A Modified Nonlinear Mohr–Coulomb Failure Criterion for Rocks Under High-Temperature and High-Pressure Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. A Nonlinear MC Failure Criterion Considering High-Temperature and High-Pressure Conditions
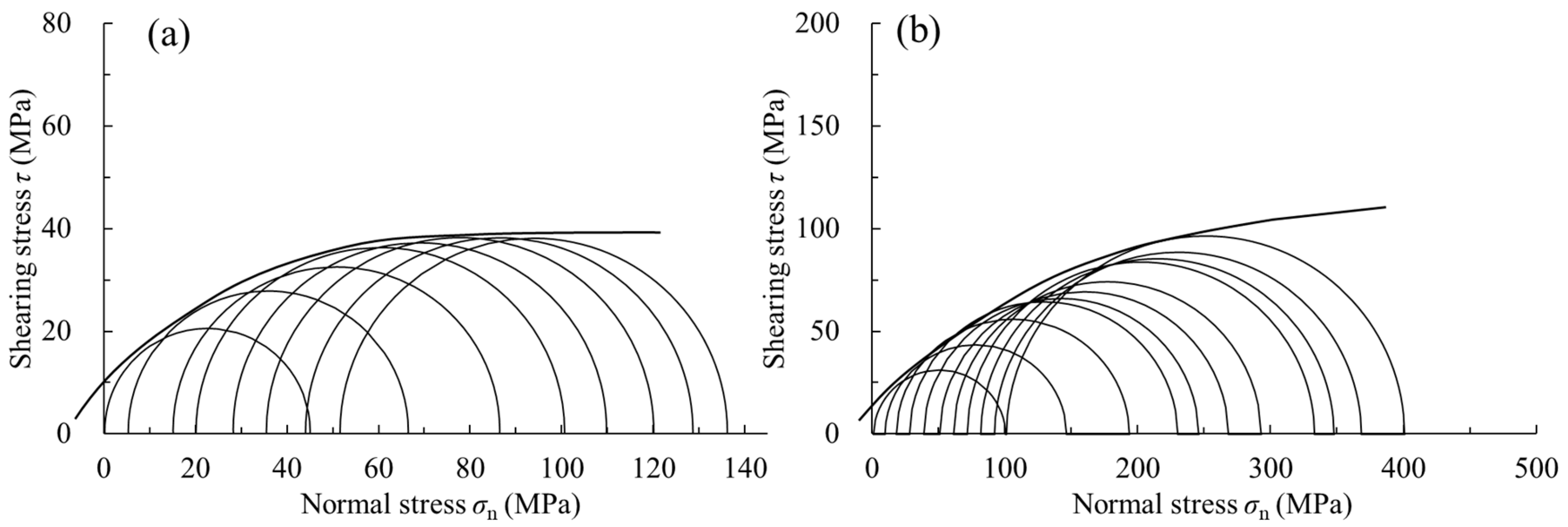
2.1. Nonlinear MC Failure Criterion Under High Stress
2.2. The Nonlinear MC Failure Criterion
2.3. Parameter Determination Method for the HTP-MC Criterion
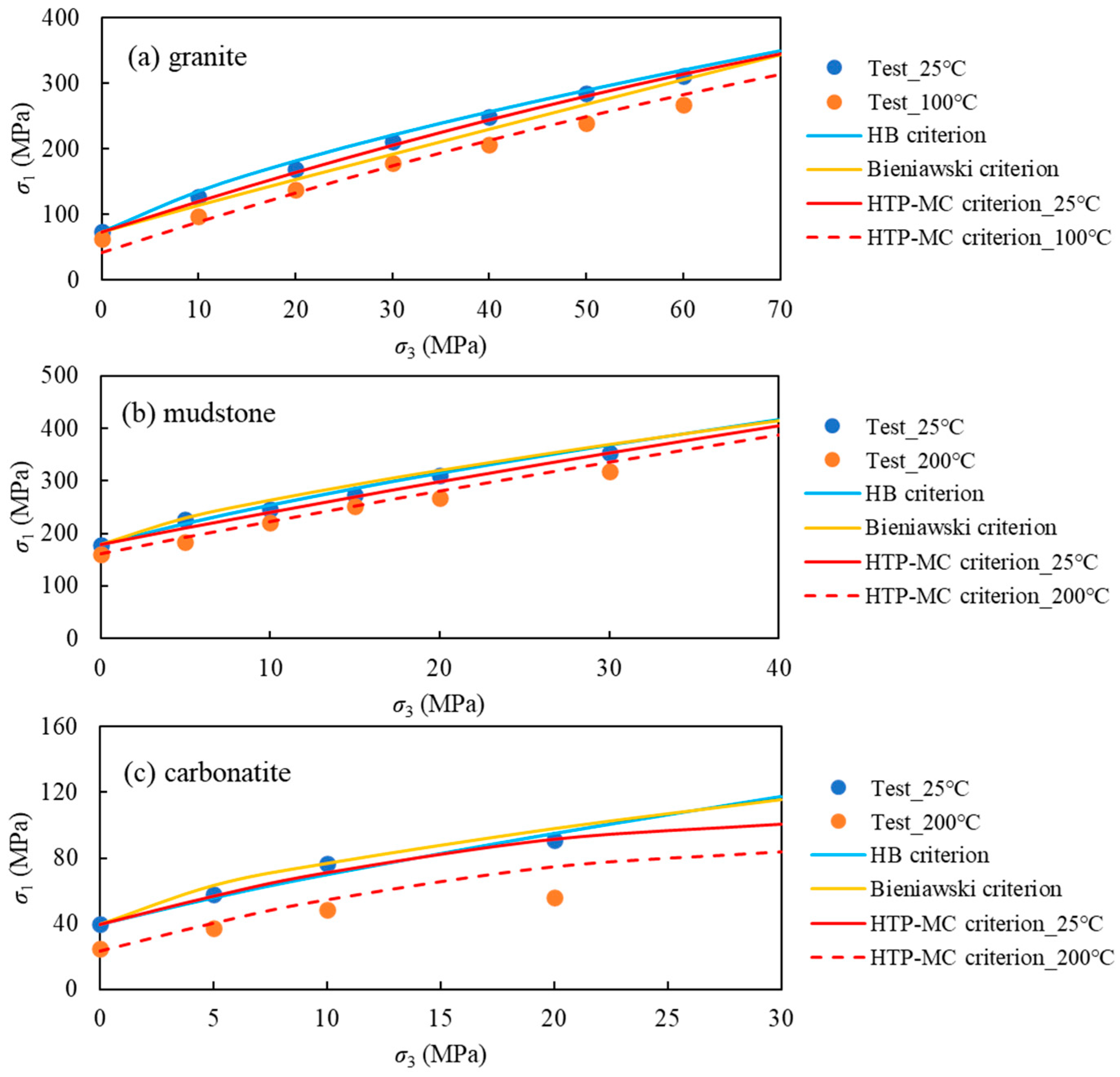
3. Verification of the HTP-MC Criterion
4. Discussion
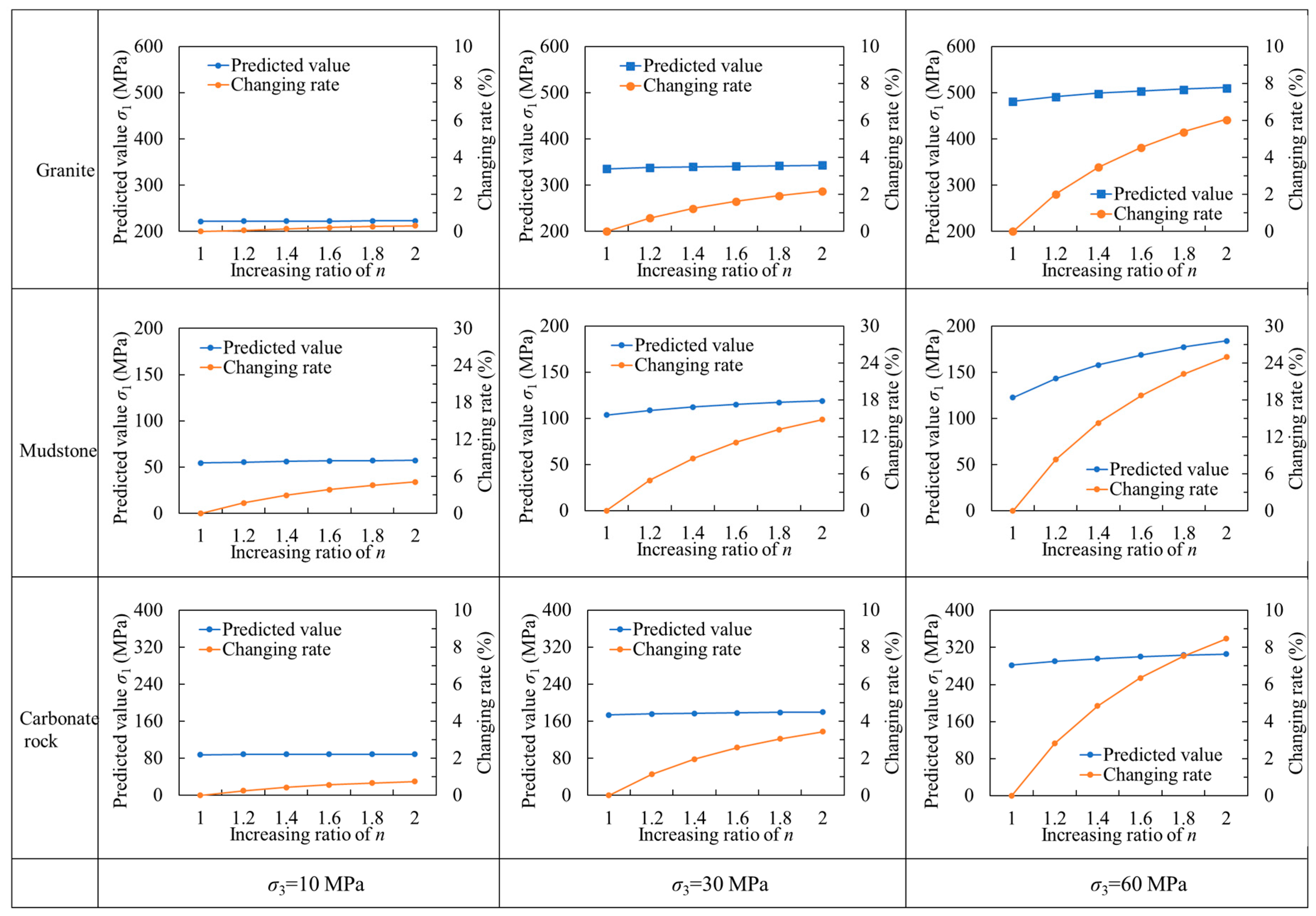
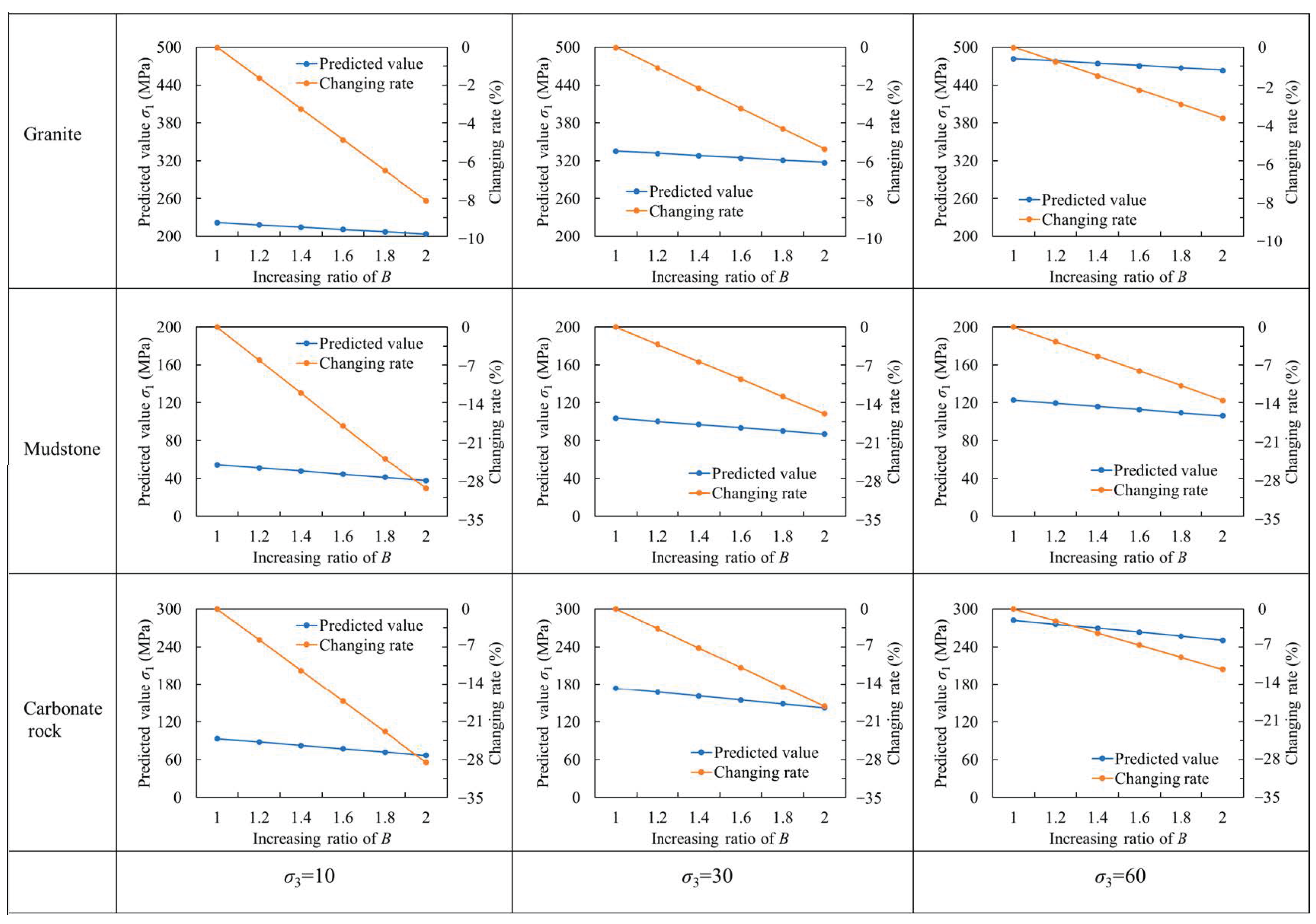
4.1. Sensitivity Analysis of the Parameters on the Predicted Results
4.2. Shortcomings and Suggestions
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Based on the classical MC criterion, an improved nonlinear MC criterion was proposed by introducing correction functions for the temperature and confining pressure. This criterion considers the critical confining pressure condition when the compressive strength remains constant as nσc rather than σc. Additionally, it assumes a linear decrease in rock compressive strength with the temperature, thus establishing a linear relationship model between temperature and rock strength.
- (2)
- By comparing the strength prediction accuracy of the HB criterion, Bieniawski criterion, and HTP-MC criterion for granite, shale, and carbonate rock, it was found that, under low confining pressure conditions, all three failure criteria show high prediction accuracy. However, under high confining pressure conditions, the HTP-MC criterion better captures the nonlinear characteristics of the rock failure envelope, significantly outperforming the other two failure criteria in terms of strength prediction accuracy.
- (3)
- The HTP-MC criterion overcomes the limitation of the Hoek–Brown and Bieniawski criteria, which cannot account for the effect of temperature on rock strength. The average MRE value for the prediction of granite, shale, and carbonate rock under high-temperature and high-pressure conditions using the HTP-MC criterion is 5.25%, demonstrating that this criterion provides high prediction accuracy for rock strength under high-temperature and high-pressure conditions.
- (4)
- All rock types exhibit the general trend that the predicted σ1 increases with the increasing parameter n and decreases with the increasing parameter B. However, the sensitivity of predicted σ1 to these parameters varies significantly among different rock types. In particular, granite shows the lowest sensitivity to both n and B, indicating better adaptability of the prediction model for granite strength. Furthermore, the predicted σ1 is generally more sensitive to changes in parameter B than in n.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anjos, S.M.; Sombra, C.L.; Spadini, A.R. Petroleum exploration and production in Brazil: From onshore to ultra-deepwaters. Petrol. Explor. Dev. 2024, 51, 912–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prischepa, O.M.; Kireev, S.B.; Nefedov, Y.V.; Martynov, A.V.; Lutsky, D.S.; Krykova, T.N.; Sinitsa, N.; Xu, R.M. Theoretical and methodological approaches to identifying deep accumulations of oil and gas in oil and gas basins of the Russian Federation. Front. Earth Sci. 2023, 11, 1192051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.F.; Jia, C.Z.; Zhao, W.Z.; Xu, F.Y.; Luo, X.R.; Liu, W.H.; Tang, Y.; Gao, S.L.; Zheng, X.J.; Li, D.; et al. Research progress and key issues of ultra-deep oil and gas exploration in China. Petrol. Explor. Dev. 2023, 50, 1333–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.X.; Cheng, H.M.; Feng, Y.H.; Zhao, H.M.; Peng, W.H. Energy Evolution Characteristics of Sandstone under Different High-Temperature Pretreatments and Different Confining Pressures. Int. J. Geomech. 2024, 24, 04024238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.X.; Liu, Z.B.; Wu, M.; Wang, C.; Shen, W.Q.; Shao, J.F. Experimental study of mechanical properties of hot dry granite under thermal-mechanical couplings. Geothermics 2024, 119, 102974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.C.; Li, M.; Zhao, Q.; Song, X.Z.; Zhang, R.S.; Yang, L.L. Wellbore pressure model for drilling fluid in ultra-deep rock salt formations at high temperatures and pressures. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 023341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.B.; Cui, S.; Meng, Y.F.; Chen, Z.X.; Sun, H.R. Study on mechanical properties and wellbore stability of deep sandstone rock based on variable parameter M-C criterion. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023, 224, 211609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.P.; Lu, J.; Li, C.B.; Li, M.H.; Gao, M.Z. Experimental study on the mechanical and failure behaviors of deep rock subjected to true triaxial stress: A review. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2022, 32, 915–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, W.G.P.; Ranjith, P.G.; Perera, M.S.A.; Li, X.; Li, L.H.; Chen, B.K.; Isaka, B.L.A.; De Silva, V.R.S. Hydraulic fracturing under high temperature and pressure conditions with micro CT applications: Geothermal energy from hot dry rocks. Fuel 2019, 230, 138–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Deng, H.C. Experimental study on failure criterion of deep tight sandstone under coupling effects of temperature and pressure. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.Y.; Liu, Z.B.; Shen, W.Q.; Feng, T.; Zhang, G.Z. Mechanical property and thermal degradation mechanism of granite in thermal-mechanical coupled triaxial compression. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. 2022, 160, 105270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, W.G.P.; Ranjith, P.G.; Perera, M.S.A.; Shao, S.; Chen, B.K.; Lashin, A.; Arifi, N.A.; Rathnaweera, T.D. Mechanical behaviour of Australian Strathbogie granite under in-situ stress and temperature conditions: An application to geothermal energy extraction. Geothermics 2017, 65, 44–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.X.; Nie, H.K.; Su, H.K.; Du, W.; Lu, T.; Chen, Y.L.; Liu, M.; Li, J.C. Porosity, permeability and rock mechanics of Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation deep shale under temperature-pressure coupling in the Sichuan Basin, SW China. Petrol. Explor. Dev. 2023, 50, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.X.; Jiang, B.; Li, F.L. Experimental study on brittle-to-ductile transition mechanism of lower Silurian organic-rich shale in south China. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2023, 170, 105543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.C.; Wang, J.X.; Zhang, S.H.; Li, M.; Song, Y.; Hou, C.L. Retrospective and prospective review of the generalized nonlinear strength theory for geomaterials. Int. J. Min. Met. Mater. 2024, 31, 1767–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Saar, M.O.; Fan, L.S. Coulomb criterion-bounding crustal stress limit and intact rock failure: Perspectives. Powder Technol. 2020, 374, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, O. Welche Umstande bedingen die Elastizitatsgrenze und den bruch eines materials. Z. Ver. Dtsch. Ingenieure 1900, 144, 1524–1530. [Google Scholar]
- Drucker, D.C.; Prager, W. Soil mechanics and plastic analysis for limit design. Q. Appl. Math. 1952, 10, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, A.A. The theory of rupture. In Proceedings of the 1st International Congress on Applied Mechanics, Delft, The Netherlands, 22–26 April 1924; pp. 54–63. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Rao, K.S.; Ayothiraman, R. Study on Mohr-Coulomb-based three-dimensional strength criteria and its application in the stability analysis of vertical borehole. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.J.; Lin, H.; Chen, Y.F.; Ma, T.X. Modified Mohr-Coulomb criterion for nonlinear strength characteristics of rocks. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 2024, 47, 2228–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.T.; Shi, J.Y.; Barton, N. An approximate nonlinear modified Mohr-Coulomb shear strength criterion with critical state for intact rocks. J. Rock Mech. Geotechnol. 2018, 10, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdellah, W.R.; Bader, S.A.; Kim, J.G.; Ali Mahrous, A.M. Numerical simulation of mechanical behavior of rock samples under uniaxial and triaxial compression tests. Min. Miner. Depos. 2023, 17, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Peng, S.; Zhao, J.Z.; Jiang, H.; Ren, L.; Zhou, B.; Wu, J.F.; Song, Y.; Shen, C. Deep/ultra-deep shale strength criterion: A case study of southern Sichuan Basin shale. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2024, 239, 212918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, R.; Eckert, J.; Zhang, Z. Tensile fracture criterion of metallic glass. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 083544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.R.; Baxter, C.D.; Hoffmann, W.; Moran, K.; Vaziri, H. Characterization of weakly cemented sands using nonlinear failure envelopes. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2011, 48, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S. A reflection on the mohr failure criterion. Mech. Mater. 2020, 148, 103442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.G.; Yao, B.W.; Fan, X.Y.; Li, Y.; Li, M.H.; Zeng, F.T.; Zhao, P.F. A modified Hoek-Brown failure criterion for unsaturated intact shale considering the effects of anisotropy and hydration. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2021, 241, 107369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.G.; Yao, B.W.; Fan, X.Y.; Li, Y.; Fantuzzi, N.; Ma, T.S.; Chen, Y.F.; Zeng, F.T.; Li, X.; Wang, L.Z. A failure criterion for shale considering the anisotropy and hydration based on the shear slide failure model. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2023, 33, 447–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.; Santamarina, J.C. Mechanical and hydraulic properties of carbonate rock: The critical role of porosity. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. 2023, 15, 814–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbo, A.; Lyamin, A.; Sloan, S.; Hambleton, J.P. A c2 continuous approximation to the mohr-coulomb yield surface. Int. J. Solid Struct. 2011, 48, 3001–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Li, K.; Su, L. Modified nonlinear mohr–coulomb fracture criteria for isotropic materials and transversely isotropic ud composites. Mech. Mater. 2020, 151, 103649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.; Li, X. An eccentric ellipse failure criterion for amorphous materials. J. Appl. Mech. 2017, 84, 081005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiq, M.; Subhash, G. An extended mohr–coulomb model for fracture strength of intact brittle materials under ultrahigh pressures. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2016, 99, 627–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakha, M.; Nejati, M.; Aminzadeh, A.; Ghouli, S.; Saar, M.O.; Driesner, T. On the validation of mixed-mode i/ii crack growth theories for anisotropic rocks. Int. J. Solid Struct. 2022, 241, 111484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoek, E. Strength of jointed rock masses. Géotechnique 1983, 23, 187–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Z.; Elsworth, D. A Phenomenological Failure Criterion for Brittle Rock. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 1991, 24, 133–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Raj, A.; Singh, B. Modified Mohr-Coulomb criterion for non-linear triaxial and polyaxial strength on intact rocks. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. 2011, 48, 546–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Xu, M.G.; Liu, Y.Z. Application of critical state confining pressure to rock failure criteria modification. Rock Soil Mech. 2016, 37, 390–398. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.; Zhang, N.; Jeon, S. A study on shear characteristics of a smooth rock surface under different thermal, hydro and mechanical conditions. In Proceedings of the ISRM International Symposium—EUROCK 2013, Wroclaw, Poland, 23–26 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.Q.; Huang, Y.H.; Tian, W.L. Influence of Water Saturation and Real-Time Testing Temperature on Mechanical Behavior of Sandstone Under Conventional Triaxial Compression. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2021, 54, 4355–4367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.H.; Sha, S.; Xu, L.D.; Quan, J.S.; Rong, G.; Jiang, M.Y. Damage Evaluation and Statistic Constitutive Model of High-Temperature Granites Subjected to Liquid Nitrogen Cold Shock. Rock. Mech. Rock Eng. 2022, 55, 2299–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masri, M.; Sibai, M.; Shao, J.F.; Mainguy, M. Experimental investigation of the effect of temperature on the mechanical behavior of Tournemire shale. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. 2014, 70, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.D.; Wang, B.Q.; Yao, J.; Jing, W.J.; Zhang, X. Experimental study on mechanical properties of carbonate rocks under real-time high temperature and heat treatment under triaxial compression. Chinese, J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2024, 43, 1347–1358. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.C.; Meng, Y.F.; Li, G. Comparative analyses of several rock failure criteria. Rock Soil Mech. 2011, 32, 209–216. [Google Scholar]
- Mi Ou Zhang, R.; Wang, X.Z.; Zhang, Z.T.; Zhang, A.L. Mechanical properties and damage characteristics of granite surrounding rock in deep tunnel under thermal-hydro-mechanical coupling condition. Tunn. Undergr. Sp. Technol. 2025, 156, 106262. [Google Scholar]

| Granite a | Mudstone b | Carbonate Rock c | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T (°C) | σ3 (MPa) | σ1 (MPa) | T (°C) | σ3 (MPa) | σ1 (MPa) | T (°C) | σ3 (MPa) | σ1 (MPa) |
| 25 | 0 | 178.5 | 20 | 0 | 39.7 | 25 | 0 | 73.1 |
| 5 | 226.5 | 5 | 58 | 10 | 126.5 | |||
| 10 | 246.5 | 10 | 76.8 | 20 | 169.2 | |||
| 15 | 273.6 | 20 | 91.1 | 30 | 211.1 | |||
| 30 | 310.5 | 200 | 0 | 24.8 | 40 | 248.9 | ||
| 200 | 0 | 354 | 5 | 37.3 | 50 | 284.3 | ||
| 5 | 160.5 | 10 | 48.4 | 60 | 311.4 | |||
| 10 | 183.7 | 20 | 55.7 | 100 | 0 | 62.1 | ||
| 15 | 221.2 | 10 | 97.4 | |||||
| 30 | 252 | 20 | 137 | |||||
| 30 | 177.7 | |||||||
| 40 | 206.6 | |||||||
| 50 | 239.8 | |||||||
| 60 | 267.6 | |||||||
| Rock Type | Failure Criteria | Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| Granite | HB criterion | m = 15.4 |
| Bieniawski criterion | A = 4.02; k = 0.74 | |
| HTP-MC criterion | c = 35.44 MPa; φ = 46.68°; n = 0.92; B = 0.103 | |
| Mudstone | HB criterion | m = 5.24 |
| Bieniawski criterion | A = 2.29; k = 0.65 | |
| HTP-MC criterion | c = 10.31 MPa; φ = 35.13°; n = 0.61; B = 0.095 | |
| Carbonate rock | HB criterion | m = 15.5 |
| Bieniawski criterion | A = 3.85; k = 0.97 | |
| HTP-MC criterion | c = 16.67 MPa; φ = 40.96°; n = 1.96; B = 0.42 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; Meng, C.; Fan, X.; Zhao, P. A Modified Nonlinear Mohr–Coulomb Failure Criterion for Rocks Under High-Temperature and High-Pressure Conditions. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 8048. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15148048
Li Z, Li H, Zhang Q, Wang J, Meng C, Fan X, Zhao P. A Modified Nonlinear Mohr–Coulomb Failure Criterion for Rocks Under High-Temperature and High-Pressure Conditions. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(14):8048. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15148048
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhuzheng, Hongxi Li, Qiangui Zhang, Jiahui Wang, Cheng Meng, Xiangyu Fan, and Pengfei Zhao. 2025. "A Modified Nonlinear Mohr–Coulomb Failure Criterion for Rocks Under High-Temperature and High-Pressure Conditions" Applied Sciences 15, no. 14: 8048. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15148048
APA StyleLi, Z., Li, H., Zhang, Q., Wang, J., Meng, C., Fan, X., & Zhao, P. (2025). A Modified Nonlinear Mohr–Coulomb Failure Criterion for Rocks Under High-Temperature and High-Pressure Conditions. Applied Sciences, 15(14), 8048. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15148048