The Influence of the Ethyl Oleate and n-Hexane Mixture on the Wetting and Lubricant Properties of Canola Oil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
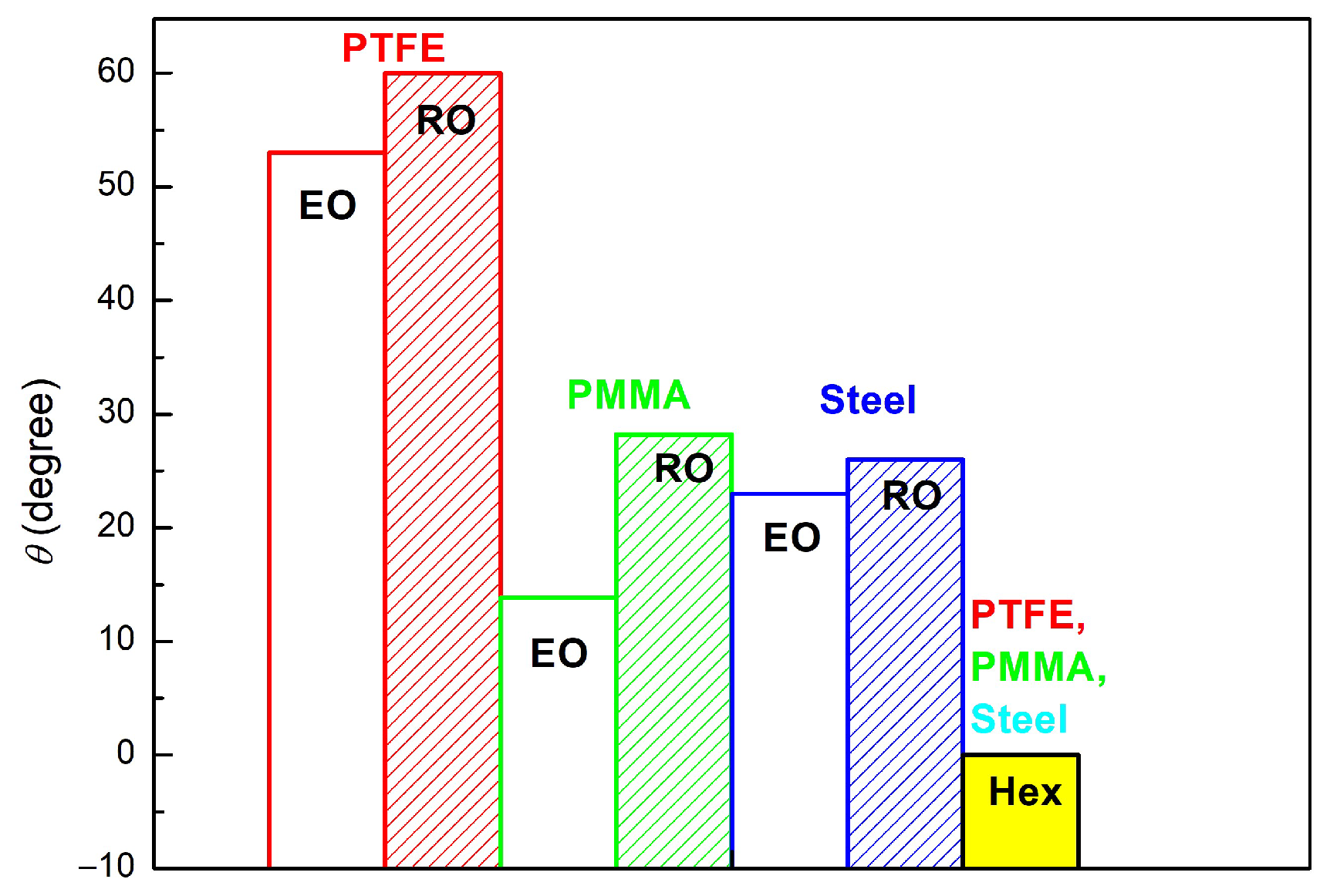
3.1. Wetting and Adhesion Properties of RO, Hex and EO
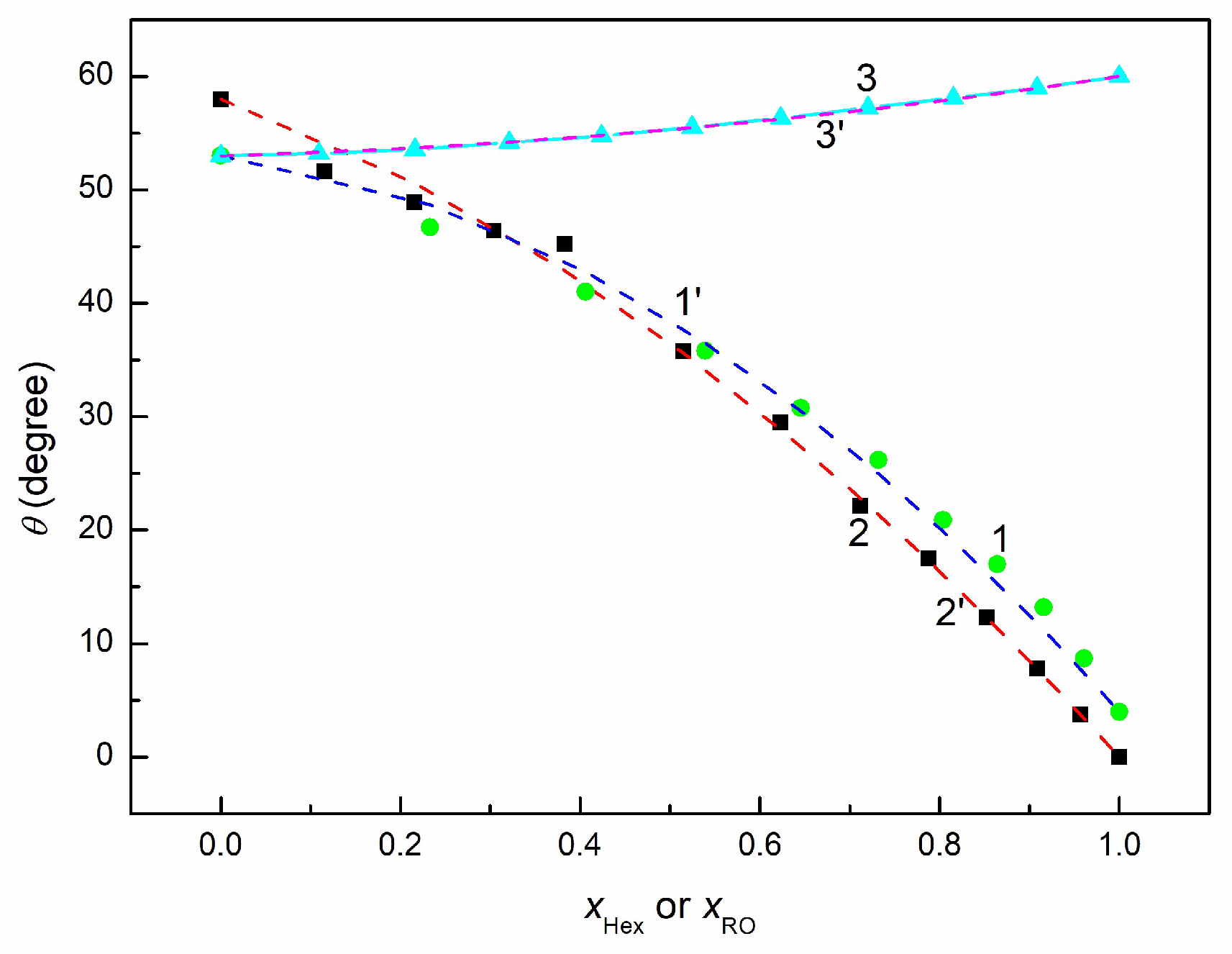
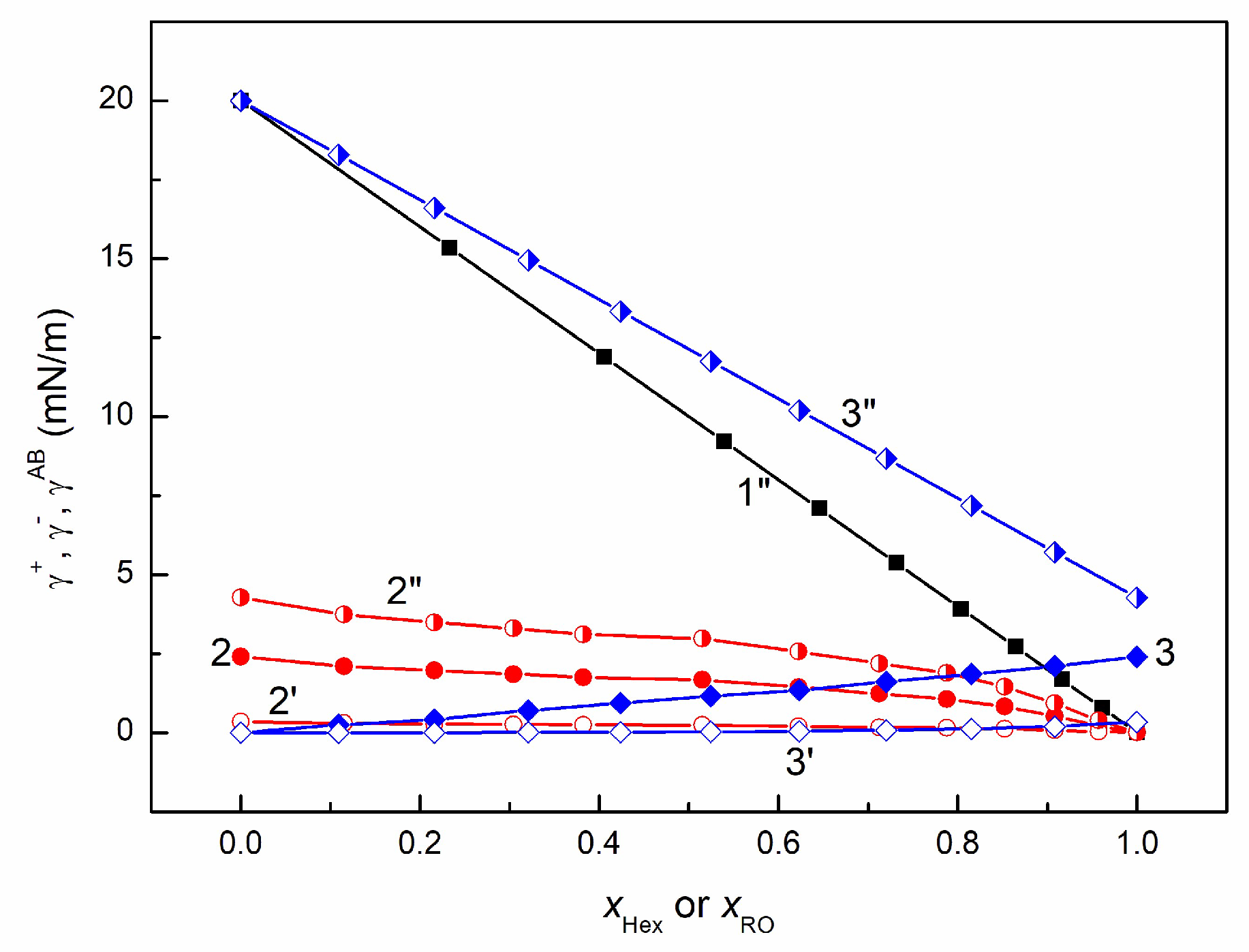
3.2. Adhesion and Wetting Behavior of EO + Hex, RO + Hex, and RO + EO Mixtures
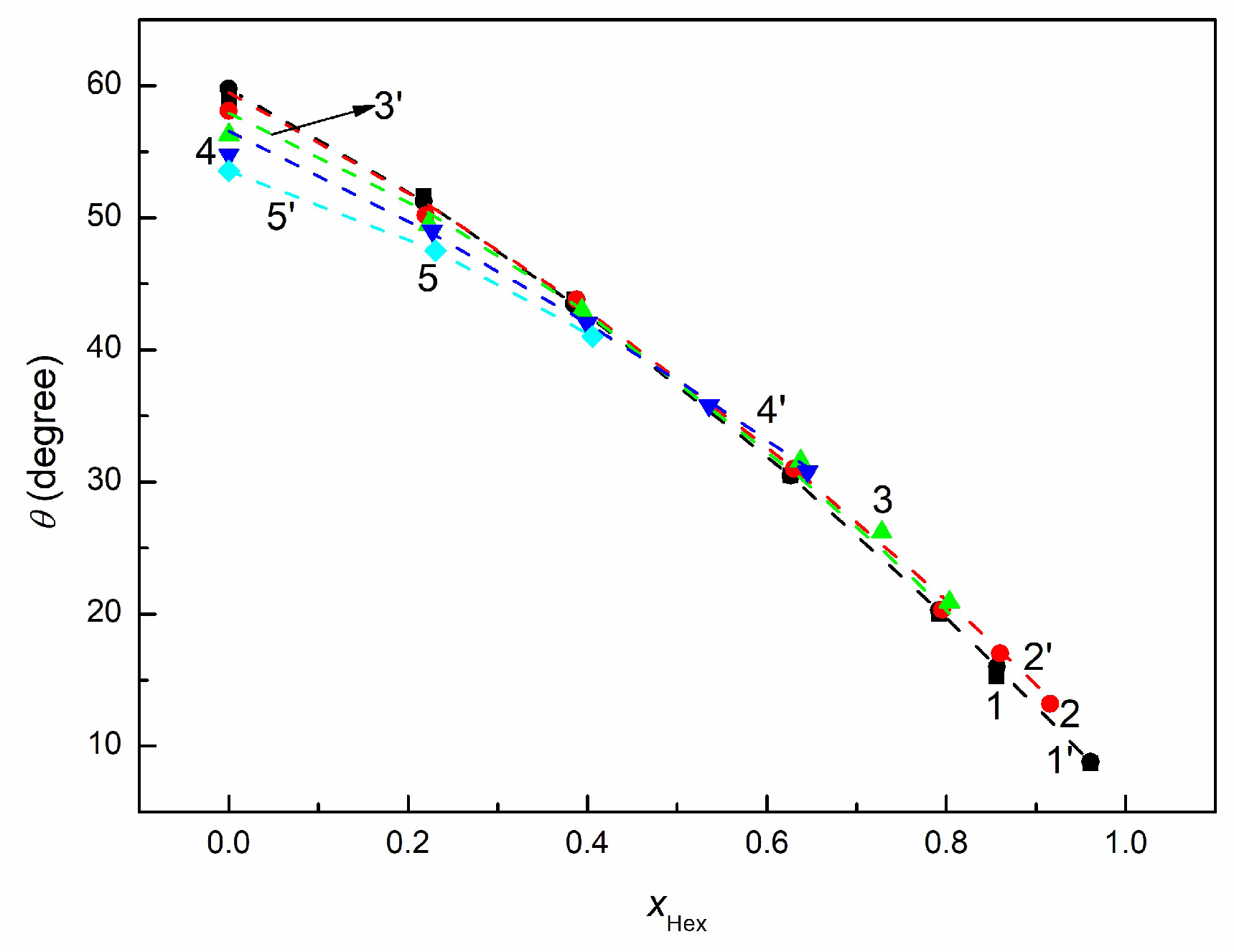
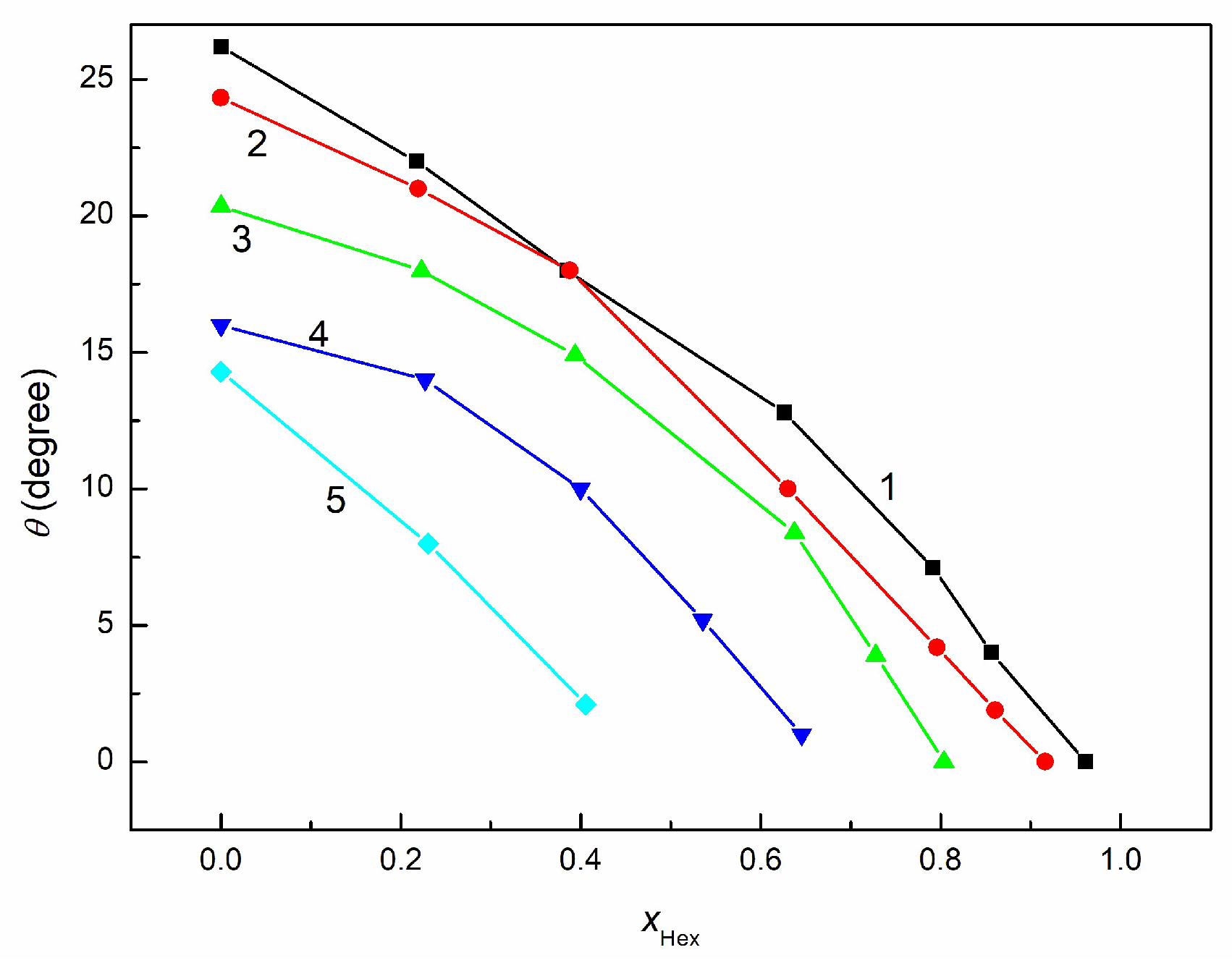
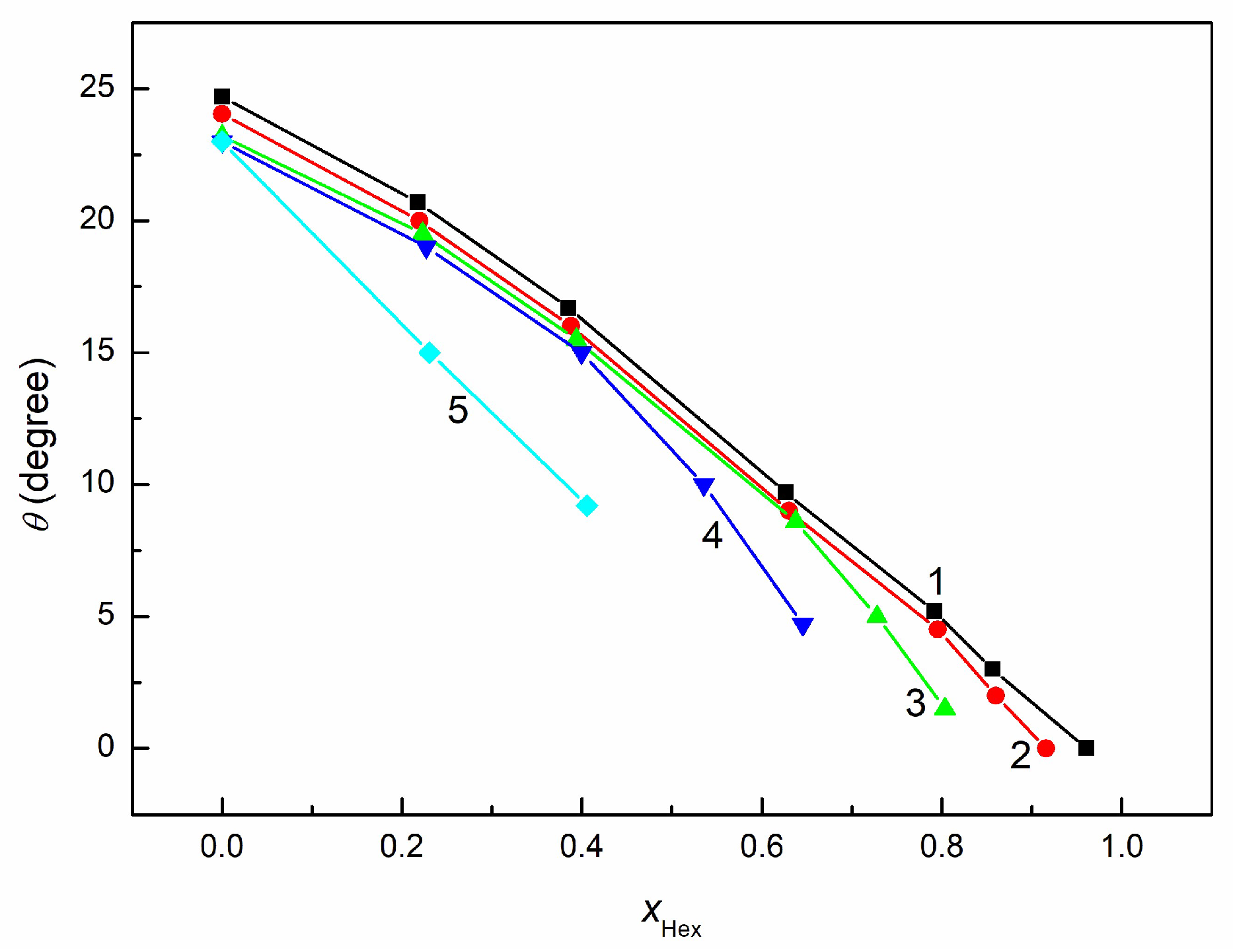
3.3. Wetting and Adhesion Properties of RO + EO + Hex Mixture
3.4. Wetting and Lubricant Properties of RO + EO + Hex Mixture
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sarma, R.N.; Vinu, R. Current status and future prospects of biolubricants: Properties and applications. Lubricants 2022, 10, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uppar, R.; Dinesha, P.; Kumar, S. A critical review on vegetable oil-based bio-lubricants: Preparation, characterization, and challenges. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 25, 9011–9046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Düzcükoǧlu, H.; Acaroǧlu, M. Lubrication properties of vegetable oils combined with boric acid and determination of their effects on wear. Energy Sources 2010, 32, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madanhire, I.; Mbohwa, C. Mitigating Environmental Impact of Petroleum Lubricants; Springer Nature: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogales-Delgado, S.; Encinar, J.M.; González, J.F. A Review on biolubricants based on vegetable oils through transesterification and the role of catalysts: Current status and future trends. Catalysts 2023, 13, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecilia, J.A.; Plata, D.B.; Saboya, R.M.A.; de Luna, F.M.T.; Cavalcante, C.L.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E. An overview of the biolubricant production process: Challenges and future perspectives. Processes 2020, 8, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saka, A.; Abor, T.K.; Okafor, A.C.; Okoronkwo, M.U. Thermo-rheological and tribological properties of low- and high-oleic vegetable oils as sustainable bio-based lubricants. RSC Sustain. 2025, 3, 1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamnas, A.; Unnikrishnan, G. Bio-lubricants from vegetable oils: Characterization, modifications, applications and challenges– Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 182, 113413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, M.I.; Mainali, K.; Sharma, B.K. Investigations on the thermal stability and kinetics of biolubricants synthesized from different types of vegetable oils. Lubricants 2025, 13, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, D. Plant-based oils for sustainable lubrication solutions—Review. Lubricants 2024, 12, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.V.; Somidi, A.K.R.; Dalai, A.K. Preparation and properties evaluation of biolubricants derived from canola oil and canola biodiesel. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 3235–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassef, B.G.; Pape, F.; Poll, G. Enhancing the performance of rapeseed oil lubricant for machinery component applications through hybrid blends of nanoadditives. Lubricants 2023, 11, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masripan, N.A.; Salim, M.A.; Omar, G.; Mansor, M.R.; Hamid, N.A.; Syakir, M.I.; Dai, F. Vegetable oil as bio-lubricant and natural additive in lubrication: A review. Int. J. Nanoelectron. Mater. 2020, 13, 161–176. [Google Scholar]
- Nagendramma, P.; Kaul, S. Development of ecofriendly/biodegradable lubricants: An Overview. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 764–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durak, E. A study on friction behavior of rapeseed oil as an environmentally friendly additive in lubricating oil. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2004, 56, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikal, E.K.; Elmelawy, M.S.; Khalil, S.A.; Elbasuny, N.M. Manufacturing of environment friendly biolubricants from vegetable oils. Egypt. J. Petrol. 2017, 26, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masudi, A.; Muraza, O. Vegetable oil to biolubricants: Review on advanced porous catalysts. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 10295–10310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybylski, R. Canola/Rapeseed Oil. In Vegetable Oils in Food Technology: Composition, Properties and Uses, 1st ed.; Gunstone, F.D., Ed.; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2011; pp. 107–136. [Google Scholar]
- Banaś, K.; Piwowar, A.; Harasym, J. The potential of rapeseed (canola) oil nutritional benefits wide spreading via oleogelation. Food Biosci. 2023, 56, 103162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Backes, F.; Wachtmeister, G. Application of canola oil operation in a diesel engine with common rail system. Fuel 2015, 159, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchal, T.M.; Patel, A.; Chauhan, D.D.; Thomas, M.; Patel, J.V. A methodological review on bio-lubricants from vegetable oil based resources. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 70, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimon, J.; Salih, N.; Yousif, E. Biolubricants: Raw materials, chemical modifications and environmental benefits. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2010, 112, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.C.; Yoon, S.K.; Choi, N.J. Using canola oil biodiesel as an alternative fuel in diesel engines: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.M.; Wang, W.; Bujold, J. Biodiesel production and comparison of emissions of a DI diesel engine fueled by biodiesel–diesel and canola oil–diesel blends at high idling operations. Appl. Energy 2013, 106, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.C.; Yoon, S.K.; Kim, M.S.; Choi, N.J. Application of Canola Oil Biodiesel/Diesel Blends in a Common Rail Diesel Engine. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymczyk, K.; Zdziennicka, A.; Jańczuk, B.; Lubas, J.; Jaworski, A.; Kuszewski, H.; Woś, P.; Longwic, R.; Sander, P. n-hexane influence on canola oil adhesion and volumetric properties. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2025, 140, 103990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longwic, R.; Sander, P.; Zdziennicka, A.; Szymczyk, K.; Jańczuk, B. Changes of some physicochemical properties of canola oil by adding n-hexane and ethanol regarding its application as diesel fuel. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymczyk, K.; Zdziennicka, A.; Jańczuk, B. The modification of the canola oil some properties by the addition of ethyl oleate and n-hexane. Energies 2025, 18, 3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.S.; Nassar, A.M. Lubrication and Lubricants. In Tribology—Fundamentals and Advancements; Gegner, J., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, A.W. Contact angles and their temperature dependence: Thermodynamic status, measurement, interpretation and application. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 1974, 4, 105–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, D.Y.; Neumann, A.W. Contact angle measurement and contact angle interpretation. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 1999, 81, 167–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, D.Y.; Neumann, A.W. Contact angle interpretation in terms of solid surface tension. Colloids Surf. 2000, 161, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowkes, F.M. Attractive forces at interfaces. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1964, 56, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Oss, C.J. Interfacial Forces in Aqueous Media, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- van Oss, C.J.; Good, R.J. Surface tension and the solubility of polymers and biopolymers: The role of polar and apolar interfacial free energies. J. Macromol. Sci. 1989, 26, 1183–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Oss, C.J.; Chaudhury, M.K.; Good, R.J. Monopolar surfaces. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 1987, 28, 35–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Oss, C.J.; Good, R.J.; Chaudhury, M.K. Additive and nonadditive surface tension components and the interpretation of contact angles. Langmuir 1988, 4, 884–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdziennicka, A.; Jańczuk, B. Modification of adsorption, aggregation and wetting properties of surfactants by short chain alcohols. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 284, 102249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S. Surface tension of solids: An equation of state analysis. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1979, 71, 605–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitazki, Y.; Hata, T. Revision of the Fowkes’s formula and evaluation of surface energy of high molecule solid material. J. Adhes. Soc. Jpn 1972, 8, 131–138. [Google Scholar]
- Adamson, A.W.; Gast, A.P. Physical Chemistry of Surfaces, 6th ed.; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Rosen, M.J. Surfactants and Interfacial Phenomena, 3rd ed.; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 34–178. [Google Scholar]
- Szymczyk, K.; Zdziennicka, A.; Jańczuk, B. Some physicochemical properties of ethyl oleate mixtures with ethanol and n-hexane. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 408, 125318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymczyk, K.; Zdziennicka, A.; Jańczuk, B. Comparison of surface tension, density, viscosity and contact angle of ethyl oleate to those of ethanol and oleic acid. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 400, 124525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jańczuk, B.; Zdziennicka, A.; Wójcik, W. Relationship between wetting of teflon by cetyltrimethylammonium bromide solution and adsorption. Eur. Polym. Sci. 1997, 33, 1093–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadava, G.; Tiwarib, S.; Jainc, M.L. Tribological analysis of extreme pressure and anti-wear properties of engine lubricating oil using four ball testers. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marko, M.D.; Kyle, J.P.; Wang, Y.S.; Terrell, E.J. Tribological investigations of the load, temperature, and time dependence of wear in sliding contact. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, D.-X. Effects of concentration and temperature on tribological properties of biodiesel. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2015, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schertzer, M.J.; Iglesias, P. Meta-Analysis Comparing Wettability Parameters and the Effect of Wettability on Friction Coefficient in Lubrication. Lubricants 2018, 6, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Mixtures | Volume RO [cm3] | Volume Hex [cm3] | Volume EO [cm3] |
|---|---|---|---|
| RO90 + Hex10 | 90 | 10 | - |
| EO90 + Hex10 | - | 10 | 90 |
| RO80 + Hex20 | 80 | 20 | - |
| EO80 + Hex20 | - | 20 | 80 |
| RO70 + Hex30 | 70 | 30 | - |
| EO70 + Hex30 | - | 30 | 70 |
| RO60 + Hex40 | 60 | 40 | - |
| EO60 + Hex40 | - | 40 | 60 |
| RO50 + Hex50 | 50 | 50 | - |
| EO50 + Hex50 | - | 50 | 50 |
| RO40 + Hex60 | 40 | 60 | - |
| EO40 + Hex60 | - | 60 | 40 |
| RO30 + Hex70 | 30 | 70 | - |
| EO30 + Hex70 | - | 70 | 30 |
| RO20 + Hex80 | 20 | 80 | - |
| EO20 + Hex80 | - | 80 | 20 |
| RO10 + Hex90 | 10 | 90 | - |
| EO10 + Hex90 | - | 90 | 10 |
| RO80EO10Hex10 | 80 | 10 | 10 |
| RO70EO10Hex20 | 70 | 20 | 10 |
| RO50EO10Hex40 | 50 | 40 | 10 |
| RO30EO10Hex60 | 30 | 60 | 10 |
| RO10EO10Hex80 | 10 | 80 | 10 |
| RO70EO20Hex10 | 70 | 10 | 20 |
| RO60EO20Hex20 | 60 | 20 | 20 |
| RO40EO20Hex40 | 40 | 40 | 20 |
| RO20EO20Hex60 | 20 | 60 | 20 |
| RO10EO20Hex70 | 10 | 70 | 20 |
| RO50EO40Hex10 | 50 | 10 | 40 |
| RO40EO40Hex20 | 40 | 20 | 40 |
| RO20EO40Hex40 | 20 | 40 | 40 |
| RO10EO40Hex50 | 10 | 50 | 40 |
| RO30EO60Hex10 | 30 | 10 | 60 |
| RO20EO60Hex20 | 20 | 20 | 60 |
| RO10EO60Hex30 | 10 | 30 | 60 |
| RO10EO80Hex10 | 10 | 10 | 80 |
| Solid | [mN/m] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hex | EO | RO | ||
| PTFE | 18.50 | 20.68 | 20.33 | 20.24 [45] |
| PMMA | 18.50 | 30.50 | 29.65 | 41.28 [26] |
| Steel | 18.50 | 29.00 | 30.18 | 40.02 [26] |
| Solid–Liquid | (mJ/m2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equation (11) () | Equation (5) | Equation (10) () | Equation (6) | |
| PTFE-Hex | 37.00 | 37.00 | 38.74 | 38.70 |
| PMMA-Hex | 37.00 | 37.00 | 59.78 | 55.30 |
| Steel-Hex | 37.00 | 37.00 | 58.52 | 53.49 |
| PTFE-EO | 52.08 | 50.30 | 51.64 | 50.42 |
| PMMA-EO | 61.90 | 61.89 | 72.68 | 72.01 |
| Steel-EO | 60.40 | 61.89 | 71.42 | 72.43 |
| PTFE-RO | 53.73 | 50.10 | 53.64 | 50.10 |
| PMMA-RO | 63.05 | 64.35 | 74.68 | 74.68 |
| Steel-RO | 63.58 | 64.35 | 73.42 | 74.71 |
| RO + EO | EO + Hex | RO + Hex | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
[mN/m] | [mJ/m2] | [mN/m] | [mJ/m2] | [mN/m] | [mJ/m2] | |||
| 0.00000 | 61.90 | 61.89 | 0.00000 | 61.90 | 61.89 | 0.00000 | 63.05 | 64.35 |
| 0.10920 | 61.92 | 61.91 | 0.23279 | 56.72 | 56.71 | 0.11526 | 60.43 | 60.38 |
| 0.21620 | 61.95 | 61.93 | 0.40572 | 52.53 | 52.52 | 0.21570 | 55.90 | 55.88 |
| 0.32104 | 61.97 | 61.95 | 0.53925 | 49.11 | 49.18 | 0.30400 | 53.39 | 53.38 |
| 0.42381 | 62.00 | 61.98 | 0.64546 | 46.48 | 46.60 | 0.38225 | 50.97 | 50.97 |
| 0.52456 | 62.07 | 62.04 | 0.73196 | 44.11 | 44.40 | 0.51475 | 46.17 | 46.17 |
| 0.62335 | 62.26 | 62.19 | 0.80378 | 41.97 | 42.40 | 0.62265 | 43.08 | 43.07 |
| 0.72023 | 62.44 | 62.35 | 0.86435 | 39.98 | 40.74 | 0.71224 | 40.94 | 40.93 |
| 0.81527 | 62.62 | 62.50 | 0.91613 | 38.08 | 39.20 | 0.78781 | 39.57 | 39.57 |
| 0.90851 | 62.79 | 62.63 | 0.9609 | 36.63 | 38.00 | 0.85241 | 38.59 | 38.59 |
| 1.00000 | 63.05 | 62.84 | 1.00000 | 35.42 | 37.04 | 0.90826 | 38.00 | 38.00 |
| 0.95704 | 37.40 | 37.40 | ||||||
| 1.00000 | 37.00 | 37.00 | ||||||
| RO + EO | EO + Hex | RO + Hex | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
[mN/m] | [mJ/m2] | [mN/m] | [mJ/m2] | [mN/m] | [mJ/m2] | |||
| 0.00000 | 72.68 | 72.00 | 0.00000 | 72.68 | 72.01 | 0.00000 | 74.68 | 74.68 |
| 0.10920 | 72.7 | 71.91 | 0.23279 | 69.79 | 68.60 | 0.11526 | 72.38 | 72.13 |
| 0.21620 | 72.73 | 71.86 | 0.40572 | 67.59 | 65.90 | 0.21570 | 69.68 | 69.61 |
| 0.32104 | 72.78 | 71.80 | 0.53925 | 65.8 | 63.73 | 0.30400 | 68.28 | 67.27 |
| 0.42381 | 72.88 | 71.85 | 0.64546 | 64.46 | 62.03 | 0.38225 | 66.98 | 65.25 |
| 0.52456 | 73.08 | 72.04 | 0.73196 | 63.19 | 60.54 | 0.51475 | 64.48 | 62.62 |
| 0.62335 | 73.38 | 72.40 | 0.80378 | 62.05 | 59.17 | 0.62265 | 62.88 | 60.12 |
| 0.72023 | 73.67 | 72.77 | 0.86435 | 60.89 | 57.60 | 0.71224 | 61.78 | 58.65 |
| 0.81527 | 73.98 | 73.24 | 0.91613 | 59.76 | 56.89 | 0.78781 | 61.08 | 57.32 |
| 0.90851 | 74.29 | 73.81 | 0.9609 | 58.91 | 56.01 | 0.85241 | 60.58 | 57.07 |
| 1.00000 | 74.68 | 74.68 | 1.00000 | 58.18 | 55.30 | 0.90826 | 60.28 | 56.70 |
| 0.95704 | 59.98 | 56.19 | ||||||
| 1.00000 | 59.78 | 55.24 | ||||||
| RO + EO | EO + Hex | RO + Hex | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
[mN/m] | [mJ/m2] | [mN/m] | [mJ/m2] | [mN/m] | [mJ/m2] | |||
| 0.00000 | 60.40 | 60.30 | 0.00000 | 60.40 | 60.30 | 0.00000 | 63.58 | 64.94 |
| 0.10920 | 60.44 | 60.34 | 0.23279 | 55.79 | 55.75 | 0.11526 | 60.94 | 60.92 |
| 0.21620 | 60.49 | 60.40 | 0.40572 | 52.04 | 52.03 | 0.21570 | 56.06 | 56.04 |
| 0.32104 | 60.59 | 60.50 | 0.53925 | 48.94 | 49.01 | 0.30400 | 53.57 | 53.57 |
| 0.42381 | 60.78 | 60.69 | 0.64546 | 46.40 | 46.52 | 0.38225 | 51.08 | 51.07 |
| 0.52456 | 61.15 | 61.06 | 0.73196 | 44.09 | 44.38 | 0.51475 | 46.25 | 46.25 |
| 0.62335 | 61.70 | 61.60 | 0.80378 | 41.96 | 42.39 | 0.62265 | 43.13 | 43.13 |
| 0.72023 | 62.19 | 62.08 | 0.86435 | 39.98 | 40.74 | 0.71224 | 40.97 | 40.97 |
| 0.81527 | 62.68 | 62.56 | 0.91613 | 38.08 | 39.20 | 0.78781 | 39.59 | 39.59 |
| 0.90851 | 63.13 | 63.00 | 0.9609 | 36.63 | 38.00 | 0.85241 | 38.60 | 38.60 |
| 1.00000 | 63.58 | 63.42 | 1.00000 | 35.42 | 37.04 | 0.90826 | 38.00 | 38.00 |
| 0.95704 | 37.40 | 37.40 | ||||||
| 1.00000 | 37.00 | 37.00 | ||||||
| RO + EO | EO + Hex | RO + Hex | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
[mN/m] | [mJ/m2] | [mN/m] | [mJ/m2] | [mN/m] | [mJ/m2] | |||
| 0.00000 | 71.42 | 72.43 | 0.00000 | 71.42 | 72.43 | 0.00000 | 73.42 | 74.26 |
| 0.10920 | 71.44 | 72.25 | 0.23279 | 68.53 | 68.80 | 0.11526 | 71.12 | 71.67 |
| 0.21620 | 71.47 | 72.11 | 0.40572 | 66.33 | 65.90 | 0.21570 | 68.42 | 69.17 |
| 0.32104 | 71.52 | 71.98 | 0.53925 | 64.54 | 63.55 | 0.30400 | 67.02 | 66.85 |
| 0.42381 | 71.62 | 71.94 | 0.64546 | 63.20 | 61.67 | 0.38225 | 65.72 | 64.84 |
| 0.52456 | 71.82 | 72.04 | 0.73196 | 61.93 | 60.03 | 0.51475 | 63.22 | 62.27 |
| 0.62335 | 72.12 | 72.29 | 0.80378 | 60.79 | 58.49 | 0.62265 | 61.62 | 59.73 |
| 0.72023 | 72.41 | 72.57 | 0.86435 | 59.63 | 57.15 | 0.71224 | 60.52 | 58.19 |
| 0.81527 | 72.72 | 72.95 | 0.91613 | 58.50 | 55.87 | 0.78781 | 59.82 | 56.80 |
| 0.90851 | 73.03 | 73.45 | 0.9609 | 57.65 | 54.77 | 0.85241 | 59.32 | 56.40 |
| 1.00000 | 73.42 | 74.26 | 1.00000 | 56.92 | 53.54 | 0.90826 | 59.02 | 55.81 |
| 0.95704 | 58.72 | 55.00 | ||||||
| 1.00000 | 58.52 | 53.49 | ||||||
| RO + EO | EO + Hex | RO + Hex | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.00000 | 9.88 | 9.21 | 0.00000 | 9.88 | 9.21 | 0.00000 | 7.88 | 8.34 |
| 0.10920 | 9.86 | 9.10 | 0.23279 | 12.78 | 11.60 | 0.11526 | 10.18 | 9.93 |
| 0.21620 | 9.83 | 8.96 | 0.40572 | 14.98 | 13.30 | 0.21570 | 12.88 | 12.81 |
| 0.32104 | 9.78 | 8.80 | 0.53925 | 16.68 | 14.53 | 0.30400 | 14.28 | 13.27 |
| 0.42381 | 9.68 | 8.65 | 0.64546 | 17.98 | 15.43 | 0.38225 | 15.58 | 13.85 |
| 0.52456 | 9.48 | 8.44 | 0.73196 | 19.08 | 16.14 | 0.51475 | 18.08 | 16.22 |
| 0.62335 | 9.18 | 8.20 | 0.80378 | 20.08 | 16.77 | 0.62265 | 19.68 | 16.92 |
| 0.72023 | 8.89 | 7.99 | 0.86435 | 20.91 | 17.26 | 0.71224 | 20.78 | 17.65 |
| 0.81527 | 8.58 | 7.84 | 0.91613 | 21.68 | 17.69 | 0.78781 | 21.48 | 17.72 |
| 0.90851 | 0.9609 | 0.85241 | 21.98 | 18.47 | ||||
| 1.00000 | 1.00000 | 0.90826 | 22.28 | 18.70 | ||||
| 0.95704 | 22.58 | 18.79 | ||||||
| 1.00000 | 22.78 | 18.24 | ||||||
| RO + EO | EO + Hex | RO + Hex | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.00000 | −0.91 | −0.91 | 0.00000 | −0.91 | −0.91 | 0.00000 | −3.75 | −2.45 |
| 0.10920 | −0.93 | −0.93 | 0.23279 | −0.28 | −0.29 | 0.11526 | −1.78 | −1.82 |
| 0.21620 | −0.96 | −0.97 | 0.40572 | −0.08 | −0.08 | 0.21570 | −0.90 | −0.92 |
| 0.32104 | −1.03 | −1.05 | 0.53925 | −0.10 | −0.02 | 0.30400 | −0.62 | −0.62 |
| 0.42381 | −1.21 | −1.22 | 0.64546 | −0.13 | −0.003 | 0.38225 | −0.43 | −0.43 |
| 0.52456 | −1.53 | −1.56 | 0.73196 | −0.29 | −0.0003 | 0.51475 | −0.23 | −0.23 |
| 0.62335 | −1.95 | −2.01 | 0.80378 | −0.43 | 0.00 | 0.62265 | −0.13 | −0.13 |
| 0.72023 | −2.35 | −2.43 | 0.86435 | −0.76 | 0.00 | 0.71224 | −0.07 | −0.07 |
| 0.81527 | −2.79 | −2.90 | 0.91613 | −1.12 | 0.00 | 0.78781 | −0.03 | −0.03 |
| 0.90851 | −3.24 | −3.39 | 0.9609 | −1.37 | 0.00 | 0.85241 | −0.01 | −0.01 |
| 1.00000 | −3.75 | −3.96 | 1.00000 | −1.62 | 0.00 | 0.90826 | −0.01 | −0.003 |
| 0.95704 | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||||||
| 1.00000 | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||||||
| RO + EO | EO + Hex | RO + Hex | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.00000 | 8.62 | 9.63 | 0.00000 | 8.62 | 9.63 | 0.00000 | 6.62 | 7.91 |
| 0.10920 | 8.60 | 9.41 | 0.23279 | 11.53 | 11.80 | 0.11526 | 8.92 | 9.47 |
| 0.21620 | 8.57 | 9.21 | 0.40572 | 13.73 | 13.30 | 0.21570 | 11.62 | 12.37 |
| 0.32104 | 8.52 | 8.98 | 0.53925 | 15.34 | 14.35 | 0.30400 | 13.02 | 12.85 |
| 0.42381 | 8.42 | 8.74 | 0.64546 | 16.60 | 15.07 | 0.38225 | 14.32 | 13.44 |
| 0.52456 | 8.22 | 8.44 | 0.73196 | 17.53 | 15.63 | 0.51475 | 16.82 | 15.87 |
| 0.62335 | 7.92 | 8.10 | 0.80378 | 18.39 | 16.09 | 0.62265 | 18.42 | 16.53 |
| 0.72023 | 7.63 | 7.79 | 0.86435 | 18.89 | 16.41 | 0.71224 | 19.52 | 17.19 |
| 0.81527 | 7.32 | 7.55 | 0.91613 | 19.30 | 16.67 | 0.78781 | 20.22 | 17.20 |
| 0.90851 | 7.01 | 7.43 | 0.9609 | 19.65 | 16.77 | 0.85241 | 20.72 | 17.80 |
| 1.00000 | 6.62 | 7.46 | 1.00000 | 19.88 | 16.50 | 0.90826 | 21.02 | 17.81 |
| 0.95704 | 21.32 | 17.60 | ||||||
| 1.00000 | 21.52 | 16.49 | ||||||
| RO + EO | EO + Hex | RO + Hex | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.00000 | −2.41 | −0.91 | 0.00000 | −2.41 | −0.91 | 0.00000 | −3.23 | −2.46 |
| 0.10920 | −2.41 | −0.93 | 0.23279 | −1.21 | −0.29 | 0.11526 | −1.26 | −1.82 |
| 0.21620 | −2.41 | −0.97 | 0.40572 | −0.56 | −0.08 | 0.21570 | −0.75 | −0.92 |
| 0.32104 | −2.41 | −1.05 | 0.53925 | −0.27 | −0.02 | 0.30400 | −0.43 | −0.62 |
| 0.42381 | −2.42 | −1.22 | 0.64546 | −0.20 | −0.004 | 0.38225 | −0.33 | −0.43 |
| 0.52456 | −2.45 | −1.56 | 0.73196 | −0.31 | −0.0003 | 0.51475 | −0.16 | −0.23 |
| 0.62335 | −2.51 | −2.01 | 0.80378 | −0.44 | 0.00 | 0.62265 | −0.08 | −0.13 |
| 0.72023 | −2.60 | −2.43 | 0.86435 | −0.76 | 0.00 | 0.71224 | −0.03 | −0.07 |
| 0.81527 | −2.73 | −2.90 | 0.91613 | −1.12 | 0.00 | 0.78781 | −0.01 | −0.03 |
| 0.90851 | −2.89 | −3.39 | 0.9609 | −1.37 | 0.00 | 0.85241 | 0.00 | −0.01 |
| 1.00000 | −3.22 | −3.96 | 1.00000 | −1.62 | 0.00 | 0.90826 | 0.00 | −0.003 |
| 0.95704 | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||||||
| 1.00000 | 0.00 | 0.00 | ||||||
| PMMA | Steel | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
[mN/m] | [mJ/m2] | [mN/m] | [mJ/m2] | [mN/m] | [mJ/m2] | [mN/m] | [mJ/m2] | |
| 10% EO | ||||||||
| 0.00000 | 62.79 | 62.63 | 74.29 | 73.81 | 63.13 | 63.00 | 73.03 | 72.88 |
| 0.21747 | 57.69 | 57.62 | 71.18 | 70.33 | 57.92 | 57.87 | 69.92 | 69.10 |
| 0.38504 | 53.10 | 53.07 | 68.48 | 67.03 | 53.27 | 53.25 | 67.22 | 65.58 |
| 0.62634 | 46.03 | 46.02 | 64.58 | 62.04 | 46.27 | 46.27 | 63.32 | 60.56 |
| 0.79174 | 42.64 | 42.64 | 62.68 | 59.36 | 42.71 | 42.71 | 61.42 | 57.80 |
| 0.85635 | 39.95 | 39.95 | 61.28 | 57.47 | 39.97 | 39.97 | 60.02 | 55.88 |
| 0.96090 | 38.00 | 38.00 | 60.28 | 56.01 | 38.00 | 38.00 | 59.02 | 54.33 |
| 20% EO | ||||||||
| 0.00000 | 62.62 | 62.50 | 73.98 | 73.24 | 62.68 | 62.56 | 72.72 | 72.39 |
| 0.21927 | 57.10 | 57.04 | 70.78 | 69.75 | 57.27 | 57.22 | 69.52 | 68.60 |
| 0.38786 | 52.90 | 52.87 | 68.38 | 66.89 | 53.17 | 53.15 | 67.12 | 65.63 |
| 0.63008 | 46.45 | 46.44 | 64.68 | 62.17 | 46.51 | 46.51 | 63.42 | 60.84 |
| 0.79571 | 42.75 | 42.74 | 62.68 | 59.29 | 42.74 | 42.73 | 61.42 | 57.89 |
| 0.86033 | 40.99 | 40.99 | 61.78 | 58.18 | 40.99 | 40.99 | 60.52 | 56.73 |
| 0.91613 | 39.20 | 39.20 | 60.88 | 56.89 | 39.20 | 39.20 | 59.62 | 55.42 |
| 40% EO | ||||||||
| 0.00000 | 62.26 | 62.19 | 73.38 | 72.40 | 61.70 | 61.60 | 72.12 | 71.73 |
| 0.22297 | 56.81 | 56.78 | 70.38 | 69.15 | 56.57 | 56.53 | 69.12 | 68.30 |
| 0.39364 | 52.52 | 52.50 | 67.98 | 66.33 | 52.44 | 52.43 | 66.72 | 65.39 |
| 0.63768 | 46.75 | 46.75 | 64.78 | 62.28 | 46.74 | 46.74 | 63.52 | 61.22 |
| 0.72793 | 44.55 | 44.55 | 63.58 | 60.66 | 44.52 | 44.52 | 62.32 | 59.60 |
| 0.80378 | 42.40 | 42.40 | 62.48 | 59.15 | 42.39 | 42.39 | 61.22 | 58.14 |
| 60% EO | ||||||||
| 0.00000 | 62.00 | 61.98 | 72.88 | 71.85 | 60.78 | 60.69 | 71.62 | 71.38 |
| 0.22680 | 56.56 | 56.55 | 69.98 | 68.48 | 55.88 | 55.83 | 68.72 | 67.93 |
| 0.39959 | 52.60 | 52.60 | 67.78 | 66.24 | 52.11 | 52.10 | 66.52 | 65.54 |
| 0.53561 | 49.70 | 49.70 | 66.18 | 64.53 | 49.43 | 49.42 | 64.92 | 63.73 |
| 0.64546 | 46.60 | 46.60 | 64.58 | 61.99 | 60.78 | 46.52 | 63.32 | 61.17 |
| 80% EO | ||||||||
| 0.00000 | 61.95 | 61.93 | 72.73 | 71.86 | 60.49 | 60.40 | 71.47 | 71.55 |
| 0.23076 | 56.92 | 56.92 | 69.88 | 68.61 | 56.24 | 56.23 | 68.62 | 68.19 |
| 0.40572 | 52.59 | 52.58 | 67.58 | 65.91 | 52.27 | 52.26 | 66.32 | 65.39 |
| PMMA | Steel | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
| 10% EO | ||||||||
| 0.00000 | −3.24 | −3.39 | 8.27 | 7.79 | −2.89 | −3.02 | 7.01 | 6.86 |
| 0.21747 | −2.11 | −2.18 | 11.38 | 10.53 | −1.88 | −1.93 | 10.12 | 9.30 |
| 0.38504 | −1.31 | −1.33 | 14.08 | 12.63 | −1.13 | −1.15 | 12.82 | 11.18 |
| 0.62634 | −0.57 | −0.58 | 17.98 | 15.45 | −0.33 | −0.33 | 16.72 | 13.96 |
| 0.79174 | −0.16 | −0.16 | 19.88 | 16.56 | −0.09 | −0.09 | 18.62 | 15.00 |
| 0.85635 | −0.05 | −0.05 | 21.28 | 17.47 | −0.03 | −0.03 | 20.02 | 15.88 |
| 0.96090 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 22.28 | 18.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 21.02 | 16.33 |
| 20% EO | ||||||||
| 0.00000 | −2.79 | −2.90 | 8.58 | 7.84 | −1.78 | −2.41 | 7.32 | 6.99 |
| 0.21927 | −1.91 | −1.96 | 11.78 | 10.75 | −1.05 | −1.21 | 10.52 | 9.60 |
| 0.38786 | −1.30 | −1.33 | 14.18 | 12.69 | −0.29 | −0.56 | 12.92 | 11.43 |
| 0.63008 | −0.36 | −0.36 | 17.88 | 15.37 | −0.07 | −0.27 | 16.62 | 14.04 |
| 0.79571 | −0.06 | −0.06 | 19.88 | 16.49 | −0.01 | −0.20 | 18.62 | 15.09 |
| 0.86033 | −0.01 | −0.01 | 20.78 | 17.18 | 0.00 | −0.31 | 19.52 | 15.73 |
| 0.91613 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 21.68 | 17.69 | −1.78 | −0.44 | 20.42 | 16.22 |
| 40% EO | ||||||||
| 0.00000 | −1.95 | −2.01 | 9.18 | 8.20 | −2.51 | −2.60 | 7.92 | 7.53 |
| 0.22297 | −1.40 | −1.42 | 12.18 | 10.95 | −1.63 | −1.67 | 10.92 | 10.10 |
| 0.39364 | −0.89 | −0.90 | 14.58 | 12.93 | −0.96 | −0.97 | 13.32 | 11.99 |
| 0.63768 | −0.26 | −0.25 | 17.78 | 15.28 | −0.26 | −0.26 | 16.52 | 14.22 |
| 0.72793 | −0.06 | −0.05 | 18.98 | 16.06 | −0.09 | −0.08 | 17.72 | 15.00 |
| 0.80378 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 20.08 | 16.75 | −0.01 | −0.01 | 18.82 | 15.74 |
| 60% EO | ||||||||
| 0.00000 | −1.21 | −1.22 | 9.68 | 8.65 | −2.42 | −2.51 | 8.18 | 8.18 |
| 0.22680 | −0.85 | −0.85 | 12.58 | 11.08 | −1.53 | −1.56 | 10.53 | 10.53 |
| 0.39959 | −0.40 | −0.40 | 14.78 | 13.24 | −0.89 | −0.90 | 12.54 | 12.54 |
| 0.53561 | −0.11 | −0.10 | 16.38 | 14.73 | −0.38 | −0.38 | 13.93 | 13.93 |
| 0.64546 | −0.01 | 0.00 | 17.98 | 15.39 | 14.18 | −0.08 | 14.57 | 14.57 |
| 80% EO | ||||||||
| 0.00000 | −0.96 | −0.97 | 9.83 | 8.96 | −2.5 | −2.41 | 8.57 | 8.65 |
| 0.23076 | −0.28 | −0.28 | 12.68 | 11.41 | −0.97 | −1.21 | 11.42 | 10.99 |
| 0.40572 | −0.02 | −0.02 | 14.98 | 13.31 | −0.34 | −0.56 | 13.72 | 12.79 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zdziennicka, A.; Szymczyk, K.; Jańczuk, B. The Influence of the Ethyl Oleate and n-Hexane Mixture on the Wetting and Lubricant Properties of Canola Oil. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9243. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179243
Zdziennicka A, Szymczyk K, Jańczuk B. The Influence of the Ethyl Oleate and n-Hexane Mixture on the Wetting and Lubricant Properties of Canola Oil. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(17):9243. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179243
Chicago/Turabian StyleZdziennicka, Anna, Katarzyna Szymczyk, and Bronisław Jańczuk. 2025. "The Influence of the Ethyl Oleate and n-Hexane Mixture on the Wetting and Lubricant Properties of Canola Oil" Applied Sciences 15, no. 17: 9243. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179243
APA StyleZdziennicka, A., Szymczyk, K., & Jańczuk, B. (2025). The Influence of the Ethyl Oleate and n-Hexane Mixture on the Wetting and Lubricant Properties of Canola Oil. Applied Sciences, 15(17), 9243. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179243








