Research on Deformation Mechanisms and Control Technology for Floor Heave in Deep Dynamic Pressure Roadway
Abstract
1. Introduction
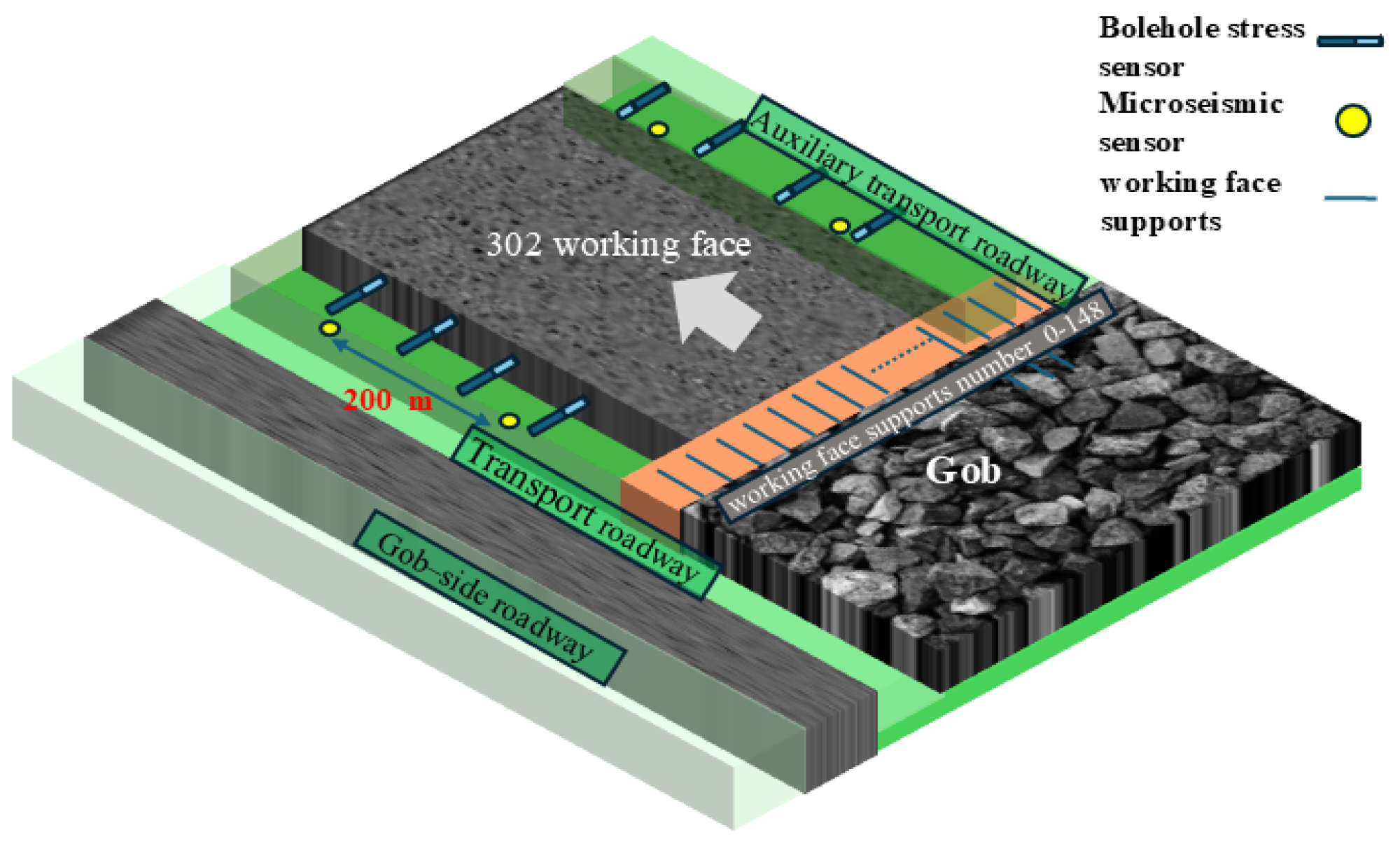
2. Engineering Background
3. Research on the Deformation Mechanism of the Floor Heave
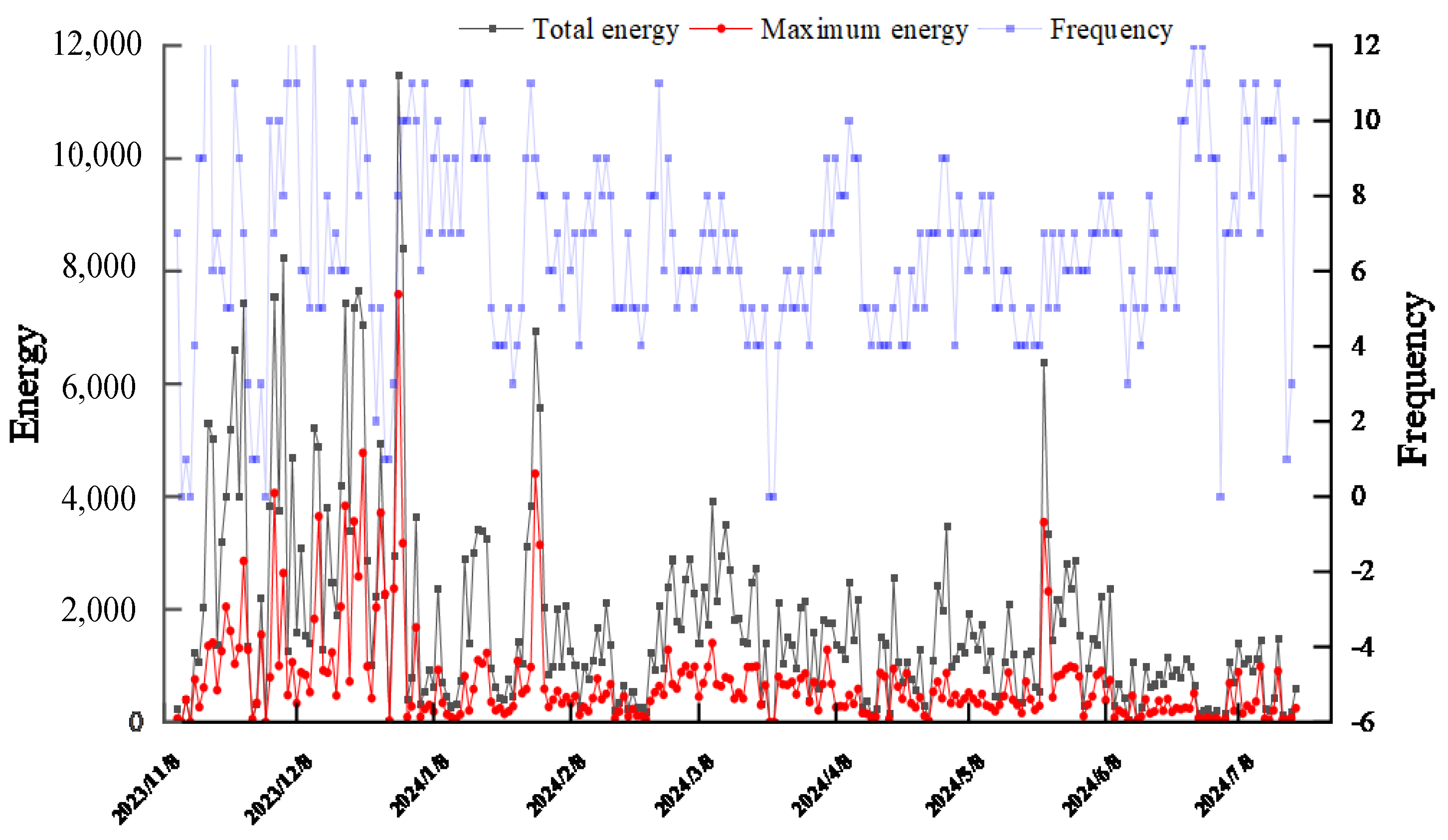
3.1. Analysis of On-Site Mine Pressure Monitoring Data
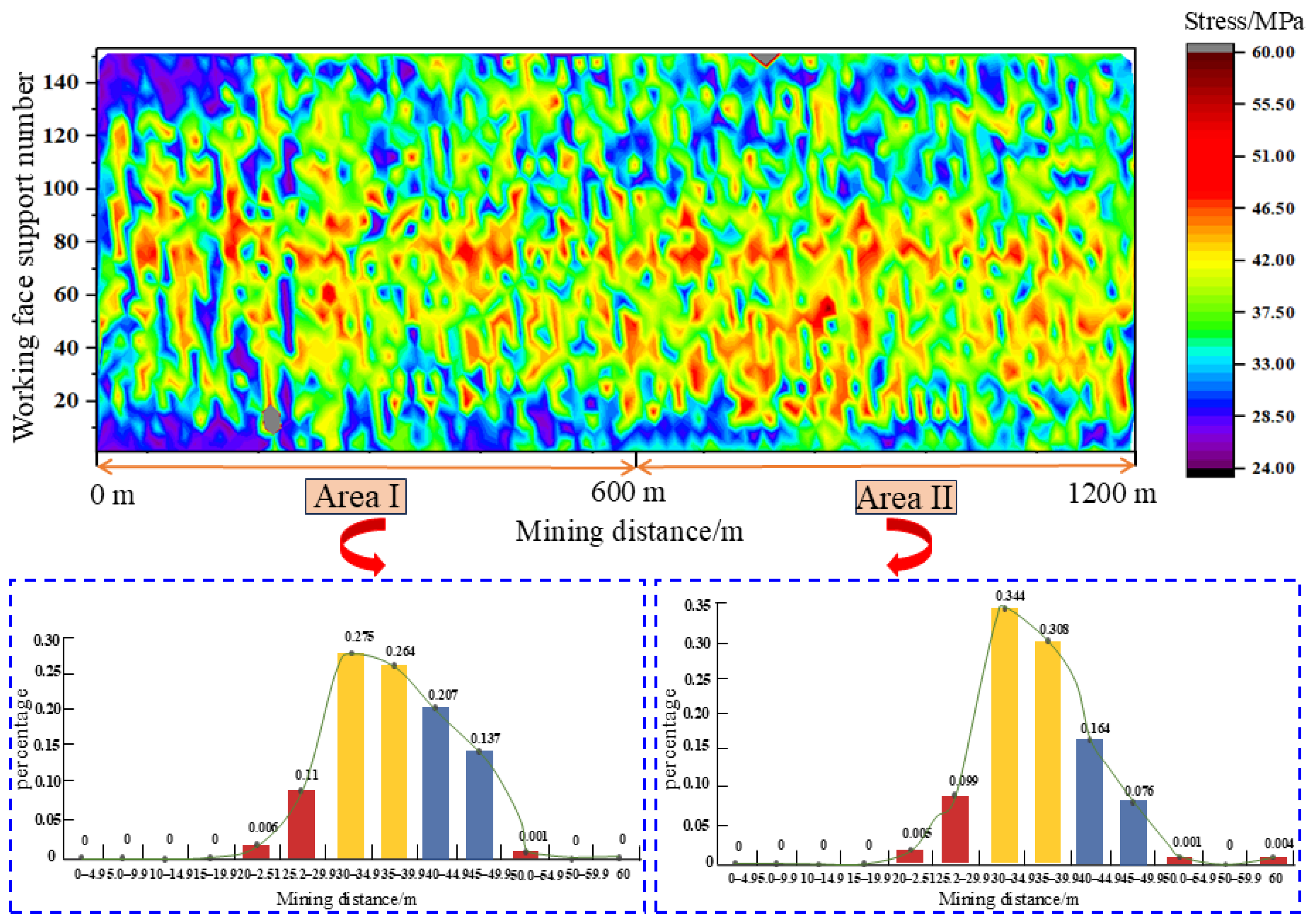
3.1.1. Analysis of Working Face Support Pressure
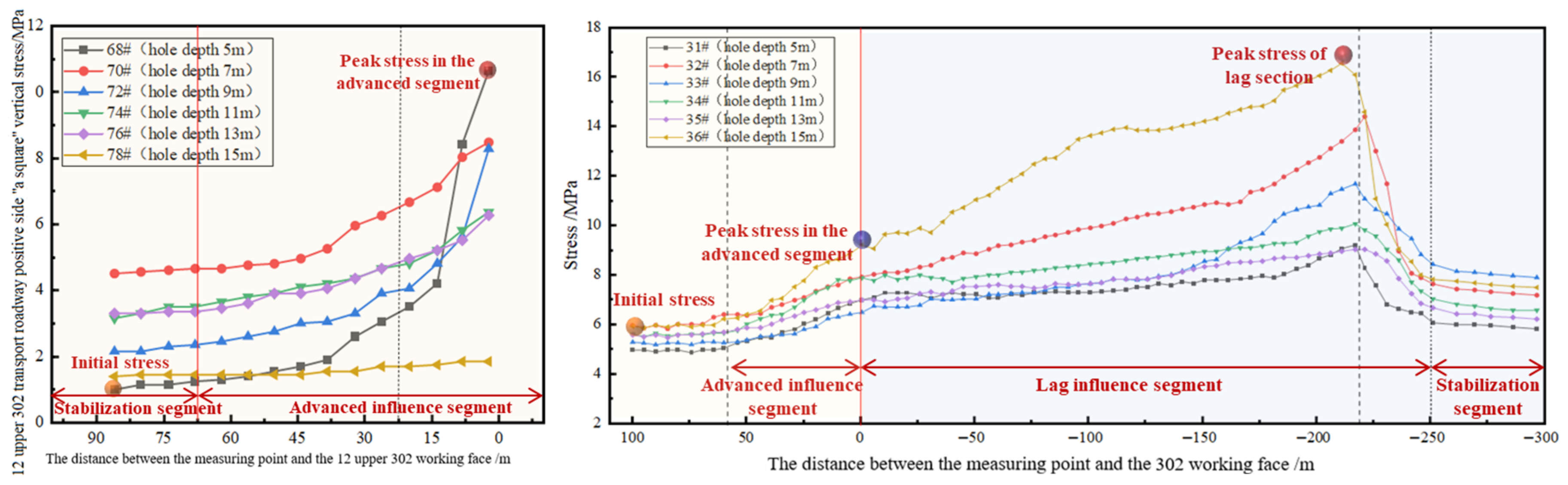
3.1.2. Analysis of Coal Body Support Pressure
3.1.3. Analysis of Microseismic Parameters in the Slope
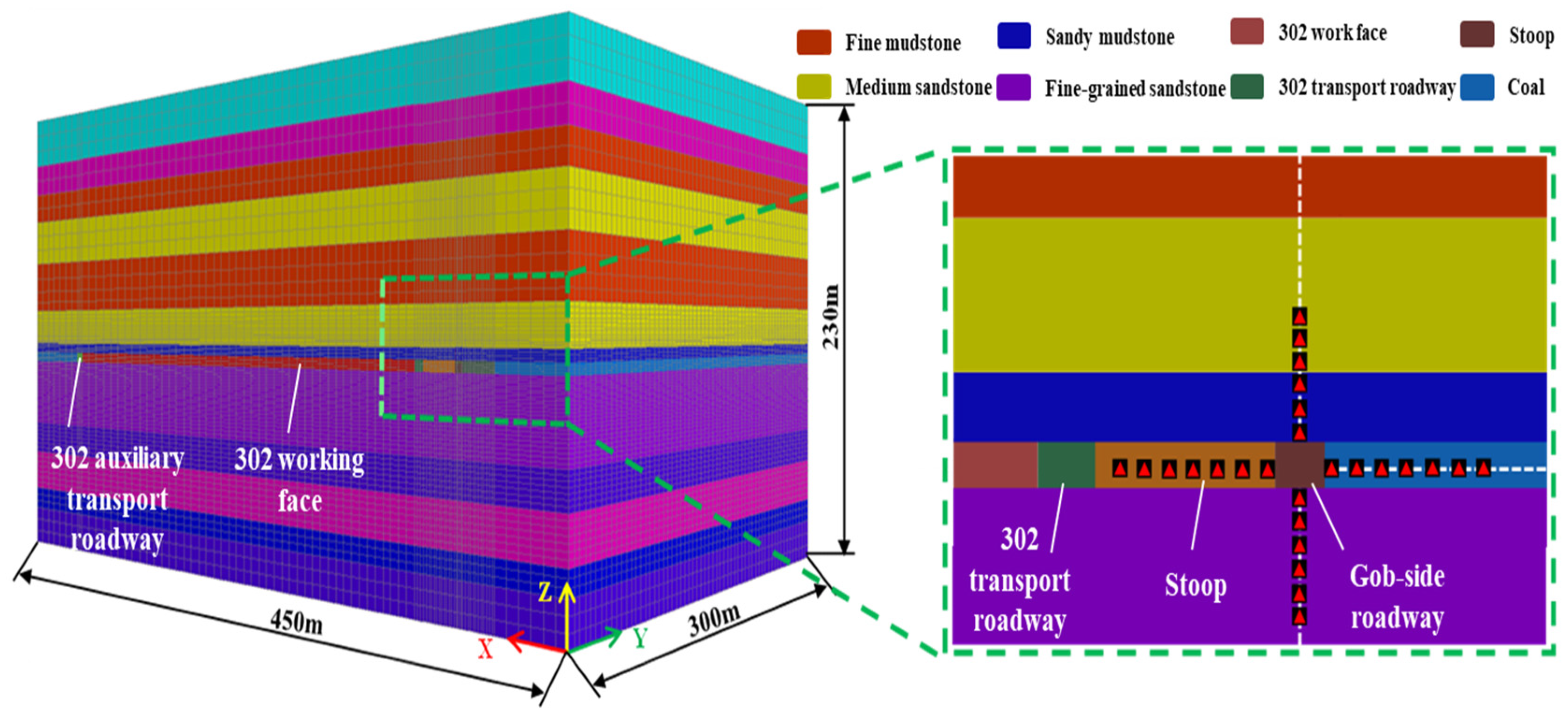
3.2. Numerical Analysis of Deformation and Damage Mechanism of Floor Heave in Roadway
3.2.1. Numerical Modeling
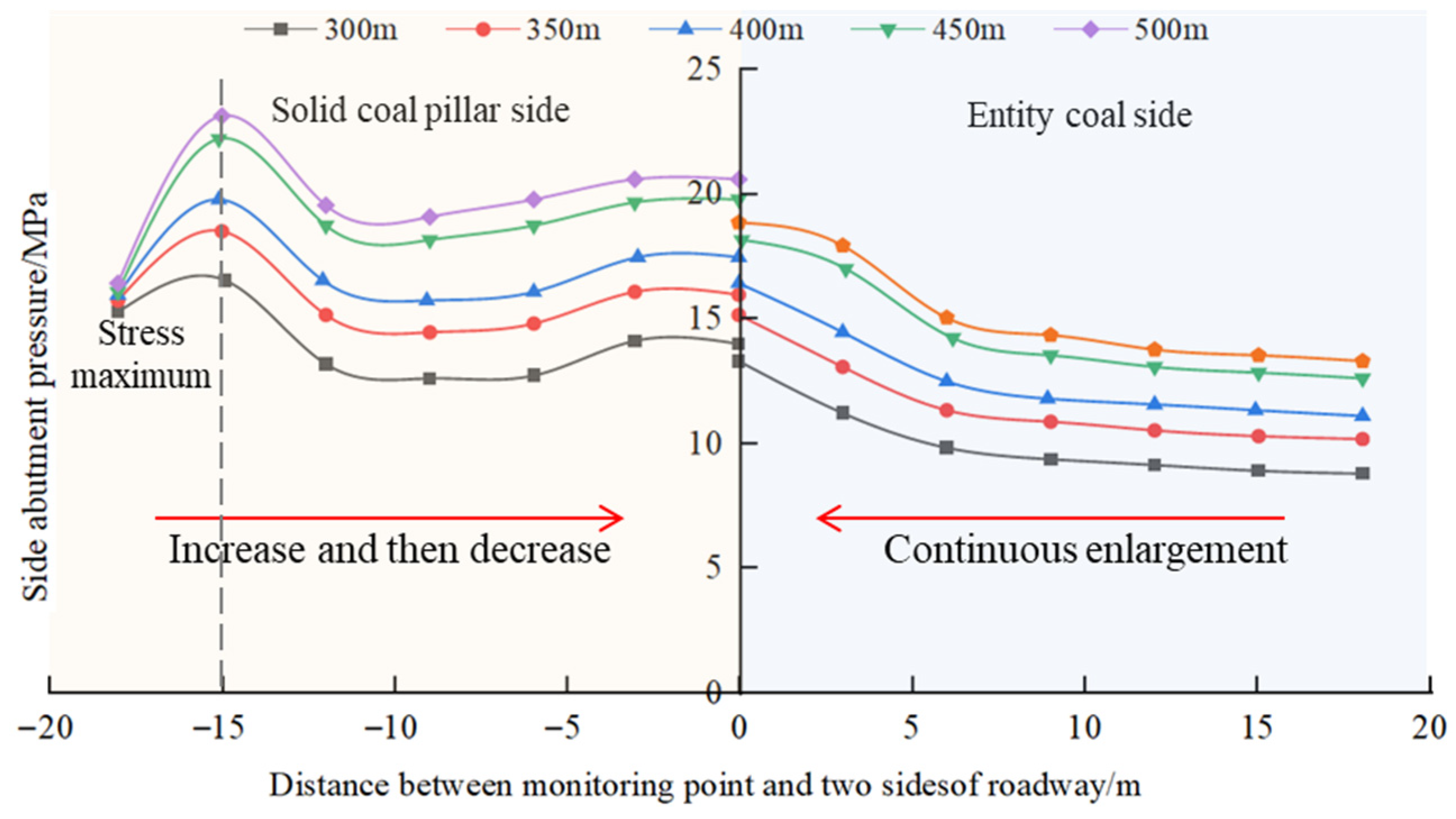
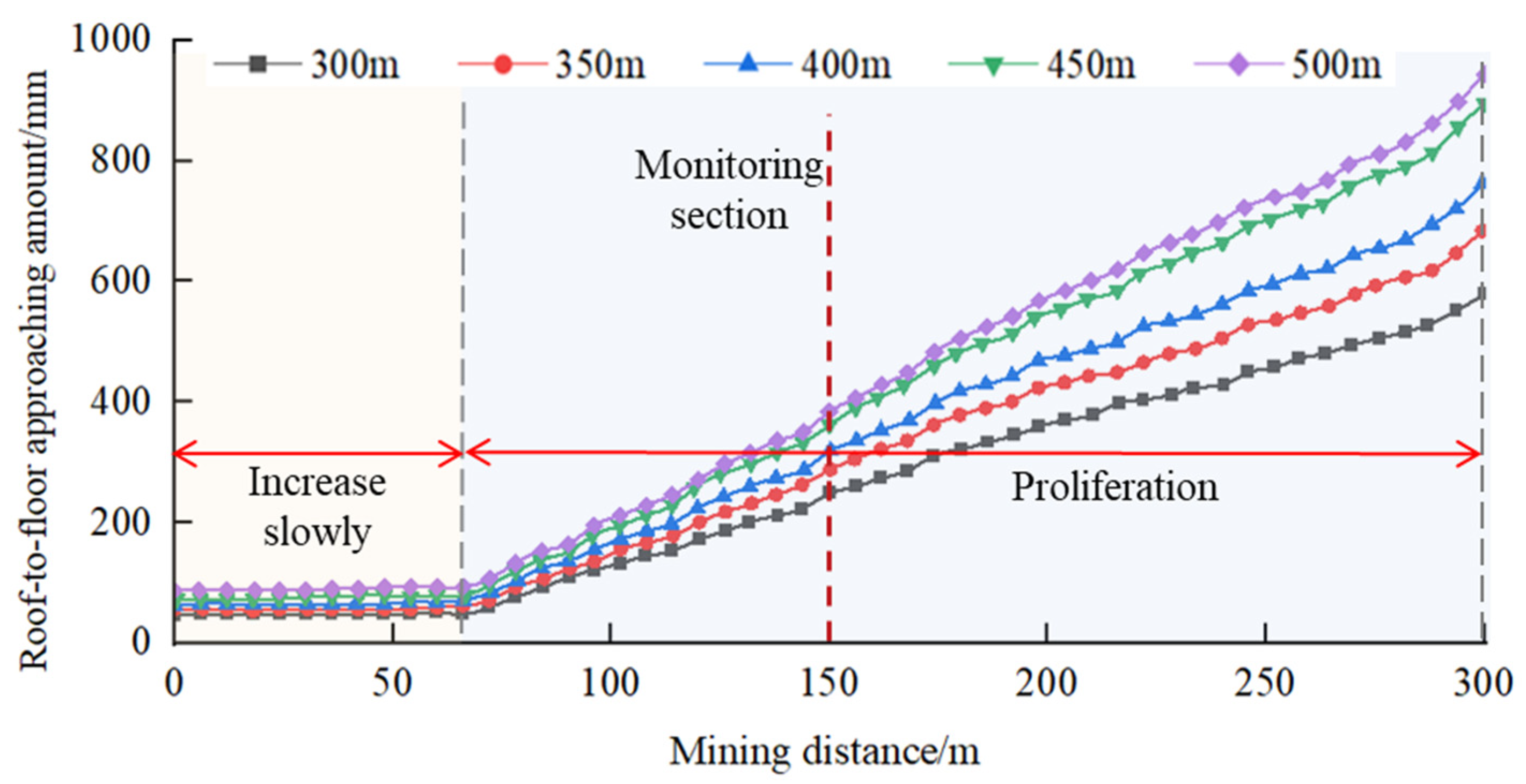
3.2.2. Influence of Coal Seam Depth on the Stability of Roadway Floor
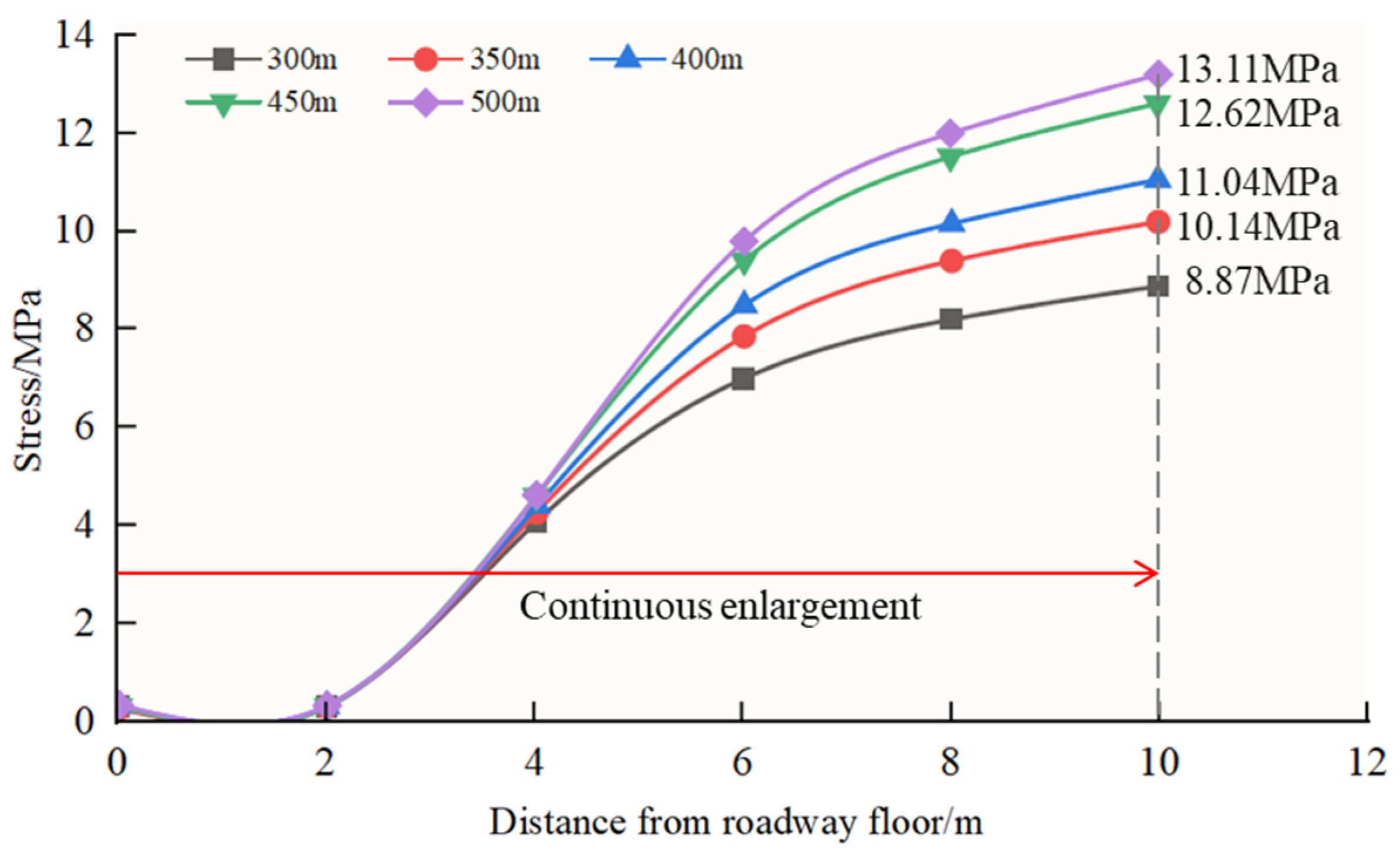
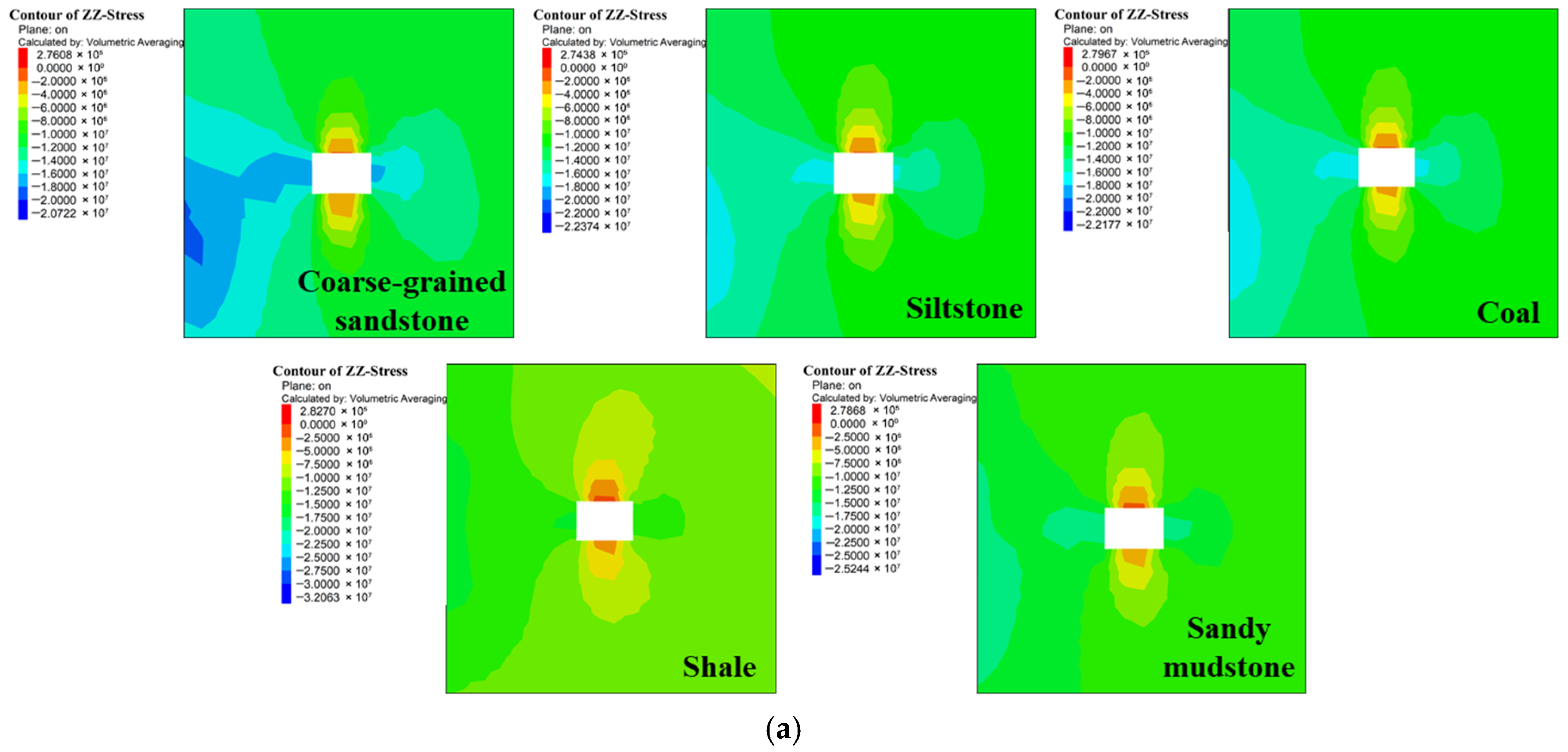
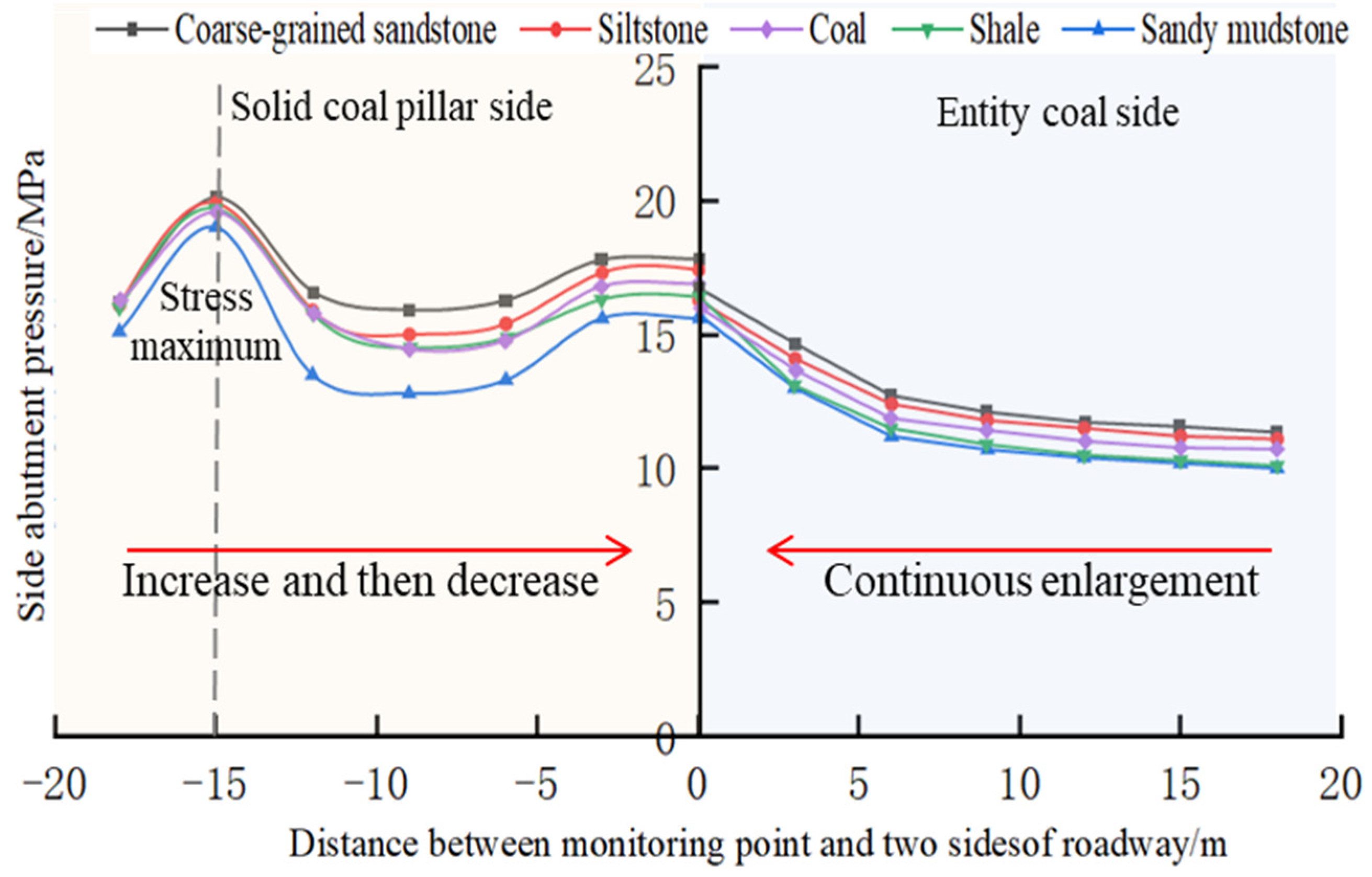
3.2.3. Influence of Floor Lithology on the Stability of the Roadway Floor
3.2.4. Analysis of Numerical Test Results
4. Integrated Design Methodology of “Roof Cutting and Pressure Relief + Floor Grouting with Bolts”
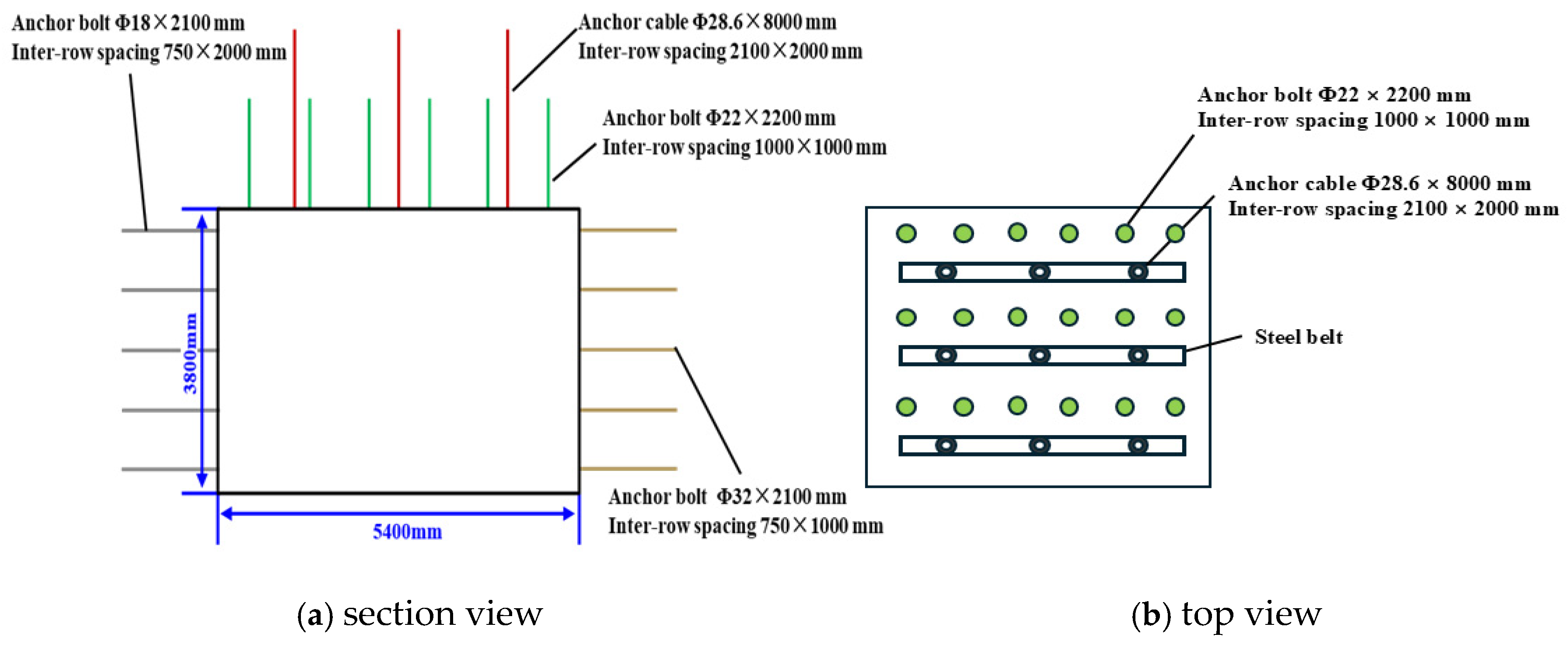
4.1. Design of Control Scheme
4.2. Analysis of Results of Control Scheme
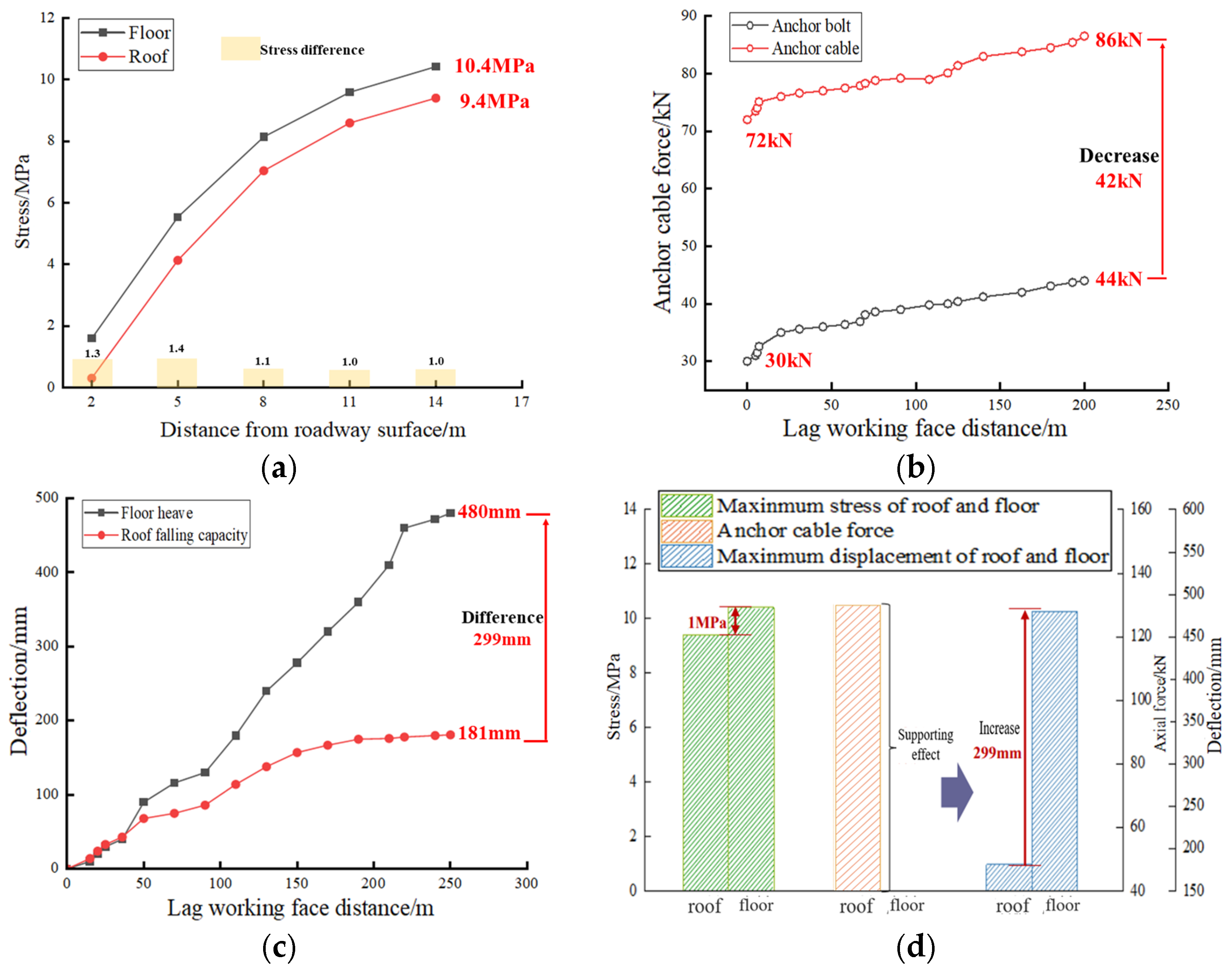
4.2.1. Analysis of Scheme O (Original Support Measures)
4.2.2. Analysis of Scheme A (Floor Grouting with Bolts)
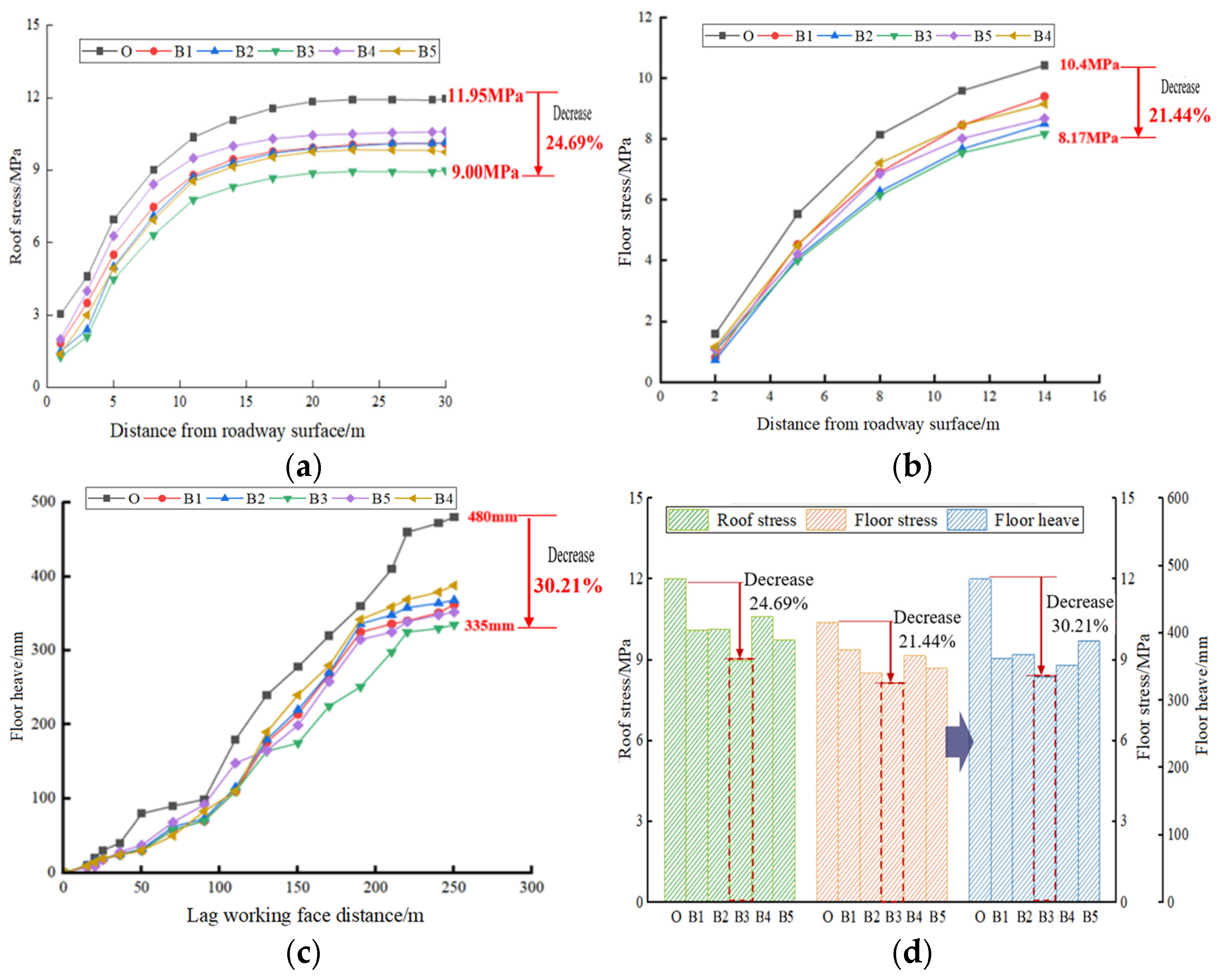
4.2.3. Analysis of Scheme B (Roof Cutting for Pressure Relief)
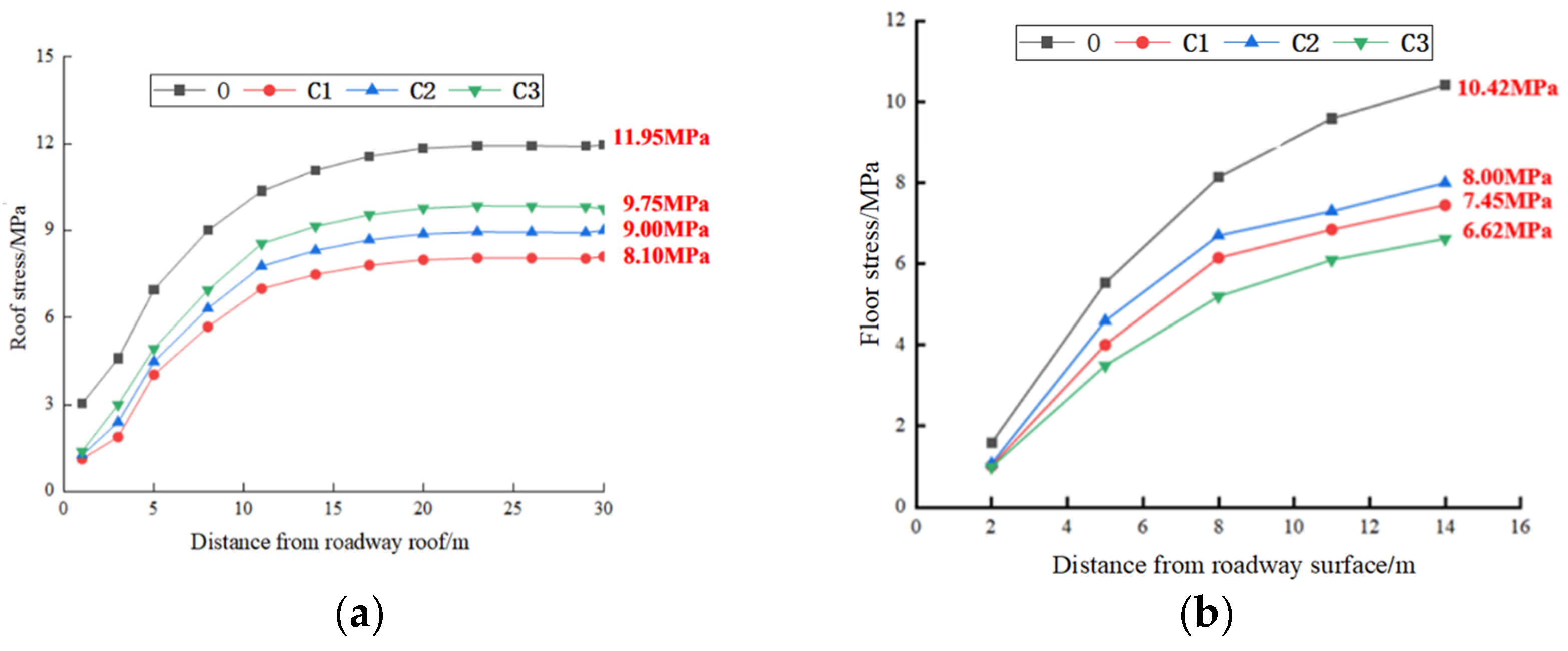
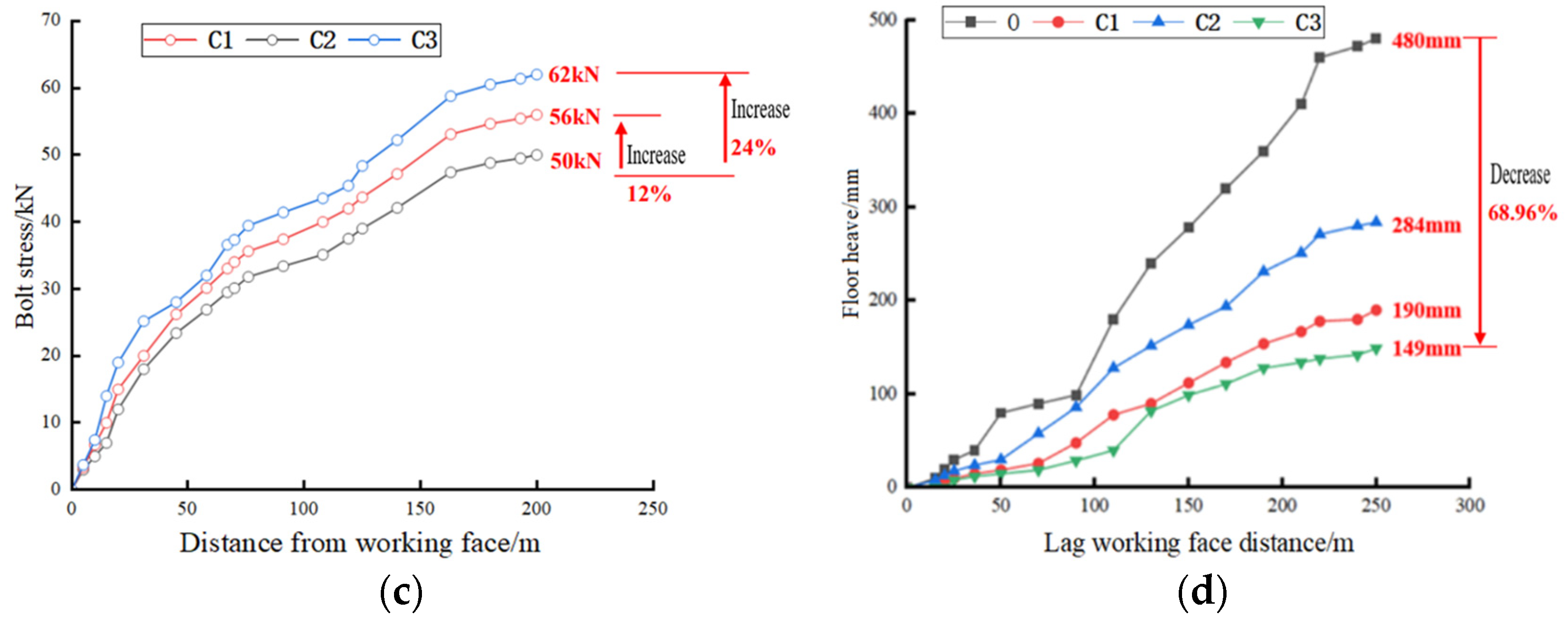
4.2.4. Analysis of Scheme C (Integrated Control Measures)
4.3. Comparative Results Analysis of Control Schemes
4.4. Optimization of Design Parameters for Cooperative Control of Roadway Floor Heave Deformation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, M.C. Research progress of deep shaft construction mechanics. J. China Coal Soc. 2021, 46, 726–746. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Pan, R.; Jiang, B.; Li, S.C.; He, M.C.; Sun, H.B.; Wang, L.; Qin, Q.; Yu, H.C.; Luan, Y.C. Study on failure mechanism of roadway with soft rock in deep coal mine and confined concrete support system. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2017, 81, 155–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; He, M.C.; Yang, J.; Gao, H.K.; Jiang, B.; Yu, H.C. Study of a no-pillar mining technique with automatically formed gob-side entry retaining for longwall mining in coal mines. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2018, 110, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otton Goth. Prevention of Roadway Floor Heave; Coal Industry Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Investigation of the effects of weak floor conditions on the stability of coal pillars: Rockaway, J D; Stephenson, R W US Bureau of Mines report OFR 12–81, July 1979, 227P. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Geomech. Abstr. 1981, 18, 119. [CrossRef]
- Chugh, Y.P.; Caudle, R.D.; Bandopadhay, C. Analysis of soft floor interaction in underground mining at an Illinois basin coal mine. In Design and Performance of Underground Excavations: ISRM Symposium—Cambridge, UK, 3–6 September 1984; Thomas Telford Publishing: London, UK, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Afrouz, A.; Hassani, F.P.; Scoble, M.J. Geotechnical assessment of the bearing capacity of coal mine floors. Int. J. Mining Geol. Eng. 1988, 6, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.B.; Tang, C.A. Numerical studies on tunnel floor heave in swelling ground under humid conditions. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2012, 55, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.X.; Zhang, Y.D.; Ma, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Song, G.Y.; Yan, W.Z.; Zhang, Y.; Lei, H. The floor heave mechanism and control technology of gob-side entry retaining of soft rock floor. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Liu, C.Y.; Gu, W.Z.; Yuan, C.F.; Wu, Y.Y.; Liu, Z.C.; Song, T.Q.; Sheng, F.T. Research on floor heave mechanisms and control technology for deep dynamic pressure roadways. Processes 2023, 11, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.X.; Deng, P.H.; Liu, Q.S.; Xu, X.L.; Wang, N.; Jiang, Y.L.; Yu, Y. Progressive fracture and swelling of anisotropic rock masses around deep tunnels: A new floor heave mechanical mechanism. Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, N. Quantitative Assessment of Rock Burst Risk in Roadway Tunneling Considering Variation of Coal Mass Parameters. J. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 8211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.G.; Bai, J.B.; Wang, X.Y.; Wu, B.W.; Wu, W.D. Mechanisms of floor heave in roadways adjacent to a goaf caused by the fracturing of a competent roof and controlling technology. Shock. Vib. 2020, 2020, 5632943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.L.; Zhai, W.L.; Liu, W.X.; Sun, N.; Song, J.Y.; Zhang, J.L.; Wu, Y.H. Floor Heave Mechanism and Control Technique of Water-Rich Soft-Rock Roadway in Thick Coal Seam. Energy Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 5316–5327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.Y.; Feng, X.T.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Yang, C.X.; Yu, X.J. The floor heave mechanism of a deep clastic rock tunnel in southwest china: An experimental study based on excavation stress paths. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2024, 57, 5575–5594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Li, X.H.; Xia, Z.; Zheng, C.K.; Li, Y.H.; Huang, G. Mechanism and control of floor heave in two entry retained roadways using dense boreholes. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 17243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, H.; Li, D.Y.; Luo, P.K.; Ru, W.K.; Zhang, G.H.; Liu, Y.P. Floor heave mechanism and stiff control technology by I-beam for deep mine roadway. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2025, 175, 109600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.Q.; Wang, Z.Y.; Liu, F.Y.; Dai, X.L.; Zhao, S.; Yu, Z.H. Study on the mechanism and technology of floor heave control of deep roadway with strong mining pressure. J. Min. Saf. Eng. 2023, 41, 666–676. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, R.; Hao, B.; Shi, C.; Li, T. Study on the Ground Pressure Manifestation Patterns of Roof Cutting and Pressure Relief. J. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 6049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liu, H.; Xie, K.; Shan, L.; Xiao, F.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y. Stability Analysis and Support Optimization for a Coal Mine Roadway Subjected to High Horizontal Stress. J. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.Z.; Wei, S.J. Control technology and simulation study of floor heave in high stress soft rock roadway. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2020, 38, 4045–4058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.L.; Zhai, W.L.; Xu, X.H.; Song, J.Y.; Li, L.; Lv, K. Study on Mechanism and Control Technology of Asymmetric Floor Heave in a Deep Soft Rock Main Roadway. Geofluids 2022, 2022, 1149000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyle, P.; Joel, B.; Kot, U.; Mark, K. Mitigation of floor heave in West Kentucky Coal Mine. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2016, 26, 521–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.J.; Jing, S.L.; Meng, F.B.; Jiang, J.Y. Control technology for floor heave of Jurassic soft rock in the Erdos Basin of China: A case study. J. Cent. South Univ. 2022, 29, 4051–4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.X.; Shi, X.Y.; Guo, W.B. Research on floor heave control technology of soft rock roadway. Geol. Explor. 2020, 56, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar]
- He, M.C.; Zhang, G.F.; Wang, G.L.; Xu, Y.L.; Wu, C.Z.; Tang, Q.D. Research on mechanism and application to floor heave control of deep gateway. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2009, 28, 2593–2598. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, R.; Chen, T.; Wang, S.; Jiang, H.; Yin, X. Study on Influencing Factors and Prediction of Tunnel Floor Heave in Gently Inclined Thin-Layered Rock Mass. J. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.J.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, B.; Jiang, Z.H.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.B.; He, M.C. Study on the method of pressure relief by roof cutting and absorbing energy in deep coal mines. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2023, 82, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, S.; Desen, K. Floor Heave Mechanism and Anti-Slide Piles Control Technology in Deep and Large-Span Chamber. J. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4576. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.B.; Zhang, Y.C.; Xue, H.J.; Tian, H.D.; Li, Y.Y. The Bearing Performance and Sectional Design Method of Yielding U-Shaped Steel Support. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Lithology | Density /(kg·m−3) | Bulk Modulus /GPa | Shear Modulus /MPa | Cohesion /MPa | Internal Friction Angle/(°) | Tensile Strength /MPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fine mudstone | 2500 | 1.95 | 0.73 | 2.10 | 25 | 0.27 |
| Medium sandstone | 2200 | 3.11 | 1.12 | 7.44 | 33.2 | 0.71 |
| Sandy mudstone | 2350 | 2.23 | 1.21 | 2.25 | 28 | 0.53 |
| Coal seam | 1400 | 1.31 | 0.45 | 1.11 | 20 | 0.41 |
| Fine-grained sandstone | 2600 | 3.43 | 1.58 | 5.92 | 33 | 1.73 |
| Scheme | No. | Specific Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| Original support measures (Comparison group) | O | — |
| Floor grouting anchorage strength | A1 | 1.2 times |
| A2 | 1.4 times | |
| A3 | 1.6 times | |
| Roof cutting for pressure relief | B1 | 0° + 30 m |
| B2 | 10° + 30 m | |
| B3 | 15° + 30 m | |
| B4 | 20° + 30 m | |
| B5 | 15° + 20 m | |
| Integrated control measures | C1 | Two bolts, roof cutting 15° + 20 m |
| C2 | Two bolts, roof cutting 15° + 30 m | |
| C3 | Five bolts, roof cutting 15° + 30 m |
| No. | Specific Parameters | Rate of Reduction of Maximum Support Pressure | Base-Plate Support Force | Reduction Rate of Substrate Stress | Reduction Rate of Floor Heave Deformation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scheme O | — | 48.9 MPa | 0 kN | 10.4 MPa | 480 mm |
| Scheme A | 1.2 times | 12.7% | 52 kN | −25.0% | 15.21% |
| 1.4 times | 12.8% | 72 kN | −50.0% | 22.71% | |
| 1.6 times | 13.0% | 91 kN | −68.8% | 33.13% | |
| Scheme B | 0° + 30 m | 20.5% | 0 kN | 10.1% | 24.50% |
| 10° + 30 m | 23.1% | 0 kN | 12.0% | 23.33% | |
| 15° + 30 m | 27.7% | 0 kN | 21.4% | 30.21% | |
| 20° + 30 m | 24.4% | 0 kN | 21.4% | 26.67% | |
| 15° + 20 m | 22.3% | 0 kN | 16.5% | 19.17% | |
| Scheme C | Two bolts, 15° + 20 m | 31.4% | 50 kN | 23.23% | 40.83% |
| Two bolts, 15° + 30 m | 35.5% | 56 kN | 28.50% | 60.42% | |
| Five bolts, 15° + 30 m | 34.9% | 62 kN | 36.46% | 68.96% |
| No. | Parameters of Roof Cutting for Pressure Relief | Parameters of Floor Grouting with Bolts |
|---|---|---|
| Scheme 1 | Height 30 m, 15° dip Apertures 153 mm Orifice distance 0.5 m | Floor corner two bolts Model Ø22 × 2500 mm Row spacing 1.5 m |
| Scheme 2 | Height 30 m, 15° dip Apertures 94 mm Orifice distance 0.5 m | Floor corner two bolts Model Ø22 × 2500 mm Row spacing 2.0 m |
| Scheme 3 | Height 30 m, 15° dip Apertures 94 mm Orifice distance 1.0 m | Floor corner two bolts Model Ø22 × 2500 mm Row spacing 2.0 m |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xue, H.; Zhang, C.; Huang, Y.; Wang, A.; Wang, J.; Li, K.; Zhang, J. Research on Deformation Mechanisms and Control Technology for Floor Heave in Deep Dynamic Pressure Roadway. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 8125. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15158125
Xue H, Zhang C, Huang Y, Wang A, Wang J, Li K, Zhang J. Research on Deformation Mechanisms and Control Technology for Floor Heave in Deep Dynamic Pressure Roadway. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(15):8125. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15158125
Chicago/Turabian StyleXue, Haojie, Chong Zhang, Yubing Huang, Ancheng Wang, Jie Wang, Kuoxing Li, and Jiantao Zhang. 2025. "Research on Deformation Mechanisms and Control Technology for Floor Heave in Deep Dynamic Pressure Roadway" Applied Sciences 15, no. 15: 8125. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15158125
APA StyleXue, H., Zhang, C., Huang, Y., Wang, A., Wang, J., Li, K., & Zhang, J. (2025). Research on Deformation Mechanisms and Control Technology for Floor Heave in Deep Dynamic Pressure Roadway. Applied Sciences, 15(15), 8125. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15158125






