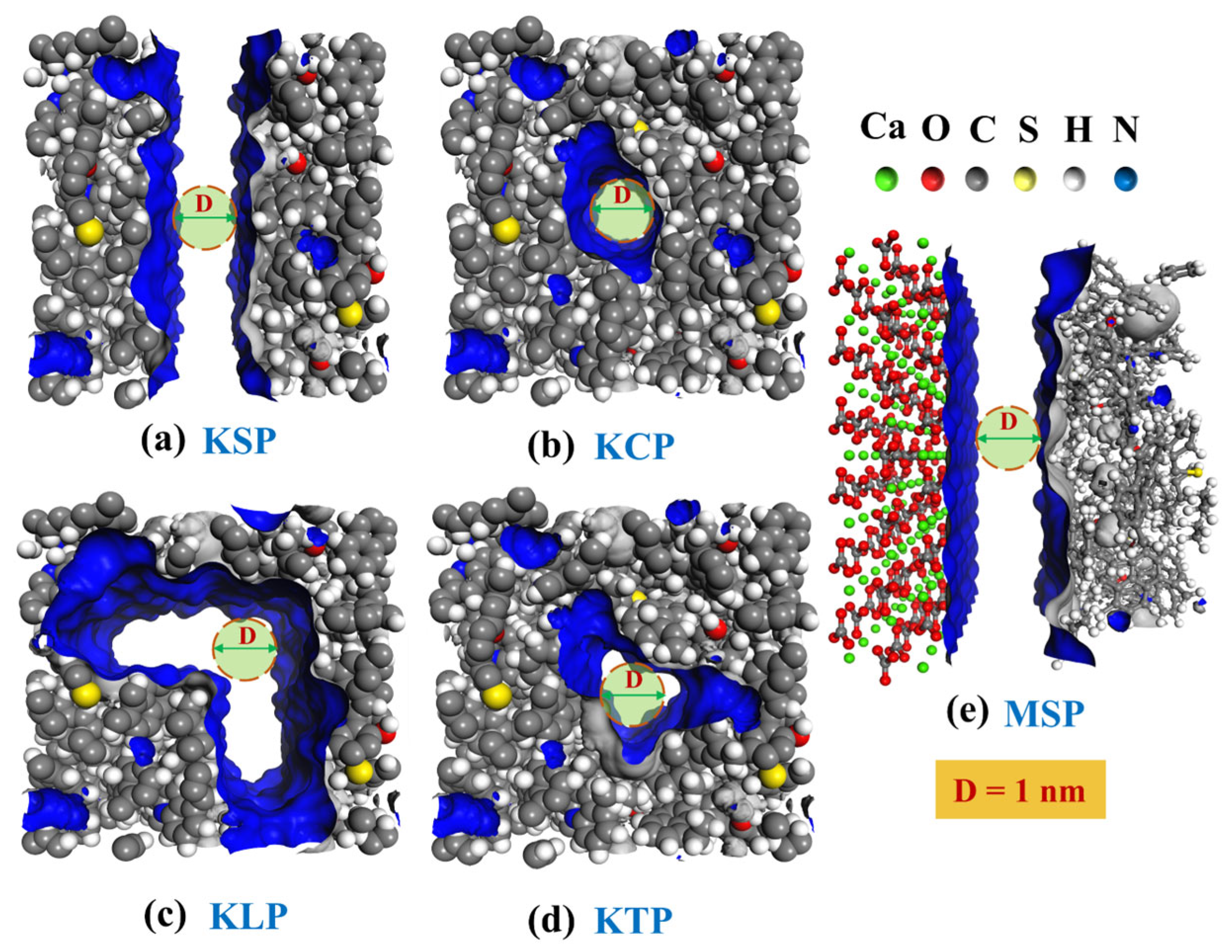






| Organic Pore Shape | KSP | KCP | KLP | KTP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pore volume (cm3/g) | 0.372 | 0.091 | 0.477 | 0.140 |
| Specific surface area (m2/g) | 924.026 | 178.832 | 1141.990 | 316.921 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, T.; Deng, C.; Guo, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Liang, D.; Li, Y. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Methane Adsorption and Diffusion in Limestone Pores in the Taiyuan Formation of the Ordos Basin, China: Effects of Pore Shapes, Apertures, and Formation Water. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9446. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179446
Shi T, Deng C, Guo X, Zhang L, Zhang Y, Bai Y, Liang D, Li Y. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Methane Adsorption and Diffusion in Limestone Pores in the Taiyuan Formation of the Ordos Basin, China: Effects of Pore Shapes, Apertures, and Formation Water. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(17):9446. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179446
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Tielian, Cunbao Deng, Xiaoyang Guo, Lemei Zhang, Yu Zhang, Yue Bai, Dengke Liang, and Yuanjing Li. 2025. "Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Methane Adsorption and Diffusion in Limestone Pores in the Taiyuan Formation of the Ordos Basin, China: Effects of Pore Shapes, Apertures, and Formation Water" Applied Sciences 15, no. 17: 9446. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179446
APA StyleShi, T., Deng, C., Guo, X., Zhang, L., Zhang, Y., Bai, Y., Liang, D., & Li, Y. (2025). Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Methane Adsorption and Diffusion in Limestone Pores in the Taiyuan Formation of the Ordos Basin, China: Effects of Pore Shapes, Apertures, and Formation Water. Applied Sciences, 15(17), 9446. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179446





