Multi-Scale Feature Analysis Method for Soil Heavy Metal Based on Two-Dimensional Empirical Mode Decomposition: An Example of Arsenic
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
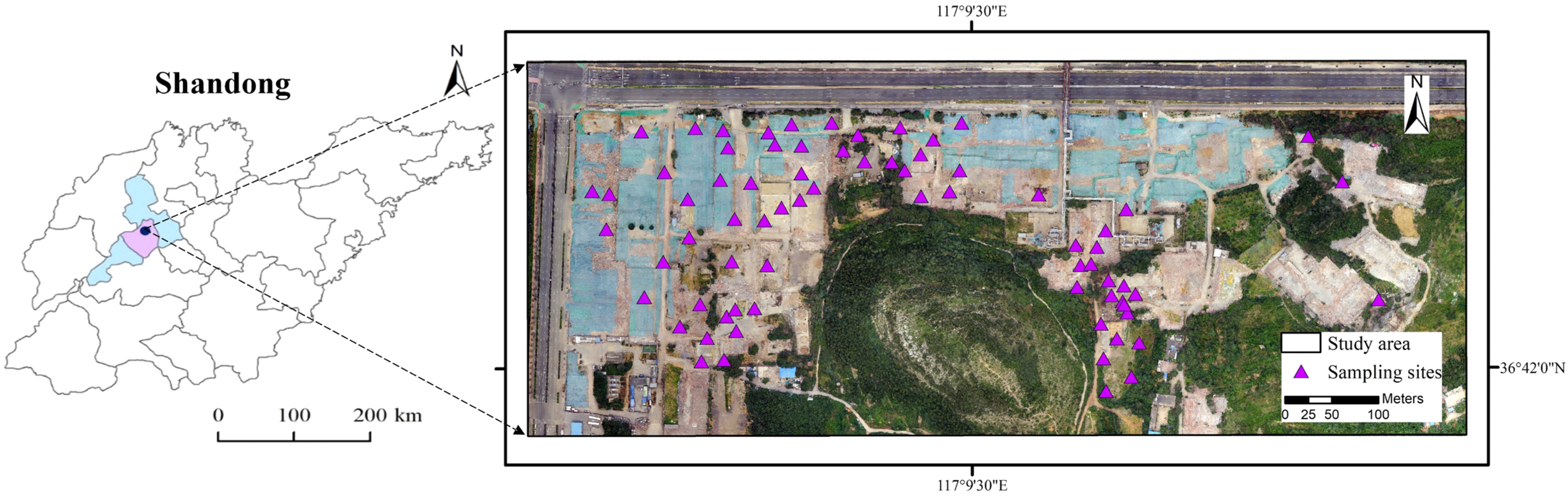
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data and Data Processing
2.2.1. Soil Sample Collection and Analysis
2.2.2. Environmental Variables
2.3. Methods
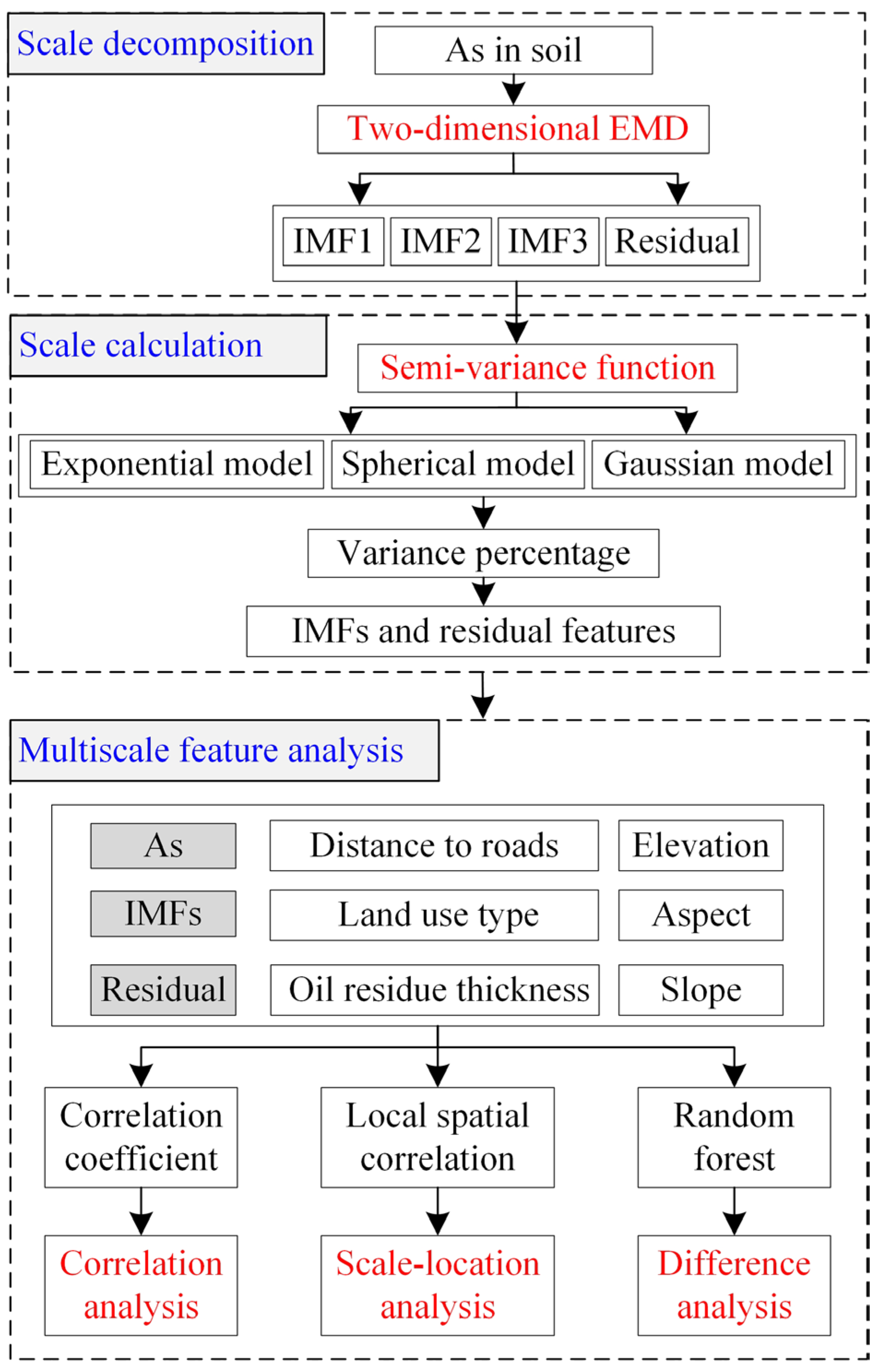
2.3.1. Two-Dimensional Empirical Mode Decomposition
2.3.2. Semi-Variance Function Model
2.3.3. Local Spatial Correlation Analysis
2.3.4. Random Forest Method
3. Results
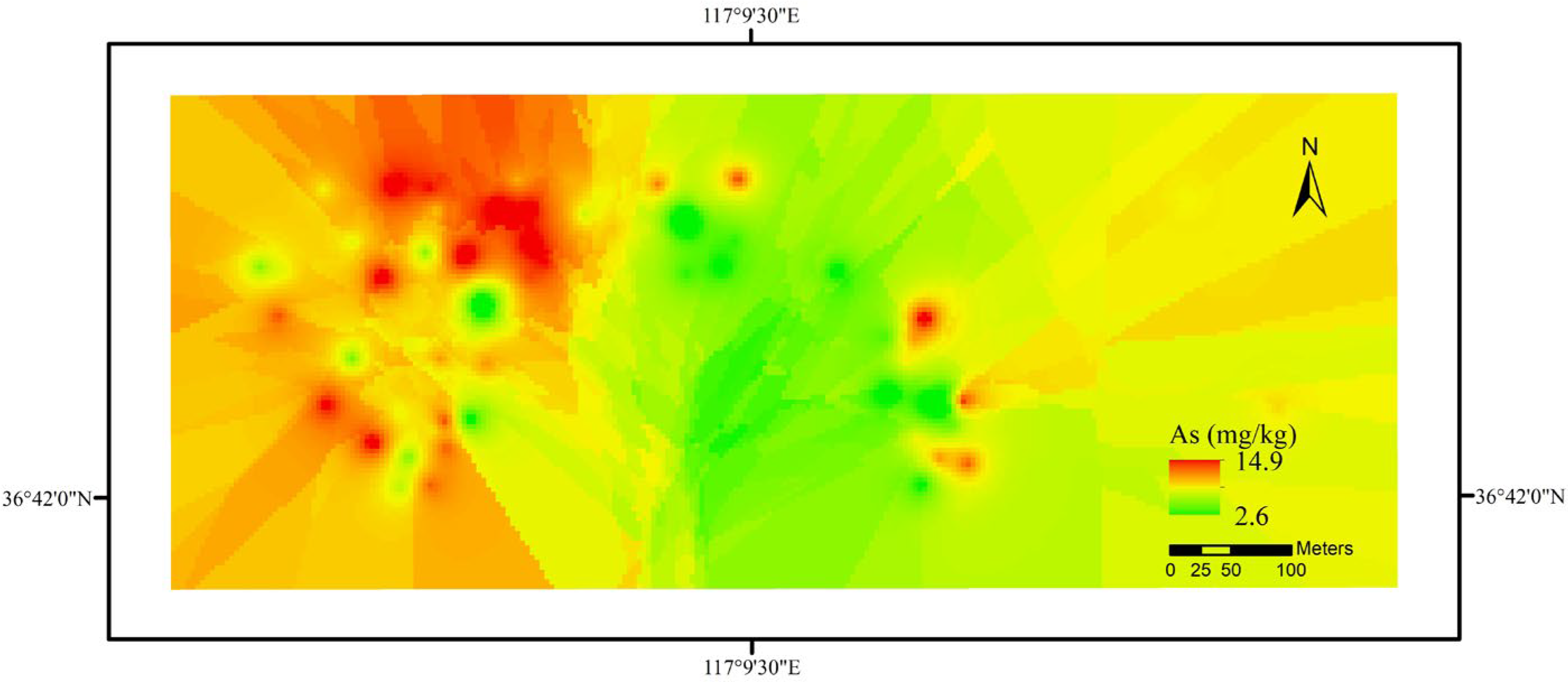
3.1. Two-Dimensional Empirical Mode Decomposition of As
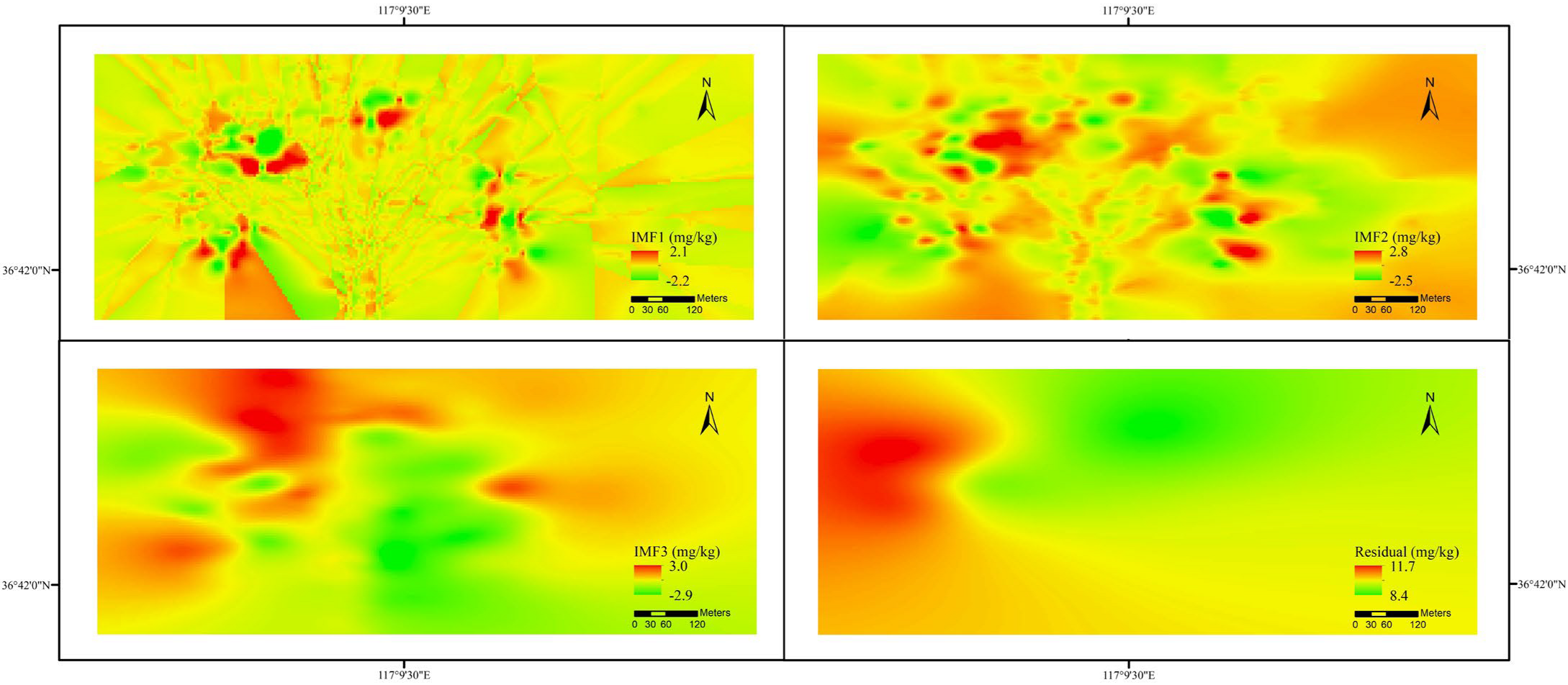
3.2. Characterization of Intrinsic Modal Functions and Residual
3.3. Analysis of Environmental Variables Influencing Heavy Metal As
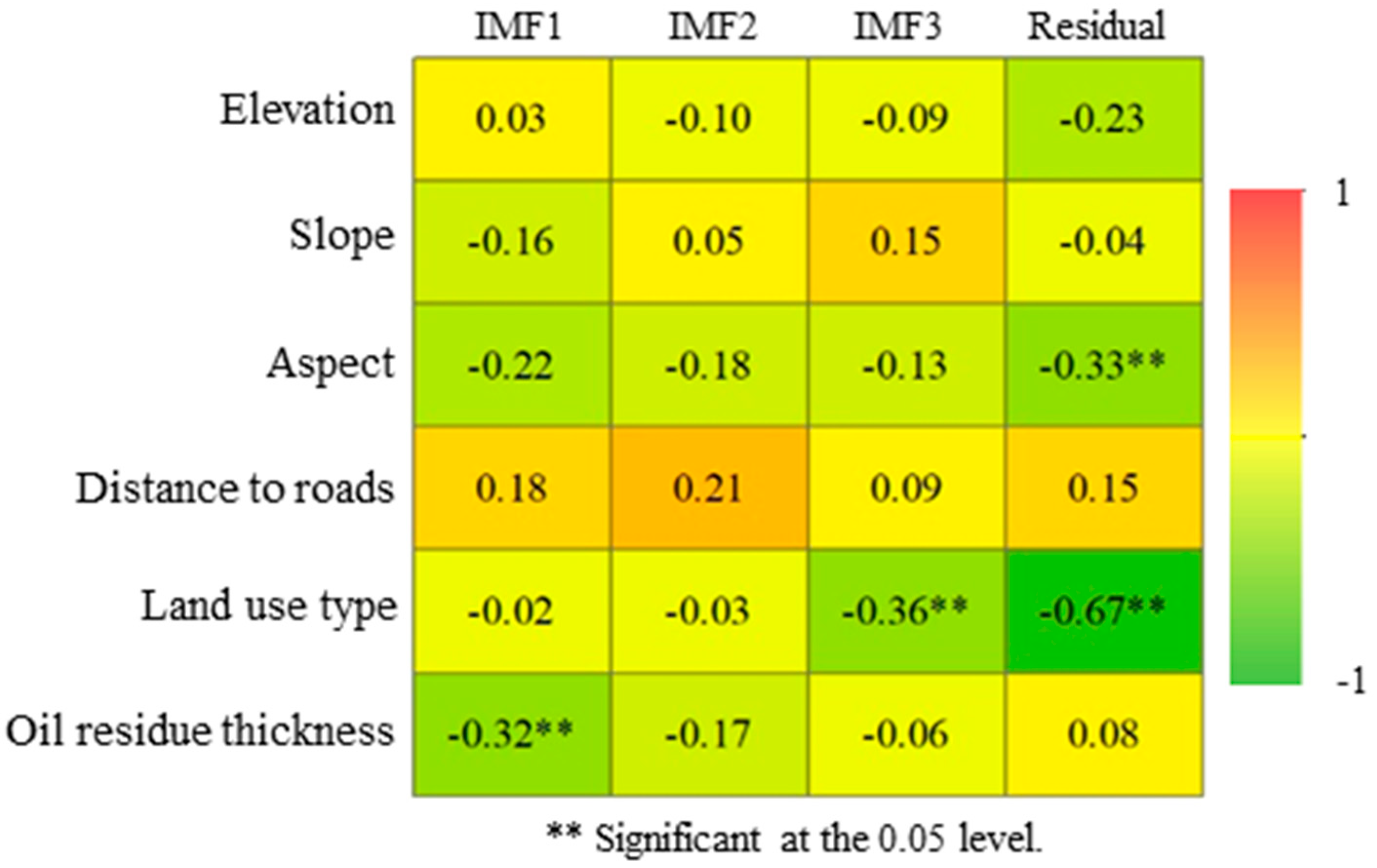
3.3.1. Correlation Analysis Between As, IMFs/Residual, and Environmental Variables
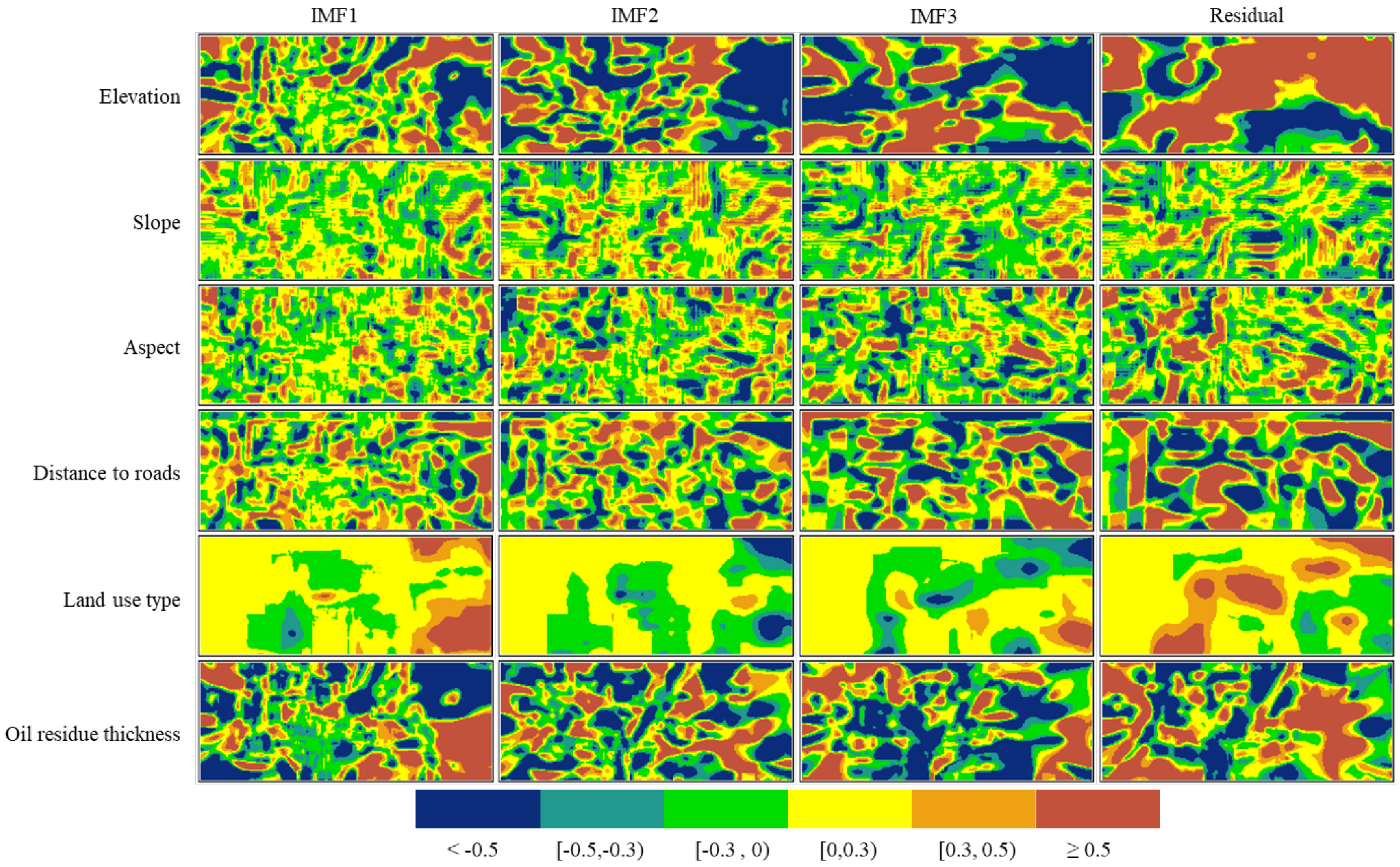
3.3.2. Scale–Location Analysis of IMFs/Residual and Environmental Variables
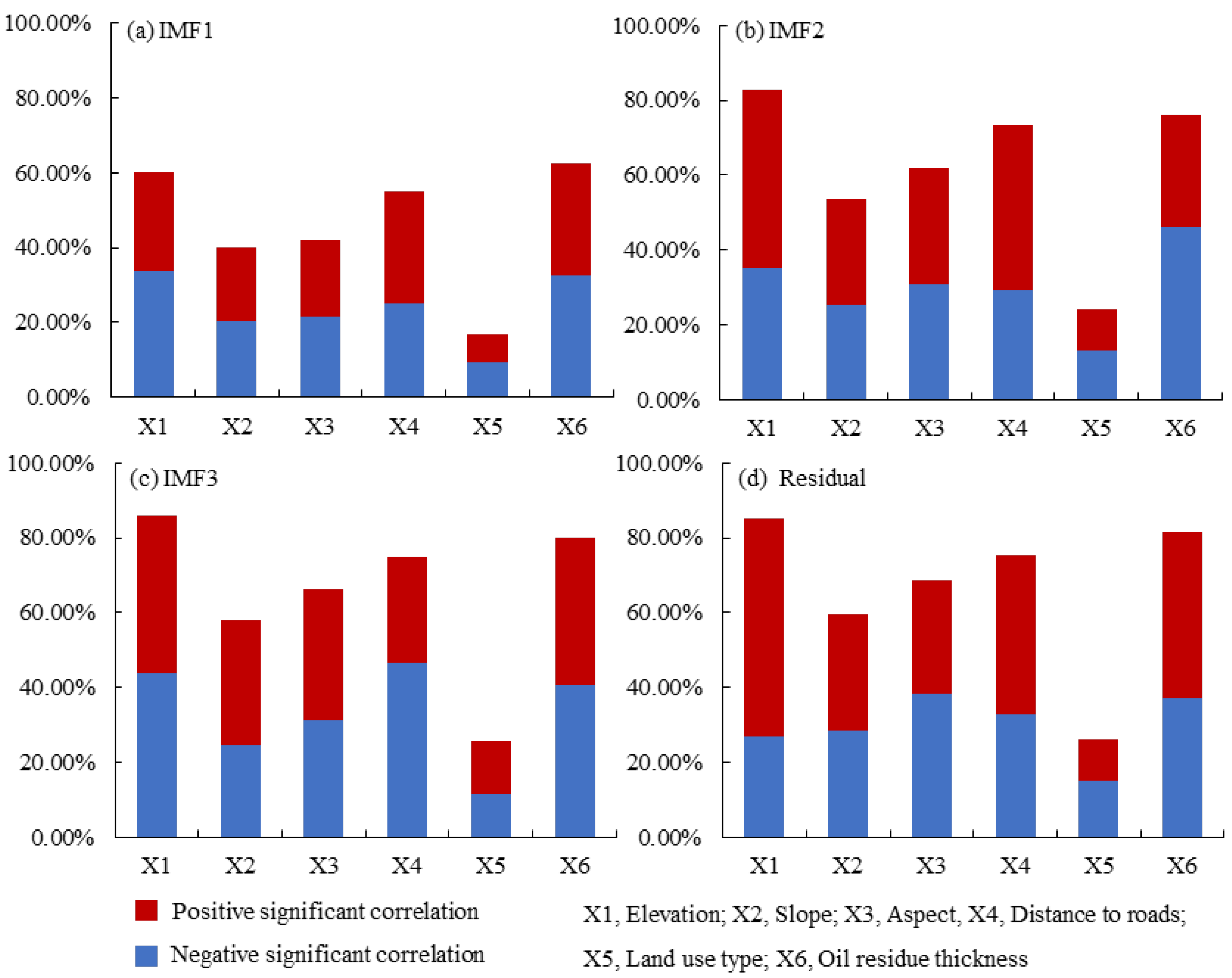
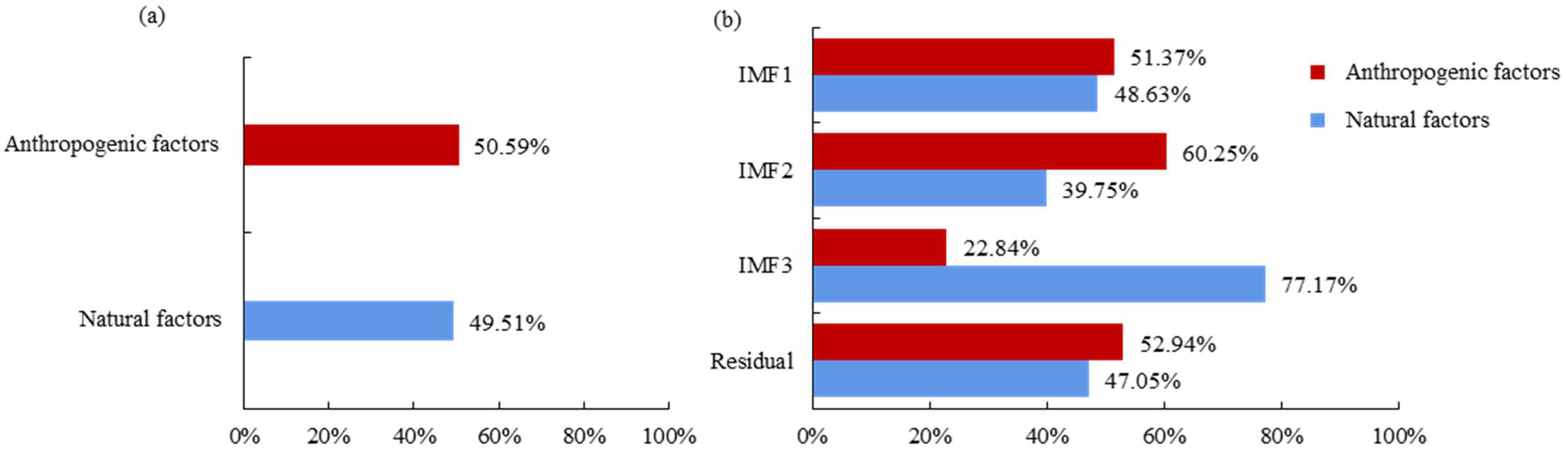
3.3.3. Difference Analysis in Environmental Variables Influencing As, and IMFs/Residual
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparisons with Related Studies
4.2. Advantages and Limitations for Analysis Results of Different Methods
4.3. Multi-Scale Determination Method for Spatial Variability of Soil Heavy Metals
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singha, W.J.; Deka, H. Ecological and human health risk associated with heavy metals (HMs) contaminant sourced from petroleum refinery oily sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 476, 135077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zhao, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, T.; Niu, Y.; Li, X. Research progress on remediation technology for heavy metal-contaminated soil in mines. J. Agri. Resour. Environ. 2023, 40, 249–260. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Qu, C.; Li, W.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, N.; Cai, H.; Wu, C.; Liu, J. Analysis of heavy metal contamination in the soil and enrichment capabilities of terrestrial plants around a typical vanadium smelter area. Chin. J. Eng. 2020, 42, 302–312. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, Y.; Ni, S.; Wang, J.; Zuo, R.; Yang, J. A geochemical survey of trace elements in agricultural and non-agricultural topsoil in Dexing area. J. Geochem. Explor. 2010, 104, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznietsov, P.M.; Biedunkova, O.O. The formation of the carbonate system of circulating cooling water of the Rivne NPP and its influence on changes in the surface waters pH levels of the Styr river. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2023; Volume 1254, p. 012102. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Qin, J.; Sun, H.; Gan, Z.; Chen, W.; Li, Z. Leaching of heavy metals and their impacting factors from a spent catalyst in the refinery industry. Environ. Chem. 2021, 40, 1147–1156. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, K.; Younas, M.; Yaseen, M.; Sher, H.; Maryam, A.; Ibrahim, S.M.; Adnan, A.; Ali, A.; Fawad, M.; Khan, A.Z.; et al. Heavy metals pollution in riverine sediments: Distribution, source, and environmental implications. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2025, 197, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncharov, G.; Soktoev, B.; Farkhutdinov, I.; Matveenko, I. Heavy metals in urban soil: Contamination levels, spatial distribution and human health risk assessment (the case of Ufa city, Russia). Environ. Res. 2024, 257, 119216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Guo, Z.; Xiao, X. Characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals in the soil around copper smelting sites. Environ. Sci. 2023, 44, 367–375. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Dong, J.; Liang, Q.; Yang, N.; Geng, Y. Heavy metal pollution characteristics and influencing factors in Baoji Arban soils. Environ. Sci. 2019, 40, 3774–3784. [Google Scholar]
- An, L.; Liu, M.; Zhang, J.; Huan, L.; Chen, Z. Sources of arsenic in soil and affecting factors of migration and release: A review. Soils 2020, 52, 234–246. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Yu, D.; Wu, H.; Du, J.; Pu, S. Soil contamination characteristics and source analysis of a copper smelting site in Guangxi. Acta Scien Circum. 2023, 43, 290–299. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Mei, Y.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Q. Spatial distribution characteristics and source analysis of soil heavy metals in county-level city. Acta Scien. Circum. 2022, 42, 287–297. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Bi, R.; Sun, R.; Xu, Z.; Lv, C.; Yang, J. Revealing the 2D scale-location specific variations of soil properties in the coal mining area of Changhe watershed, China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 2775–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Jin, Y.; Stein, A.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Cheng, Q.; Bai, H.; Liu, M.; Atkinson, P. Principles and methods of scaling geospatial earth science data. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2019, 197, 102897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Jiang, K.; Shi, H.; Xu, J.; Wu, H.; Luo, C. Differences of soil pollution source analysis models based on geostatistics. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2022, 41, 2181–2189. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Hu, W.; Jing, Y.; Cao, Y.; Bi, R.; Yang, W. Soil organic carbon prediction based on scale-specific relationships with environmental factors by discrete wavelet transform. Geoderma 2018, 330, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Dai, J.; Dai, B.; Zhu, Y. Identifying the origins and spatial distributions of heavy metals in soils of Ju country (Eastern China) using multivariate and geostatistical approach. J. Soil. Sediment. 2014, 15, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazirtiali, K.; Li, X. Inversion model of soil heavy metal content in lakeside oasis in the west bank of Bosten lake based on continuous wavelet transform. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 45, 201–207. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, X.; Li, H.; Sun, D.; Zhou, L.; Li, B. Multi-scale spatial structure of heavy metals in agricultural soils in Beijing. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 164, 605–616. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, K.; Wang, S.; Li, H.; Huang, F.; Li, B. Spatial scaling effects on variability of soil organic matter and total nitrogen in suburban Beijing. Geoderma 2014, 226, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Wang, Y.; Ding, F.; Chen, X.; Wang, J. Comparison of analysis methods of soil heavy metal pollution sources in China in last ten years. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2021, 52, 1000–1008. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Dai, B. Multivariate geostatistical analyses of heavy metals in soils: Spatial multi-scale variations in Wulian, Eastern China. Ecotox. Environ. Safe 2014, 107, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalbermatten, M.; Van De Ville, D.; Turberg, P.; Tuia, D.; Joost, S. Multiscale analysis of geomorphological and geological features in high resolution digital elevation models using the wavelet transform. Geomorphology 2012, 138, 352–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, B. Spatial scaling analyses of soil physical properties: A review of spectral and wavelet methods. Vadose Zone J. 2008, 7, 547–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, A.; Cresswell, H.P.; Chau, H.W.; Rossel, R.A.V.; Si, B. Separating scale-specific soil spatial variability: A comparison of multi-resolution analysis and empirical mode decomposition. Geoderma 2013, 209, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Bi, R.; Guo, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Chai, M.; Guo, Z. Source apportionment analysis of trace metal contamination in soils of Guangdong province, China. Acta Scien. Circum. 2018, 38, 704–714. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, D.; Yan, B.; Chen, Y. Spatial differentiation and influencing factor analysis of soil heavy metal content at town level based on geographic detector. Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 4566–4577. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 22105.2-2008; Soil Quality—Analysis of Total Mercury, Arsenic and Lead Contents—Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry—Part 2: Analysis of Total Arsenic Contents in Soils. General Administration of Quality Supervision. Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2008.
- Iqbal, J.; Thomasson, J.A.; Jenkins, J.N.; Owens, P.R.; Whisler, F.D. Spatial variability analysis of soil physical properties of alluvial soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2005, 69, 1338–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Biswas, A.; Ma, Z.; Lu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Shi, Z. Revealing the scale-specific controls of soil organic matter at large scale in Northeast and North China. Geoderma 2016, 271, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y. High Resolution Mapping of Soil Organic Carbon and Its Spatial Multiscale Controlling Factors in Tibet. Ph.D. Thesis, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.F.; Huang, J.Y.; Minasny, B.; Zhu, H. Two-dimensional empirical mode decomposition of heavy metal spatial variation in agricultural soils, Southeast China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 8302–8314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhao, L.; Chen, M.; Fang, H.; Yue, G.; Chen, J.; Pang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Ding, Y. Soil organic carbon and its relationship to vegetation communities and soil properties in permafrost areas of the central western Qinghai-Tibet plateau, China. Permafrost Periglac. 2012, 23, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lark, R.M.; Webster, R. Analysing soil variation in two dimensions with the discrete wavelet transform. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2004, 55, 777–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, H.; Shi, Q.; Zhang, H.; Liu, D.; Zhao, Y. Spatial heterogeneity of heavy metals and influencing factors in the surface cultivated soil of the loess hilly-gully region, China. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2019, 38, 2465–2475. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Wu, T.; Jiang, G.; Pu, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Xu, F.; Xie, X. Source identification and spatial differentiation of health risks of cultivated soil heavy metals in Jinhua City. Acta Scien. Circum. 2022, 42, 257–266. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, W.; Shi, H.; Wang, M.; Xu, C. Comparative case study on the influence of spatial distribution of heavy metals in regional area. Res. Environ. Sci. 2019, 32, 1213–1223. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Szymczak, S. A review on longitudinal data analysis with random forest. Brief. Bioinform. 2023, 24, bbad002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, T.; Su, Z.; Hou, C.; Feng, R. An optimized dimensionality reduction method of characteristic parameters for retrieving oasis soil moisture using random forest. J. Northwest Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2022, 52, 181–191. [Google Scholar]
- GB 36600-2018; Soil Environmental Quality Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Development Land. China Envi-ronmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Dai, J.; Pang, X.; Yu, C.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Hu, X. Geochemical baselines and background values and element enrichment characteristics in soils in eastern Shandong Province. Geochimica 2011, 40, 577–587. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, X.; Gao, B.; Pan, Y.; Yang, J.; Gao, Y. Influence factor analysis of heavy metal pollution in large-scale soil based on the geographical detector. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2019, 38, 2476–2486. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.; Li, L.; Zhou, X.; Shi, P.; Huang, D. Influence factor analysis of soil heavy metal based on geographic detector and its pollution risk assessment. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2021, 30, 173–180. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.J. Safe Utilization Evaluation and Regulation of Agricultural Land Soil Contaminated by Heavy Metal Elements in a Chinese County. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, X.; Ou, Y.; Yang, L.; Li, F. Concentration, risk assessment and sources of heavy metals in soil around Bohai Rim. Acta Scien. Circum. 2019, 39, 1979–1988. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Wei, W.; Huang, J.; Zhao, G. Heavy metal pollution characteristics and health risk assessment of soil-crops system in Anhui section of the Yangtze River basin. Environ. Sci. 2023, 44, 1686–1697. [Google Scholar]

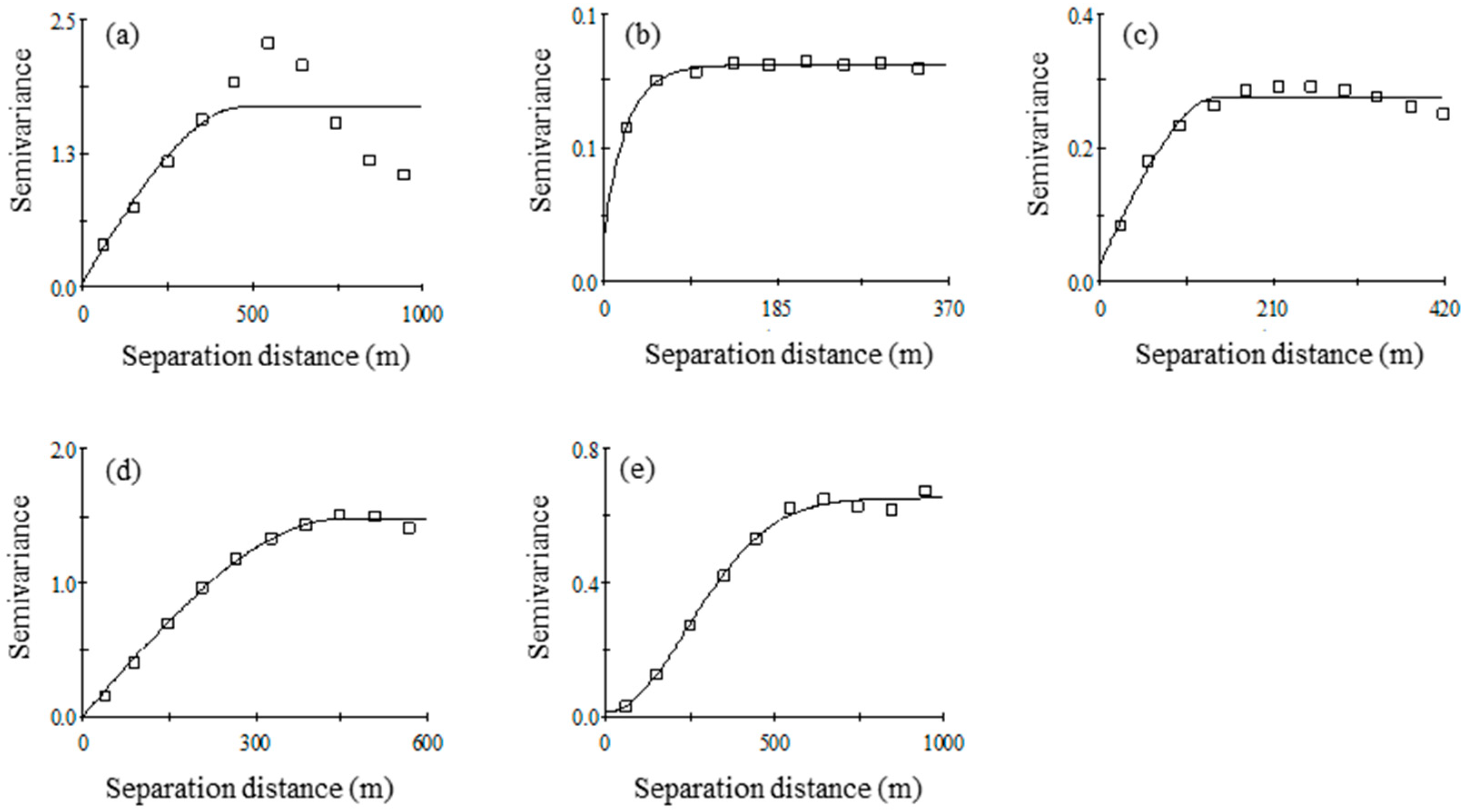
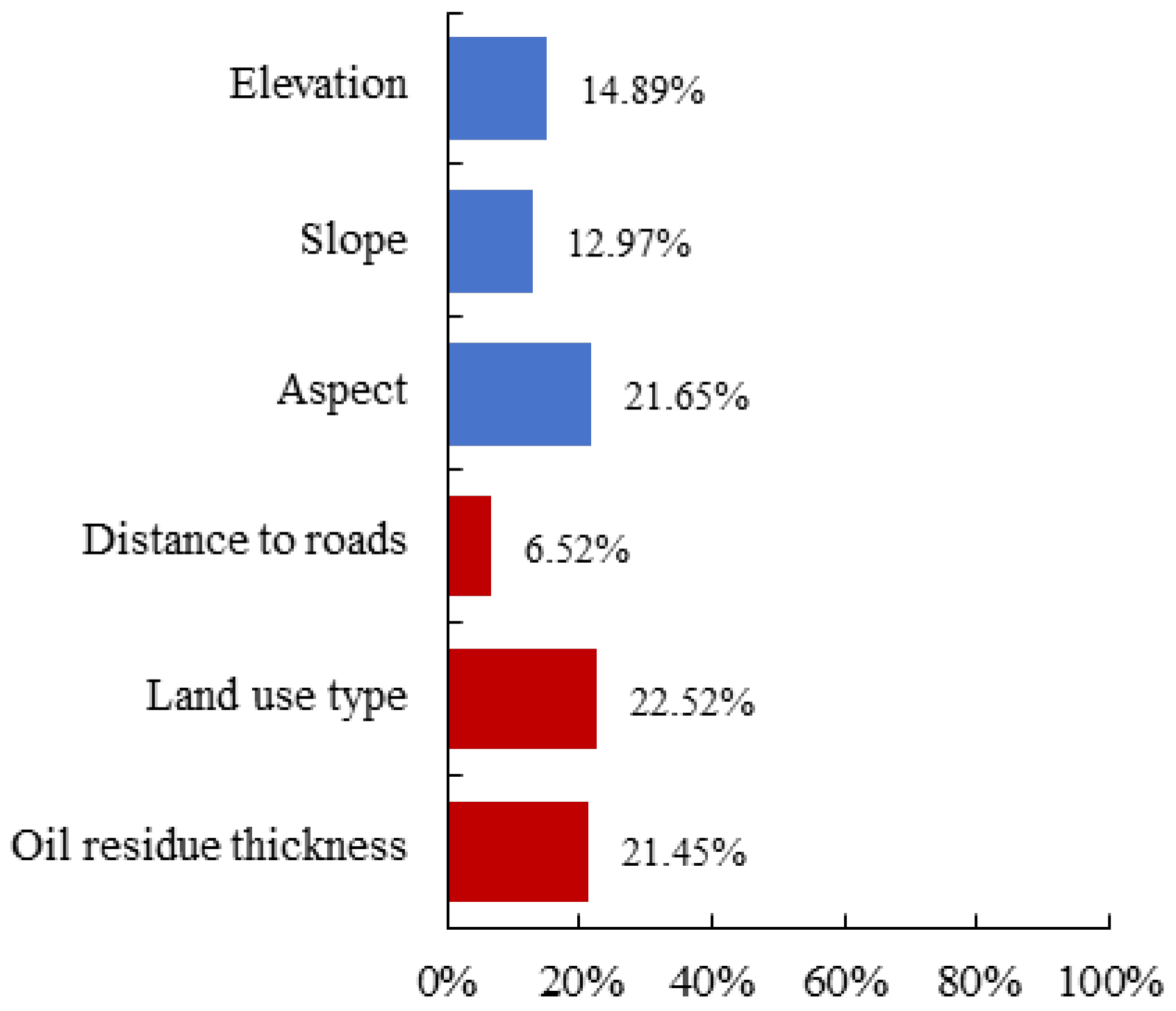
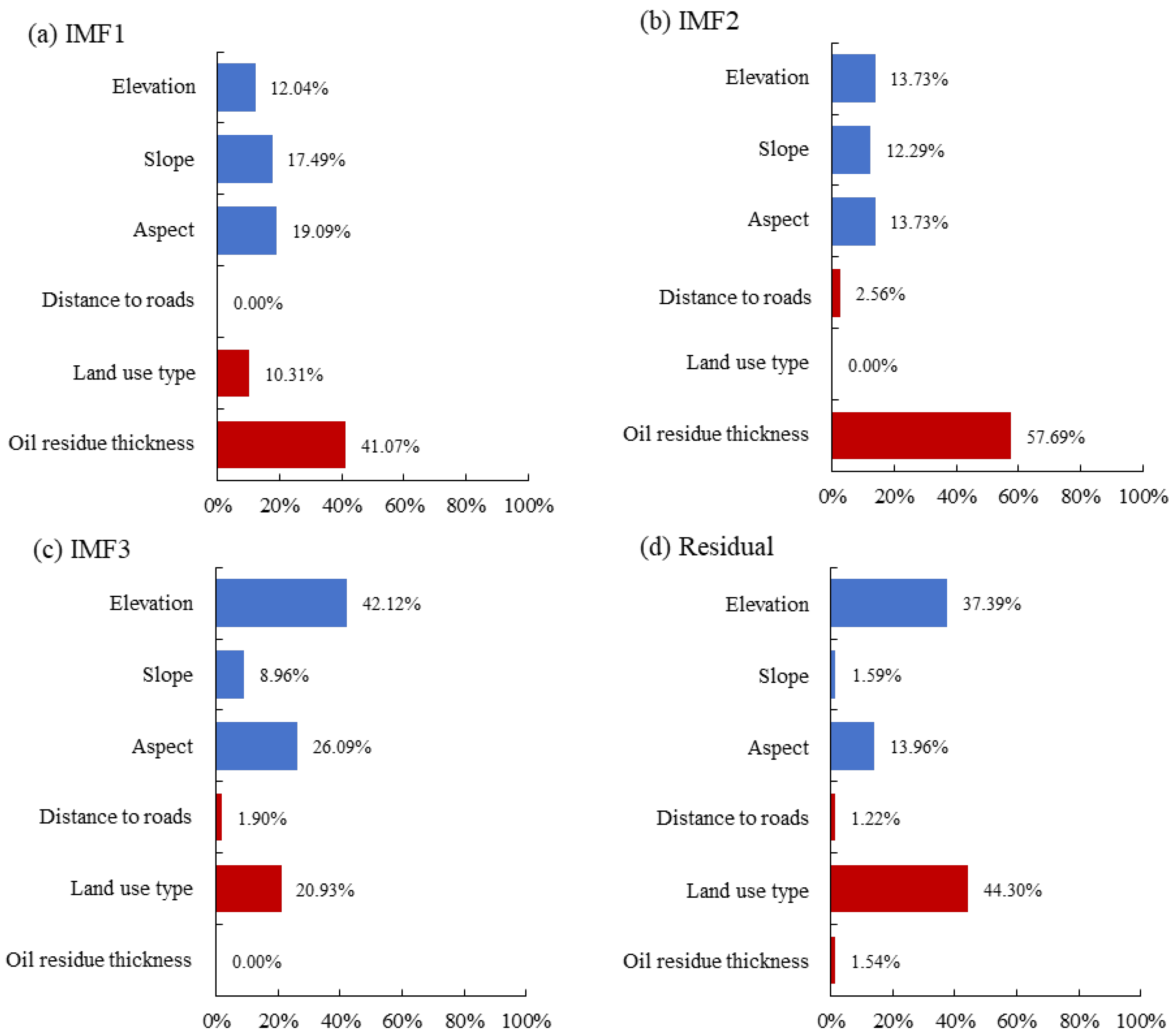
| Parameter | Model | Separation Distance (m) | R2 | Variance Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| As | Spherical | 466.00 | 0.61 | 100 |
| IMF1 | Exponential | 72.60 | 0.98 | 3.72 |
| IMF2 | Spherical | 159.30 | 0.97 | 14.13 |
| IMF3 | Spherical | 448.00 | 0.99 | 57.56 |
| Residual | Gaussian | 592.36 | 0.97 | 24.59 |
| Environment Variables | Elevation | Slope | Aspect | Distance to Roads | Land Use Type | Oil Residue Thickness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Correlation coefficient | −0.05 | 0.04 | −0.28 * | 0.22 | −0.35 ** | −0.18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, M.; Ge, L.; Yao, C.; Zhu, J.; Wang, W.; Ma, Q.; Guo, C.-E.; Sun, Q.; Dong, S. Multi-Scale Feature Analysis Method for Soil Heavy Metal Based on Two-Dimensional Empirical Mode Decomposition: An Example of Arsenic. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9078. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15169078
Yang M, Ge L, Yao C, Zhu J, Wang W, Ma Q, Guo C-E, Sun Q, Dong S. Multi-Scale Feature Analysis Method for Soil Heavy Metal Based on Two-Dimensional Empirical Mode Decomposition: An Example of Arsenic. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(16):9078. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15169078
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Maowei, Lin Ge, Chaofeng Yao, Jinjie Zhu, Wenqiang Wang, Qingwei Ma, Chang-En Guo, Qiangqiang Sun, and Shiwei Dong. 2025. "Multi-Scale Feature Analysis Method for Soil Heavy Metal Based on Two-Dimensional Empirical Mode Decomposition: An Example of Arsenic" Applied Sciences 15, no. 16: 9078. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15169078
APA StyleYang, M., Ge, L., Yao, C., Zhu, J., Wang, W., Ma, Q., Guo, C.-E., Sun, Q., & Dong, S. (2025). Multi-Scale Feature Analysis Method for Soil Heavy Metal Based on Two-Dimensional Empirical Mode Decomposition: An Example of Arsenic. Applied Sciences, 15(16), 9078. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15169078







