The Effects of Vagus Nerve Stimulation on Stress, Competitive Anxiety, and Depression in Elite Shooters: Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedure
2.3. Psychologic Measure
2.4. Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS)
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
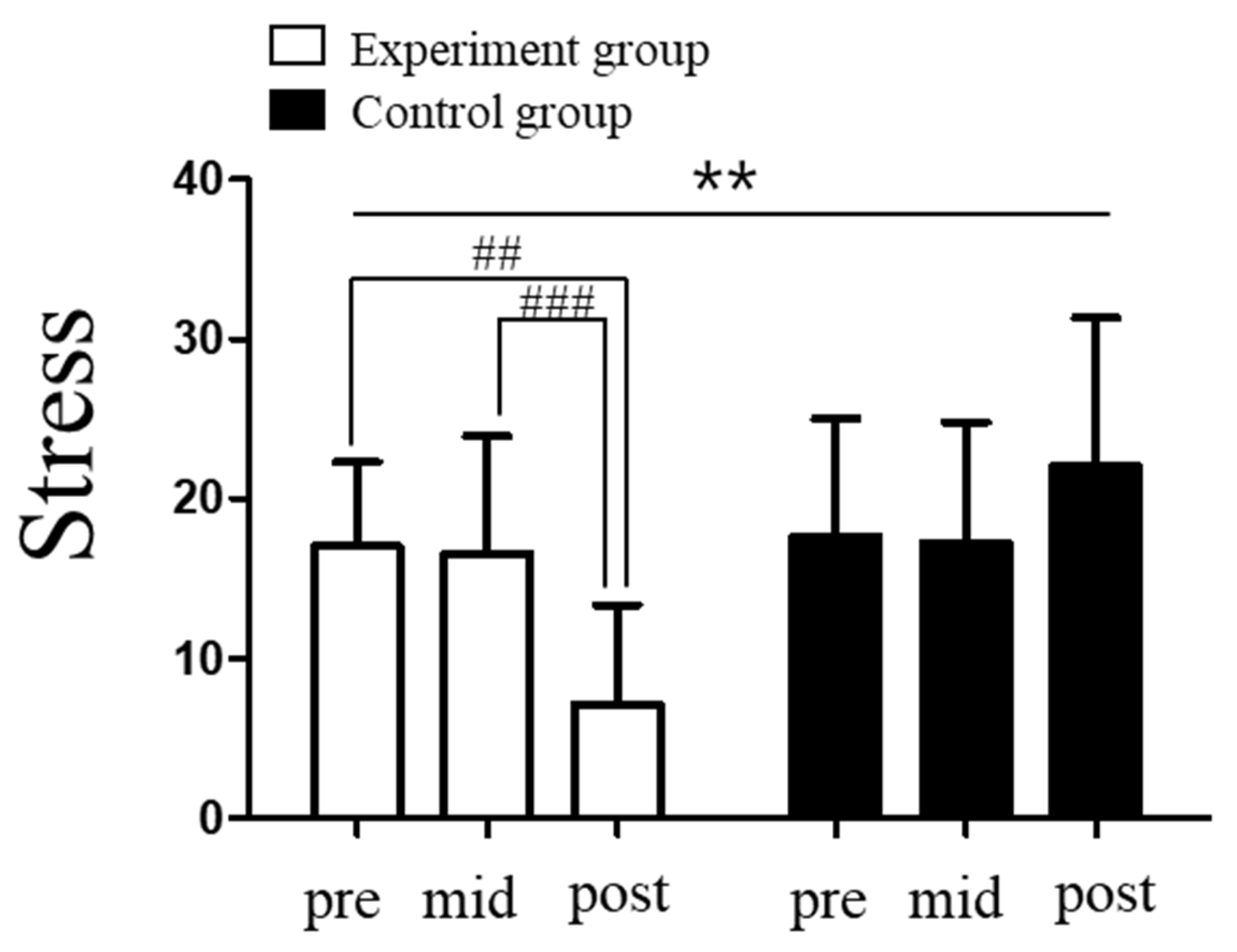
3.1. Changes in Stress Levels in Response to Vagus Nerve Stimulation
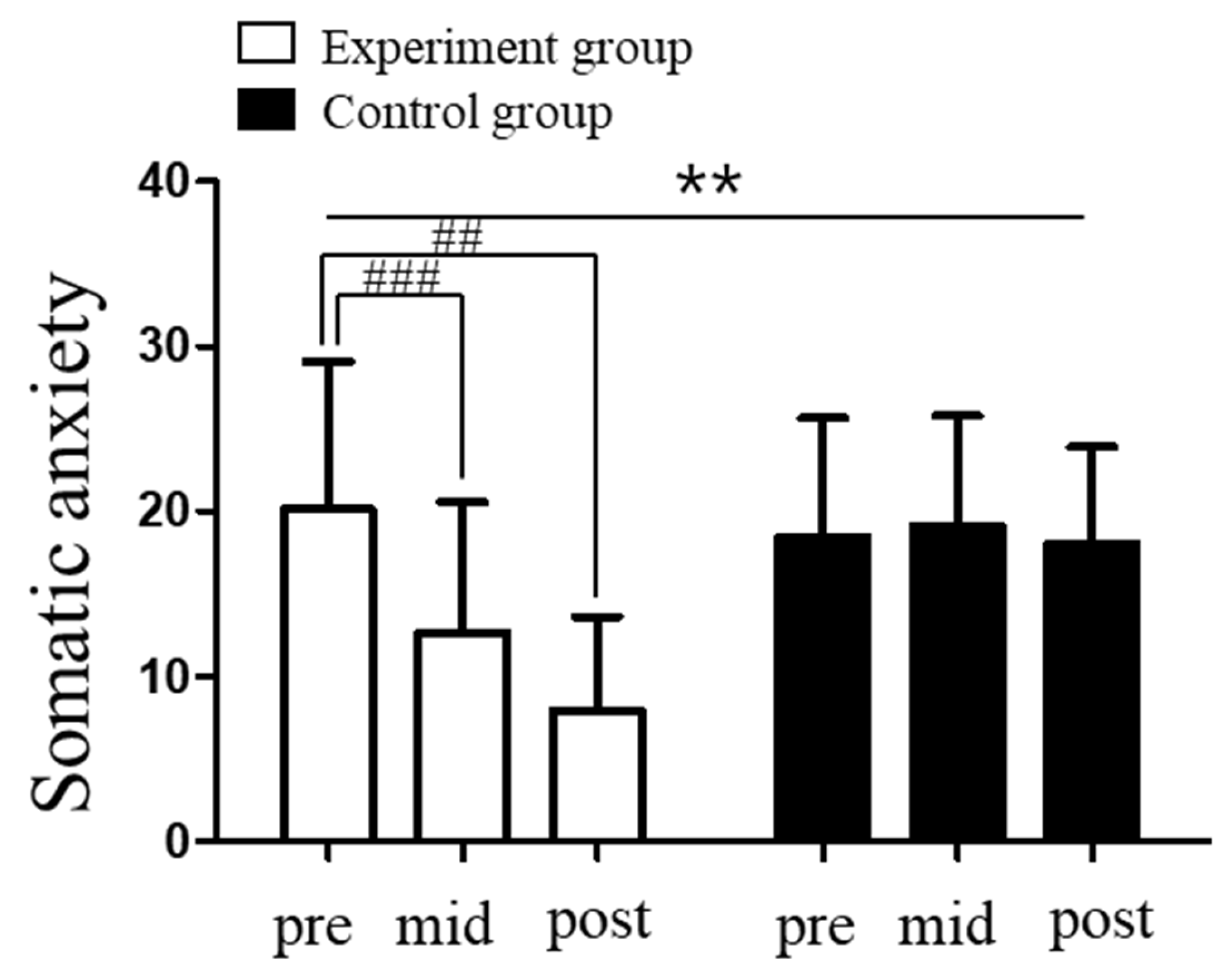
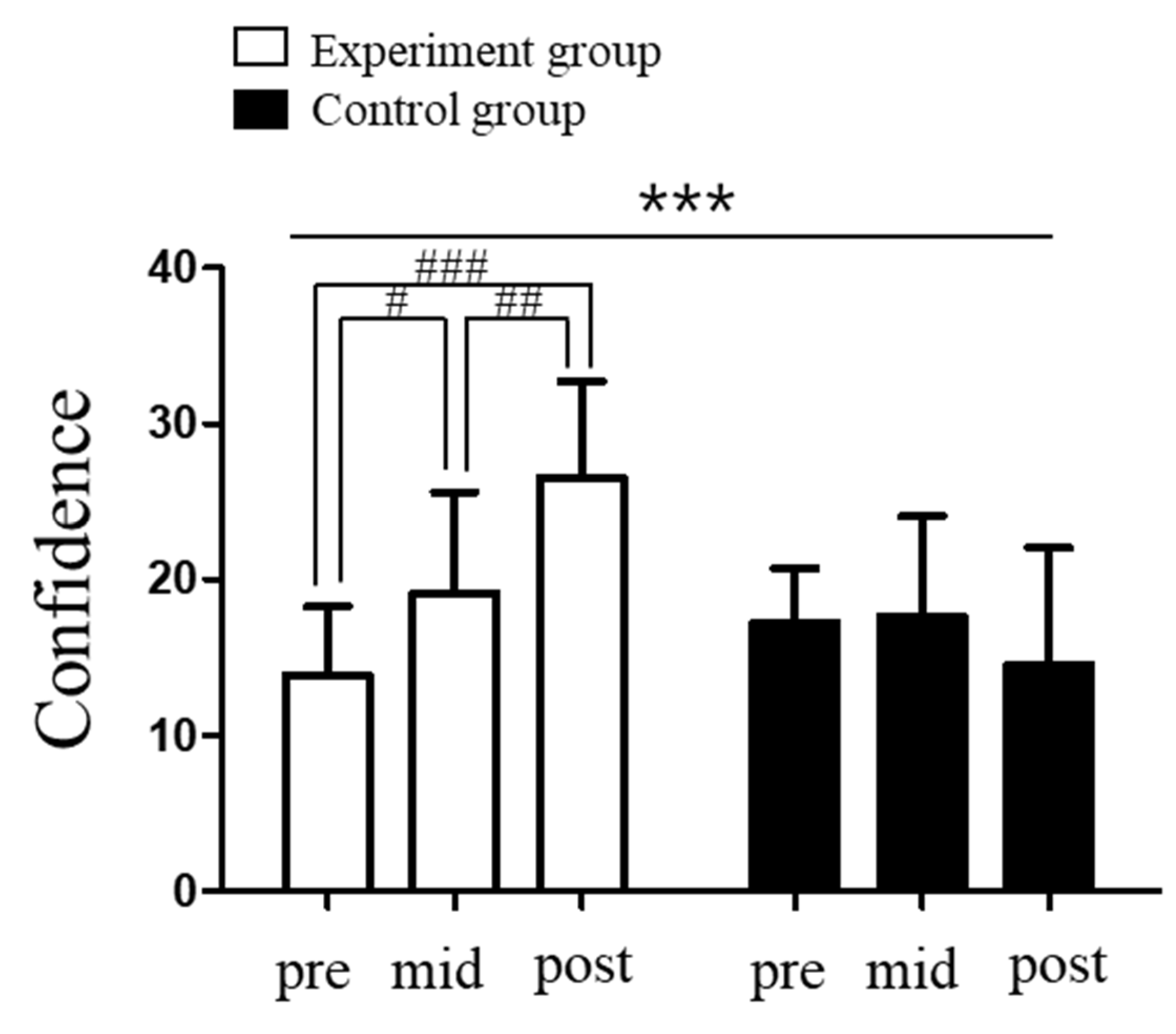
3.2. Changes in Competitive State Anxiety Levels in Response to Vagus Nerve Stimulation
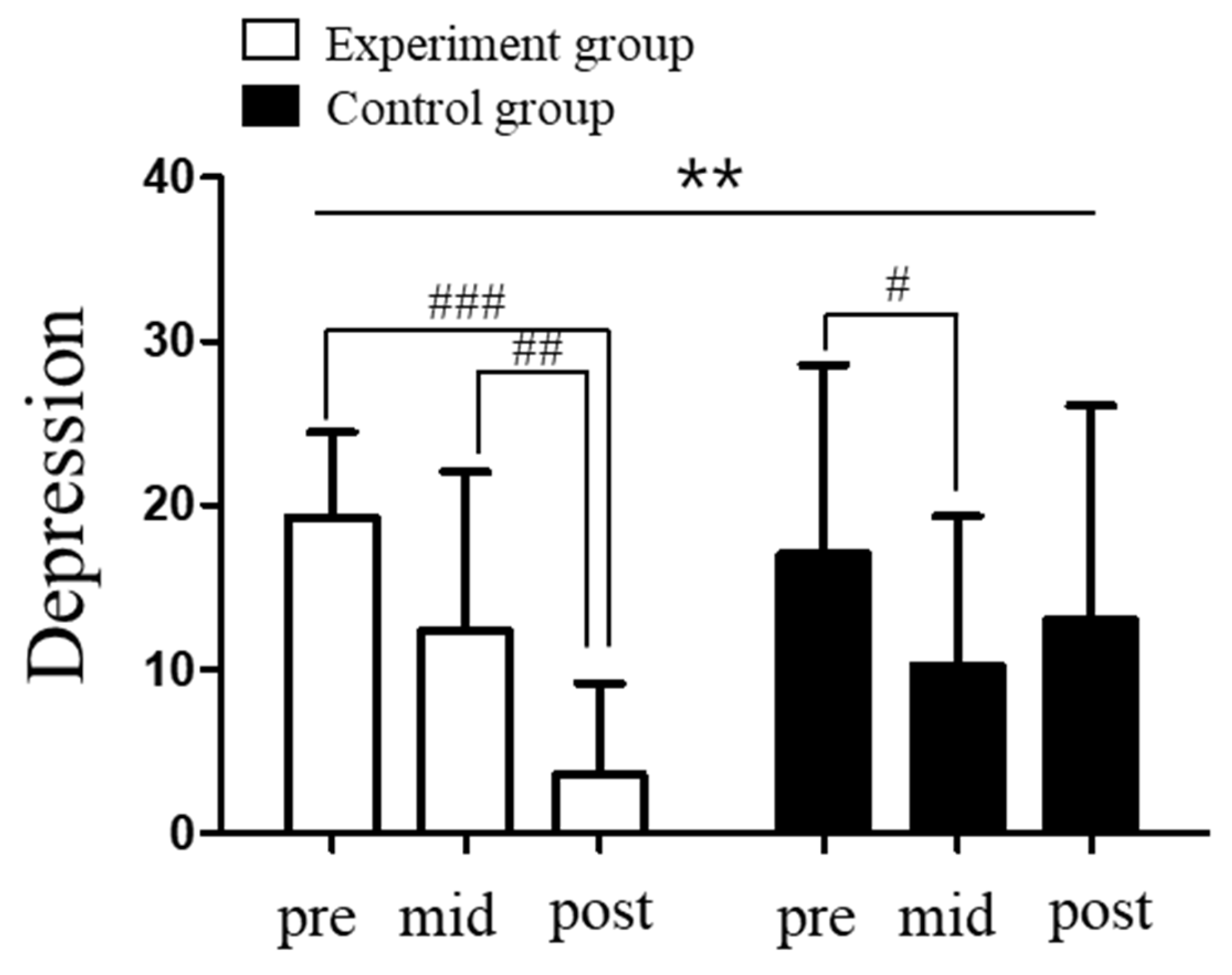
3.3. Changes in Depression in Elite Shooters Following Vagus Nerve Stimulation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Selye, H. The stress concept and some of its implications. In Human Stress and Cognition: An Information-Processing Approach; Hamilton, V., Warburton, D.M., Eds.; John Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1979; pp. 11–32. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Zhou, X.; Yu, L.; Jiang, H. Low level non-invasive vagus nerve stimulation: A novel feasible therapeutic approach for atrial fibrillation. Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 182, 189–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straube, A.; Ellrich, J.; Eren, O.; Blum, B.; Ruscheweyh, R. Treatment of chronic migraine with transcutaneous stimulation of the auricular branch of the vagal nerve (auricular t-VNS): A randomized, monocentric clinical trial. J. Headache Pain 2015, 16, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, M.S.; Ward, H.E., Jr.; Ninan, P.T.; Pollack, M.; Nahas, Z.; Anderson, B.; Kose, S.; Howland, R.H.; Goodman, W.K.; Ballenger, J.C. A pilot study of vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) for treatment-resistant anxiety disorders. Brain Stimul. 2008, 1, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, K.M.; Kim, M.S. An event-related potential study of spatial working memory deficits in college students with ADHD traits. Korean J. Cogn. Biol. Psychol. 2018, 30, 309–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.; Moon, H. New Methods of Vagus Nerve Stimulation: Therapeutic Effects of Non-Invasive Vagus Nerve Stimulation by TENS Application. J. Korean Soc. Integr. Med. 2016, 4, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindley, K. Effect of Transcutaneous Vagus Nerve Stimulation on Sports Performance. Master’s Thesis, Arizona State University, Tempe, AZ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hatik, S.H.; Asrlan, M.; Demirbilek, Ö.; Özden, A.V. The effect of transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation on cycling ergometry and recovery in healthy young individuals. Brain Behav. 2023, 13, e3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connaughton, D.; Wadey, R.; Hanton, S.; Jones, G. The development and maintenance of mental toughness in the world’s best performers. J. Sports Sci. 2008, 26, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.; Button, C.; Pepping, G.J.; Collins, D. Unnatural selection: Talent identification and development in sport. Nonlinear Dyn. Psychol. Life Sci. 2005, 9, 61–88. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.J. Component Factors on Collective Intelligence According to the Stapes of Volleyball Team Performance. Master’s Thesis, Department of Physical Education Graduate School, Korea National Sport University, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Song, S.H.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, H.S. Sports Activities and Activity of Autonomic Nervous System in Cardiac Rhythm. J. Korean Acad. Kinesiol. 2013, 15, 47–60. [Google Scholar]
- Jo, E.J. The Effect of Dancesport Exerciseon Neurotransmitter and Concentration in Youth. Master’s Thesis, Graduate School of Social Education, Myongji University, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, S. Effects of Participation in Contact Sports on Neurocognitive Scores and Dual-Task Walking in Retired Athletes. Korean J. Sport Biomech. 2020, 30, 265–273. [Google Scholar]
- Çali, A.; Özden, A.V.; Ceylan, İ. Effects of a single session of noninvasive auricular vagus nerve stimulation on sports performance in elite athletes: An open-label randomized controlled trial. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2024, 21, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.; Janicki-Deverts, D.; Miller, G.E. Psychological stress and disease. JAMA 2007, 298, 1685–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Shin, C.; Ko, Y.H.; Lim, J.H.; Joe, S.H.; Kim, S.H.; Jun, I.K.; Han, C. The Reliability and Validity Studies of the Korean Version of the Perceived Stress Scale. Korean J. Psychosom. Med. 2012, 20, 127–134. [Google Scholar]
- Martens, R.; Burton, D.; Vealey, R.S.; Bump, L.A.; Smith, D.E. Development and validation of the competitive state anxiety inventory-2. Compet. Anxiety Sport 1990, 3, 117–190. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, A.T.; Epstein, N.; Brown, G.; Steer, R.A. An inventory for measuring clinical anxiety: Psychometric properties. J. Consult Clin. Psychol. 1988, 56, 893–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Park, I.H.; Lim, S.T.; Lee, E. Changes in Psychological Anxiety and Physiological Stress Hormones in Korea National Shooters. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, S.; Ursin, H. What is stress? In Stress, Neurobiology and Neuro Endocrinology; Rivier, M.R., Koob, G., Eds.; Marcel Decker: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, S.; Kessler, R.C.; Gordon, L.U. Strategies for measuring stress in studies of psychiatric and physical disorders. In Measuring Stress: A Guide for Health and Social Scientists; Carnegie Mellon University: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 1995; Volume 28, pp. 3–26. [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich-Lai, Y.M.; Herman, J.P. Neural regulation of endocrine and autonomic stress responses. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremayne, P.; Barry, R.J. Elite pistol shooters: Physiological patterning of best vs. worst shots. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2001, 41, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, M.S. Implementation of Non-Invasive Vagus Nerve Stimulation System and Regression Analysis of Autonomic Nervous System Indicators. Master’s Thesis, Department of IT Convergence Graduate School, Ajou University, Suwon, Republic of Korea, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Manta, S.; Mansari, M.E.; Debonnel, G.; Blier, P. Electrophysiological and neurochemical effects of long-term vagus nerve stimulation on the rat monoaminergic systems. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013, 16, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, R.; Gould, D. Psychological Foundations in Sport and Exercise; Human Kinetics Press: Chapaigh, IL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Giraudier, M.; Ventura-Bort, C.; Weymar, M. Transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation (tVNS) improves high-confidence recognition memory but not emotional word processing. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eljamel, S. Vagus nerve stimulation for major depressive episodes. Prog. Neurol. Surg. 2015, 29, 53–63. [Google Scholar]
- Sackeim, H.A.; Rush, A.J.; George, M.S.; Marangell, L.B.; Husain, M.M.; Nahas, Z.; Johnson, C.R.; Seidman, S.; Giller, C.; Haines, S.; et al. Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) for treatment-resistant depression: Efficacy, side effects, and predictors of outcome. Neuropsychopharmacology 2001, 25, 713–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, L.J.; Souza, R.R.; McIntyre, C.K. Vagus nerve stimulation as a tool for enhancing extinction in exposure-based therapies. Psychopharmacology 2019, 236, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corning, J.L. Electrization of the sympathetic and pneumogastric nerves, with simultaneous bilateral compression of the carotids. N. Y. Med. J. 1884, 39, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Sackeim, H.A.; Brannan, S.K.; Rush, A.J.; George, M.S.; Marangell, L.B.; Allen, J. Durability of antidepressant response to vagus nerve stimulation (VNS). Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2007, 10, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frangos, E.; Richards, E.A.; Bushnell, M.C. Do the psychological effects of vagus nerve stimulation partially mediate vagal pain modulation? Neurobiol. Pain 2017, 1, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; Rong, P.; Hong, Y.; Fan, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, H. Transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation modulates default mode network in major depressive disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 79, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, S.-H.; Seong, C.; Kang, N.; Jeon, K.; Kil, S.; Ahn, H.; Lim, S.-T. The Effects of Vagus Nerve Stimulation on Stress, Competitive Anxiety, and Depression in Elite Shooters: Randomized Controlled Trial. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9105. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15169105
Park S-H, Seong C, Kang N, Jeon K, Kil S, Ahn H, Lim S-T. The Effects of Vagus Nerve Stimulation on Stress, Competitive Anxiety, and Depression in Elite Shooters: Randomized Controlled Trial. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(16):9105. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15169105
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Sang-Hyuk, Changhoon Seong, Nyeonju Kang, Kyoungkyu Jeon, Sekee Kil, Hyosung Ahn, and Seung-Taek Lim. 2025. "The Effects of Vagus Nerve Stimulation on Stress, Competitive Anxiety, and Depression in Elite Shooters: Randomized Controlled Trial" Applied Sciences 15, no. 16: 9105. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15169105
APA StylePark, S.-H., Seong, C., Kang, N., Jeon, K., Kil, S., Ahn, H., & Lim, S.-T. (2025). The Effects of Vagus Nerve Stimulation on Stress, Competitive Anxiety, and Depression in Elite Shooters: Randomized Controlled Trial. Applied Sciences, 15(16), 9105. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15169105







