Antimicrobial Activity of Chemical Hop (Humulus lupulus) Compounds: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search Strategy and Eligibility Criteria of Selected Studies
2.2. Data Extraction
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Studies’ Selection and Characteristics
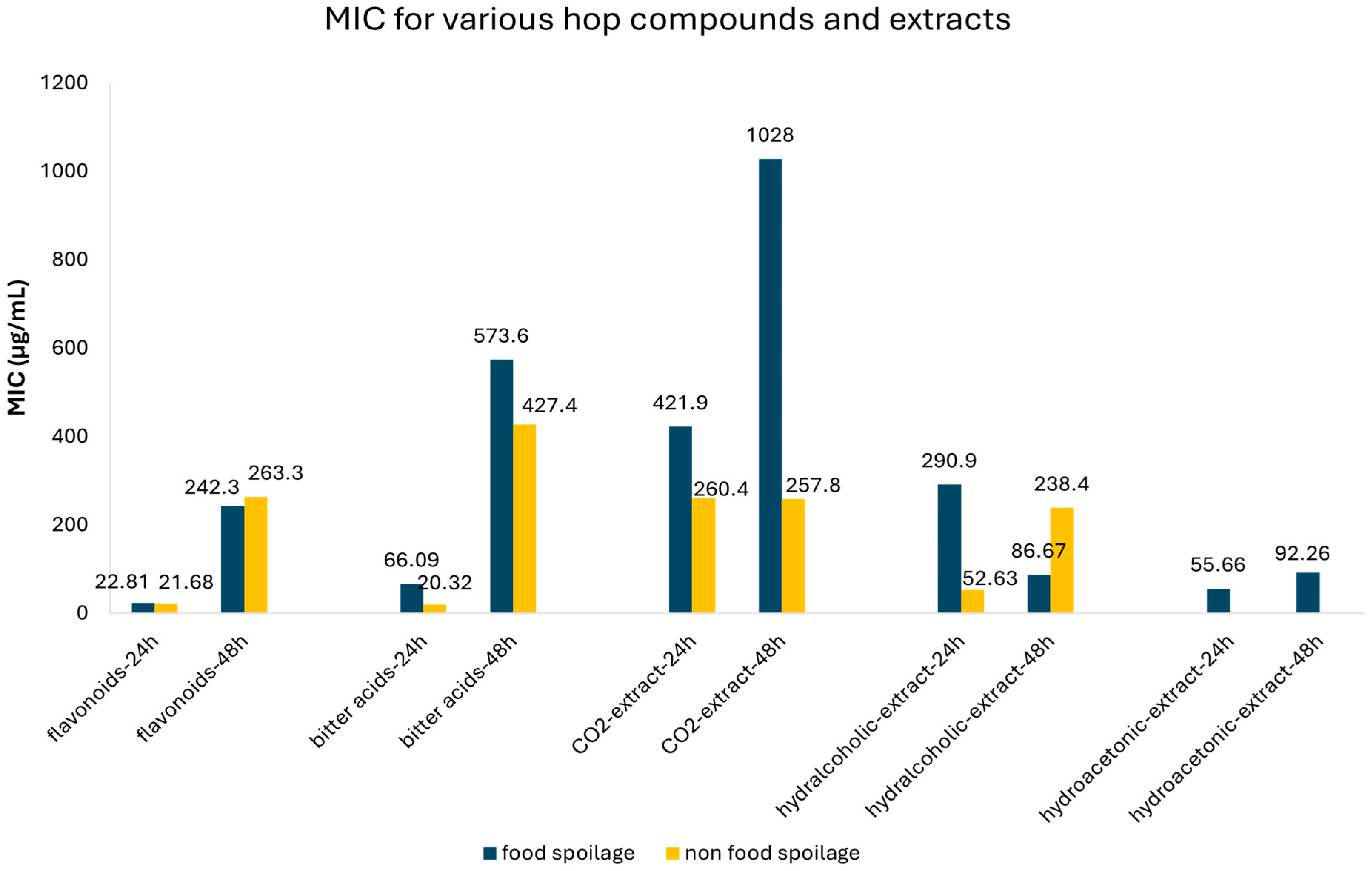
3.2. Meta-Analysis of MIC Values of Classes of Hop Compounds and Extracts
3.3. Stratification Meta-Analysis of MIC Values of Each Hop Compound
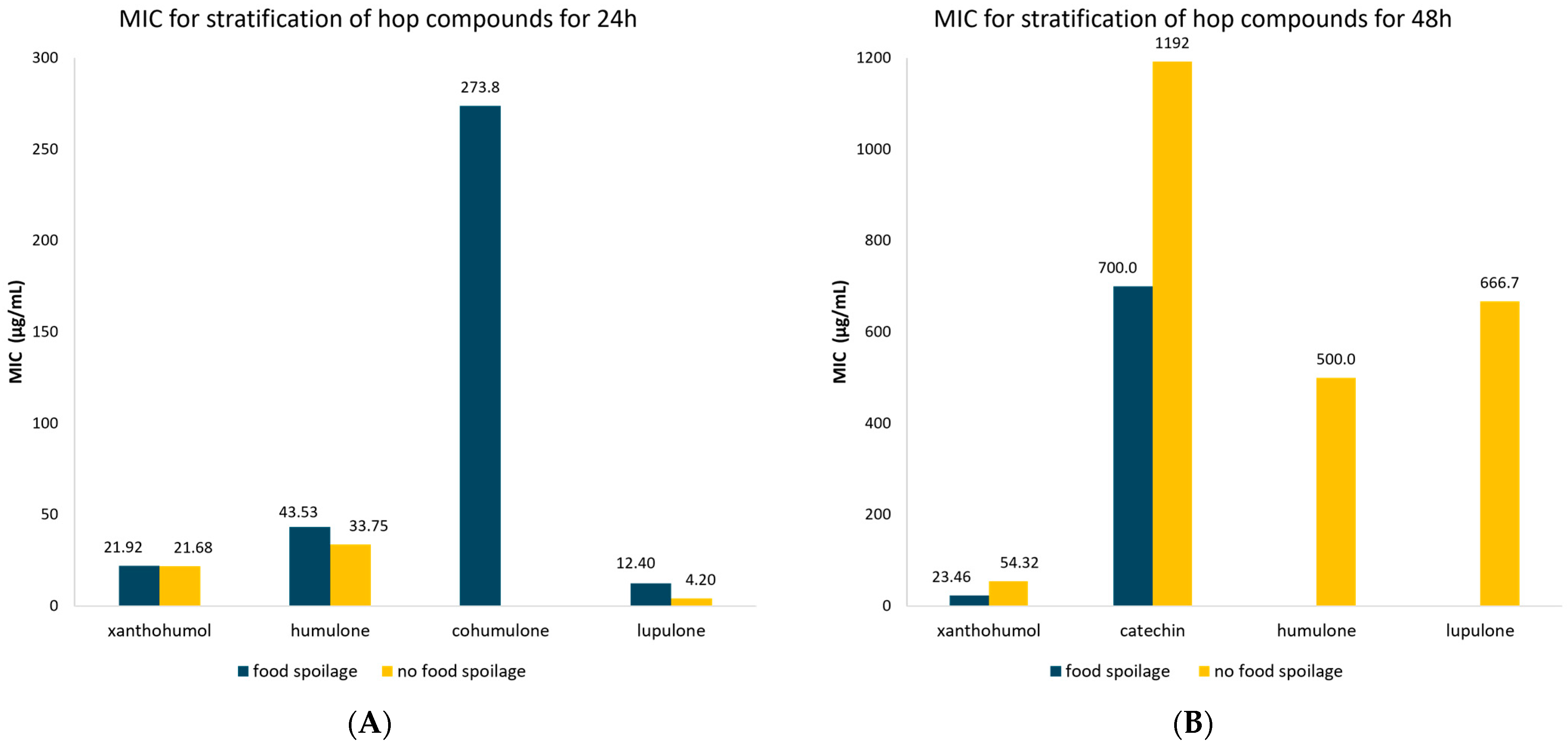
3.4. Meta-Analysis of MIC Values of Hop Compounds and Extracts for Food Spoilage and Non-Food Spoilage Microorganisms
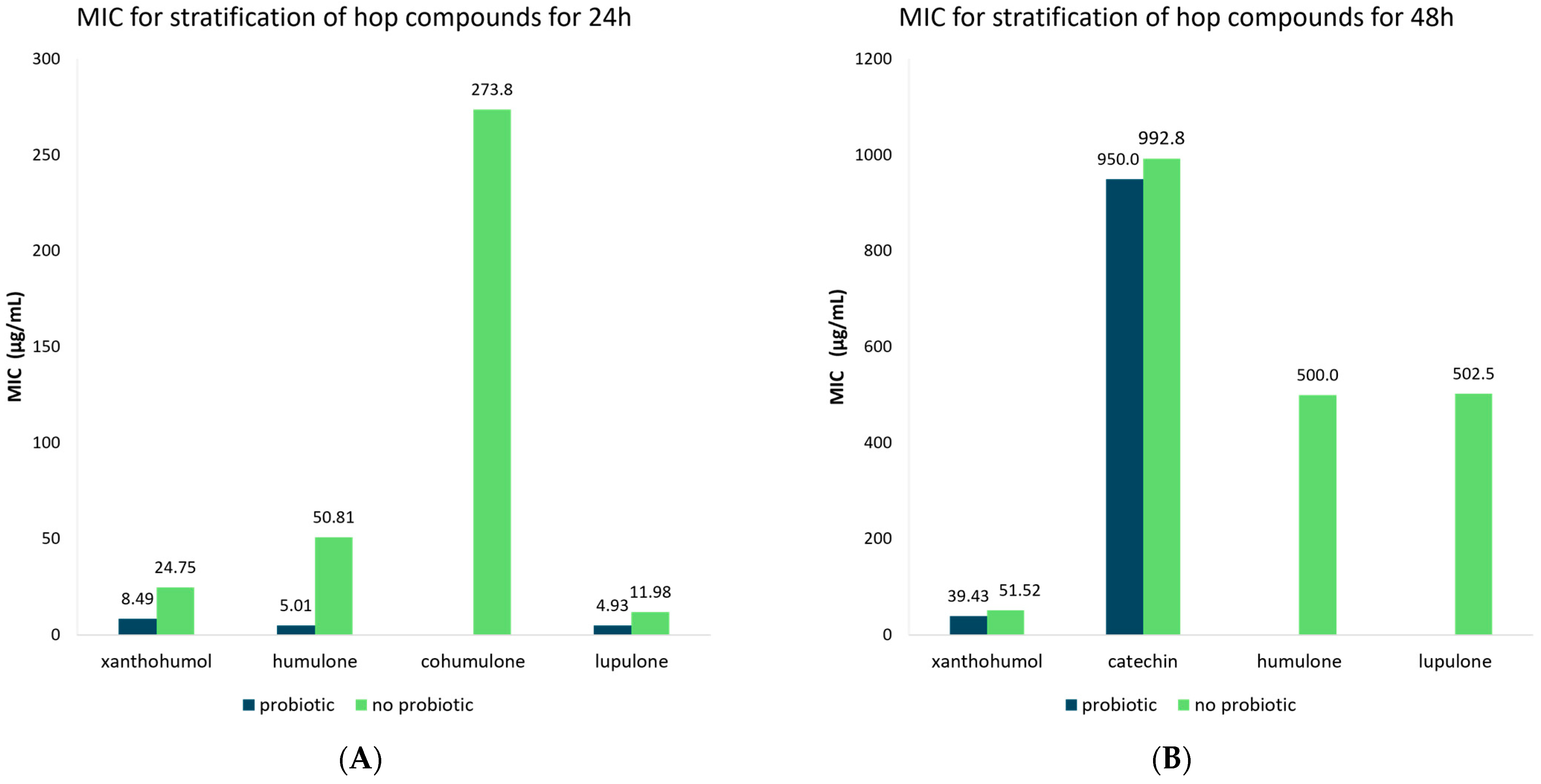
3.5. Meta-Analysis of MIC Values of Hop Compounds and Extracts for Probiotic and Non-Probiotic Microorganisms
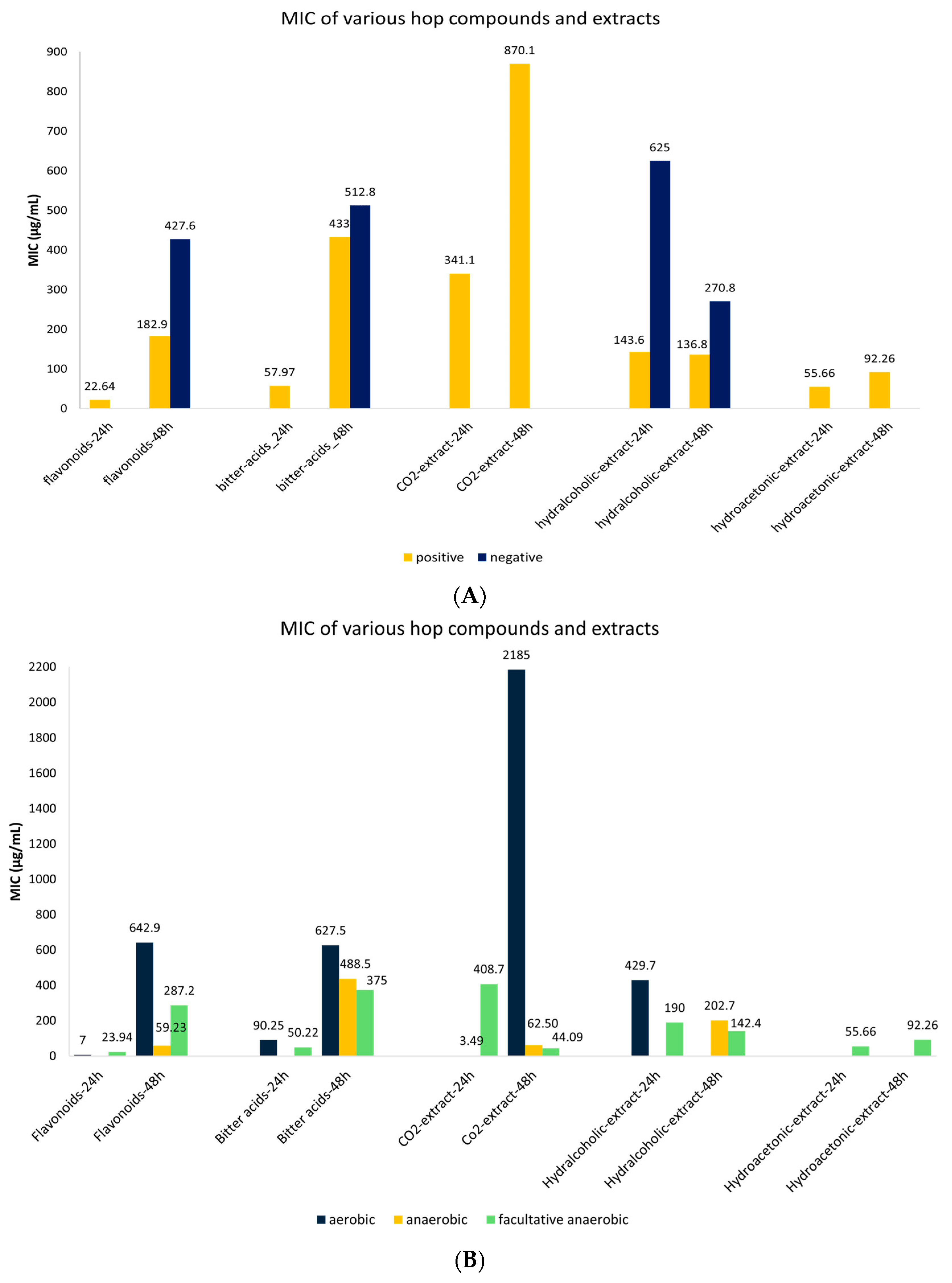
3.6. Meta-Analysis of MIC Values of Hop Compounds and Extracts Stratified According to Gram +/− and Oxygen-Requirement Microorganisms
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MIC | Minimum Inhibitory Concentration |
| SFE | Supercritical fluid extracts |
References
- Bocquet, L.; Sahpaz, S.; Hilbert, J.L.; Rambaud, C.; Rivière, C. Humulus lupulus L., a Very Popular Beer Ingredient and Medicinal Plant: Overview of Its Phytochemistry, Its Bioactivity, and Its Biotechnology. Phytochem. Rev. 2018, 17, 1047–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksen, R.L.; Padgitt-Cobb, L.K.; Townsend, M.S.; Henning, J.A. Gene Expression for Secondary Metabolite Biosynthesis in Hop (Humulus lupulus L.) Leaf Lupulin Glands Exposed to Heat and Low-Water Stress. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dostálek, P.; Karabín, M.; Jelínek, L. Hop Phytochemicals and Their Potential Role in Metabolic Syndrome Prevention and Therapy. Molecules 2017, 22, 1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Wang, X.; Yuan, A.; Liu, J.; Li, Z.; Xie, D.; Zhang, H.; Luo, W.; Xu, H.; Liu, J.; et al. Chemical Constituents and Bioactivities of Hops (Humulus lupulus L.) and Their Effects on Beer-related Microorganisms. Food Energy Secur. 2022, 11, e367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knez Hrnčič, M.; Španinger, E.; Košir, I.J.; Knez, Ž.; Bren, U. Hop Compounds: Extraction Techniques, Chemical Analyses, Antioxidative, Antimicrobial, and Anticarcinogenic Effects. Nutrients 2019, 11, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannusch, V.B.; Viebahn, L.; Briesen, H.; Minceva, M. Predicting the Essential Oil Composition in Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Extracts from Hop Pellets Using Mathematical Modeling. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbatini, G.; Mari, E.; Ortore, M.G.; Di Gregorio, A.; Fattorini, D.; Di Carlo, M.; Galeazzi, R.; Vignaroli, C.; Simoni, S.; Giorgini, G.; et al. Hop Leaves: From Waste to a Valuable Source of Bioactive Compounds—A Multidisciplinary Approach to Investigating Potential Applications. Heliyon 2024, 10, e37593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paniagua-García, A.I.; Ibáñez, A.; Díez-Antolínez, R. Green Antimicrobials: Innovative Applications of Hops Extracts as Biocontrol Agents. Pathogens 2025, 14, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyres, G.; Dufour, J.-P. Hop Essential Oil: Analysis, Chemical Composition and Odor Characteristics. In Beer in Health and Disease Prevention; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, K.; Gervasi, F. An Updated Review of the Genus Humulus: A Valuable Source of Bioactive Compounds for Health and Disease Prevention. Plants 2022, 11, 3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condón, S.; García, M.L.; Otero, A.; Sala, F.J. Effect of Culture Age, Pre-incubation at Low Temperature and pH on the Thermal Resistance of Aeromonas Hydrophila. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1992, 72, 322–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerhauser, C.; Alt, A.; Heiss, E.; Gamal-Eldeen, A.; Klimo, K.; Knauft, J.; Neumann, I.; Scherf, H.-R.; Frank, N.; Bartsch, H.; et al. Cancer Chemopreventive Activity of Xanthohumol, a Natural Product Derived from Hop. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2002, 1, 959–969. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bolton, J.L.; Dunlap, T.L.; Hajirahimkhan, A.; Mbachu, O.; Chen, S.-N.; Chadwick, L.; Nikolic, D.; Van Breemen, R.B.; Pauli, G.F.; Dietz, B.M. The Multiple Biological Targets of Hops and Bioactive Compounds. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2019, 32, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodino, S.; Butu, A.; Negoescu, C.; Petrache, P.; Condei, R.; Nicolae, I.; Cornea, C.P. Antimicrobial Activity of Humulus lupulus Extract. J. Biotechnol. 2014, 185, S66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, N.; Biehler, K.; Schwabe, K.; Haarhaus, B.; Quirin, K.-W.; Frank, U.; Schempp, C.M.; Wölfle, U. Hop Extract Acts as an Antioxidant with Antimicrobial Effects against Propionibacterium Acnes and Staphylococcus Aureus. Molecules 2019, 24, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, J.F.; Page, J.E. Xanthohumol and Related Prenylflavonoids from Hops and Beer: To Your Good Health! Phytochemistry 2004, 65, 1317–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Pastor, R.; Carrera-Pacheco, S.E.; Zúñiga-Miranda, J.; Rodríguez-Pólit, C.; Mayorga-Ramos, A.; Guamán, L.P.; Barba-Ostria, C. Current Landscape of Methods to Evaluate Antimicrobial Activity of Natural Extracts. Molecules 2023, 28, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eloff, J.N. Avoiding Pitfalls in Determining Antimicrobial Activity of Plant Extracts and Publishing the Results. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 19, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubonja-Šonje, M.; Knežević, S.; Abram, M. Challenges to Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing of Plant-Derived Polyphenolic Compounds. Arch. Ind. Hyg. Toxicol. 2020, 71, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golus, J.; Sawicki, R.; Widelski, J.; Ginalska, G. The Agar Microdilution Method—a New Method for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing for Essential Oils and Plant Extracts. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 121, 1291–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balouiri, M.; Sadiki, M.; Ibnsouda, S.K. Methods for in Vitro Evaluating Antimicrobial Activity: A Review. J. Pharm. Anal. 2016, 6, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska-Krochmal, B.; Dudek-Wicher, R. The Minimum Inhibitory Concentration of Antibiotics: Methods, Interpretation, Clinical Relevance. Pathogens 2021, 10, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sackett, D.L.; Rosenberg, W.M.C.; Gray, J.A.M.; Haynes, R.B.; Richardson, W.S. Evidence Based Medicine: What It Is and What It Isn’t. BMJ 1996, 312, 71–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papaefthimiou, M.; Kontou, P.I.; Bagos, P.G.; Braliou, G.G. Antioxidant Activity of Leaf Extracts from Stevia Rebaudiana Bertoni Exerts Attenuating Effect on Diseased Experimental Rats: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papaefthimiou, M.; Kontou, P.I.; Bagos, P.G.; Braliou, G.G. Integration of Antioxidant Activity Assays Data of Stevia Leaf Extracts: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopewell, S.; McDonald, S.; Clarke, M.; Egger, M. Grey Literature in Meta-Analyses of Randomized Trials of Health Care Interventions. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2007, 2007, MR000010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, T.A.; Barbui, C.; Cipriani, A.; Brambilla, P.; Watanabe, N. Imputing Missing Standard Deviations in Meta-Analyses Can Provide Accurate Results. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2006, 59, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, M.; Smith, G.D.; Schneider, M.; Minder, C. Bias in Meta-Analysis Detected by a Simple, Graphical Test. BMJ 1997, 315, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DerSimonian, R.; Laird, N. Meta-Analysis in Clinical Trials. Control. Clin. Trials 1986, 7, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stata User’s Guide Release 13; StataCorp LP: College Station, TX, USA, 2013.
- Kramer, B.; Thielmann, J.; Hickisch, A.; Muranyi, P.; Wunderlich, J.; Hauser, C. Antimicrobial Activity of Hop Extracts against Foodborne Pathogens for Meat Applications. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 118, 648–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cermak, P.; Olsovska, J.; Mikyska, A.; Dusek, M.; Kadleckova, Z.; Vanicek, J.; Nyc, O.; Sigler, K.; Bostikova, V.; Bostik, P. Strong Antimicrobial Activity of Xanthohumol and Other Derivatives from Hops (Humulus lupulus L.) on Gut Anaerobic Bacteria. APMIS Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Immunol. Scand. 2017, 125, 1033–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogdanova, K.; Röderova, M.; Kolar, M.; Langova, K.; Dusek, M.; Jost, P.; Kubelkova, K.; Bostik, P.; Olsovska, J. Antibiofilm Activity of Bioactive Hop Compounds Humulone, Lupulone and Xanthohumol toward Susceptible and Resistant Staphylococci. Res. Microbiol. 2018, 169, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, A.E.; Yu, R.R.; Lee, O.A.; Price, S.; Haas, G.J.; Johnson, E.A. Antimicrobial Activity of Hop Extracts against Listeria Monocytogenes in Media and in Food. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1996, 33, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimek, K.; Tyśkiewicz, K.; Miazga-Karska, M.; Dębczak, A.; Rój, E.; Ginalska, G. Bioactive Compounds Obtained from Polish “Marynka” Hop Variety Using Efficient Two-Step Supercritical Fluid Extraction and Comparison of Their Antibacterial, Cytotoxic, and Anti-Proliferative Activities In Vitro. Molecules 2021, 26, 2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocquet, L.; Sahpaz, S.; Bonneau, N.; Beaufay, C.; Mahieux, S.; Samaillie, J.; Roumy, V.; Jacquin, J.; Bordage, S.; Hennebelle, T.; et al. Phenolic Compounds from Humulus lupulus as Natural Antimicrobial Products: New Weapons in the Fight against Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus, Leishmania Mexicana and Trypanosoma Brucei Strains. Molecules 2019, 24, 1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, P.; Katta, S.; Andrei, I.; Babu Rao Ambati, V.; Leonida, M.; Haas, G.J. Positive Antibacterial Co-Action between Hop (Humulus lupulus) Constituents and Selected Antibiotics. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2008, 15, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engels, C.; Schieber, A.; Gänzle, M.G. Inhibitory Spectra and Modes of Antimicrobial Action of Gallotannins from Mango Kernels (Mangifera indica L.). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 2215–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozalski, M.; Micota, B.; Sadowska, B.; Stochmal, A.; Jedrejek, D.; Wieckowska-Szakiel, M.; Rozalska, B. Antiadherent and Antibiofilm Activity of Humulus lupulus L. Derived Products: New Pharmacological Properties. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 101089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flesar, J.; Havlik, J.; Kloucek, P.; Rada, V.; Titera, D.; Bednar, M.; Stropnicky, M.; Kokoska, L. In Vitro Growth-Inhibitory Effect of Plant-Derived Extracts and Compounds against Paenibacillus Larvae and Their Acute Oral Toxicity to Adult Honey Bees. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 145, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanova, K.; Kolar, M.; Langova, K.; Dusek, M.; Mikyska, A.; Bostikova, V.; Bostik, P.; Olsovska, J. Inhibitory Effect of Hop Fractions against Gram-Positive Multi-Resistant Bacteria. A Pilot Study. Biomed. Pap. Med. Fac. Univ. Palacky Olomouc Czechoslov. 2018, 62, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhavya, M.L.; Chandu, A.G.S.; Devi, S.S.; Quirin, K.-W.; Pasha, A.; Vijayendra, S.V.N. In-Vitro Evaluation of Antimicrobial and Insect Repellent Potential of Supercritical-Carbon Dioxide (SCF-CO2) Extracts of Selected Botanicals against Stored Product Pests and Foodborne Pathogens. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 1071–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilna, J.; Vlkova, E.; Krofta, K.; Nesvadba, V.; Rada, V.; Kokoska, L. In Vitro Growth-Inhibitory Effect of Ethanol GRAS Plant and Supercritical CO2 Hop Extracts on Planktonic Cultures of Oral Pathogenic Microorganisms. Fitoterapia 2015, 105, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmalreck, A.F.; Teuber, M. Structural Features Determining the Antibiotic Potencies of Natural and Synthetic Hop Bitter Resins, Their Precursors and Derivatives. Can. J. Microbiol. 1975, 21, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maia, N.J.L.; Corrêa, J.A.F.; Rigotti, R.T.; da Silva Junior, A.A.; Luciano, F.B. Combination of Natural Antimicrobials for Contamination Control in Ethanol Production. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 35, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Liang, J.; Shi, Q.; Yuan, P.; Meng, R.; Tang, X.; Yu, L.; Guo, N. Genome-Wide Transcription Analyses in Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Treated with Lupulone. Braz. J. Microbiol. Publ. Braz. Soc. Microbiol. 2014, 45, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolenc, Z.; Langerholc, T.; Hostnik, G.; Ocvirk, M.; Štumpf, S.; Pintarič, M.; Košir, I.J.; Čerenak, A.; Garmut, A.; Bren, U. Antimicrobial Properties of Different Hop (Humulus lupulus) Genotypes. Plants 2022, 12, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegopoulos, K.; Fountas, D.V.; Andronidou, E.-M.; Bagos, P.G.; Kolovos, P.; Skavdis, G.; Pergantas, P.; Braliou, G.G.; Papageorgiou, A.C.; Grigoriou, M.E. Assessing Genetic Diversity and Population Differentiation in Wild Hop (Humulus lupulus) from the Region of Central Greece via SNP-NGS Genotyping. Diversity 2023, 15, 1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappa, S.A.; Kontou, P.I.; Bagos, P.G.; Braliou, G.G. Urine-Based Molecular Diagnostic Tests for Leishmaniasis Infection in Human and Canine Populations: A Meta-Analysis. Pathogens 2021, 10, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagybákay, N.E.; Syrpas, M.; Vilimaitė, V.; Tamkutė, L.; Pukalskas, A.; Venskutonis, P.R.; Kitrytė, V. Optimized Supercritical CO2 Extraction Enhances the Recovery of Valuable Lipophilic Antioxidants and Other Constituents from Dual-Purpose Hop (Humulus lupulus L.) Variety Ella. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkel-Shirley, B. Flavonoid Biosynthesis. A Colorful Model for Genetics, Biochemistry, Cell Biology, and Biotechnology. Plant Physiol. 2001, 126, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, K.; Konings, W.N. Beer Spoilage Bacteria and Hop Resistance. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2003, 89, 105–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, W.J.; Smith, A.R. Factors Affecting Antibacterial Activity of Hop Compounds and Their Derivatives. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1992, 72, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Saavedra, M.; González de Llano, D.; Moreno-Arribas, M.V. Beer Spoilage Lactic Acid Bacteria from Craft Brewery Microbiota: Microbiological Quality and Food Safety. Food Res. Int. Ott. Ont. 2020, 138 Pt A, 109762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, D.S.; Boyer-Chammard, T.; Jarvis, J.N. Emerging Concepts in HIV-Associated Cryptococcal Meningitis. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 32, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leus, I.V.; Adamiak, J.; Chandar, B.; Bonifay, V.; Zhao, S.; Walker, S.S.; Squadroni, B.; Balibar, C.J.; Kinarivala, N.; Standke, L.C.; et al. Functional Diversity of Gram-Negative Permeability Barriers Reflected in Antibacterial Activities and Intracellular Accumulation of Antibiotics. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2023, 67, e01377-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, T.M.; Chakraborty, A.J.; Khusro, A.; Zidan, B.R.M.; Mitra, S.; Emran, T.B.; Dhama, K.; Ripon, M.K.H.; Gajdács, M.; Sahibzada, M.U.K.; et al. Antibiotic Resistance in Microbes: History, Mechanisms, Therapeutic Strategies and Future Prospects. J. Infect. Public Health 2021, 14, 1750–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhydzetski, A.; Głowacka-Grzyb, Z.; Bukowski, M.; Żądło, T.; Bonar, E.; Władyka, B. Agents Targeting the Bacterial Cell Wall as Tools to Combat Gram-Positive Pathogens. Molecules 2024, 29, 4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.G.P. The Role of the Outer Membrane of Gram-Negative Bacteria in Antibiotic Resistance: Ajax’ Shield or Achilles’ Heel? In Antibiotic Resistance; Coates, A.R.M., Ed.; Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 211, pp. 67–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Imlay, J.A. When Anaerobes Encounter Oxygen: Mechanisms of Oxygen Toxicity, Tolerance and Defence. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 774–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, A.C.; Debande, L.; Marteyn, B.S. The Selective Advantage of Facultative Anaerobes Relies on Their Unique Ability to Cope with Changing Oxygen Levels during Infection. Cell. Microbiol. 2021, 23, e13338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, O.; Chauhan, A.; Green, S.J. The Study of Microbial Physiology Under Microoxic Conditions Is Critical but Neglected. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2025, 17, e70108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez-Cervantes, G.I.; Ortega, D.R.; Blanco Ayala, T.; Pérez De La Cruz, V.; Esquivel, D.F.G.; Salazar, A.; Pineda, B. Redox and Anti-Inflammatory Properties from Hop Components in Beer-Related to Neuroprotection. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, K.; Margolles, A.; Van Veen, H.W.; Konings, W.N. Hop Resistance in the Beer Spoilage Bacterium Lactobacillus Brevis Is Mediated by the ATP-Binding Cassette Multidrug Transporter HorA. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 5371–5375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Lodovico, S.; Menghini, L.; Ferrante, C.; Recchia, E.; Castro-Amorim, J.; Gameiro, P.; Cellini, L.; Bessa, L.J. Hop Extract: An Efficacious Antimicrobial and Anti-Biofilm Agent Against Multidrug-Resistant Staphylococci Strains and Cutibacterium Acnes. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schurr, B.C.; Hahne, H.; Kuster, B.; Behr, J.; Vogel, R.F. Molecular Mechanisms behind the Antimicrobial Activity of Hop Iso-α-Acids in Lactobacillus Brevis. Food Microbiol. 2015, 46, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapari, A.; Braliou, G.G.; Papaefthimiou, M.; Mavriki, H.; Kontou, P.I.; Nikolopoulos, G.K.; Bagos, P.G. Performance of Antigen Detection Tests for SARS-CoV-2: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chassagne, F.; Samarakoon, T.; Porras, G.; Lyles, J.T.; Dettweiler, M.; Marquez, L.; Salam, A.M.; Shabih, S.; Farrokhi, D.R.; Quave, C.L. A Systematic Review of Plants With Antibacterial Activities: A Taxonomic and Phylogenetic Perspective. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 11, 586548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontou, P.I.; Braliou, G.G.; Dimou, N.L.; Nikolopoulos, G.; Bagos, P.G. Antibody Tests in Detecting SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiler, K.C. Mechanisms of Ribosome Rescue in Bacteria. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Wang, J.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Chen, D. Formation Chitosan-Based Hydrogel Film Containing Silicon for Hops β-Acids Release as Potential Food Packaging Material. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 191, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatib, N.; Varidi, M.J.; Mohebbi, M.; Varidi, M.; Hosseini, S.M.H. Replacement of Nitrite with Lupulon–Xanthohumol Loaded Nanoliposome in Cooked Beef-Sausage: Experimental and Model Based Study. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 2629–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleha, R.; Radochova, V.; Mikyska, A.; Houska, M.; Bolehovska, R.; Janovska, S.; Pejchal, J.; Muckova, L.; Cermak, P.; Bostik, P. Strong Antimicrobial Effects of Xanthohumol and Beta-Acids from Hops against Clostridioides Difficile Infection In Vivo. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- María Bonilla-Luque, O.; Nunes Silva, B.; Ezzaky, Y.; Possas, A.; Achemchem, F.; Cadavez, V.; Gonzales-Barron, Ú.; Valero, A. Meta-Analysis of Antimicrobial Activity of Allium, Ocimum, and Thymus Spp. Confirms Their Promising Application for Increasing Food Safety. Food Res. Int. 2024, 188, 114408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Jiang, S.; Jia, W.; Guo, T.; Wang, F.; Li, J.; Yao, Z. Natural Antimicrobials from Plants: Recent Advances and Future Prospects. Food Chem. 2024, 432, 137231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

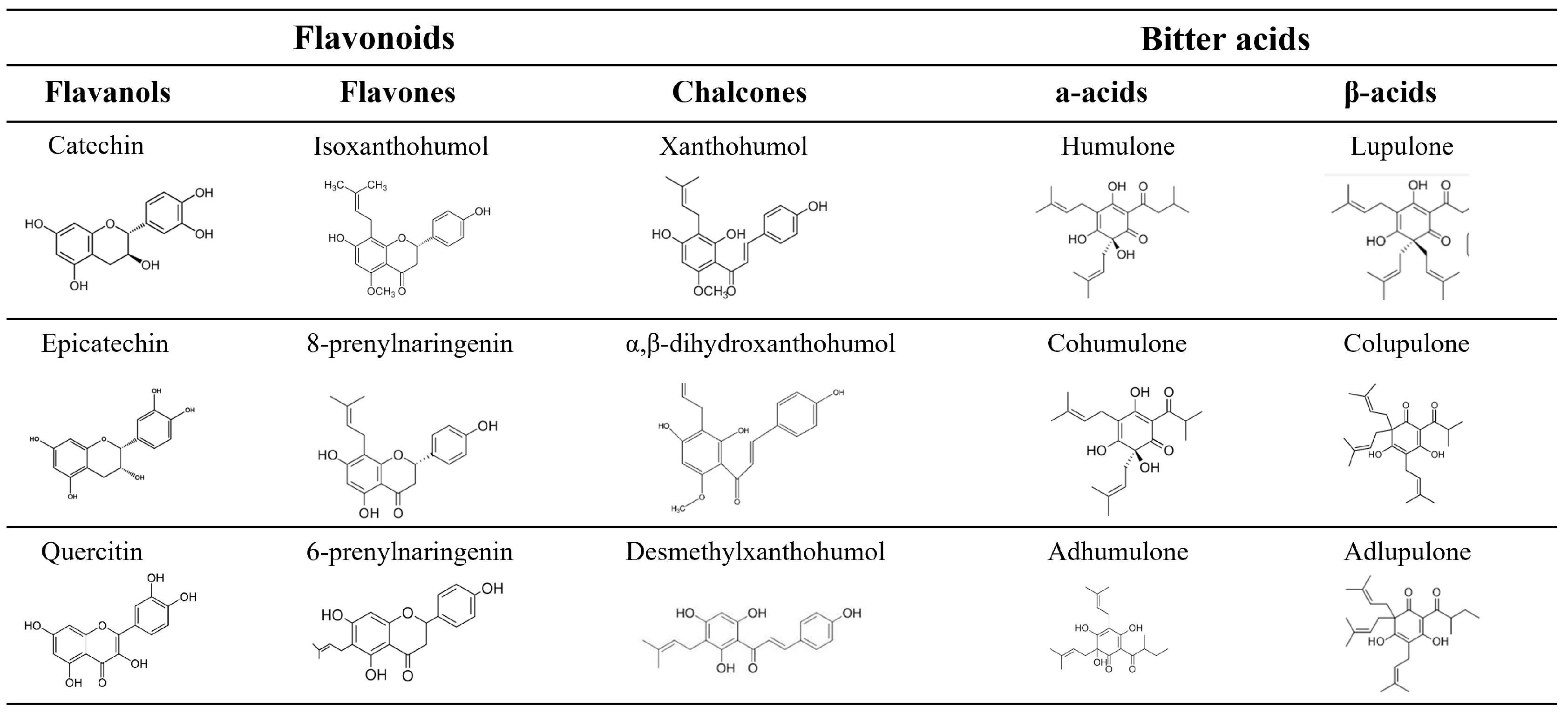

| Author | Year | Strain | Type of Compounds/Extracts | Number of Experiments | Time (h) | Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kramer et al. [32] | 2015 | Staphylococcus aureus/Listeria monocytogenes/Escherichia coli/Salmonella enterica | Xanthohumol/CO2-extract | 4 | 48 | 37 |
| Weber et al. [15] | 2019 | Propionibacterium acnes/Staphylococcus aureus | CO2-extract | 3 | 24 | 37 |
| Cermak et al. [33] | 2017 | Bacteroides fragilis/Clostridium perfringens/Clostridium difficile/ | α-acids/β-acids/xanthohumol | 4 | 48 | 37 |
| Bogdanova et al. [34] | 2018 | Staphylococcus epidermidis/Staphylococcus capitis/Staphylococcus aureus/ | Humulone/Lupulone/Xanthohumol | 3 | 24 | 37 |
| Larsona et al. [35] | 1996 | Listeria monocytogenes | CO2-extract | 4 | 24 | 37 |
| Klimek et al. [36] | 2021 | Staphylococcus aureus/Staphylococcus epidermidis/Streptococcus mutans/Streptococcus sanguinis/Propionibacterium acnes | Humulone/Lupulone/Xanthohumol | 3 | 24/48 | 37 |
| Bocquet et al. [37] | 2019 | Corynebacterium/Enterococcus faecalis/Enterococcus sp./Mycobacterium smegamtis/Staphylococcus aureus/Staphylococcus epidermidis/Staphylococcus lugdunensis/Staphylococcus warneri/Staphylococcus agalactiae/Staphylococcus dysgalactiae/Acinetobacter baumannii/Pseudomonas aeruginosa/Stenotrophomonas maltophilia/Candida albicans | Hydralcoholic-extract/Desmethylxanthohumol/Lupulone/Xanthohumol/Cohumulone/Humulone/Colupulone | 3 | 24 | 37 |
| Natarajana et al. [38] | 2008 | Bacillus subtilis/Bacillus megaterium/Streptococcus salivarius/Streptococcus saprophyticus | Humulone/Lupulone/Xanthohumol | 2 | 24 | 37 |
| Engels et al. [39] | 2011 | Bacillus subtilis/Bacillus cereus/Staphylococcus aureus/Listeria monocytogenes/Pediococcus acidilaactici/Lactococcus lactis/Pseudomonas fluorescens/Bacillus amyloliquefaciens/Staphylococcus warneri/Lactobacillus plantarum/Enterococcus faecalis/Campylobacter jejuni/Mucor plumbeus/Aspergillus niger/Penicillium spp. | Catechin | 3 | 48 | 37 |
| Rozalski et al. [40] | 2013 | Streptococcus aureus/Enterococcus faecalis | Hydralcoholic-extract/Xanthohumol/CO2-extract | 4 | 24 | 37 |
| Flesar et al. [41] | 2010 | Paenibacillus larvae | Organic-ethanolic extract/Organic-extract/Catechin | 3 | 48 | 37 |
| Bogdanova et al. [42] | 2018 | Staphylococcus aureus/Enterococcus faecalis/Staphylococcus haemolyticus/Candida albicans/Candida krusei/Candida tropicalis/Candida parapsilosis | Humulone/Lupulone/Xanthohumol/CO2-extract | 4 | 48 | 25 |
| Bhavya et al. [43] | 2020 | Staphylococcus aureus/Listeria monocytogenes/Bacillus subtilis | CO2-extract | 4 | 48 | 25 |
| Pilna et al. [44] | 2015 | Bifidobacterium dentium/Bifidobacterium longum/Lactobacillus salivarius/Streptococcus mutans/Streptococcus salivarius/Streptococcus sobrinus/Fusobacterium nucleatum/Candida albicans | Hydralcoholic-extract | 3 | 48 | 37 |
| Schmalreck et al. [45] | 1974 | Bacillus subtilis | Cohumulone/Isohumulone/Colupulone | 3 | 24 | 37 |
| Maia et al. [46] | 2019 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae/Lactobacillus fermentum/Leuconostoc mesenteroides | CO2 extract | 2 | 48 | 37 |
| Wei et al. [47] | 2014 | Mycobacterium smegmatis | Humulone | 4 | 24 | 37 |
| Kolenc et al. [48] | 2022 | Staphylococcus aureus/Lactobacillus acidophilus | Hydroacetonic extract | 4 | 24 | 37 |
| Compound | Time (h) | Strain | MIC | 95% CI | Number of Studies | Publication Bias (p-Value) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
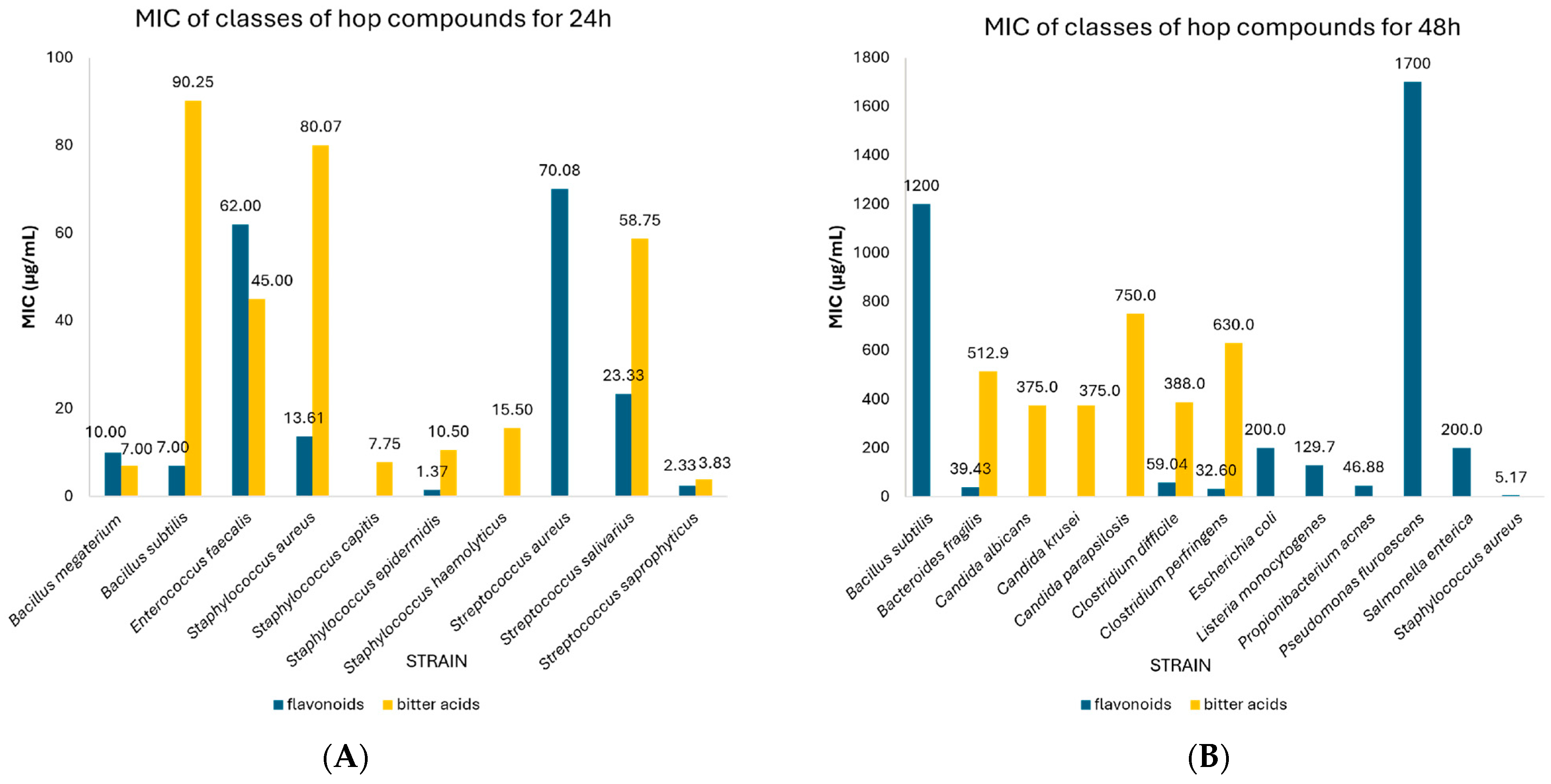
| Flavonoids | 24 | Staphylococcus epidermidis | 1.37 | 0.12–2.61 | 3 | N/A |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 13.61 | 6.41–20.81 | 15 | 0.272 | ||
| Bacillus subtilis | 7.00 | 1.12–12.88 | 3 | N/A | ||
| Bacillus megaterium | 10.00 | 9.20–10.80 | 3 | N/A | ||
| Streptococcus salivarius | 23.33 | 10.27–36.40 | 3 | N/A | ||
| Streptococcus saprophyticus | 2.33 | 1.03–3.64 | 3 | N/A | ||
| Streptococcus aureus | 70.08 | 29.81–110.36 | 6 | 0.019 | ||
| Enterococcus faecalis | 62.00 | 61.31–62.69 | 2 | N/A | ||
| 48 | Staphylococcus aureus | 5.17 | 3.14–7.20 | 3 | N/A | |
| Listeria monocytogenes | 129.68 | 0.00–353.71 | 4 | N/A | ||
| Escherichia coli | 200.0 | 199.43–200.57 | 3 | N/A | ||
| Salmonella enterica | 200.0 | 199.43–200.57 | 3 | N/A | ||
| Bacteroides fragilis | 39.43 | 27.76–51.06 | 7 | 0.001 | ||
| Clostridium perfringens | 32.60 | 18.72–46.48 | 5 | 0.010 | ||
| Clostridium difficile | 59.04 | 51.64–66.43 | 28 | 0.00 | ||
| Propionibacterium acnes | 46.88 | 16.25–77.50 | 2 | N/A | ||
| Bacillus subtilis | 1200.0 | 569.96–1830.0 | 3 | N/A | ||
| Pseudomonas fluroescens | 1700.0 | 1699.2–1700.8 | 2 | N/A | ||
| Bitter acids | 24 | Staphylococcus epidermidis | 10.50 | 0.00–23.54 | 4 | N/A |
| Staphylococcus capitis | 7.75 | 0.00–21.96 | 2 | N/A | ||
| Staphylococcus aureus | 80.07 | 40.13–120.0 | 25 | 0.185 | ||
| Bacillus subtilis | 90.25 | 0.00–255.52 | 12 | 0.587 | ||
| Bacillus megaterium | 7.00 | 3.51–10.49 | 4 | N/A | ||
| Streptococcus salivarius | 58.75 | 11.01–106.49 | 4 | N/A | ||
| Streptococcus saprophyticus | 3.83 | 1.71–5.94 | 6 | N/A | ||
| Enterococcus faecalis | 45.00 | 15.60–74.4 | 3 | N/A | ||
| Staphylococcus haemolyticus | 15.50 | 0.00–43.92 | 2 | N/A | ||
| 48 | Bacteroides fragilis | 512.90 | 287.91–737.80 | 14 | 0.001 | |
| Clostridium perfringens | 630.0 | 323.01–936.99 | 10 | 0.003 | ||
| Clostridium difficile | 388.0 | 274.54–501.46 | 56 | 0.00 | ||
| Candida albicans | 375.0 | 130.01–620.0 | 2 | N/A | ||
| Candida krusei | 375.0 | 130.01–620.0 | 2 | N/A | ||
| Candida parapsilosis | 750.0 | 260.01–1240.0 | 2 | N/A | ||
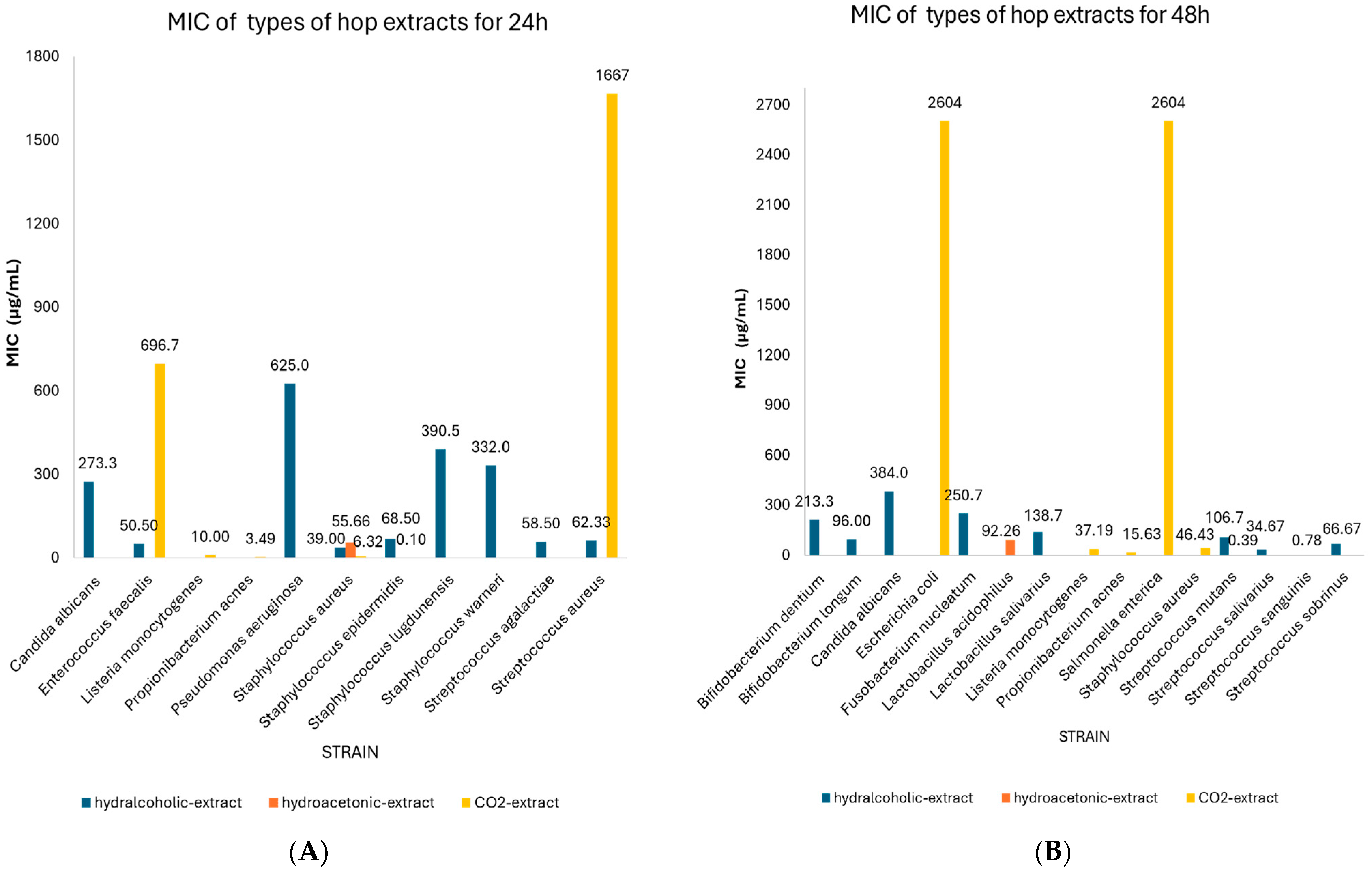
| CO2-extract | 24 | Propionibacterium acnes | 3.49 | 2.73–4.25 | 4 | N/A |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 6.32 | 2.21–10.43 | 6 | 0.03 | ||
| Listeria monocytogenes | 10.00 | 9.31–10.69 | 2 | N/A | ||
| Staphylococcus epidermidis | 0.10 | 0.00–0.90 | 2 | N/A | ||
| Streptococcus aureus | 1666.7 | 1013.4–2320.0 | 3 | N/A | ||
| Enterococcus faecalis | 696.67 | 0.00–1974.0 | 3 | N/A | ||
| 48 | Staphylococcus aureus | 46.43 | 0.00–99.10 | 7 | 0.135 | |
| Listeria monocytogenes | 37.19 | 0.00–90.93 | 7 | 0.224 | ||
| Escherichia coli | 2604.2 | 1041.29–4167.1 | 6 | 0.022 | ||
| Salmonella enterica | 2604.2 | 1041.29–4167.1 | 6 | 0.022 | ||
| Streptococcus mutans | 0.39 | 0.00–1.19 | 2 | N/A | ||
| Streptococcus sanguinis | 0.78 | 0.00–1.58 | 2 | N/A | ||
| Propionibacterium acnes | 15.63 | 15.06–16.19 | 4 | N/A | ||
| Hydralcoholic extract | 24 | Enterococcus faecalis | 50.50 | 27.96–73.04 | 2 | N/A |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 39.00 | 38.20–39.80 | 2 | N/A | ||
| Staphylococcus epidermidis | 68.50 | 10.68–126.32 | 2 | N/A | ||
| Staphylococcus lugdunensis | 390.50 | 0.00–850.11 | 2 | N/A | ||
| Staphylococcus warneri | 332.0 | 0.00–906.27 | 2 | N/A | ||
| Streptococcus agalactiae | 58.50 | 20.28–96,18 | 2 | N/A | ||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 625.0 | 624.20–625.80 | 2 | N/A | ||
| Candida albicans | 273.33 | 0.00–624.26 | 3 | N/A | ||
| Streptococcus aureus | 62.33 | 0.92–123,75 | 3 | N/A | ||
| 48 | Bifidobacteriumm dentium | 213.33 | 160.44–266.22 | 6 | 0.001 | |
| Bifidobacterium longum | 96.00 | 67.95–124.05 | 6 | 0.001 | ||
| Lactobacillus salivarius | 138.67 | 88.32–189.02 | 6 | 0.003 | ||
| Streptococcus mutans | 106.67 | 80.22–133,11 | 6 | 0.001 | ||
| Streptococcus salivarius | 34.67 | 22.08–47.25 | 6 | 0.003 | ||
| Streptococcus sobrinus | 66.67 | 38.14–95,20 | 6 | 0.006 | ||
| Fusobacterium nucleatum | 250.67 | 154.91–346.42 | 12 | 0.00 | ||
| Candida albicans | 384.0 | 239.16–528.84 | 4 | N/A | ||
| Hydroacetonic extract | 24 | Staphylococcus aureus | 55.66 | 12.15–99.16 | 14 | 0.026 |
| 48 | Lactobacillus acidophilus | 92.26 | 71.86–112.66 | 14 | 0.00 |
| Class of Compound | Compound | Time (h) | Strain | MIC | 95% CI | Number of Studies | Publication Bias (p-Value) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
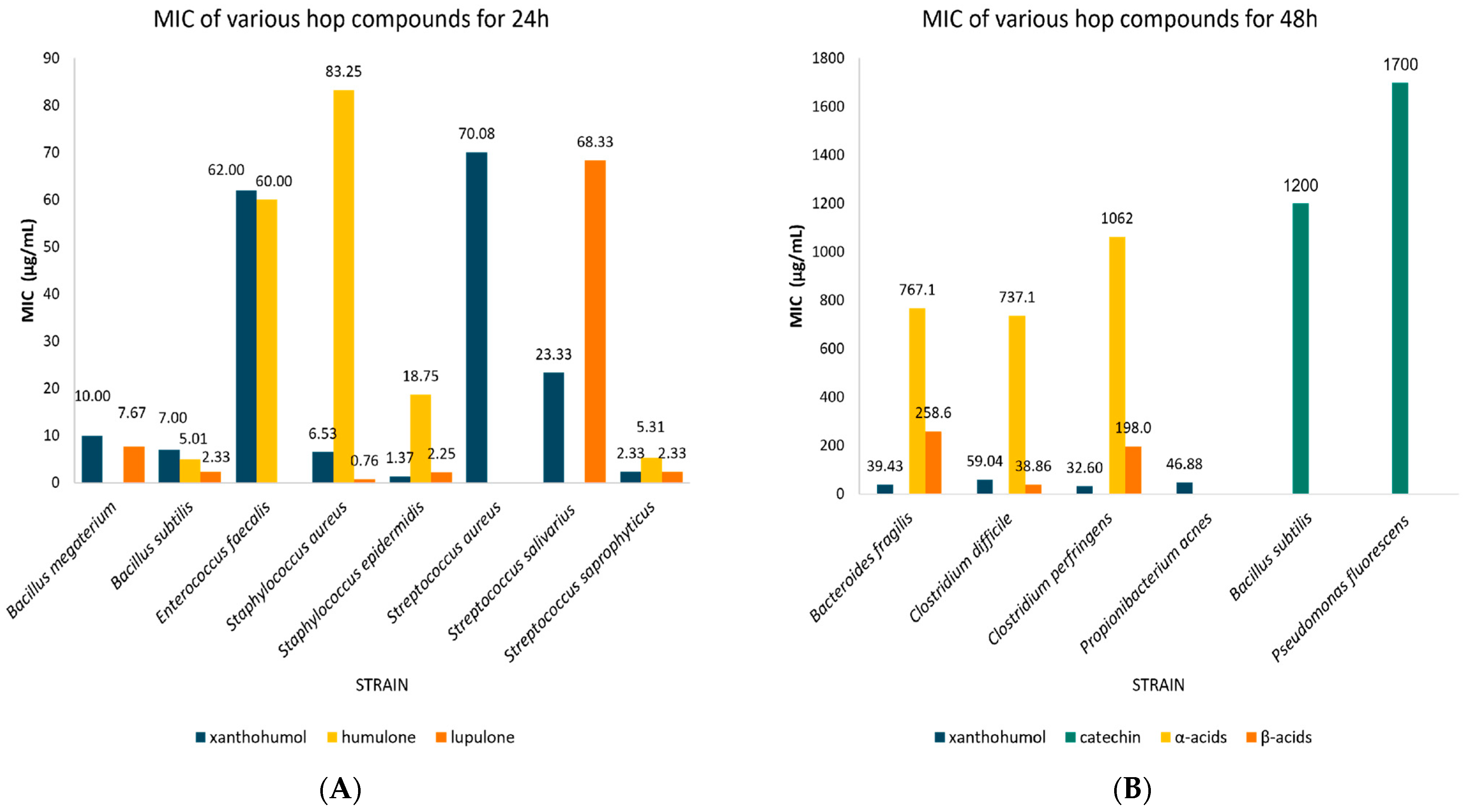
| Flavonoids | Xanthohumol | 24 | Staphylococcus epidermidis | 1.37 | 0.12–2.61 | 3 | N/A |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 6.53 | 3.05–10.01 | 10 | 0.473 | |||
| Bacillus subtilis | 7.00 | 1.12–12.88 | 3 | N/A | |||
| Bacillus megaterium | 10.00 | 9.20–10.80 | 3 | N/A | |||
| Streptococcus salivarius | 23.33 | 10.27–36.40 | 3 | N/A | |||
| Streptococcus saprophyticus | 2.33 | 1.03–3.64 | 3 | N/A | |||
| Streptococcus aureus | 70.08 | 29.81–110.36 | 6 | 0.019 | |||
| Enterococcus faecalis | 62.00 | 61.31–62.96 | 2 | N/A | |||
| 48 | Bacteroides fragilis | 39.43 | 27.80–51.06 | 7 | 0.001 | ||
| Clostridium perfringens | 32.60 | 18.72–46.48 | 5 | 0.010 | |||
| Clostridium difficile | 59.04 | 51.64–66.43 | 28 | 0.00 | |||
| Propionibacterium acnes | 46.88 | 16.25–77.50 | 2 | N/A | |||
| Catechin | 48 | Bacillus subtilis | 1200.0 | 569.96–1830.0 | 3 | N/A | |
| Pseudomonas fluorescens | 1700.0 | 1698.9–1701.1 | 2 | N/A | |||
| Bitter acids | Humulone | 24 | Staphylococcus epidermidis | 18.75 | 0.00–40.80 | 2 | N/A |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 83.25 | 39.87–126.63 | 8 | 0.323 | |||
| Bacillus subtilis | 5.01 | 0.33–9.69 | 4 | N/A | |||
| Streptococcus saprophyticus | 5.31 | 1.20–9.42 | 3 | N/A | |||
| Enterococcus faecalis | 60.00 | 59.31–60.69 | 2 | N/A | |||
| Cohumulone | 24 | Staphylococcus aureus | 273.75 | 196.82–350.68 | 4 | N/A | |
| α-acids (collectively) | 48 | Bacteroides fragilis | 767.14 | 408.98–1125.3 | 7 | 0.006 | |
| Clostridium perfringens | 1062.0 | 808.46–1315.5 | 5 | 0.001 | |||
| Clostridium difficile | 737.14 | 604.15–870.14 | 28 | 0.00 | |||
| Lupulone | 24 | Staphylococcus epidermidis | 2.25 | 0.00–5.68 | 2 | N/A | |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 0.76 | 0.38–1.15 | 9 | 0.945 | |||
| Bacillus subtilis | 2.33 | 1.03–3.64 | 3 | N/A | |||
| Bacillus megaterium | 7.67 | 3.093–12.24 | 3 | N/A | |||
| Streptococcus salivarius | 68.33 | 6.27–130.40 | 3 | N/A | |||
| Streptococcus saprophyticus | 2.33 | 1.03–3.64 | 3 | N/A | |||
| β-acids (collectively) | 48 | Bacteroides fragilis | 258.57 | 168.10–349.04 | 7 | 0.001 | |
| Clostridium perfringens | 198.00 | 161.123–234.877 | 5 | 0.00 | |||
| Clostridium difficile | 38.39 | 39.40–130.10 | 28 | 0.00 |
| Compound | Time (h) | Food Spoilage/Non-Food Spoilage | MIC | 95% CI | Number of Studies | Publication Bias (p-Value) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flavonoids | 24 | Food spoilage | 22.81 | 11.54–34.08 | 33 | 0.550 | |
| Non-food spoilage | 21.68 | 0.00–47.71 | 6 | 0.00 | |||
| 48 | Food spoilage | 242.25 | 9.61–474.88 | 26 | 0.00 | ||
| Non-food spoilage | 263.28 | 130.45–396.11 | 49 | 0.190 | |||
| Xanthohumol | 24 | Food spoilage | 21.92 | 9.02–34.83 | 28 | 0.632 | |
| Non-food spoilage | 21.68 | 0.00–47.71 | 6 | 0.00 | |||
| 48 | Food spoilage | 23.46 | 8.76–38.15 | 7 | 0.060 | ||
| Non-food spoilage | 54.32 | 48.10–60.54 | 40 | 0.643 | |||
| Catechin | 48 | Food spoilage | 700.0 | 271.78–1128.2 | 7 | 0.265 | |
| Non-food spoilage | 1192.0 | 658.25–1725.8 | 9 | 0.038 | |||
| Bitter acids | 24 | Food spoilage | 66.09 | 3.23–128.59 | 51 | 0.333 | |
| Non-food spoilage | 20.32 | 6.64–34.0 | 11 | 0.090 | |||
| 48 | Food spoilage | 573.64 | 277.54–869.74 | 11 | 0.410 | ||
| Non-food spoilage | 427.38 | 332.38–522.01 | 77 | 0.00 | |||
| Humulone | 24 | Food spoilage | 43.35 | 20.31–66.39 | 17 | 0.054 | |
| Non-food spoilage | 33.75 | 15.96–51.55 | 6 | 0.059 | |||
| 48 | Non-food spoilage | 500.0 | 153.52–846.48 | 4 | N/A | ||
| Cohumulone | 24 | Food spoilage | 273.75 | 196.82–350.68 | 4 | N/A | |
| Lupulone | 24 | Food spoilage | 12.40 | 2.66–22.14 | 21 | 0.157 | |
| Non-food spoilage | 4.20 | 0.00–9.97 | 5 | 0.349 | |||
| 48 | Non-food spoilage | 666.67 | 340.01–993.33 | 3 | N/A | ||
| CO2-extract | 24 | Food spoilage | 421.91 | 0.95–842.87 | 12 | 0.296 | |
| Non-food spoilage | 260.35 | 0.00–625.64 | 12 | 0.283 | |||
| 48 | Food spoilage | 1028.1 | 448.06–1608.1 | 31 | 0.252 | ||
| Non-food spoilage | 257.81 | 10.61–505.01 | 8 | 0.044 | |||
| Hydralcoholic extract | 24 | Food spoilage | 52.65 | 28.39–76.86 | 8 | 0.573 | |
| Non-food spoilage | 290.94 | 163.21–418.68 | 18 | 0.349 | |||
| 48 | Food spoilage | 86.67 | 64.58–108.75 | 24 | 0.00 | ||
| Non-food spoilage | 238.35 | 180.99–295.71 | 29 | 0.00 | |||
| Hydroacetonic extract | 24 | Food spoilage | 55.66 | 12.15–99.16 | 14 | 0.026 | |
| 48 | Food spoilage | 92.26 | 71.86–112.66 | 14 | 0.00 |
| Compound | Time (h) | Probiotic | MIC | 95% CI | Number of Studies | Publication Bias (p-Value) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flavonoids | 24 | No probiotic | 25.21 | 12.67–37.74 | 33 | 0.009 | |
| Probiotic | 8.47 | 4.70–12.30 | 6 | 0.627 | |||
| 48 | No probiotic | 213.28 | 110.83–315.72 | 62 | 0.691 | ||
| Probiotic | 459.69 | 85.84–833.55 | 13 | 0.065 | |||
| Xanthohumol | 24 | No probiotic | 24.75 | 10.17–39.33 | 28 | 0.015 | |
| Probiotic | 8.49 | 4.70–12.27 | 6 | 0.627 | |||
| 48 | No probiotic | 51.52 | 44.42–56.11 | 40 | 0.021 | ||
| Probiotic | 39.43 | 27.79–51.06 | 7 | 0.001 | |||
| Catechin | 48 | No probiotic | 992.8 | 564.73–1420.9 | 10 | 0.323 | |
| Probiotic | 950.0 | 428.99–1471.0 | 6 | 0.949 | |||
| Bitter acids | 24 | No probiotic | 53.98 | 30.39–77.57 | 46 | 0.304 | |
| Probiotic | 69.44 | 0.00–209.31 | 16 | 0.564 | |||
| 48 | No probiotic | 432.95 | 354.94–535.50 | 74 | 0.492 | ||
| Probiotic | 512.86 | 287.91–737.8 | 14 | 0.001 | |||
| Humulone | 24 | No probiotic | 50.81 | 27.03–74.58 | 18 | 0.198 | |
| Probiotic | 5.01 | 0.97–9.05 | 5 | 0.549 | |||
| 48 | No probiotic | 500.0 | 153.52–846.48 | 4 | N/A | ||
| Cohumulone | 24 | No probiotic | 273.75 | 196.82–350.68 | 3 | N/A | |
| Lupulone | 24 | No probiotic | 11.98 | 0.71–23.25 | 20 | 0.046 | |
| Probiotic | 4.93 | 2.71–7.15 | 6 | 0.071 | |||
| 48 | No probiotic | 502.5 | 140.19–846.81 | 4 | N/A | ||
| CO2-extract | 24 | No probiotic | 326.46 | 14.29–638.63 | 22 | 0.206 | |
| Probiotic | 502.5 | 0.00–1477.6 | 2 | N/A | |||
| 48 | No probiotic | 892.11 | 385.11–1399.1 | 38 | 0.108 | ||
| Hydralcoholic extract | 24 | No probiotic | 217.62 | 120.96–314.27 | 26 | 0.143 | |
| 48 | No probiotic | 180.11 | 124.26–235.97 | 35 | 0.00 | ||
| Probiotic | 149.33 | 115.7–182.97 | 18 | 0.00 | |||
| Hydroacetonic extract | 24 | No probiotic | 55.66 | 12.15–99.16 | 14 | 0.026 | |
| 48 | Probiotic | 92.26 | 71.86–112.66 | 14 | 0.00 |
| Compound | Time (h) | Gram | MIC | 95% CI | Number of Studies | Publication Bias (p-Value) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flavonoids | 24 | Positive | 22.64 | 12.42–32.85 | 39 | 0.667 |
| 48 | Positive | 182.91 | 52.78–313.0 | 63 | 0.00 | |
| Negative | 427.6 | 70.30–784.9 | 10 | 0.840 | ||
| Bitter acids | 24 | Positive | 57.97 | 4.19–111.8 | 62 | 0.206 |
| 48 | Positive | 432.95 | 333.4–532.5 | 74 | 0.492 | |
| Negative | 512.86 | 287.9–737.8 | 14 | 0.001 | ||
| CO2-extract | 24 | Positive | 341.13 | 73.5–608.8 | 24 | 0.365 |
| 48 | Positive | 870.01 | 393.2–1347 | 39 | 0.360 | |
| Hydralcoholic extract | 24 | Positive | 143.55 | 61.69–225.4 | 22 | 0.330 |
| Negative | 625.0 | 624.4–625.6 | 4 | N/A | ||
| 48 | Positive | 136.8 | 101.2–172.4 | 40 | 0.00 | |
| Negative | 270.8 | 174.3–367.3 | 13 | 0.00 | ||
| Hydroacetonic extract | 24 | Positive | 55.66 | 12.15–99.16 | 14 | 0.026 |
| 48 | Positive | 92.26 | 71.86–112.7 | 14 | 0.00 |
| Compound | Time (h) | Probiotic | MIC | 95% CI | Number of Studies | Publication Bias (p-Value) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flavonoids | 24 | Facultative anaerobic | 23.94 | 12.20–35.68 | 36 | 0.006 |
| Aerobic | 7 | 1.12–12.88 | 3 | N/A | ||
| 48 | Facultative anaerobic | 287.2 | 48.54–525.88 | 16 | 0.807 | |
| Aerobic | 642.9 | 273.8–1012 | 13 | 0.059 | ||
| Anaerobic | 59.23 | 45.99–58.46 | 43 | 0.749 | ||
| Bitter acids | 24 | Facultative anaerobic | 50.22 | 28.04–72.40 | 50 | 0.473 |
| Aerobic | 90.25 | 0–255.5 | 12 | 0.587 | ||
| 48 | Facultative anaerobic | 375 | 130.0–620.0 | 2 | N/A | |
| Anaerobic | 438.5 | 343.7–533.4 | 82 | 0.00 | ||
| Aerobic | 627.5 | 214.3–1040 | 4 | N/A | ||
| CO2-extract | 24 | Facultative anaerobic | 408.7 | 98.99–718.3 | 20 | 0.272 |
| Anaerobic | 3.49 | 2.73–4.25 | 4 | N/A | ||
| 48 | Facultative anaerobic | 44.09 | 7.92–80.25 | 19 | 0.278 | |
| Aerobic | 2.19 | 1197–3173 | 15 | 0.022 | ||
| Anaerobic | 62.5 | 0–162.2 | 5 | |||
| Hydralcoholic-extract | 24 | Facultative anaerobic | 190.0 | 94.481–285.4 | 23 | 0.196 |
| Aerobic | 429.7 | 46.820–812.5 | 3 | N/A | ||
| 48 | Facultative anaerobic | 142.3 | 89.950–194.7 | 29 | 0.00 | |
| Anaerobic | 202.7 | 147.354–257.9 | 24 | 0.00 | ||
| Hydroacetonic-extract | 24 | Facultative anaerobic | 55.66 | 12.15–99.16 | 14 | 0.026 |
| 48 | Facultative anaerobic | 92.26 | 71.86–112.66 | 14 | 0.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kiofentzoglou, D.; Andronidou, E.M.; Kontou, P.I.; Bagos, P.G.; Braliou, G.G. Antimicrobial Activity of Chemical Hop (Humulus lupulus) Compounds: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 7806. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147806
Kiofentzoglou D, Andronidou EM, Kontou PI, Bagos PG, Braliou GG. Antimicrobial Activity of Chemical Hop (Humulus lupulus) Compounds: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(14):7806. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147806
Chicago/Turabian StyleKiofentzoglou, Despina, Elisavet M. Andronidou, Panagiota I. Kontou, Pantelis G. Bagos, and Georgia G. Braliou. 2025. "Antimicrobial Activity of Chemical Hop (Humulus lupulus) Compounds: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Applied Sciences 15, no. 14: 7806. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147806
APA StyleKiofentzoglou, D., Andronidou, E. M., Kontou, P. I., Bagos, P. G., & Braliou, G. G. (2025). Antimicrobial Activity of Chemical Hop (Humulus lupulus) Compounds: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Applied Sciences, 15(14), 7806. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147806








