The Effect of Practicing Selected Sports on the Value of the Center of Pressure (COP): A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Approach to the Problem and Participants
2.2. Testing Procedures
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Static Test
3.2. Dynamic Study
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations
4.2. Practical Application
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kuczyński, M.; Podbielska, M.; Bieć, D.; Paluszak, A.; Kręcisz, K. The basics of postural control assessment: What, how and why do we need to measure? Acta Bio-Opt. Inform. Med. Inżynieria Biomed. 2012, 18, 243–249. [Google Scholar]
- Romano, F.; Colagiorgio, P.; Buizza, A.; Sardi, F.; Ramat, S. In Extraction of traditional COP-based features from COM sway in postural stability evaluation. In Proceedings of the 2015 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Milan, Italy, 25–29 August 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 3715–3718. [Google Scholar]
- Masani, K.; Vette, A.H.; Abe, M.O.; Nakazawa, K. Center of pressure velocity reflects body acceleration rather than body velocity during quiet standing. Gait Posture 2014, 39, 946–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ocetkiewicz, T.; Skalska, A.; Grodzicki, T. Evaluation of static balance with the use of the posturographic platform in poorly visionaries and blind persons. Gerontol. Pol. 2006, 14, 144–148. [Google Scholar]
- Riley, M.A.; Turvey, M.T. Variability and determinism in motor behavior. J. Mot. Behav. 2002, 34, 99–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trajković, N.; Kozinc, Ž.; Smajla, D.; Šarabon, N. Relationship between ankle strength and range of motion and postural stability during single-leg quiet stance in trained athletes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cássia Libardoni, T.; da Silveira, C.B.; Sinhorim, L.M.B.; de Oliveira, A.S.; Dos Santos, M.J.; Santos, G.M. Reference values and equations reference of balance for children of 8 to 12 years. Gait Posture 2018, 60, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, T.L.; Newton, R.U.; Burnett, A.F. Reliability of traditional and fractal dimension measures of quiet stance center of pressure in young, healthy people. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2005, 86, 2034–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturnieks, D.L.; St George, R.; Lord, S.R. Balance disorders in the elderly. Neurophysiol. Clin./Clin. Neurophysiol. 2008, 38, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcolin, G.; Cogliati, M.; Cudicio, A.; Negro, F.; Tonin, R.; Orizio, C.; Paoli, A. Neuromuscular Fatigue Affects Calf Muscle Activation Strategies, but Not Dynamic Postural Balance Control in Healthy Young Adults. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 799565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczyk-Suszek, M.; Martowska, B.; Sapuła, R. Analysis of the Stability of the Body in a Standing Position When Shooting at a Stationary Target—A Randomized Controlled Trial. Sensors 2022, 22, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Błaszczyk, J.; Beck, M.; Sadowska, D. Assessment of postural stability in young healthy subjects based on directional features of posturographic data: Vision and gender effects. Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 2014, 74, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winiarska, A.; Ziółkowska, A.; Świtaj, K.; Wojtczak, P. Balance of individuals at different age involved in physical activity–review of publications. J. Educ. Health Sport 2017, 7, 978–985. [Google Scholar]
- Winter, D.A.; Patla, A.E.; Ishac, M.; Gage, W.H. Motor mechanisms of balance during quiet standing. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2003, 13, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovács, B.; Kóbor, I.; Gyimes, Z.; Sebestyén, Ö.; Tihanyi, J. Lower leg muscle–tendon unit characteristics are related to marathon running performance. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieć, E.; Kuczyński, M. Postural control in 13-year-old soccer players. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 110, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrin, P.; Deviterne, D.; Hugel, F.; Perrot, C. Judo, better than dance, develops sensorimotor adaptabilities involved in balance control. Gait Posture 2002, 15, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinsault, N.; Vuillerme, N. Test–retest reliability of centre of foot pressure measures to assess postural control during unperturbed stance. Med. Eng. Phys. 2009, 31, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sá Ferreira, A.; Baracat, P.J.F. Test–retest reliability for assessment of postural stability using center of pressure spatial patterns of three-dimensional statokinesigrams in young health participants. J. Biomech. 2014, 47, 2919–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.; Huang, C.-K.; Sadeghi, M.; Akinwuntan, A.E.; Devos, H. Proof-of-concept of the virtual reality comprehensive balance assessment and training for sensory organization of dynamic postural control. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horak, F.B. Postural orientation and equilibrium: What do we need to know about neural control of balance to prevent falls? Age Ageing 2006, 35 (Suppl. S2), ii7–ii11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davlin, C.D. Dynamic balance in high level athletes. Percept. Mot. Ski. 2004, 98 (Suppl. S3), 1171–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadkanlu Ostad, M.; Norasteh, A.A.; Babagoltabar Samakoush, H. Comparison of Static and Dynamic Balance of Athletes of Different Sports in Conditions With and Without Posture Disturbances. J. Sport Biomech. 2019, 4, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srokowska, A.; Foss, J.; Lewandowski, A.; Siedlaczek, M.; Srokowski, G.; Radzimińska, A.; Weber-Rajek, M.; Zukow, W. Statistical and dynamical functional evaluation of the selected foot parameters. J. Educ. Health Sport 2015, 5, 568–589. [Google Scholar]
- Bogdanowicz, M. Left-Handedness in Children; Wydawnictwo WSiP: Warszawa, Poland, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Stanisz, A. An Affordable Statistic Course Using STATISTICA PL on Examples of Medicine; StatSoft Polska Sp. z oo Kraków: Krakow, Poland, 2006; p. 532. [Google Scholar]
- Van Gent, R.; Siem, D.; van Middelkoop, M.; Van Os, A.; Bierma-Zeinstra, S.; Koes, B. Incidence and determinants of lower extremity running injuries in long distance runners: A systematic review. Br. J. Sports Med. 2007, 41, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohan, A.; Nyc, M.; Rogóż, A.; Furgiel, J. Changes in plantar pressure distribution after long-distance running. New Med. 2017, 21, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reenalda, J.; Maartens, E.; Homan, H.; Buurke, J.H. Continuous three dimensional analysis of running mechanics during a marathon by means of inertial magnetic measurement units to objectify changes in running mechanics. J. Biomech. 2016, 49, 3362–3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bibro, M.; Drwal, A.; Jankowicz-Szymańska, A. The assessment of the effect of strength training of lower limbs on arching and force distribution of the sole in young men. Health Promot. Phys. Act. 2018, 3, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollander, K.; Hamacher, D.; Zech, A. Running barefoot leads to lower running stability compared to shod running-results from a randomized controlled study. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoenig, T.; Hamacher, D.; Braumann, K.-M.; Zech, A.; Hollander, K. Analysis of running stability during 5000 m running. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2019, 19, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storey, A.; Smith, H.K. Unique aspects of competitive weightlifting. Sports Med. 2012, 42, 769–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagao, H.; Kubo, Y.; Tsuno, T.; Kurosaka, S.; Muto, M. A biomechanical comparison of successful and unsuccessful snatch attempts among elite male weightlifters. Sports 2019, 7, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoover, D.L.; Carlson, K.M.; Christensen, B.K.; Zebas, C.J. Biomechanical analysis of women weightlifters during the snatch. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2006, 20, 627. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Kang, Z.; Mu, D.; Zhao, H.; Yang, F. T2 mapping for quantitative assessment of ankle cartilage of weightlifters. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 19160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demura, T.; Demura, S.-i.; Shin, S. Comparison of gait properties during level walking and stair ascent and descent with varying loads. Health 2010, 2, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudry, S.; Duchateau, J. Age-related influence of vision and proprioception on Ia presynaptic inhibition in soleus muscle during upright stance. J. Physiol. 2012, 590, 5541–5554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanenko, Y.; Gurfinkel, V.S. Human postural control. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, C.; Peterka, R.J. A new interpretation of spontaneous sway measures based on a simple model of human postural control. J. Neurophysiol. 2005, 93, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willems, T.M.; De Ridder, R.; Roosen, P. The effect of a long-distance run on plantar pressure distribution during running. Gait Posture 2012, 35, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, S.; Demura, S.; Uchiyama, M. Centre of pressure sway characteristics during static one-legged stance of athletes from different sports. J. Sports Sci. 2008, 26, 775–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albaladejo-García, C.; Moreno, F.J.; García-Aguilar, F.; Caballero, C. One-Leg Stance Postural Sway Is Not Benefited by Bicycle Motocross Practice in Elite Riders. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2023, 8, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonavolontà, V.; Gallotta, M.C.; Zimatore, G.; Curzi, D.; Ferrari, D.; Vinciguerra, M.G.; Guidetti, L.; Baldari, C. Chronic Effects of Asymmetric and Symmetric Sport Load in Varsity Athletes across a Six Month Sport Season. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, D.; Polin, D.; Tourny-Chollet, C.; Weber, J. Spatial and temporal gait variable differences between basketball, swimming and soccer players. Int. J. Sports Med. 2000, 21, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, T.-H.; Chen, Y.-S.; Wang, J.-C. Characteristics of plantar pressures and related pain profiles in elite sprinters and recreational runners. J. Am. Podiatr. Med. Assoc. 2018, 108, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asseman, F.; Caron, O.; Cremieux, J. Effects of the removal of vision on body sway during different postures in elite gymnasts. Int. J. Sports Med. 2005, 26, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauk, J.; Daunoraviciene, K.; Ihnatouski, M.; Griskevicius, J.; Raso, J.V. Analysis of the plantar pressure distribution in children with foot deformities. Acta Bioeng. Biomech. 2010, 12, 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- Kozel, M.; Škrečková, G.; Potašová, M.; Kutiš, P.; Ondrušková, L. One-Side Weight Sports and the Impact of Their Load on the Feet and the Occurrence of Posture Disorders in Professional Football and Handball Players. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 10387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, C.; Barbado, D.; Moreno, F. El procesado del desplazamiento del centro de presiones para el estudio de la relación complejidad/rendimiento observada en el control postural en bipedestación. Rev. Andal. Med. Deporte 2013, 6, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | GROUP | M ± SD | df | F | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | C PL M | 23.7 ± 1.29 22.83 ± 0.92 28.06 ± 2.73 | df1 = 2, df2 = 82 | F = 12.206 | p = 0.0000 |
| Body height (BH) (cm) | C PL M | 165.97 ± 6.56 163.12 ± 4.46 165.68 ± 4.70 | df1 = 2, df2 = 82 | F = 2.1890 | p = 0.1185 |
| Body mass (BM) (kg) | C PL M | 60.17 ± 8.19 76.87 ± 88.08 59.97 ± 7.89 | df1 = 2, df2 = 82 | F = 1.0949 | p = 0.3394 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | C PL M | 21.88 ± 3.02 29.13 ± 34.57 21.84 ± 2.68 | df1 = 2, df2 = 82 | F = 1.3360 | p = 0.2685 |
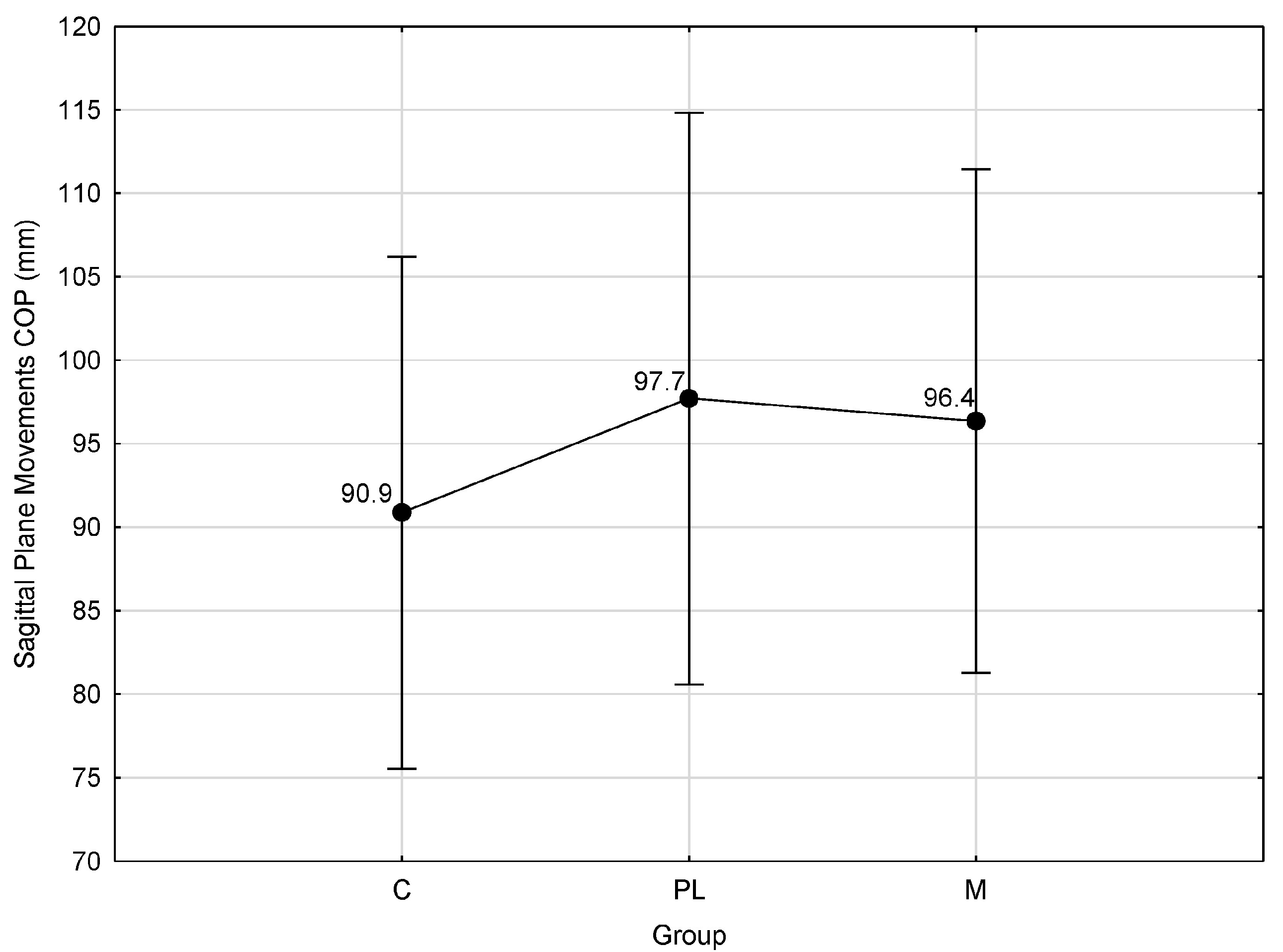
| GROUP | N | M | SD | df | F | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 30 | 90.9 | 43.2 | df1 = 2, df2 = 82 | F = 0.2083 | p = 0.8124 |
| PL | 24 | 97.7 | 41.9 | |||
| M | 31 | 96.4 | 41.4 |
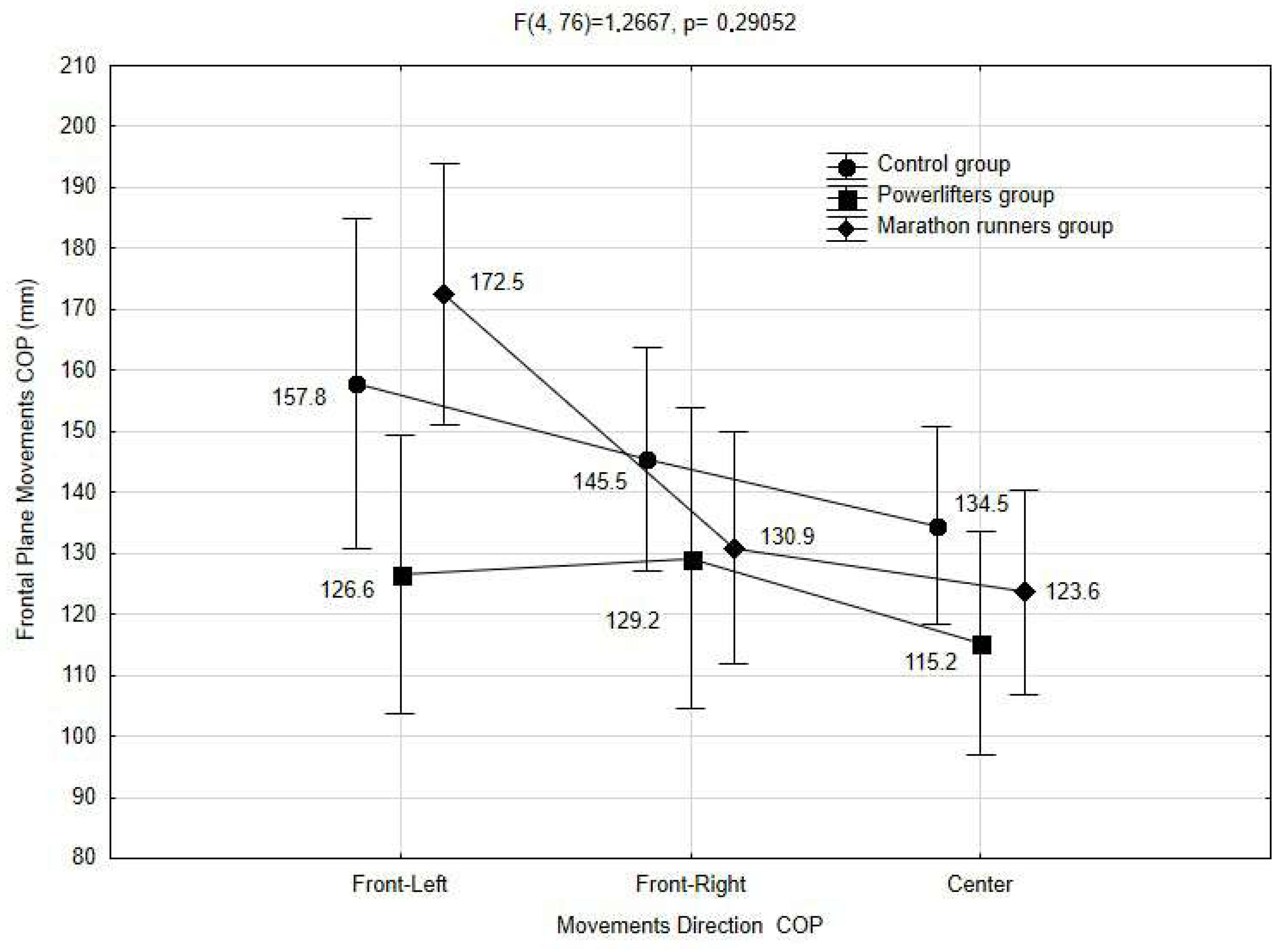
| GROUP | COP Displacement | N | M | SD | df | F | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | Front-left | 5 | 157.8 | 18.0 | df1 = 4 df2 = 76 | F = 1.2667 | p = 0.2905 |
| Front-right | 11 | 145.5 | 27.6 | ||||
| Center | 14 | 134.5 | 30.3 | ||||
| PL | Front-left | 7 | 126.6 | 15.9 | |||
| Front-right | 6 | 129.2 | 33.9 | ||||
| Center | 11 | 115.2 | 26.6 | ||||
| M | Front-left | 8 | 172.5 | 33.9 |
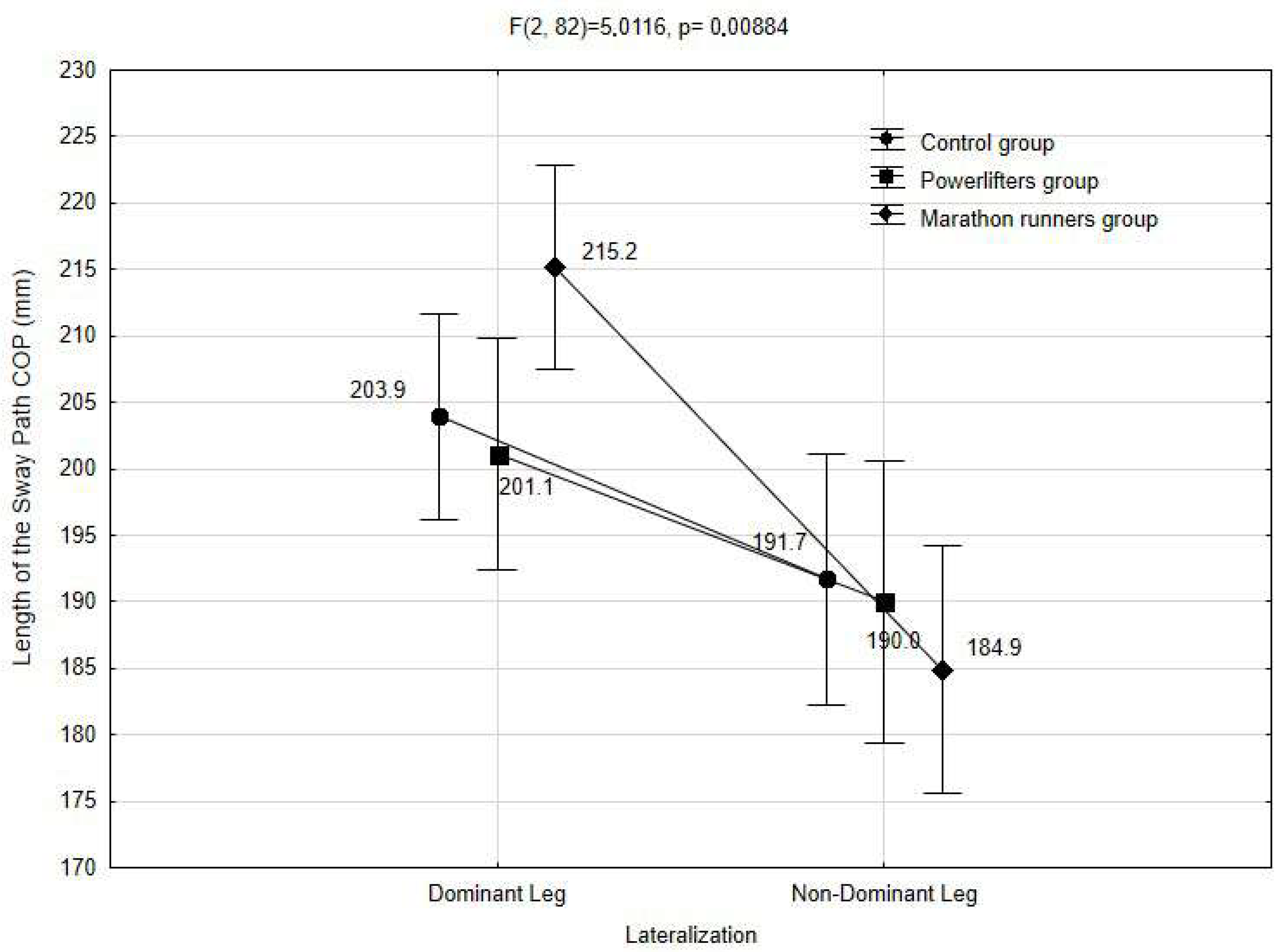
| GROUP | Lateralization | N | M | SD | df | F | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | Dominant limb | 30 | 203.9 | 11.5 | df1 = 2 df2 = 82 | F = 5.0116 | p = 0.0088 |
| Non-dominant limb | 191.7 | 18.2 | |||||
| PL | Dominant limb | 24 | 201.1 | 13.6 | |||
| Non-dominant limb | 190.0 | 20.9 | |||||
| M | Dominant limb | 31 | 215.2 | 31.3 | |||
| Non-dominant limb | 184.9 | 34.6 |
| No. Group | Post-Hoc Bonferroni Test; p-Value Variable: SP COP (Sway Path) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GROUP | Lateralization | {1} M1 203.92 | {2} M2 191.69 | {3} M3 201.10 | {4} M4 190.00 | {5} M5 215.18 | {6} M6 184.87 | |
| 1 | C | Dominant limb | ||||||
| 2 | C | Non-dominant limb | 0.1803 | |||||
| 3 | PL | Dominant limb | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | ||||
| 4 | PL | Non-dominant limb | 0.5193 | 1.0000 | 0.6031 | |||
| 5 | M | Dominant limb | 1.0000 | 0.0027 | 0.4714 | 0.0023 | ||
| 6 | M | Non-dominant limb | 0.0328 | 1.0000 | 0.2014 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | |
| r-Pearson Variable: Length of Sway Path COP α = 0.05 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lateralization | GROUP | M | SD | r | R2 | t | p | N |
| Dominant limb | C | 203.92 | 11.49 | 0.75 | 0.56 | 5.99 | 0.0000 | 30 |
| Non-dominant limb | C | 191.69 | 18.18 | |||||
| Dominant limb | PL | 201.09 | 13.64 | 0.73 | 0.53 | 5.00 | 0.0000 | 24 |
| Non-dominant limb | PL | 189.99 | 20.89 | |||||
| Dominant limb | M | 215.18 | 31.34 | 0.29 | 0.08 | 1.62 | 0.1160 | 31 |
| Non-dominant limb | M | 184.87 | 34.62 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hawrylak, A.; Demidaś, A.; Hawrylak, A. The Effect of Practicing Selected Sports on the Value of the Center of Pressure (COP): A Pilot Study. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 8774. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15168774
Hawrylak A, Demidaś A, Hawrylak A. The Effect of Practicing Selected Sports on the Value of the Center of Pressure (COP): A Pilot Study. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(16):8774. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15168774
Chicago/Turabian StyleHawrylak, Arletta, Aneta Demidaś, and Adam Hawrylak. 2025. "The Effect of Practicing Selected Sports on the Value of the Center of Pressure (COP): A Pilot Study" Applied Sciences 15, no. 16: 8774. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15168774
APA StyleHawrylak, A., Demidaś, A., & Hawrylak, A. (2025). The Effect of Practicing Selected Sports on the Value of the Center of Pressure (COP): A Pilot Study. Applied Sciences, 15(16), 8774. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15168774






