The Role of Large Language Models in Improving Diagnostic-Related Groups Assignment and Clinical Decision Support in Healthcare Systems: An Example from Radiology and Nuclear Medicine
Abstract
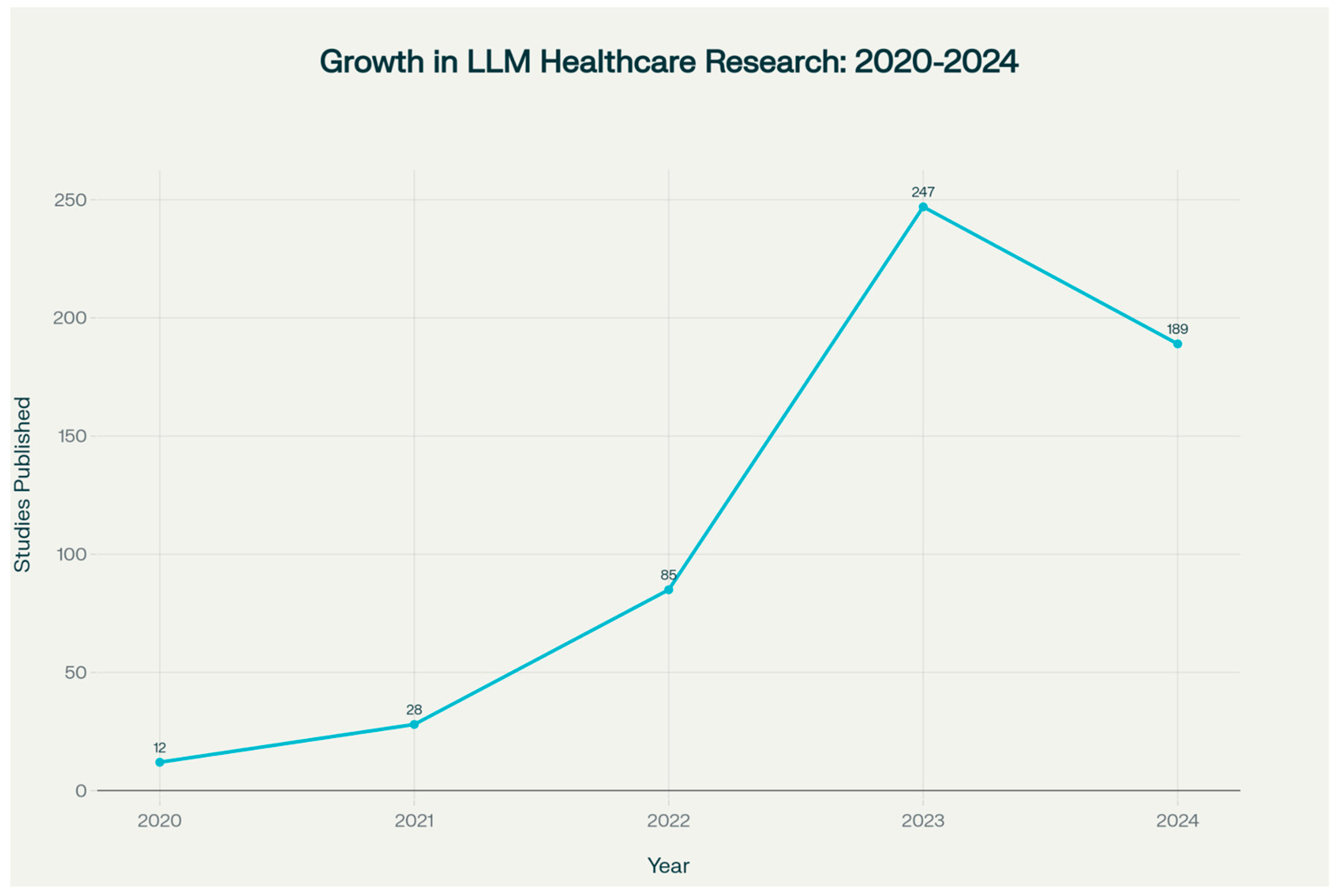
1. Introduction
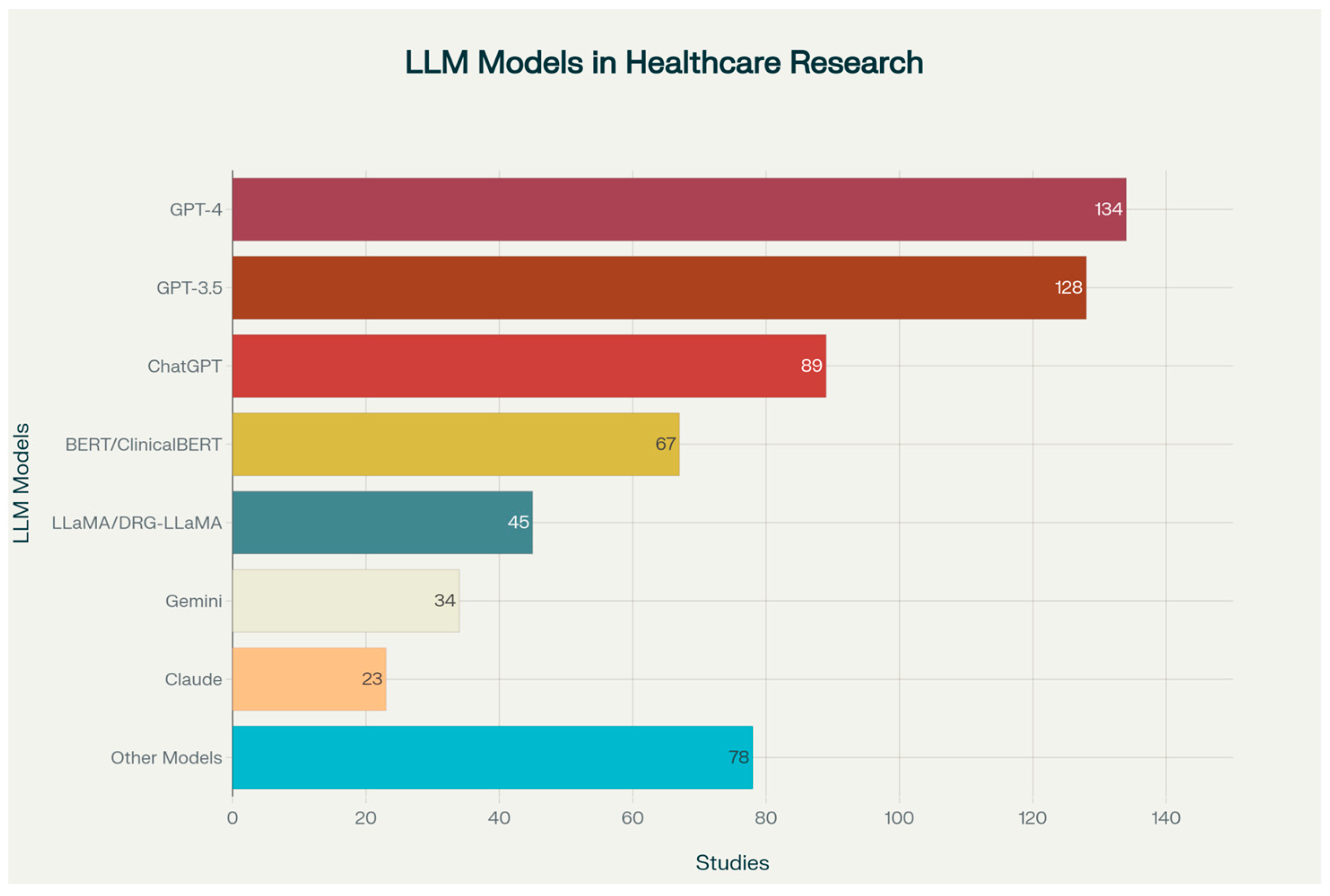
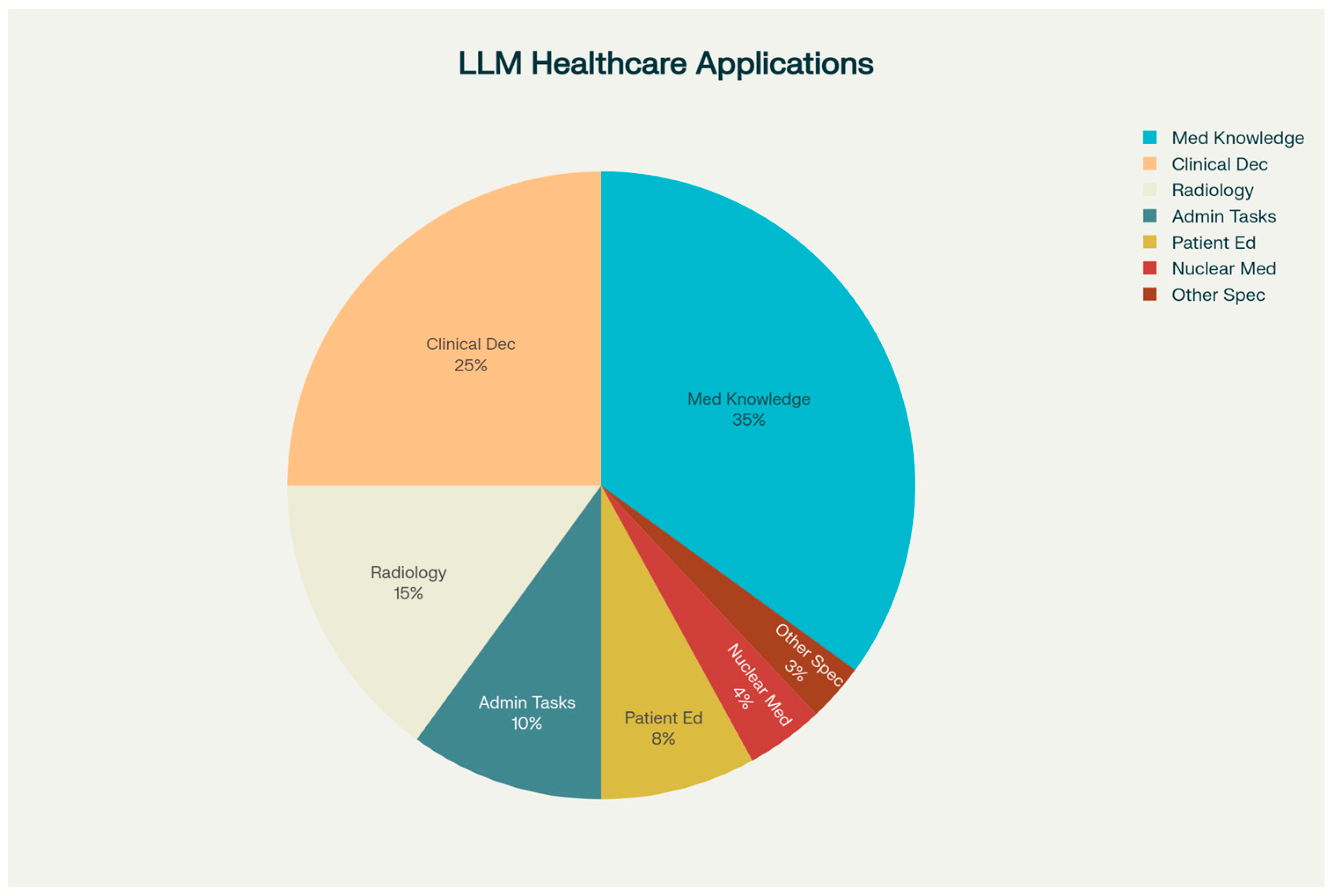
2. Scope of LLM Integration in Healthcare
2.1. LLM Applications in DRG Assignment
2.2. Clinical Decision Support Systems Enhanced by LLMs
2.3. Radiology-Specific Applications
2.4. Nuclear Medicine Applications
3. Implementation Challenges
3.1. Ethical and Safety Considerations
3.2. Economic Impact and Cost-Effectiveness
3.3. Technical Performance and Validation
4. Future Directions and Research Priorities
4.1. Emerging LLM Technologies and Capabilities
4.2. Integration with Precision Medicine and Personalized Care
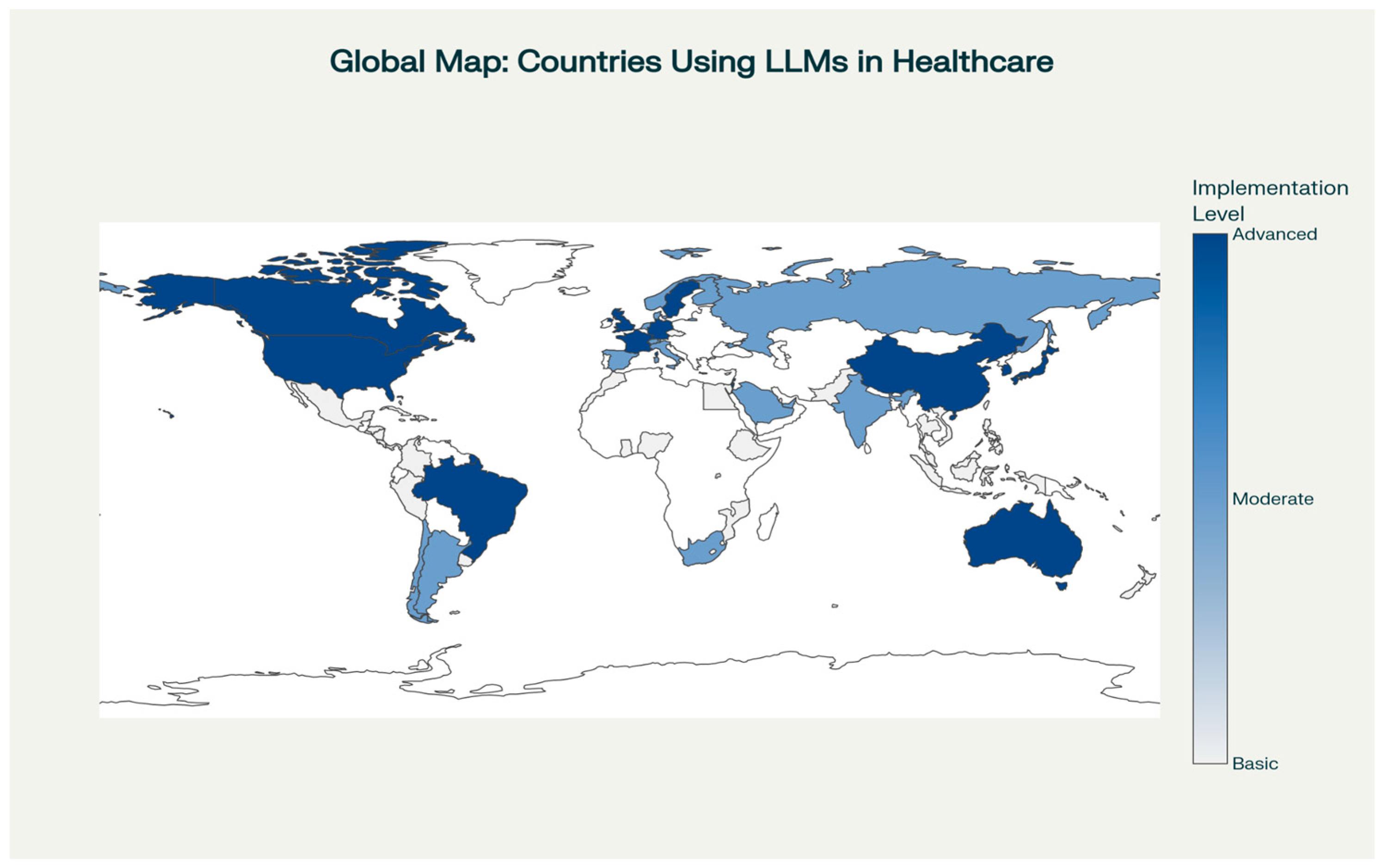
4.3. Global Implementation Strategies
5. Limitations of the Review
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| BI-RADS | Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System |
| CDS | Clinical Decision Support |
| CDSS | Clinical Decision Support System(s) |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| DRG | Diagnosis-Related Group |
| DRG-LLaMA | Diagnosis-Related Group-LLaMA (LLM fine-tuned for DRG) |
| EHR | Electronic Health Record |
| EMR | Electronic Medical Record |
| GPT | Generative Pre-trained Transformer |
| GPT-3.5/GPT-4 | Generative Pre-trained Transformer, Versions 3.5 and 4 |
| HIPAA | Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act |
| IE | Information Extraction |
| LLaMa | Large Language Model Meta AI |
| LI-RADS | Liver Imaging Reporting and Data System |
| LLM | Large Language Model |
| MRScore | Model-based Radiology Score (LLM-based radiology eval.) |
| NLP | Natural Language Processing |
| PAC | Picture Archiving and Communication System |
| PET | Positron Emission Tomography |
| PI-RADS | Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System |
| RAG | Retrieval-Augmented Generation |
| RIS | Radiology Information System |
| SR | Structured Reporting |
| XAI | Explainable Artificial Intelligence |
References
- Maity, S.; Saikia, M.J. Large Language Models in Healthcare and Medical Applications: A Review. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Garadi, M.; Mungle, T.; Ahmed, A.; Sarker, A.; Miao, Z.; Matheny, M.E. Large Language Models in Healthcare. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2503.04748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, P.; Henkel, M.; Bamberg, F.; Kotter, E. Integration von Large Language Models in die Klinik: Revolution in der Analyse und Verarbeitung von Patientendaten zur Steigerung von Effizienz und Qualität in der Radiologie [Integration of large language models into the clinic: Revolution in analysing and processing patient data to increase efficiency and quality in radiology]. Radiologie 2025, 65, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Yan, X.; Zhang, K.; Liu, D.; Cui, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Cao, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; et al. The application of large language models in medicine: A scoping review. iScience 2024, 27, 109713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Shu, P.; Zhong, A.; Jiang, H.; Pan, Y.; Yang, L.; Ju, C.; Wu, Z.; Ma, C.; et al. Radiology-GPT: A large language model for radiology. Meta Radiol. 2025, 3, 100153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, H.A.; Aoun, A.; Munshi, S.; Abdel-Megid, H.; Nazario-Johnson, L.; Ahn, S.H. The Application of Large Language Models for Radiologic Decision Making. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2024, 21, 1072–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’aNtonoli, T.A.; Stanzione, A.; Bluethgen, C.; Vernuccio, F.; Ugga, L.; Klontzas, M.E.; Cuocolo, R.; Cannella, R.; Koçak, B. Large language models in radiology: Fundamentals, applications, ethical considerations, risks, and future directions. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2024, 30, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, F.; Hoffmann, L.; dos Santos, D.P.; Makowski, M.R.; Saba, L.; Prucker, P.; Hadamitzky, M.; Navab, N.; Kather, J.N.; Truhn, D.; et al. Large language models for structured reporting in radiology: Past, present, and future. Eur. Radiol. 2024, 35, 2589–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Xu, H.; Hu, X.; Deng, C. Leveraging Generative AI and Large Language Models: A Comprehensive Roadmap for Healthcare Integration. Healthcare 2023, 11, 2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkalbani, A.M.; Alrawahi, A.S.; Salah, A.; Haghighi, V.; Zhang, Y.; Alkindi, S.; Sheng, Q.Z. A Systematic Review of Large Language Models in Medical Specialties: Applications, Challenges and Future Directions. Information 2025, 16, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Gao, C.; Dantona, C.; Hull, B.; Sun, J. DRG-LLaMA: Tuning LLaMA model to predict diagnosis-related group for hospitalized patients. NPJ Digit. Med. 2024, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhou, Z.; Lyu, H.; Wang, Z. Large language models-powered clinical decision support: Enhancing or replacing human expertise? Intell. Med. 2025, 5, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaber, F.; Shaik, M.; Allega, F.; Bilecz, A.J.; Busch, F.; Goon, K.; Franke, V.; Akalin, A. Evaluating large language model workflows in clinical decision support for triage and referral and diagnosis. NPJ Digit. Med. 2025, 8, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrdoljak, J.; Boban, Z.; Vilović, M.; Kumrić, M.; Božić, J. A Review of Large Language Models in Medical Education, Clinical Decision Support, and Healthcare Administration. Healthcare 2025, 13, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oumano, M.A.; Pickett, S.M. Comparison of Large Language Models’ Performance on 600 Nuclear Medicine Technology Board Examination-Style Questions. J. Nucl. Med. Technol. 2025. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargari, O.K.; Habibi, G. Enhancing medical AI with retrieval-augmented generation: A mini narrative review. Digit. Health 2025, 11, 20552076251337177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vithanage, D.; Deng, C.; Wang, L.; Yin, M.; Alkhalaf, M.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, P. Adapting Generative Large Language Models for Information Extraction from Unstructured Electronic Health Records in Residential Aged Care: A Comparative Analysis of Training Approaches. J. Health Inf. Res. 2025, 9, 191–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, S.; Sukumaran, R.; Cook, T.S. Efficient healthcare with large language models: Optimizing clinical workflow and enhancing patient care. J. Am. Med. Inf. Assoc. 2024, 31, 1436–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Liang, X.; Liu, L.; Wang, L.; Zhou, L. MRScore: Evaluating Radiology Report Generation with LLM-based Reward System. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.17778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voinea, Ş.V.; Mămuleanu, M.; Teică, R.V.; Florescu, L.M.; Selișteanu, D.; Gheonea, I.A. GPT-Driven Radiology Report Generation with Fine-Tuned Llama 3. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, X.; Liu, B. Large Language Models in Summarizing Radiology Report Impressions for Lung Cancer in Chinese: Evaluation Study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2025, 27, e65547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, H.; Sun, X.; He, H.; Feng, J. Prompt-Guided Generation of Structured Chest X-Ray Report Using a Pre-trained LLM. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.11209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhaldi, A.; Alnajim, R.; Alabdullatef, L.; Alyahya, R.; Chen, J.; Zhu, D.; Alsinan, A.; Elhoseiny, M. MiniGPT-Med: Large Language Model as a General Interface for Radiology Diagnosis. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.04106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altalla’, B.; Ahmad, A.; Bitar, L.; Al-Bssol, M.; Al Omari, A.; Sultan, I. Radiology Report Annotation Using Generative Large Language Models: Comparative Analysis. Int. J. Biomed. Imaging 2025, 2025, 5019035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huemann, Z.; Lee, C.; Hu, J.; Cho, S.Y.; Bradshaw, T.J. Domain-adapted Large Language Models for Classifying Nuclear Medicine Reports. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 2023, 5, e220281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Lee, D.; Kang YKoo Suh, M. Empowering PET imaging reporting with retrieval-augmented large language models and reading reports database: A pilot single center study. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2025, 52, 2452–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, K.; Matsui, Y.; Yamada, A.; Fujioka, T.; Yanagawa, M.; Nakaura, T.; Ito, R.; Ueda, D.; Fujita, S.; Tatsugami, F.; et al. Generative AI and large language models in nuclear medicine: Current status and future prospects. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2024, 38, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberts, I.L.; Mercolli, L.; Pyka, T.; Prenosil, G.; Shi, K.; Rominger, A.; Afshar-Oromieh, A. Large language models (LLM) and ChatGPT: What will the impact on nuclear medicine be? Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2023, 50, 1549–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koller, P.; Clement, C.; van Eijk, A.; Seifert, R.; Zhang, J.; Prenosil, G.; Sathekge, M.M.; Herrmann, K.; Baum, R.; Weber, W.A.; et al. Optimizing theranostics chatbots with context-augmented large language models. Theranostics 2025, 15, 5693–5704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vachatimanont, S.; Kingpetch, K. Exploring the capabilities and limitations of large language models in nuclear medicine knowledge with primary focus on GPT-3.5, GPT-4 and Google Bard. J. Med. Artif. Intell. 2024, 7, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Yang, G.; Jiang, Z.; Cui, S.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Tao, L.; Sun, Y.; Song, Z.; et al. Medical large language model for diagnostic reasoning across specialties. Nat. Med. 2025, 31, 743–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Jeong, H.; Chen, S.; Li, S.S.; Lu, M.; Alhamoud, K.; Mun, J.; Grau, C.; Jung, M.; Gameiro, R. Medical Hallucinations in Foundation Models and Their Impact on Healthcare. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2503.05777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, N. AI hallucinations can’t be stopped—But these techniques can limit their damage. Nature 2025, 637, 778–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asgari, E.; Montaña-Brown, N.; Dubois, M.; Khalil, S.; Balloch, J.; Yeung, J.A.; Pimenta, D. A framework to assess clinical safety and hallucination rates of LLMs for medical text summarisation. NPJ Digit. Med. 2025, 8, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiseleva, A.; Kotzinos, D.; De Hert, P. Transparency of AI in Healthcare as a Multilayered System of Accountabilities: Between Legal Requirements and Technical Limitations. Front. Artif. Intell. 2022, 5, 879603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeghi, Z.; Alizadehsani, R.; Cifci, M.A.; Kausar, S.; Rehman, R.; Mahanta, P.; Bora, P.K.; Almasri, A.; Alkhawaldeh, R.S.; Hussain, S.; et al. A review of Explainable Artificial Intelligence in healthcare. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2024, 118, 109370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Heacock, L.; Elias, J.; Hentel, K.D.; Reig, B.; Shih, G.; Moy, L. ChatGPT and Other Large Language Models Are Double-edged Swords. Radiology 2023, 307, e230163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Gulhane, A.; Mastrodicasa, D.; Wu, W.; Wang, E.J.; Sahani, D.; Patel, S. Demographic bias of expert-level vision-language foundation models in medical imaging. Sci. Adv. 2025, 11, eadq0305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Jin, Q.; Huang, F.; Lu, Z. Unmasking and quantifying racial bias of large language models in medical report generation. Commun. Med. 2024, 4, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, S.L.; Shapiro, D. An Ethically Supported Framework for Determining Patient Notification and Informed Consent Practices When Using Artificial Intelligence in Health Care. Chest 2024, 166, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, H.; Fotheringham, K. Artificial intelligence in clinical decision-making: Rethinking liability. Med. Law Int. 2020, 20, 131–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuadas, M.; Albikawi, Z.; Rayani, A. The impact of an AI-focused ethics education program on nursing students’ ethical awareness, moral sensitivity, attitudes, and generative AI adoption intention: A quasi-experimental study. BMC Nurs. 2025, 24, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aucouturier, E.; Grinbaum, A. Training Bioethics Professionals in AI Ethics: A Framework. J. Law Med. Ethic 2025, 53, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Tang, K.; Chen, M.; Wang, B. A Comprehensive Survey on Evaluating Large Language Model Applications in the Medical Industry. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.15777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasian, M.; Khatibi, E.; Azimi, I.; Oniani, D.; Abad, Z.S.H.; Thieme, A.; Sriram, R.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Lin, B.; et al. Foundation metrics for evaluating effectiveness of healthcare conversations powered by generative AI. NPJ Digit. Med. 2024, 7, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Yu, J.; Chen, S.; Liu, C.; Wan, Z.; Bitterman, D.; Wang, F.; Shu, K. ClinicalBench: Can LLMs Beat Traditional ML Models in Clinical Prediction? arXiv 2024, arXiv:2411.06469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Han, K. Methodologic Guide for Evaluating Clinical Performance and Effect of Artificial Intelligence Technology for Medical Diagnosis and Prediction. Radiology 2018, 286, 800–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Li, Z.; Zhou, H.; Yin, Q.; Yang, J.; Tang, X.; Luo, C.; Zeng, M.; Jiang, H.; Gao, Y.; et al. Large Language Models Are Poor Clinical Decision-Makers: A Comprehensive Benchmark. In Proceedings of the 2024 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Miami, FL, USA, 12–16 November 2024; pp. 13696–13710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldock, W.J.; Zhang, J.; Guni, A.; Nabeel, A.; Darzi, A.; Ashrafian, H. The Accuracy and Capability of Artificial Intelligence Solutions in Health Care Examinations and Certificates: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Med. Internet Res. 2024, 26, e56532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takita, H.; Kabata, D.; Walston, S.L.; Tatekawa, H.; Saito, K.; Tsujimoto, Y.; Miki, Y.; Ueda, D. A systematic review and meta-analysis of diagnostic performance comparison between generative AI and physicians. NPJ Digit. Med. 2025, 8, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.; Choi, D.; Kim, T.; Cha, W.C.; Kim, M.; Yoo, H.; Oh, N.; Yi, Y.; Lee, K.H.; Choi, E. Evaluation Framework of Large Language Models in Medical Documentation: Development and Usability Study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2024, 26, e58329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, S.; Jiang, L.Y.; Gabriel, S.; Aphinyanaphongs, Y.; Oermann, E.K.; Chunara, R. Generalization in Healthcare AI: Evaluation of a Clinical Large Language Model. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.10965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Meng, X.; Yan, X.; Ji, J.; Liu, J.; Xu, H.; Zhang, H.; Liu, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; et al. Revolutionizing Health Care: The Transformative Impact of Large Language Models in Medicine. J. Med. Internet Res. 2025, 27, e59069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Huang, Y.; Shao, J.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; Wang, G.; Wang, C. The potential of large language models to advance precision oncology. EBioMedicine 2025, 115, 105695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aththanagoda, A.K.N.L.; Kulathilake, K.A.S.H.; Abdullah, N.A. Precision and Personalization: How Large Language Models Redefining Diagnostic Accuracy in Personalized Medicine—A Systematic Literature Review. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2025. online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennstädt, F.; Hastings, J.; Putora, P.M.; Schmerder, M.; Cihoric, N. Implementing large language models in healthcare while balancing control, collaboration, costs and security. NPJ Digit. Med. 2025, 8, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kufel, J.; Bargieł, K.; Koźlik, M.; Czogalik, Ł.; Dudek, P.; Jaworski, A.; Magiera, M.; Bartnikowska, W.; Cebula, M.; Nawrat, Z.; et al. Usability of Mobile Solutions Intended for Diagnostic Images—A Systematic Review. Healthcare 2022, 10, 2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorin, V.; Klang, E.; Sklair-Levy, M.; Cohen, I.; Zippel, D.B.; Lahat, N.B.; Konen, E.; Barash, Y. Large language model (ChatGPT) as a support tool for breast tumor board. NPJ Breast Cancer 2023, 9, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Papageorgiou, P.S.; Christodoulou, R.C.; Pitsillos, R.; Petrou, V.; Vamvouras, G.; Kormentza, E.V.; Papagelopoulos, P.J.; Georgiou, M.F. The Role of Large Language Models in Improving Diagnostic-Related Groups Assignment and Clinical Decision Support in Healthcare Systems: An Example from Radiology and Nuclear Medicine. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9005. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15169005
Papageorgiou PS, Christodoulou RC, Pitsillos R, Petrou V, Vamvouras G, Kormentza EV, Papagelopoulos PJ, Georgiou MF. The Role of Large Language Models in Improving Diagnostic-Related Groups Assignment and Clinical Decision Support in Healthcare Systems: An Example from Radiology and Nuclear Medicine. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(16):9005. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15169005
Chicago/Turabian StylePapageorgiou, Platon S., Rafail C. Christodoulou, Rafael Pitsillos, Vasileia Petrou, Georgios Vamvouras, Eirini Vasiliki Kormentza, Panayiotis J. Papagelopoulos, and Michalis F. Georgiou. 2025. "The Role of Large Language Models in Improving Diagnostic-Related Groups Assignment and Clinical Decision Support in Healthcare Systems: An Example from Radiology and Nuclear Medicine" Applied Sciences 15, no. 16: 9005. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15169005
APA StylePapageorgiou, P. S., Christodoulou, R. C., Pitsillos, R., Petrou, V., Vamvouras, G., Kormentza, E. V., Papagelopoulos, P. J., & Georgiou, M. F. (2025). The Role of Large Language Models in Improving Diagnostic-Related Groups Assignment and Clinical Decision Support in Healthcare Systems: An Example from Radiology and Nuclear Medicine. Applied Sciences, 15(16), 9005. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15169005






