Abstract
The localization and pose estimation of clinicians in the operating room is a critical component for building intelligent perception systems, playing a vital role in enhancing surgical standardization and safety. Multi-view, multi-person 3D pose estimation is a highly challenging task—especially in the operating room, where the presence of sterile clothing, occlusion from surgical instruments, and limited data availability due to privacy concerns exacerbate the difficulty. While voxel-based 3D pose estimation methods have shown promising results in general scenarios, their performance is significantly challenged in surgical environments with limited camera views and severe occlusions. To address these issues, this paper proposes a fine-grained voxel feature reconstruction method enhanced with depth information, effectively mitigating projection errors caused by reduced viewpoints. Additionally, an attention mechanism is integrated into the encoder–decoder architecture to improve the network’s capacity for global information modeling and enhance the accuracy of keypoint regression. Experiments conducted in real-world operating room scenarios, using the Multi-View Operating Room (MVOR) dataset, demonstrate that the proposed method maintains high accuracy even under limited camera views and outperforms existing state-of-the-art multi-view 3D pose estimation approaches. This work provides a novel and efficient solution for human pose estimation (HPE) in complex medical environments.
1. Introduction
Surgery is a high-risk, high-tech medical intervention, and its safety management is related to the vital interests of patients. Intelligent perception systems in operating rooms based on vision and other sensors can simplify clinical processes, detect adverse events, and automatically analyze clinical activities for real-time decision making [1,2]. Clinicians are the main dynamic participants in the operating room, so human posture estimation models are a key component for building various intelligent assistance applications. Existing studies [3] have proposed that human posture estimation in the operating room is a crucial task, which may provide important clues for surgical workflow analysis. For example, by real-time monitoring and analysis of the movements of surgical team members, the standardization and fluency of surgical operations can be evaluated. However, unlike common human posture estimation, operating room scenes have challenges, such as dense distribution of personnel, similar clothing, severe occlusion caused by a large number of medical devices, and difficulty in data acquisition.
In recent years, voxel-based approaches such as those in [4,5] have shown promising performance by reconstructing 3D feature volumes through back-projection of 2D pose heatmaps or features from multiple views, enabling direct prediction of 3D human poses from the aggregated 3D representation. Faster VoxelPose [6] builds on this by reprojecting the 3D feature body to the 2D coordinate plane, enabling the use of 2D Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) to process the features and greatly improving the speed of model inference. However, the performance of these methods tends to degrade as the number of camera views decreases. While using fewer cameras can lower system costs and offer better privacy protection—particularly important in operating room settings—it also presents new challenges worth investigating. Zhuang et al. [7] introduced Depth-wise Projection Decay (DPD) to improve this problem. Using a depth estimation network, the depth information is incorporated into the process of projecting the 2D pose heatmap into the 3D space, retaining richer spatial information and improving the accuracy of the method under fewer camera perspectives. In this method, depth values are estimated by the network and assumed to be uniform across the bounding box of a person. However, in reality, the depths of different joints within the same individual can vary significantly. Furthermore, in densely populated environments—such as those commonly found in operating rooms—person a detection bounding box often partially overlaps, making it difficult to accurately assign depth values to the overlapping regions. The Multi-View Operating Room (MVOR) dataset [8] for 3D HPE in an operating room provides not only Red–Green–Blue (RGB) images of each camera perspective, but also depth images of the same resolution. Inspired by Faster VoxelPose+, we propose a Fine-Grained Depth-Wise Projection Decay (FDPD) method that leverages depth information at the voxel level, rather than restricting it to the coarser scale at the person level.
Meanwhile, inspired by the strong performance of Transformers in computer vision tasks [9], we design an encoder–decoder architecture incorporating an attention mechanism. After downsampling the feature map twice, a self-attention module is applied at the bottleneck to capture global dependencies. The features are then upsampled to recover spatial resolution. This design enables the model to effectively capture both local details and global context, allowing it to better handle challenges such as limb occlusion and complex spatial relationships in human pose estimation.
The main contributions of this paper are as follows:
- We are the first to apply a voxel-based 3D multi-person pose estimation framework to real-world operating room scenarios, achieving a favorable balance between accuracy and computational efficiency, which is critical for clinical applications.
- We propose a Fine-Grained Depth-Wise Projection Decay (FDPD) strategy that directly incorporates high-resolution depth maps into voxel space reconstruction. This approach effectively reduces depth ambiguity and significantly improves pose estimation accuracy, especially under limited camera views.
- We design an attention-enhanced encoder–decoder architecture that integrates positional encoding and a gating mechanism. This enables the model to capture both local features and global context, enhancing robustness to occlusions and complex spatial configurations commonly found in surgical environments.
2. Related Works
2.1. Multi-Person Multi-View 3D Pose Estimation
Human pose estimation (HPE) is a well-studied topic in computer vision, focusing on predicting the positions of human joints from sensor data such as images or videos. It provides valuable geometric and motion-related information and is widely applied in areas like human–computer interaction [10,11,12], motion analysis [13,14,15], augmented reality, virtual reality [16,17], and healthcare [18,19,20]. Three-dimensional HPE, which estimates joint positions in 3D space, has gained increasing attention for its ability to capture rich structural information. Multi-view approaches help address occlusions and viewpoint limitations in 2D pose estimation, but acquiring accurate 3D annotations and resolving cross-view identity associations remain major challenges. Datasets commonly used for multi-person 3D pose estimation include the CMU Panoptic dataset [21], the Shelf dataset [22], the Campus dataset [22], MP-3DHP [23], and WorldPose [24]. However, none of the above datasets are specifically prepared for operating room scenarios. VoxelPose [25] aggregated multi-view features into a 3D voxel space to reduce per-view estimation errors, using a cuboid proposal network and a pose regression network for person localization and 3D pose prediction. In order to reduce the computational cost of VoxelPose, Ye et al. proposed Faster VoxelPose [6], which reprojects the feature volume to three two-dimensional coordinate planes to estimate their X, Y, and Z coordinates. Faster VoxelPose has an fps of 31.1, which is almost 10 times faster than VoxelPose. On this basis, Zhuang et al. [7] proposed Faster VoxelPose+, which introduces depth information and uses the Depth-wise Projection Decay strategy to improve the accuracy of 3D pose estimation without reducing the inference speed, especially when the number of cameras is reduced.
Transformer-based models have recently shown strong global modeling capabilities in vision tasks. PoseFormer [26] was the first to apply a pure Transformer architecture to 3D HPE, capturing both spatial and temporal dependencies. Multi-view Pose Transformer [27] further advanced this by directly regressing 3D poses from multi-view images using geometry-guided attention. SVTformer [28] improved accuracy by hierarchically learning spatial, view, and temporal dependencies. However, methods based on the Transformer architecture are often computationally intensive and not conducive to fast reasoning. Chen et al. [29] applied an iterative processing strategy to match the 2D pose of each view with the 3D pose, while iteratively updating the 3D pose. Compared with previous methods whose running time may explode with the increase in the number of cameras, their method has linear time complexity.
2.2. 3D HPE in Operating Room (OR)
Fine-grained 3D HPE of clinicians in Multi-View Operating Room (OR) scenarios is a key element in designing the next generation of OR support systems [30,31]. The operating room is an extremely complex environment. The challenges include patients wearing sterile gowns, masks, hairnets, and goggles, which are very different from ordinary clothing. In addition, instruments such as surgical lights, hanging screens, and monitoring equipment cause occlusions, causing people to be frequently obscured from the camera. These instruments do not have fixed positions and can move during the operation. Finally, the sensitive nature of surgical data makes it extremely challenging to obtain large annotated datasets. Existing 3D HPE for operating rooms typically uses synchronized color or depth pictures from multiple camera angles [32]. Srivastav et al. [8] established a public MVOR dataset, providing camera calibration parameters, color and depth frames, human bounding boxes, and 2D/3D pose annotations, and tested the baseline results of several 2D/3D pose estimation methods. The 4D-OR dataset [33] is a publicly available dataset capturing ten simulated total knee replacement surgeries using six RGB-D cameras in a realistic operating room setting. It contains 6734 frames with annotations including human and object poses, clinical roles, and semantic scene graphs, providing a rich resource for surgical scene understanding and 4D perception tasks. Common methods usually use a two-step approach. First, the 2D pose estimator detects the position of body joints or generates probability heatmaps for each view. Second, the position is projected into 3D space, fused to all views, and post-processed [34,35]. Srivastav et al. [36] proposed AdaptOR, which generates pseudo labels through geometric constraints and combines disentangled feature normalization to achieve unsupervised domain adaptation from natural images to low-resolution operating room images, thereby jointly completing HPE and instance segmentation. Gerats et al. [37] proposed to directly optimize the positioning of 3D space by training a 2D CNN end to end based on a 3D loss function back-propagated through each camera projection parameter.
3. Methods
3.1. Overview
The main structure of our voxel-based 3D HPE method is shown in Figure 1. The network mainly consists of three parts. First, RGB-D images of multiple views are obtained, and 2D pose heatmaps are extracted from the images using an pre-trained pose estimation model. Second, the human detection module first constructs a 3D feature volume using voxel-level FDPD to back-project 2D heatmaps, then projects it onto the xy-plane and uses an attention-based encoder–decoder to predict each person’s bounding box. In the joint localization stage, a refined voxel volume is created for each individual, and its projections onto the xy, yz, and zx planes are processed by another attention-based encoder–decoder to estimate 2D joint positions, which are then fused to reconstruct the 3D pose.
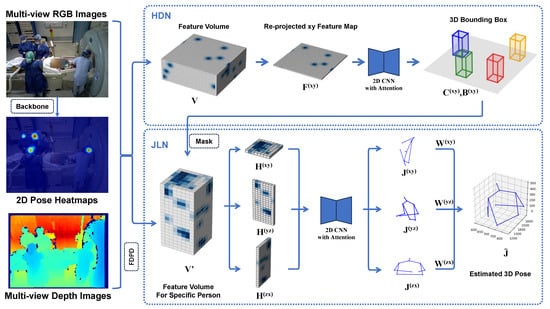
Figure 1.
The architecture of our method. It is mainly composed of the human detection network (HDN) and joint localization network (JLN).
In this part, we will first focus on the voxel-level FDPD method that introduces depth information and the encoder–decoder structure that introduces the attention mechanism, and then introduce the human detection network and the joint localization network, respectively.
3.2. The Fine-Grained Depth-Wise Projection Decay (FDPD)
In traditional voxel-based methods, each pixel in the 2D pose heatmap is projected with equal intensity along a ray in 3D space. While this allows multi-view fusion, it inherits the limitations of two-stage approaches—specifically, the loss of rich contextual information from the original image. In cases of severe occlusion or limited camera views, 2D pose estimation becomes error-prone, and these errors are inevitably propagated to later stages. The method proposed in [7] introduces depth information through a depth projection decay mechanism. However, due to the lack of ground-truth depth data, it relies on an additional network to predict the root joint depth, and struggles with overlapping 2D bounding boxes, where voxel ownership becomes ambiguous. In contrast, the MVOR dataset provides origin RGB and depth images. Leveraging this, we propose a fine-grained voxel-level depth projection strategy that eliminates the need for depth prediction networks and person-level bounding box detection.
Fine-Grained Depth Projection Decay (FDPD) is a projection method for constructing 3D voxel features. Here, we focus on the application of FDPD in the human detection network, and the principle is similar in the joint localization network. As shown in Figure 2, first, we discretize the stereo space into positions , and reproject the 2D pose heatmap into 3D space using camera parameters to construct the feature volume F. The heatmap of the camera view is regarded as , where K is the number of joints, and H and W are the height and width of the image. For each voxel grid at position , it is projected onto the camera imaging plane using the camera parameters to obtain . The heatmap value at is obtained by bilinear interpolation, denoted as .
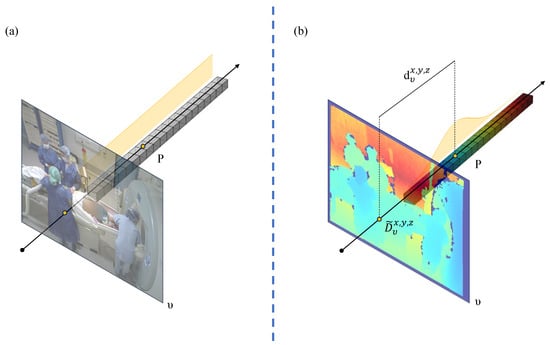
Figure 2.
Fine-Grained Depth-Wise Projection Decay, DPD: (a) the projection method in most voxel-based models and (b) our projection method using a depth map. Depth values are visualized using a Jet colormap, where colors range from blue (near) to red (far), with intermediate values represented by green and yellow.
In previous work, was assigned a Gaussian weight during back-projection based on the depth of the human root joint and the distance between the voxel and the camera plane. Voxels farther from the root joint along the projection direction were suppressed, effectively leveraging depth information for voxel feature reconstruction. While effective, this method has limitations. In crowded operating room environments, where detection frames often overlap, it becomes ambiguous which root joint depth should be used for weighting. Moreover, it assumes that all joints lie at the same depth as the root joint (typically the hip), which is unrealistic—joints such as arms can be significantly offset. To overcome these issues, we propose a more fine-grained approach that utilizes pixel-level depth information from the original depth map, enabling more accurate voxel feature reconstruction. The specific reprojection value can be calculated as
where is the distance from to the camera plane ; is the value of in the depth map; reflecting the true depth of the voxel; and is set to 200 based on experience. As Equation (1) shows, heatmap values are attenuated such that voxels closer to the true depth along the same projection ray receive higher weights, while those farther away are increasingly suppressed or eliminated. By directly using the sensor-captured depth map as a reference, this approach avoids reliance on depth estimation networks and pre-generated person detection boxes. Subsequently, the feature vector at spatial position within the feature volume F is obtained by averaging the heatmap values across all camera views, as shown in the following Equation (2):
where V is the number of camera views.
3.3. Encoder–Decoder Structure with Attention Mechanism
In order to better process the information of 2D voxels, we introduced an attention mechanism in the encoder–decoder so that the network can understand multi-scale information more comprehensively.The network structure is shown in Figure 3.
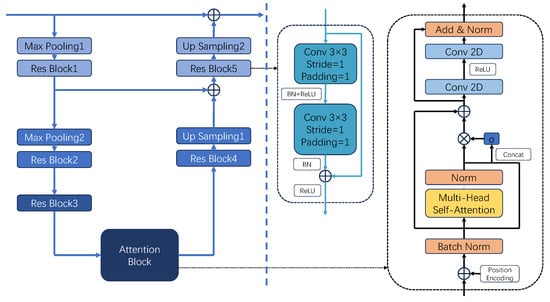
Figure 3.
The encoder–decoder with an attention mechanism.
This network adopts a symmetric encoder–decoder architecture to fuse multi-scale information from 2D voxel features. Features are downsampled twice to one-quarter resolution, and a self-attention module is incorporated at the bottleneck to enhance global context modeling. The encoder employs residual blocks with skip connections to retain multi-scale representations, while the decoder progressively restores spatial details via deconvolution and merges them with encoder features. This design integrates the local feature extraction strengths of CNNs with the global modeling capabilities of attention mechanisms, enabling effective long-range dependency capture while maintaining computational efficiency. Furthermore, the dense connectivity introduced by residual and skip connections helps mitigate gradient vanishing. Overall, the architecture strikes a balance between local detail and global context extraction.
In the Transformer block, spatial awareness is enhanced through positional encoding implemented via convolutions, which are fused with the input features. The resulting representations are then normalized and passed through a multi-head self-attention mechanism to capture global dependencies. The number of attention heads is set to 4 and adopts a channel expansion ratio of 2 within the MLP module. Query (Q), Key (K), and Value (V) matrices are obtained via convolution, followed by self-attention computation as the following Equation (3):
A gating mechanism is introduced to combine the original features with the attention output, generating a gated matrix via convolution. A sigmoid function constrains the gating values between 0 and 1, allowing dynamic adjustment of the attention contribution. This is followed by an MLP layer with channel expansion and compression to further enhance feature representation. Together, this module integrates positional encoding, global attention, dynamic gating, and multi-layer perception. Its strong global modeling capacity enables the network to effectively handle limb occlusion and complex spatial relationships in HPE.
3.4. Human Detection Network
Similar to previous works, our voxel-based network is divided into two stages, a human detection network and a joint localization network. The human detection network is used to locate each person. First, 2D keypoint heatmaps for each camera view are generated using a pre-trained HRNet [38], and the corresponding depth maps are used as additional input for the subsequent network stages. The joint heatmap is back-projected into the voxel space , where K represents the number of joints; X, Y, and Z represent the number of voxels on the x, y, and z axes in the space, respectively; and the actual size of the space is 8 m × 8 m × 2 m. In general, it is less likely that one person is exactly on top of another person, so constructing a two-dimensional bird’s-eye view representation from the feature volume can cleverly and effectively detect people. The voxel space features are projected into xy plane features using maximum pooling along the z axis to obtain . Next, the features are sent to the 2D CNN to predict the person detection box on the xy plane. The output of the 2D CNN consists of two parts. One part is the prediction of the center point of each person from the bird’s-eye view, , which represents the distribution probability of the center point of the human body at each position in the xy plane; the other part is the detection box of each person, , which reflects the width and height of the person detection box.
To supervise the network training, we generate the GT confidence map by placing a Gaussian kernel at the root joint of the human body. The confidence of the (i, j) position can be calculated as
Among them, represents the root joint GT coordinates of the th person, and N is the total number of people. The loss function of this part adopts the mean square error loss, as follows:
To train bounding box estimation, we derive the ground-truth bounding box map from the 3D pose annotations. For each root joint on the xy plane, the bounding box is defined by expanding the 3D pose’s 2D bounding rectangle by 200 mm. Let U denote the set of the above neighboring points, assuming that N is the number of people in the image. We compute the loss for each center point in U, as follows:
Finally, we select higher confidence bounding boxes after non-maximum suppression (NMS) and raise them by a fixed height (e.g., 2000 mm) to form 3D bounding box candidates. These candidates will be input into the joint localization network (JLN) for estimating the 3D pose. In general, the loss function of the human detection network is
where is set to 0.02 according to the backbone.
3.5. The Joint Localization Network
In the joint localization network, we construct fine-grained voxel features based on the 3D detection box obtained by the human detection network to estimate the 3D posture of each person. First, a small space with a size of 2 m × 2 m × 2 m is cut out from the overall space, which is determined according to the theoretical range of motion of a person. The subspace is divided into a voxel grid V’ of . The voxel feature values of the 3D space are obtained by FDPD. The voxel features outside each 3D bounding box are zeroed to mitigate overlap between individuals. Then, the person-specific feature volumes are orthogonally projected onto the xy, yz, and zx planes via max pooling. These 2D projections are fed into an attention-based encoder–decoder to estimate 2D poses on each plane, which are then fused using a lightweight scoring network to reconstruct the 3D pose. Two-dimensional CNN produces a reasonable heatmap estimate for each reprojected plane, denoted as . The joint point coordinates are obtained by calculating the center of mass on the 2D pose heatmap instead of directly taking the maximum value. The joint coordinates estimated for each plane are calculated as
We supervise the joint coordinate estimation through the joint GT value of each plane, and the loss value is calculated as
Similarly, we use a lightweight CNN to calculate a weight for each plane, and apply it to the weighted fusion of the 2D joint estimates of the three planes into 3D pose estimation. The final 3D joint coordinates are calculated as
represents the first component of the 2D joint coordinates on the xy plane, that is, the x-axis component, and the rest of the representations have similar meanings. The weight generation network is supervised by loss, where J represents the GT of the 3D joint point, as follows:
In general, the overall loss of the joint localization network is defined as
4. Experiments
4.1. Datasets
The MVOR dataset [8] is mainly used to train and validate our method. This dataset is a collection of color and depth images from three perspectives collected in real operating room scenes with a resolution of 640 × 480. The dataset recorded four operations in four days, with 57, 330, 223, and 122 frames of static multi-view images. The dataset contains 1061 upper-body poses and is annotated in 2D and 3D formats. These poses contain 10 body joints: head, neck, shoulder, hip, elbow, and wrist, of which the last four joints include left and right parts. Compared with the commonly used CMU Panoptic dataset [21], the Shelf dataset [22], and the Campus dataset [22] for 3D pose estimation, the MVOR dataset has a denser distribution of people in the operating room scenes, and there are more occlusions of medical equipment, making recognition more difficult.
4.2. Metrics
Similar to the method tested on the MVOR dataset before, we adopt the widely used mean per-joint position error (MPJPE) metric. MPJPE measures the average Euclidean distance between the predicted 3D keypoint positions and the corresponding true keypoint positions to quantitatively evaluate the accuracy of pose estimation. MPJPE is computed as follows:
where N is the number of joints, , and represent the predicted and ground-truth 3D coordinates of the i-th joint. At the same time, the average precision () metric is added for evaluation. measures the proportion of correctly estimated poses under a distance threshold K. A pose is considered correct if its MPJPE is less than or equal to K mm, as follows:
By varying K (e.g., 100, 125, 150 mm), we can evaluate the accuracy of pose estimation under different tolerance levels. A higher indicates better robustness and reliability of the model.
4.3. Implementation Details
We use a GeForce RTX 2080 Ti GPU to train our model and conduct all experiments. We use 4-fold cross validation, where each fold retains 1 day of images as the test set. All reported scores are the average of the 4 folds. ResNet-50 is used as the backbone, pre-trained on the COCO dataset, and the weights are jointly fine-tuned on the Panoptic dataset [21]. Specifically, the backbone network pre-trained on the Panoptic dataset adopts a 15-joint skeleton format, with joint indices defined as 0—neck, 1—nose, 2—mid-hip, 3—left shoulder, 4—left elbow, 5—left wrist, 6—left hip, 7—left knee, 8—left ankle, 9—right shoulder, 10—right elbow, 11—right wrist, 12—right hip, 13—right knee, and 14—right ankle. In contrast, the MVOR dataset focuses only on the upper body and defines 10 keypoints: 0—head, 1—neck, 2—left shoulder, 3—right shoulder, 4—left hip, 5—right hip, 6—left elbow, 7—right elbow, 8—left wrist, and 9—right wrist. To align the model output with MVOR’s joint definitions, we modify the fully connected output layer of the backbone by discarding lower-body joints and remapping the remaining channels according to the MVOR format. Additionally, the “nose” joint in Panoptic is treated as the “head” joint in MVOR to ensure semantic consistency between the two datasets. The overall network batch size is set to 8, the epoch is set to 50, the learning rate is set to 1 × 10−4, and the optimizer is Adam.
4.4. Comparison with SOTA
The authors’ method is compared with the SOTA multi-view multi-person 3D pose estimation method on MVOR [8,37]. Due to the limited number of methods verified on MVOR, we also include the voxel-based SOTA method [6]. The results are tested under 3, 2, and 1 views. All comparative methods were retrained or tested on the same dataset splits.
It can be seen in Table 1 that our method consistently achieves the lowest Mean per Joint Position Error (MPJPE) across all view configurations. Specifically, with 3 views, the method achieves an average MPJPE of 7.2 cm, outperforming Faster VoxelPose (8.9 cm) and Gerats et al. (8.3 cm). As the number of views decreases, the method maintains competitive accuracy with an average MPJPE of 9.0 cm in the 2-view case and 12.6 cm in the challenging single-view scenario. In contrast, the performance of other methods drops significantly under fewer views (e.g., MV3DReg reaches 26.9 cm with 1 view).

Table 1.
MPJPE (cm) for different methods and views. Following the convention, the average MPJPE is calculated over shoulders, hips, elbows, and wrists, excluding heads and necks. Standard deviations are calculated over a 4-fold cross validation. Bold indicates the best performance.
Furthermore, the authors’ method demonstrates particularly strong performance on occlusion-prone joints such as the elbow and wrist, indicating enhanced robustness in cluttered operating room environments. These results highlight the effectiveness of the Fine-Grained Depth-Wise Projection Decay and attention-based encoder–decoder in achieving accurate and reliable 3D pose estimation, even under limited camera perspectives.
As for inference time and speed, here is a comparison of the efficiency of Faster VoxelPose and this method on a single NVIDIA RTX 2080Ti GPU. Our method achieves an inference time of 21.73 ms per frame, corresponding to an inference speed of 46.05 frames per second (FPS). In comparison, Faster VoxelPose achieves a faster inference time of 18.50 ms per frame and a higher frame rate of 54.05 FPS. It can be seen that the two have similar real-time performance.
4.5. Ablation Study
4.5.1. Evaluation of FDPD
We conducted extensive experiments to investigate the impact of the Gaussian parameter in the FDPD mechanism, as shown in Table 2. As controls the spread of the Gaussian function, it directly influences the suppression strength applied to voxels during depth-guided projection. A smaller results in a more concentrated Gaussian, causing stronger suppression of voxels farther from the estimated depth, while a larger yields a flatter distribution and weaker suppression.

Table 2.
Performance of FDPD under different values of . Bold indicates the best performance.
Initially, we set = 200 mm following prior work, but this setting led to suboptimal performance, with an MPJPE of 11.2 cm and relatively low AP scores. This is likely due to inherent noise in the MVOR dataset’s depth maps, where overly strict suppression may eliminate informative features. Specifically, a smaller (e.g., 200 mm) results in narrow Gaussian decay, strongly suppressing voxels deviating from estimated depth, but may also attenuate valid joints due to depth noise. A larger (e.g., 2000 mm) increases robustness to sensor noise, which is critical in the MVOR dataset where depth maps are known to be noisy. As increases, performance improves, reaching optimal results at = 2000 mm, with the lowest MPJPE of 7.2 cm and the highest AP scores: = 68.93, = 77.51, and = 83.15.
However, setting to be too large (e.g., 3000 mm) again degrades performance, likely due to insufficient differentiation between in-depth and out-of-depth voxels, leading to a loss of spatial precision. These results demonstrate that choosing an appropriate is crucial for balancing depth sensitivity and robustness to noise, with = 2000 mm providing the best overall performance in our setup.
4.5.2. Evaluation of Attention Mechanism
To thoroughly assess the contribution of each component in our attention-enhanced encoder–decoder architecture, we conduct an ablation study focusing on the attention mechanism, position encoding, and gating mechanism. The results are presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
Ablation study results on attention mechanism. The results demonstrate the effectiveness of our design using attention mechanism, position encoding, and gating mechanism. √: module is used; ×: module is not used. Bold indicates the best performance.
To begin with, a baseline model (row (a)) does not include any of the three modules. Adding only the attention mechanism (row (b)) results in a notable improvement, reducing the Mean per Joint Position Error (MPJPE) from 9.8 cm to 9.4 cm and increasing and by nearly , indicating the effectiveness of global feature modeling through self-attention.
Next, we investigate the impact of the position encoding module. As shown in row (c) of Table 3, incorporating position encoding into the attention module further enhances performance, achieving 60.31 and 75.10 and reducing MPJPE to 8.3 cm. This demonstrates that position encoding helps the model better capture spatial structure, providing critical cues for joint localization.
We then evaluate the gating mechanism (row (d)), which adaptively balances the contribution of attention features and original features. This configuration achieves 57.95 , 74.19 , and 8.7 cm MPJPE—outperforming the attention-only model and confirming the benefit of dynamic feature fusion.
Finally, when all three components are combined (row (e), our full model), we achieve the best results across all metrics: 68.93 , 83.15 , and 7.2 cm MPJPE. These results clearly demonstrate the complementary effects of attention, position encoding, and gating. The attention mechanism enhances global context modeling, position encoding improves spatial awareness, and the gating mechanism refines feature fusion—all contributing to more accurate and robust 3D HPE.
4.6. Qualitative Study
Figure 4 presents the qualitative results of our method on the MVOR dataset, including 3D pose estimations; 2D projections on the xy, yz, and zx planes; and 2D keypoint projections overlaid on the original camera images.
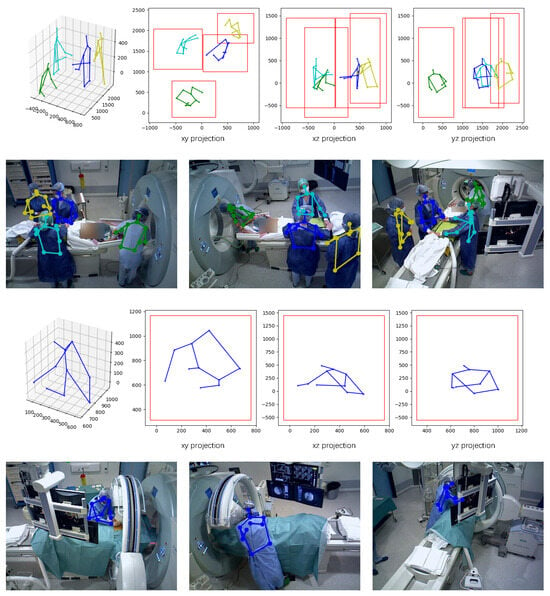
Figure 4.
The qualitative result of our method on MVOR. Red bounding boxes indicate human detection bounding boxes on each projection plane. 3D and 2D Pose estimation of different individuals are marked in distinct colors.
In the first scene, we demonstrate a complex operating room scenario involving four clinicians densely distributed around the patient bed. Each camera view exhibits severe mutual occlusions, with multiple individuals blocking each other. Despite these challenges, our method accurately localizes each person in 3D space from a bird’s-eye view and generates well-separated 2D bounding boxes on the xy plane, effectively minimizing overlap. The estimated 3D joint positions are precise, and their reprojected 2D keypoints remain accurate, even for joints heavily occluded in all views. These results highlight the strength of our approach in handling crowded, occlusion-heavy surgical environments.
The second scene provides a more detailed look at a single individual. In the second view, the subject’s wrist and elbow are self-occluded by the torso, while in the third view, the upper body is almost entirely obscured by surgical equipment. Nonetheless, our method successfully recovers both the 3D pose and its 2D projections with high accuracy. This demonstrates the robustness of our framework to both inter-person and object-induced occlusions.
Overall, these qualitative examples confirm that our method can generate accurate and coherent 3D human poses under real-world surgical conditions, characterized by heavy occlusions, cluttered backgrounds, and limited camera views.
5. Conclusions
This paper presents the first attempt to apply a voxel-based, real-time, multi-person, multi-view 3D HPE framework to operating room (OR) environments, which are characterized by densely distributed personnel and severe occlusions caused by medical equipment and human interactions. To address the unique challenges of OR scenarios, we propose two key technical contributions.
First, we improve the voxel feature volume construction process by introducing Fine-Grained Depth-Wise Projection Decay (FDPD), which leverages pixel-level depth information from real sensor data instead of relying on additional depth prediction networks or coarse root joint approximations. This approach significantly enhances the model’s ability to reconstruct accurate voxel features, particularly when the number of available camera views is limited.
Second, we integrate an attention-enhanced encoder–decoder architecture that incorporates self-attention, position encoding, and a gating mechanism to effectively capture both local and global spatial relationships. This design improves the network’s robustness to severe occlusions and enables better modeling of complex human interactions in constrained surgical spaces.
Extensive experiments on the MVOR dataset demonstrate that the authors’ method outperforms existing state-of-the-art approaches across various metrics, especially under reduced camera views. Our model achieves lower MPJPE and higher AP scores, while maintaining real-time performance. The results confirm the effectiveness, efficiency, and practical value of our approach in realistic clinical scenarios, paving the way for intelligent, vision-based surgical monitoring and human behavior understanding in the operating room.
While the method is developed for operating room scenarios, the framework can be extended to other constrained environments, such as industrial workspaces, or human–robot collaboration setups. However, the surgical setting imposes limitations on data availability and camera configuration, which may affect generalization.
Naturally, the proposed method also has certain limitations. For instance, it constructs 3D voxels based solely on single-frame information and does not fully exploit the temporal correlations between consecutive frames. In addition, the method relies heavily on the extrinsic calibration of multi-view cameras. Its performance degrades significantly when the camera configuration changes due to environmental variations, indicating limited generalization capability.
In future research, we aim to tackle several key challenges in 3D HPE for surgical environments. First, the acquisition of large-scale, high-quality annotated data in operating rooms is constrained by privacy concerns, limited camera deployment, and the complexity of generating accurate ground-truth labels. To address this, we plan to investigate unsupervised or weakly supervised learning approaches, which refer to training models with limited or imprecise labels (e.g., pseudo-labels, partial annotations), as an intermediate paradigm between fully supervised and unsupervised learning that reduce reliance on manual annotations. Second, we are interested in exploring privacy-preserving multi-modal learning, leveraging modalities such as depth, infrared, or inertial signals to enhance robustness while minimizing the exposure of sensitive visual information.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.L.; methodology, J.L. and X.R.; software, J.L.; validation, J.L.; formal analysis, J.L.; investigation, J.L.; resources, J.L.; data curation, J.L.; writing—original draft preparation, J.L.; writing—review and editing, J.L.; visualization, J.L.; supervision, J.L.; project administration, J.L., S.X. and T.Q.; funding acquisition, Y.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 32472005.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original data presented in this study are openly available in GitHub at https://github.com/CAMMA-public/mvor (accessed on 1 March 2025).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Mascagni, P.; Padoy, N. OR black box and surgical control tower: Recording and streaming data and analytics to improve surgical care. J. Visc. Surg. 2021, 158, S18–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özsoy, E.; Pellegrini, C.; Czempiel, T.; Tristram, F.; Yuan, K.; Bani-Harouni, D.; Eck, U.; Busam, B.; Keicher, M.; Navab, N. Mm-or: A large multimodal operating room dataset for semantic understanding of high-intensity surgical environments. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Conference, Nashville, TN, USA, 11–15 June 2025; pp. 19378–19389. [Google Scholar]
- Profetto, L.; Gherardelli, M.; Iadanza, E. Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) in health care: Where are we? A scoping review. Health Technol. 2022, 12, 879–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, H.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, N.; Zeng, W. Cross view fusion for 3D human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27–28 October 2019; pp. 4342–4351. [Google Scholar]
- Iskakov, K.; Burkov, E.; Lempitsky, V.; Malkov, Y. Learnable triangulation of human pose. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27–28 October 2019; pp. 7718–7727. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, H.; Zhu, W.; Wang, C.; Wu, R.; Wang, Y. Faster voxelpose: Real-time 3D human pose estimation by orthographic projection. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; pp. 142–159. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, Z.; Zhou, Y. FasterVoxelPose+: Fast and accurate voxel-based 3D human pose estimation by depth-wise projection decay. In Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Machine Learning, Hanoi, Vietnam, 5–8 December 2024; pp. 1763–1778. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastav, V.; Issenhuth, T.; Kadkhodamohammadi, A.; de Mathelin, M.; Gangi, A.; Padoy, N. MVOR: A multi-view RGB-D operating room dataset for 2D and 3D human pose estimation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1808.08180. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16×16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Lupión, M.; Polo-Rodríguez, A.; Medina-Quero, J.; Sanjuan, J.F.; Ortigosa, P.M. 3D human pose estimation from multi-view thermal vision sensors. Inf. Fusion 2024, 104, 102154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldo, M.; De Marchi, M.; Martini, E.; Aldegheri, S.; Quaglia, D.; Fummi, F.; Bombieri, N. Real-time multi-camera 3D human pose estimation at the edge for industrial applications. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 252, 124089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Ye, X. GAN-BodyPose: Real-time 3D human body pose data key point detection and quality assessment assisted by generative adversarial network. Image Vis. Comput. 2024, 149, 105144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastav, V.; Chen, K.; Padoy, N. Selfpose3d: Self-supervised multi-person multi-view 3D pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 2502–2512. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.J.; Xu, Y.; Khirodkar, R.; Park, J.; Kitani, K. Multi-person 3D pose estimation from multi-view uncalibrated depth cameras. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.15616. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Z.; Lu, K.; Xue, J.; Wang, J. Skeleton Cluster Tracking for robust multi-view multi-person 3D human pose estimation. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2024, 246, 104059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amara, K.; Guerroudji, M.A.; Zenati, N.; Kerdjidj, O.; Atalla, S.; Mansoor, W.; Ramzan, N. Augmented Reality localisation using 6 DoF phantom head Pose Estimation-based generalisable Deep Learning model. In Proceedings of the 2024 8th International Conference on Image and Signal Processing and their Applications (ISPA), Biskra, Algeria, 21–22 April 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.; Shu, Q.; Huang, Z.; Chen, G.; Poslad, S. ARLO: Augmented Reality Localization Optimization for Real-Time Pose Estimation and Human–Computer Interaction. Electronics 2025, 14, 1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Xiao, M.; Xie, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Jin, G.; Shuai, L. In-bed human pose estimation using multi-source information fusion for health monitoring in real-world scenarios. Inf. Fusion 2024, 105, 102209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoy, A.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, M.; Yang, W.; Geng, H.; Jiang, K.; Yuan, X.; Geng, Z. Image-free single-pixel keypoint detection for privacy preserving human pose estimation. Opt. Lett. 2024, 49, 546–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehin, S.; Kearney, S.; Gurbuz, Z. Kinematic Cycle Consistency Using Wearables and RF Data for Improved Human Skeleton Estimation. In Proceedings of the 2024 58th Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems, and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 27–30 October 2024; pp. 1215–1219. [Google Scholar]
- Joo, H.; Liu, H.; Tan, L.; Gui, L.; Nabbe, B.; Matthews, I.; Kanade, T.; Nobuhara, S.; Sheikh, Y. Panoptic studio: A massively multiview system for social motion capture. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 3334–3342. [Google Scholar]
- Belagiannis, V.; Amin, S.; Andriluka, M.; Schiele, B.; Navab, N.; Ilic, S. 3D pictorial structures for multiple human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 1669–1676. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Du, X.; Quan, S.; Xu, Y. PoP-Net: Pose Over Parts Network for Multi-Person 3D Pose Estimation From a Depth Image. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2022; pp. 1240–1249. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, T.; Billingham, J.; Müksch, S.; Zarate, J.; Evans, N.; Oswald, M.; Pollefeys, M.; Hilliges, O.; Kaufmann, M.; Song, J. WorldPose: A World Cup Dataset for Global 3D Human Pose Estimation. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, H.; Wang, C.; Zeng, W. Voxelpose: Towards multi-camera 3D human pose estimation in wild environment. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Proceedings, Part I 16. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 197–212. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, C.; Zhu, S.; Mendieta, M.; Yang, T.; Chen, C.; Ding, Z. 3D human pose estimation with spatial and temporal transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 11656–11665. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Cai, Y.; Yan, S.; Feng, J. Direct multi-view multi-person 3D pose estimation. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 13153–13164. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, M.; Liu, H.; Li, W. SVTformer: Spatial-View-Temporal Transformer for Multi-View 3D Human Pose Estimation. Proc. Aaai Conf. Artif. Intell. 2025, 39, 10148–10156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ai, H.; Chen, R.; Zhuang, Z.; Liu, S. Cross-view tracking for multi-human 3D pose estimation at over 100 fps. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 3279–3288. [Google Scholar]
- Maier-Hein, L.; Eisenmann, M.; Sarikaya, D.; März, K.; Collins, T.; Malpani, A.; Fallert, J.; Feussner, H.; Giannarou, S.; Mascagni, P.; et al. Surgical data science–from concepts toward clinical translation. Med. Image Anal. 2022, 76, 102306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özsoy, E.; Czempiel, T.; Örnek, E.P.; Eck, U.; Tombari, F.; Navab, N. Holistic or domain modeling: A semantic scene graph approach. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2024, 19, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belagiannis, V.; Wang, X.; Shitrit, H.B.B.; Hashimoto, K.; Stauder, R.; Aoki, Y.; Kranzfelder, M.; Schneider, A.; Fua, P.; Ilic, S.; et al. Parsing human skeletons in an operating room. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2016, 27, 1035–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özsoy, E.; Örnek, E.P.; Eck, U.; Czempiel, T.; Tombari, F.; Navab, N. 4d-or: Semantic scene graphs for or domain modeling. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Singapore, 18–22 September 2022; pp. 475–485. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, L.; Siebert, M.; Diesel, J.; Heinrich, M.P. Fusing information from multiple 2D depth cameras for 3D human pose estimation in the operating room. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2019, 14, 1871–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadkhodamohammadi, A.; Padoy, N. A generalizable approach for multi-view 3D human pose regression. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2021, 32, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastav, V.; Gangi, A.; Padoy, N. Unsupervised domain adaptation for clinician pose estimation and instance segmentation in the operating room. Med. Image Anal. 2022, 80, 102525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerats, B.G.; Wolterink, J.M.; Broeders, I.A. 3D human pose estimation in multi-view operating room videos using differentiable camera projections. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. Imaging Vis. 2023, 11, 1197–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Xiao, B.; Liu, D.; Wang, J. Deep high-resolution representation learning for human pose estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 5693–5703. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).