Analyzing and Forecasting Vessel Traffic Through the Panama Canal: A Comparative Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
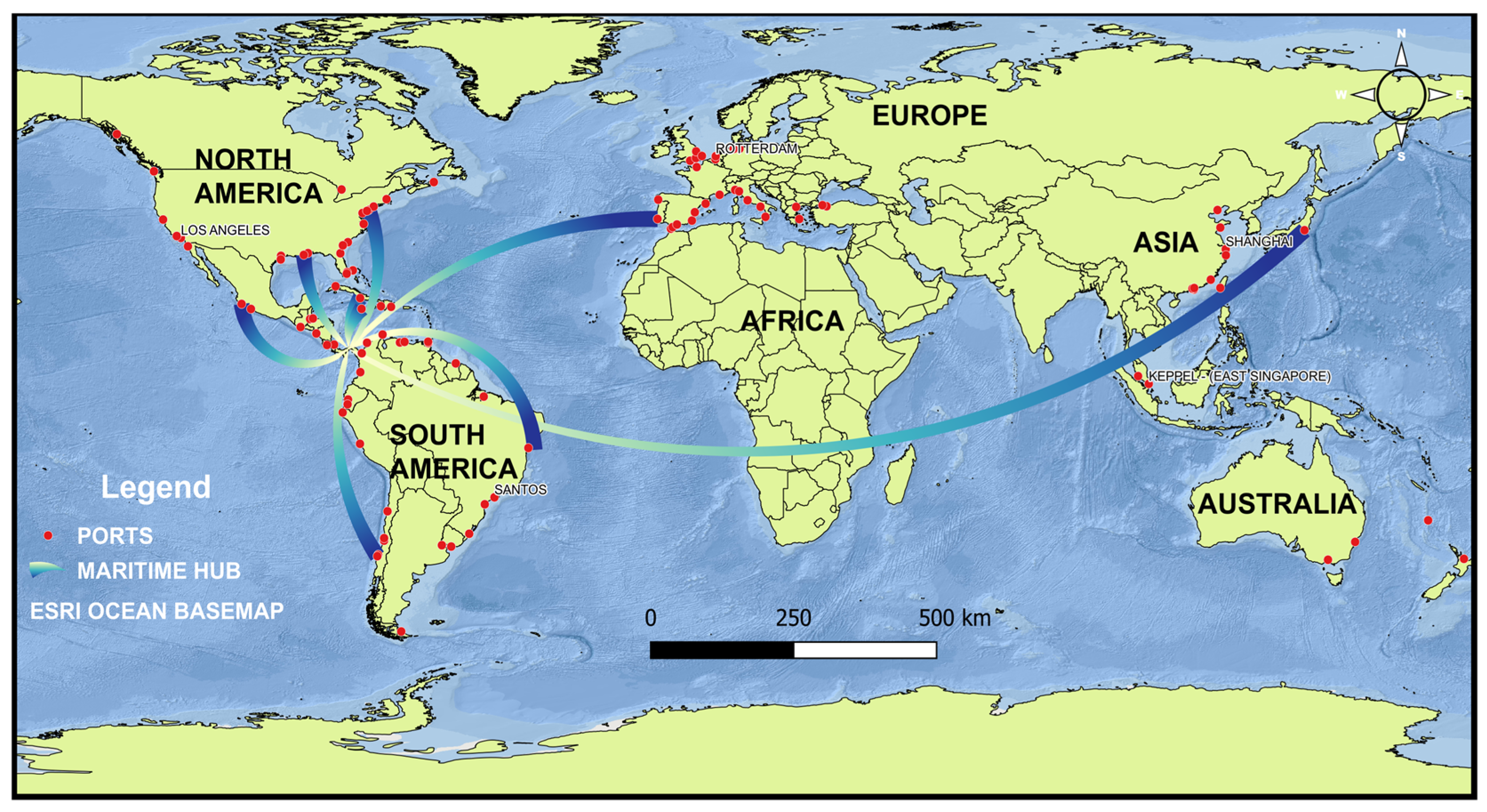
2.1. Data Description
2.2. Methodology
2.2.1. Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA)
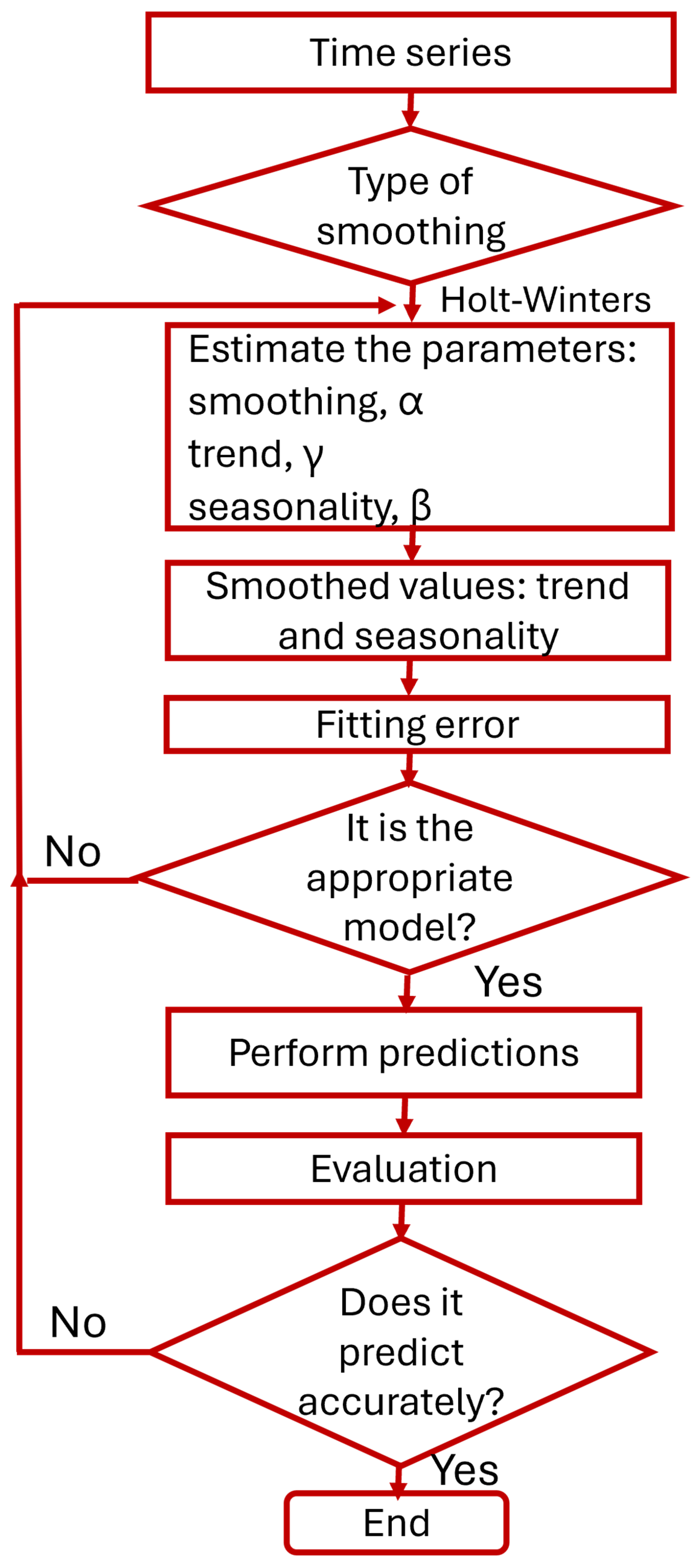
2.2.2. Holt–Winters Method
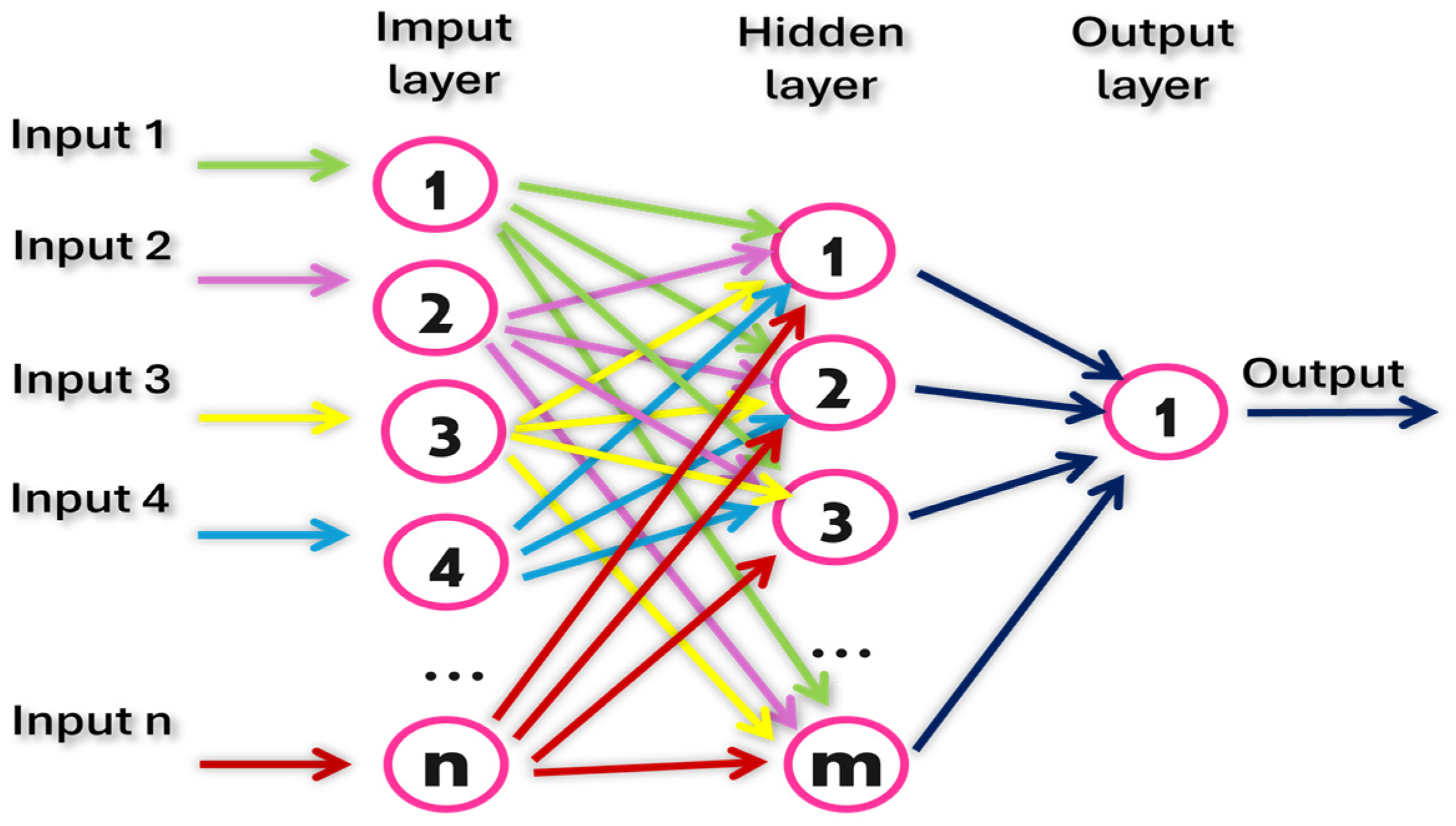
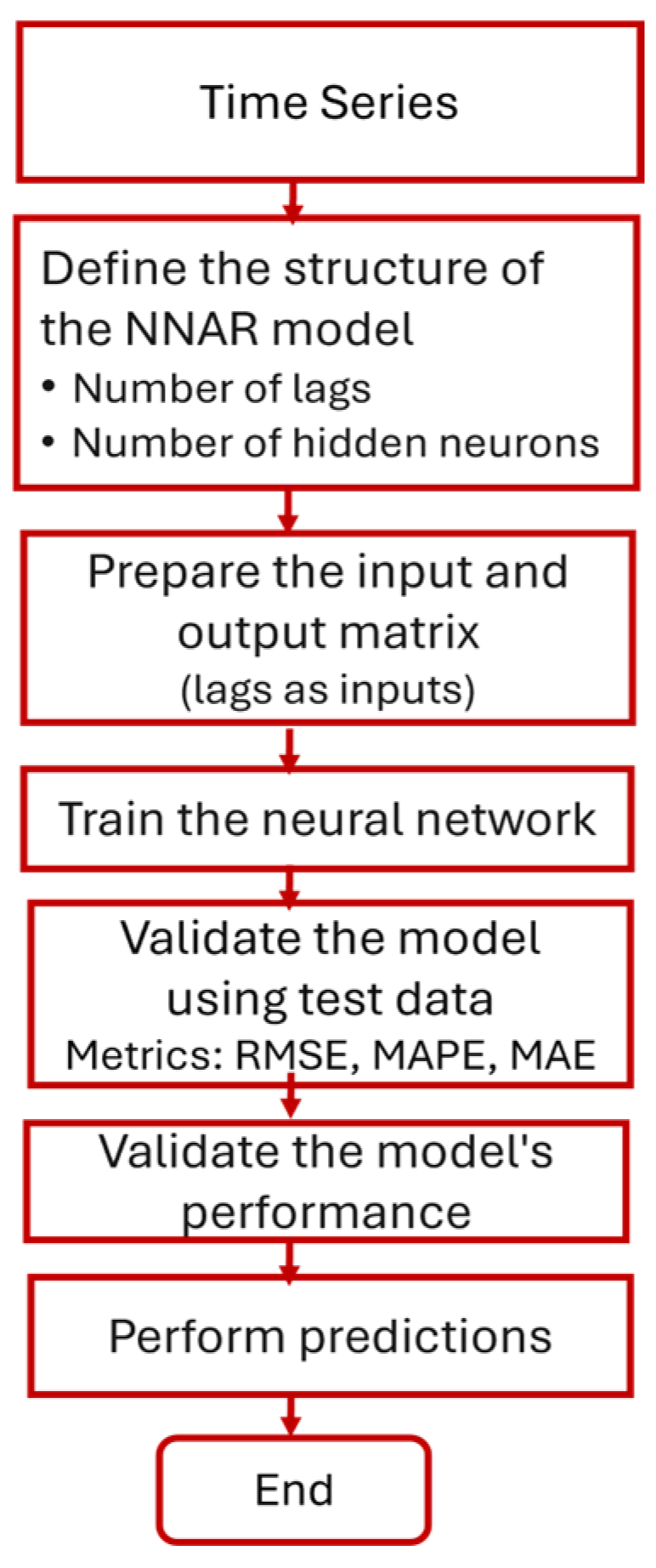
2.2.3. Neural Network Autoregressive (NNAR)
2.2.4. Performance Indicators
3. Results
3.1. Seasonal Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average Model (SARIMA Model)
3.2. Holt–Winters Model
3.3. Neural Network Model
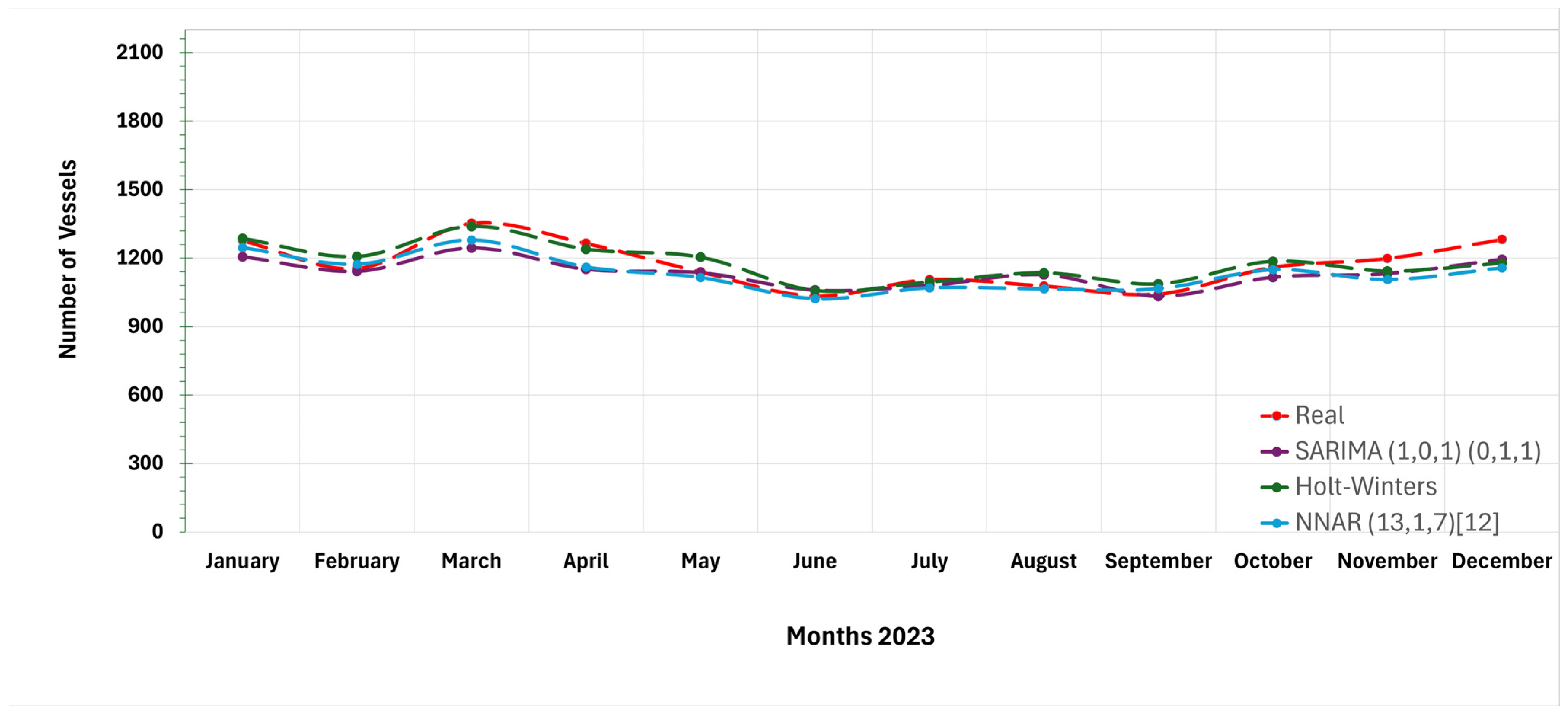
3.4. Model Comparison and Statistical Validation
3.5. Diebold–Mariano (DM) Test
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bustamante Chong, M.; Bustamante Chong, C.; Caamaño Bustamante, V. Un Hub Logístico de Panamá y Su Impacto En Las Américas: Panama’s Logistics Hub and Its Impact on the Americas. J. Bus. Sci. 2020, 1, 23–36. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez Delgado, I. Estudio Inicial de Identificación de Invasiones de Peces Marinos En El Canal de Panamá: Un Enfoque de Metabarcoding. Master’s Thesis, Universidade da Coruña, Coruña, Spain, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Sabonge, R. La Ampliación Del Canal de Panamá: Impulsor de Cambios En El Comercio Internacional. Available online: https://repositorio.cepal.org/entities/publication/50fbfaf5-228f-4abb-9541-e2eaf44a4551 (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- Huebner, G. Economic Aspects of the Panama Canal. Am. Econ. Rev. 1915, 5, 816. [Google Scholar]
- Carral, L.; Tarrío-Saavedra, J.; Naya, S.; Bogle, J.; Sabonge, R. Effect of Inaugurating the Third Set of Locks in the Panama Canal on Vessel Size, Manoeuvring and Lockage Time. J. Navig. 2017, 70, 1205–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carral, L.; Tarrio-Saavedra, J.; Castro-Santos, L.; Lamas-Galdo, I.; Sabonge, R. Effects of the Expanded Panama Canal on Vessel Size and Seaborne Transport. Promet-Traffic Transp. 2018, 30, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsson, E.; Karlsson, L. The Consequences of Low Water Level in the Panama Canal and Possible Route Alternatives Comparing Four Routes Through and Around Panama from China to the US East Coast Regarding Emissions and Time Efficiency. Bachelor’s Thesis, Chalmers University of Technology, Gothenburg, Sweden, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Canal de Panamá. Available online: https://pancanal.com/informes-anuales/ (accessed on 12 April 2025).
- Portal Logístico de Panamá. Available online: https://logistics.gatech.pa (accessed on 16 February 2025).
- Nie, Y.; Liu, K.; Xin, X.; Yu, Q. A Novel Through Capacity Model for One-Way Channel Based on Characteristics of the Vessel Traffic Flow. Int. J. Mar. Navig. Saf. Sea Transp. 2017, 11, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hasan, P.; Khan, T.D.; Alam, I.; Haque, M.E. Dengue in Tomorrow: Predictive Insights from ARIMA and SARIMA Models in Bangladesh: A Time Series Analysis. Health Sci. Rep. 2024, 7, e70276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, A.L.M.; Rodrigues, G.A.P.; dos Martins, P.H.S.; Saiki, G.M.; Filho, G.P.R.; Gonçalves, V.P.; de Albuquerque, R.O. Statistical Comparison of Time Series Models for Forecasting Brazilian Monthly Energy Demand Using Economic, Industrial, and Climatic Exogenous Variables. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 5846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chudo, S.B.; Terdik, G. Modeling and Forecasting Time-Series Data with Multiple Seasonal Periods Using Periodograms. Econometrics 2025, 13, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapundzhi, F.; Chikalov, A.; Georgiev, S.; Georgiev, I. Predictive Modeling of Photovoltaic Energy Yield Using an ARIMA Approach. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 11192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, B.K.; Srivastava, S.K.; Arasu, P.T.; Singh, P. Time Series Modeling of Tuberculosis Cases in India from 2017 to 2022 Based on the SARIMA-NNAR Hybrid Model. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2023, 2023, 5934552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargari, N.S.; Panahi, R.; Akbari, H.; Ng, A.K.Y. Long-Term Traffic Forecast Using Neural Network and Seasonal Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average: Case of a Container Port. Transp. Res. Rec. 2022, 2676, 236–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.-R.; Park, Y.-S.; Jeong, J.-S.; Kim, C.-S.; Jeong, J.-Y. A Forecast Method of Marine Traffic Volume through Time Series Analysis. J. Korean Soc. Mar. Environ. Saf. Res. Pap. 2013, 19, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaolei, L.; Jinli, X.; Mingjun, L. Research on Ship Traffic Flow Forecast Based on SARIMA Model. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. 2017, 2, 329–332. [Google Scholar]
- Boudghene Stambouli, A.; Guizani, L. Neural Network-Based Prediction of Amplification Factors for Nonlinear Soil Behaviour: Insights into Site Proxies. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.-L.; Kim, J.-S.; Jeong, J.-S.; Jeong, J.-Y. A Prediction of Marine Traffic Volume using Artificial Neural Network and Time Series Analysis. J. Korean Soc. Mar. Environ. Saf. 2014, 20, 33–041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millán, P.; Pérez, L.; Hontañón, P.; de Sabando, I. Modelización y Predicción Del Tráfico Marítimo En Los Puertos Españoles. An. De ASEPUMA 2019, 27, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Liu, R.W.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J. Similarity Grouping-Guided Neural Network Modeling for Maritime Time Series Prediction. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 72647–72659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, M.M. Forecasting the Suez Canal Traffic: A Neural Network Analysis. Marit. Policy Manag. 2004, 31, 139–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daranda, A. A Neural Network Approach to Predict Marine Traffic. Trans. Balt. J. Mod. Comput 2016, 3, 483–495. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Zhou, Y.; Chang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, G.; Chen, Z. TG-PGAT: An AIS Data-Driven Dynamic Spatiotemporal Prediction Model for Ship Traffic Flow in the Port. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tимoшeнкoвa, Ю.C.; Kyжбaнoвa, E.A.; Пopшнeв, C.B. Oпыт Пpoгнoзиpoвaния Интeнcивнocти Mopcкoгo Tpaфикa Ha Ocнoвe Koмпьютepнoгo Aнaлизa Online-Mopcких Kapт Пaнaмcкoгo Kaнaлa. Int. J. Open Inf. Technol. 2025, 13, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Panama Canal Commission 10 Year Report, FY 1980 to FY 1989: A Decade of Progress in Canal Operations and Treaty Implementation; The Panama Canal Commission: Washington, DC, USA, 1989.
- Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Censo. Available online: https://www.inec.gob.pa/buscador/Default.aspx? (accessed on 13 April 2025).
- Mgale, Y.J.; Yan, Y.; Timothy, S. A Comparative Study of ARIMA and Holt-Winters Exponential Smoothing Models for Rice Price Forecasting in Tanzania. Open Access Libr. J. 2021, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- RStudio. Integrated Development for R; RStudio PBC: Boston, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Aguirre, J. Introduccioón al Tratamiento de Series Temporales: Aplicacioón a Las Ciencias de La Salud; Dióaz de Santos: Madrid, Spain, 1994; ISBN 84-7978-153-X. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Du, Y.H.; Zhang, X.T. Theory and Application with Seasonal Time Series; Nankai University Press: Tianjin, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Aladag, C.; Egrioglu, E.; Letters, C.K. Forecasting Nonlinear Time Series with a Hybrid Methodology. Appl. Math. Lett. 2009, 22, 1467–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, G. Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control; Holden Day: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Makridakis, S.; Hibon, M. ARMA Models and the Box–Jenkins Methodology. J. Forecast. 1997, 16, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakar, N.A.; Rosbi, S. Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA) Model for Forecasting Cryptocurrency Exchange Rate in High Volatility Environment: A New Insight of Bitcoin. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Res. Sci. 2017, 4, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanke, J.; Wichern, D. Business Forecasting, 5th ed.; Pearson Education: London, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Winters, P.R. Forecasting Sales by Exponentially Weighted Moving Averages. Manag. Sci 1960, 6, 324–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uriel, E.; Muñiz, M. Estadística Económica y Empresarial: Teoría y Ejercicios; Editorial AC: Madrid, Spain, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Sudheer, G.; Suseelatha, A. Short Term Load Forecasting Using Wavelet Transform Combined with Holt–Winters and Weighted Nearest Neighbor Models. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2015, 64, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negnevitsky, M. A Guide to Intelligence Systems; Pearson Education: London, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Elseidi, M. MSTL-NNAR: A New Hybrid Model of Machine Learning and Time Series Decomposition for Wind Speed Forecasting. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2024, 38, 2613–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jierula, A.; Wang, S.; Oh, T.M.; Wang, P. Study on Accuracy Metrics for Evaluating the Predictions of Damage Locations in Deep Piles Using Artificial Neural Networks with Acoustic Emission Data. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrehova, S.; Antosz, K.; Husár, J.; Vagaska, A. From Simulation to Validation in Ensuring Quality and Reliability in Model-Based Predictive Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Aubin, P.; Agard, B. Precision and Reliability of Forecasts Performance Metrics. Forecasting 2022, 4, 882–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyndman, R.J.; Athanasopoulos, G. Forecasting: Principles and Practice. 2018. Available online: https://otexts.org/fpp2/ (accessed on 12 April 2025).
- Diebold, F.; Mariano, R.S. Comparing Predictive Accuracy. J. Bus. Econ. Stat. 2002, 20, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappello, C.; Congedi, A.; De Iaco, S.; Mariella, L. Traditional Prediction Techniques and Machine Learning Approaches for Financial Time Series Analysis. Mathematics 2025, 13, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wan, Q.; Wang, Y. Refined Diebold-Mariano Test Methods for the Evaluation of Wind Power Forecasting Models. Energies 2014, 7, 4185–4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, S.; Gao, S.; Yang, W. Daily Ship Traffic Volume Statistics and Prediction Based on Automatic Identification System Data. In Proceedings of the 2017 9th International Conference on Intelligent Human-Machine Systems and Cybernetics (IHMSC), Hangzhou, China, 26–27 August 2017; Volume 2, pp. 149–154. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Y. Vessel Traffic Flow Forecasting with the Combined Model Based on Support Vector Machine. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Transportation Information and Safety (ICTIS), Wuhan, China, 25–28 June 2015; Volume 3, pp. 695–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, F.; Xie, Y. Using Deep Learning to Forecast Maritime Vessel Flows. Sensors 2020, 20, 1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.R.; Wang, H.; Gupta, C. Predictive Analysis for Optimizing Port Operations. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber, S.M.; Thowai, K.Z.; Rahman, M.A.; Hassan, M.M.; Thowai, Z.; Hassan, M.; Mainul Bari, A.B.M.; Raihan, A. High-Accuracy Prediction of Vessels’ Estimated Time of Arrival in Seaports: A Hybrid Machine Learning Approach Optimizing the Estimated Time of Arrival (ETA) For. Marit. Transp. Res. 2025, 8, 100133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


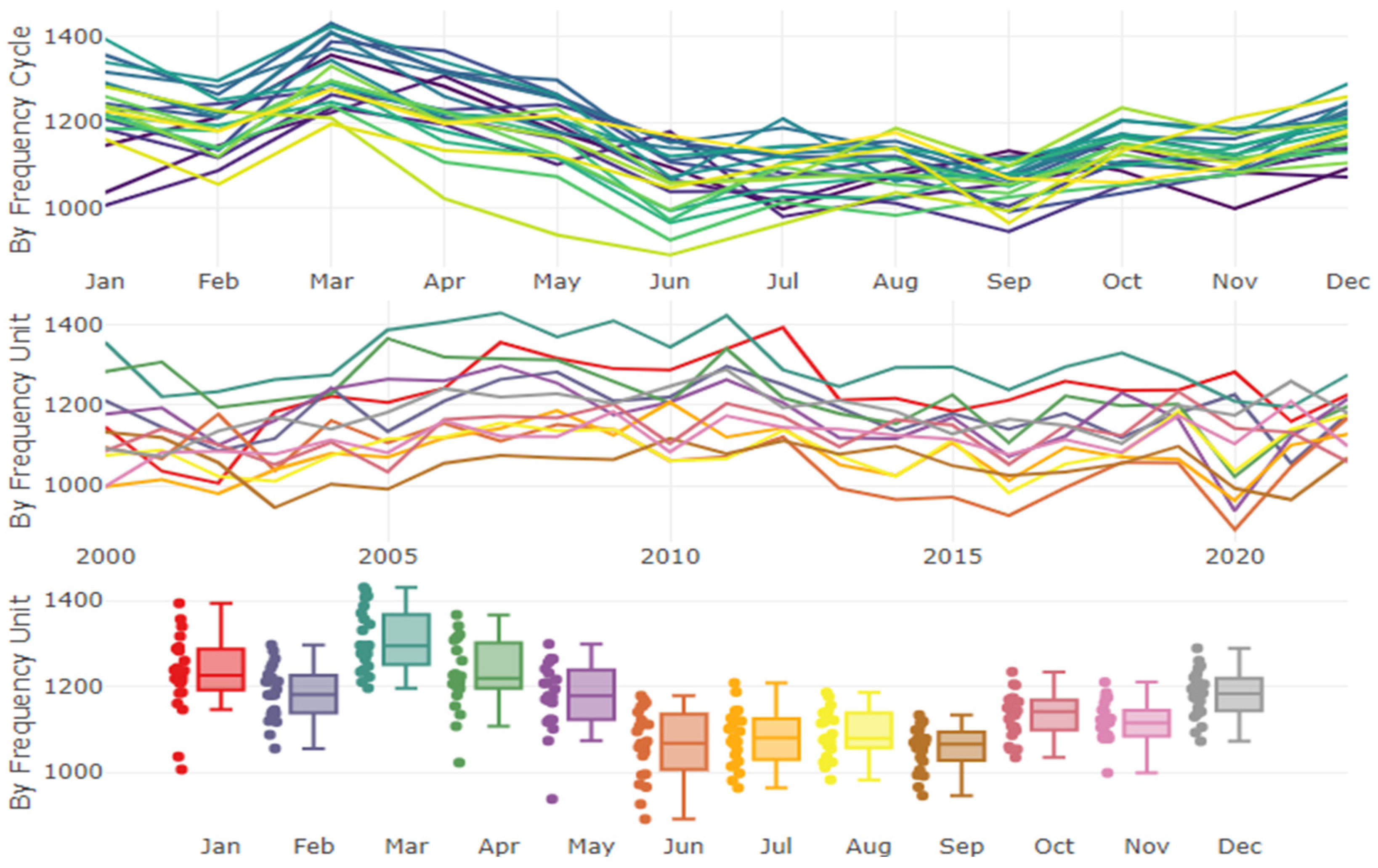
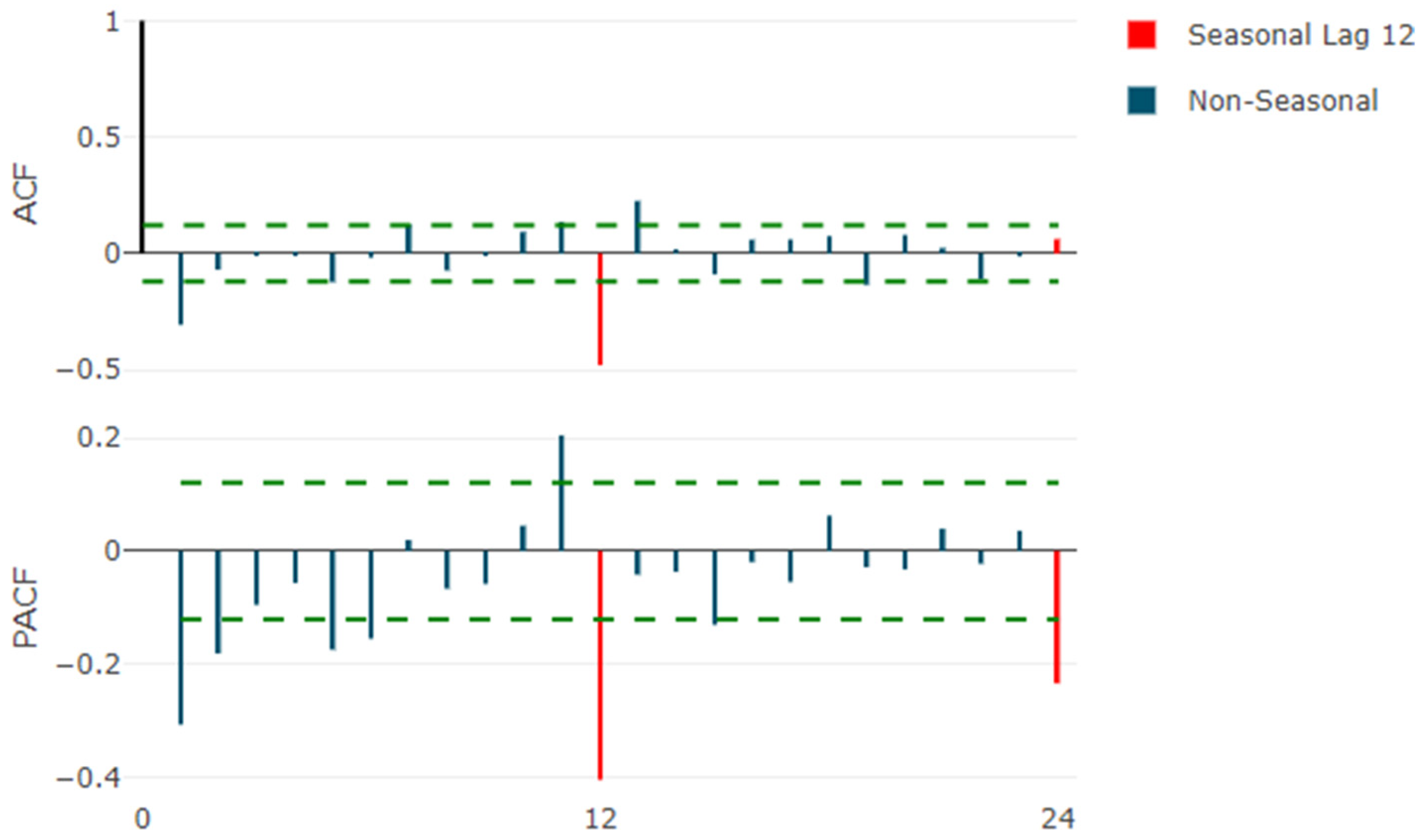
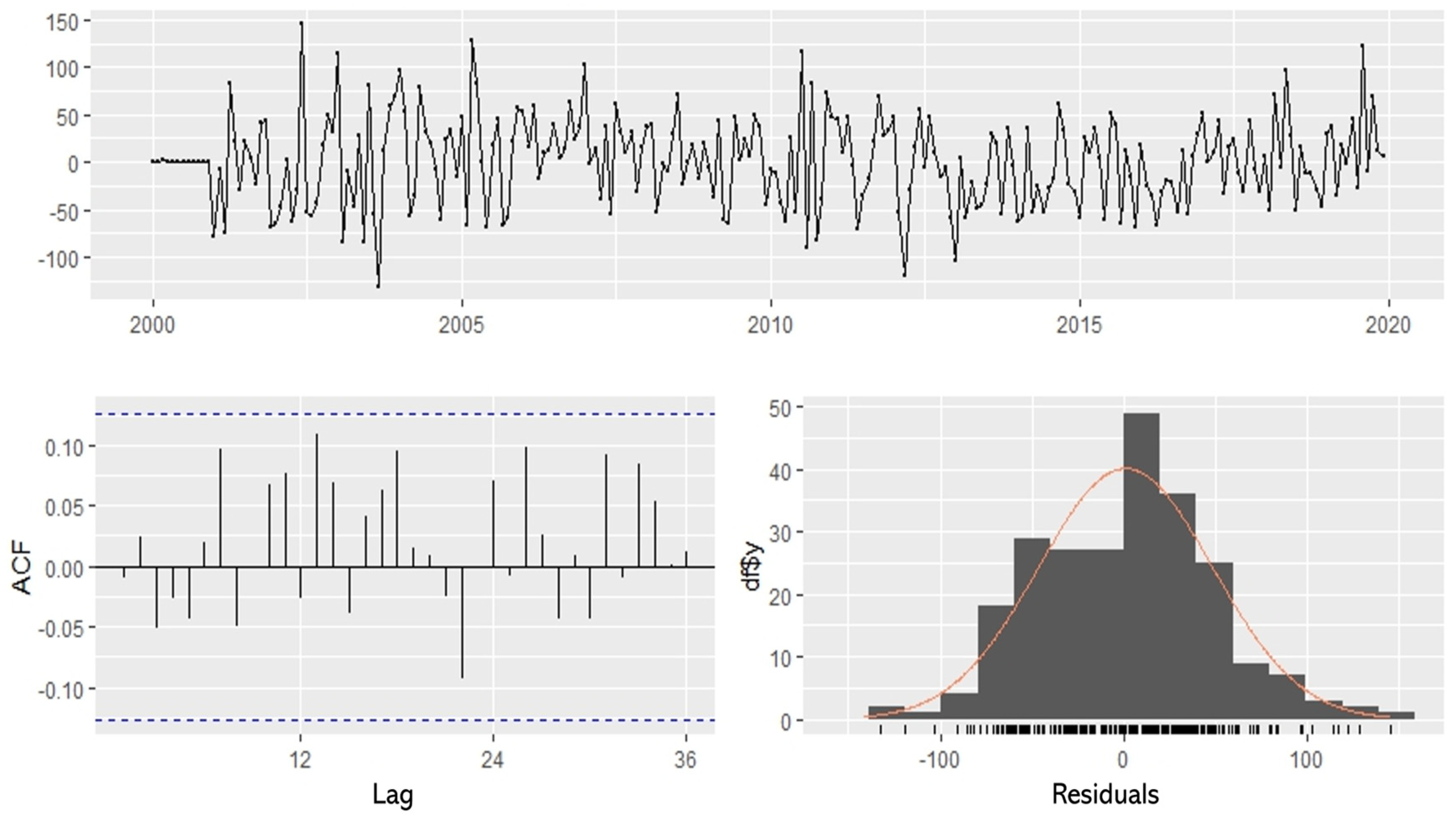
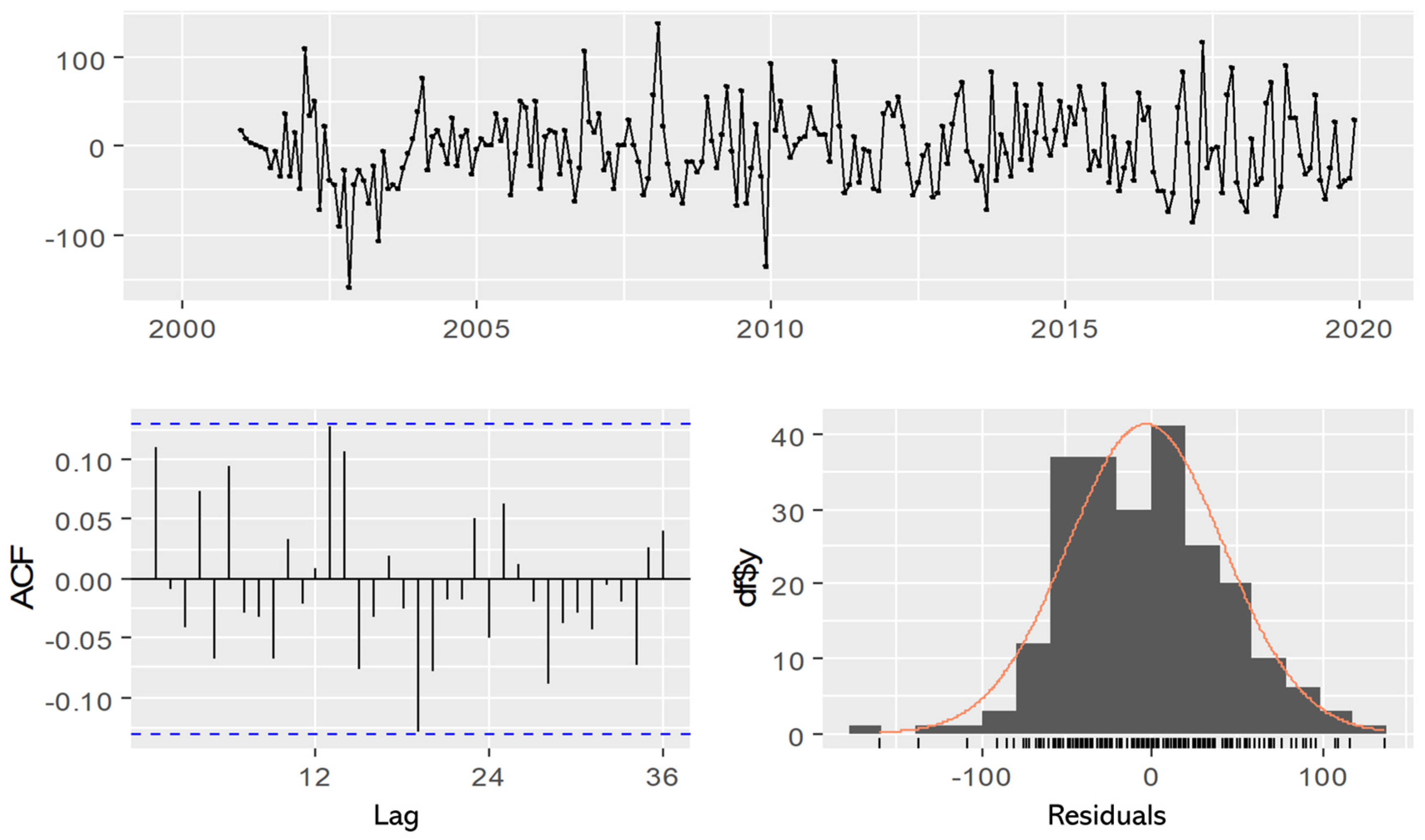
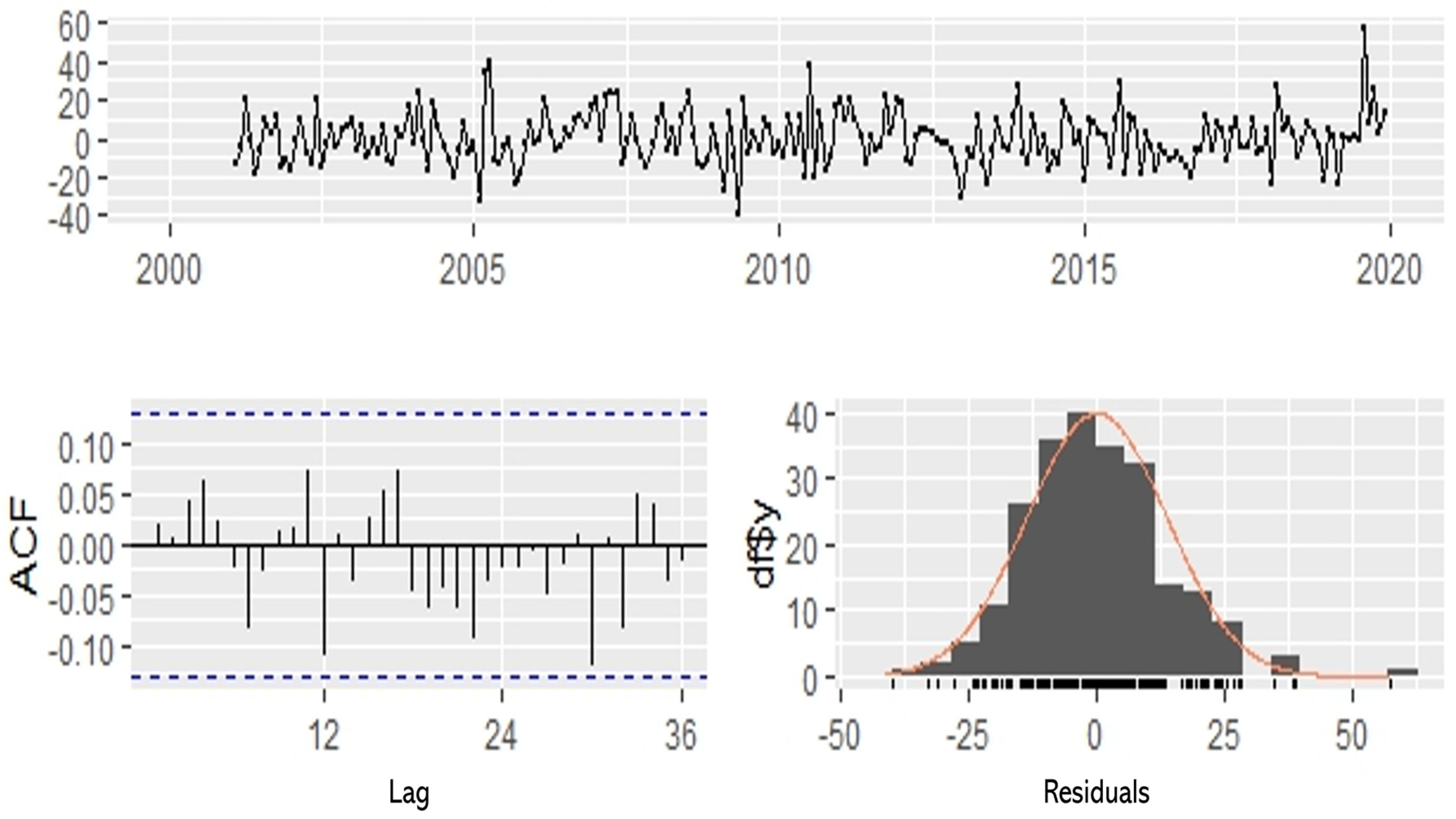
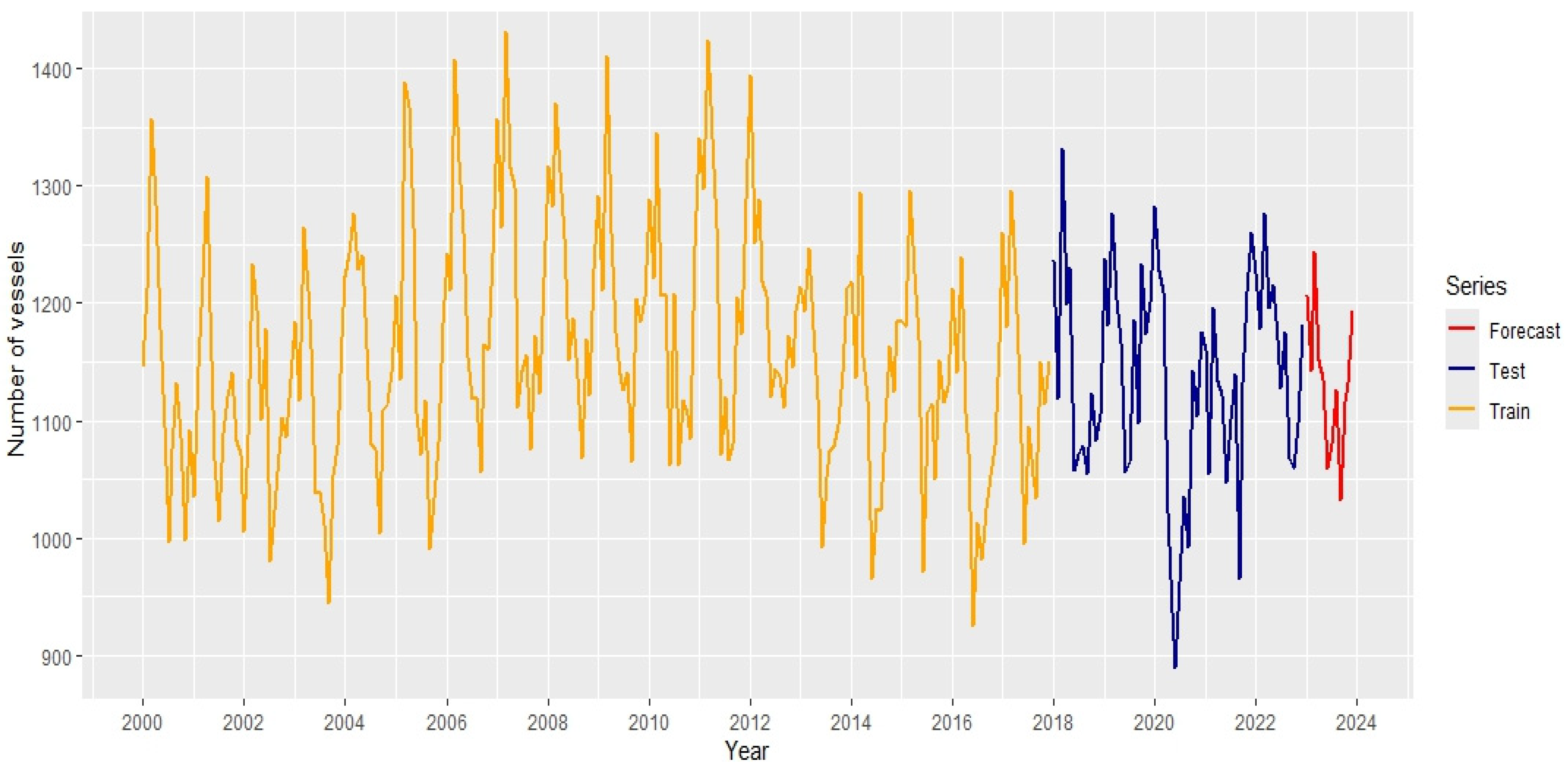


| Measure | Values |
|---|---|
| Mean | 1154 |
| Standard Deviation | 99 |
| Minimum | 890 |
| Maximum | 1431 |
| First Quartile | 1082 |
| Median | 1145 |
| Third Quartile | 1216 |
| Model | Effectiveness | Box–Ljung Test | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | MAE | MAPE | |||
| SARIMA (1,0,1)(0,1,1) [12] | 87.58 | 67.49 | 6.31 | 15.90 | 0.72 |
| Holt–Winters | 106.17 | 82.36 | 7.71 | 79.77 | 0.00 |
| NNAR (13,1,7) [12] | 83.96 | 68.21 | 6.33 | 17.46 | 0.83 |
| Model | DM Test | p-Value DM | Is There a Significant Difference? |
|---|---|---|---|
| SARIMA and Holt–Winters | 2.6139 | 0.01204 | Yes |
| Holt–Winters and NNAR | 5.3064 | 0.000125 | Yes |
| NNAR and SARIMA | −0.0716 | 0.9442 | No |
| Month/Year | Prediction | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimate | 95% CI | Estimate | 95% CI | Estimate | 95% CI | |
| January 2023 | 1206 | 1105–1306 | 1286 | 1107–1465 | 1246 | 1201–1342 |
| February 2023 | 1142 | 1028–1256 | 1207 | 1034–1379 | 1173 | 1134–1295 |
| March 2023 | 1244 | 1124–1364 | 1339 | 1154–1525 | 1279 | 1215–1322 |
| April 2023 | 1151 | 1028–1274 | 1239 | 1062–1416 | 1161 | 1073–1249 |
| May 2023 | 1136 | 1011–1261 | 1204 | 1029–1379 | 1115 | 1025–1146 |
| June 2023 | 1060 | 935–1185 | 1058 | 895–1221 | 1022 | 972–1204 |
| July 2023 | 1080 | 955–1206 | 1095 | 928–1265 | 1070 | 1016–1118 |
| August 2023 | 1127 | 1002–1253 | 1135 | 964–1307 | 1065 | 1013–1124 |
| September 2023 | 1033 | 907–1158 | 1087 | 918–1255 | 1066 | 1016–1130 |
| October 2023 | 1116 | 990–1241 | 1186 | 1007–1365 | 1149 | 1082–1195 |
| November 2023 | 1132 | 1006–1258 | 1143 | 967–1318 | 1106 | 1075–1258 |
| December 2023 | 1194 | 1068–1319 | 1178 | 858–1498 | 1157 | 1120–1266 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cubilla-Montilla, M.; Ramírez, A.; Escudero, W.; Cruz, C. Analyzing and Forecasting Vessel Traffic Through the Panama Canal: A Comparative Study. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 8389. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15158389
Cubilla-Montilla M, Ramírez A, Escudero W, Cruz C. Analyzing and Forecasting Vessel Traffic Through the Panama Canal: A Comparative Study. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(15):8389. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15158389
Chicago/Turabian StyleCubilla-Montilla, Mitzi, Anabel Ramírez, William Escudero, and Clara Cruz. 2025. "Analyzing and Forecasting Vessel Traffic Through the Panama Canal: A Comparative Study" Applied Sciences 15, no. 15: 8389. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15158389
APA StyleCubilla-Montilla, M., Ramírez, A., Escudero, W., & Cruz, C. (2025). Analyzing and Forecasting Vessel Traffic Through the Panama Canal: A Comparative Study. Applied Sciences, 15(15), 8389. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15158389







