Abstract
This study aimed to investigate the differences in proprioceptive changes at different time points (Pre vs. Post vs. 90 min vs. 24 h) before and after ischemic preconditioning. It followed a within-subject, self-controlled design, and a total of 21 trained male participants were assessed using two-point discrimination threshold tests on thigh and knee joint position sense testing. The results demonstrated that ischemic preconditioning effectively improved proprioceptive accuracy (two-point discrimination, right lower limb, p < 0.001; two-point discrimination, left lower limb, p < 0.001; knee position sense, right lower limb, p = 0.001; knee position sense, left lower limb, p = 0.014) and stability (two-point discrimination, right lower limb, p < 0.001; two-point discrimination, left lower limb, p = 0.002; knee position sense, right lower limb, p < 0.001; knee position sense, left lower limb, p = 0.003), with the optimal time point for enhancement identified at 90 min. This research suggests administering IPC 90 min before warm-up or competition to enhance athletic performance.
1. Introduction
Proprioception plays a pivotal role in the execution of movement processes. The coordination, balance, and rapid response perceptions during physical activity heavily rely upon proprioceptive input [1]. Within the realm of movement, the human body is reliant upon proprioceptive feedback [2]. Only when sensory receptors convey accurate information to the central nervous system can the organism execute corresponding actions and subsequently perceive position, enabling the central nervous system to facilitate posture control and adjustment. Impairments within the proprioceptive system can lead to delays or inaccuracies in information transmission, consequently instigating disruptions in position perception, thereby impeding posture control and movement performance and resulting in adverse effects on bodily control [3]. The proper functioning of the proprioceptive system holds paramount importance in eliciting responsive and coordinated actions amidst bodily movements [4].
Ischemic preconditioning represents a non-invasive approach for acute skill enhancement [5]. It involves the transient induction of circulatory ischemia and subsequent reperfusion in the limbs through the application of pressure cuffs prior to physical activity. This preconditioning procedure elicits a hypoxic stress response, stimulating the secretion of protective factors like adenosine and kinins [6], thereby facilitating local vasodilation, optimizing blood flow distribution, enhancing oxygen delivery, and ultimately augmenting exercise performance [7].
Ischemic preconditioning (IPC) has garnered increasing attention within the field of exercise science. Current research on the effects of IPC primarily focuses on changes in strength, power, and endurance. Previous studies indicate that IPC can enhance not only power output, maximal muscular strength, and anaerobic endurance but also improve subjects’ aerobic capacity and fatigue resistance [8]. The ergogenic mechanisms of IPC likely involve modulating vasoregulatory effects, attenuating perceptions of fatigue or pain during exercise, and transiently enhancing skeletal muscle metabolic efficiency [9,10].
While the role of IPC in enhancing exercise performance is receiving growing research interest, investigations have predominantly concentrated on its impacts on strength, power, and endurance, overlooking potential alterations in proprioception. However, muscular coordination and coordinated neuromuscular signaling rely heavily on proprioceptive input [8]. Changes in proprioception are crucial for the quality of movement execution and the feedback necessary for movement adjustments [1,2,3,4]. In many sports, athletes cannot rely solely on visual feedback to adjust their movements during competition or training in real time; these adjustments primarily depend on proprioceptive feedback. Athletes possessing superior proprioceptive acuity would benefit during movement adjustment processes, leading to more precise movements and, ultimately, enhanced athletic performance.
Currently, no research has investigated the potential influence of IPC on proprioception. Given the known physiological mechanisms through which IPC induces changes in the human body, IPC may enhance proprioception through neuromodulatory pathways. However, whether IPC indeed affects proprioception, and the optimal time window for any such effect, remain entirely unknown. While no studies have yet investigated the effects of IPC on proprioception, this does not diminish the potential research significance of this topic. In athletic practice, prolonged activities requiring fine motor control—such as basketball shooting and baseball pitching—demand high levels of proprioceptive precision and stability. Should research demonstrate that IPC can effectively enhance the precision and stability of an athlete’s proprioception at specific time points, this could yield a potentially positive impact on competitive performance.
This study examined the temporal dynamics of proprioception relative to IPC application across four timepoints: pre-IPC, and 0 min, 90 min, and 24 h post-IPC. The objectives were to determine whether IPC influences proprioception and to identify the optimal time frame for any observed effect. This study hypothesizes that IPC may improve proprioceptive stability and precision. Peak effectiveness in both stability and precision is anticipated to occur at one of the following time points: immediately after IPC intervention, at 90 min post-intervention, or at 24 h post-intervention.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
The sample size was determined using G*power (3.1, Kiel University, Kiel, Germany) with the following parameters: input effect size f = 0.5; α err prob = 0.05; Power (1-β err prob) = 0.95; achieved power = 0.87. The minimum sample size required was 10 individuals, and 21 male participants (n = 19, age: 22.8 ± 2.2 years; height: 179.9 ± 5.5 cm; mass: 79.8 ± 7.8 kg) were ultimately included with two dropouts. All participants were undergraduate students majoring in sport training at Beijing Sport University, possessing a solid background in both athletics and strength training. Participants were required to meet strict inclusion criteria, which included being physically active, while also satisfying exclusion criteria, such as having absolute or relative contraindications to the study protocols; recent joint surgery; use of prostheses, orthoses, or assistive devices; chronic heart, lung, or skin conditions. Other inclusion criteria included an absence of physical disabilities, adequate cognitive abilities to understand the test protocols, and independence in performing activities of daily living. The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Sports Science Experiment Ethics Committee of Beijing Sport University (approval no. 2025125H).
2.2. Design
Participants underwent pre-testing followed by ischemic preconditioning. After the completion of ischemic preconditioning, participants underwent post-testing at three time points (immediately, 90 min, and 24 h after the completion of ischemic preconditioning) (Figure 1).
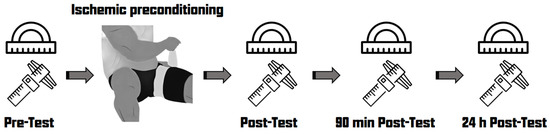
Figure 1.
Experimental procedure.
2.3. Ischemic Preconditioning
The ischemic preconditioning protocol involved rapidly inflating a blood pressure cuff (Technogym international trading Ltd., Cesena, Italy) positioned at the top of the thigh. In the ischemic preconditioning condition, the cuff was inflated to 220 Hg for three 5 min periods, with 5 min rest/reperfusion intervals [11].
2.4. Two-Point Discrimination Test
The measurements were conducted using a DL90150 electronic caliper (Deli Technology Co., Ltd., Ningbo, China) with a range of 0–130 mm and an accuracy of 0.01 mm. Participants were seated with their eyes closed. For the two-point discrimination test of the lower limbs, the examiner placed the probes vertically on the anterior side of the thigh at the midpoint of the rectus femoris belly. Equal pressure was applied for two seconds, and participants immediately reported whether they felt one or two points of stimuli. If participants could not differentiate or only felt one stimulus, the minimum distance between two stimuli was recorded [12,13]. The entire testing process was performed by a single examiner for consistency. The interval between stimuli was more than five seconds, and the measurement was repeated three times. The collected data was used to calculate the average, representing the participant’s two-point discrimination threshold accuracy, and the variance, reflecting the stability of their threshold.
m: mean; TPD: two-point discrimination.
2.5. Knee Position Sense Test
The measurements were performed using a Syntek electronic joint angle measurement device (Deqingshengtaixin Technology Co., Ltd., Deqing, China), which has a range of 0–180°, a resolution of 0.1°, and an accuracy of ±0.3°. Participants were instructed to lie supine with their eyes closed, knees flexed at 90°, and hips flexed at 90°, supported by a surface. The examiner positioned the goniometer with its center at the tibial tuberosity, one side aligned with the line connecting the tibial tuberosity and the greater trochanter of the femur, and the other side aligned with the line connecting the tibial tuberosity and the lateral malleolus. Participants were then asked to lift their lower leg at 40° without making adjustments during the process (Figure 2). Measurements were taken once the knee joint angle stabilized. The examiner repeated the measurement three times, with an interval of over five seconds between each measurement [14,15]. The entire testing process was conducted by the same examiner to ensure consistency, with the examiner remaining silent to avoid providing verbal feedback that could influence the results. The collected data was used to calculate the average, reflecting the accuracy of the participant’s knee position sense, and the variance, reflecting the stability of their knee position sense.
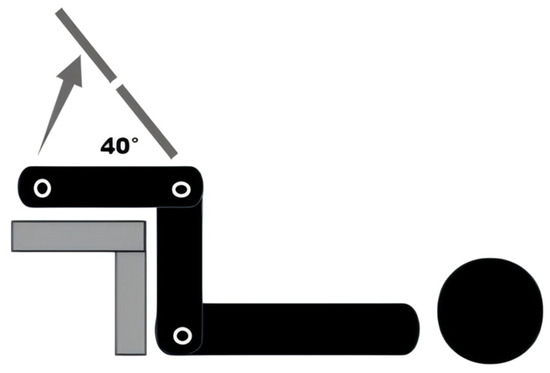

Figure 2.
Knee position sense test.
TP: target position; m: mean.
2.6. Statistical Analyses
The study data were analyzed using SPSS software (version 26; SPSS, IBM Corporation, Armonk, New York, NY, USA) and WPS software (version 2023; Kingsoft Office Co., Ltd., Beijing, China). All variables are presented as means and standard deviations (SDs). The data were tested for the assumption of sphericity. If the assumption was violated, the Greenhouse–Geisser correction coefficient was applied to adjust the degrees of freedom for the relevant mean squares, ensuring the reliability of the analysis of variance. A one-way repeated-measures analysis of variance (ANOVA) was conducted to examine the changes in body perception at different time points (Pre vs. Post vs. 90 min vs. 24 h) among participants. A confidence interval of 95% was utilized. Based on Cohen’s conventions [16], the effect sizes reported as Cohen’s d (small: d = 0.2, medium: d = 0.5, large: d = 0.8).
3. Results
The experimental results indicate that there are significant differences (p < 0.05) in the accuracy and stability of two-point discrimination thresholds and knee joint position sense across different time points (Pre vs. Post vs. 90 min vs. 24 h) (Table 1 and Table 2). Partial eta-squared values indicated large effect size across all significant comparisons (η2 > 0.14, 95% CI).

Table 1.
Descriptive statistics. TPDR: two-point discrimination threshold on right lower limb; TPDL: two-point discrimination threshold on left lower limb; D40R: difference in position sense test of right lower limb; D40L: difference in position sense test of left lower limb.

Table 2.
Results of one-way repeated ANOVA. TPDR: two-point discrimination threshold on right lower limb; TPDL: two-point discrimination threshold on left lower limb; D40R: difference in position sense test of right lower limb; D40L: difference in position sense test of left lower limb. Mauchly’s test of sphericity indicated violations for AccuracyTPDR, AccuracyD40L, StabilityTPDR, StabilityTPDL, StabilityD40R, and StabilityD40L. Consequently, Greenhouse–Geisser corrections were applied to these measures.
In pairwise comparisons of proprioceptive accuracy, significant differences were observed for TPDR between Pre and Post (p = 0.002), Pre and 90 min (p < 0.001), and Pre and 24 h (p = 0.002); Post and 90 min (p < 0.001) and Post and 24 h (p < 0.001); and 90 min and 24 h (p < 0.001). For TPDL, significant differences occurred between Pre and Post (p = 0.001), Pre and 90 min (p < 0.001), Pre and 24 h (p = 0.023); Post and 90 min (p = 0.004); and 90 min and 24 h (p < 0.001). For D40R, significant differences were found between Pre and Post (p = 0.002) and Pre and 90 min (p = 0.016). For D40L, a significant difference was detected between Pre and Post (p = 0.035) (Table 3).

Table 3.
The results of paired comparisons of the accuracy of proprioception. TPDR: two-point discrimination threshold on right lower limb; TPDL: two-point discrimination threshold on left lower limb; D40R: difference in position sense test of right lower limb; D40L: difference in position sense test of left lower limb. Based on estimated marginal means, the significance level (“*”) for mean differences was set at 0.05, with multiplicity adjustment via the Bonferroni method.
In pairwise comparisons of proprioceptive stability, significant differences were observed: For TPDR: between Pre and 90 min (p < 0.001), Post and 90 min (p = 0.010), and 90 min and 24 h (p < 0.001). For TPDL: between Pre and 90 min (p = 0.003), Post and 90 min (p = 0.002), and 90 min and 24 h (p = 0.003). For D40R: between Pre and 90 min (p < 0.001), Post and 90 min (p = 0.006), and 90 min and 24 h (p = 0.009). For D40L: between Pre and 90 min (p = 0.001) and 90 min and 24 h (p = 0.003) (Table 4).

Table 4.
The results of paired comparisons of the stability of proprioception. TPDR: two-point discrimination threshold on right lower limb; TPDL: two-point discrimination threshold on left lower limb; D40R: difference in position sense test of right lower limb; D40L: difference in position sense test of left lower limb. Based on estimated marginal means, the significance level (“*”) for mean differences was set at 0.05, with multiplicity adjustment via the Bonferroni method.
After ischemic preconditioning, the accuracy and stability of two-point discrimination thresholds were improved (Figure 3 and Figure 4). The greatest improvement was observed at 90 min after ischemic preconditioning. On the following day (24 h after ischemic preconditioning), the two-point discrimination thresholds remained close to the levels immediately after ischemic preconditioning. There were no significant differences observed between the left and right sides.
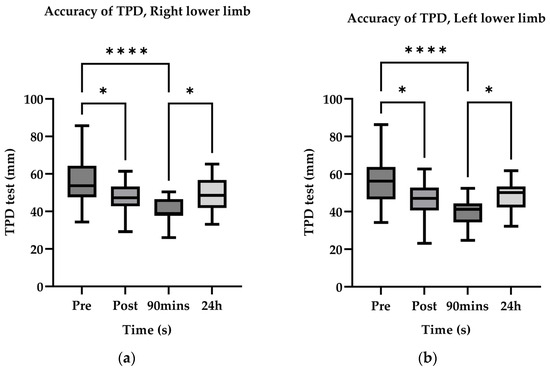
Figure 3.
AccuracyTPD estimate marginal mean values. The upper and lower boundaries of the box denote the 75th and 25th percentiles, respectively. Whiskers span 1.5 × IQR, with observations beyond this range designated as outliers. A solid horizontal line within the box indicates the median value. Asterisks (*) denote statistically significant differences between competitive level groups: *, p < 0.05; ****, p < 0.0001.
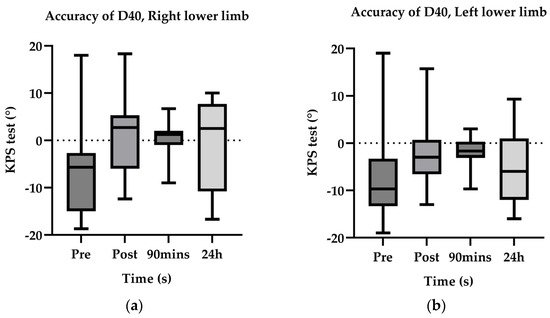
Figure 4.
StabilityTPD estimate marginal mean values.
Following ischemic preconditioning, there was a notable enhancement in both the accuracy and stability of knee joint proprioception (Figure 5 and Figure 6). The optimal improvement was attained at the 90-min mark after ischemic preconditioning. Interestingly, even on the subsequent day (24 h after ischemic preconditioning), knee joint proprioception was able to maintain a level similar to that immediately following ischemic preconditioning, with no significant disparities observed between the left and right sides. These findings align with the outcomes observed for two-point discrimination thresholds.
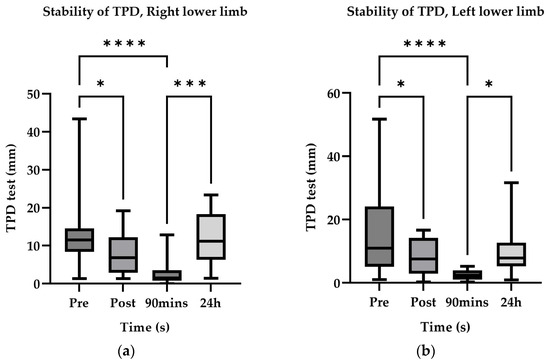
Figure 5.
AccuracyD40° estimate marginal mean value. *, p < 0.05; ***, p < 0.001; ****, p < 0.0001.
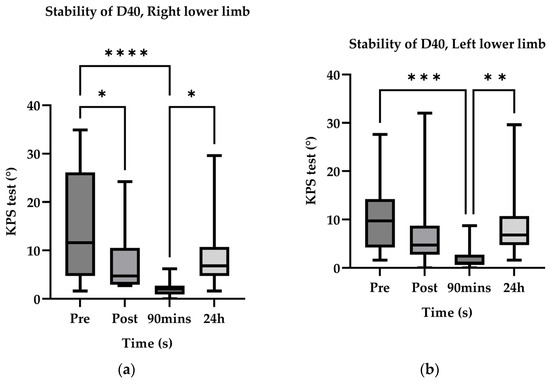
Figure 6.
StabilityD40° estimate marginal mean value. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; ****, p < 0.0001.
4. Discussion
This study employed a self-controlled pre–post experimental design, using a single-factor repeated-measures analysis of variance (ANOVA) to examine differences in proprioception across distinct time points relative to IPC application (pre-IPC vs. immediately post-IPC vs. 90 min post-IPC vs. 24 h post-IPC). The objectives were to investigate whether IPC influences proprioception and to identify the optimal time frame for its effect. The findings demonstrate that ischemic preconditioning optimized proprioceptive accuity and precision, with the peak enhancement observed at the 90-min post-IPC time point. The findings provide a degree of theoretical support for the pre-competition implementation of IPC to optimize proprioceptive accuity and precision in sports disciplines that rely on proprioception during practical performance.
4.1. Effect of IPC on Proprioception
IPC optimizes proprioceptive accuity and precision. Previous research [7,9,10,11,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29] has robustly established the ergogenic benefits of IPC for maximal strength, muscular endurance, anaerobic power output, and endurance performance. During incremental exercise tests, IPC has been shown to prolong time to exhaustion and reduce ratings of perceived exertion (RPE) [7] while concurrently enhancing maximal oxygen uptake (VO2max), attenuating fatigue sensitivity, and improving exercise efficiency [17]. These enhancements in aerobic exercise capacity are attributed to accelerated blood flow velocity and augmented oxygen delivery [18]. Furthermore, IPC enhances maximal voluntary isometric contraction (MVIC) torque output [30] and endurance capacity [19], with peak improvements in anaerobic power typically observed between 45 and 50 min post-application [20]. However, contradictory findings regarding the impact of IPC on anaerobic capacity have generated controversy within the literature [21,22]. The findings in the present study provide stronger support for the perspective that IPC can acutely enhance anaerobic capacity. We posit that enhanced proprioceptive accuracy optimizes movement economy during anaerobic exercise execution, thereby mediating the observed acute improvement in anaerobic capacity. IPC exerts regulatory effects on target organs by stimulating autonomic and neural pathways [27]. This process involves IPC enhancing afferent neuronal excitability [28]. Additional research suggests IPC may induce the production of humoral factors such as nitric oxide (NO) and bradykinin to potentiate afferent signaling [29]. Collectively, these studies share the commonality of supporting IPC’s capacity to augment afferent neural function, offering compelling neurohumoral explanations for the improvement in proprioceptive accuracy and stability. The current study aligns with this consensus perspective. However, the primary focus of these prior investigations has been on acute performance enhancement, largely overlooking the potential contribution of altered proprioception to these acute performance gains. While the current study cannot substantiate this perspective, it proposes a novel hypothesis: IPC may achieve acute performance enhancement through improved proprioception. Subsequent investigations should prioritize exploring this proposed mechanistic pathway.
4.2. Optimal Time Frame for IPC’s Effect on Proprioception
IPC was observed to enhance proprioception at 90 min post-application. Following brief cycles of ischemia and reperfusion, IPC induces the release of substances such as adenosine and norepinephrine into the coronary effluent, ultimately entering the systemic circulation [6]. IPC-induced ischemia–reperfusion generates reactive oxygen species (ROS) that activate downstream protein kinases (e.g., protein kinase C [PKC]), subsequently opening KATP channels [23]. Crucially, KATP channel activity modulates sympathetic vasoconstriction in humans [31], thereby regulating sympathetic nervous function and ultimately enhancing proprioceptive acuity. This study hypothesizes that the mechanism underlying the enhanced proprioceptive adaptation following IPC may be analogous to these humoral mechanisms. These findings align closely with the described physiological mechanisms: the temporal delay inherent in humoral regulation likely explains why the 90-min post-IPC time window represents the peak period for proprioceptive enhancement, an effect that persisted until at least the following day. The capacity for continuous rapid motor responses during human movement fundamentally relies on intrinsic bodily signaling. Proprioceptors provide essential afferent signals regarding limb and trunk position and motion. Conscious motor control critically depends on the proprioceptive system, wherein muscle spindles, Golgi tendon organs, joint receptors, and cutaneous receptors transduce joint position, muscle length changes, and force generation. Post-exertional movement deterioration and instability stem not merely from muscular fatigue but also from degraded proprioceptive acuity in fatigued extremities and trunk. Fatigue induces not only metabolic depletion but also diminished activation at the spinal and cortical levels. This progressive proprioceptive decline during sustained exercise precipitates motor clumsiness. Prolonged muscular work induces both structural damage and proprioceptive disruption. Exercise-induced muscle soreness similarly alters proprioception via group III and IV afferent pathways [32]. Notably, ischemic preconditioning (IPC) enhances the functionality of these group III/IV afferents [24]. Proprioceptive input and output depend on signaling from muscle spindles, which primarily function through length-sensitive mechanoreceptors within group Ia and II afferent fibers [33]. Consequently, IPC may not only influence group III and IV afferents but could also exert a modulatory influence on the function of group I and II afferent fibers. The present study corroborates the aforementioned research, positing that the observed enhancement in proprioceptive accuity and precision is precisely attributable to the acute humoral regulation and sympathetic nervous adaptations induced by the transient ischemia–reperfusion stimulus inherent to IPC. Furthermore, this study addresses an aspect overlooked in prior investigations: the fundamental mechanism through which IPC enhances athletic performance (e.g., strength, speed, power output) resides in the optimization of movement economy resulting from improved proprioceptive accuity and precision.
4.3. Practical Application of IPC for Influencing Proprioception
Existing research has demonstrated that IPC intervention can enhance subsequent maximal strength levels and the number of repetitions performed at submaximal force intensities [25]. Furthermore, IPC has been shown to effectively improve anaerobic capacity [26] and aerobic capacity [24] during exercise. A limited number of studies also support an acute enhancement effect of IPC on power output and speed [9]. However, factors influencing athletic performance extend beyond strength, speed, power, and metabolic capacity; they also encompass fine motor control governed by proprioception. Indeed, the accuity and precision of such fine motor control constitute a prerequisite for the expression of other performance-related factors. The findings of the present study support the notion that IPC can improve the accuity and precision of proprioception, with this optimal effect occurring at 90 min post-IPC. Based on the findings of this study, coaching teams may consider implementing IPC approximately 90 min prior to important competitions to enhance proprioceptive function. The acute proprioceptive enhancements induced by IPC find application in specific sporting scenarios, including basketball free throws, soccer penalty kicks, and gymnastics apparatus-based routines. These proprioceptive improvements may mediate enhanced motor performance in such athletic disciplines, ultimately contributing to superior competitive outcomes. Nevertheless, whether acute improvements in sport-specific proprioception interfere with the consolidation of established motor adaptations warrants further systematic investigation. Future research should delve into these directions to refine the relevant theoretical framework.
5. Conclusions
Functioning as a non-invasive conditioning strategy, IPC effectively enhances the accuracy and stability of proprioception, with the optimal gains observed after 90 min. This study suggests that athletes can benefit from performing ischemic preconditioning 90 min before warm-up or competition to obtain improved proprioceptive feedback; such proprioceptive refinements may confer potential benefits for the enhancement of motor skills and athletic performance.
6. Limitation
This study reveals the acute effects of IPC on proprioceptive adaptation. However, the sustainability of proprioceptive optimization and the underlying adaptive mechanisms following long-term repeated IPC protocols remain poorly understood. It may be subject to placebo and learning effects; our research team will address these potential confounders in a subsequent series of investigations. As the participant cohort exclusively comprised trained male individuals, the findings may be more applicable to male athletic populations. Generalizability to other demographics (e.g., females, older adults, or other groups) remains undetermined. Future studies in this series may employ EMG/fNIRS methodologies to elucidate the mechanisms underlying IPC’s effects on proprioception.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, writing—original draft preparation, J.W.; software, validation, P.Z.; investigation, resources, funding acquisition, Y.S. (Yuying Su) and Y.S. (Yu Shi); data curation, visualization, supervision, Y.Z.; project administration, writing—review and editing, C.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Sports Science Experiment Ethics Committee of Beijing Sport University (approval no. 2025125H, 31th March 2025).
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent was obtained from the patients to publish this paper.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express gratitude to the School of Strength Training and Conditioning at Beijing Sport University and all the participants involved in this study for their support and assistance.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| TPD | Two-point discrimination |
| KPS | Knee position sense |
| D40 | Difference in knee position sense test |
| TPDR | Two-point discrimination threshold on right lower limb |
| TPDL | Two-point discrimination threshold on left lower limb |
| D40R | Difference in position sense test of right lower limb |
| D40L | Difference in position sense test of left lower limb |
References
- Franco, P.G.; Santos, K.B.; Rodacki, A.L. Joint positioning sense, perceived force level and two-point discrimination tests of young and active elderly adults. Braz. J. Phys. Ther. 2015, 19, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shields, R.K.; Madhavan, S.; Cole, K. Sustained muscle activity minimally influences dynamic position sense of the ankle. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2005, 35, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jones, L.A.; Sarter, N.B. Tactile displays: Guidance for their design and application. Hum. Factors 2008, 50, 90–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandevia, S.C. Spinal and supraspinal factors in human muscle fatigue. Physiol. Rev. 2001, 81, 1725–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murry, C.E.; Jennings, R.B.; Reimer, K.A. Preconditioning with ischemia: A delay of lethal cell injury in ischemic myocardium. Circulation 1986, 74, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, C.H.; Wang, L.; Nielsen, J.M.; Tropak, M.B.; Fu, Y.Y.; Kato, H.; Callahan, J.; Redington, A.N.; Caldarone, C.A. Remote cardioprotection by transfer of coronary effluent from ischemic preconditioned rabbit heart preserves mitochondrial integrity and function via adenosine receptor activation. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2014, 28, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Groot, P.C.E.; Thijssen, D.H.J.; Sanchez, M.; Ellenkamp, R.; Hopman, M.T.E. Ischemic preconditioning improves maximal performance in humans. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 108, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilhodes, J.C.; Roll, J.P.; Tardy-Gervet, M.F. Perceptual and motor effects of agonist-antagonist muscle vibration in man. Exp. Brain Res. 1986, 61, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, S.D.; Bezodis, N.E.; Glaister, M.; Pattison, J.R. The effect of ischemic preconditioning on repeated sprint cycling performance. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2015, 47, 1652–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva Novaes, J.; da Silva Telles, L.G.; Monteiro, E.R.; da Silva Araujo, G.; Vingren, J.L.; Panza, P.S.; Reis, V.M.; Laterza, M.C.; Vianna, J.M. Ischemic preconditioning improves resistance training session performance. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2021, 35, 2993–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pethick, J.; Casselton, C.; Winter, S.L.; Burnley, M. Ischemic Preconditioning Blunts Loss of Knee Extensor Torque Complexity with Fatigue. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2021, 53, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, S.; Wang, Q.; Semeah, L.M.; Jia, H.; Lv, T.; Li, X.; Wang, R. Immediate Effect of Local Vibration Therapy for Sport-induced Fatigue Based on Traditional Chinese Medicine’s Holistic Theory. J. Multidiscip. Healthc. 2020, 13, 1993–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Park, S.; Jung, S.; Choi, Y.; Song, H. Comparisons of changes in the two-point discrimination test following muscle fatigue in healthy adults. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2015, 27, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Franco, N.; Romero-Franco, J.; Jiménez-Reyes, P. Jogging and Practical-Duration Foam-Rolling Exercises and Range of Motion, Proprioception, and Vertical Jump in Athletes. J. Athl. Train. 2019, 54, 1171–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, F.; Monjo, F.; Gioda, J.; Blain, G.M.; Piponnier, E.; Corcelle, B.; Colson, S.S. Knee position sense and knee flexor neuromuscular function are similarly altered after two submaximal eccentric bouts. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2023, 123, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, C. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences (2nd ed.). J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1988, 84, 1096. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz, R.S.; de Aguiar, R.A.; Turnes, T.; Pereira, K.L.; Caputo, F. Effects of ischemic preconditioning on maximal constant-load cycling performance. J. Appl. Physiol. 2015, 119, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffries, O.; Waldron, M.; Pattison, J.R.; Patterson, S.D. Enhanced Local Skeletal Muscle Oxidative Capacity and Microvascular Blood Flow Following 7-Day Ischemic Preconditioning in Healthy Humans. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marocolo, M.; Marocolo, I.C.; da Mota, G.R.; Simão, R.; Maior, A.S.; Coriolano, H.-J.A. Beneficial Effects of Ischemic Preconditioning in Resistance Exercise Fade over Time. Int. J. Sports Med. 2016, 37, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvador, A.F.; De Aguiar, R.A.; Lisbôa, F.D.; Pereira, K.L.; Cruz, R.S.d.O.; Caputo, F. Ischemic Preconditioning and Exercise Performance: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2016, 11, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clevidence, M.W.; Mowery, R.E.; Kushnick, M.R. The effects of ischemic preconditioning on aerobic and anaerobic variables associated with submaximal cycling performance. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2012, 112, 3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, P.; Billaut, F. Time-Trial Performance in Elite Speed Skaters After Remote Ischemic Preconditioning. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2018, 13, 1308–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.; Marsh, R.; Cunniffe, B.; Cardinale, M.; Yellon, D.M.; Davidson, S.M. From Protecting the Heart to Improving Athletic Performance—The Benefits of Local and Remote Ischaemic Preconditioning. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2015, 29, 573–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crisafulli, A.; Tangianu, F.; Tocco, F.; Concu, A.; Mameli, O.; Mulliri, G.; Caria, M.A. Ischemic preconditioning of the muscle improves maximal exercise performance but not maximal oxygen uptake in humans. J. Appl. Physiol. 2011, 111, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, A.L.; Ide, B.N.; Sasaki, J.E.; DE Oliveira, D.C.X.; Assumpção, C.D.O.; Marocolo, M.; Mota, G.R. Ischemic preconditioning improves the bench-press maximal strength in resistance-trained men. Int. J. Exerc. Sci. 2023, 16, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kraus, A.S.; Pasha, E.P.; Machin, D.R.; Alkatan, M.; Kloner, R.A. Bilateral upper limb remote ischemic preconditioning improves anaerobic power. Open Sports Med. J. 2015, 15, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donato, M.; Buchholz, B.; Rodriguez, M.; Pérez, V.; Inserte, J.; García-Dorado, D.; Gelpi, R.J. Role of the parasym pathetic nervous system in cardioprotection by remote hindlimb ischemic preconditioning. Exp. Physiol. 2013, 98, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, C.C.; Yan, Z.M.; Wei, D.; Gao, X.; Chen, X.; Zhao, H. Limb remote ischemic post conditioning protects against focal ischemia in rats. Brain Res. 2009, 1288, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastitskaya, S.; Marina, N.; Gourine, A.; Gilbey, M.P.; Spyer, K.M.; Teschemacher, A.G.; Kasparov, S.; Trapp, S.; Ackland, G.L.; Gourine, A.V. Cardioprotection evoked by remote ischemic preconditioning is critically dependent on the activity of vagal pre-ganglionic neurones. Cardiovasc. Res. 2012, 95, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niespodziński, B.; Mieszkowski, J.; Kochanowicz, M.; Kochanowicz, A.; Antosiewicz, J. Effect of 10 consecutive days of remote ischemic preconditioning on local neuromuscular performance. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2021, 60, 102584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, D.M.; Ogoh, S.; Greene, S.; Olivencia-Yurvati, A.; Raven, P.B. Inhibition of KATP channel activity augments baroreflex-mediated vasoconstriction in exercising human skeletal muscle. J. Physiol. 2004, 561, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proske, U.; Gandevia, S.C. The proprioceptive senses: Their roles in signaling body shape, body position and movement, and muscle force. Physiol. Rev. 2012, 92, 1651–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roll, J.P.; Vedel, J.P.; Ribot, E. Alteration of proprioceptive messages induced by tendon vibration in man: A microneurographic study. Exp. Brain Res. 1989, 76, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).