An Intelligent Thermal Management Strategy for a Data Center Prototype Based on Digital Twin Technology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. IDC Prototype Details and Fast Thermal Reconstruction Method
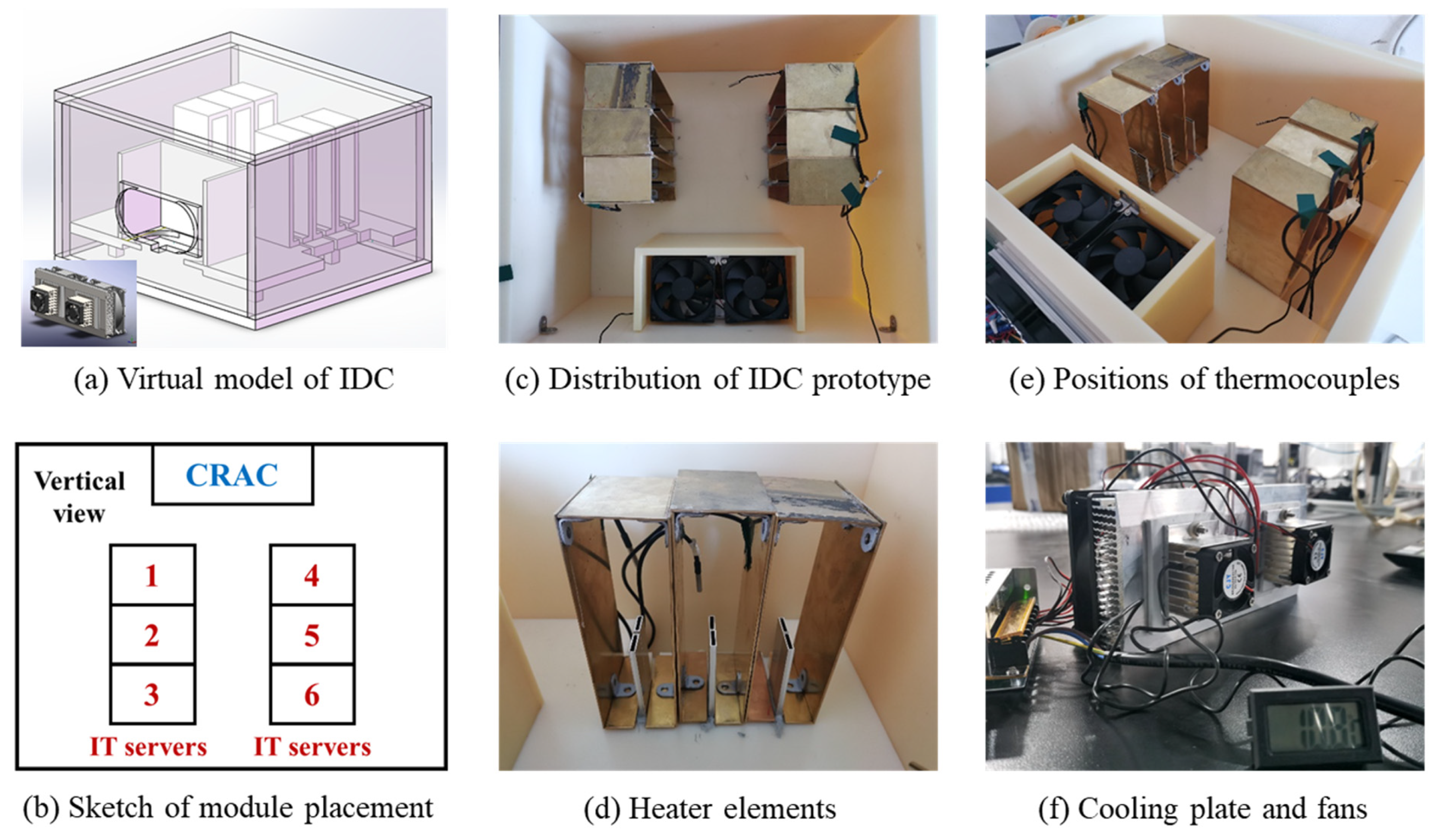
2.1. Experimental Setup of IDC Prototype
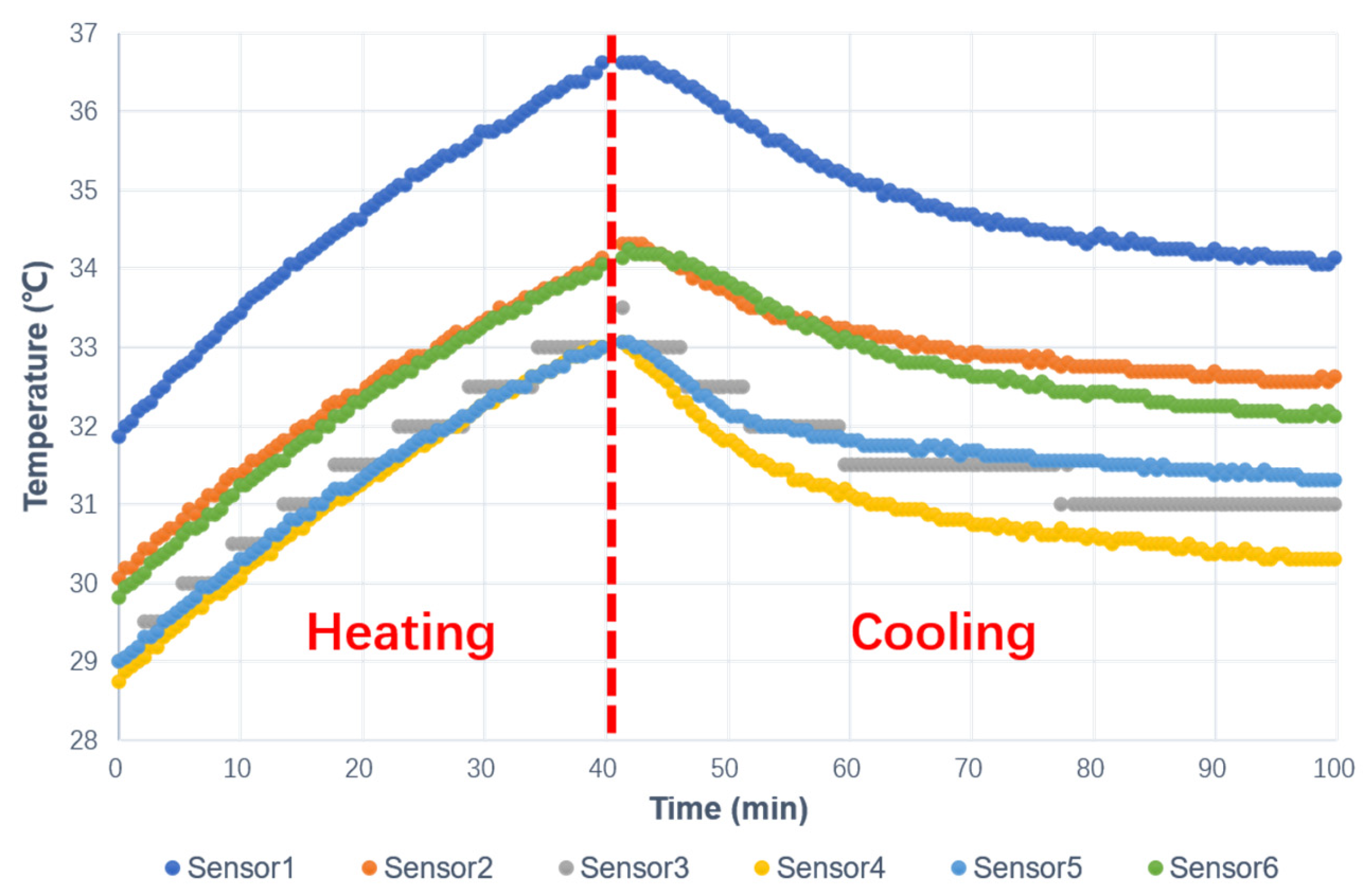
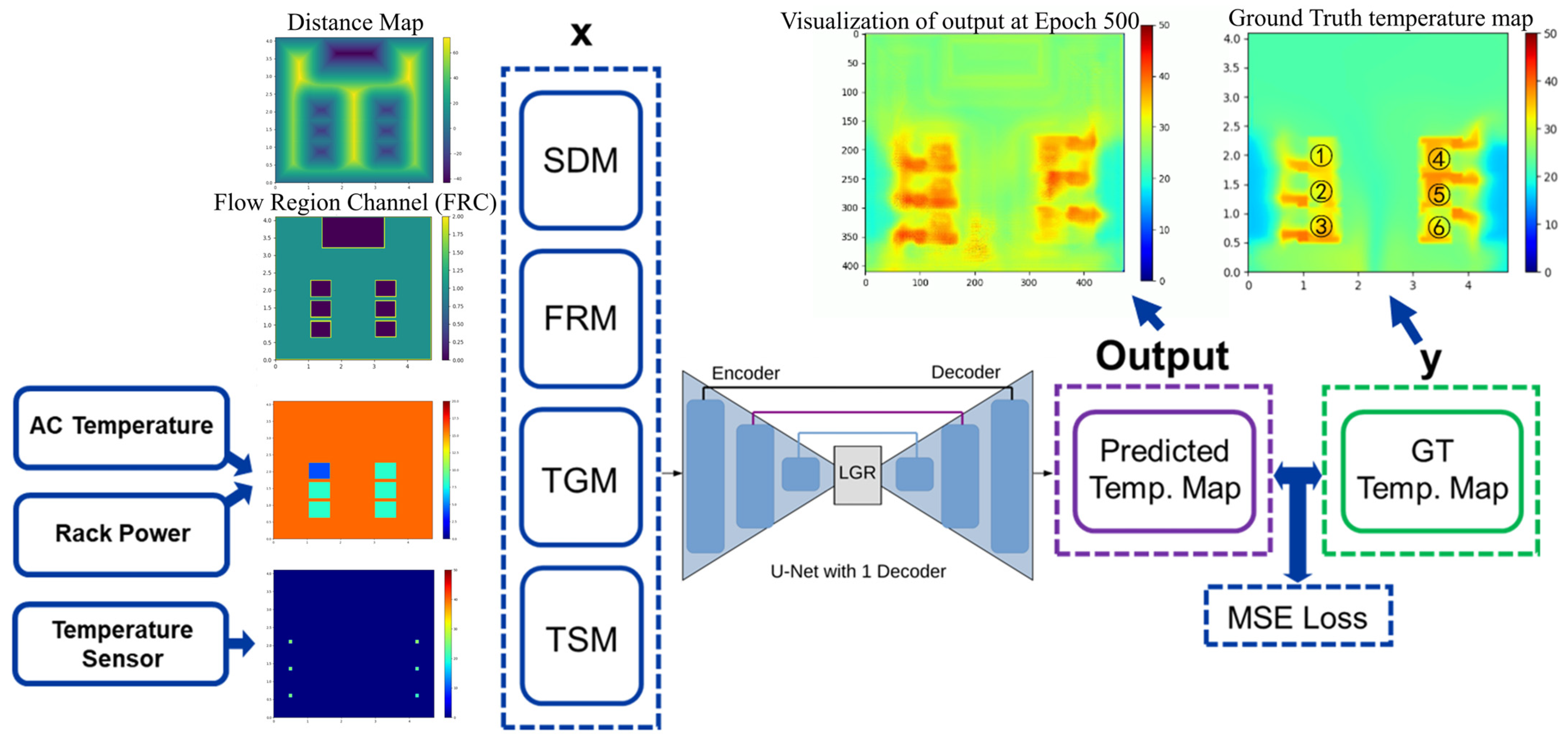
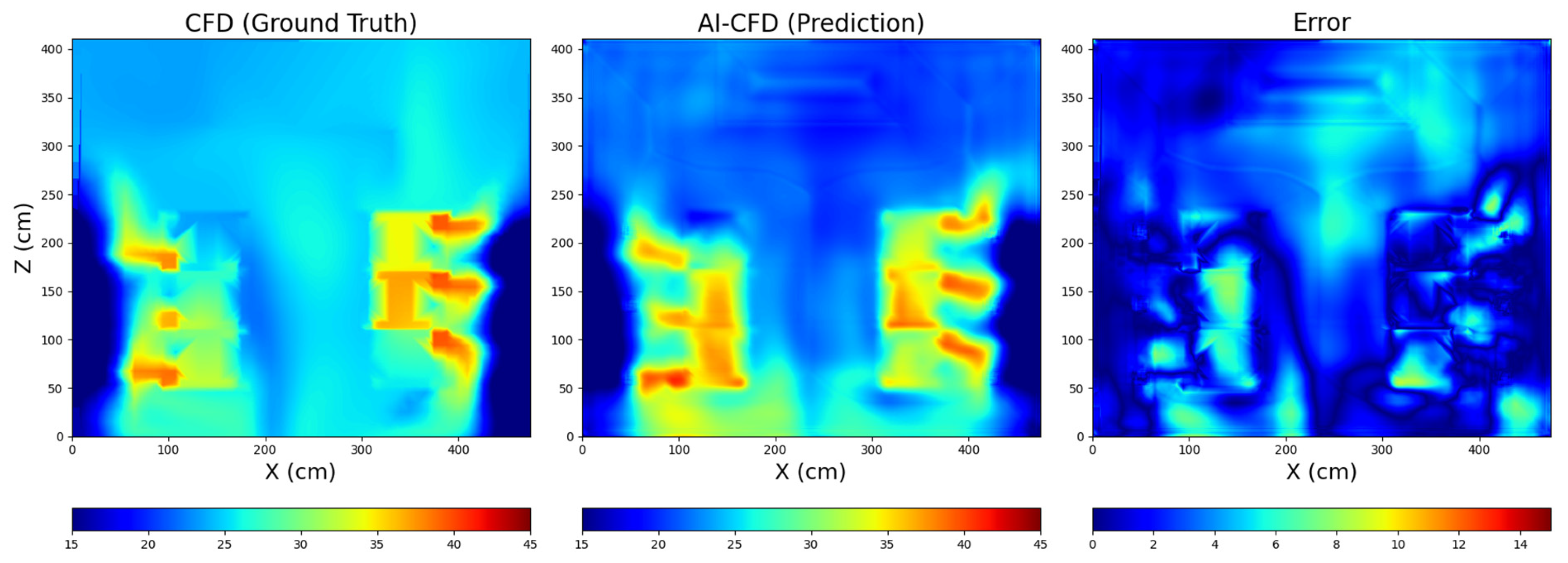
2.2. Real-Time Thermal Environment Reconstruction Method
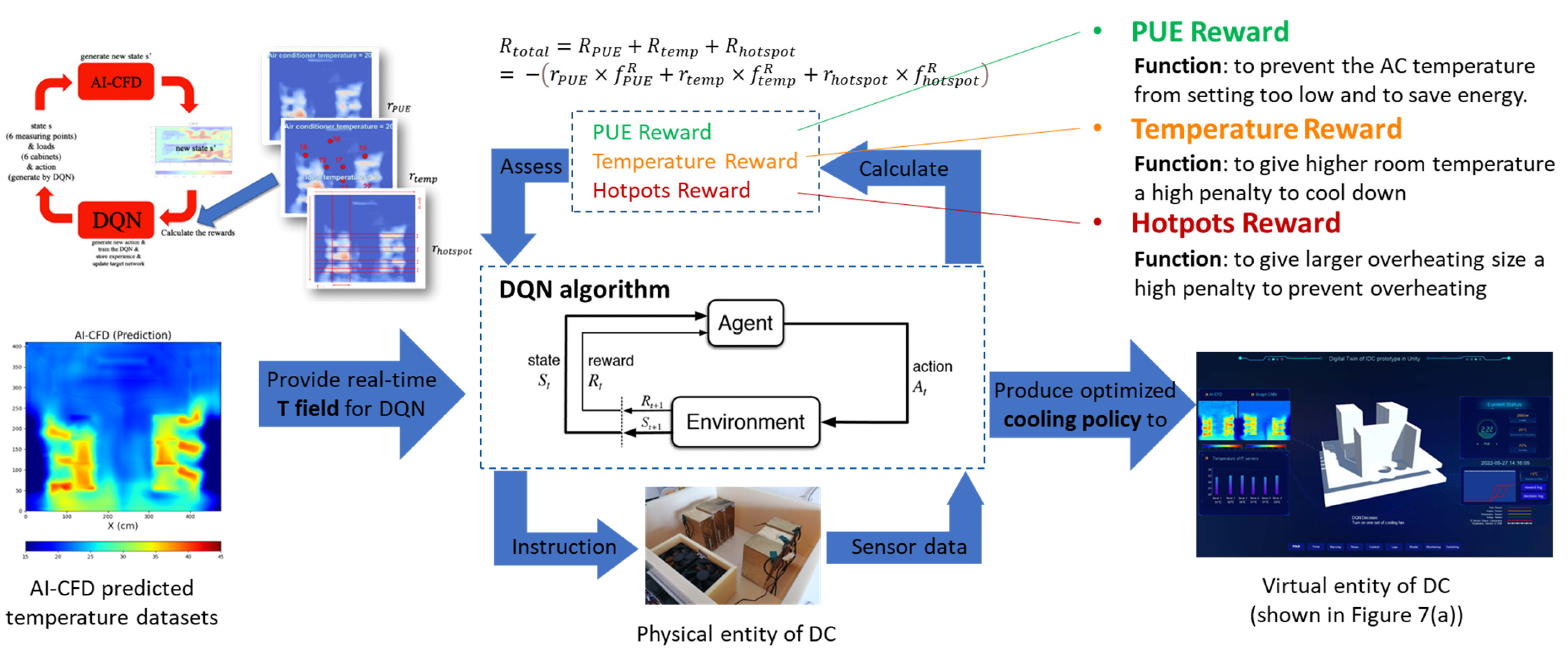
3. DQN-Based Intelligent Thermal Management Technique
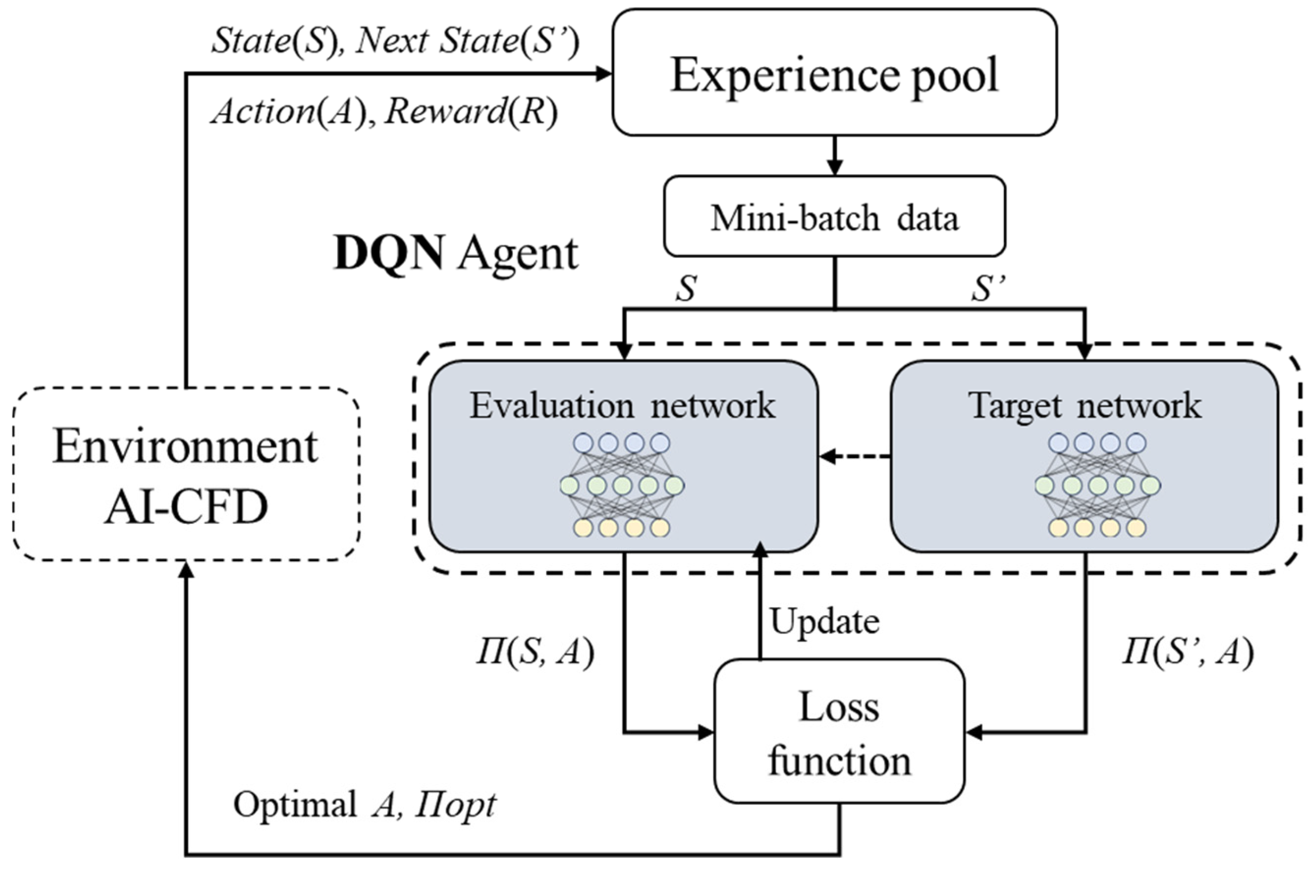
3.1. The Architecture Design of the DQN Decision-Making Agent
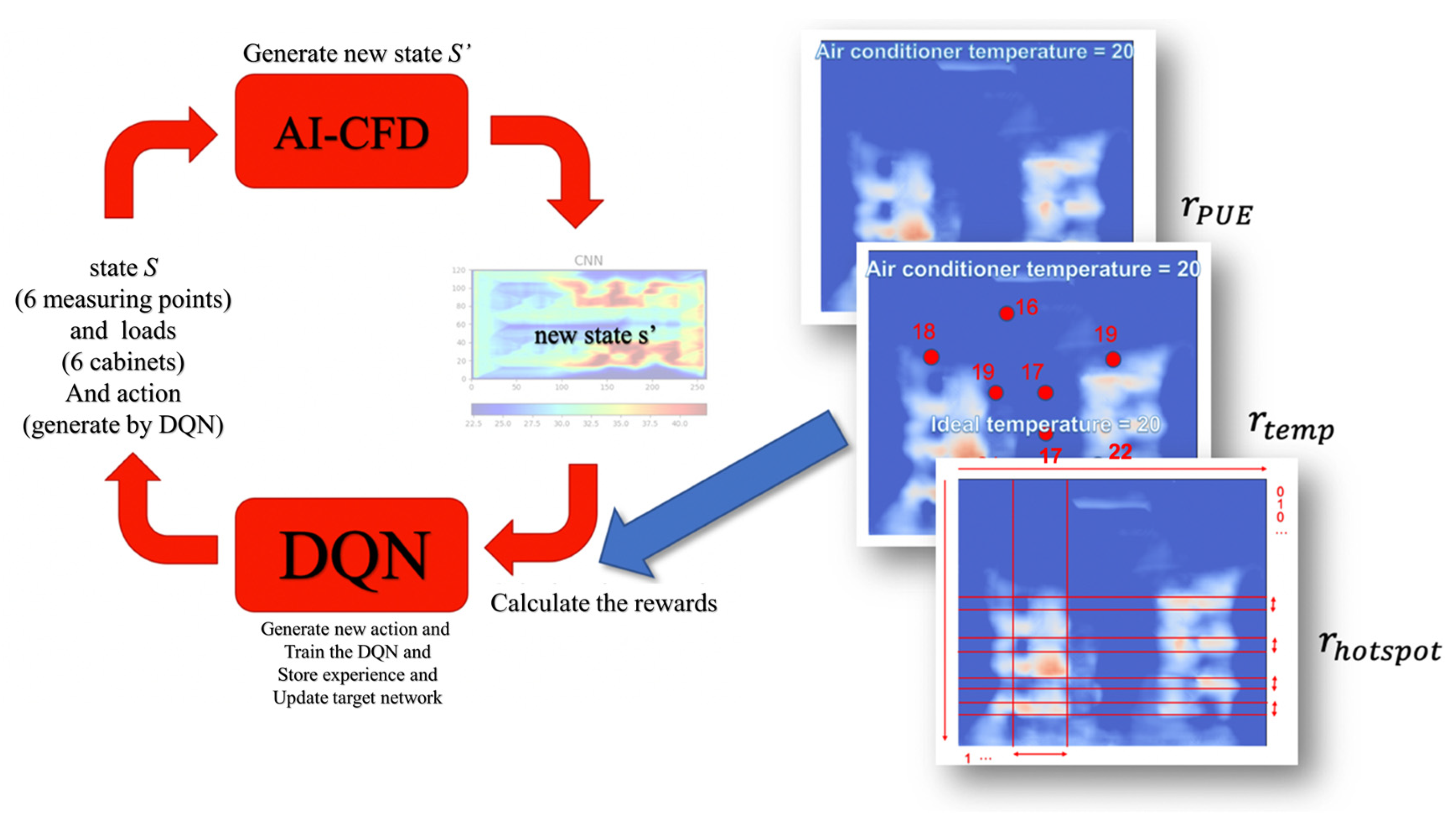
3.2. Reward Details
3.2.1. Reward of PUE Reduction
3.2.2. Reward of Temperature Uniformity
3.2.3. Reward of Local Hotspot Inhibition
3.2.4. Total Reward
4. A Case Study: DQN-Based Intelligent Thermal Management System
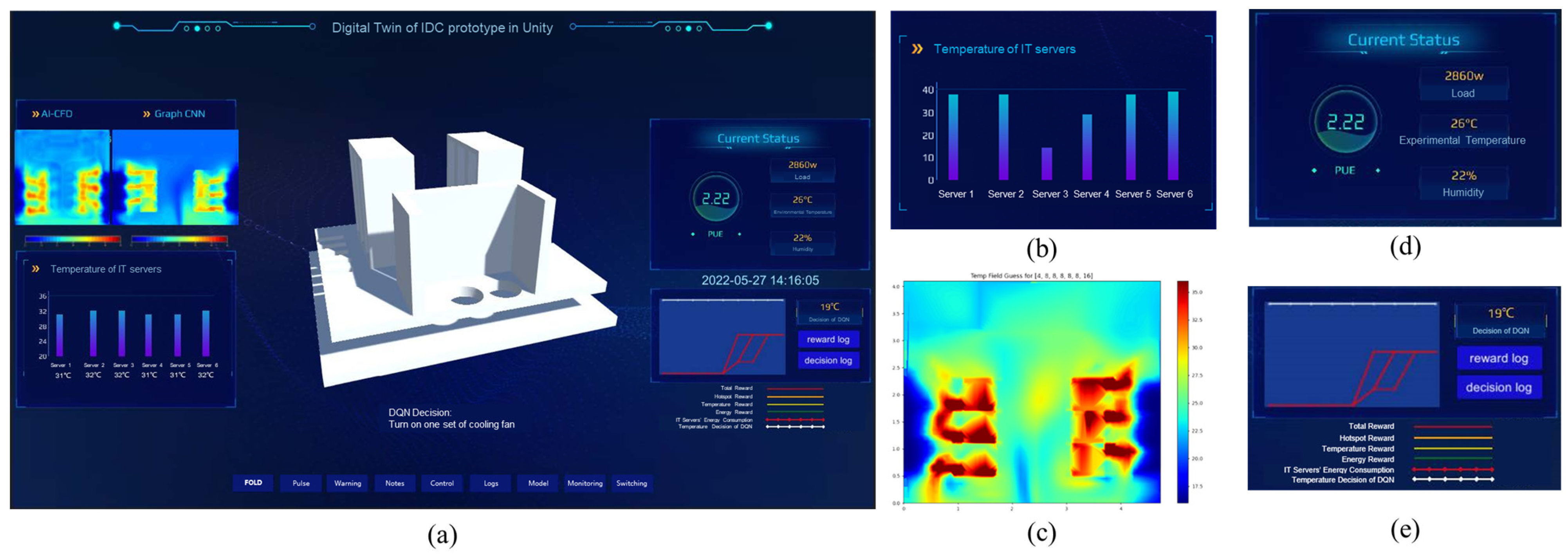
4.1. Implementation of Digital Twin Platform for IDC Prototype
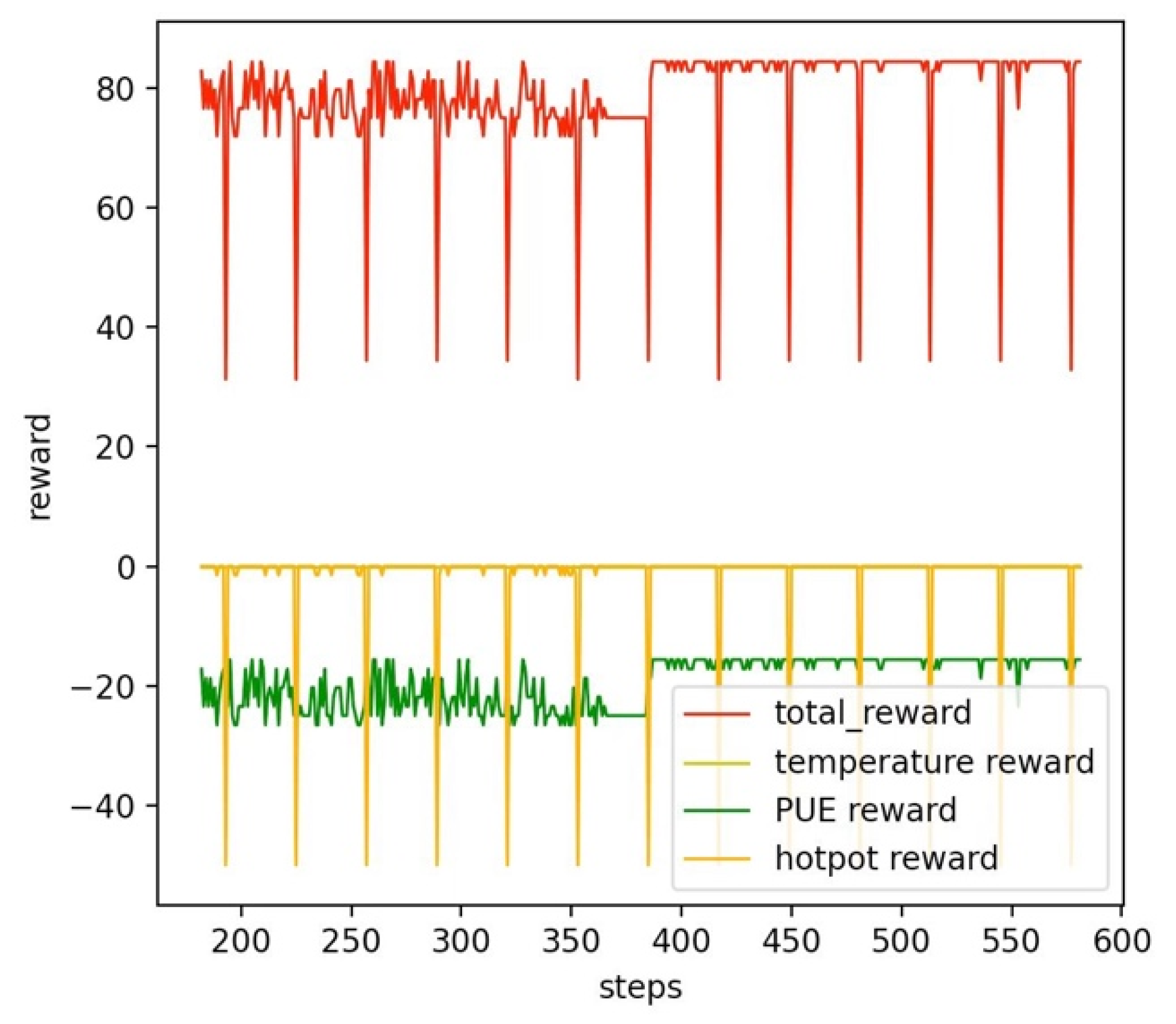
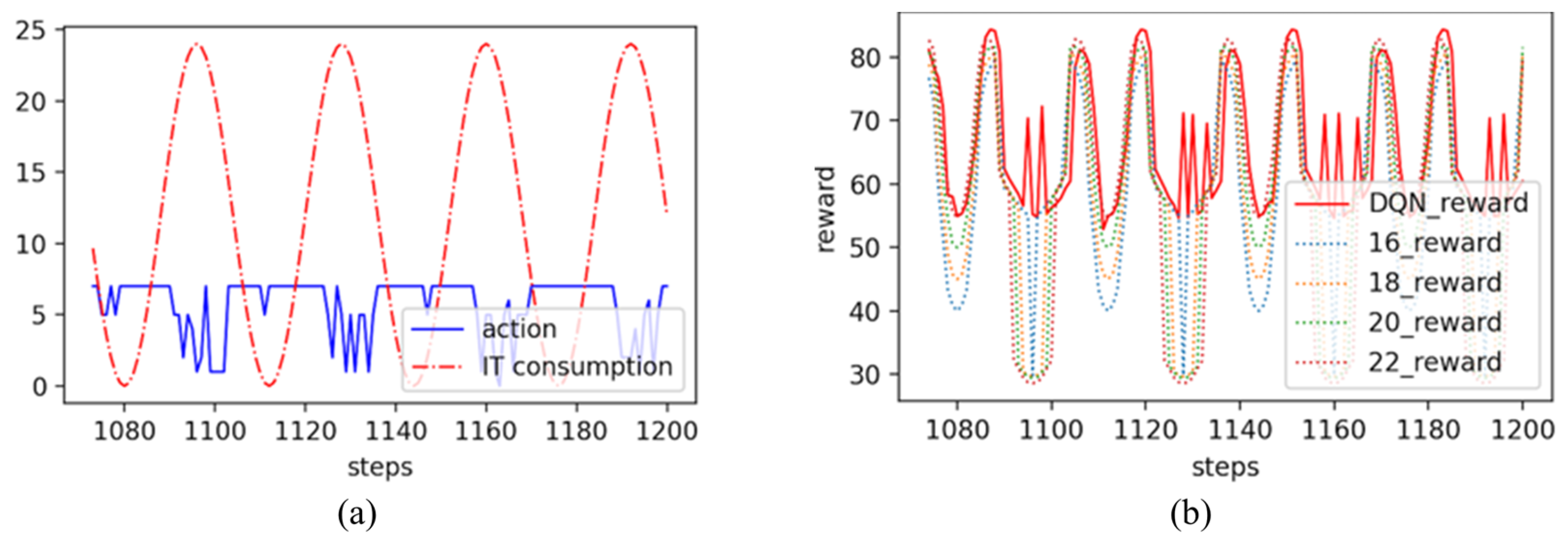
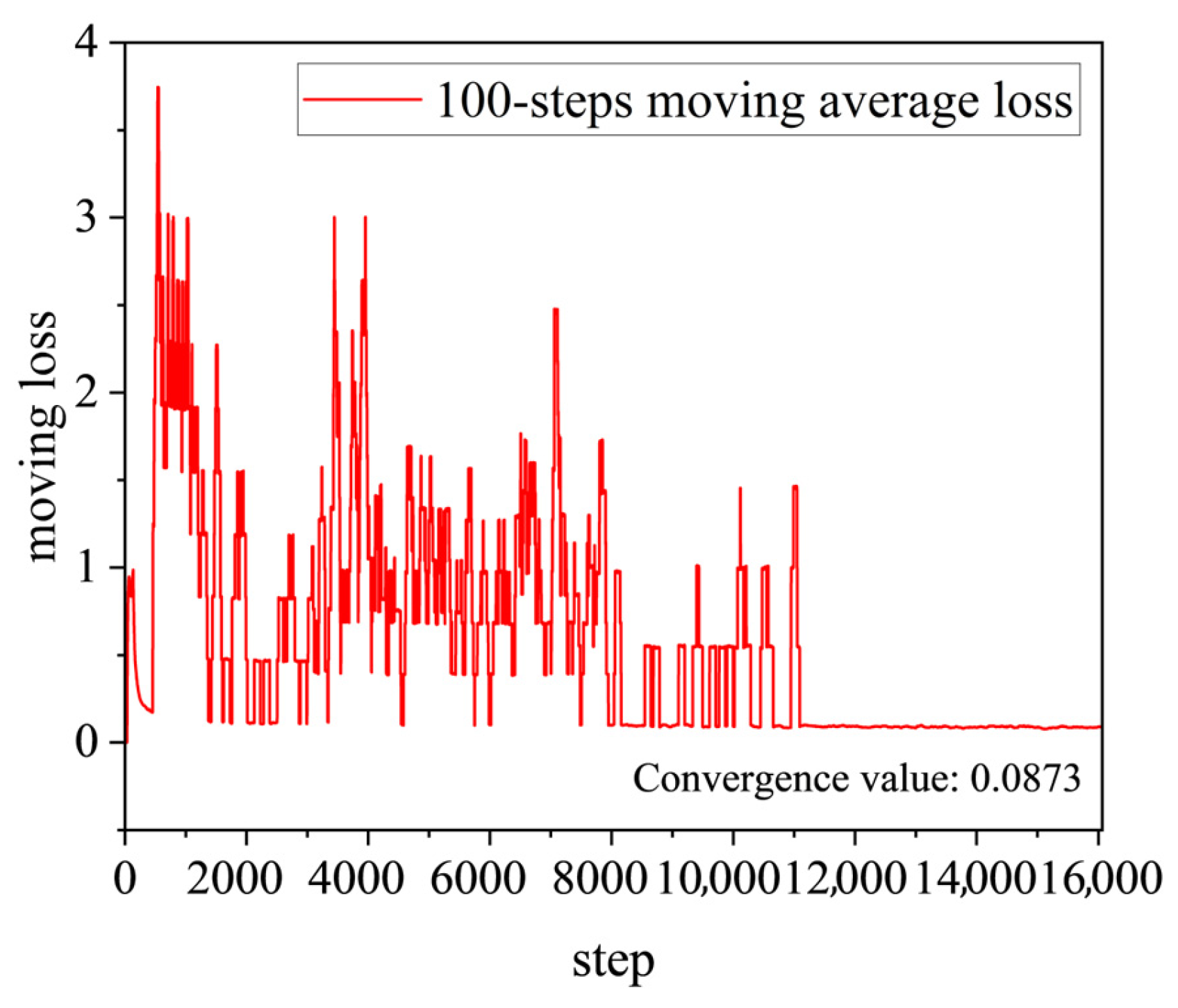
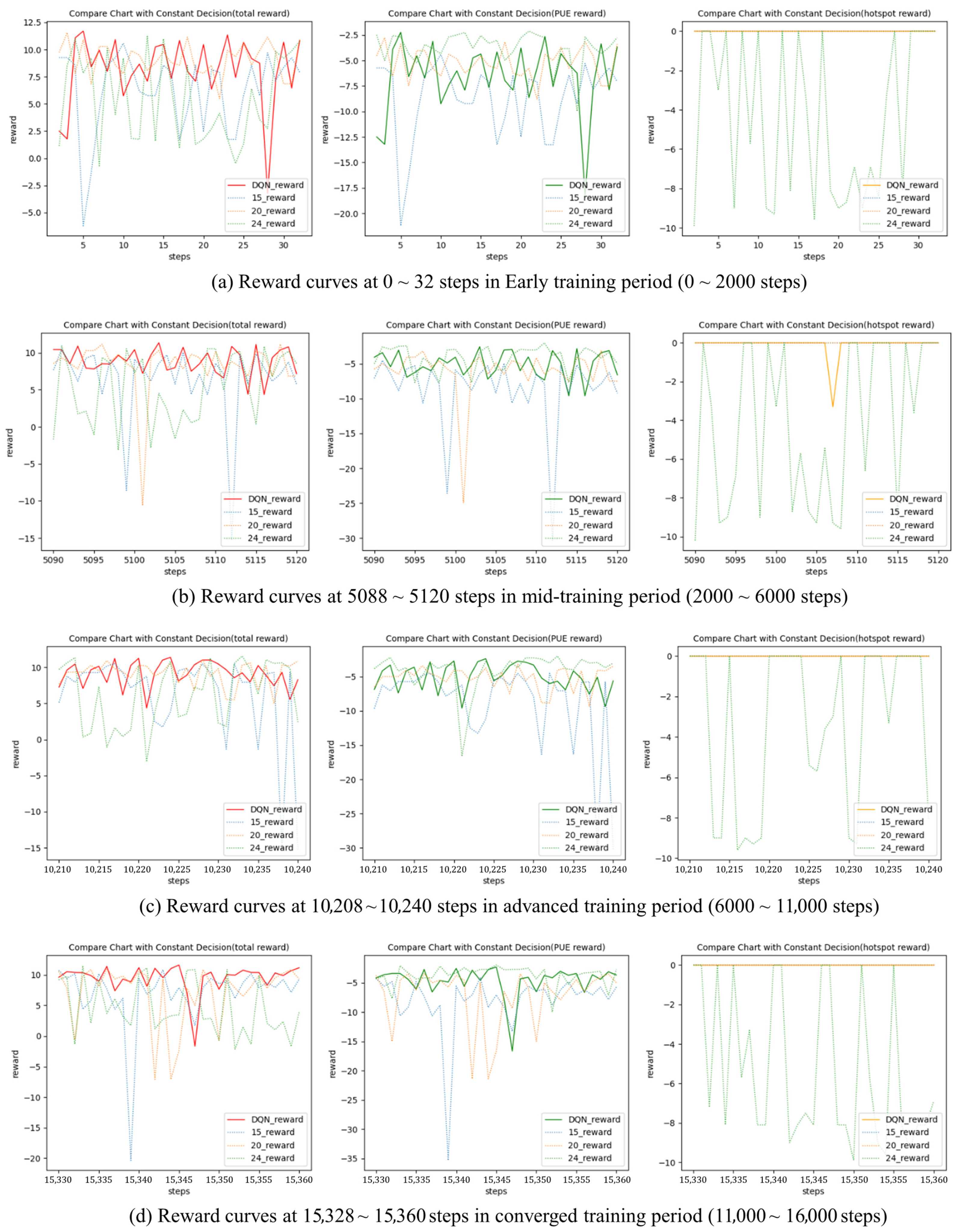
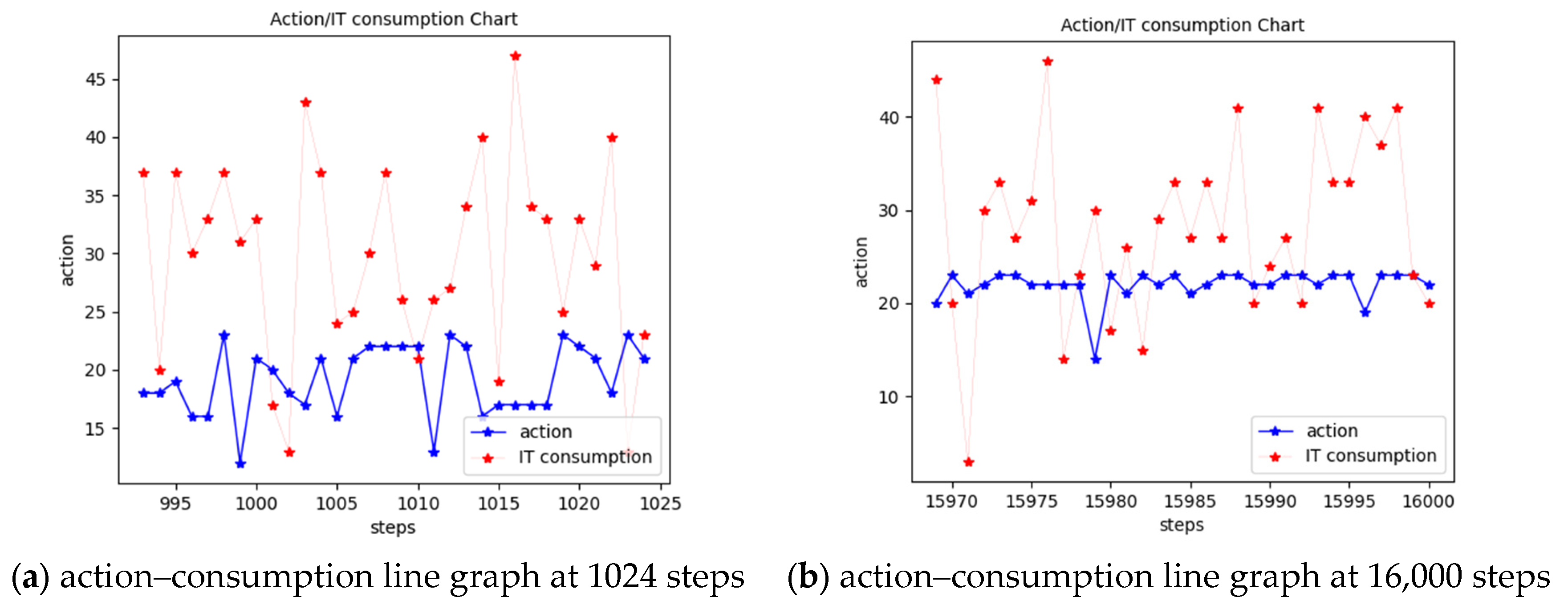
4.2. Performance of DQN-Based Intelligent Decision Making
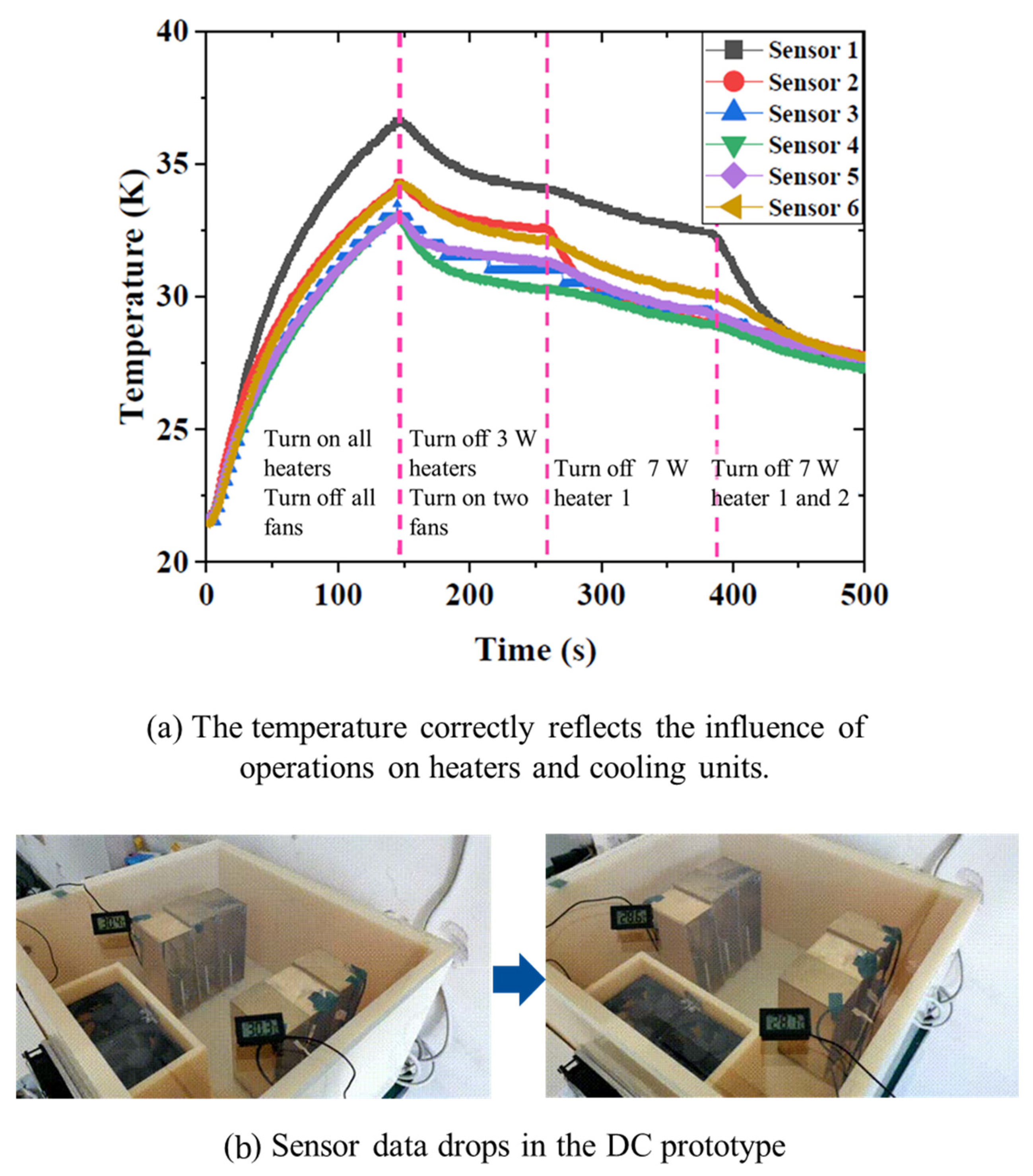
4.3. Thermal Management Process Using a DQN-Based Intelligent Strategy
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Masanet, E.; Shehabi, A.; Lei, N.; Smith, S.; Koomey, J. Recalibrating global data center energy-use estimates. Science 2020, 367, 984–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, N. How to stop data centres from gobbling up the world’s electricity. Nature 2018, 561, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Woo, J. Development and experimental study of an independent row-based cooling system for improving thermal performance of a data center. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2020, 169, 114857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayarathna, M.; Wen, Y.; Fan, R. Data center energy consumption modeling: A survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2015, 18, 732–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lindberg, T.; Xiong, N.; Vyatkin, V.; Mousavi, A. Cooling energy consumption investigation of data center it room with vertical placed server. Energy Procedia 2017, 105, 2047–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zheng, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, X. Data center power minimization with placement optimization of liquid-cooled servers and free air cooling. Sustain. Comput. Inform. Syst. 2016, 11, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehabi, A.; Smith, S.; Sartor, D.; Brown, R.; Herrlin, M.; Koomey, J.; Masanet, E.; Horner, N.; Azevedo, I.; Lintner, W. United States Data Center Energy Usage Report; Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Qingshan, J.; Jingxian, T.; Junjie, W.; Xiao, H.; Yiting, L.; Heng, X. Reinforcement learning for green and reliable data center. Chin. J. Intell. Sci. Technol. 2020, 2, 341–347. [Google Scholar]
- Athavale, J.; Yoda, M.; Joshi, Y. Comparison of data driven modeling approaches for temperature prediction in data centers. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 135, 1039–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Mao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Yin, M.; Karniadakis, G.E. Physics-informed neural networks (PINNs) for fluid mechanics: A review. Acta Mech. Sin. 2021, 37, 1727–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S.; Perdikaris, P.; Karniadakis, G.E. Physics-informed neural networks for heat transfer problems. J. Heat Transf. 2021, 143, 060801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, C.; Sun, H.; Liu, Y. Physics-informed deep learning for incompressible laminar flows. Theor. Appl. Mech. Lett. 2020, 10, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, S.; San, O.; Aksoylu, B.; Rasheed, A.; Kvamsdal, T. Physics guided machine learning using simplified theories. Phys. Fluids 2021, 33, 011701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M.D.; Rehman, A.; Ahmed, S.; Dengel, A. DeepCFD: Efficient steady-state laminar flow approximation with deep convolutional neural networks. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.08826. [Google Scholar]
- Kochkov, D.; Smith, J.A.; Alieva, A.; Wang, Q.; Brenner, M.P.; Hoyer, S. Machine learning–accelerated computational fluid dynamics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2101784118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashefi, A.; Rempe, D.; Guibas, L.J. A point-cloud deep learning framework for prediction of fluid flow fields on irregular geometries. Phys. Fluids 2021, 33, 027104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Li, G.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Deng, X. TransCFD: A transformer-based decoder for flow field prediction. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 123, 106340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jindal, L.; Doohan, N.V.; Vaidya, S.; Patel, H.; Deo, A. Deep learning-based heat optimization techniques for forecasting indoor temperature changes. Spat. Inf. Res. 2024, 32, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandi, S.; Piscitelli, M.S.; Martellacci, M.; Capozzoli, A. Deep reinforcement learning to optimise indoor temperature control and heating energy consumption in buildings. Energy Build. 2020, 224, 110225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, P.; Singh, M.M.; Chen, X. Explainable AI for engineering design: A unified approach of systems engineering and component-based deep learning demonstrated by energy-efficient building design. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2024, 62, 102843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, Z.; Geng, Y.; Lin, B. Interpreting the neural network model for HVAC system energy data mining. Build. Environ. 2022, 209, 108449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnih, V.; Kavukcuoglu, K.; Silver, D.; Rusu, A.A.; Veness, J.; Bellemare, M.G.; Graves, A.; Riedmiller, M.; Fidjeland, A.K.; Ostrovski, G. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning. Nature 2015, 518, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhao, C.; Wang, F.; Chen, Y. Smart DC: An AI and digital twin-based energy-saving solution for data centers. In Proceedings of the NOMS 2022-2022 IEEE/IFIP Network Operations and Management Symposium, Budapest, Hungary, 25–29 April 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wen, Y.; Tao, D.; Guan, K. Transforming cooling optimization for green data center via deep reinforcement learning. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2019, 50, 2002–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grishina, A.; Chinnici, M.; Kor, A.-L.; Rondeau, E.; Georges, J.-P. A machine learning solution for data center thermal characteristics analysis. Energies 2020, 13, 4378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Cao, Z.; Zhou, X.; Wen, Y.; Tan, R. Green Data Center Cooling Control via Physics-Guided Safe Reinforcement Learning. ACM Trans. Cyber-Phys. Syst. 2024, 8, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Y.; Zhou, X.; Hu, H.; Wen, Y. Optimizing data center energy efficiency via event-driven deep reinforcement learning. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 2022, 16, 1296–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Jia, Y.; Han, S. Reinforcement learning control for data center refrigeration systems. Comput. Eng. Sci. 2025, 47, 422. [Google Scholar]
- Silver, D.; Huang, A.; Maddison, C.J.; Guez, A.; Sifre, L.; Van Den Driessche, G.; Schrittwieser, J.; Antonoglou, I.; Panneershelvam, V.; Lanctot, M. Mastering the game of Go with deep neural networks and tree search. Nature 2016, 529, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Wang, X.; Shen, R.; Li, Y.; Gu, L.; Zheng, R.; Zhao, J.; Tian, X. Global optimization strategy of prosumer data center system operation based on multi-agent deep reinforcement learning. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 91, 109519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Cheng, B.; Jiang, G.; Zhou, H. DQN-Based Chiller Energy Consumption Optimization in IoT-Enabled Data Center. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 23rd International Conference on Communication Technology (ICCT), Wuxi, China, 20–22 October 2023; pp. 985–990. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, H.; Xu, X.; Li, C.; Dong, H.; Lv, X.; Jin, Q. DDQN-based data laboratory energy consumption control model. Int. J. Sens. Netw. 2024, 44, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zohdi, T. A digital-twin and machine-learning framework for precise heat and energy management of data-centers. Comput. Mech. 2022, 69, 1501–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Lin, B. Digital twin-driven energy consumption management of integrated heat pipe cooling system for a data center. Appl. Energy 2024, 373, 123840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piras, G.; Agostinelli, S.; Muzi, F. Smart Buildings and Digital Twin to Monitoring the Efficiency and Wellness of Working Environments: A Case Study on IoT Integration and Data-Driven Management. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, F.; Cheng, J.; Qi, Q.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, H.; Sui, F. Digital twin-driven product design, manufacturing and service with big data. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 94, 3563–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malone, C.; Belady, C. Metrics to characterize data center & IT equipment energy use. In Proceedings of the Digital Power Forum, Richardson, TX, USA, 18–20 September 2006. [Google Scholar]
| Learning Rate | Dataset Size | Temperature Guess Map (TGM) | MAE (°C) | MAPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0003 | 91 simulations | Interpolation | 2.27 | 9.21% |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Learning rate | lr = 0.0001 |
| Exponential decay | λ = 0.95 |
| Discount factor | γ = 0.5 |
| Exploration parameters | ϵ0 = 0.6, ϵmin = 0.2 ϵdecay = 0.99 |
| Reward weights | Rtemp = 0.2, RPUE = 2.5, Rhotspot = 0.3 |
| Thermal threshold | Tthres = 50 °C, Tideal = 25 °C |
| Experience replay capacity | C = 104 |
| DQN | Const. 15 °C | Const. 20 °C | Const. 24 °C | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | −5.96 | −8.05 | −8.20 | −9.64 |
| PUE | −4.52 | −7.53 | −7.05 | −3.90 |
| Hotspot | 0.09 | 0.18 | 0.27 | −3.47 |
| Training 16,000 Episodes | Deploying | |
|---|---|---|
| Time | 35.59 h (128,112.47 s) | 1.46 ± 0.1 s |
| Devices | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4070 SUPER (28 GB) with Intel Core i7-9700 CPU, Beihang University, Beijing, China. | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, H.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, D.; Xue, T.; Wen, D.; Yao, G. An Intelligent Thermal Management Strategy for a Data Center Prototype Based on Digital Twin Technology. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 7675. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147675
Yuan H, Zhang Z, Yang D, Xue T, Wen D, Yao G. An Intelligent Thermal Management Strategy for a Data Center Prototype Based on Digital Twin Technology. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(14):7675. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147675
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Hang, Zeyu Zhang, Duobing Yang, Tianyou Xue, Dongsheng Wen, and Guice Yao. 2025. "An Intelligent Thermal Management Strategy for a Data Center Prototype Based on Digital Twin Technology" Applied Sciences 15, no. 14: 7675. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147675
APA StyleYuan, H., Zhang, Z., Yang, D., Xue, T., Wen, D., & Yao, G. (2025). An Intelligent Thermal Management Strategy for a Data Center Prototype Based on Digital Twin Technology. Applied Sciences, 15(14), 7675. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15147675







