Abstract
Lately, anaerobic digestion has become a promising method for producing bioenergy from organic waste and is considered a model of the circular economy. At the same time, the concept of circular economy has gained particular attention in environmental policy agendas supporting the transition towards climate neutrality and the promotion of clean energy sources. Although the main objective of anaerobic digestion is to produce biogas, a significant part of the used substrate is converted into digestate, a by-product. Digestate is composed of organic and inorganic matter, which are considered dangerous contaminants for the environment if not properly treated, but also potential renewable resources if properly recovered. Digestate has enormous potential as an organic fertilizer, soil improver and landfill cover soil, but its disposal and use present significant challenges. The main aim of this review paper is to present the current routes for solid and liquid anaerobic digestate valorization according to circular economy principles and to highlight the relation between anaerobic digestion processes and circular economy models. It further focuses on the aspects regarding anaerobic digestate processing technologies, standards and regulations for digestate use and environmental benefits of its use as soil fertilizer.
1. Introduction
Lately, global waste generation has increased dramatically, with the main contributing factors being human population growth, accelerated urbanization, rapid industrialization and numerous anthropogenic activities [1]. Statistics show that more than two billion tons of municipal solid waste are produced annually worldwide, and this amount is estimated to increase by about 70% by 2050 [2]. This massive increase in waste contributes significantly to environmental degradation and has become a worldwide concern [3,4].
In addition, the burning of fossil fuels, improper waste disposal and unsustainable agricultural activities pose a threat to the future of humanity and ecosystems [5].
Improper waste management practices, including uncontrolled waste disposal, continue to remain a global threat to climate change. In this context, the implementation of effective waste management techniques is essential to reduce the amount of waste landfilled, thus contributing to a sustainable future [3]. Waste management plays an essential role in supporting the principles of sustainable development, as can be seen in various international directives and agendas, such as the 2030 Agenda, Transforming our world: the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development [6,7]. In addition, the concept of circular economy is strongly linked to sustainable development, focusing on continuous resource use, minimizing waste and maximizing resource efficiency [8].
In this context, worldwide, many countries have established targets to decrease waste disposal and increase recycling rates, transforming organic waste into bioenergy. In the European Union (EU), anaerobic digestion (AD) and composting are the most popular methods for treating organic waste [9]. AD is a well implemented and widely utilized technology used both for treating sludge produced in wastewater treatment plants and for managing organic waste [10]. Thus, AD is positioned at the intersection of wastewater treatment and effective management of organic waste, offering an integrated approach for both the valorization of organic waste and the generation of renewable energy.
In comparison with thermal and chemical methods, AD represents an effective solution for organic waste valorization, due to its merits, such as reducing the environmental impact by minimizing the volume of stored waste and energy recovery. In addition, AD is also used as a treatment method for stabilizing sewage sludge [11]. In the AD process, organic substrates are decomposed by complex microbial consortia to produce biogas, a renewable energy source, and a nutrient-rich digestate as by-product, which can be used to produce bio-based fertilizers [12,13,14]. The biogas and digestate are the most promising alternatives to fossil fuels and biofertilizers. Furthermore, the AD process provides a practical approach to waste management, energy recovery and nutrient recycling, being in accordance with the EU directives involving waste reduction and recovery and promoting clean technologies. Thus, AD is a promising solution that combines several economic and environmental benefits [15,16,17]. The specialized literature includes studies focusing on the anaerobic digestion process of organic waste and digestate production, as well as their integration into the circular economy. Seruga et al. [9] presented an anaerobic digestion method as a component of circular bioeconomy. Their results indicated that the average biogas production rate of 120 Nm3/ton of fresh waste can be achieved. Furthermore, the reduction of CO2 emissions was between 25.3 and 26.6% total, considering the fact that using biogas is environmentally friendly. In his review article, Huang X. [10] highlights the importance of the circular economy in achieving low-carbon goals. In addition, the author presents a comprehensive overview of the advances and challenges of anaerobic digestion technology in waste treatment plants, identifying critical challenges, such as high investment costs, technical inefficiencies, and regulatory barriers, particularly in developing countries. In another paper, Rizzioli et al. [13] reviewed several technologies in terms of nitrogen recovery for various bio-based fertilizers.
In 2020, according to data provided by the European Biogas Association (EBA), over 20,000 biogas installations were operating in Europe. Furthermore, EBA has estimated the total amount of digestate produced in Europe for the years 2030 and 2050; namely, 75 million tons (Mt) of dry matter (DM) of digestate can be produced by 2030, while 177 Mt DM is the total digestate potential for 2050 [18,19]. Due to its properties, the main utilization of digestate produced in biogas plants is as a bio-fertilizer in agriculture, but, depending on the application type, different processing techniques, such as solid–liquid separation, dehydration, biological and thermal processes may be required [20]. However, without proper treatment, the discharge of digestate threatens the environment and produces significant amounts of greenhouse gas emissions. [21]. Other significant environmental risks associated with untreated digestate include the potential presence of pathogenic microorganisms, heavy metals—particularly in digestate produced by biogas plants that process sewage sludge—and antibiotic resistance genes, especially when antibiotics have been used in the treatment of sick animals [22,23].
The main aim of this review paper is to present the current routes for solid and liquid anaerobic digestate valorization in accordance with circular economy principles and to highlight the relationship between AD processes and circular economy models. It further focuses on the aspects regarding anaerobic digestate processing technologies, standards and regulations for digestate use and environmental benefits of its use as soil fertilizer.
2. Anaerobic Digestion and Circular Economy Model
The concepts of waste management and circular economy are interconnected, and both are essential for promoting sustainable development. Today’s economy mainly follows a linear model, based on the “take-make-use-dispose” principle, in which resources are extracted, utilized and ultimately disposed of as waste. The transition from the current linear economy to a circular one involves extending the life cycle of products through actions such as reuse, repair and recycling. The implementation of the circular economy concept is based on preventing and minimizing waste generation [24,25]. This means that this concept is based on the fact that waste generated from a technological process can be used as raw material for other processes, which supports the notion of waste elimination. Thus, adopting a circular economy model allows for the assessment of the degree of circularity in waste management, while also promoting sustainable development [26]. In 2020, the European Commission adopted the circular economy action plan, aiming, among other objectives, to promote the use of secondary raw materials, what will support sustainable development [27].
Different strategies have been proposed to support the transition from linear to circular economy. The concepts supporting these strategies include, among others: sustainable and eco-friendly product design, energy efficiency, the application of the 3R’s strategy (reduce–reuse–recycle), sometimes extended to the 9R’s strategy (refuse, rethink, reduce, reuse, repair, refurbish, remanufacture, repurpose, recycle or recover), and industrial symbiosis (by-products of one industry form raw materials for another industry) [28,29,30,31].
Applying the circular economy concept also promotes environmental protection while supporting economic growth, in line with sustainable development [32]. Thus, a sustainable way to mitigate current environmental challenges is to turn waste into renewable energy [5]. The waste valorization process allows the integration of circular economy principles, based on the conversion of waste into valuable products, thus leading to a considerable reduction in the carbon footprint [33].
The EU’s energy and climate policies have encouraged the promotion of renewable energy resources. The Renewable Energy Directive (RED II) [34] and the EU Action Plan on Circular Economy [27] promote both the sustainable use of biodegradable waste and the transition to renewable energy sources such as biogas. In this context, AD has become one of the most promising methods to recover energy from organic waste. In Europe, biogas is produced by anaerobic fermentation in anaerobic digesters using agricultural waste, municipal organic waste, manure, energy crops and sewage sludge as feedstock [9,35]. The process of AD not only generates energy from biogas but also helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions, recover nutrients and reduce dissolved oxygen, thus contributing to the achievement of SDGs [36].
Biogas serves as the primary vector for producing bioenergy from organic waste through anaerobic digestion (AD) in the modern bioeconomy [37]. This process not only generates renewable energy but also yields a by-product known as digestate—a solid–liquid residue with a high moisture content and rich in nutrients. As a result, AD contributes to the production of a stable and agronomically valuable organic fertilizer [5,38]. The valorization of organic waste through AD aligns with circular economy principles by transforming waste into bioenergy and value-added products, thereby supporting the transition to a low-carbon future [37,39]. Consequently, the overall sustainability of AD plants relies not only on energy production but also on the efficient and responsible management of digestion residues [40]. In particular, the high water content of the anaerobic digestate leads to high transportation volumes and costs, transportation distances depending on the location of the biogas plant [41]. Consequently, sustainable digestate management systems need to be developed, including options for digestate processing within the biogas plant or ex-situ digestate processing [42]. To overcome this limitation, the digestate is separated into two phases: the liquid fraction and the more fibrous solid fraction, to decrease the volume and, hence, the transportation cost [43]. Digestate is frequently used as a soil amendment due to its nutrient content or as a substrate for pyrolysis and gasification processes to produce biochar. However, the variety of microorganisms found in digestate may help to increase the range of possible uses for it. Digestate has proven to contain agronomically beneficial microorganisms, such as nitrogen-fixing bacteria, denitrifying and nitrifying bacteria, saprophytic fungi and soil methanogens. Moreover, microorganisms obtained from digestate can also be used in the soil bioremediation process, due to their ability to degrade aliphatic hydrocarbons from oil-polluted soils [44]. Based on corn production, the liquid digestate fraction from food waste, corn silage co-digestate and swine manure can replace commercial N fertilizer with greater environmental advantages, particularly for soil health. In addition, the liquid fraction of the digestate can be diluted and used as a medium for the cultivation of micro- and macroalgae, which are subsequently used as feedstock for biofuel production. On the other hand, the solid fraction of the co-digestate can be composted to enhance the quality of the digestate [45].
3. Anaerobic Biogas Digestate: Production and Processing
AD is a biological process where microorganisms break down organic matter (such as agricultural residues, food waste, animal manure or sewage sludge) in the absence of oxygen, producing biogas (a mixture of methane and carbon dioxide) and a nutrient-rich residue called digestate [46].
Most biogas plant owners are mainly focused on maximizing revenues from biomethane or electricity production, while digestate is considered a by-product. In line with this, the EU has introduced, within the Circular Economy Package, essential principles for sustainable digestate management. Thus, from a circular economy perspective, the nutrient and stable organic carbon content of digestate are valuable resources that can be recovered [47,48].
The digestate resulting from the AD process is taken out of the digester tank and placed in special containers. It is essential to note that the amount of produced digestate is directly related to the quantity and type of utilized substrate for biogas production, their susceptibility to decomposition, as well as the technologies used for pretreatment and fermentation. The quantity of digestate produced usually represents 70–90% of the feedstock weight [49]. Moreover, the composition of biogas digestate varies depending on the feedstock used for digestion, the process conditions and the efficiency of the AD process [50]. However, the composition of the anaerobic digestate is influenced by various factors, including the operating conditions of the biogas plant, how the digestate is stored and, most importantly, the substrate used [51]. The type of substrate used in the anaerobic digestion process is an essential factor in biogas production, as it can determine the efficiency of the process, but also the properties of the digestate. The main types of feedstocks used in digesters are animal manure, agricultural residues, food waste, energy crops, wastewater sludge and the organic fraction of municipal solid waste. Apart from used feedstock, temperature and pH represent other important parameters that determine the efficiency and stability of the anaerobic digestion process. The optimal temperature range for the mesophilic regime is between 35 and 40 °C, while that for the thermophilic regime is between 50 and 55 °C [50]. The optimum range for the substrate pH is between 6.8 and 7.5.
Typically, anaerobic digestate contains organic compounds (carbon (C)) that could not be degraded in the fermentation process, macronutrients (such as nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P)), micronutrients (potassium (K), sodium (Na), calcium (Ca) and others), organisms’ biomass and water [21,52]. The moisture content of the digestate is influenced by the AD process type, which can be wet or dry [53].
To prevent environmental risks, anaerobic digestate must be treated appropriately, as it may contain heavy metals, such as cadmium (Cd), chromium (Cr), copper (Cu), lead (Pb), nickel (Ni), zinc (Zn) and arsenic (As), and generates greenhouse gas emissions [54].
For example, Golovko et al. [55] examined the characteristics of anaerobic digestate based on food waste from three biogas plants in Sweden. The heavy metal concentrations reported by the authors for the tested biofertilizer samples are presented in Table 1. These values were compared with the European Union standards specified in Regulation (EU) 2019/1009 for organic fertilizers [56].

Table 1.
Heavy metals concentrations in digestate and comparison with EU limit values [55,56].
The anaerobic digestate produced annually in a typical 1 MWe agricultural biogas plant can reach tens of thousands of Mg. These are huge quantities that can be managed profitably [57].
Generally, there are three types of anaerobic digestate, namely the solid fraction (rich in C and P), the liquid fraction (rich in K and N) and whole digestate (combination of the two fractions in sludge form) [38,58].
Depending on the substrate used, digestates are classified into two different component material categories (CMCs) [13]:
- ➢
- CMC 4 for digestates derived from crops exclusively intended for biogas production (e.g., energy crops);
- ➢
- CMC 5 for digestates derived from (i) biowaste according to Directive 2008/98/EC [59] and (ii) derived products according to EU Regulation 1069/2009 [60], which includes, among others, manure and digestion residues.
3.1. Solid–Liquid Separation
Separating anaerobic digestate into a solid and liquid fraction is a simple and economical process that is often performed prior to any additional digestate post-treatment [61]. The solid–liquid phases are obtained by separation processes using mechanical separators, centrifuges, stripping, drying or evaporation [38]. Thus, solid–liquid separation represents the first step in digestate processing. The separation of anaerobic digestate results in two phases, namely a liquid fraction with a higher moisture content and a solid fraction, which is a fibrous material with a lower moisture content. Both need to be stored and handled separately [62].
Thus, after the solid–liquid separation, the liquid fraction of digestate was found to contain a high percentage of organic N and K in the form of K ions and ammonium, and the solid fraction of digestate contained a high content of P and N [50,53,63].
A few of the most popular mechanical separators used for digestate separation are the belt press, sieve drum, screw press, sieve centrifuge and decanter centrifuge. Figure 1 presents two of the most common equipment used for liquid–solid separation of the digestate, namely the screw press and the decanter centrifuge. The working principle of the screw presses is based on separating particles by their geometric dimensions. This means that the digestate is forced through a sieve with a mesh that only allows liquids and solid particles smaller than the mesh size to pass through; they will form the liquid fraction. In the case of decanter centrifuges, the separation is based on the particle’s density. Thus, the digestate is fed into a rotating drum and an internal screw conveyor leads the solid particles to the solids discharge port. Comparing these two pieces of equipment, it can be concluded that decanter centrifuges are able to recover smaller-sized particles than screw presses [64].
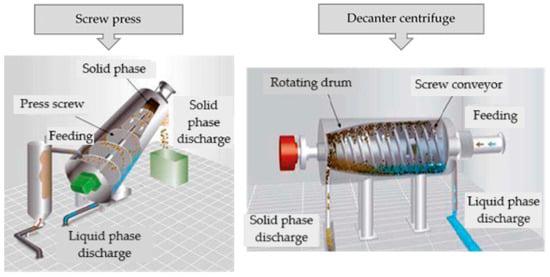
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of solid–liquid separation by screw press and decanter centrifuge (adapted from [65,66]).
Carraro et al. [41] reported that centrifuges are able to separate 60% more DM and total P than screw presses.
Chemical methods, such as precipitation and flocculation, allow the formation of larger particles and thus aid in the separation phase. Thus, the performance of solid–liquid separation can be improved by adding different products into digestate, such as flocculants or organic polymers (acrylamide) and precipitating agents (ferric sulfate, Fe2(SO4)3; aluminum sulfate, Al2SO4; ferric chloride, FeCl3; and lime Ca(OH)2). Furthermore, functionalized chitosan may be used to increase the effectiveness of solid–liquid separation, according to recent research [38,67,68,69].
Another solution for digestate processing is to dry the digestate. The method can use the heat generated in cogeneration, but this solution is rarely used since raw digestate has a high moisture level. Another attractive method is digestate thickening using an evaporator that rapidly evaporates water under low pressure at temperatures below 60–75 °C [49].
Several separation techniques were tested, and the efficiency of solid–liquid separation and the quality of the fractions were evaluated [23,62,70]. Nowak’s research regarding the screw presses showed that there is a strong relation between the dry matter concentration of the digestate and how well it can be separated. It showed that only around 60% of the original liquid fraction can be extracted. However, when the pulp has a dry matter content of 5%, up to 95% of the liquid fraction can be separated [23]. Lyons et al. [62] evaluated two mechanical separation technologies (screw press and decanting centrifuge) that could be used in the agro-zootechnical and AD sectors for enhancing manure sustainability and improving anaerobic digestate management. According to the study’s conclusions, screw press separation is the more cost-effective choice when approving the export of small quantities of P off-farm. On the other hand, decanting centrifugation is an effective option if greater amounts of P removal are needed.
Tambone et al. [70] studied the effect of solid–liquid separation of anaerobic digestate on DM, nitrogen (TKN), phosphorus (P2O5) and heavy metals distribution into these two phases. After chemical characterization, the authors reported that liquid fraction can be used as a substitute for mineral N fertilizers because of its high N content, while solid fraction can be proposed as an NP-based organic fertilizer.
3.2. Digestate Fractions: Liquid and Solid
The liquid fraction of anaerobic digestate may contain a higher proportion of macro- and micronutrients; however, it is not recommended to apply it directly to the soil because of the presence of pathogens (such as Salmonella and Campylobacter), greenhouse gas emissions, odors, phytotoxic volatile fatty acids and high humidity (70–80%), which make soil application difficult [50].
Akhiar et al. [71] analyzed how substrate origin, process parameters and solid–liquid separation techniques affected the residual compounds in the liquid fractions of digestate. According to the authors, the used substrate and the combined effects of the solid–liquid separation method mostly affect the characteristics of the residual organic matter in the liquid fractions of digestates. The liquid fraction of the anaerobic digestate can be used to dilute the new amount of feedstock fed into the biogas plant reactor. In this way, the beneficial microorganisms involved in AD are added to the process, in addition to saving large amounts of water [49]. Moreover, its richness in micronutrients, organic matter, and plant macronutrients such as N, K, P and sulfur (S) makes it excellent plant fertilizer [67].
In parallel, the solid fraction, also known as pressed cake, concentrates nutrients, mostly organic N and P, and DM (between 20 and 30%) and is usually applied as a soil fertilizer [61]. In order to improve the safety use of digestate, many treatment methods have been proposed [38,45,72]. For example, the solid fraction of digestate can be converted into biochar by thermal treatment (gasification and pyrolysis), or biostimulants such as humic and fulvic acids can be obtained. Biochar is a solid product with a porous structure that can contribute to climate change mitigation by sequestering CO2, making it a valuable product. When added to soil, biochar improves microbial activity, water holding capacity and nutrient retention [38]. Composting digestate is another way to add value to it. This method reduces the number of pathogens, increases biological stability and produces organic fertilizers that can be used in agriculture [45].
On the other hand, depending on the type of anaerobic digestion process used for biogas production (wet or dry fermentation), the resulted digestate can be classified as wet or dry. Wet digestates are flowable and can be applied to fields for fertilization, since wet digestion techniques are used for substrates with total solid concentrations less than 10%. Dry digestion methods are used for materials that have a 15–35% total solids concentration. Dry digestate is richer in nutrients and fiber, making it suitable for processes such as composting [72].
Thus, the two separated fractions of anaerobic digestate, the solid and liquid fraction, support the circular bioeconomy and sustainable agricultural practices.
4. Anaerobic Digestate Valorization According to Circular Economy
The growing number of biogas plants throughout Europe is creating an increasing issue in digestate management [73]. In the EU, about 180 million tons of digestate are produced each year. The majority of the digestate generated (120 million tons) comes from agriculture; the organic component of urban solid waste produces approximately 46 million tons; at least 7 million tons comes from biowaste separated by source; and sewage sludge and by-products from the agri-food sector provide about 1.7 million tons each [61].
As the volume of digestate from biogas plants increases rapidly, it becomes imperative to develop effective protocols for its handling. The strategic location of local biogas plants near areas with large amounts of organic waste facilitates efficient collection from regional producers. In addition, the resulting digestate can be used to enrich the soil of surrounding farms, thus reducing transportation costs [50,74]. For digestate from biogas installations to be classified as a ‘product’ and not ‘waste’ and to comply with the regulations, it must undergo biological or physico-chemical treatment [75]. Due to its high micro- and macronutrient content, anaerobic digestate is an optimal alternative for reducing the application of chemical fertilizers. However, digestate may affect soil and growth of plants if it is used incorrectly. For example, applying digestate too early, combined with a prolonged retention period in the soil before plant uptake may result in nitrate (NO3) emissions into groundwater or nutrient loss and migration to deeper soil layers [76]. Moreover, the concentration of nutrients in the digestate is variable and an excess of a particular element can lead to soil pollution [38]. The presence of pollutants such as pathogens, heavy metals, pesticides and steroid hormones can also pose a drawback for soil application (Figure 2) [77].
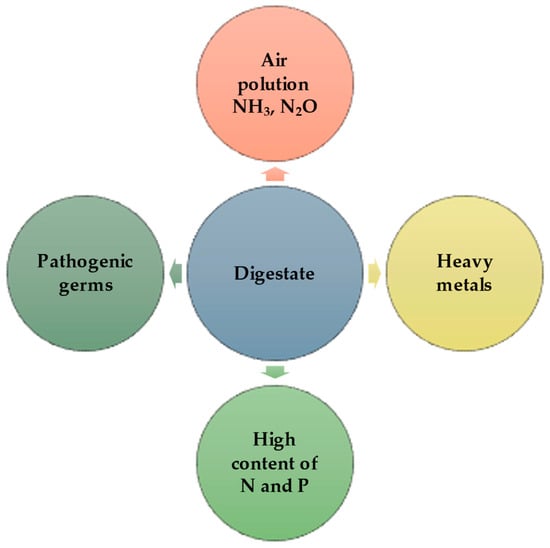
Figure 2.
Environmental risks associated with the use of raw digestate (own creation).
In addition, transportation costs, nutrient surplus, market acceptance and seasonal agricultural demands are the main barriers to the use of digestate for agricultural purposes. Other disadvantages of the improper use of digestate are unpleasant odors and uncontrolled leachate flow into the soil and groundwater, emissions of ammonia or greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane (CH4) into the atmosphere [78].
Consequently, studying different methods for the management and utilization of digestate is essential [75].
Treating digestate before application to the soil is fundamental to ensure its optimal use as a fertilizer. The processing of the solid phase includes methods such as composting, drying/pelletizing and thermochemical conversion (gasification, hydrothermal carbonization and pyrolysis). On the other hand, the liquid fraction can be treated using, among others, the following methods: membrane filtration, vacuum evaporation, ammonia stripping and struvite precipitation [61,63,79].
From the point of view of circular bioeconomy, field application is the simplest and most economical way to valorize anaerobic digestate. However, excessive field application of digestate can lead to N pollution and the eutrophication of the aquatic environment [54].
Apart from land applications, there are various ways to reuse digestate, as shown in Figure 3, depending on the quality and source of the raw material used in the anaerobic fermentation process, which defines the digestate’s primary properties [21,80].
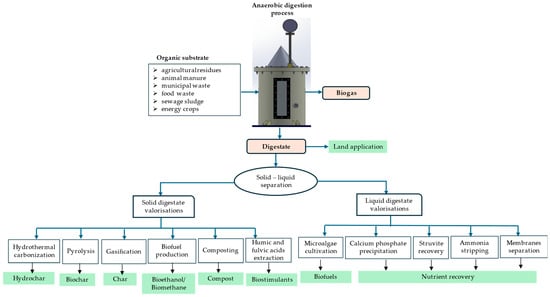
Figure 3.
Directions of digestate valorization based on [38,50,54,81].
Proper digestate management is a key element in the efficient operation of biogas plants, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, odor problems and nutrient leaching [50].
4.1. Digestate as Fertilizer
Due to its high content of N, P and K, the most common use of anaerobic digestate is its application to the soil as a fertilizer and soil amendment [38,80].
Before being used as a fertilizer, the chemical composition of digestate must be carefully evaluated to avoid contamination of the soil and thus of the human food chain [76].
Numerous investigations have demonstrated that digestate is a valuable source of nutrients for agriculture [52,82], and that the digestate’s chemical properties are mostly determined by the feedstock and the operating conditions of the anaerobic digester [83].
According to the study conducted by Panuccio et al. [84], two digestate fractions, liquid and solid, were investigated for their effects on tomato growth and the nutritional value of cultivated tomato fruits. The results demonstrated that both digestate types had beneficial effects on tomatoes’ nutritional content, as evidenced by higher levels of essential health components such as vitamin C, phenolic compounds and flavonoids. The authors reported that the solid digestate fraction obtained from a digester fed with animal manure, at a concentration of 20%, doubled the number of flowers compared to the control group. In contrast, the solid digestate fraction from a digester fed mainly with olive waste and citrus pulp had a significant effect on the leaf area, which registered a 150% increase compared to the control group.
In another study, Ferdous et al. [85] evaluated the effect of biogas slurry combined with synthetic fertilizer on tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) yield. The highest fruit yield was obtained, according to the authors, from the application of synthetic fertilizer and poultry bio-slurry. According to [86], the use of solid and liquid digestate enhanced plant growth in hydroponic baby leaf lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) culture. Digestate has also been used in alfalfa cultivation, and analyses have shown an increase in the content of macro-nutrients in alfalfa leaves [87].
4.2. Termochemical Methods of Solid Digestate Valorization
The main thermochemical methods of solid digestate valorization are pyrolysis, gasification and hydrothermal carbonization. Pyrolysis is a thermochemical process that produces non condensable gases, bio-oil, and solid carbon-rich residues (biochar) from organic materials in an oxygen-free medium [88]. Digestate has recently been used in the production of biochar, a process considered essential for reducing negative environmental impacts and increasing the financial viability of AD plants [89]. Due to its efficacy, the “slow pyrolysis” method is recommended for producing biochar, which enhances P availability and immobilizes metals [90]. Biochar has a very wide range of applications due to its sorption properties, including fertilization, composting, wastewater treatment and environmental protection. Biochar facilitates the absorption of nutrients and organic materials in soil, functioning effectively as a natural fertilizer [91]. In addition, biochar has been shown to improve digestate quality when added to AD processes, especially in terms of nutrients conservation, higher C/N ratio and decreased nutrient leaching [92].
In a study conducted in 2016 [93], Shariff and collaborators observed that the highest biochar yield is obtained at the lowest temperature. The same was observed in the paper [94]. Liu J. and colab. [89] evaluated food waste solid digestate resulted from AD process as a potential source for biochar preparation by pyrolysis. The authors reported that the obtained results offer a different approach for waste disposal resulted from the AD of food waste. Other studies indicate that biochar derived from solid digestate exhibits enhanced qualities in terms of raising pH and increasing adsorption capacity compared to biochar directly produced from raw biomass [95,96].
Gasification is another thermochemical method used to valorize anaerobic digestate. The gasification process takes place in the presence of an oxidizing agent at temperatures ranging from 600 to 1300 °C. The final products include tar, a condensable product, composed of aromatics compounds, a solid carbonaceous material with a porous structure called char, and syngas, a gaseous combustible product [88]. Gasification char is an economical alternative to activated carbon in multiple applications, such as catalysis and adsorption [97].
The hydro-thermal carbonization process involves heating biomass in a water environment at temperatures between 160 and 280 °C while applying pressure ranging from 2 to 10 MPa. In this process, the resulted products are a solid product, which is called hydrochar, liquid and gaseous phases. The hydrochar can be used as soil fertilizer due to the nutrient content, as solid fuel and as adsorbent for environmental remediation [98,99]. In another study [100], heavy metals in the digestate were effectively immobilized during hydrothermal dehydration and pyrolysis processes, which contributed to obtaining a quality biochar, with the optimal pyrolysis temperature being set at 500 °C.
Belete Y.Z. et al. [101] investigated the hydrothermal carbonization of raw manure and anaerobic digestate manure with water or whey as the liquid phase in order to recover energy and nutrients. The authors reported that manure hydrochar is suitable as an energy product, with energy properties similar to lignite (manure + water), while digestate hydrochar is more suitable for soil amendment. The results showed that among the produced hydrochars, the calorific value of the hydrochar derived from whey was the highest at 19.4 MJ kg−1, followed by that obtained from manure and from digestate (16.0 MJ kg−1). On the other hand, the hydrochar derived from digestate contained up to 1.8% phosphorus, which was higher than that of the hydrochar derived from manure, which reached a maximum of 1.5%.
4.3. Biofuel Production
An additional viable approach for the valorization of liquid and solid digestates is the synthesis of bioethanol via biological fermentation [77]. A few studies highlight the potential of anaerobically treated waste as a feedstock for bioethanol production, due to the remaining hydrocarbon components [102]. In study [103], digestate was used instead of fresh water and fertilizers in bioethanol production. The results showed that ethanol output increased by up to 18% compared to the production using freshwater.
Chen et al. [104] evaluated the effects of digestate recirculation on the performance of two-stage thermophilic–mesophilic co-digestion of swine manure and rice straw. The authors reported that digestate recirculation improved the performance of the two-stage anaerobic co-digestion by increasing the methane production by 9.92%. In addition, digestate recirculation improved the performance of the co-digestion process by increasing the abundance of Methanosarcina (from 4.1% to 7.5–10.7% and 35.7%). In another study [105], bio-hydrogen and bio-methane production from food waste were studied to observe the effects of digestate recirculation on energy efficiency and process stability. The results showed that stable hydrogen and methane production was obtained by the recirculation rate at 0.3. At this recirculation rate, maximum hydrogen and methane production were obtained (3 L L−1d−1 and 2.9 L L−1d−1). Compared to a system without recirculation, digestate recirculation reduced the need for alkali addition to maintain the pH in the H2 reactor by 54%.
4.4. Compost Production
Composting is one of the most widely used and effective methods for stabilizing digestate and reducing the concentration of volatile organic compounds [50]. Digestate contains N and P, which are important for plant growth, so the resulting compost can replace or reduce the need for synthesized fertilizers. In addition, using compost instead of synthetic fertilizers saves energy and water used in fertilizer production [106]. However, the high moisture content and low C/N ratio of the digestate are factors that influence its efficient composting. Thus, mixing with different types of waste is necessary to enhance the digestate composition before composting [107]. Song et al. [108] investigated the co-composting of food waste digestate with sawdust and mature compost. Their results demonstrated that, within two weeks of co-composting, combining food waste digestate with sawdust, either alone or in combination with mature compost, can result in high-quality compost with a high seed germination index (>80%) and low NH4+-N (<700 mg kg−1 DM).
In other paper, Weldon and colab. [109] used biogas digestate, garden waste and biochar in the composting experiment. The authors reported that the addition of biochar improves the digestate composting, without further negative effects on plants. Furthermore, using biochar decreased cumulative N2O emissions by 65–70%, but it had no noticeable effect on CO2 or CH4 emissions.
4.5. Humic and Fulvic Acid Extraction
Humic substances are usually classified into three subcategories according to their solubility: humic acids, fulvic acids and humins. Among them, humic and fulvic acids are of interest because they can be obtained from anaerobic digestate. Humic substances are the most important natural soil improvers due to their ability to improve the chemical and physical properties of the soil, thus promoting plant growth [38,110].
The digestate resulting from AD processes is rich in both essential macronutrients (N, P and K), and humic acids, which play a fundamental role in ecological processes and terrestrial lives. Humic acid, used as a biostimulant in horticulture, can improve processes such as seed germination, root development and overall plant growth [111]. Biostimulants are defined as substances or microorganisms that have beneficial effects on the growth and development of plants, independent of any nutritional properties [112].
Humic acids contribute to stimulating root growth by supplying essential metals needed for plant development, while fulvic acids facilitate micronutrient mobilization and absorption, especially iron [113].
In the study by Anielak et al. [114] humic substances were recovered from digested sewage sludge. The recovered humic substances contained relatively high amounts of plant nutrients (including N and P), making them suitable for use as biostimulants.
In the work of Chaves et al., conducted in 2025 [112], the biostimulant properties of several fractions derived from raw digestate on winter rye were evaluated: humic and fulvic acids obtained through alkaline-acid extraction, their mixture (humic substances), the water-soluble fraction, as well as the raw and liquid digestate. The results demonstrated that, in hydroponic settings, the recovered fulvic acid greatly increased the winter rye’s root DM (0.381 g plant−1), root carbon quantity (163 mg plant−1), root N levels (8.06 mg plant−1) and its projected leaf area (80.5 cm2).
4.6. Nutrient Recovery
Mineral fertilizers of fossil origin have N, P and K as their main components. Given the non-renewable nature of the resources from which they come, the production of these fertilizers is considered unsustainable, raising concerns about their long-term availability [13]. In 2023, Europe used 9.3 Mt of mineral fertilizers (N and P) for agricultural production, which represents a 3.7% annual reduction and a total loss of 20.5% from the comparable peak in 2017 [115]. In this context, the agricultural digestate resulting from AD processes is recognized as a potential valuable material for the recovery and valorization of biofertilizers [13].
The recovery of nutrients from the anaerobic digestate involves several methods, such as vacuum evaporation, ammonia stripping, adsorption, struvite precipitation, membrane filtration and reverse osmosis. The performance of nutrient recovery methods varies depending on the type of waste, processing conditions and the specific recovery technology used [13,50,110]. The most widely developed technologies are ammonia stripping and struvite precipitation, which allow an average removal and recovery efficiency of 80–90% for both N and P [13]. Under current regulations, the recovery of nutrients from digestate is a priority for AD plants. Nutrient recovery from digestate can thus play a significant role in reducing dependence on mineral fertilizers based on N and P, while supporting the implementation of the principles of circular economy [116].
4.6.1. Ammonia Stripping
Ammonium (NH4+) is the main N compound in the liquid digestate. During the ammonia-stripping process, ammonia (NH3) is separated from the liquid fraction of the digestate by means of a gas stream, usually air, in an ammonia-stripping reactor, which results in the transfer of NH3 from the aqueous phase to the gaseous phase. The released NH3 is removed in a chemical air scrubber by washing it with a concentrated acid solution, such as sulfuric acid or nitric acid. The reaction between NH3 and sulfuric acid (H2SO4) leads to the formation of ammonium sulfate, and the reaction with nitric acid (HNO3) generates ammonium nitrate. Having a high N content, both products obtained can be used as N fertilizers [117]. Brienza et al. [118] evaluated the performance of a full scale digestate processing cascade that includes an innovative vacuum side stream NH3 stripping and scrubbing system. According to mass and nutrient balances, 57% of the ammonium N contained in digestate was recovered as 22% ammonium sulfate, while 7.5% was recovered in the form of a liming substrate. In another study, Abba et al. [119] investigated the performance and energy consumption of a full-scale ammonia stripping plant. Stripping tests were carried out on the liquid digestate fraction, and the results showed that AD coupled with stripping was a suitable solution for removing up to 81% of the NH4+ without the need for external energy input or reagent dosage. However, the efficiency of ammonia stripping depends mainly on pH, temperature, air–liquid ratio and feed characteristics. In 2022, ammonia recovery from anaerobic digesters via side-stream stripping was investigated by Palakodeti and colab. [120]. Ammonia recovery was controlled to maintain a constant ammonia concentration. During the experiment, methane yields of 60–80 mL (gVS.d)−1 and volatile fatty acid concentrations of 0–500 mg L−1 were reported.
However, ammonia stripping has been reported to be economically feasible only when ammonia N concentrations are greater than 1500 mg/L [121].
4.6.2. Struvite Precipitation
Struvite precipitation is an established method that is used mainly for P recovery. Struvite is a crystalline mineral composed of magnesium (Mg), NH4+ and phosphate (PO4) with the chemical formula MgNH4PO4⋅6H2O. This product can be considered as a slow-release fertilizer [121,122]. Moreover, the struvite precipitation process facilitates the simultaneous recovery of NH4+ and orthophosphate, conditional on the presence of an external source of Mg [116].
Trotta et al. [116] tested a method which combines struvite precipitation and ammonia stripping to observe the efficiency of nutrient recovery/removal from cow manure digestate. Their results indicated that more than 60% of total P was removed as struvite, which can be used in N–P fertilizer, thus substituting synthetic mineral fertilizers. In a study published in 2023, Pepe Sciarria and collaborators [123] analyzed the possibility of P recovery in the form of struvite from the liquid fraction of digestate from pig manure, having a high total solid content. The study results indicated that at a total solids content of 4.5% and a molar ratio Mg/P of 2:1, the highest recovery of phosphorus was 85%, and that of nitrogen was 52%. Further, the authors assessed the generated struvite’s fertilizing capacity by comparing it with poultry dung and traditional phosphate mineral fertilizers. Brassica rapa chinensis was used in agronomic experiments. Struvite showed comparable performance to conventional fertilizers in terms of N, total biomass and P (mineral fertilizers: 5.6; poultry manure: 5.7; struvite: 5.9 g kg−1).
4.7. Microalgae Cultivation
Recently, the decline in fossil fuel resources, coupled with rising greenhouse gas emissions, has led to a transition to renewable energy sources, with a particular focus on microalgae biofuels [124]. During microalgae cultivation, in addition to water, CO2 and light, nutrients must also be supplied. Thus, the cultivation of microalgae in the digestate resulting from the anaerobic fermentation process represents a sustainable alternative to the artificial nutrients currently used. However, growing microalgae on digestate is cost-effective, as it reduces the cost of nutrients needed for biomass growth, but it is still a challenge, as the liquid fraction of digestate is characterized by turbidity and bacterial contamination, which could negatively affect cultivation [125]. In this case, the liquid fraction of the digestate must be processed before its use as a nutrient source for microalgae culture. Depending on its composition, the most commonly used methods are centrifugation to remove solids and ammonia stripping and dilution for the adjustment of nutrient concentrations [126,127]. Fernandes et al. studied the performance of a digestate resulting from the AD of food and kitchen waste, treated by dilution, settlement and membrane processing technologies. The treated digestate was subsequently tested as a nutrient source for Chlorella vulgaris cultivation. The authors reported that the treated digestate was a suitable substrate to support the growth of Chlorella vulgaris [128]. In other studies [125,129], Chlorella sorokiniana and Chlorella vulgaris microalgae were cultured using ultrafiltered digestate.
4.8. Standards and Regulations for Digestate at EU Level
The aim of introducing the digestate management regulation is to protect human health and the environment by setting standards for the production and use of anaerobic digestate in certain applications [53]. Moreover, digestate management legislation is important for determining sustainable practices in the biogas industry [79]. Policies governing digestate at EU level include the Waste Framework Directive, the Animal By-products Regulation, the Fertilizers Regulation, the Nitrates Directive and the Sewage Sludge Directive [19]. The European Union approved legislation on biofertilizers in 2019 through the Fertilizers Regulation 1009/2019, which promotes safe circular digestate management [56]. The EU began regulating the application of digestate in 1991 with the European Council Directive (EC) concerning the protection of waters against pollution caused by nitrates from agricultural sources, also known as the Nitrates Directive. According to this directive, the amount of manure applied to the land each year shall not exceed 170 kg of N per hectare [130].
The existing EU regulation on fertilizers (EC, 2003/2003) [131] only stipulates the placing on the market, and therefore the trade, of mineral fertilizers in the EU market [74].
The European Union has set standards for certifying the quality of digestate. The main quality parameters in the standards include nutrients, heavy metals, pathogens, organic/inorganic pollutants and digestate stability/maturity. Most standards specify that digestate should include no more than two viable seeds per liter and no more than 0.5 g/kg of pollutants (plastic, glass and metal). In addition, to maintain hygiene, Escherichia coli should be less than 1000 CFU/g and Salmonella sp. should not be present in 25 g of fresh digestate [132,133].
Table 2 summarizes the relevant standards related to anaerobic digestate quality.

Table 2.
Standards for digestate certification.
5. Effect of Anaerobic Digestate Application on Agricultural Soil
As the application of mineral fertilizers on agricultural land is associated with a negative impact on the environment, more and more activities are focusing on the use of organic fertilizers [137]. Due to its high nutrient content, mainly N, anaerobic digestate can be successfully utilized as a fertilizer. Incorporating anaerobic digestate into the soil involves adding organic matter and N, which can increase the humification process [51,57]. Applying digestate as fertilizer not only closes the nutrient loop, but also reduces the demand for mineral fertilizer, which requires a high input of raw materials and energy for production [74].
The use of anaerobic digestate as fertilizer in the agricultural sector is a solution recommended by numerous studies conducted worldwide. In his study, Czekala [57] determined the content of total nitrogen (Ntot) and its selected fractions (N-NH4, N-NO3 and Norganic) in the raw and processed digestate derived from five agricultural biogas plants. The author reported that the tested digestate can be considered a multi-component fertilizer, with the content of Ntot in the tested samples ranging from 1.63 g kg−1 to 13.22 g kg−1 fresh matter.
Cichy et al. [138] used direct soil testing to analyze the influence of fish sludge and liquid digestate from the AD of food waste on the growth of Lepidium sativum and Triticum aestivum plants. According to the results, applying this digestate delayed the germination process and had a negative impact on the plants’ early growth in the first days of the experiment, but this effect progressively diminished.
In another study, Slepetiene and colab. [51] showed that different rates of separated liquid and solid phases of anaerobic digestate influenced the contents of carbon and N in different layers of Fluvisol. The authors reported that the application of solid digestate increased the soil organic carbon content in the 0–10 cm layer, and the liquid digestate significantly increased the soil organic carbon content in the deeper layers, specifically the 20–30 cm layer. The treatment fertilized with 170 N rate of both digestates had a noticeably higher concentration of soil organic carbon in the examined soil layer (0–30 cm).
In another investigation, Jurgutis et al. [78] assessed the fertilizing potential and chemical composition of several types of digestates coming from eight agricultural biogas installations. The results obtained show that spreading solid and liquid digestate to low-fertility soils near biogas plants can increase the amount of biomass suitable for biogas by up to three times. In addition, the digestate’s value was assessed to be between EUR 2.88 and 7.89 Mg−1 for liquid digestate and EUR 7.62 and 13.61 Mg−1 for solid digestate, based on the market prices of commercial fertilizers.
Nabel et al. [139] assessed the potential of the Sida hermaphrodita energy plant to grow in a marginal sandy soil. The authors used different fertilization treatments in their experiment, either digestate from biogas production or a commercial mineral NPK fertilizer. Their results showed that the anaerobic digestate was the best performing fertilizer because it produced similar yields as the NPK fertilization but minimized nitrate leaching.
6. Life Cycle Assessment and Greenhouse Gas Emissions in the Valorization of Anaerobic Digestate
Life cycle assessment (LCA) is a technique for evaluating the environmental impact of services and products, including the entire life cycle from the extraction of raw materials to the disposal of waste. For each stage of LCA, resource use, emissions and waste generation are quantitatively described. LCA has various uses, such as determining a country’s waste treatment strategies [140]. LCA is an essential tool for optimizing digestate production by establishing impacts on the environment, promoting the transition to a circular economy through sustainable waste management and the generation of value-added products. In the case of anaerobic digestate production, LCA identifies emissions generated within the system during feedstock handling, digestate post-treatment, storage, field application, anaerobic digestion process and transport. These steps contribute significantly to energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions [141].
In the literature, studies have been conducted to investigate the effects of anaerobic digestion on the environment. Some studies have compared anaerobic digestion methods with other solid waste treatment methods using LCA [142,143,144,145]. The anaerobic digestion process produces renewable energy and organic fertilizer, which can reduce greenhouse gas emissions from energy production, agriculture and waste management [146]. Compared to mineral fertilizers, digestate can be more environmentally friendly regarding the greenhouse gas emissions associated with the production of synthetic fertilizers. Sarec et al. [147] investigated the influence of two digestate application methods (disc injection and band spreading) on permanent grassland over a four-year period. Among the analyzed hypotheses, the authors investigated whether, independent of application technique, greenhouse gas and ammonia (NH3) emissions increase proportionately with increasing digestate rates. The authors reported that disk injection reduced NH3 emissions by over 66% on average, although this was in comparison to digestate band application. However, the most effective approach to minimizing emissions while maintaining good agronomic performance was the combination of split-dose fertilization and disc injection. The results showed that NH3 and CO2 emissions increased proportionally with the digestate dose. Regarding CH4, the flux did not increase significantly with higher application doses.
Timonen et al. [146] used different techniques to evaluate the climatic emissions of the complete AD chain, from the purchase of raw materials to the use of energy and digestate. The authors conducted a life cycle analysis of three anaerobic digestion scenarios using pig slurry and various secondary feedstocks. The comparative analysis of the scenarios with different co-substrates showed that the highest total emissions associated with digestate were recorded in scenario S1 (8.4 kg CO2 eq kg−1 N), while the lowest were observed in scenario S2 (8.2 kg CO2 eq kg−1 N). Although the difference is modest, it highlights the sensitivity of emission outcomes to the chosen allocation method, particularly when 100% of the emissions during phase 1 of anaerobic digestion are attributed to energy production. In another study [148], the authors reported that compared with direct land application, mono-digestion of pig manure decreases direct greenhouse gas emissions by 48% (190 tons CO2 eq). On the other hand, co-digestion with grass silage increases the total energy recovery by 226% (1592 MWh) compared to mono-digestion.
The authors of [149] investigated the decrease in greenhouse gas emissions that can be achieved by replacing mineral fertilizers with the digestate resulting from agricultural biogas plants utilizing various co-substrates. They reported that the calculated reduction in greenhouse gas emissions was 27.9–61.6 kg CO2 eq Mg−1 of digestate. This indicates that fertilizing with a yearly quantity of digestate from the biogas plants being studied lowers emissions by almost 570 Mg CO2 eq for the smallest biogas plant and by more than 3000 Mg CO2 eq for the largest biogas installation.
7. Future Directions
While significant progress has been made in the valorization of AD within the framework of a circular economy, several technical, economic and environmental challenges remain unaddressed. Current limitations include the variability in digestate composition, the inefficiency of conventional separation methods, low nutrient recovery rates and the lack of standardization for end-use applications. Therefore, future research should prioritize the development of efficient, cost-effective and scalable technologies for the physical and chemical separation of digestate fractions, alongside advanced nutrient recovery strategies. Moreover, innovative pathways for generating value-added products—from biofertilizers and soil amendments to bio-based materials—should be explored to enhance market viability. Equally important is the integration of digestate into modern precision agriculture systems, supported by digital tools and site-specific application techniques, which can maximize nutrient use efficiency and minimize environmental risks. Furthermore, advancing the use of smart sensor technologies and real-time monitoring tools—capable of tracking key parameters such as pH, volatile fatty acids and ammonia—will be essential for improving process stability and enabling more responsive, data-driven control of anaerobic digestion systems. These advancements should be complemented by comprehensive economic assessments and the establishment of clear regulatory frameworks to ensure safe, sustainable and widespread implementation.
8. Conclusions
This review provided a comprehensive overview of sustainable routes for the efficient valorization of digestate resulting from biogas plants. Adequate digestate management is crucial for the effective utilization of nutrients and for environmental protection. This review contributes to the understanding of sustainable management of digestate generated from the anaerobic fermentation process in the context of the circular economy and carbon neutrality, providing perspectives for future research.
Lately, the AD of organic waste has been intensively promoted under the current EU legislative framework. In addition to generating renewable energy, this biological treatment method also permits the recycling and recovery of organic matter and nutrients contained in biodegradable waste. AD is considered a circular economy model that produces energy in the form of biogas from organic waste while recycling nutrients in the form of digestate. Discharging digestate without adequate treatment poses a threat to the environmental quality and leads to significant greenhouse gas emissions. Various methods, such as pyrolysis, gasification, hydrothermal carbonization, ammonia stripping and struvite recovery, offer economical ways to transform anaerobic digestate into valuable resources. Applying these digestate value-adding techniques reduces waste and its negative effects on the environment while promoting a more circular and sustainable agriculture system. Thus, the AD process can improve the circular economy through proper management and valorization of digestate.
Anaerobic digestate can be used as a fertilizer in agriculture and for soil improvement, thus replacing the use of manure and mineral fertilizers for these purposes. Moreover, the biogas digestate is produced from renewable sources, thus supporting sustainable production by taking into account climate change and limited fossil resources. Thus, the recovery of anaerobic digestate represents an effective approach within the circular economy by increasing resource efficiency, minimizing the quantity of organic waste and reducing the carbon footprint related to waste management processes. These benefits promote sustainable agriculture and significantly decrease greenhouse gas emissions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.-N.D., G.P. and M.F.; methodology, G.P. and M.F.; validation, M.F., G.M. and B.-Ș.Z.; formal analysis, M.I., B.-Ș.Z. and M.-N.D.; investigation, G.M. and M.I.; writing—original draft preparation, B.-Ș.Z., M.I., M.-N.D. and G.M.; writing—review and editing, G.M., G.P., M.-N.D. and M.F.; visualization, M.-N.D., B.-Ș.Z., M.I. and G.M.; supervision, M.F., G.P. and M.-N.D.; funding acquisition, M.-N.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from the National Program for Research of the National Association of Technical Universities—GNAC ARUT 2023.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available on request from the authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, L.; Yang, M.; Osman, A.I.; Farghali, M.; Liu, E.; Hassan, D.; et al. Municipal solid waste management challenges in developing regions: A comprehensive review and future perspectives for Asia and Africa. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 930, 172794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Waste Generation—Statistics & Facts. Available online: https://www.statista.com/topics/4983/waste-generation-worldwide/#topicOverview (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Hajam, Y.A.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, A. Environmental waste management strategies and vermi transformation for sustainable development. Environ. Chall. 2023, 13, 100747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaza, S.; Yao, L.; Bhada-Tata, P.; Van Woerden, F. What a Waste 2.0: A Global Snapshot of Solid Waste Management to 2050; Urban Development Series; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2018; p. 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasiński, S.; Dębowski, M. Municipal Solid Waste as a Renewable Energy Source: Advances in Thermochemical Conversion Technologies and Environmental Impacts. Energies 2024, 17, 4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubakar, I.R.; Maniruzzaman, K.M.; Dano, U.L.; AlShihri, F.S.; AlShammari, M.S.; Ahmed, S.M.S.; Al-Gehlani, W.A.G.; Alrawaf, T.I. Environmental Sustainability Impacts of Solid Waste Management Practices in the Global South. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United Nations. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/2030agenda (accessed on 12 January 2025).
- Agovino, M.; Cerciello, M.; Musella, G.; Garofalo, A. European waste management regulations and the transition towards circular economy. A shift-and-share analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 354, 120423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seruga, P.; Krzywonos, M.; den Boer, E.; Niedzwiecki, L.; Urbanowska, A.; Pawlak-Kruczek, H. Anaerobic Digestion as a Component of Circular Bioeconomy—Case Study Approach. Energies 2023, 16, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X. The Promotion of Anaerobic Digestion Technology Upgrades in Waste Stream Treatment Plants for Circular Economy in the Context of “Dual Carbon”: Global Status, Development Trend, and Future Challenges. Water 2024, 16, 3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Domínguez, E.; Rubio, J.Á.; Lyng, J.; Toro, E.; Estévez, F.; García-Morales, J.L. Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Sewage Sludge and Organic Solid By-Products from Table Olive Processing: Influence of Substrate Mixtures on Overall Process Performance. Energies 2025, 18, 3812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldani, E.; Cabianca, A.; Dahlin, P.; Ruthes, A.C. Biogas digestate as potential source for nematicides. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 29, 103025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzioli, F.; Bertasini, D.; Bolzonella, D.; Frison, N.; Battista, F. A critical review on the techno-economic feasibility of nutrients recovery from anaerobic digestate in the agricultural sector. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 306 Pt B, 122690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streche, C.; Collaguazo, G.; Stan, C.; Apostol, T.; Rusu, V.; Vladuca, I.; Badea, A. Performances of anaerobic digestion technologies to treat the organic fraction of municipal solid waste. Univ. Politeh. Buchar. Sci. Bull. Ser. C 2016, 78, 225–236. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, D.J.P.; Mishra, R.K.; Chinnam, S.; Binnal, P.; Dwivedi, N. A comprehensive study on anaerobic digestion of organic solid waste: A review on configurations, operating parameters, techno-economic analysis and current trends. Biotechnol. Notes 2024, 5, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Waste Framework Directive. Available online: https://environment.ec.europa.eu/topics/waste-and-recycling/waste-framework-directive_en (accessed on 16 January 2025).
- Kaidi, K.; Moghrani, H.; Djaafri, M.; Sahli, Y.; Kalloum, S.; Taleb Ahmed, M. Valorization study of the organic waste resulting from the tomato canning by methanisation. Univ. Politeh. Buchar. Sci. Bull. Ser. B 2020, 82, 95–108. [Google Scholar]
- Abdalla, N.; Bürck, S.; Fehrenbach, H.; Köppen, S.; Staigl, T.J. Biomethane in Europe; Institut für Energie-und Umweltforschung: Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; Available online: https://www.ifeu.de/fileadmin/uploads/ifeu_ECF_biomethane_EU_final_01.pdf (accessed on 16 January 2025).
- Decorte, M.; Papa, G.; Pasteris, M.; Sever, L.; Gaffuri, C.; Cancian, G. Exploring Digestate’s Contribution to Healthy Soils; European Biogas Association: Etterbeek, Belgium, 2024; Available online: https://www.europeanbiogas.eu/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Exploring-digestate-contribution-to-health-soils_EBA-Report.pdf (accessed on 16 January 2025).
- Baştabak, B.; Koçar, G. A review of the biogas digestate in agricultural framework. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2020, 22, 1318–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lee, D.J. Valorization of anaerobic digestion digestate: A prospect review. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 323, 124626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visca, A.; Barra Caracciolo, A.; Grenni, P.; Patrolecco, L.; Rauseo, J.; Massini, G.; Mazzurco Miritana, V.; Spataro, F. Anaerobic Digestion and Removal of Sulfamethoxazole, Enrofloxacin, Ciprofloxacin and Their Antibiotic Resistance Genes in a Full-Scale Biogas Plant. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, M.; Czekała, W. Sustainable Use of Digestate from Biogas Plants: Separation of Raw Digestate and Liquid Fraction Processing. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edirisinghe, L.G.L.M.; de Alwis, A.A.P.; Wijayasundara, M.; Hemali, N.A. Quantifying circularity factor of waste: Assessing the circular economy potential of industrial zones. Clean. Environ. Syst. 2024, 12, 100160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Circular Economy: Definition, Importance and Benefits. Available online: https://www.europarl.europa.eu/topics/en/article/20151201STO05603/circular-economy-definition-importance-and-benefits (accessed on 25 April 2025).
- Ufitikirezi, J.d.D.M.; Filip, M.; Ghorbani, M.; Zoubek, T.; Olsan, P.; Bumbalek, R.; Strob, M.; Bartos, P.; Umurungi, S.N.; Murindangabo, Y.T.; et al. Agricultural Waste Valorization: Exploring Environmentally Friendly Approaches to Bioenergy Conversion. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament, the Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions. A New Circular Economy Action Plan. Brussels. 2020. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:52020DC0098 (accessed on 25 April 2025).
- Dragomir, V.D.; Dumitru, M. The state of the research on circular economy in the European Union: A bibliometric review. Clean. Waste Syst. 2024, 7, 100127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, P.K.; Salling, K.B.; Pigosso, D.C.A.; McAloone, T.C. Closing the loop: Establishing reverse logistics for a circular economy, a systematic review. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 328, 117017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona, B.; Shen, L.; Reike, D.; Carreon, J.R.; Worrell, E. Towards sustainable development through the circular economy—A review and critical assessment on current circularity metrics. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 151, 104498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velenturf, A.P.M.; Purnell, P. Principles for a sustainable circular economy. Sustain. Prod. Consump. 2021, 27, 1437–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grdic, Z.S.; Nizic, M.K.; Rudan, E. Circular Economy Concept in the Context of Economic Development in EU Countries. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungureanu, N.; Vlăduț, V.; Biriș, S.-Ș. Sustainable Valorization of Waste and By-Products from Sugarcane Processing. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union. Official Journal of the European Union, Directive (EU) 2018/2001 of the European Parliament and of the Council on the Promoting of the Use of Energy from Renewable Sources (Recast), L 328/82, 22.12.2018. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=uriserv:OJ.L_.2018.328.01.0082.01.ENG&toc=OJ:L:2018:328:TOC (accessed on 12 July 2025).
- Scarlat, N.; Dallemand, J.F.; Fahl, F. Biogas: Developments and perspectives in Europe. Renew. Energy 2018, 129 Pt A, 457–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A.I.; Mehta, N.; Elgarahy, A.M.; Al-Hinai, A.; Al-Muhtaseb, A.H.; Rooney, D.W. Conversion of biomass to biofuels and life cycle assessment: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 4075–4118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamantis, V.; Eftaxias, A.; Stamatelatou, K.; Noutsopoulos, C.; Vlachokostas, C.; Aivasidis, A. Bioenergy in the era of circular economy: Anaerobic digestion technological solutions to produce biogas from lipid-rich wastes. Renew. Energy 2021, 168, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzanti, G.; Demichelis, F.; Fino, D.; Tommasi, T. A closed-loop valorization of the waste biomass through two-stage anaerobic digestion and digestate exploitation. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2025, 207, 114938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.Y.; Tsai, C.Y.; Liu, C.W.; Wang, S.W.; Kim, H.; Fan, C. Anaerobic co-digestion of agricultural wastes toward circular bioeconomy. iScience 2021, 24, 102704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teglia, C.; Tremier, A.; Martel, J.L. Characterization of Solid Digestates: Part 1, Review of Existing Indicators to Assess Solid Digestates Agricultural Use. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 2011, 2, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carraro, G.; Tonderski, K.; Enrich-Prast, A. Solid-liquid separation of digestate from biogas plants: A systematic review of the techniques’ performance. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 356, 120585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feiz, R.; Carraro, G.; Brienza, C.; Meers, E.; Verbeke, M. Systems analysis of digestate primary processing techniques. Waste Manag. 2022, 150, 352–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Midden, C.; Harris, J.; Shaw, L.; Sizmur, T. The impact of anaerobic digestate on soil life: A review. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 191, 105066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roopnarain, A.; Akindolire, M.A.; Rama, H.; Ndaba, B. Casting Light on the Micro-Organisms in Digestate: Diversity and Untapped Potential. Fermentation 2023, 9, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karki, R.; Chuenchart, W.; Surendra, K.C.; Shrestha, S.; Raskin, L.; Sung, S.; Hashimoto, A.; Khanal, S.K. Anaerobic co-digestion: Current status and perspectives. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 330, 125001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- André, L.; Pauss, A.; Ribeiro, T. Solid anaerobic digestion: State-of-art, scientific and technological hurdles. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 1027–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Brussels, 2016. Proposal for a Regulation of the European Parliament and the Council Laying Down Rules on the Making Available on the Market of CE Marked Fertilising Products and Amending Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 and (EC) No 1107/2009. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=COM%3A2016%3A0157%3AFIN (accessed on 17 January 2025).
- Beggio, G.; Schievano, A.; Bonato, T.; Hennebert, P.; Pivato, A. Statistical analysis for the quality assessment of digestates from separately collected organic fraction of municipal solid waste (OFMSW) and agro-industrial feedstock. Should input feedstock to anaerobic digestion determine the legal status of digestate? Waste Manag. 2019, 87, 546–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czekała, W.; Jasinski, T.; Grzelak, M.; Witaszek, K.; Dach, J. Biogas Plant Operation: Digestate as the Valuable Product. Energies 2022, 15, 8275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chojnacka, K.; Moustakas, K. Anaerobic digestate management for carbon neutrality and fertilizer use: A review of current practices and future opportunities. Biomass Bioenergy 2024, 180, 106991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slepetiene, A.; Ceseviciene, J.; Amaleviciute-Volunge, K.; Mankeviciene, A.; Parasotas, I.; Skersiene, A.; Jurgutis, L.; Volungevicius, J.; Veteikis, D.; Mockeviciene, I. Solid and Liquid Phases of Anaerobic Digestate for Sustainable Use of Agricultural Soil. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moller, K.; Muller, T. Effects of anaerobic digestion on digestate nutrient availability and crop growth: A review. Eng. Life Sci. 2012, 12, 242–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, M.; Visvanathan, C. Management strategies for anaerobic digestate of organic fraction of municipal solid waste: Current status and future prospects. Waste Manag. Res. 2018, 37, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chang, J.S.; Lee, D.J. Anaerobic digestate valorization beyond agricultural application: Current status and prospects. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 373, 128742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golovko, O.; Ahrens, L.; Schelin, J.; Sorengard, M.; Bergstrand, K.J.; Asp, H.; Hultberg, M.; Wiberg, K. Organic micropollutants, heavy metals and pathogens in anaerobic digestate based on food waste. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 313, 114997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EUR–Lex. Regulation (EU) 2019/1009 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 5 June 2019 Laying Down Rules on the Making Available on the Market of EU Fertilising Products and Amending Regulations (EC) No 1069/2009 and (EC) No 1107/2009 and Repealing Regulation (EC) No 2003/2003. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2019/1009/oj/eng (accessed on 8 July 2025).
- Czekala, W. Digestate as a Source of Nutrients: Nitrogen and Its Fractions. Water 2022, 14, 4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, C.C.; Cheng, Y.W.; Ishak, S.; Lam, M.K.; Lim, J.W.; Tan, I.S.; Show, P.L.; Lee, K.T. Anaerobic digestate as a low-cost nutrient source for sustainable microalgae cultivation: A way forward through waste valorization approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 803, 150070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union. Official Journal of the European Union, Directive 2008/98/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 19 November 2008 on Waste and Repealing Certain Directives. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32008L0098 (accessed on 20 January 2025).
- European Union. Official Journal of the European Union, Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 21 October 2009 Laying Down Health Rules as Regards Animal by-Products and Derived Products Not Intended for Human Consumption and Repealing Regulation (EC) No 1774/2002 (Animal by-Products Regulation). 2009. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2009/1069/oj/eng (accessed on 2 February 2025).
- Kovacic, D.; Loncaric, Z.; Jovic, J.; Samac, D.; Popovic, B.; Tišma, M. Digestate Management and Processing Practices: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, G.A.; Cathcart, A.; Frost, J.P.; Wills, M.; Johnston, C.; Ramsey, R.; Smyth, B. Review of Two Mechanical Separation Technologies for the Sustainable Management of Agricultural Phosphorus in Nutrient-Vulnerable Zones. Agronomy 2021, 11, 836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilayn, F.; Jimenez, J.; Rouez, M.; Crest, M.; Patureau, D. Digestate mechanical separation: Efficiency profiles based on anaerobic digestion feedstock and equipment choice. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 274, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cathcart, A.; Smyth, B.M.; Lyons, G.; Murray, S.T.; Rooney, D.; Johnston, C.R. Optimising mechanical separation of anaerobic digestate for total solids and nutrient removal. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhiar, A. Characterization of Liquid Fraction of Digestates After Solid-Liquid Separation from Anaerobic Co-Digestion Plants. Chemical and Process Engineering. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Montpellier, Montpellier, France, 2017. Available online: https://theses.hal.science/tel-01684830 (accessed on 14 January 2025). (In English).
- Hjorth, M.; Christensen, K.V.; Christensen, M.L.; Sommer, S.G. Solid—Liquid separation of animal slurry in theory and practice. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2010, 30, 153–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drosg, B.; Fuchs, W.; Al Seadi, T.; Madsen, M.; Linke, B. Nutrient Recovery by Biogas Digestate Processing; IEA Bioenergy: Paris, France, 2015; Available online: https://www.ieabioenergy.com/blog/publications/nutrient-recovery-by-biogas-digestate-processing/ (accessed on 17 January 2025).
- Meixner, K.; Fuchs, W.; Valkova, T.; Svardal, K.; Loderer, C.; Neureiter, M.; Bochmann, G.; Drosg, B. Effect of precipitating agents on centrifugation and ultrafiltration performance of thin stillage digestate. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 145, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghislain, D.; Negrell, C.; Vachoud, L.; Ruiz, E.; Delalonde, M.; Wisniewski, C. An environmental application of functionalized chitosan: Enhancement of the separation of the solid and liquid fractions of digestate from anaerobic digestion. Pure Appl. Chem. 2016, 88, 1155–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambone, F.; Orzi, V.; D’Imporzano, G.; Adani, F. Solid and liquid fractionation of digestate: Mass balance, chemical characterization, and agronomic and environmental value. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 243, 1251–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhiar, A.; Guilayn, F.; Torrijos, M.; Battimelli, A.; Shamsuddin, A.H.; Carrère, H. Correlations between the Composition of Liquid Fraction of Full-Scale Digestates and Process Conditions. Energies 2021, 14, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, K.; Toyota, K. Effects of the application of digestates from wet and dry anaerobic fermentation to Japanese paddy and upland soils on short-term nitrification. Microbes Environ. 2015, 30, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrazzi, S.; Allesina, G.; Bello, T.; Rinaldini, C.A.; Tartarini, P. Digestate as biofuel in domestic furnaces. Fuel Process. Technol. 2015, 130, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturmer, B.; Pfundtner, E.; Kirchmeyr, F.; Uschnig, S. Legal requirements for digestate as fertilizer in Austria and the European Union compared to actual technical parameters. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 253, 109756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Pivato, A. Sustainable Management of Digestate from the Organic Fraction of Municipal Solid Waste and Food Waste Under the Concepts of Back to Earth Alternatives and Circular Economy. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 2019, 10, 465–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamolinara, B.; Pérez-Martínez, A.; Guardado-Yordi, E.; Fiallos, C.G.; Diéguez-Santana, K.; Ruiz-Mercado, G.J. Anaerobic digestate management, environmental impacts, and techno-economic challenges. Waste Manag. 2022, 140, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monlau, F.; Sambusiti, C.; Ficara, E.; Aboulkas, A.; Barakat, A.; Carrère, H. New opportunities for agricultural digestate valorization: Current situation and perspectives. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 2600–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurgutis, L.; Slepetiene, A.; Slepetys, J.; Ceseviciene, J. Towards a Full Circular Economy in Biogas Plants: Sustainable Management of Digestate for Growing Biomass Feedstocks and Use as Biofertilizer. Energies 2021, 14, 4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alengebawy, A.; Ran, Y.; Osman, A.I.; Jin, K.; Samer, M.; Ai, P. Anaerobic digestion of agricultural waste for biogas production and sustainable bioenergy recovery: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2024, 22, 2641–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mammarella, D.; Di Giuliano, A.; Gallucci, K. Reuse and Valorization of Solid Digestate Ashes from Biogas Production. Energies 2024, 17, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decker, S.R.; Milbrandt, A. Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste: Products and Their Uses; NREL/BR-2700-81676; National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Golden, CO, USA, 2022. Available online: https://www.nrel.gov/docs/fy22osti/81676.pdf (accessed on 17 January 2025).
- Barzee, T.J.; Edalati, A.; El-Mashad, H.; Wang, D.; Scow, K.; Zhang, R. Digestate Biofertilizers Support Similar or Higher Tomato Yields and Quality than Mineral Fertilizer in a Subsurface Drip Fertigation System. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2019, 3, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscolo, A.; Settineri, G.; Papalia, T.; Attinà, E.; Basile, C.; Panuccio, M.R. Anaerobic co-digestion of recalcitrant agricultural wastes: Characterizing of biochemical parameters of digestate and its impacts on soil ecosystem. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 746–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panuccio, M.R.; Mallamaci, C.; Attinà, E.; Muscolo, A. Using Digestate as Fertilizer for a Sustainable Tomato Cultivation. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdous, Z.; Ullah, H.; Datta, A.; Anwar, M.; Ali, A. Yield and Profitability of Tomato as Influenced by Integrated Application of Synthetic Fertilizer and Biogas Slurry. Int. J. Veg. Sci. 2018, 24, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronga, D.; Setti, L.; Salvarani, C.; De Leo, R.; Bedin, E.; Pulvirenti, A.; Milc, J.; Pecchioni, N.; Francia, E. Effects of solid and liquid digestate for hydroponic baby leaf lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) cultivation. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 244, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koszel, M.; Lorencowicz, E. Agricultural use of biogas digestate as a replacement fertilizers. Agric. Agric. Sci. Procedia 2015, 7, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, H.E.P.; Jesus, M.; Santos, J.; Rodrigues, A.C.; Pires, P.; Ruzene, D.S.; Silva, I.P.; Silva, D.P. Lignocellulosic Biomass Gasification: Perspectives, Challenges, and Methods for Tar Elimination. Sustainability 2025, 17, 1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Huang, S.; Chen, K.; Wang, T.; Mei, M.; Li, J. Preparation of biochar from food waste digestate: Pyrolysis behavior and product properties. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 302, 122841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberst, D.A.; Cole, A.J.; Whelan, A.; de Nys, R.; Paul, N.A. Slow pyrolysis enhances the recovery and reuse of phosphorus and reduces metal leaching from biosolids. Waste Manag. 2017, 64, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czekała, W.; Jezowska, A.; Chełkowski, D. The use of biochar for the production of organic fertilizers. J. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 20, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zbair, M.; Limousy, L.; Drané, M.; Richard, C.; Juge, M.; Aemig, Q.; Trably, E.; Escudié, R.; Peyrelasse, C.; Bennici, S. Integration of Digestate-Derived Biochar into the Anaerobic Digestion Process through Circular Economic and Environmental Approaches—A Review. Materials 2024, 17, 3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariff, A.; Aziz, N.S.M.; Saleh, N.M.; Ruzali, N.S.I. The Effect of Feedstock Type and Slow Pyrolysis Temperature on Biochar Yield from Coconut Wastes. Int. J. Chem. Mol. Eng. 2016, 10, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefaniuk, M.; Oleszczuk, P. Characterization of biochars produced from residues from biogas production. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 2015, 115, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Fang, W.; Liang, J.; Nabi, M.; Cai, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, G. Biochar application in anaerobic digestion: Performances, mechanisms, environmental assessment and circular economy. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 188, 106720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Song, Y.; Xue, S.; Liu, L.; Lvy, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, G. Coupling biochar with anaerobic digestion in a circular economy perspective: A promising way to promote sustainable energy, environment and agriculture development in China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 144, 110973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaal, A.; Benedetti, V.; Villot, A.; Patuzzi, F.; Gerente, C.; Baratieri, M. Innovative Pathways for the Valorization of Biomass Gasification Char: A Systematic Review. Energies 2023, 16, 4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecchi, M.; Baratieri, M. Coupling anaerobic digestion with gasification, pyrolysis or hydrothermal carbonization: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 105, 462–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikusińska, J.; Kuźnia, M.; Czerwińska, K.; Wilk, M. Hydrothermal Carbonization of Digestate Produced in the Biogas Production Process. Energies 2023, 16, 5458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, J.; Pan, L.; Zhu, X.; Xie, S.; Yu, G.; Wang, Y.; Pan, X.; Zhu, G.; Angelidaki, I. Treatment of digestate residues for energy recovery and biochar production: From lab to pilot-scale verification. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 265, 121852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belete, Y.Z.; Mau, V.; Spitzer, R.Y.; Posmanik, R.; Jassby, D.; Iddya, A.; Kassem, N.; Tester, J.W.; Gross, A. Hydrothermal carbonization of anaerobic digestate and manure from a dairy farm on energy recovery and the fate of nutrients. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 333, 125164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoumpou, V.; Novakovic, J.; Kontogianni, N.; Barampouti, E.M.; Mai, S.; Moustakas, K.; Malamis, D.; Loizidou, M. Assessing straw digestate as feedstock for bioethanol production. Renew. Energy 2020, 153, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Li, X. Using thermophilic anaerobic digestate effluent to replace freshwater for bioethanol production. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 2126–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, W.; Wu, J.; Chen, X.; Liu, R.; Han, Y.; Xiao, B.; Yu, Z.; Peng, Y. Improving two-stage thermophilic-mesophilic anaerobic co-digestion of swine manure and rice straw by digestate recirculation. Chemosphere 2021, 274, 129787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algapani, D.E.; Qiao, W.; Ricci, M.; Bianchi, D.; Wandera, S.M.; Adani, F.; Renjie, D. Bio-hydrogen and bio-methane production from food waste in a two-stage anaerobic digestion process with digestate recirculation. Renew. Energy 2019, 130, 1108–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Xu, F.; Ge, X.; Li, Y. Improving the sustainability of organic waste management practices in the food-energy-water nexus: A comparative review of anaerobic digestion and composting. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 89, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, M.; Aboudi, K.; Pisharody, L.; Singh, A.; Rajesh Banu, J.; Bhatia, S.K.; Varjani, S.; Kumar, S.; González-Fernández, C.; Kumar, S.; et al. Biorefinery of anaerobic digestate in a circular bioeconomy: Opportunities, challenges and perspectives. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 166, 112642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Manu, M.K.; Li, D.; Wang, C.; Varjani, S.; Ladumor, N.; Lui, M.; Xu, Y.; Wong, W.C.J. Food waste digestate composting: Feedstock optimization with sawdust and mature compost. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 341, 125759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weldon, S.; Rivier, P.A.; Joner, E.J.; Coutris, C.; Budai, A. Co-composting of digestate and garden waste with biochar: Effect on greenhouse gas production and fertilizer value of the matured compost. Environ. Technol. 2022, 44, 4261–4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehto, J.; Jarvela, E. Valorisation of anaerobic digestate to nutrients and humic substances. Waste Manag. 2025, 192, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lyu, T.; Dong, R.; Liu, H.; Wu, S. Dynamic evolution of humic acids during anaerobic digestion: Exploring an effective auxiliary agent for heavy metal remediation. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 320 Pt A, 124331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, B.; Salomez, M.; Sambusiti, C.; Thévenin, N.; Vieublé-Gonod, L.; Richard-Molard, C. Digestate as a source of biostimulants for winter rye growth. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2025, 29, 102057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, P.; Nelson, L.; Kloepper, J.W. Agricultural uses of plant biostimulants. Plant Soil 2014, 383, 3–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anielak, A.M.; Kłeczek, A.; Łuszczek, B. Innovative Method of Extraction of Humic Substances from Digested Sludge and Assessment of the Impact of Their on the Growth of Selected Plants. Energies 2023, 16, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eurostat. Agri-Environmental Indicator—Mineral Fertiliser Consumption—Statistics Explained. 2025. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php?title=Agri-environmental_indicator_-_mineral_fertiliser_consumption (accessed on 13 July 2025).
- Trotta, S.; Adani, F.; Fedele, M.; Salvatori, M. Nitrogen and phosphorus recovery from cow digestate by struvite precipitation: Process optimization to maximize phosphorus recovery. Results Eng. 2023, 20, 101478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigurnjak, I.; Brienza, C.; Snauwaert, E.; De Dobbelaere, A.; De Mey, J.; Vaneeckhaute, C.; Michels, E.; Schoumans, O.; Adani, F.; Meers, E. Production and performance of bio-based mineral fertilizers from agricultural waste using ammonia (stripping-) scrubbing technology. Waste Manag. 2019, 89, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brienza, C.; Sigurnjak, I.; Meier, T.; Michels, E.; Adani, F.; Schoumans, O.; Vaneeckhaute, C.; Meers, E. Techno-economic assessment at full scale of a biogas refinery plant receiving nitrogen rich feedstock and producing renewable energy and biobased fertilisers. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 308, 127408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbà, A.; Domini, M.; Baldi, M.; Pedrazzani, R.; Bertanza, G. Ammonia Recovery from Livestock Manure Digestate through an Air-Bubble Stripping Reactor: Evaluation of Performance and Energy Balance. Energies 2023, 16, 1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palakodeti, A.; Rupani, P.F.; Azman, S.; Dewil, R.; Appels, L. Novel approach to ammonia recovery from anaerobic digestion via side-stream stripping at multiple pH levels. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 361, 127685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Chen, Q.; Liu, R.; Song, L.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, X. Ammonia recovery from anaerobic digestate: State of the art, chalenges and prospects. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 363, 127957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorick, D.; Macura, B.; Ahlström, M.; Grimvall, A.; Harder, R. Effectiveness of struvite precipitation and ammonia stripping for recovery of phosphorus and nitrogen from anaerobic digestate: A systematic review. Environ. Evid. 2020, 9, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepè Sciarria, T.; Zangarini, S.; Tambone, F.; Trombino, L.; Puig, S.; Adani, F. Phosphorus recovery from high solid content liquid fraction of digestate using seawater bittern as the magnesium source. Waste Manag. 2023, 155, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaurav, K.; Neeti, K.; Singh, R. Microalgae-based biodiesel production and its challenges and future opportunities: A review. Green Technol. Sustain. 2024, 2, 100060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinska, M.; Rusanowska, P.; Zielinski, M.; Dudek, M.; Kazimierowicz, J.; Quattrocelli, P.; Debowski, M. Liquid fraction of digestate pretreated with membrane filtration for cultivation of Chlorella vulgaris. Waste Manag. 2022, 146, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, L.; Ranglová, K.; Masojídek, J.; Drosg, B.; Meixner, K. Digestate as Sustainable Nutrient Source for Microalgae—Challenges and Prospects. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.; Mantovani, M.; Marazzi, F.; Bellucci, M.; Casagli, F.; Mezzanotte, V.; Ficara, E. Microalgal cultivation on digestate: Process efficiency and economics. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 460, 141753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, F.; Silkina, A.; Grünewald, C.H.; Wood, E.E.; Ndovela, V.L.S.; Oatley-Radcliffe, D.L.; Lovitt, R.W.; Llewellyn, C.A. Valorising nutrient-rich digestate: Dilution, settlement and membrane filtration processing for optimisation as a waste-based media for microalgal cultivation. Waste Manag. 2020, 118, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barzee, T.J.; Yothers, C.; Edalati, A.; Rude, K.; Chio, A.; El Mashad, H.M.; Franz, A.; Zhang, R. Pilot microalgae cultivation using food waste digestate with minimal resource inputs. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2022, 19, 101200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union. Council Directive of 12 December 1991 Concerning the Protection of Waters Against Pollution Caused by Nitrates from Agricultural Sources (91/676/EEC). Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:01991L0676-20081211 (accessed on 19 January 2025).
- EUR-Lex. Regulation (EC) No 2003/2003 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 13 October 2003 Relating to Fertilisers. 2003. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32003R2003 (accessed on 11 July 2025).
- EUR-Lex. Commission Regulation (EC) No 208/2006 of 7 February 2006 Amending Annexes VI and VIII to Regulation (EC) No 1774/2002 of the European Parliament and of the Council as Regards Processing Standards for Biogas and Composting Plants and Requirements for Manure. 2006. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2006/208/oj/eng (accessed on 15 July 2025).
- Aso, N.S. Digestate: The Coproduct of Biofuel Production in a Circular Economy, and New Results for Cassava Peeling Residue Digestate. In Renewable Energy—Technologies and Applications; Taner, T., Tiwari, A., Ustun, T.S., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ECN–QAS. European Quality Assurance Scheme for Compost and Digestate. 2014. Available online: https://www.compostnetwork.info/wordpress/wp-content/uploads/141015_ECN-QAS-Manual_2nd-edition_final_summary.pdf (accessed on 6 August 2025).
- The British Standards Institution. PAS 110:2014, Specification for Whole Digestate, Separated Liquor and Separated Fibre Derived from the Anaerobic Digestion of Source-Segregated Biodegradable Materials. 2014. Available online: https://www.wrap.ngo/sites/default/files/2021-03/PAS110_2014.pdf (accessed on 6 August 2025).
- Food and Agriculture Organization. English Summary of SPCR 120—Certification Rules for Digestate from Biowaste by the Quality Assurance System of Swedish Waste Management. 2007. Available online: https://www.fao.org/fileadmin/user_upload/nr/sustainability_pathways/docs/Certification%20rules%20for%20digestate%20from%20biowaste.pdf (accessed on 6 August 2025).
- Czekala, W.; Lewicki, A.; Pochwatka, P.; Czekala, A.; Wojcieszak, D.; Jozwiakowski, K.; Waliszewska, H. Digestate management in polish farms as an element of the nutrient cycle. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 242, 118454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cichy, P.; Tomczak-Wandzel, R.; Szatkowska, B.; Kalka, J.; Yadav, R.S. Closing the Loop: Can Anaerobic Digestates from Food Waste Be Universal Source of Nutrients for Plant Growth? Sustainability 2024, 16, 6171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabel, M.; Temperton, V.M.; Poorter, H.; Lücke, A.; Nicolai, D. Jablonowski. Energizing marginal soils—The establishment of the energy crop Sida hermaphrodita as dependent on digestate fertilization, NPK, and legume intercropping. Biomass Bioenergy 2016, 87, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widheden, J.; Ringstrom, E. Life Cycle Assessment. In Handbook for Cleaning/Decontamination of Surfaces; Johansson, I., Somasundaran, P., Eds.; Elsevier Science B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 695–720. ISBN 9780444516640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Sanz-Garrido, C.; Revuelta-Aramburu, M.; Santos-Montes, A.M.; Morales-Polo, C. A Review on Anaerobic Digestate as a Biofertilizer: Characteristics, Production, and Environmental Impacts from a Life Cycle Assessment Perspective. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 8635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugwu, S.N.; Harding, K.; Enweremadu, C.C. Comparative life cycle assessment of enhanced anaerobic digestion of agro-industrial waste for biogas production. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 345, 131178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Qi, S.; Wang, R.; Li, H.; Song, G.; Li, H.; Yin, Q. Life cycle assessment of food waste energy and resource conversion scheme via the integrated process of anaerobic digestion and hydrothermal carbonization. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 52 Pt A, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasciucco, F.; Francini, G.; Pecorini, I.; Baccioli, A.; Lombardi, L.; Ferrari, L. Valorization of biogas from the anaerobic co-treatment of sewage sludge and organic waste: Life cycle assessment and life cycle costing of different recovery strategies. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 401, 136762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayawickrama, K.; Ruparathna, R.; Seth, R.; Biswas, N.; Hafez, H.; Tam, E. Challenges and Issues of Life Cycle Assessment of Anaerobic Digestion of Organic Waste. Environments 2024, 11, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timonen, K.; Sinkko, T.; Luostarinen, S.; Tampio, E.; Joensuu, K. LCA of anaerobic digestion: Emission allocation for energy and digestate. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 235, 1567–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šařec, P.; Novák, V.; Látal, O.; Dědina, M.; Korba, J. Digestate Application on Grassland: Effects of Application Method and Rate on GHG Emissions and Forage Performance. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhan, X. Environmental sustainability assessment of pig manure mono- and co-digestion and dynamic land application of the digestate. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 137, 110476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk-Juśko, A.; Pochwatka, P.; Mazurkiewicz, M.; Pulka, J.; Kępowicz, B.; Janczak, D.; Dach, J. Reduction of Greenhouse Gas Emissions by Replacing Fertilizers with Digestate. J. Ecol. Eng. 2023, 24, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).