Deep Learning-Based Vehicle Speed Estimation Using Smartphone Sensors in GNSS-Denied Environment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
3. Proposed System
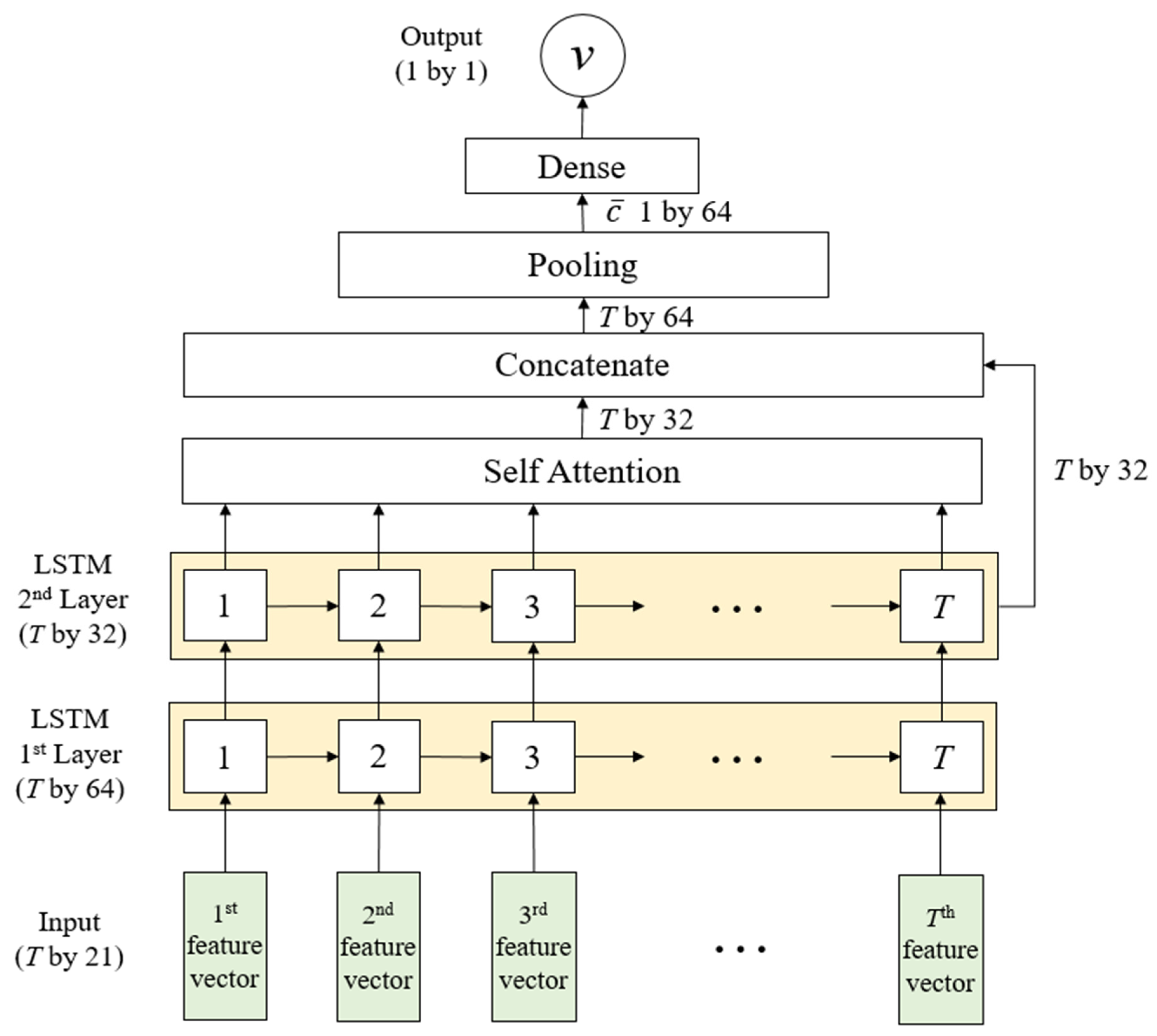
3.1. LSTM with Attention Layer
3.2. LSTM Input
4. Experimental Results
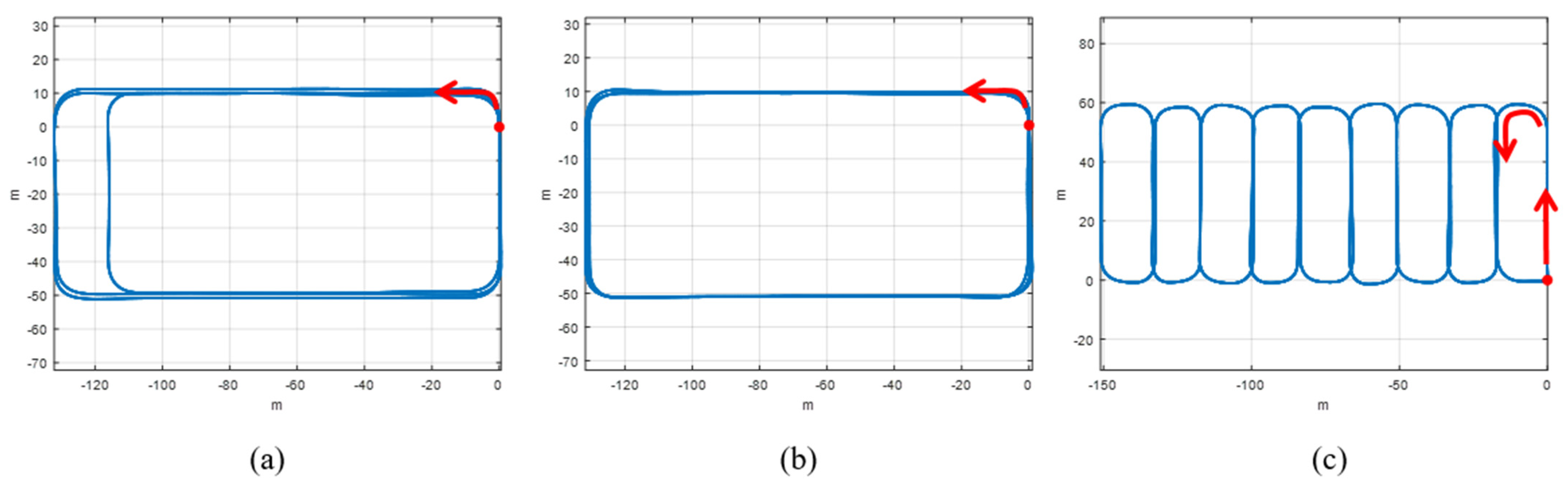
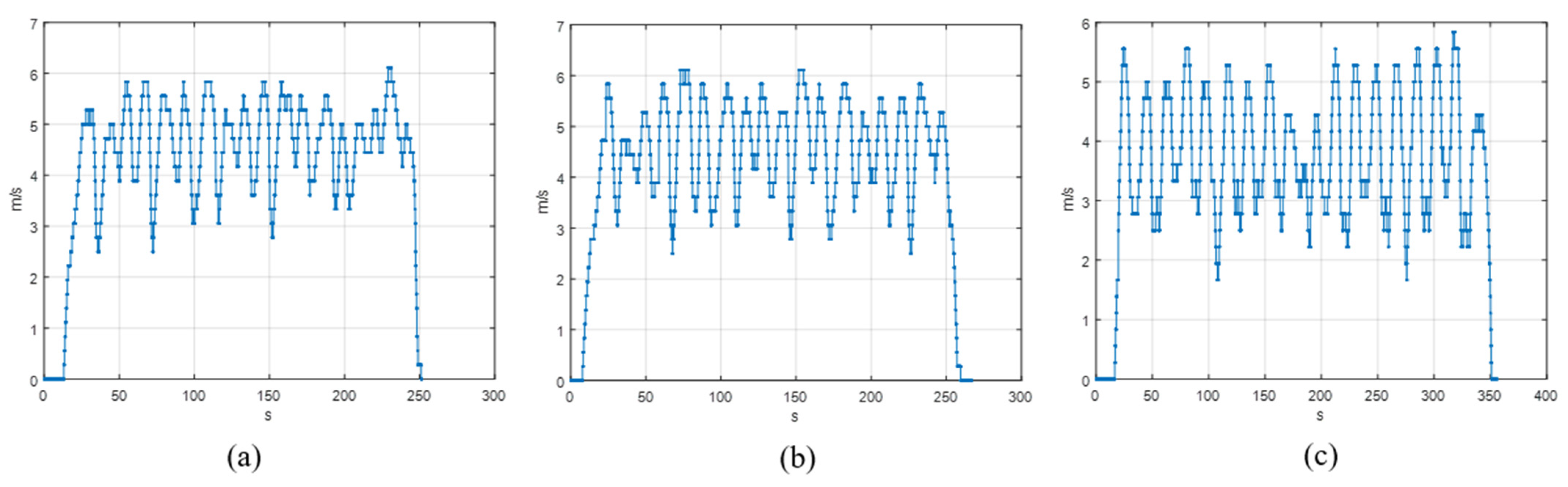
4.1. Experimental Setting and Scenario
4.2. Model Architecture Overview and Training Configuration
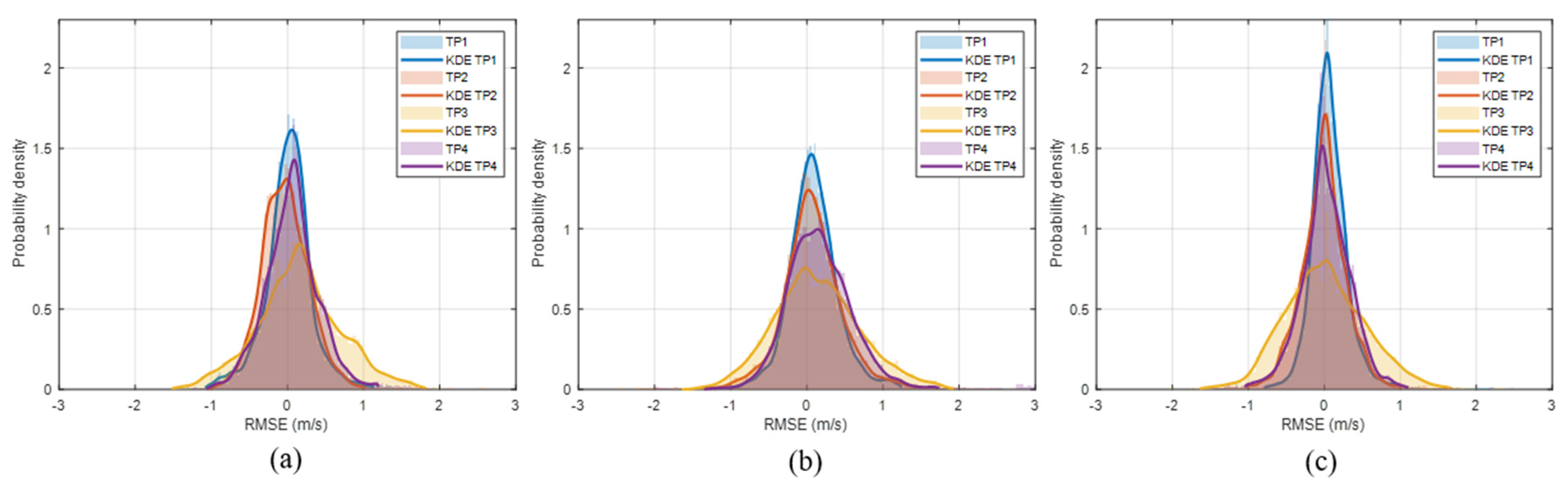
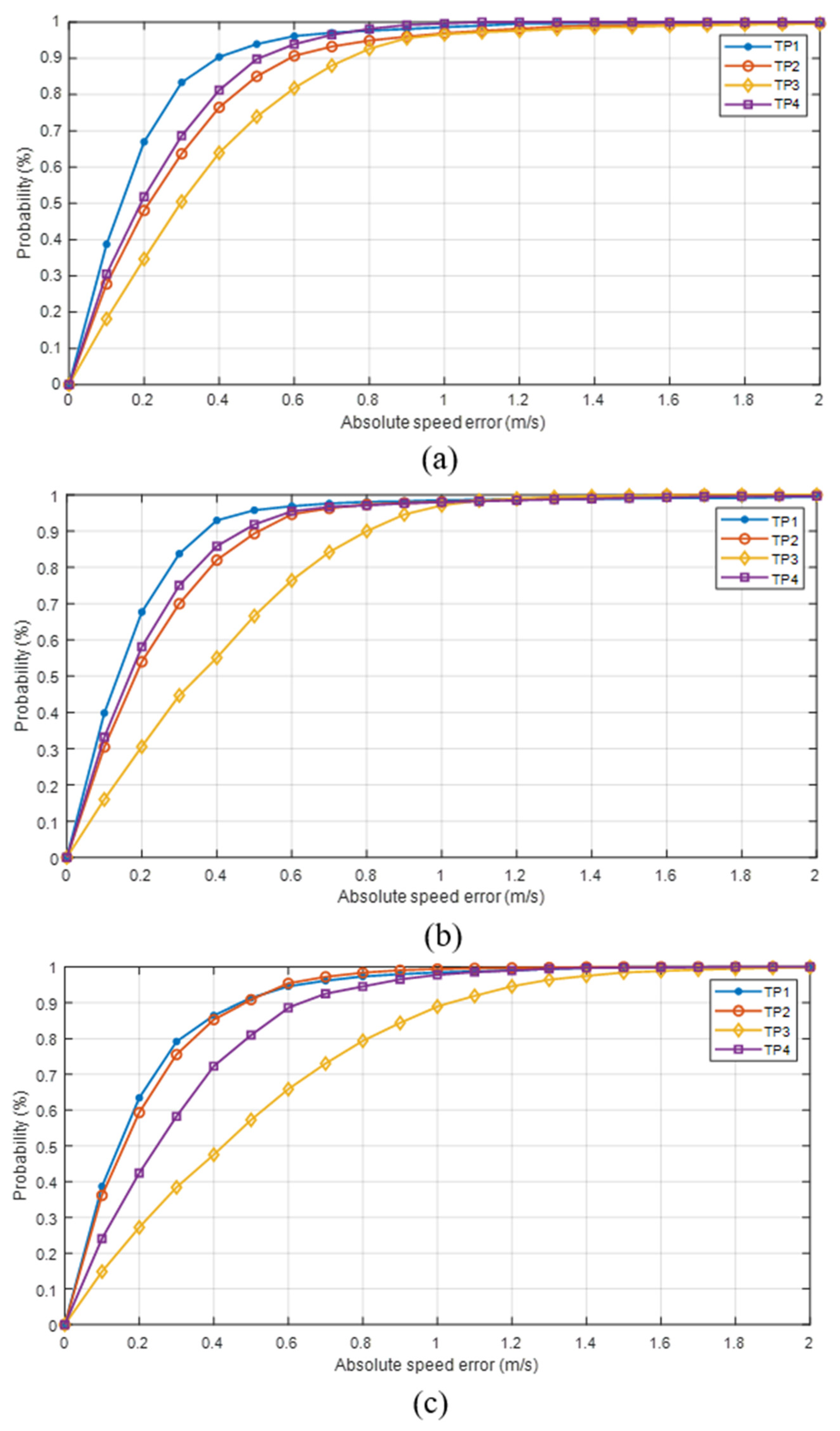
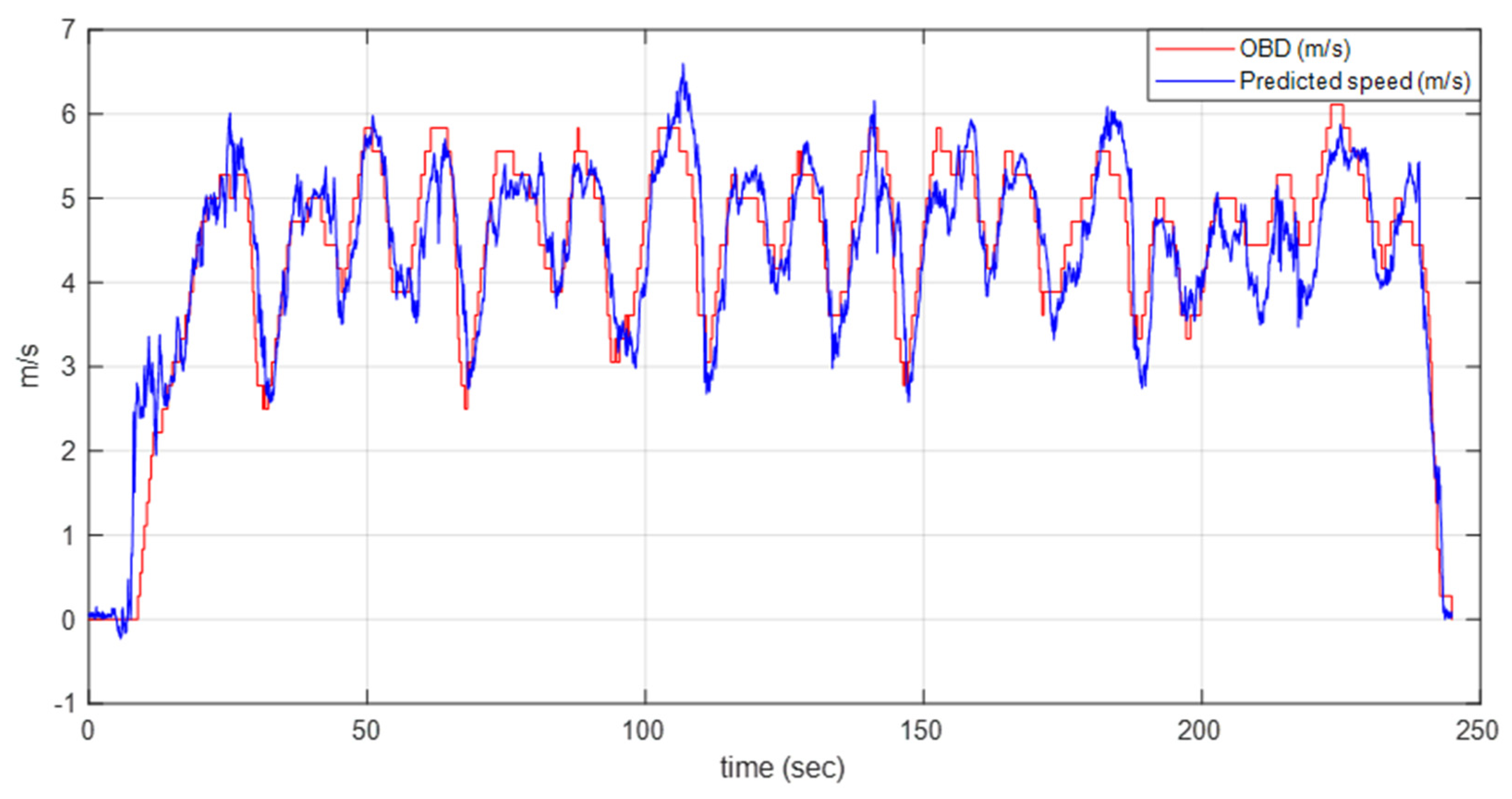
4.3. Model Performance Analysis
4.3.1. Comparison of Model Performance Using Different Feature Inputs
4.3.2. Model Performance Using All Feature Types (Raw + Statistical) with a Sequence Length of 200
4.4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| T | Scenario | TP1 RMSE (m/s) | TP1 MAE (m/s) | TP2 RMSE (m/s) | TP2 MAE (m/s) | TP3 RMSE (m/s) | TP3 MAE (m/s) | TP4 RMSE (m/s) | TP4 MAE (m/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | First | 0.31 | 0.23 | 0.49 | 0.34 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.51 | 0.38 |
| Second | 0.36 | 0.26 | 0.41 | 0.31 | 0.65 | 0.49 | 0.41 | 0.29 | |
| Third | 0.33 | 0.24 | 0.35 | 0.26 | 0.83 | 0.62 | 0.43 | 0.31 | |
| 200 | First | 0.32 | 0.23 | 0.40 | 0.29 | 0.49 | 0.37 | 0.42 | 0.31 |
| Second | 0.40 | 0.21 | 0.35 | 0.26 | 0.47 | 0.36 | 0.34 | 0.24 | |
| Third | 0.38 | 0.28 | 0.31 | 0.24 | 0.69 | 0.56 | 0.38 | 0.30 | |
| 300 | First | 0.36 | 0.23 | 0.36 | 0.26 | 0.52 | 0.39 | 0.41 | 0.29 |
| Second | 0.34 | 0.22 | 0.37 | 0.27 | 0.54 | 0.42 | 0.38 | 0.28 | |
| Third | 0.44 | 0.27 | 0.32 | 0.24 | 0.71 | 0.56 | 0.39 | 0.29 | |
| 400 | First | 0.38 | 0.29 | 0.45 | 0.33 | 0.53 | 0.39 | 0.43 | 0.32 |
| Second | 0.45 | 0.29 | 0.42 | 0.29 | 0.52 | 0.38 | 0.46 | 0.31 | |
| Third | 0.43 | 0.33 | 0.4 | 0.28 | 0.73 | 0.57 | 0.51 | 0.37 | |
| 500 | First | 0.29 | 0.19 | 0.33 | 0.27 | 0.57 | 0.42 | 0.46 | 0.31 |
| Second | 0.59 | 0.29 | 0.44 | 0.28 | 0.53 | 0.4 | 0.57 | 0.32 | |
| Third | 0.41 | 0.31 | 0.44 | 0.32 | 0.76 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.39 |
| T | Scenario | TP1 RMSE (m/s) | TP1 MAE (m/s) | TP2 RMSE (m/s) | TP2 MAE (m/s) | TP3 RMSE (m/s) | TP3 MAE (m/s) | TP4 RMSE (m/s) | TP4 MAE (m/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | First | 0.51 | 0.35 | 0.76 | 0.56 | 0.46 | 0.34 | 0.78 | 0.5 |
| Second | 0.52 | 0.37 | 0.71 | 0.53 | 0.47 | 0.34 | 0.48 | 0.35 | |
| Third | 0.57 | 0.4 | 0.85 | 0.66 | 0.43 | 0.3 | 0.55 | 0.36 | |
| 200 | First | 0.34 | 0.24 | 0.57 | 0.40 | 0.56 | 0.39 | 0.70 | 0.44 |
| Second | 0.43 | 0.28 | 0.47 | 0.31 | 0.50 | 0.40 | 0.50 | 0.36 | |
| Third | 0.40 | 0.28 | 0.44 | 0.29 | 0.71 | 0.57 | 0.45 | 0.34 | |
| 300 | First | 0.36 | 0.26 | 0.62 | 0.46 | 0.61 | 0.4 | 0.51 | 0.36 |
| Second | 0.5 | 0.31 | 0.64 | 0.47 | 0.5 | 0.32 | 0.48 | 0.32 | |
| Third | 0.42 | 0.27 | 0.82 | 0.63 | 0.4 | 0.29 | 0.6 | 0.42 | |
| 400 | First | 0.48 | 0.37 | 0.62 | 0.46 | 0.77 | 0.54 | 0.58 | 0.46 |
| Second | 0.55 | 0.4 | 0.77 | 0.54 | 0.75 | 0.51 | 0.59 | 0.43 | |
| Third | 0.62 | 0.45 | 1 | 0.73 | 0.69 | 0.46 | 0.81 | 0.59 | |
| 500 | First | 0.48 | 0.37 | 0.81 | 0.52 | 0.63 | 0.45 | 0.58 | 0.44 |
| Second | 0.53 | 0.42 | 0.74 | 0.51 | 0.65 | 0.47 | 0.66 | 0.45 | |
| Third | 0.61 | 0.49 | 0.89 | 0.67 | 0.61 | 0.47 | 0.93 | 0.65 |
| T | Scenario | TP1 RMSE (m/s) | TP1 MAE (m/s) | TP2 RMSE (m/s) | TP2 MAE (m/s) | TP3 RMSE (m/s) | TP3 MAE (m/s) | TP4 RMSE (m/s) | TP4 MAE (m/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | First | 0.33 | 0.22 | 0.7 | 0.53 | 0.48 | 0.33 | 0.46 | 0.33 |
| Second | 0.32 | 0.21 | 0.57 | 0.44 | 0.37 | 0.28 | 0.4 | 0.29 | |
| Third | 0.32 | 0.22 | 0.74 | 0.57 | 0.33 | 0.25 | 0.39 | 0.29 | |
| 200 | First | 0.28 | 0.19 | 0.41 | 0.29 | 0.49 | 0.37 | 0.31 | 0.24 |
| Second | 0.30 | 0.19 | 0.34 | 0.24 | 0.49 | 0.40 | 0.34 | 0.23 | |
| Third | 0.30 | 0.21 | 0.29 | 0.21 | 0.63 | 0.50 | 0.40 | 0.30 | |
| 300 | First | 0.29 | 0.2 | 0.44 | 0.33 | 0.38 | 0.29 | 0.34 | 0.28 |
| Second | 0.37 | 0.23 | 0.51 | 0.39 | 0.38 | 0.26 | 0.37 | 0.23 | |
| Third | 0.42 | 0.3 | 0.69 | 0.55 | 0.35 | 0.26 | 0.41 | 0.31 | |
| 400 | First | 0.28 | 0.2 | 0.52 | 0.4 | 0.35 | 0.27 | 0.32 | 0.26 |
| Second | 0.38 | 0.22 | 0.56 | 0.42 | 0.46 | 0.3 | 0.44 | 0.29 | |
| Third | 0.44 | 0.31 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.49 | 0.32 | 0.55 | 0.36 | |
| 500 | First | 0.33 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 0.44 | 0.42 | 0.32 | 0.4 | 0.35 |
| Second | 0.61 | 0.24 | 0.61 | 0.41 | 0.51 | 0.29 | 0.46 | 0.27 | |
| Third | 0.41 | 0.26 | 0.81 | 0.63 | 0.55 | 0.36 | 0.57 | 0.37 |
References
- Zhu, N.; Marais, J.; Betaille, D.; Berbineau, M. GNSS Position Integrity in Urban Environments: A Review of Literature. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2018, 19, 2762–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, B.; Lee, J.H.; Yu, C.; Kim, C.; Lee, T. Underground parking lot navigation system using long-term evolution signal. Sensors 2021, 21, 1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-Merino, C.S.; Luo-Chen, H.Q.; Khatib, E.J.; Barco, R. WiFi FTM, UWB and Cellular-Based Radio Fusion for Indoor Positioning. Sensors 2021, 21, 7020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, C.; Liu, C.; Xiao, D. Indoor Multifloor Localization Method Based on WiFi Fingerprints and LDA. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2019, 15, 5225–5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Zhou, J.; Jang, K.; Kim, Y. Indoor Localization Based on Integration of Wi-Fi with Geomagnetic and Light Sensors on an Android Device Using a DFF Network. Electronics 2023, 12, 5032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Kim, D. WiFi Fingerprint Indoor Localization Employing Adaboost and Probability-One Access Point Selection for Multi-Floor Campus Buildings. Future Internet 2024, 16, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Shin, B.; Shin, D.; Kim, J.; Park, J.; Lee, T. Precise Indoor Localization: Rapidly-Converging 2D Surface Correlation-Based Fingerprinting Technology Using LTE Signal. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 172829–172838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.; Ji, M.; Lee, J.; Han, K.-S.; Cho, Y. Deep Learning-Based Emergency Rescue Positioning Technology Using Matching-Map Images. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, B.; Lee, J.-H.; Yu, C.; Kyung, H.; Lee, T. Magnetic Field-Based Vehicle Positioning System in Long Tunnel Environment. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, N.; Chen, X.; Feng, R.; Wu, Y. High-Precision Pedestrian Indoor Positioning Method Based on Inertial and Magnetic Field Information. Sensors 2025, 25, 2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wei, D.; Li, W.; Ji, X.; Yuan, H. A Map-Aided Fast Initialization Method for the Magnetic Positioning of Vehicles. Electronics 2024, 13, 1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zhuang, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Wang, W. A Performance Evaluation Framework for Direction Finding Using BLE AoA/AoD Receivers. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 3331–3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Tang, H.; Chen, J. Survey on NLOS Identification and Error Mitigation for UWB Indoor Positioning. Electronics 2023, 12, 1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Rangel, H.; Morales-Rosales, L.A.; Imperial-Rojo, R.; Roman-Garay, M.A.; Peralta-Peñuñuri, G.E.; Lobato-Báez, M. Analysis of Statistical and Artificial Intelligence Algorithms for Real-Time Speed Estimation Based on Vehicle Detection with YOLO. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, X.; Hu, Z. Attention-Based LiDAR–Camera Fusion for 3D Object Detection in Autonomous Driving. World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.; Wu, J.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J. Integrating Advanced Computer Vision and AI Algorithms for Autonomous Driving Systems. J. Theory Pract. Eng. Sci. 2024, 4, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.-H.; Chang, Y.-H.; Lin, Y.-Z.; Chow, C.-W. Real-Time Indoor Visible Light Positioning (VLP) Using Long Short Term Memory Neural Network (LSTM-NN) with Principal Component Analysis (PCA). Sensors 2024, 24, 5424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Jia, J.; Chen, J.; Yang, L.; Guo, L.; Wang, X. Real-time indoor localization using smartphone magnetic with LSTM networks. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 10093–10110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Jia, J.; Chen, J.; Deng, Y.; Wang, X.; Aghvami, A.H. Indoor Localization Fusing WiFi With Smartphone Inertial Sensors Using LSTM Networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 13608–13623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Hu, P.; Liu, S.; Pang, T. Attention Mechanism and LSTM Network for Fingerprint-Based Indoor Location System. Sensors 2024, 24, 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Zhang, S.; Ma, J. Self-Attention-Based Deep Convolution LSTM Framework for Sensor-Based Badminton Activity Recognition. Sensors 2023, 23, 8373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.-h.; Kim, H.-j.; Lee, D.-s.; Kwon, S.-k. Indoor Positioning Method by CNN-LSTM of Continuous Received Signal Strength Indicator. Electronics 2024, 13, 4518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Liu, S.; Hwang, S.-H. Local Batch Normalization-Aided CNN Model for RSSI-Based Fingerprint Indoor Positioning. Electronics 2025, 14, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, L.; Liu, J.; Guinness, R.; Chen, Y.; Kuusniemi, H.; Chen, R. Using LS-SVM Based Motion Recognition for Smartphone Indoor Wireless Positioning. Sensors 2012, 12, 6155–6175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, T.; Guo, N.; Backén, S.; Akos, D. Monocular Camera/IMU/GNSS Integration for Ground Vehicle Navigation in Challenging GNSS Environments. Sensors 2012, 12, 3162–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, K.-W.; Lin, C.-A.; Duong, T.-T. The Performance Analysis of the Tactical Inertial Navigator Aided by Non-GPS Derived References. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 12511–12526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Li, P.; Tian, W.; Wei, D.; Zhang, H.; Liao, W.; Cao, Y. A fast dynamic pose estimation method for vision-based trajectory tracking control of industrial robots. Measurement 2024, 231, 114506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinescu, M.; Olivares, A.; Staffetti, E.; Sun, J. On the Estimation of Vector Wind Profiles Using Aircraft-Derived Data and Gaussian Process Regression. Aerospace 2022, 9, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, S.; Di Lauro, F. An Overview of Sensors for Long Range Missile Defense. Sensors 2022, 22, 9871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freydin, M.; Or, B. Learning car speed using inertial sensors for dead reckoning navigation. IEEE Sens. Lett. 2022, 6, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Xiao, X.; Zhu, S.; Xing, W.; Li, C.; Liu, L.; Ma, L.; Chai, H. Glow in the dark: Smartphone inertial odometry for vehicle tracking in GPS blocked environments. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 12955–12967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Gu, Z.; Gu, F.; Wu, P.; Yang, C.; Liu, X.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Li, Q. DeepVIP: Deep learning-based vehicle indoor positioning using smartphones. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2022, 71, 13299–13309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Zhu, S.; Ren, X.; Zhong, Q.; Tao, D.; Li, C.; Liu, L.; Gao, R. Vehicle Inertial Tracking via Mobile Crowdsensing: Experience and Enhancement. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 2505513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staudemeyer, R.C.; Morris, E.R. Understanding LSTM—A Tutorial into Long Short-Term Memory Recurrent Neural Networks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.09586. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, X.; Li, W. Time Series Prediction Based on LSTM-Attention-LSTM Model. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 48322–48331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, G.; Abed-Meraim, K. Analysis of Magnetic Field Measurements for Indoor Positioning. Sensors 2022, 22, 4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, I.; Zikria, Y.B.; Hur, S.; Park, Y. A Comprehensive Analysis of Magnetic Field Based Indoor Positioning With Smartphones: Opportunities, Challenges and Practical Limitations. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 228548–228571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Xin, S.; Huang, Q.; Shen, S. An Improved Velocity-Aided Method for Smartphone Single-Frequency Code Positioning in Real-World Driving Scenarios. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Reference | Learning Model | Used Sensor | Output | Testbed | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [30] | DNN + LSTM | accelerometer gyroscope | Speed | Urban and highway | MAE: 0.5 m/s |
| [31] | TCN | accelerometer gyroscope | Trajectory | Urban | RMSE: 3.2 m |
| [32] | LSTM (DeepVIP-L) LSTM (DeepVIP-M) | accelerometer gyroscope magnetometer gravity sensor | Speed and heading | Indoor parking lot | RMSE: 2.5 m |
| [33] | TCN | accelerometer gyroscope | Trajectory | Urban | RMSE: 2.8 m |
| Feature | T | Scenario | TP1 | TP2 | TP3 | TP4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE (m/s) | MAE (m/s) | MAE (m/s) | MAE (m/s) | |||
| Raw | 200 | First | 0.23 | 0.29 | 0.37 | 0.31 |
| Second | 0.21 | 0.26 | 0.36 | 0.24 | ||
| Third | 0.28 | 0.24 | 0.56 | 0.30 | ||
| Statistical | 200 | First | 0.24 | 0.40 | 0.39 | 0.44 |
| Second | 0.28 | 0.31 | 0.40 | 0.36 | ||
| Third | 0.28 | 0.29 | 0.57 | 0.34 | ||
| Raw + Statistical | 200 | First | 0.19 | 0.29 | 0.37 | 0.24 |
| Second | 0.19 | 0.24 | 0.40 | 0.23 | ||
| Third | 0.21 | 0.21 | 0.50 | 0.30 |
| Feature | T | Scenario | TP1 | TP2 | TP3 | TP4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE (m/s) | RMSE (m/s) | RMSE (m/s) | RMSE (m/s) | |||
| Raw | 200 | First | 0.32 | 0.40 | 0.49 | 0.42 |
| Second | 0.40 | 0.35 | 0.47 | 0.34 | ||
| Third | 0.38 | 0.31 | 0.69 | 0.38 | ||
| Statistical | 200 | First | 0.34 | 0.57 | 0.56 | 0.70 |
| Second | 0.43 | 0.47 | 0.50 | 0.50 | ||
| Third | 0.40 | 0.44 | 0.71 | 0.45 | ||
| Raw + Statistical | 200 | First | 0.28 | 0.41 | 0.49 | 0.31 |
| Second | 0.30 | 0.34 | 0.49 | 0.34 | ||
| Third | 0.30 | 0.29 | 0.63 | 0.40 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shin, B.; Li, S.; Kim, B. Deep Learning-Based Vehicle Speed Estimation Using Smartphone Sensors in GNSS-Denied Environment. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 8824. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15168824
Shin B, Li S, Kim B. Deep Learning-Based Vehicle Speed Estimation Using Smartphone Sensors in GNSS-Denied Environment. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(16):8824. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15168824
Chicago/Turabian StyleShin, Beomju, Shiyi Li, and Boseong Kim. 2025. "Deep Learning-Based Vehicle Speed Estimation Using Smartphone Sensors in GNSS-Denied Environment" Applied Sciences 15, no. 16: 8824. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15168824
APA StyleShin, B., Li, S., & Kim, B. (2025). Deep Learning-Based Vehicle Speed Estimation Using Smartphone Sensors in GNSS-Denied Environment. Applied Sciences, 15(16), 8824. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15168824







