MINTFormer: Multi-Scale Information Aggregation with CSWin Vision Transformer for Medical Image Segmentation
Abstract
1. Introduction
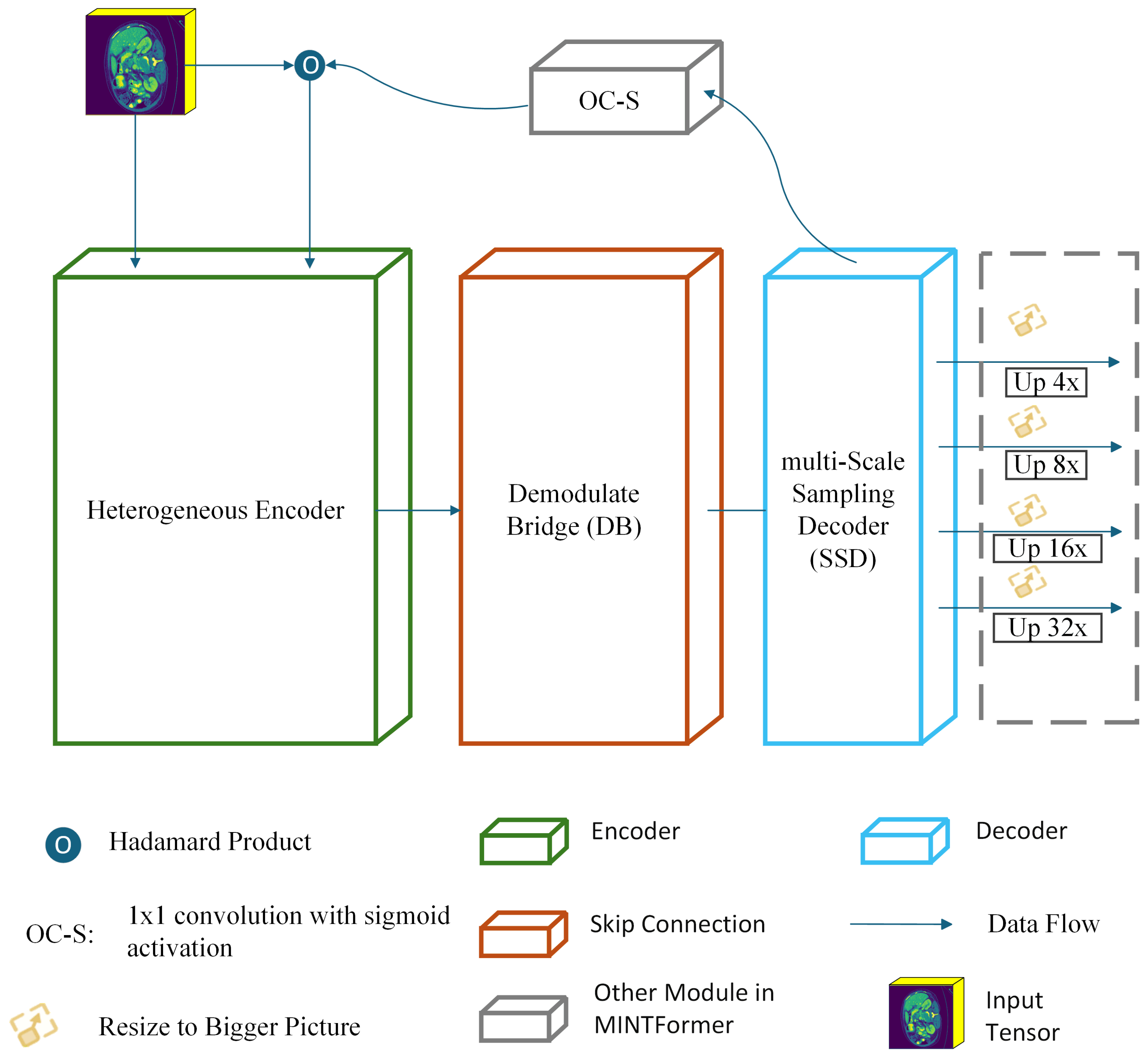
- This study presents a novel encoder structure, the Heterogeneous encoder, designed to leverage the strengths of both MaxViT and CSWin. The heterogeneous encoder integrates the capacity of CSWin to capture global information with the aptitude of MaxViT to discern local information, thereby optimizing the advantages of both models.
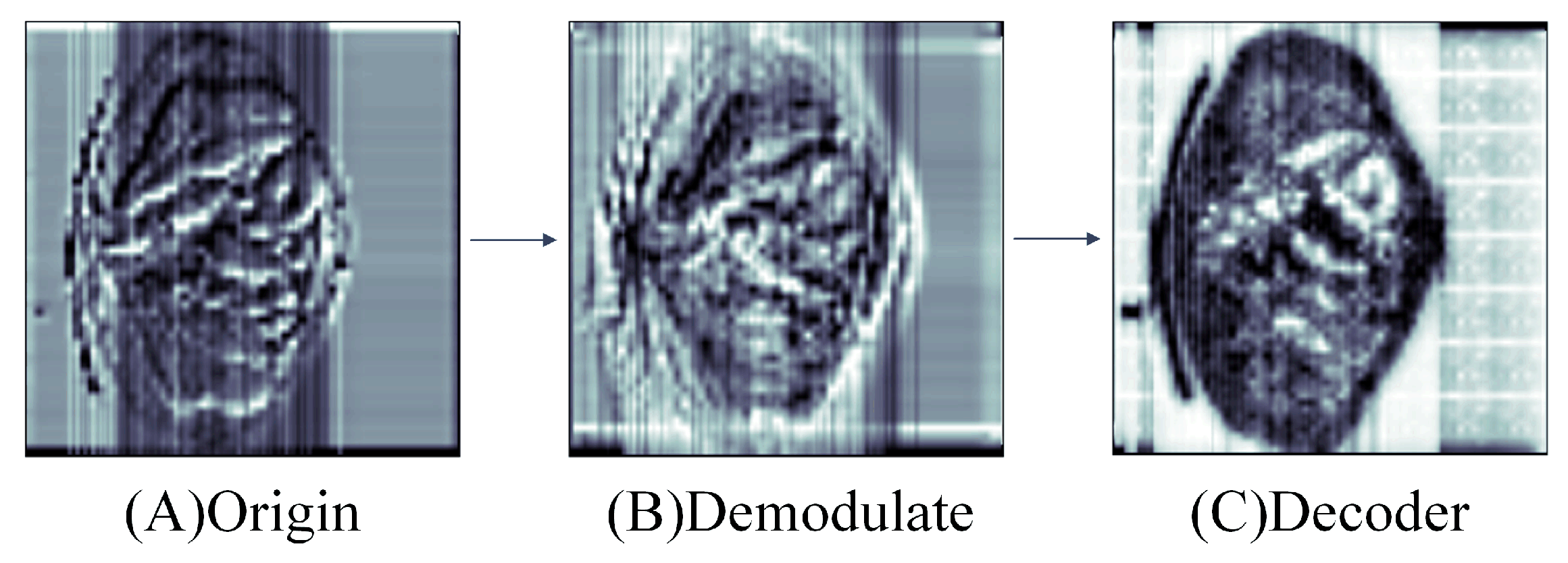
- We devised the Demodulate Bridge within a skip connection. The Demodulate Bridge is capable of filtering redundant textures in the feature maps output by CSWin and MaxViT while retaining the features extracted by the encoder. Then it combines feature maps with disparate focus to obtain feature maps that retain both local and global information.
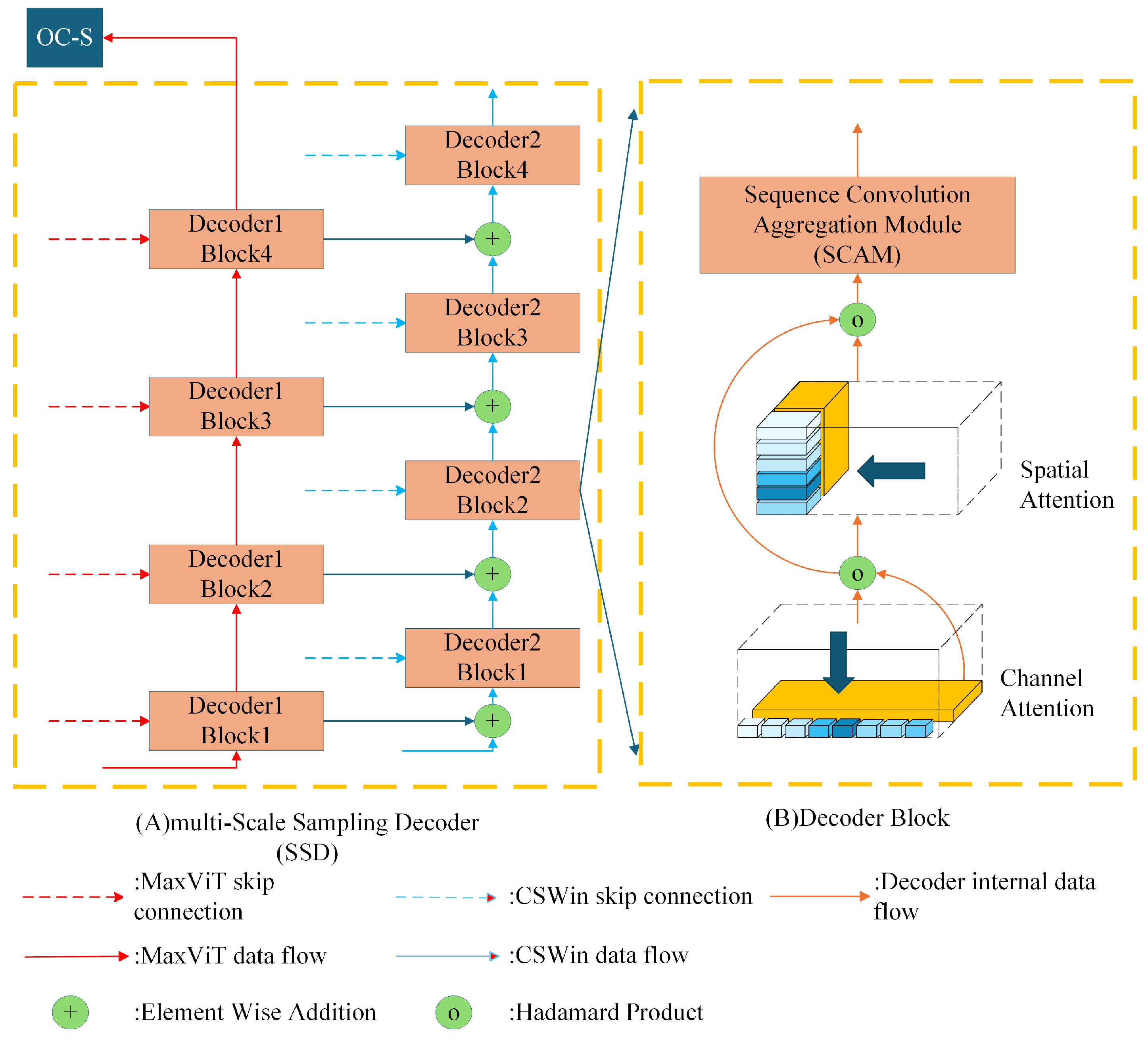
- In the decoder component, MINTFormer is equipped with a multi-Scale Sampling Decoder. This decoder employs a series of convolution groups, each comprising a set of convolution kernels of varying sizes. This approach enables the decoder to fully preserve organ information of different sizes during upsampling.
2. Related Work
2.1. Application of Self-Attention Mechanism in Semantic Segmentation
2.2. Skip Connection in Semantic Segmentation Applications
3. Method
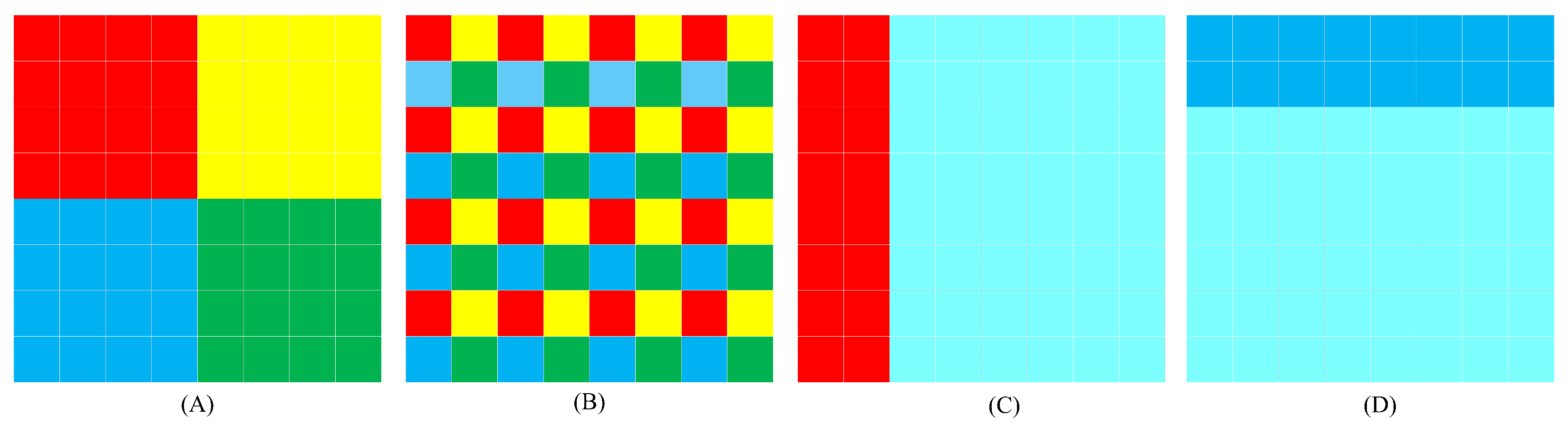
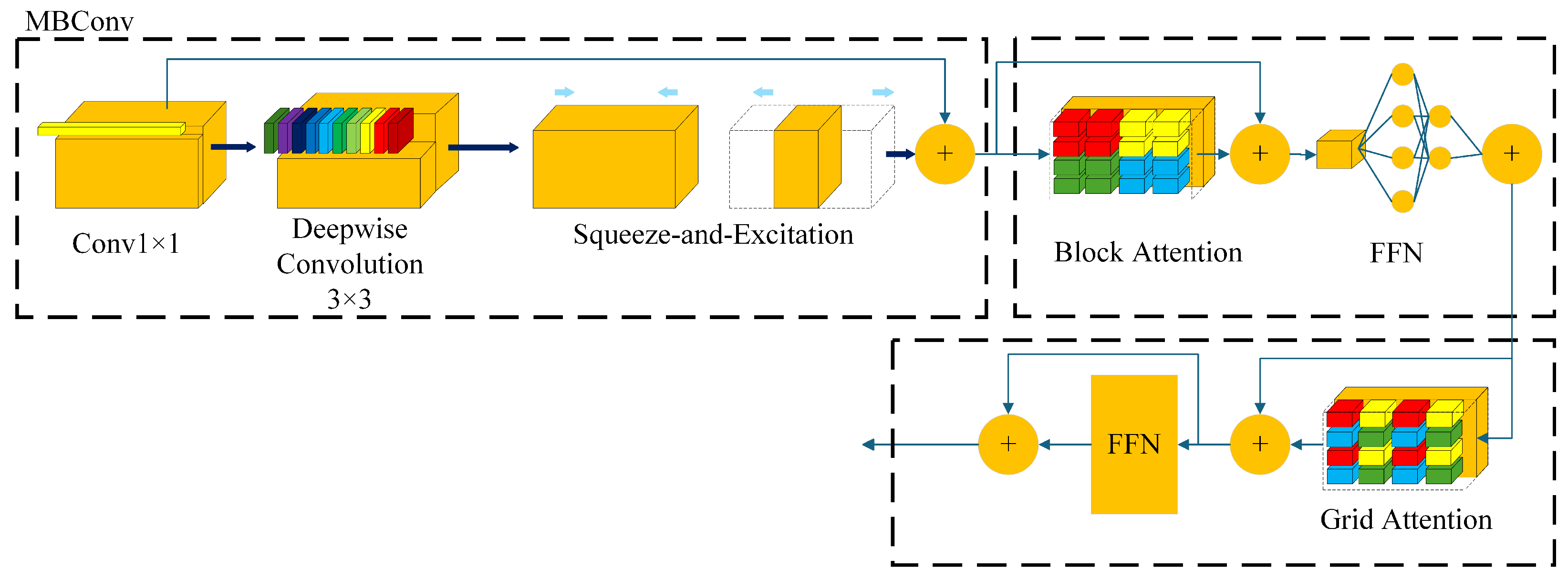
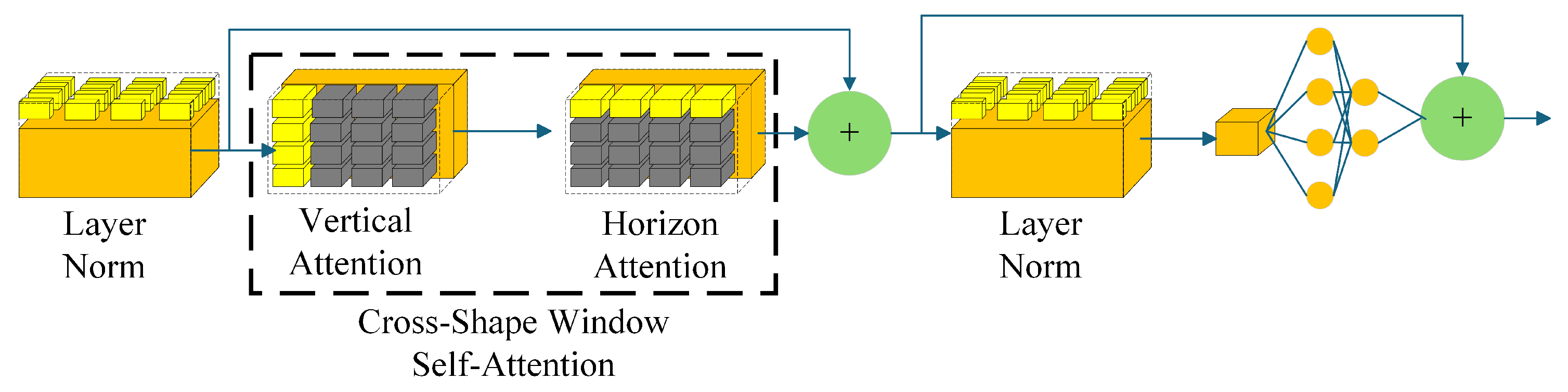
3.1. Heterogeneous Encoder
3.1.1. MaxViT Block
3.1.2. CSWin Block
3.2. Demodulate Bridge
3.3. Multi-Scale Sampling Decoder
3.3.1. Channel Attention
3.3.2. Spatial Attention
3.3.3. Sequence Convolution Aggregation Module
4. Experiments
4.1. Dataset
4.1.1. Synapse Dataset
4.1.2. ACDC Dataset
4.1.3. Kvasir-SEG Dataset
4.1.4. Skin Lesion Segmentation Datasets
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
4.2.1. Dice
4.2.2. HD95
4.3. Result
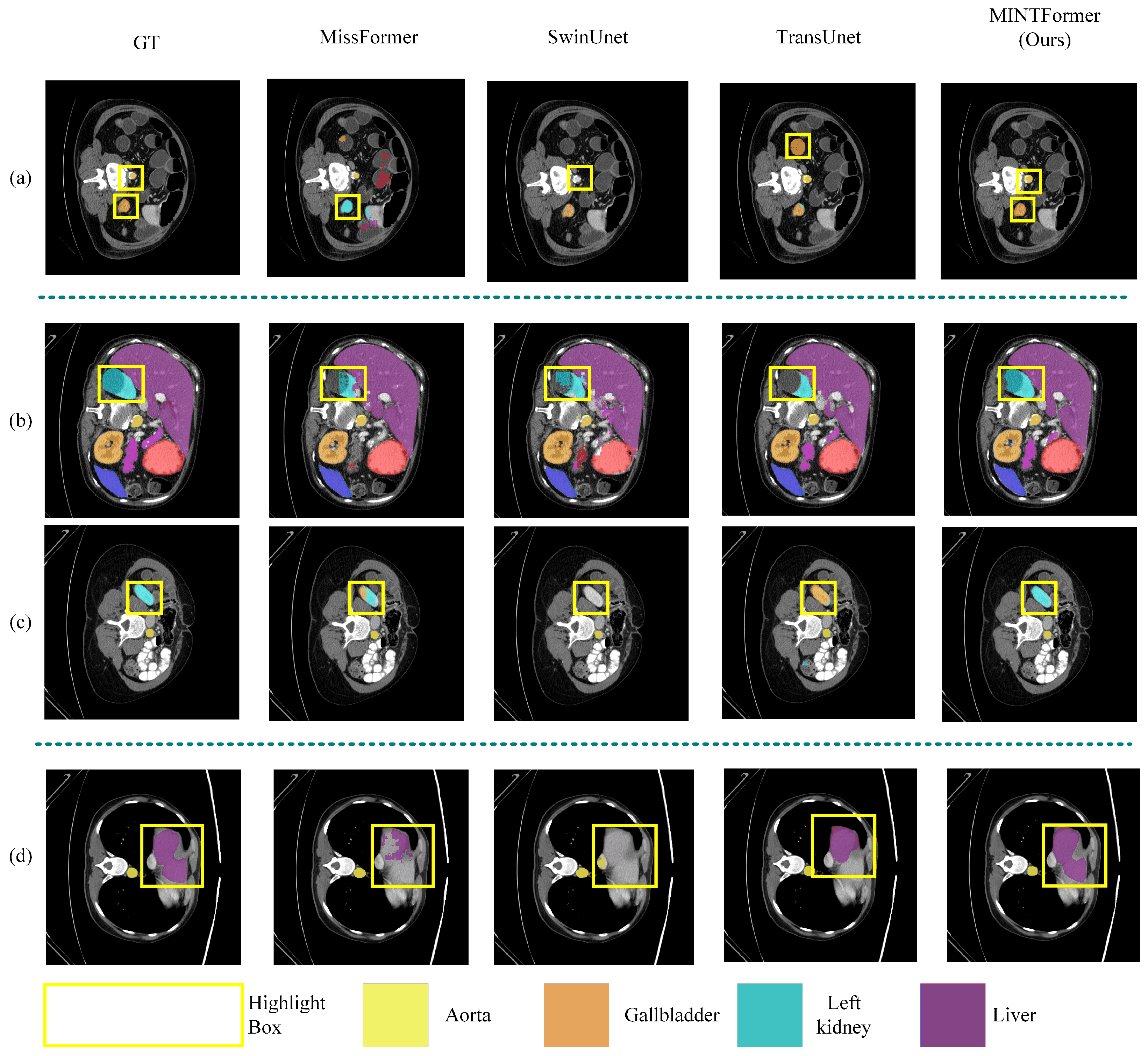
4.3.1. Experimental Results of Multi-Scale Organ Information Dataset
Synapse Dataset
Result of ACDC
4.4. Experimental Results of Single-Scale Organ Information Dataset
4.4.1. Experimental Results on the Kvasir-SEG Dataset
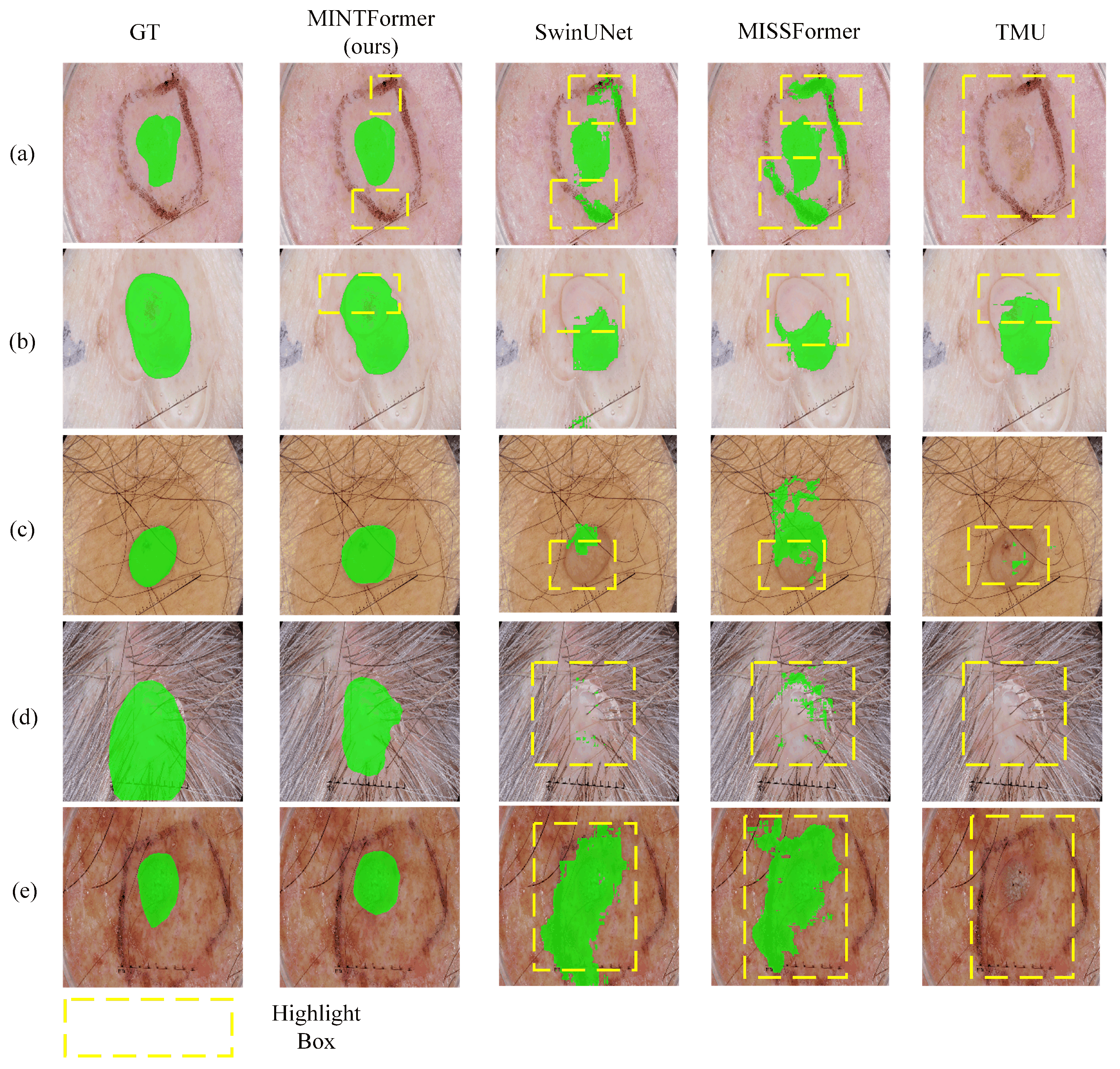
4.4.2. Experimental Results on Skin Lesion Segmentation Datasets
4.5. Ablation Study
4.5.1. Selection of the Maximum Convolution Kernel in the Convolution Group of the Decoder
4.5.2. Selection of Convolution Parameters in the Demodulate Bridge
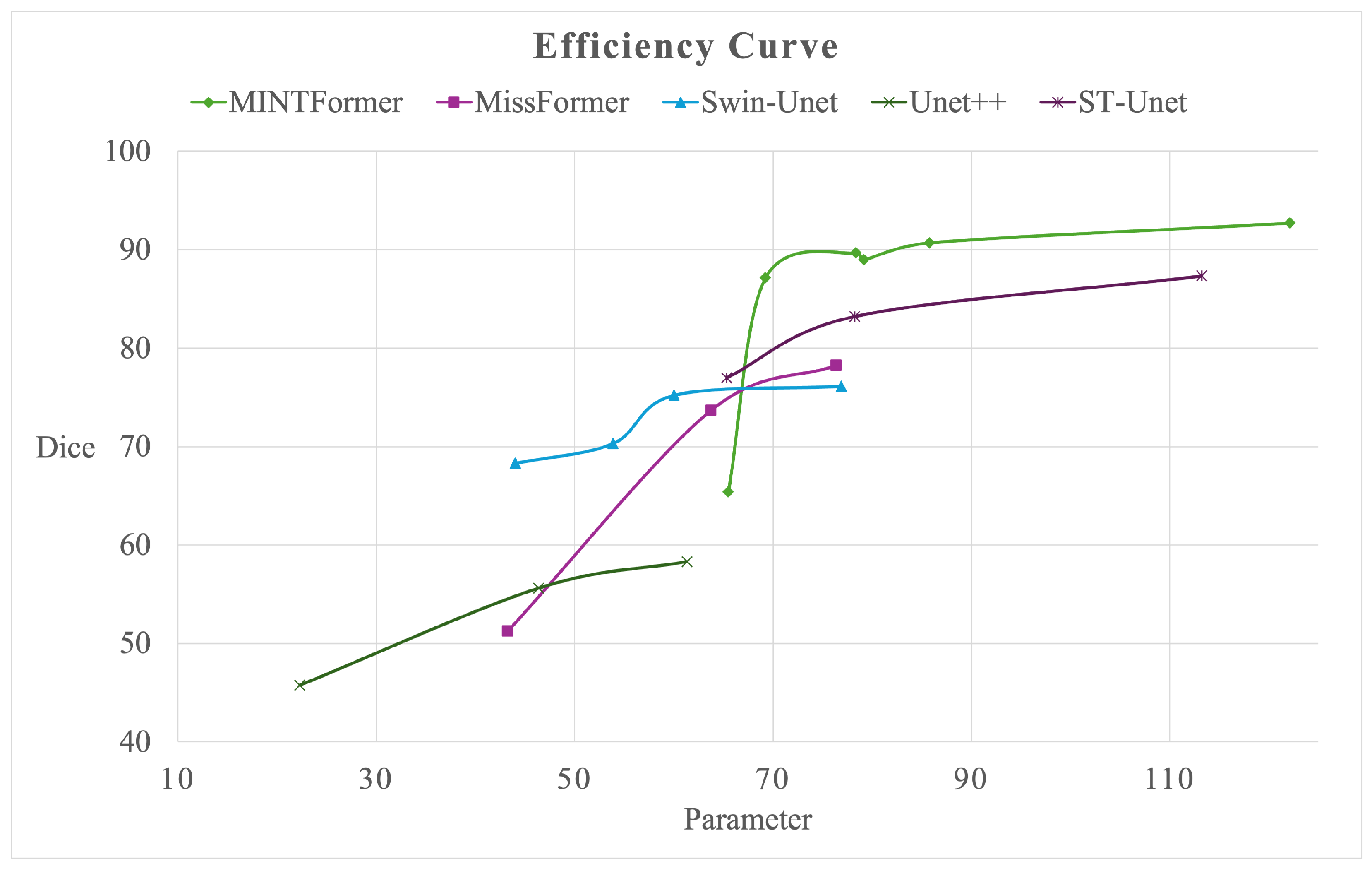
4.6. Efficiency Analysis
4.7. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Asgari Taghanaki, S.; Abhishek, K.; Cohen, J.P.; Cohen-Adad, J.; Hamarneh, G. Deep semantic segmentation of natural and medical images: A review. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2021, 54, 137–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, I.; Yan, J.; Abbas, Q.; Shaheed, K.; Riaz, A.B.; Wahid, A.; Khan, M.W.J.; Szczuko, P. Medical image segmentation using deep semantic-based methods: A review of techniques, applications and emerging trends. Inf. Fusion 2023, 90, 316–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Lei, T.; Cui, R.; Zhang, B.; Meng, H.; Nandi, A.K. Medical image segmentation using deep learning: A survey. IET Image Process. 2022, 16, 1243–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Proceedings, Part III 18. pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Azad, R.; Fayjie, A.R.; Kauffmann, C.; Ben Ayed, I.; Pedersoli, M.; Dolz, J. On the texture bias for few-shot cnn segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2021; pp. 2674–2683. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Lu, Y.; Yu, Q.; Luo, X.; Adeli, E.; Wang, Y.; Lu, L.; Yuille, A.L.; Zhou, Y. Transunet: Transformers make strong encoders for medical image segmentation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.04306. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, M.; Zhou, Q.; Tao, B.; Shcherbakov, P.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, X. Short-term and long-term memory self-attention network for segmentation of tumours in 3D medical images. CAAI Trans. Intell. Technol. 2023, 8, 1524–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Qi, H.; Xiong, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y. Deformable convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 764–773. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Girshick, R.; Gupta, A.; He, K. Non-local neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7794–7803. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaswani, A. Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F. Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.07122. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid scene parsing network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2881–2890. [Google Scholar]
- Zagoruyko, S. End-to-end object detection with transformers. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, Y. Mix-ViT: Mixing attentive vision transformer for ultra-fine-grained visual categorization. Pattern Recognit. 2023, 135, 109131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Rochan, M.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y. Cross-modal self-attention network for referring image segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 10502–10511. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Gao, P.; Yu, T.; Wang, F.; Yuan, R.Y. CSWin-UNet: Transformer UNet with cross-shaped windows for medical image segmentation. Inf. Fusion 2025, 113, 102634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.; Bao, J.; Chen, D.; Zhang, W.; Yu, N.; Yuan, L.; Chen, D.; Guo, B. Cswin transformer: A general vision transformer backbone with cross-shaped windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–24 June 2022; pp. 12124–12134. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, Z.; Talebi, H.; Zhang, H.; Yang, F.; Milanfar, P.; Bovik, A.; Li, Y. MaxViT: Multi-axis vision transformer. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; pp. 459–479. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, H.; Na, C.; Oh, J.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.; Choe, S.; Lee, J.; Kim, T.; Yang, J. Reciprocal Attention Mixing Transformer for Lightweight Image Restoration. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 5992–6002. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.; Ren, W.; Gao, X.; Wang, R.; Cao, X. Restoring images in adverse weather conditions via histogram transformer. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 111–129. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Dai, X.; Chen, D.; Liu, M.; Dong, X.; Yuan, L.; Liu, Z. Mobile-former: Bridging mobilenet and transformer. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–24 June 2022; pp. 5270–5279. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, D.; El-Sharkawy, M. Thin mobilenet: An enhanced mobilenet architecture. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 10th Annual Ubiquitous Computing, Electronics & Mobile Communication Conference (UEMCON), New York, NY, USA, 10–12 October 2019; pp. 0280–0285. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Zhong, F.; Luo, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, Y. Edgevit: Efficient visual modeling for edge computing. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Wireless Algorithms, Systems, and Applications, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–24 June 2022; pp. 393–405. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Rahman Siddiquee, M.M.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J. Unet++: A nested u-net architecture for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support: 4th International Workshop, DLMIA 2018, and 8th International Workshop, ML-CDS 2018, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2018, Granada, Spain, 20 September 2018; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Lin, L.; Tong, R.; Hu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Iwamoto, Y.; Han, X.; Chen, Y.W.; Wu, J. Unet 3+: A full-scale connected unet for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020—2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; pp. 1055–1059. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Deng, Z.; Li, D.; Yuan, X. Missformer: An effective medical image segmentation transformer. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2109.07162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, Q.; You, S.; Gevers, T. Learning content-enhanced mask transformer for domain generalized urban-scene segmentation. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–27 February 2024; Volume 38, pp. 819–827. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, B.; Misra, I.; Schwing, A.G.; Kirillov, A.; Girdhar, R. Masked-attention mask transformer for universal image segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 1290–1299. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, Q.; You, S.; Gevers, T. Learning generalized segmentation for foggy-scenes by bi-directional wavelet guidance. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–27 February 2024; Volume 38, pp. 801–809. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, X.; Tian, Q.; Wang, M. Swin-unet: Unet-like pure transformer for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel-Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; pp. 205–218. [Google Scholar]
- Isensee, F.; Jaeger, P.F.; Kohl, S.A.; Petersen, J.; Maier-Hein, K.H. nnU-Net: A self-configuring method for deep learning-based biomedical image segmentation. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xie, E.; Li, X.; Fan, D.P.; Song, K.; Liang, D.; Lu, T.; Luo, P.; Shao, L. Pyramid vision transformer: A versatile backbone for dense prediction without convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 568–578. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Xie, E.; Li, X.; Fan, D.P.; Song, K.; Liang, D.; Lu, T.; Luo, P.; Shao, L. Pvt v2: Improved baselines with pyramid vision transformer. Comput. Vis. Media 2022, 8, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Marculescu, R. Multi-scale hierarchical vision transformer with cascaded attention decoding for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging with Deep Learning, PMLR, Lausanne, Switzerland, 10–12 July 2024; pp. 1526–1544. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. Segnet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Cao, H.; Udupa, J.K.; Tong, Y.; Torigian, D.A. DiSegNet: A deep dilated convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for lymph node segmentation on PET/CT images. Comput. Med Imaging Graph. 2021, 88, 101851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Feris, R.S.; Wang, X.; Metaxas, D.N. Red-net: A recurrent encoder–decoder network for video-based face alignment. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2018, 126, 1103–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, J.; Nie, L.; Shao, J.; Liu, W.; Chua, T.S. Sca-cnn: Spatial and channel-wise attention in convolutional networks for image captioning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 5659–5667. [Google Scholar]
- Sakaridis, C.; Dai, D.; Van Gool, L. ACDC: The adverse conditions dataset with correspondences for semantic driving scene understanding. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 10765–10775. [Google Scholar]
- Codella, N.C.; Gutman, D.; Celebi, M.E.; Helba, B.; Marchetti, M.A.; Dusza, S.W.; Kalloo, A.; Liopyris, K.; Mishra, N.; Kittler, H. Skin lesion analysis toward melanoma detection: A challenge at the 2017 international symposium on biomedical imaging (isbi), hosted by the international skin imaging collaboration (isic). In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 15th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2018), Washington, DC, USA, 4–7 April 2018; pp. 168–172. [Google Scholar]
- Codella, N.; Rotemberg, V.; Tschandl, P.; Celebi, M.E.; Dusza, S.; Gutman, D.; Helba, B.; Kalloo, A.; Liopyris, K.; Marchetti, M. Skin lesion analysis toward melanoma detection 2018: A challenge hosted by the international skin imaging collaboration (isic). arXiv 2019, arXiv:1902.03368. [Google Scholar]
- Mendonça, T.; Ferreira, P.M.; Marques, J.S.; Marcal, A.R.; Rozeira, J. PH 2-A dermoscopic image database for research and benchmarking. In Proceedings of the 2013 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013; pp. 5437–5440. [Google Scholar]
- Jha, D.; Smedsrud, P.H.; Riegler, M.A.; Halvorsen, P.; De Lange, T.; Johansen, D.; Johansen, H.D. Kvasir-seg: A segmented polyp dataset. In Proceedings of the MultiMedia Modeling: 26th International Conference, MMM 2020, Daejeon, Republic of Korea, 5–8 January 2020; Proceedings, part II 26. pp. 451–462. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, S.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Shen, W.; Fishman, E.; Yuille, A. Domain adaptive relational reasoning for 3d multi-organ segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2020: 23rd International Conference, Lima, Peru, 4–8 October 2020; Proceedings, Part I 23. pp. 656–666. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.M.; Marculescu, R. Medical image segmentation via cascaded attention decoding. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 2–7 January 2023; pp. 6222–6231. [Google Scholar]
- Tomar, N.K.; Shergill, A.; Rieders, B.; Bagci, U.; Jha, D. TransResU-Net: Transformer based ResU-Net for real-time colonoscopy polyp segmentation. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.08985. [Google Scholar]
- Milletari, F.; Navab, N.; Ahmadi, S.A. V-net: Fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2016 Fourth International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Stanford, CA, USA, 25–28 October 2016; pp. 565–571. [Google Scholar]
- Oktay, O.; Schlemper, J.; Folgoc, L.L.; Lee, M.; Heinrich, M.; Misawa, K.; Mori, K.; McDonagh, S.; Hammerla, N.Y.; Kainz, B. Attention u-net: Learning where to look for the pancreas. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.03999. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Huang, Q.; Tang, F.; Meng, J.; Su, J.; Song, S. Stepwise feature fusion: Local guides global. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Singapore, 18–22 September 2022; pp. 110–120. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, B.; Wang, W.; Fan, D.P.; Li, J.; Fu, H.; Shao, L. Polyp-pvt: Polyp segmentation with pyramid vision transformers. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.06932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xie, S.; Lin, L.; Iwamoto, Y.; Han, X.H.; Chen, Y.W.; Tong, R. Mixed transformer u-net for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022—2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, 22–27 May 2022; pp. 2390–2394. [Google Scholar]
- You, C.; Zhao, R.; Liu, F.; Dong, S.; Chinchali, S.; Topcu, U.; Staib, L.; Duncan, J. Class-aware adversarial transformers for medical image segmentation. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 29582–29596. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Xu, Z.; Fan, J.; Xu, L. BDG-Net: Boundary distribution guided network for accurate polyp segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2022: Image Processing, SPIE, San Diego, CA, USA, 20–24 February 2022; Volume 12032, pp. 792–799. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.Z.; Jeon, W.S.; Rhee, S.Y. ATT-UNet: Pixel-wise Staircase Attention for Weed and Crop Detection. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Fuzzy Theory and Its Applications (iFUZZY), Bangkok, Thailand, 1–3 December 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Solar, M.; Astudillo, H.; Valdes, G.; Iribarren, M.; Concha, G. Identifying weaknesses for Chilean e-Government implementation in public agencies with maturity model. In Proceedings of the Electronic Government: 8th International Conference, EGOV 2009, Linz, Austria, 31 August–3 September 2009; Proceedings 8. pp. 151–162. [Google Scholar]
- Wisaeng, K. U-Net++ DSM: Improved U-Net++ for brain tumor segmentation with deep supervision mechanism. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 132268–132285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatamizadeh, A.; Tang, Y.; Nath, V.; Yang, D.; Myronenko, A.; Landman, B.; Roth, H.R.; Xu, D. Unetr: Transformers for 3d medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2022; pp. 574–584. [Google Scholar]
- Biswas, R. Polyp-sam++: Can a text guided sam perform better for polyp segmentation? arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.06623. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Lin, Z.; Fu, P.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W. Connecting targets via latent topics and contrastive learning: A unified framework for robust zero-shot and few-shot stance detection. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022—2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2022; pp. 7812–7816. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Huang, W.; Gong, H.; Yu, C.; You, Z. PEFNet: Position enhancement faster network for object detection in roadside perception system. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 73007–73023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Yin, H.; Zhu, Z. St-unet: A spatio-temporal u-network for graph-structured time series modeling. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1903.05631. [Google Scholar]
- Jha, D.; Tomar, N.K.; Sharma, V.; Bagci, U. TransNetR: Transformer-based residual network for polyp segmentation with multi-center out-of-distribution testing. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging with Deep Learning, PMLR, Lausanne, Switzerland, 10–12 July 2024; pp. 1372–1384. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Li, R.; Zhang, C.; Fang, S.; Duan, C.; Meng, X.; Atkinson, P.M. UNetFormer: A UNet-like transformer for efficient semantic segmentation of remote sensing urban scene imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 190, 196–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, D.; Smedsrud, P.H.; Riegler, M.A.; Johansen, D.; De Lange, T.; Halvorsen, P.; Johansen, H.D. Resunet++: An advanced architecture for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Symposium on Multimedia (ISM), San Diego, CA, USA, 9–11 December 2019; pp. 225–2255. [Google Scholar]
- Heidari, M.; Kazerouni, A.; Soltany, M.; Azad, R.; Aghdam, E.K.; Cohen-Adad, J.; Merhof, D. Hiformer: Hierarchical multi-scale representations using transformers for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 2–7 January 2023; pp. 6202–6212. [Google Scholar]
- Reza, A.; Moein, H.; Yuli, W.; Dorit, M. Contextual Attention Network: Transformer Meets U-Net. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.01932. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Yuan, G.; Wen, Y.; Hu, J.; Evangelidis, G.; Tulyakov, S.; Wang, Y.; Ren, J. Efficientformer: Vision transformers at mobilenet speed. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 12934–12949. [Google Scholar]
- Wadekar, S.N.; Chaurasia, A. Mobilevitv3: Mobile-friendly vision transformer with simple and effective fusion of local, global and input features. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2209.15159. [Google Scholar]



| Methods | Backbone | Average | Aorta ↑ | GB ↑ | KL ↑ | KR ↑ | Liver ↑ | PC ↑ | SP ↑ | SM ↑ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dice ↑ | HD95 ↓ | ||||||||||
| V-Net [54] (2016) | CNN | 68.81 | - | 75.34 | 51.87 | 77.1 | 80.75 | 87.84 | 40.05 | 80.56 | 56.98 |
| DARR [51] (2020) | CNN | 69.77 | - | 74.74 | 53.77 | 72.31 | 73.24 | 94.08 | 54.18 | 89.9 | 45.96 |
| UNet [4] (2015) | CNN | 70.11 | 44.69 | 84 | 56.7 | 72.41 | 62.64 | 86.98 | 48.73 | 81.48 | 67.96 |
| AttnUNet [55] (2018) | CNN | 71.7 | 34.47 | 82.61 | 61.94 | 76.07 | 70.42 | 87.54 | 46.7 | 80.67 | 67.66 |
| R50+UNet [7] (2021) | CNN | 74.68 | 36.87 | 84.18 | 62.84 | 79.19 | 71.29 | 93.35 | 48.23 | 84.41 | 73.92 |
| R50+AttnUNet [7] (2021) | CNN | 75.57 | 36.97 | 55.92 | 63.91 | 79.2 | 72.71 | 93.56 | 49.37 | 87.19 | 74.95 |
| TransUNet [7] (2021) | CNN+Transformer | 77.48 | 31.69 | 87.23 | 63.13 | 81.87 | 77.02 | 94.08 | 55.86 | 85.08 | 75.62 |
| SSFormerPVT [56] (2022b) | CNN+Transformer | 78.01 | 25.72 | 82.78 | 63.74 | 80.72 | 78.11 | 93.53 | 61.53 | 87.07 | 76.61 |
| PolypPVT [57] (2021) | CNN+Transformer | 78.08 | 25.61 | 82.34 | 66.14 | 81.21 | 73.78 | 94.37 | 59.34 | 88.05 | 79.4 |
| MT-UNet [58] (2022a) | CNN+Transformer | 78.59 | 26.59 | 87.92 | 64.99 | 81.47 | 77.29 | 93.06 | 59.46 | 87.75 | 76.81 |
| Swin-Unet [35] (2021) | Transformer | 79.13 | 21.55 | 85.47 | 66.53 | 83.28 | 79.61 | 94.29 | 56.58 | 90.66 | 76.6 |
| PVT-CASCADE [52] (2023) | CNN+Transformer | 81.06 | 20.23 | 83.01 | 70.59 | 82.23 | 80.37 | 94.08 | 64.43 | 90.1 | 83.69 |
| Missformer [31] (2021) | Transformer | 81.96 | 18.2 | 86.99 | 68.65 | 85.21 | 82 | 94.41 | 65.67 | 91.92 | 80.81 |
| CASTformer [59] (2022) | CNN+Transformer | 82.55 | 22.73 | 89.05 | 67.48 | 86.05 | 82.17 | 95.61 | 67.49 | 91 | 81.55 |
| TransCASCADE [52] (2023) | CNN+Transformer | 82.68 | 17.34 | 86.63 | 68.48 | 87.66 | 84.56 | 94.43 | 65.33 | 90.79 | 83.52 |
| MINTFormer (ours) | CNN+Transformer | 84.74 | 14.03 | 87.62 | 73.95 | 89.27 | 86.47 | 95.38 | 69.72 | 90.66 | 84.85 |
| ACDC | Kvasir-SEG | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Dice | RV | MYO | LV | Architecture | Dice | SE | SP | ACC |
| U-Net [4] | 87.55 | 87.10 | 80.63 | 94.92 | BDG-Net [60] | 91.50 | 68.53 | 92.74 | 74.11 |
| Att-Unet [61] | 86.75 | 87.58 | 79.20 | 93.47 | KDAS3 [62] | 91.30 | 66.03 | 93.93 | 76.25 |
| nnUNet [36] | 90.91 | 89.21 | 90.20 | 93.35 | U-Net++ [63] | 82.10 | 44.62 | 84.48 | 72.01 |
| UNetR [64] | 88.61 | 85.29 | 86.52 | 94.02 | Polyp-SAM++ [65] | 90.20 | 67.29 | 96.82 | 73.56 |
| TransUNet [7] | 89.71 | 88.86 | 84.53 | 95.73 | U-Net [4] | 81.80 | 64.28 | 86.90 | 70.21 |
| Swin-Unet [35] | 90.00 | 88.55 | 85.63 | 95.83 | TGA-Net [66] | 89.82 | 62.53 | 84.89 | 75.43 |
| CSWin-Unet [20] | 91.46 | 89.68 | 88.94 | 95.76 | PEFNet [67] | 88.18 | 59.98 | 76.32 | 66.34 |
| ST-Unet [68] | 89.73 | 87.65 | 82.11 | 94.39 | TransNetR [69] | 87.06 | 56.45 | 79.54 | 78.67 |
| UNetFormer [70] | 89.09 | 88.92 | 87.88 | 95.03 | ResUNet++ [71] | 81.33 | 44.60 | 77.30 | 72.66 |
| MINTFormer | 92.11 | 90.62 | 89.80 | 95.90 | MINTFormer | 92.54 | 66.14 | 98.64 | 79.23 |
| Method | Backbone | ISIC2017 | ISIC2018 | PH2 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dice ↑ | SE ↑ | SP ↑ | ACC ↑ | Dice ↑ | SE ↑ | SP ↑ | ACC ↑ | Dice ↑ | SE ↑ | SP ↑ | ACC ↑ | ||
| U-Net [4] | CNN | 81.59 | 81.72 | 96.80 | 91.64 | 85.45 | 88.00 | 96.97 | 94.04 | 89.36 | 91.25 | 95.88 | 92.33 |
| Att-Unet [61] | CNN | 80.82 | 79.98 | 97.76 | 91.45 | 85.66 | 86.74 | 98.63 | 93.76 | 90.03 | 92.05 | 96.40 | 92.76 |
| TransUNet [7] | CNN+Transformer | 81.23 | 82.63 | 95.77 | 92.07 | 84.99 | 85.78 | 96.53 | 94.52 | 88.40 | 90.63 | 94.27 | 92.00 |
| HiFormer [72] | CNN+Transformer | 92.53 | 91.55 | 98.40 | 97.02 | 91.02 | 91.19 | 97.55 | 96.21 | 94.60 | 94.20 | 97.72 | 96.61 |
| Swin-UNet [35] | Transformer | 91.83 | 91.42 | 97.98 | 97.01 | 89.46 | 90.56 | 97.98 | 96.45 | 94.49 | 94.10 | 95.64 | 96.78 |
| MissFormer [31] | Transformer | 89.03 | 89.24 | 97.25 | 95.69 | 91.01 | 90.31 | 97.45 | 94.42 | 94.01 | 93.05 | 96.91 | 96.14 |
| TMU [73] | Transformer | 91.64 | 91.28 | 97.89 | 96.60 | 90.59 | 90.38 | 97.46 | 96.03 | 91.14 | 93.95 | 97.56 | 96.47 |
| CSWin-Unet [20] | Transformer | 91.47 | 93.79 | 98.56 | 97.26 | 91.11 | 92.31 | 97.88 | 95.25 | 94.29 | 95.63 | 97.82 | 96.82 |
| MINTFormer | Heterogeneous Transformer | 92.71 | 94.38 | 97.73 | 97.07 | 91.59 | 90.63 | 98.81 | 96.42 | 94.81 | 95.59 | 98.01 | 96.89 |
| MaxConvKernel | Dice ↑ | Aorta ↑ | Gallbladder ↑ | Kidney (L) ↑ | Kidney (R) ↑ | Liver ↑ | Pancreas ↑ | Spleen ↑ | Stomach ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H | 80.02 | 84.49 | 55.51 | 72.91 | 87.68 | 96.53 | 67.45 | 90.26 | 85.32 |
| 80.50 | 86.51 | 58.03 | 73.21 | 87.71 | 96.01 | 67.45 | 90.13 | 84.91 | |
| 84.74 | 87.62 | 73.95 | 89.27 | 86.47 | 95.38 | 69.72 | 90.66 | 84.85 | |
| 81.30 | 87.93 | 74.01 | 70.03 | 85.31 | 89.76 | 69.92 | 90.18 | 83.29 |
| Stage1 | Stage2 | Stage3 | Stage4 | Dice ↑ | HD95 ↓ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| plan1 | 7 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 84.7 | 14 |
| plan2 | 9 | 7 | 5 | 3 | 80.1 | 21.5 |
| plan3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 83.7 | 13.5 |
| plan4 | None | None | None | None | 75.3 | 25.3 |
| Model Scale | Heterogeneous Encoder Plan | ISIC2017 | Parameter | Flops | FPS | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dice ↑ | SE ↑ | SP ↑ | ACC ↑ | |||||
| Large | CSWin [22]+MaxViT [23] | 92.71 | 94.38 | 97.73 | 97.07 | 122.12 M | 814.16 G | 5131.12 |
| Middle | CSWin [22]+EfficientFormer [74] | 88.96 | 89.61 | 86.50 | 83.75 | 79.17 M | 655.47 G | 6230.04 |
| CSWin [22]+MobileViTv3 [75] | 87.15 | 88.13 | 84.99 | 82.09 | 69.25 M | 607.35 G | 6833.45 | |
| MaxViT [23]+EfficientFormer [74] | 90.70 | 92.11 | 88.03 | 87.10 | 85.77 M | 718.38 G | 5595.21 | |
| MaxViT [23]+MobileViTv3 [75] | 89.69 | 86.29 | 83.46 | 85.94 | 78.34 M | 702.74 G | 5873.37 | |
| Small | MobileViTv3 [75]+EfficientFormer [74] | 65.38 | 64.59 | 74.86 | 73.58 | 65.49 M | 533.21 G | 8907.76 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, C.; Qin, X. MINTFormer: Multi-Scale Information Aggregation with CSWin Vision Transformer for Medical Image Segmentation. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 8626. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15158626
Deng C, Qin X. MINTFormer: Multi-Scale Information Aggregation with CSWin Vision Transformer for Medical Image Segmentation. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(15):8626. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15158626
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Chao, and Xiao Qin. 2025. "MINTFormer: Multi-Scale Information Aggregation with CSWin Vision Transformer for Medical Image Segmentation" Applied Sciences 15, no. 15: 8626. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15158626
APA StyleDeng, C., & Qin, X. (2025). MINTFormer: Multi-Scale Information Aggregation with CSWin Vision Transformer for Medical Image Segmentation. Applied Sciences, 15(15), 8626. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15158626






