Mapping Dissolved Organic Carbon and Identifying Drivers in Chaohu Lake: A Novel Convolutional Multi-Head Attention Fusion Network with Hyperspectral Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- To propose a hybrid deep learning model that integrates convolutional modules and attention mechanisms for remote sensing-based estimation of DOC concentrations in inland waters, and to evaluate its prediction performance.
- (2)
- To explore the potential of hybrid algorithm-based hyperspectral remote sensing in characterizing the spatial distribution of DOC concentrations and identifying their driving factors in lake environments.
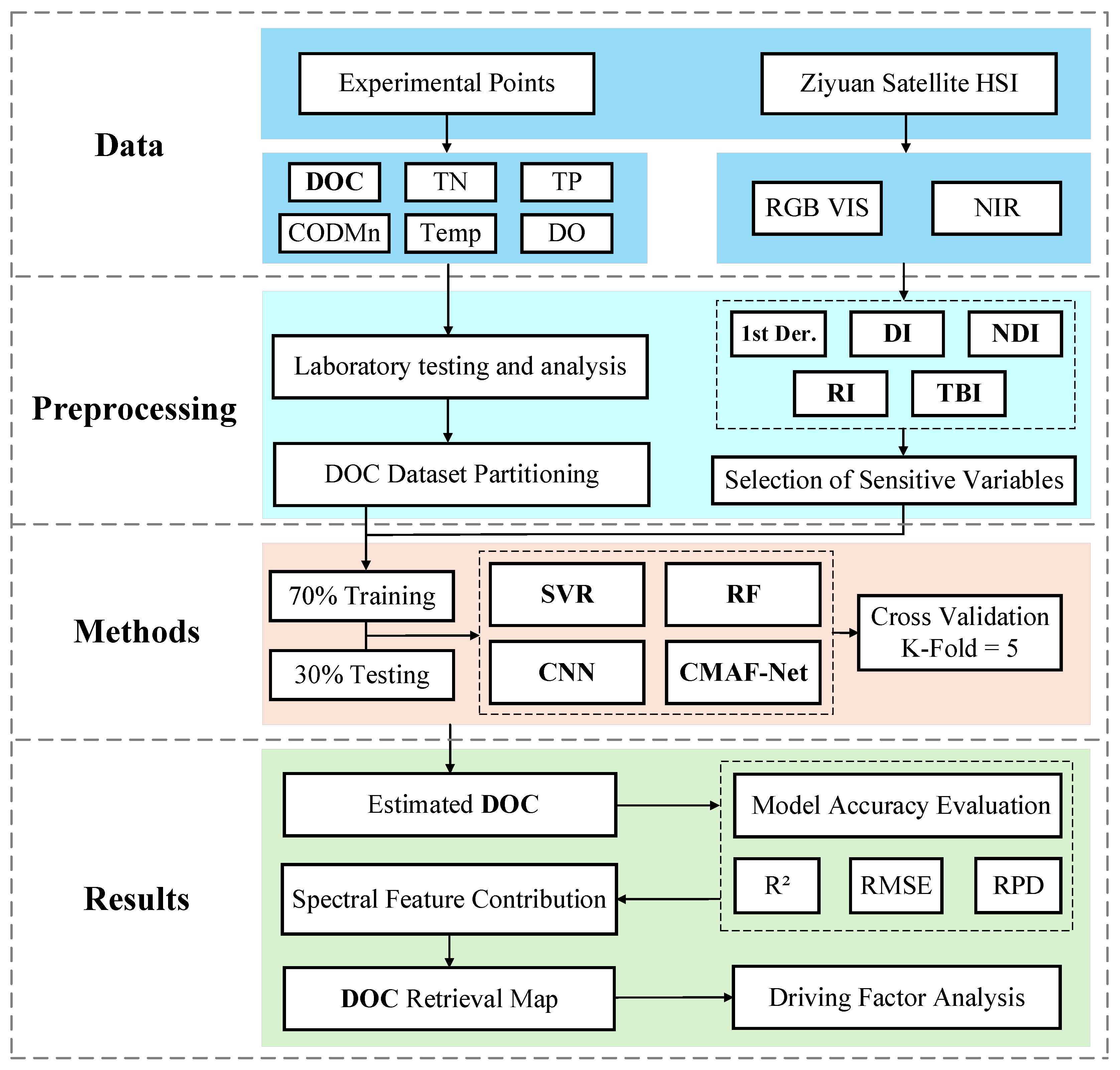
2. Materials and Methods
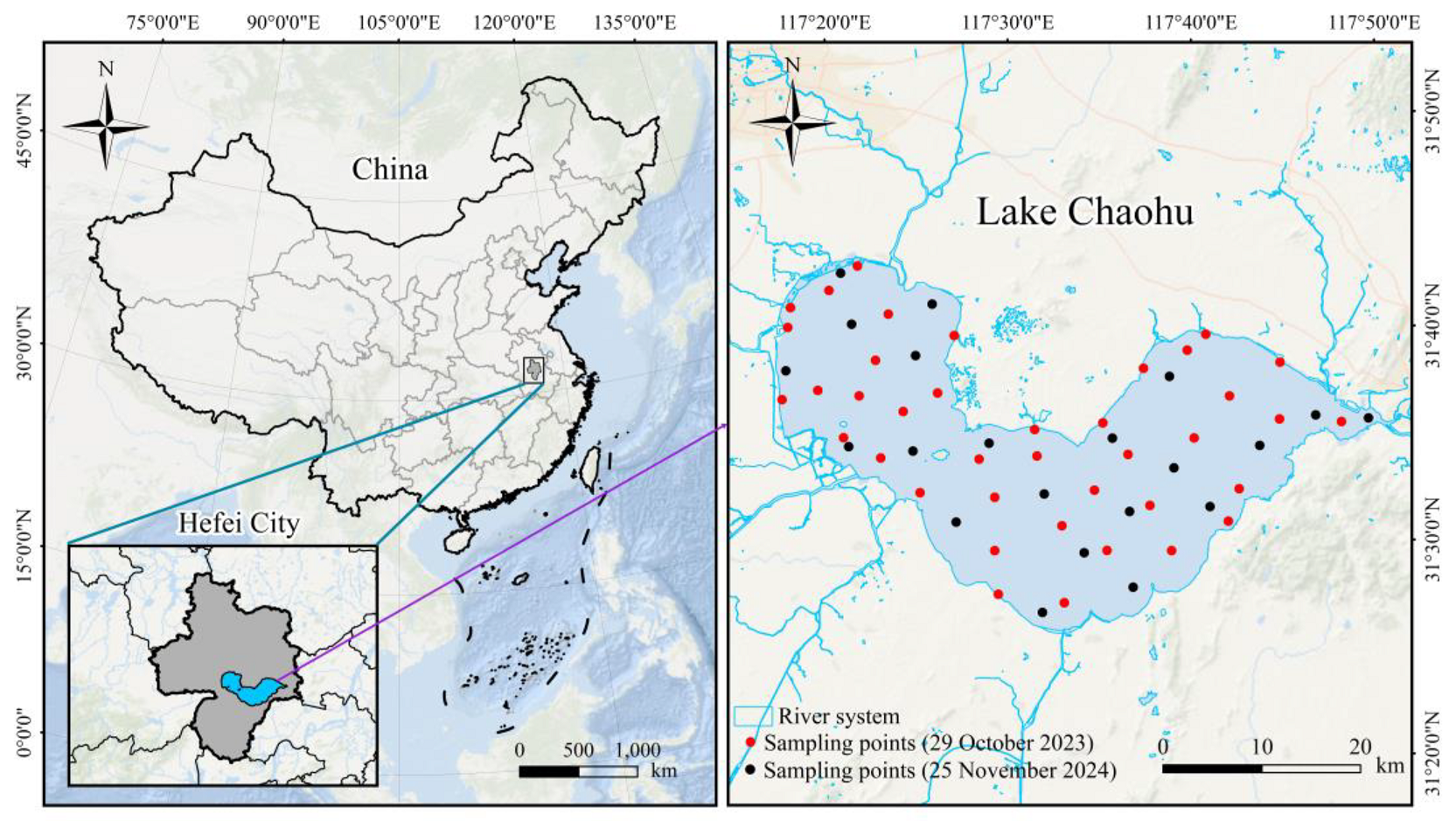
2.1. Study Area Overview
2.2. Data Acquisition and Preprocessing
2.2.1. Water Samples and Environmental Dataset
2.2.2. Satellite Data
2.2.3. Data Preprocessing
2.3. Algorithm Development
2.3.1. Support Vector Regression (SVR)
2.3.2. Random Forest (RF)
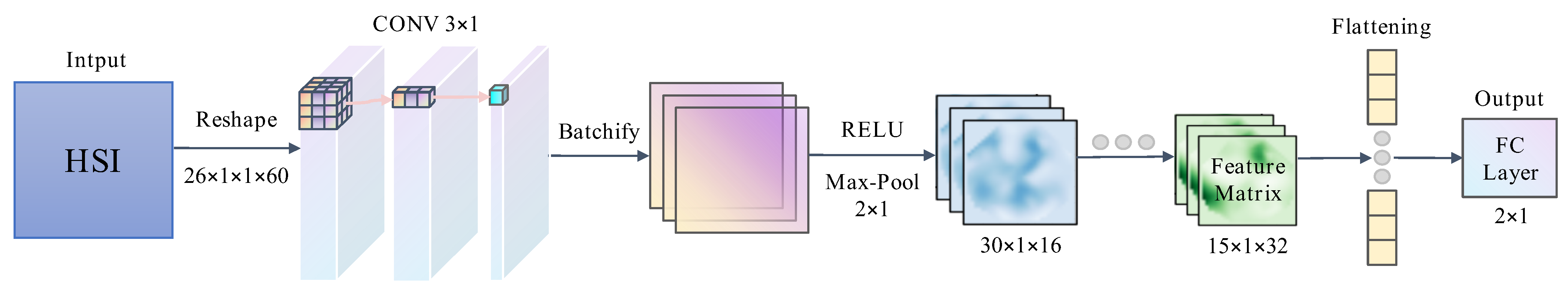
2.3.3. Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)
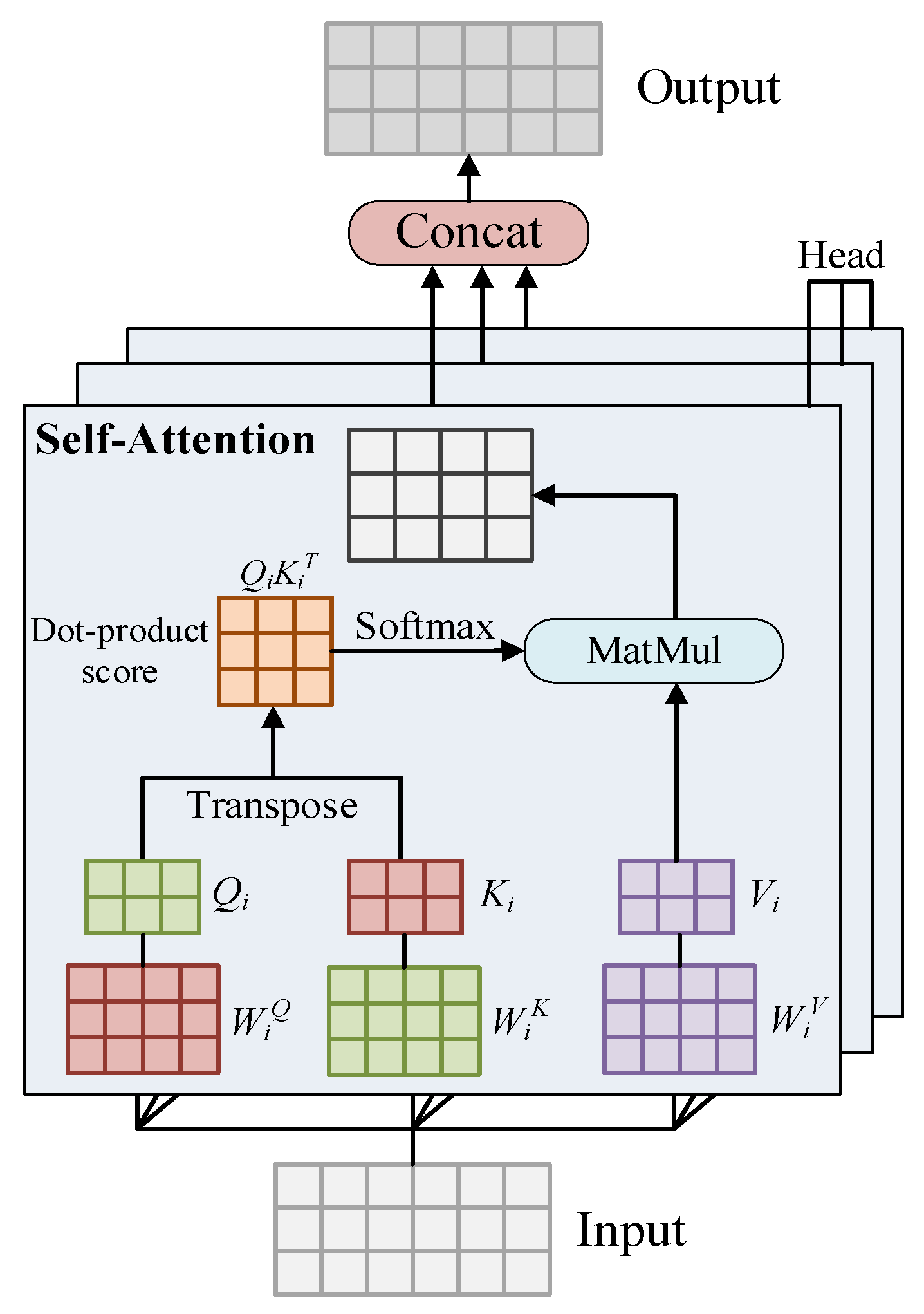
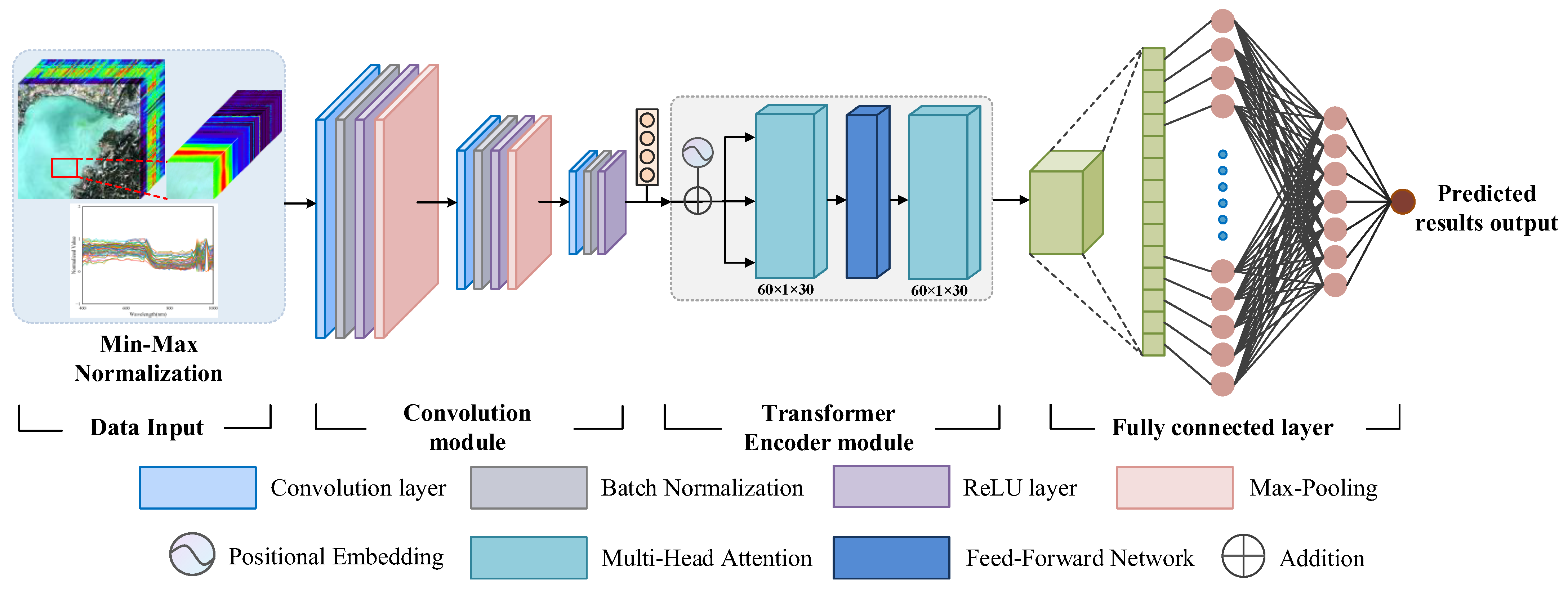
2.3.4. Convolutional Multi-Head Attention Fusion Network (CMAF-Net)
2.4. Model Accuracy Evaluation
2.5. Construction of Predictive Models
3. Results
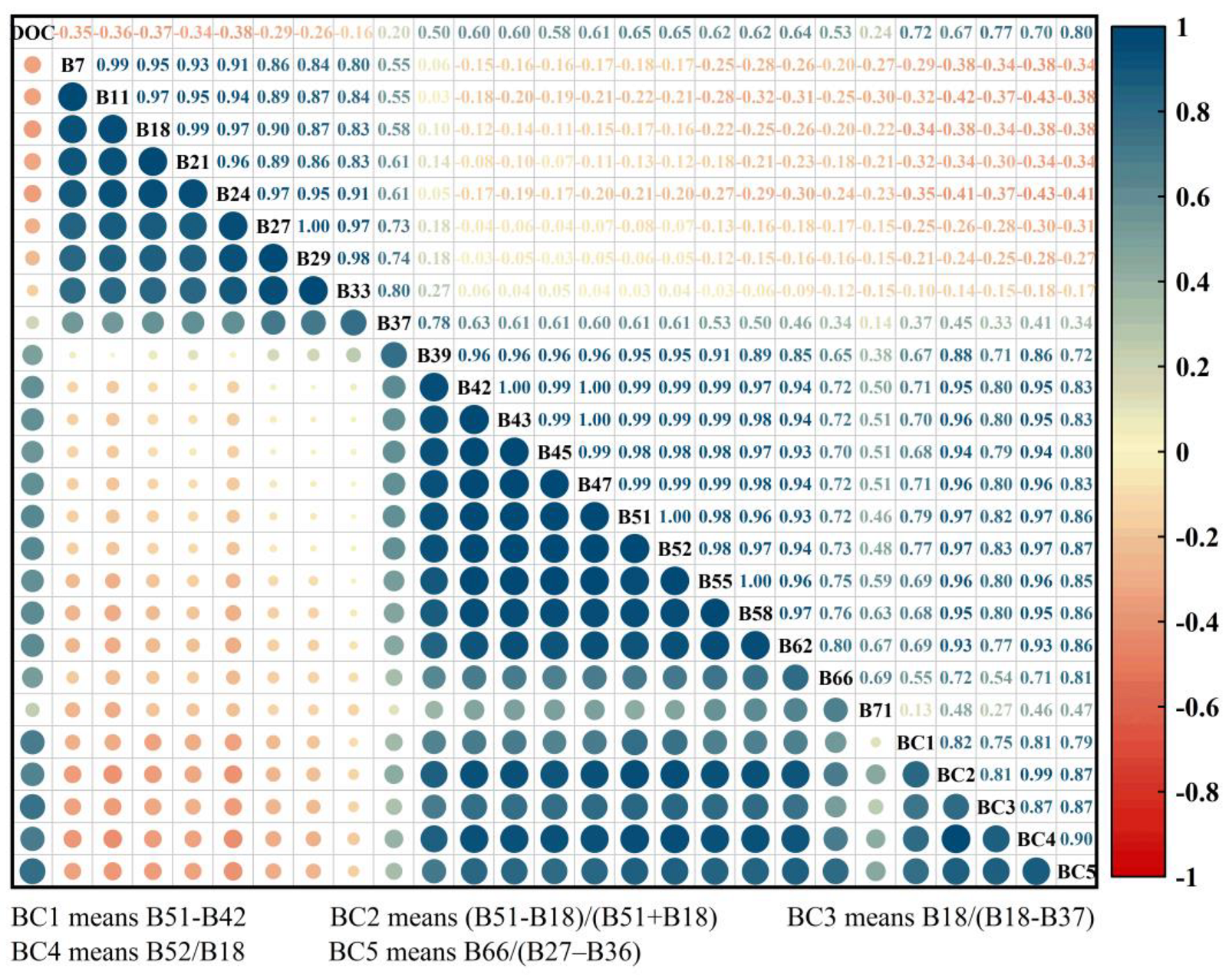
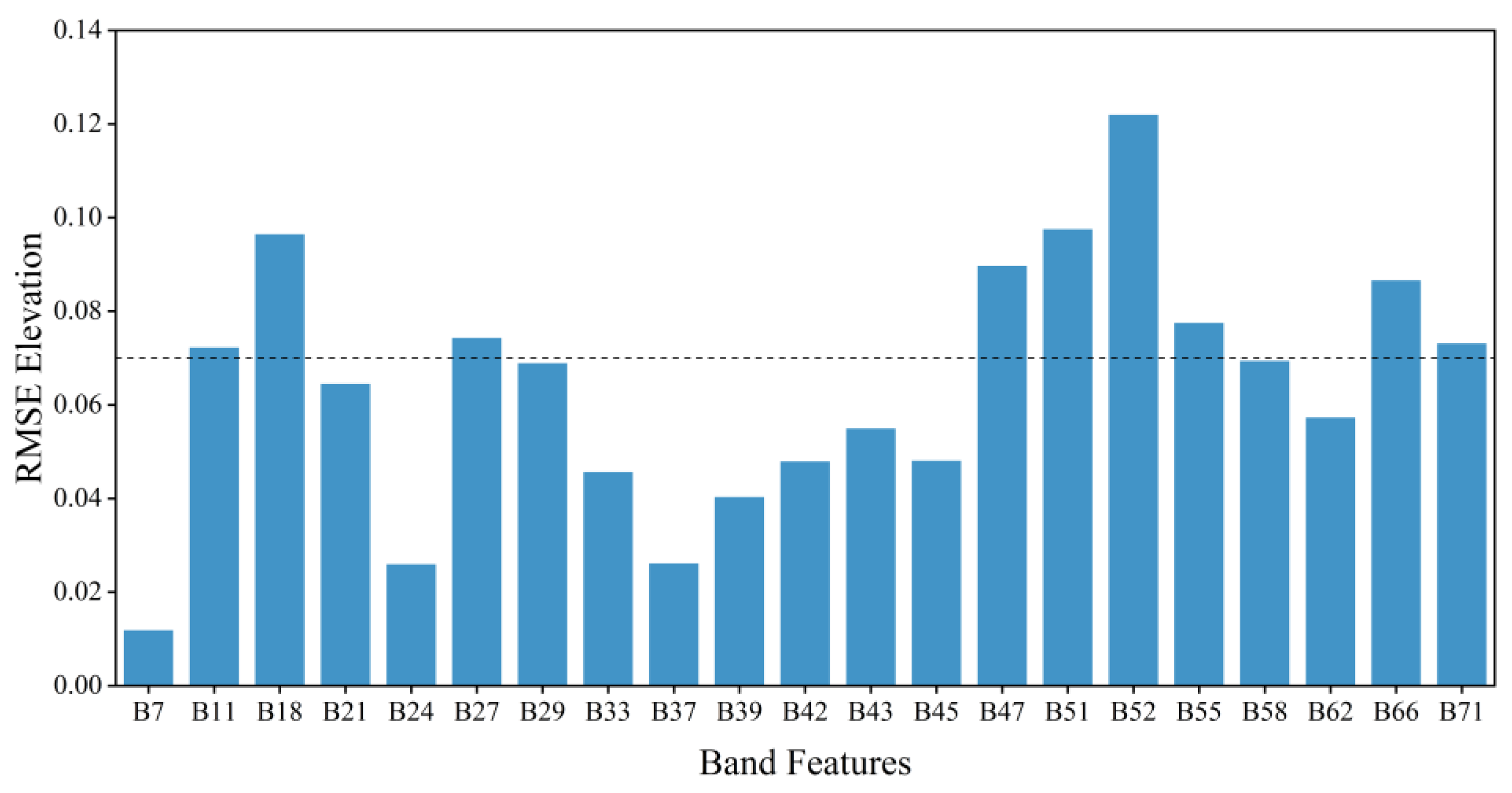
3.1. Optimal Selection of Characteristic Bands
3.2. DOC Model Analysis
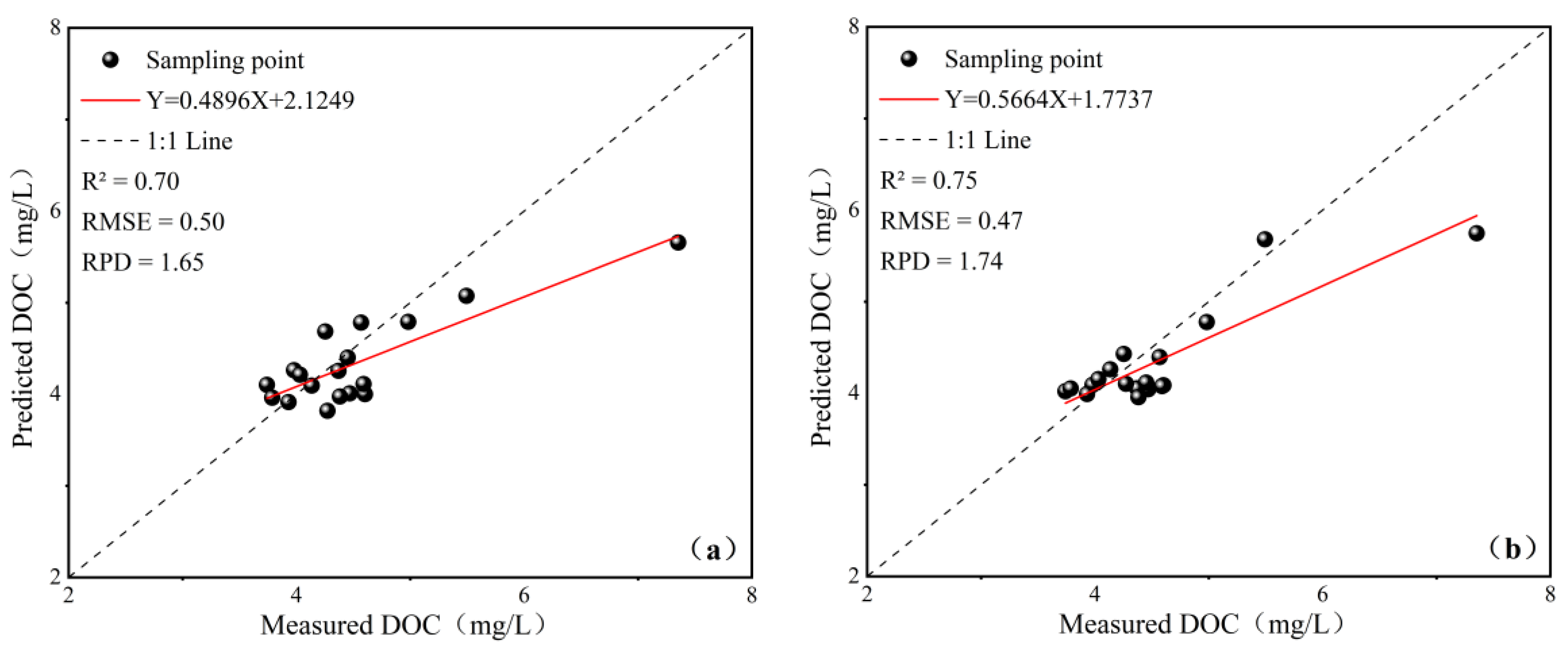
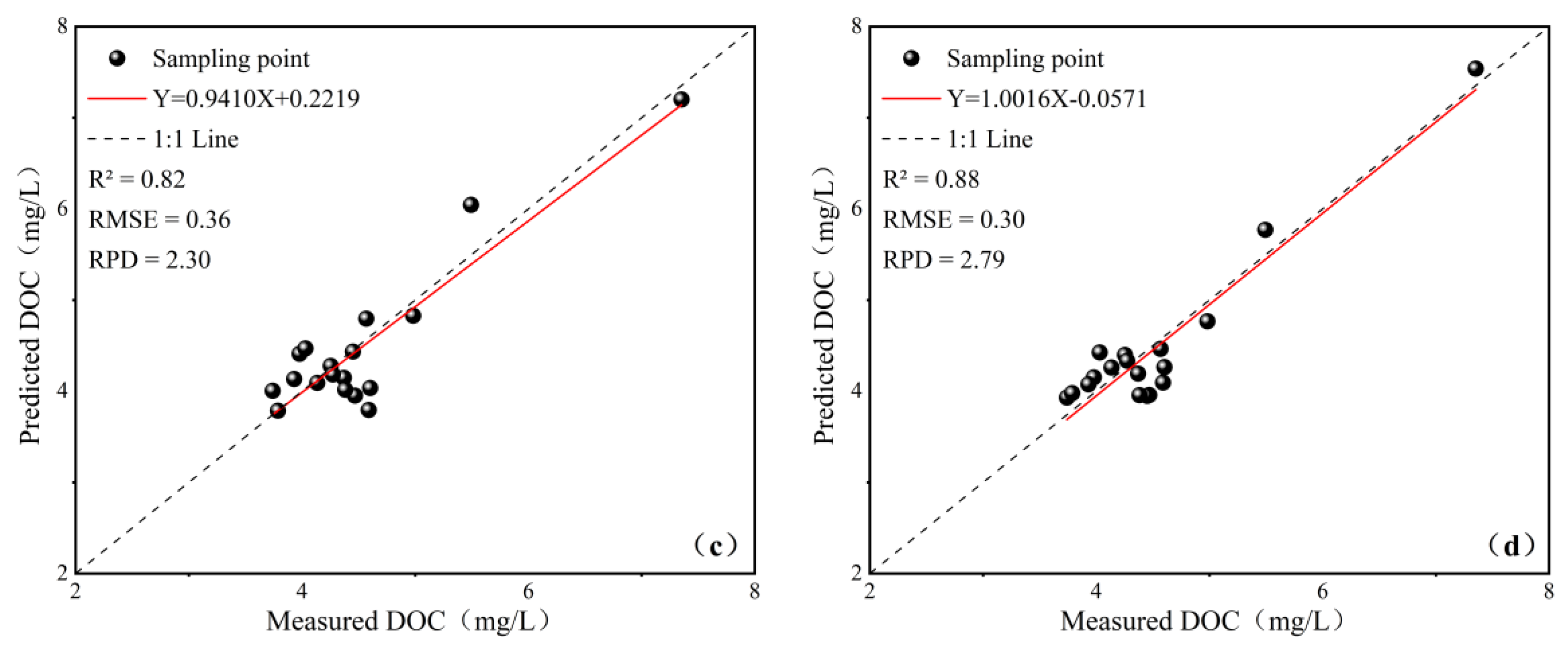
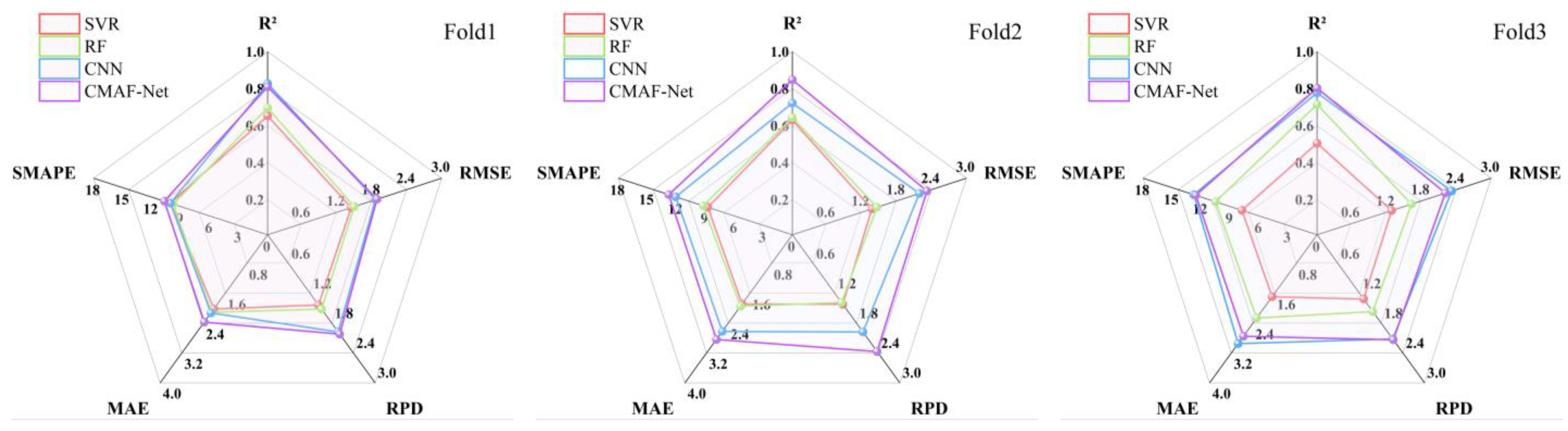
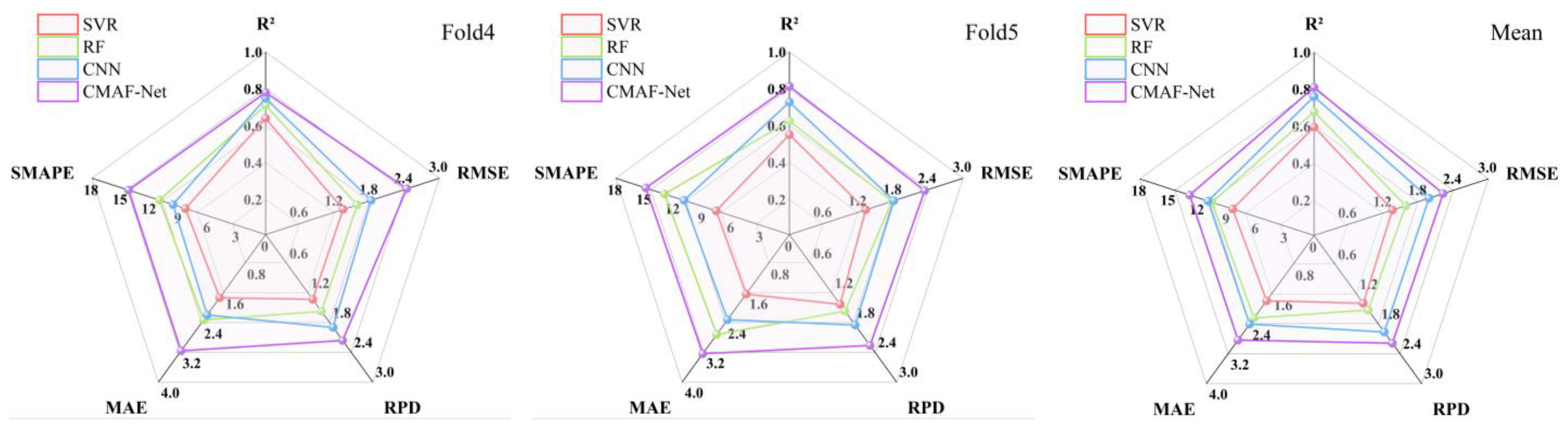
3.3. Validation of DOC Prediction Models
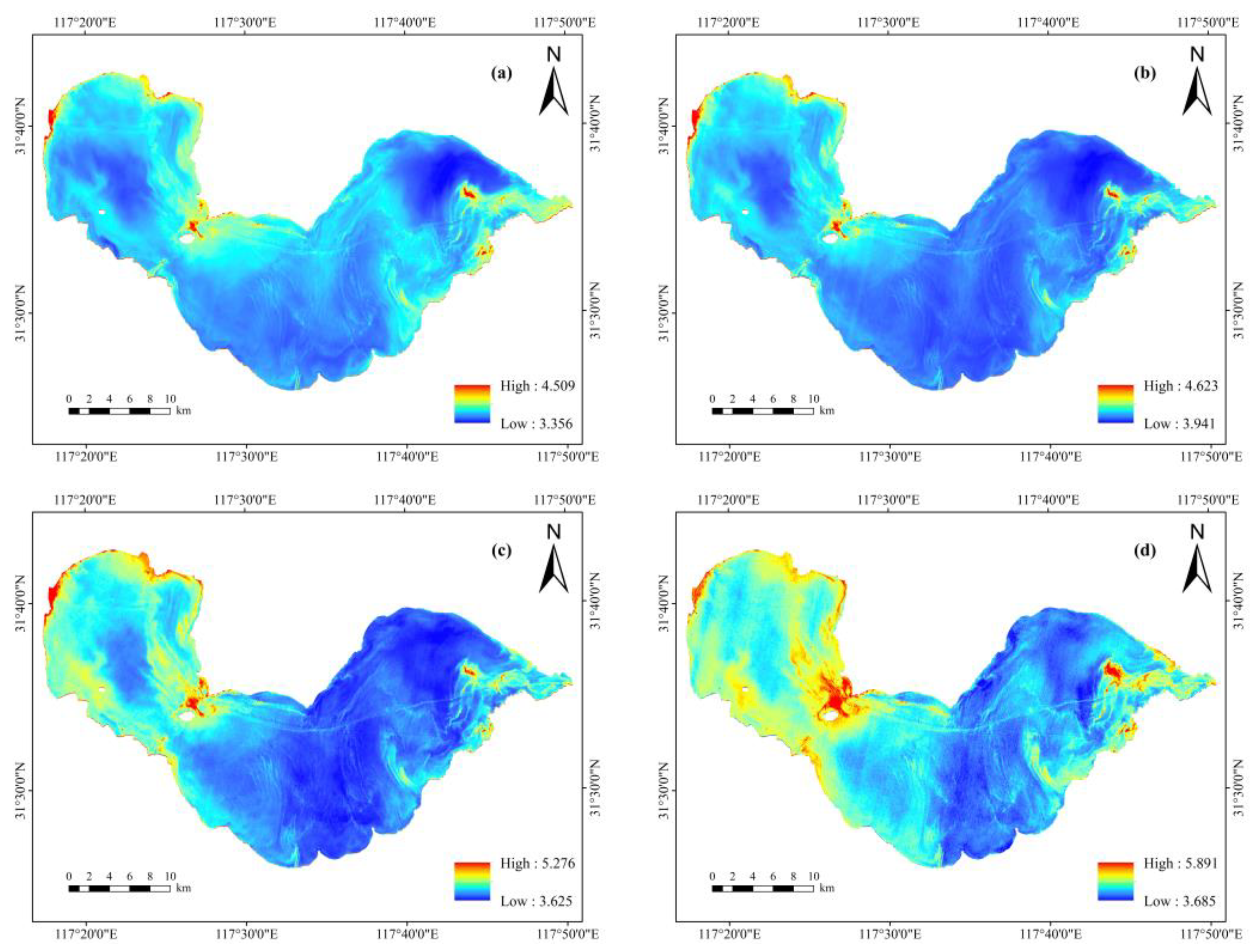
3.4. Inversion Results and Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis of Spectral Feature Contributions
4.2. Algorithm Performance
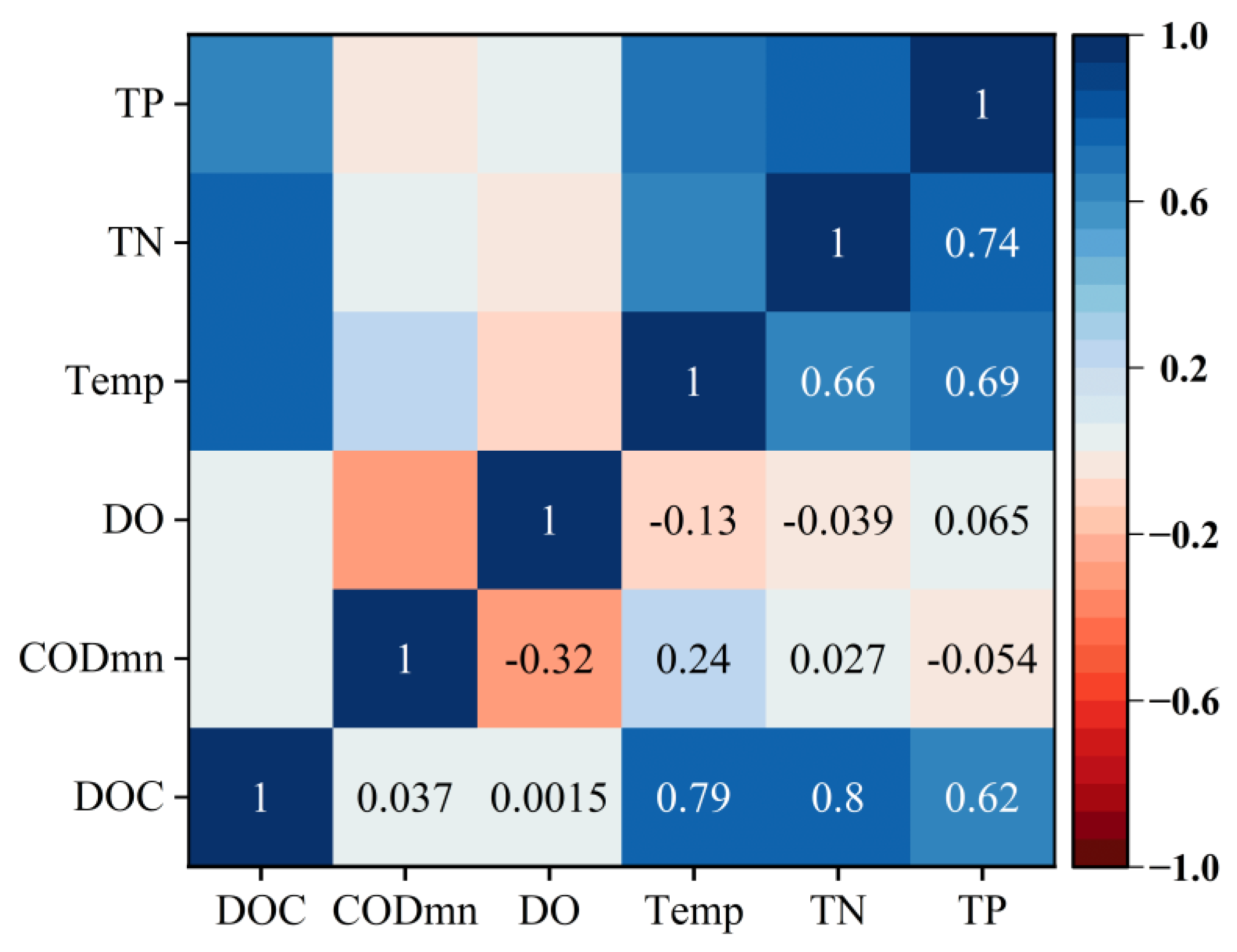
4.3. Analysis of Driving Factors
4.4. Limitations and Future Research
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The SVR, RF, and CNN models exhibited a certain level of predictive capacity for DOC in inland lakes. Among them, the CNN model performed best, achieving an R2 of 0.82, an RMSE of 0.36 mg/L, and an RPD of 2.30. After constructing CMAF-Net by combining the lightweight Transformer encoder with CNN, R2 reached 0.88, RMSE was 0.29 mg/L, and RPD was 2.79, within the range of high performance. Compared to CNN alone, R2 and RPD increased by 7.32% and 21.3%, respectively, and RMSE decreased by 19.4%, indicating that the introduction of the attention mechanism significantly enhanced the ability of the CNN model to identify key spectral features.
- (2)
- Satellite-based retrieval results show that the DOC concentration in Chaohu Lake ranges from 3.685 to 5.891 mg/L, with an average concentration of 4.45 mg/L. Higher concentrations of DOC are observed in the western part of the lake, around the islands, and near the river inflow zones, while lower concentrations appear in the central and eastern regions. Overall, the spatial distribution of the DOC exhibited a clear west–high to east–low pattern. This spatial heterogeneity reflects the combined effects of regional nutrient inputs, hydrodynamic conditions, and anthropogenic activities.
- (3)
- Five water environmental variables generally showed higher concentrations in the western half of Chaohu Lake. Among them, nitrogen, phosphorus, and water temperature were strongly positively correlated with DOC concentrations, suggesting that they are the main drivers of the spatial patterns of DOC in Chaohu Lake.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiao, Q.; Xu, X.; Qi, T.; Luo, J.; Lee, X.; Duan, H. Lakes Shifted from a Carbon Dioxide Source to a Sink over Past Two Decades in China. Sci. Bull. 2024, 69, 1857–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Gao, Y.; Jia, J.; Lu, Y.; Wang, J.; Ha, X.; Li, Z.; Sun, K. Determining Whether Hydrological Processes Drive Carbon Source and Sink Conversion Shifts in a Large Floodplain-Lake System in China. Water Res. 2022, 224, 119105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jeppesen, E.; Weyhenmeyer, G.A. Rainstorm-Induced Organic Matter Pulses: A Key Driver of Carbon Emissions from Inland Waters. Innov. 2025, 6, 100746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paíz, R.; Pierson, D.C.; Lindqvist, K.; Naden, P.S.; De Eyto, E.; Dillane, M.; McCarthy, V.; Linnane, S.; Jennings, E. Accounting for Model Parameter Uncertainty Provides More Robust Projections of Dissolved Organic Carbon Dynamics to Aid Drinking Water Management. Water Res. 2025, 276, 123238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Hou, J.; Suo, C.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Fu, R.; Wu, F. Molecular-Level Composition of Dissolved Organic Matter in Distinct Trophic States in Chinese Lakes: Implications for Eutrophic Lake Management and the Global Carbon Cycle. Water Res. 2022, 217, 118438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Peng, H.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; Wu, Z.; Shao, B.; Xing, G.; Huang, Z.; Zhao, F.; Cui, H.; et al. Unveiling the Global Dynamics of Dissolved Organic Carbon in Aquatic Ecosystems: Climatic and Anthropogenic Impact, and Future Predictions. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 958, 178109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; He, Z.; Tang, Z.; Liu, L.; Hou, J.; Li, T.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Q.; Giesy, J.P.; Wu, F. Linking the Molecular Composition of Autochthonous Dissolved Organic Matter to Source Identification for Freshwater Lake Ecosystems by Combination of Optical Spectroscopy and FT-ICR-MS Analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 134764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilla, R.M.; Couture, R. Attenuation of Photosynthetically Active Radiation and Ultraviolet Radiation in Response to Changing Dissolved Organic Carbon in Browning Lakes: Modeling and Parametrization. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2021, 66, 2278–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Qian, M.; Song, Y.; Chen, B.; Yang, J. Surface pCO2 and Air-Water CO2 Fluxes Dominated by Submerged Aquatic Vegetation: Implications for Carbon Flux in Shallow Lakes. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, D.; Li, L.; Ning, R.; Yu, S.; Gao, N. Application of Remote Sensing Technology in Water Quality Monitoring: From Traditional Approaches to Artificial Intelligence. Water Res. 2024, 267, 122546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Shi, K.; Zhang, Y. Remote Sensing Estimation of Dissolved Organic Carbon Concentrations in Chinese Lakes Based on Landsat Images. J. Hydrol. 2024, 638, 131466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonelli, A.G.; Loisel, H.; Jorge, D.S.F.; Mangin, A.; d’Andon, O.F.; Vantrepotte, V. A New Method to Estimate the Dissolved Organic Carbon Concentration from Remote Sensing in the Global Open Ocean. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 281, 113227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, C.; Tan, K.; Wang, X.; Pan, C. Mapping Nutrient Pollution in Inland Water Bodies Using Multi-Platform Hyperspectral Imagery and Deep Regression Network. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 488, 137314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.; Wang, J.; Chen, R.; Kang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Lv, Z.; Ding, D.; Feng, H. Research Progress of Inland River Water Quality Monitoring Technology Based on Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Hyperspectral Imaging Technology. Environ. Res. 2024, 257, 119254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Alem, A.; Chokmani, K.; Venkatesan, A.; Lhissou, R.; Martins, S.; Campbell, P.; Cardille, J.; McGeer, J.; Smith, S. Modeling Dissolved Organic Carbon in Inland Waters Using an Unmanned Aerial Vehicles-Borne Hyperspectral Camera. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 954, 176258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Wang, Z.; Huang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xia, H.; Cao, L. Transparency Estimation of Narrow Rivers by UAV-Borne Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Imagery. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 168137–168153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dev, P.J.; Sukenik, A.; Mishra, D.R.; Ostrovsky, I. Cyanobacterial Pigment Concentrations in Inland Waters: Novel Semi-Analytical Algorithms for Multi- and Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Data. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 805, 150423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zheng, Z.; Li, Y.; Lyu, H.; Ren, J.; Cai, X.; Du, C.; Chen, N.; Liu, G.; Lei, S.; et al. A Hybrid Algorithm for Estimating Total Nitrogen from a Large Eutrophic Plateau Lake Using Orbita Hyperspectral (OHS) Satellite Imagery. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2024, 131, 103971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobley, C.; Stramski, D.; Bissett, P.; Boss, E. Optical Modeling of Ocean Waters: Is the Case 1-Case 2 Classification Still Useful? Oceanography 2004, 17, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shea, R.E.; Pahlevan, N.; Smith, B.; Boss, E.; Gurlin, D.; Alikas, K.; Kangro, K.; Kudela, R.M.; Vaičiūtė, D. A Hyperspectral Inversion Framework for Estimating Absorbing Inherent Optical Properties and Biogeochemical Parameters in Inland and Coastal Waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 295, 113706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-M.; Kuo, C.-Y.; Yang, C.-H.; Kao, H.-C.; Tseng, K.-H.; Lan, W.-H. Assessment of Hydrological Changes in Inland Water Body Using Satellite Altimetry and Landsat Imagery: A Case Study on Tsengwen Reservoir. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 44, 101227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Knudby, A.; Pahlevan, N.; Lapen, D.; Zeng, C. Sensor-Generic Adjacency-Effect Correction for Remote Sensing of Coastal and Inland Waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 315, 114433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Song, K.; Wen, Z.; Liu, G.; Shang, Y.; Fang, C.; Wang, Q. Remote Sensing of Total Suspended Matter of Inland Waters: Past, Current Status, and Future Directions. Ecol. Inform. 2025, 86, 103062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, D.; Yang, S.X.; Gharabaghi, B. Review of Recent Advances in Remote Sensing and Machine Learning Methods for Lake Water Quality Management. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhang, J. Prediction of Chlorophyll a and Risk Assessment of Water Blooms in Poyang Lake Based on a Machine Learning Method. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 347, 123501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozbayram, O.; Olivier, A.; Graham-Brady, L. Heteroscedastic Gaussian Process Regression for Material Structure–Property Relationship Modeling. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2024, 431, 117326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codden, C.J.; Snauffer, A.M.; Mueller, A.V.; Edwards, C.R.; Thompson, M.; Tait, Z.; Stubbins, A. Predicting Dissolved Organic Carbon Concentration in a Dynamic Salt Marsh Creek via Machine Learning. Limnol. Ocean. Methods 2021, 19, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harkort, L.; Duan, Z. Estimation of Dissolved Organic Carbon from Inland Waters at a Large Scale Using Satellite Data and Machine Learning Methods. Water Res. 2023, 229, 119478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichstein, M.; Camps-Valls, G.; Stevens, B.; Jung, M.; Denzler, J.; Carvalhais, N. Prabhat Deep Learning and Process Understanding for Data-Driven Earth System Science. Nature 2019, 566, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, H.J.; Lutz, D.A.; Steele, B.G.; Cottingham, K.L.; Weathers, K.C.; Ducey, M.J.; Palace, M.; Johnson, K.M.; Chipman, J.W. Remote Sensing of Lake Water Clarity: Performance and Transferability of Both Historical Algorithms and Machine Learning. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Zhou, G.; Pablo Antezana Lopez, F.; Xu, C.; Jing, G.; Tan, Y. Deep Learning for Water Quality Multivariate Assessment in Inland Water across China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2024, 133, 104078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandasamy, L.; Mahendran, A.; Sangaraju, S.H.V.; Mathur, P.; Faldu, S.V.; Mazzara, M. Enhanced Remote Sensing and Deep Learning Aided Water Quality Detection in the Ganges River, India Supporting Monitoring of Aquatic Environments. Results Eng. 2025, 25, 103604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyo, J.; Park, L.J.; Pachepsky, Y.; Baek, S.-S.; Kim, K.; Cho, K.H. Using Convolutional Neural Network for Predicting Cyanobacteria Concentrations in River Water. Water Res. 2020, 186, 116349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhimathi, G.; Chellaswamy, C.; Thiruvalar Selvan, P. Comprehensive River Water Quality Monitoring Using Convolutional Neural Networks and Gated Recurrent Units: A Case Study along the Vaigai River. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 365, 121567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fichot, C.G.; Tzortziou, M.; Mannino, A. Remote Sensing of Dissolved Organic Carbon (DOC) Stocks, Fluxes and Transformations along the Land-Ocean Aquatic Continuum: Advances, Challenges, and Opportunities. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2023, 242, 104446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleissaee, A.A.; Kumar, A.; Anwer, R.M.; Khan, S.; Cholakkal, H.; Xia, G.-S.; Khan, F.S. Transformers in Remote Sensing: A Survey. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An Image Is Worth 16 × 16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale 2021. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Hu, M.; Hou, S.; Shang, R.; Feng, J.; Xu, S. Group-Spectral Superposition and Position Self-Attention Transformer for Hyperspectral Image Classification. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 265, 125846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, R.; Yang, J.; Feng, J.; Li, Y.; Xu, S. Hyperspectral Image Classification Based on ConvGRU and Spectral–Spatial Joint Attention. Appl. Soft Comput. 2025, 174, 112949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidi, S.; Sellami, A. Attention-Driven Multi-Feature Fusion for Hyperspectral Image Classification via Multi-Criteria Optimization and Multi-View Convolutional Neural Networks. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 138, 109434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fu, H.; Yang, X.; Liu, Z. Anthropogenically Driven Changes to Organic Matter Input in Sediments of Lake Chaohu, Eastern China, over the Past 166 Years. CATENA 2023, 231, 107285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Li, Y.; Jiang, B.; Alatalo, J.M.; Li, C.; Ni, C. Tracking Spatio-Temporal Dynamics of Harmful Algal Blooms Using Long-Term MODIS Observations of Chaohu Lake in China from 2000 to 2021. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Liu, H.; Zhong, P.; Hu, Z.; Cao, Z.; Shen, M.; Tan, Z.; Liu, W.; Liu, C.; Li, D.; et al. Remote Retrieval of Dissolved Organic Carbon in Rivers Using a Hyperspectral Drone System. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2024, 17, 2358863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Liu, M.; Li, Z.; Gao, X.; Yang, R.; Ni, M.; Xu, Y.J.; Wang, Y.; Ye, C.; Yuan, D.; et al. Eutrophication Constrains Driving Forces of Dissolved Organic Carbon Biodegradation in Metropolitan Lake Systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 953, 176177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Xi, S.; Li, G.; Li, H.; Chen, X.; Song, F.; et al. Spatiotemporal Variation and Influencing Factors of Phosphorus in Asia’s Longest River Based on Receptor Model and Machine Learning. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 171, 113217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 11892-1989; Water Quality—Determination of Permanganate Index. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 1989.
- Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Yang, K.; Zhao, H. Inversion Monitoring of Heavy Metal Pollution in Corn Crops Based on ZY-1 02D Hyperspectral Imaging. Microchem. J. 2025, 208, 112305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Fang, S.; Shen, W.; Li, X.; Mao, Z.; Wu, S. Integration of Geographic Features and Bathymetric Inversion in the Yangtze River’s Nantong Channel Using Gradient Boosting Machine Algorithm with ZY-1E Satellite and Multibeam Data. Geomatica 2024, 76, 100027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subi, X.; Eziz, M.; Zhong, Q.; Li, X. Estimating the Chromium Concentration of Farmland Soils in an Arid Zone from Hyperspectral Reflectance by Using Partial Least Squares Regression Methods. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 161, 111987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Xu, Y.; Fang, C.; Zhang, C.; Xin, Z.; Liu, Z. SVR Model and OLCI Images Reveal a Declining Trend in Phycocyanin Levels in Typical Lakes across Northeast China. Ecol. Inform. 2025, 85, 102965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scornet, E.; Biau, G.; Vert, J.-P. Consistency of Random Forests. Ann. Statist. 2015, 43, 1716–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Tang, X.; Ren, Q. Power Prediction for Salinity-Gradient Osmotic Energy Conversion Based on Multiscale and Multidimensional Convolutional Neural Network. Energy 2024, 313, 133729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soylu, E.; Gül, S.; Koca, K.A.; Türkoğlu, M.; Terzi, M.; Şengür, A. Speech Signal-Based Accurate Neurological Disorders Detection Using Convolutional Neural Network and Recurrent Neural Network Based Deep Network. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2025, 149, 110558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, X.-P.; He, Y. A Deep Learning Model Based on Transformer Structure for Radar Tracking of Maneuvering Targets. Inf. Fusion 2024, 103, 102120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, L.; Ren, P.; Wang, J.; Ren, G.; Liu, B. A Spatial–Spectral Fusion Convolutional Transformer Network with Contextual Multi-Head Self-Attention for Hyperspectral Image Classification. Neural Netw. 2025, 187, 107350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.; Wang, H.; Lou, J. A Temporal Prediction Model for Ship Maneuvering Motion Based on Multi-Head Attention Mechanism. Ocean. Eng. 2024, 309, 118464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention Is All You Need. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.03762. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, X.; See, K.W.; Li, P.; Shan, K.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Lim, K.C.; Zhang, N. A Novel State-of-Health Estimation for the Lithium-Ion Battery Using a Convolutional Neural Network and Transformer Model. Energy 2023, 262, 125501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Bao, N.; Yu, M.; Cao, Y. Estimating and Mapping Tailings Properties of the Largest Iron Cluster in China for Resource Potential and Reuse: A New Perspective from Interpretable CNN Model and Proposed Spectral Index Based on Hyperspectral Satellite Imagery. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2025, 139, 104512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Bai, Y.; Yu, Q.; Ding, L.; Song, W.; Liu, W.; Ren, H.; Song, Q. Novel Hybrid Data-Driven Modeling Based on Feature Space Reconstruction and Multihead Self-Attention Gated Recurrent Unit: Applied to PM2.5 Concentrations Prediction. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 17087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Zhang, J.; Meng, H.; Lai, Y.; Xu, M. Remote Sensing Inversion of Water Quality Parameters in the Yellow River Delta. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 155, 110914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Yan, X.; Qiao, X.; Wei, K.; Zhang, X.; Yang, S.; Wang, C.; Yang, W.; Feng, M.; Xiao, L.; et al. Multivariate Prediction of Soil Aggregate-Associated Organic Carbon by Simulating Satellite Sensor Bands. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 209, 107859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Pan, Y.; Ren, S.; Gao, Y.; Wu, H.; Ma, G. Accurate Vegetation Destruction Detection Using Remote Sensing Imagery Based on the Three-Band Difference Vegetation Index (TBDVI) and Dual-Temporal Detection Method. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2024, 127, 103669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottin, A.; Zulian, M.; Pécuchet, N.; Guilloux, A.; Katsahian, S. MS-CPFI: A Model-Agnostic Counterfactual Perturbation Feature Importance Algorithm for Interpreting Black-Box Multi-State Models. Artif. Intell. Med. 2024, 147, 102741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocki, L.; Chung, N.C. Feature Perturbation Augmentation for Reliable Evaluation of Importance Estimators in Neural Networks. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2023, 176, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neil, C.; Spyrakos, E.; Hunter, P.D.; Tyler, A.N. A Global Approach for Chlorophyll-a Retrieval across Optically Complex Inland Waters Based on Optical Water Types. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 229, 159–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Spyrakos, E.; Tyler, A.; Shi, K.; Duan, H. Satellite Algorithms for Retrieving Dissolved Organic Carbon Concentrations in Chinese Lakes. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 955, 177117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, A.G.; Krickov, I.V.; Pokrovsky, O.S. Organic Carbon, Major and Trace Element Release from and Adsorption onto Particulate Suspended Matter of the Ob River, Western Siberia. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 948, 174735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Lin, J.; Lin, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Pfister, H.; Timofte, R.; Gool, L.V. MST++: Multi-Stage Spectral-Wise Transformer for Efficient Spectral Reconstruction. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–20 June 2022; pp. 744–754. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Zhong, P.; Zhan, X.; Chen, X.; Huang, F. Progressive CNN-Transformer Alternating Reconstruction Network for Hyperspectral Image Reconstruction—A Case Study in Red Tide Detection. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2024, 134, 104129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Farooque, G.; Liu, Q.; Hadi, F.; Xiao, L. MSTSENet: Multiscale Spectral–Spatial Transformer with Squeeze and Excitation Network for Hyperspectral Image Classification. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 134, 108669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanthini, K.S.; George, S.N.; OV, A.C.; Jinumol, K.M.; Keerthana, P.; Francis, J.; George, S. NorBlueNet: Hyperspectral Imaging-Based Hybrid CNN-Transformer Model for Non-Destructive SSC Analysis in Norwegian Wild Blueberries. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2025, 235, 110340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.-C.; Roth, H.R.; Gao, M.; Lu, L.; Xu, Z.; Nogues, I.; Yao, J.; Mollura, D.; Summers, R.M. Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Computer-Aided Detection: CNN Architectures, Dataset Characteristics and Transfer Learning. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2016, 35, 1285–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, K.; Wu, S.; Shi, H.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhuang, H.; Fu, E. An Investigation of a Multidimensional CNN Combined with an Attention Mechanism Model to Resolve Small-Sample Problems in Hyperspectral Image Classification. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.; Wang, S.; Zou, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y. Seasonal Surface Urban Heat Island Analysis Based on Local Climate Zones. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 159, 111669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Hu, M.; Weng, Q.; Zhang, H. Spatial Heterogeneity Modeling of Water Quality Based on Random Forest Regression and Model Interpretation. Environ. Res. 2021, 202, 111660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Du, Y.; Wu, T.; Jiang, X.; Deng, B.; Li, M.; Gan, Y.; Song, M.; Liao, S.; Zhang, R.; et al. Spatial and Temporal Variability in Molecular Characteristics of Dissolved Organic Matter in a Large Freshwater Lake: A Case from the Dongting Lake, Central China. J. Hydrol. 2025, 661, 133831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, S.; Chen, S.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, S.; Fedorova, I.V. Seasonal Effects of Hydrometeorological Factors on the Distribution and Partition of Organic Carbon in the Yangtze River Estuary. Estuaries Coasts 2025, 48, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou, C.-Y.; Yue, F.-J.; Zhou, B.; Fu, X.; Ma, Z.-N.; Gong, Y.-Q.; Chen, S.-N. Chronic Increasing Nitrogen and Endogenous Phosphorus Release from Sediment Threaten to the Water Quality in a Semi-Humid Region Reservoir. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 931, 172924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Bai, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, M.; Wang, H.; Bai, Y. Variations of Sediment Organic Phosphorus and Organic Carbon during the Outbreak and Decline of Algal Blooms in Lake Taihu, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2024, 139, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corman, J.R.; Bertolet, B.L.; Casson, N.J.; Sebestyen, S.D.; Kolka, R.K.; Stanley, E.H. Nitrogen and Phosphorus Loads to Temperate Seepage Lakes Associated With Allochthonous Dissolved Organic Carbon Loads. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 5481–5490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntington, T.G.; Shanley, J.B. A Systematic Increase in the Slope of the Concentration Discharge Relation for Dissolved Organic Carbon in a Forested Catchment in Vermont, USA. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 844, 156954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Yu, S.; Xiao, Q.; Qi, T.; Duan, H. Satellite Estimation of Dissolved Organic Carbon in Eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 264, 112572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Xue, R.; Luo, M.; Wang, W.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y. Advances in Dissolved Organic Carbon Remote Sensing Inversion in Inland Waters: Methodologies, Challenges, and Future Directions. Sustainability 2025, 17, 6652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

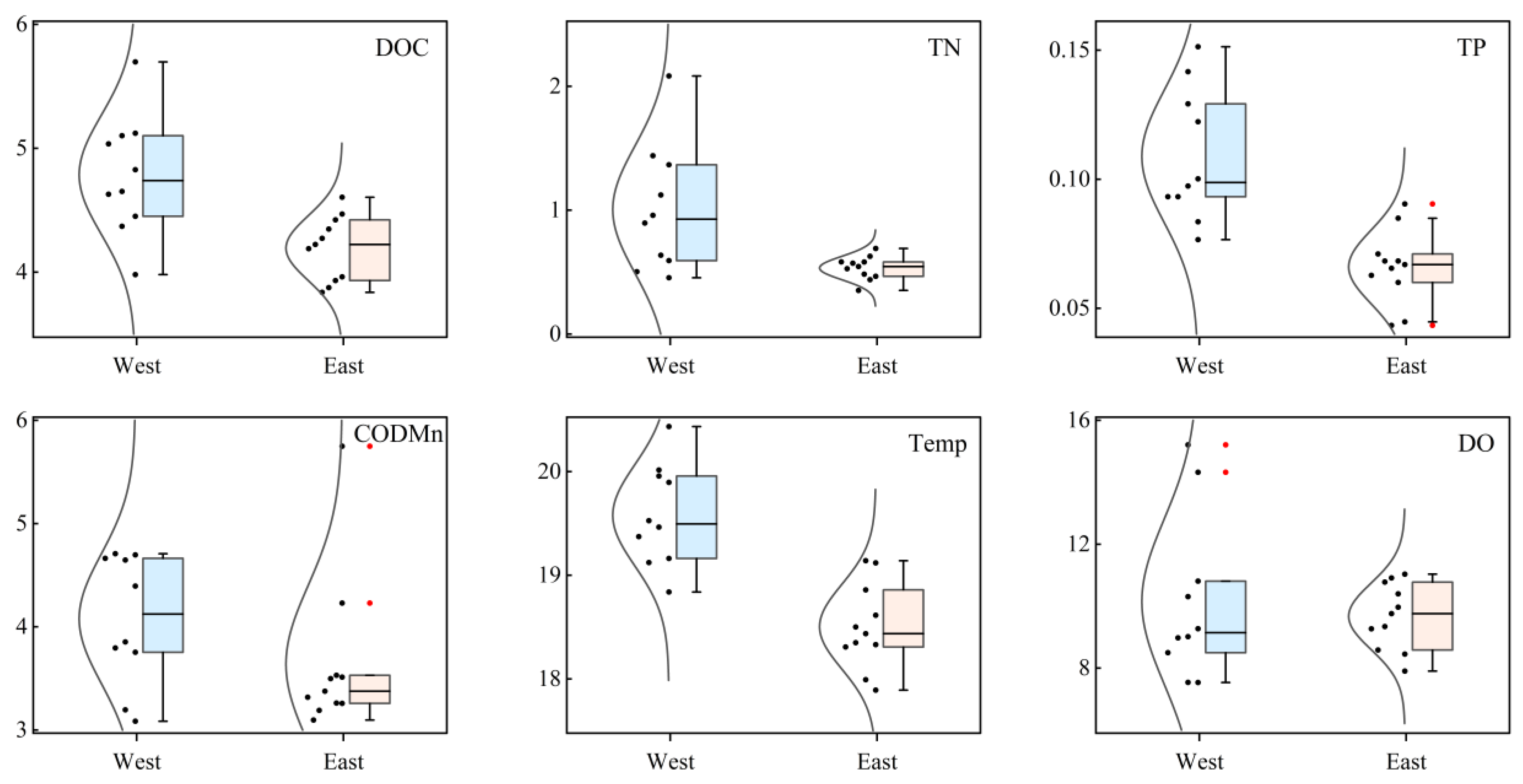
| Sampling Date | Number | Min (mg/L) | Max (mg/L) | Mean (mg/L) | Standard Deviation | IQR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 29 October 2023 | 39 | 3.53 | 9.03 | 4.40 | 1.11 | 0.76 |
| 25 November 2024 | 21 | 3.84 | 5.70 | 4.48 | 0.48 | 0.46 |
| Satellite Payload | ZY1-02D | ZY1-02E |
|---|---|---|
| Launch date | 12 September 2019 | 26 December 2021 |
| Number of spectral bands | 166 | 166 |
| Spectral range (nm) | 400–2500 | 400–2500 |
| Spectral resolution (nm) | 10(VNIR) 20(SWIR) | 10(VNIR) 20(SWIR) |
| Spatial resolution (m) | 30 | 30 |
| Swath width (km) | 60 | 60 |
| Revisit period (days) | 3 | 3 |
| Sample Set | Number | DOC Content (mg/L) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | Max | Mean | Standard Deviation | ||
| Training Set | 42 | 3.53 | 9.03 | 4.39 | 0.98 |
| Test Set | 18 | 3.66 | 7.35 | 4.52 | 0.82 |
| Total Set | 60 | 3.53 | 9.03 | 4.43 | 0.93 |
| Model Type | Training Set | Test Set | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSE | RPD | R2 | RMSE | RPD | |
| SVR | 0.78 | 0.49 | 2.01 | 0.70 | 0.50 | 1.65 |
| RF | 0.82 | 0.40 | 2.44 | 0.75 | 0.47 | 1.74 |
| CNN | 0.87 | 0.32 | 3.07 | 0.82 | 0.36 | 2.30 |
| CMAF-Net | 0.93 | 0.26 | 3.77 | 0.88 | 0.29 | 2.79 |
| Model Type | Validation Set (CV-Score) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | RPD | SMAPE | MAE | R2 | |
| SVR | 0.74 | 1.38 | 11.89% | 0.57 | 0.60 ± 0.06 |
| RF | 0.63 | 1.51 | 9.49% | 0.45 | 0.68 ± 0.04 |
| CNN | 0.50 | 1.96 | 9.13% | 0.42 | 0.76 ± 0.04 |
| CMAF-Net | 0.45 | 2.18 | 7.78% | 0.35 | 0.81 ± 0.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, B.; Gao, Q.; Diao, Z.; Liu, W.; Huang, L.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Du, J.; Shu, Y. Mapping Dissolved Organic Carbon and Identifying Drivers in Chaohu Lake: A Novel Convolutional Multi-Head Attention Fusion Network with Hyperspectral Data. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 8867. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15168867
Pan B, Gao Q, Diao Z, Liu W, Huang L, Li J, Wang Q, Du J, Shu Y. Mapping Dissolved Organic Carbon and Identifying Drivers in Chaohu Lake: A Novel Convolutional Multi-Head Attention Fusion Network with Hyperspectral Data. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(16):8867. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15168867
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Banglong, Qianfeng Gao, Zhuo Diao, Wuyiming Liu, Lanlan Huang, Jiayi Li, Qi Wang, Juan Du, and Ying Shu. 2025. "Mapping Dissolved Organic Carbon and Identifying Drivers in Chaohu Lake: A Novel Convolutional Multi-Head Attention Fusion Network with Hyperspectral Data" Applied Sciences 15, no. 16: 8867. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15168867
APA StylePan, B., Gao, Q., Diao, Z., Liu, W., Huang, L., Li, J., Wang, Q., Du, J., & Shu, Y. (2025). Mapping Dissolved Organic Carbon and Identifying Drivers in Chaohu Lake: A Novel Convolutional Multi-Head Attention Fusion Network with Hyperspectral Data. Applied Sciences, 15(16), 8867. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15168867






