Effect of Complex Contrast Training on Change of Direction Performance in Team-Sport Athletes: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Selection Criteria
2.3. Search Strategy
2.4. Data Extraction
2.5. Meta-Analysis
2.6. Study Quality Assessment
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Basic Characteristics of the Included Studies
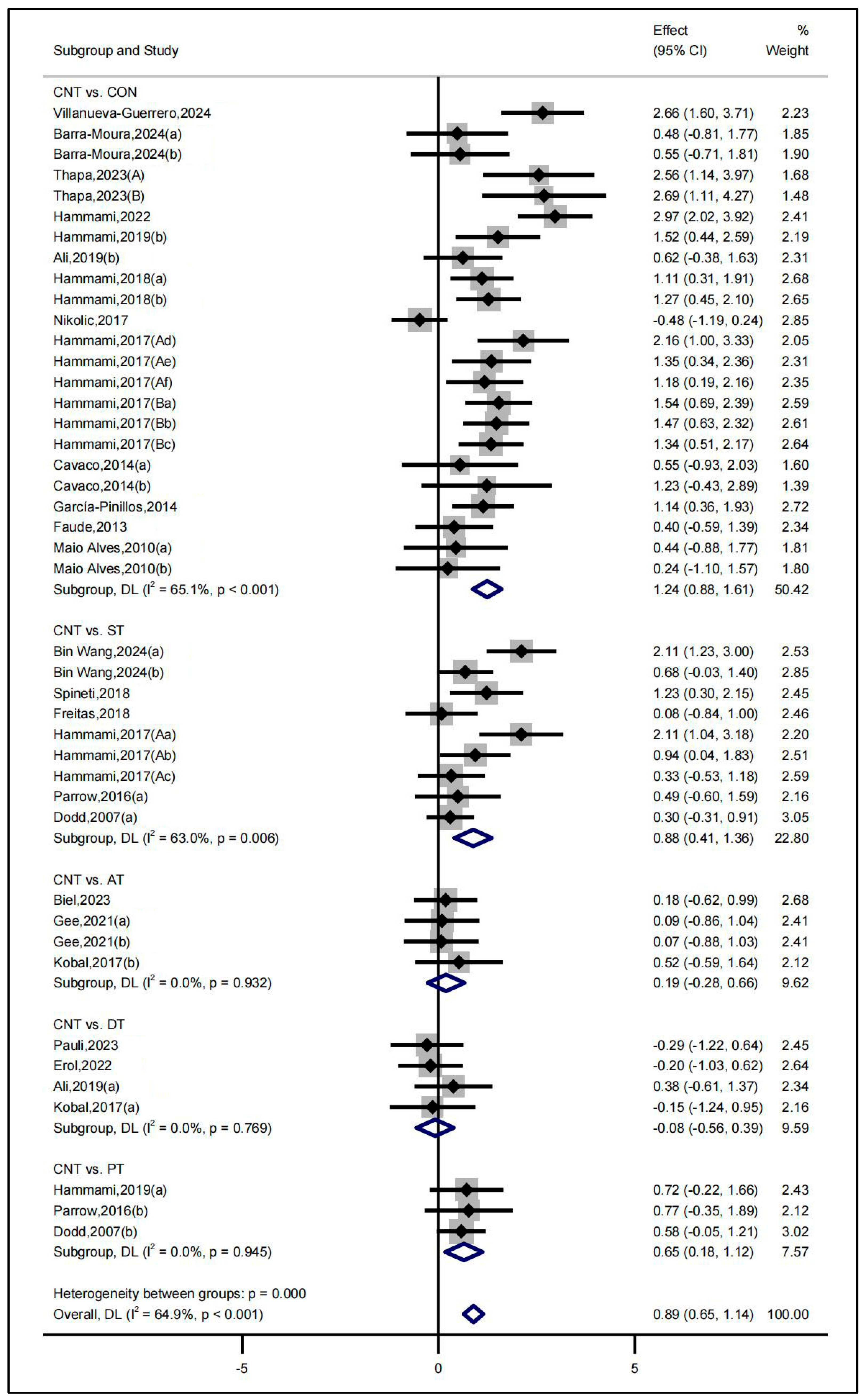
3.3. Results of Meta-Analysis
3.4. Results of Study Quality Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| COD | Change of direction |
| CNT | Complex contrast training |
| ST | Strength training |
| PT | Plyometric training |
| DT | Complex descending training |
| AT | Complex ascending training |
| PAP | Post-activation potentiation |
Appendix A
| Criteria | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Was the study described as randomized, a randomized trial, a randomized clinical trial, or an RCT? | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Was the method of randomization adequate (i.e., use of randomly generated assignment)? | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Was the treatment allocation concealed (so that assignments could not be predicted)? | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Were study participants and providers blinded to treatment group assignment? | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Were the people assessing the outcomes blinded to the participants’ group assignments? | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Were the groups similar at baseline on important characteristics that could affect outcomes (e.g., demographics, risk factors, co-morbid conditions)? | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Was the overall drop-out rate from the study at endpoint 20% or lower of the number allocated to treatment? | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Was the differential drop-out rate (between treatment groups) at endpoint 15 percentage points or lower? | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Was there high adherence to the intervention protocols for each treatment group? | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Were other interventions avoided or similar in the groups (e.g., similar background treatments)? | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Were outcomes assessed using valid and reliable measures, implemented consistently across all study participants? | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Did the authors report that the sample size was sufficiently large to be able to detect a difference in the main outcome between groups with at least 80% power? | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Were outcomes reported or subgroups analyzed pre-specified (i.e., identified before analyses were conducted)? | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Were all randomized participants analyzed in the group to which they were originally assigned, i.e., did they use an intention-to-treat analysis? | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Total | 10 | 12 | 11 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 8 | 11 | 9 | 11 | 11 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 10 | 10 | 8 | 10 |
References
- Spiteri, T.; Cochrane, J.L.; Hart, N.H.; Haff, G.G.; Nimphius, S. Effect of strength on plant foot kinetics and kinematics during a change of direction task. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2013, 13, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheppard, J.M.; Young, W.B. Agility literature review: Classifications, training and testing. J. Sports Sci. 2006, 24, 919–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimphius, S.; Callaghan, S.J.; Spiteri, T.; Lockie, R.G. Change of direction deficit: A more isolated measure of change of direction performance than total 505 time. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2016, 30, 3024–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalen, T.; Jørgen, I.; Gertjan, E.; Havard, H.G.; Ulrik, W. Player load, acceleration, and deceleration during forty-five competitive matches of elite soccer. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2016, 30, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Jiang, M.; Jing, Y.; Li, M.; Li, Y.; Yang, X. Associations Between Sprint Mechanical Properties and Change of Direction Ability and Asymmetries in COD Speed Performance in Basketball and Volleyball Players. Life 2024, 14, 1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Xie, E.; Liang, P.; Liu, T.; Zhu, J.; Qin, G.; Su, X. Transforming performance: The impact of an 8-week complex training program on strength, power, and change of direction in female basketball athletes. Medicine 2024, 103, e38524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spineti, J.; Figueiredo, T.; Willardson, J.; Bastos de Oliveira, V.; Assis, M.; Fernandes de Oliveira, L.; Miranda, H.; Machado de Ribeiro Reis, V.M.; Simão, R. Comparison between traditional strength training and complex contrast training on soccer players. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2018, 59, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnow, A.; Derakhshandeh, S.; Hosseini, A. The Effect of 4-week Difference Training Methods on Some Fitness Variables inYouth Handball Players. Int. J. Appl. Exerc. Physiol. 2016, 5, 46–56. [Google Scholar]
- Biel, P.; Ewertowska, P.; Stastny, P.; Krzysztofik, M. Effects of Complex Training on Jumping and Change of Direction Performance, and Post-Activation Performance Enhancement Response in Basketball Players. Sports 2023, 11, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauli, P.H.; de Borba, E.F.; da Silva, M.P.; Martins, M.V.S.; Batista, M.M.; Tartaruga, M.P. Effects of Complex and Contrast Training on Strength, Power, and Agility in Professional Futsal Players: A Preliminary Study. J. Sci. Sport Exerc. 2023, 6, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cormie, P.; McGuigan, M.R.; Newton, R.U. Developing maximal neuromuscular power: Part 1—Biological basis of maximal power production. Sports Med. 2011, 41, 17–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boer, P.; Van Aswegen, M. Effect of combined versus repeated sprint training on physical parameters in subelite football players in South Africa. J. Phys. Educ. Sport 2016, 16, 964. [Google Scholar]
- Dodd, D.J.; Alvar, B.A. Analysis of acute explosive training modalities to improve lower-body power in baseball players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2007, 21, 1177–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobal, R.; Loturco, I.; Barroso, R.; Gil, S.; Cuniyochi, R.; Ugrinowitsch, C.; Roschel, H.; Tricoli, V. Effects of Different Combinations of Strength, Power, and Plyometric Training on the Physical Performance of Elite Young Soccer Players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2017, 31, 1468–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, R.K.; Kumar, G.; Weldon, A.; Moran, J.; Chaabene, H.; Ramirez-Campillo, R. Effects of complex-contrast training on physical fitness in male field hockey athletes. Biomed. Hum. Kinet. 2023, 15, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, J.M.V.M.; Rebelo, A.N.; Abrantes, C.; Sampaio, J. Short-term effects of complex and contrast training in soccer players’ vertical jump, sprint, and agility abilities. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2010, 24, 936–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cormier, P.; Freitas, T.T.; Loturco, I.; Turner, A.; Virgile, A.; Haff, G.G.; Blazevich, A.J.; Agar-Newman, D.; Henneberry, M.; Baker, D.G.; et al. Within Session Exercise Sequencing During Programming for Complex Training: Historical Perspectives, Terminology, and Training Considerations. Sports Med. 2022, 52, 2371–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebben, W.P.; Watts, P.B. A review of combined weight training and plyometric training modes: Complex training. Strength Cond. J. 1998, 20, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, T.T.; Martinez-Rodriguez, A.; Calleja-Gonzalez, J.; Alcaraz, P.E. Short-term adaptations following complex training in team-sports: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Docherty, D.; Robbins, D.; Hodgson, M. Complex training revisited: A review of its current status as a viable training approach. Strength Cond. J. 2004, 26, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi; Romadhoni, S.; Yudhistira, D. Implementing Complex Training Method: Its Effects on Endurance, Speed, Power, and Agility of Adolescent Basketball Players. Phys. Educ. Theory Methodol. 2024, 24, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gee, T.I.; Harsley, P.; Bishop, D.C. Effect of 10 Weeks of Complex Training on Speed and Power in Academy Soccer Players. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2021, 16, 1134–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva-Guerrero, O.; Lozano, D.; Roso-Moliner, A.; Nobari, H.; Lago-Fuentes, C.; Mainer-Pardos, E. Effects of different strength and velocity training programs on physical performance in youth futsal players. Heliyon 2024, 10, e30747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolic, D.; Beric, D.; Kocic, M.; Daskalovski, B. Complex training and sprint abilities of young basketball players. Facta Univ. Ser. Phys. Educ. Sport 2017, 15, 25–36. [Google Scholar]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. Bmj 2009, 339, b2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drevon, D.; Fursa, S.R.; Malcolm, A.L. Intercoder reliability and validity of WebPlotDigitizer in extracting graphed data. Behav. Modif. 2017, 41, 323–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, F.; Gilbody, S. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. Increase in studies of publication bias coincided with increasing use of meta-analysis. BMJ Br. Med. J. 1998, 316, 471. [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins, W.; Marshall, S.; Batterham, A.; Hanin, J. Progressive statistics for studies in sports medicine and exercise science. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cormier, P.; Freitas, T.T.; Rubio-Arias, J.Á.; Alcaraz, P.E. Complex and contrast training: Does strength and power training sequence affect performance-based adaptations in team sports? A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2020, 34, 1461–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, R.K.; Uysal, H.Ş.; Clemente, F.M.; Afonso, J.; Ramirez-Campillo, R. Effects of complex training compared to resistance training alone on physical fitness of healthy individuals: A systematic review with meta-analysis. J. Sports Sci. 2024, 42, 1367–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, R.K.; Lum, D.; Moran, J.; Ramirez-Campillo, R. Effects of Complex Training on Sprint, Jump, and Change of Direction Ability of Soccer Players: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Psychol. 2021, 11, 627869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naveen Raj, A.; Kamalakannan, M.; Anitha, A.; Ramana, K. Recent Experimental Investigation on the Effectiveness of Complex Training for Intermediate Football Players. Indian J. Physiother. Occup. Ther. 2024, 18, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Moya, R.; Silva, A.F.; Clemente, F.M.; González-Fernández, F.T. Effects of combined plyometric, strength and running technique training program on change-of-direction and countermovement jump: A two-armed parallel study design on young soccer players. Gait Posture 2023, 105, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooroshfard, N.; Rahimi, Z. The Effect of the Neuromuscular, Strength, and Combined Training on Balance and Performance in Female Basketball Players. Phys. Treat. 2022, 12, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Sanchez, J.; Ramirez-Campillo, R.; Petisco, C.; Hernandez, D.; Yuzo Nakamura, F. Effects of short-term strength and jumping exercises distribution on soccer player’s physical fitness. Kinesiology 2021, 53, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dass, B.; Madiha, K.; Hotwani, R.; Arora, S.P. Impact of strength and plyometric training on agility, anaerobic power and core strength in badminton players. J. Med. Pharm. Allied Sci. 2021, 10, 3254–3258. [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura, K.; Roschel, H.; Loturco, I.; Lamas, L.; Tricoli, V.; João, P.V.; Fellingham, G.; Ugrinowitsch, C. Strength and power training improve skill performance in volleyball players. Mot. Rev. Educ. Física 2020, 26, e10200034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zghal, F.; Colson, S.S.; Blain, G.; Behm, D.G.; Granacher, U.; Chaouachi, A. Combined Resistance and Plyometric Training Is More Effective Than Plyometric Training Alone for Improving Physical Fitness of Pubertal Soccer Players. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latorre Román, P.; Villar Macias, F.J.; García Pinillos, F. Effects of a contrast training programme on jumping, sprinting and agility performance of prepubertal basketball players. J. Sports Sci. 2018, 36, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Distefano, L.J.; Distefano, M.J.; Frank, B.S.; Clark, M.A.; Padua, D.A. Comparison of integrated and isolated training on performance measures and neuromuscular control. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2013, 27, 1083–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzinikolaou, A.; Michaloglou, K.; Avloniti, A.; Leontsini, D.; Deli, C.K.; Vlachopoulos, D.; Gracia-Marco, L.; Arsenis, S.; Athanailidis, I.; Draganidis, D.; et al. The Trainability of Adolescent Soccer Players to Brief Periodized Complex Training. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2018, 13, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrini, M.; Asian-Clemente, J.; Bagattini, G.; Suarez-Arrones, L. A Combined 7-Week Strength and Power Training: Effects on Body Composition, Strength, Speed, and Agility in U14 and U16 Youth Elite Soccer Players. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Shao, Y.; Saha, S.; Zhao, Z.; Karmakar, D. Maximizing sprint performance among adolescent sprinters: A controlled evaluation of functional, traditional, and combined training approaches. Front. Public Health 2025, 13, 1596381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valappil, I.N.K.; Gavoutamane, G.; Elayaraja, M.; Orhan, B.E.; Astuti, Y.; Katanic, B.; Karmakar, D.; Tiroumourougane, K.; Murugesan, R.; Govindasamy, K. Impact of Three Weekly Sessions of Complex versus French Contrast Training on Physical and Physiological Responses in Field Hockey Players: A Randomized Control Trial. Montenegrin J. Sports Sci. Med. 2025, 14, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chnini, Z.; Salem, A.; Trabelsi, K.; Ammar, A.; Souissi, N.; Chtourou, H. Light load jump squat and plyometric training enhance jumping, sprinting, change of direction, and balance performance of male soccer players (U-19): A randomized controlled trial. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2024, 64, 719–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzysztofik, M.; Jarosz, J.; Urbanski, R.; Aschenbrenner, P.; Stastny, P. Effects of 6 weeks of complex training on athletic performance and post-activation performance enhancement effect magnitude in soccer players: A cross-sectional randomized study. Biol. Sport 2025, 42, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Pandey, V.; Thapa, R.K.; Weldon, A.; Granacher, U.; Ramirez-Campillo, R. Effects of Exercise Frequency with Complex Contrast Training on Measures of Physical Fitness in Active Adult Males. Sports 2023, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatsalya, K.R.; Chaturvedi, P.; Apparao, P.; Swamy, C.G. Effectiveness of Contrast Training Versus Core Strengthening Training in Improvement of Dynamic Balance and Agility in Collegiate Badminton Players. Sciences 2023, 38, 6–12. [Google Scholar]
- Chakshuraksha, P.; Apanukul, S. Effects of Accentuated Eccentric Loading Combined with Plyometric Training on Strength, Power, Speed, and Agility in Male Rugby Players. J. Exerc. Physiol. Online 2021, 24, 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Wallenta, C.; Granacher, U.; Lesinski, M.; Schünemann, C.; Muehlbauer, T. Effects of Complex Versus Block Strength Training on the Athletic Performance of Elite Youth Soccer Players. Sportverletz. Sportschaden Organ Ges. Orthop.-Traumatol. Sportmed. 2016, 30, 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Hammami, M.; Gaamouri, N.; Shephard, R.J.; Chelly, M.S. Effects of Contrast Strength vs. Plyometric Training on Lower-Limb Explosive Performance, Ability to Change Direction and Neuromuscular Adaptation in Soccer Players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2019, 33, 2094–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, K.; Verma, S.; Ahmad, I.; Singla, D.; Saleem, M.; Hussain, M.E. Comparison of Complex Versus Contrast Training on Steroid Hormones and Sports Performance in Male Soccer Players. J. Chiropr. Med. 2019, 18, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammami, M.; Gaamouri, N.; Aloui, G.; Shephard, R.J.; Chelly, M.S. Effects of a Complex Strength-Training Program on Athletic Performance of Junior Female Handball Players. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2018, 14, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, T.T.; Calleja-González, J.; Carlos-Vivas, J.; Marín-Cascales, E.; Alcaraz, P.E. Short-term optimal load training vs a modified complex training in semi-professional basketball players. J. Sports Sci. 2018, 37, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammami, M.; Negra, Y.; Shephard, R.J.; Chelly, M.S. Effects of leg contrast strength training on sprint, agility and repeated change of direction performance in male soccer players. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2017, 57, 1424–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammami, M.; Negra, Y.; Shephard, R.J.; Chelly, M.S. The Effect of Standard Strength vs. Contrast Strength Training on the Development of Sprint, Agility, Repeated Change of Direction, and Jump in Junior Male Soccer Players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2017, 31, 901–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Pinillos, F.; Martínez-Amat, A.; Hita-Contreras, F.; Martínez-López, E.J.; Latorre-Román, P.A. Effects of a Contrast Training Program Without External Load on Vertical Jump, Kicking Speed, Sprint, and Agility of Young Soccer Players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2014, 28, 2452–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaco, B.; Sousa, N.; Dos Reis, V.M.; Garrido, N.; Saavedra, F.; Mendes, R.; Vilaça-Alves, J. Short-term effects of complex training on agility with the ball, speed, efficiency of crossing and shooting in youth soccer players. J. Hum. Kinet. 2014, 43, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faude, O.; Roth, R.; Di Giovine, D.; Zahner, L.; Donath, L. Combined strength and power training in high-level amateur football during the competitive season: A randomised-controlled trial. J. Sports Sci. 2013, 31, 1460–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barra-Moura, H.; Vieira, J.G.; Werneck, F.Z.; Wilk, M.; Pascoalini, B.; Queiros, V.; de Assis, G.G.; Bichowska-Paweska, M.; Vianna, J.; Vilaca-Alves, J. The effect of complex contrast training with different training frequency on the physical performance of youth soccer players: A randomized study. PeerJ 2024, 12, e17103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thapa, R.K.; Kumar, G.; Raizada, S.; Bagchi, A. Effects of contrast training with two sessions weekly frequency on physical fitness of university-level male soccer players. Phys. Educ. Theory Methodol. 2023, 23, 886–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammami, M.; Gaamouri, N.; Cherni, Y.; Gaied, S.; Chelly, M.S.; Hill, L.; Nikolaidis, P.T.; Knechtle, B. Effects of complex strength training with elastic band program on repeated change of direction in young female handball players: Randomized control trial. Int. J. Sports Sci. Coach. 2022, 17, 1396–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erol, S. An Investigation of the Effects of 8-Week Complex and Contrast Strength Trainings Applied to Soccer Players on Some Physical Properties. Int. Online J. Educ. Teach. 2022, 9, 1600–1613. [Google Scholar]
- Markovic, G.; Mikulic, P. Neuro-musculoskeletal and performance adaptations to lower-extremity plyometric training. Sports Med. 2010, 40, 859–895. [Google Scholar]
- Oxfeldt, M.; Overgaard, K.; Hvid, L.G.; Dalgas, U. Effects of plyometric training on jumping, sprint performance, and lower body muscle strength in healthy adults: A systematic review and meta-analyses. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2019, 29, 1453–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaabene, H.; Negra, Y.; Sammoud, S.; Moran, J.; Ramirez-Campillo, R.; Granacher, U.; Prieske, O. The Effects of Combined Balance and Complex Training Versus Complex Training Only on Measures of Physical Fitness in Young Female Handball Players. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2021, 16, 1439–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fathi, A.; Hammami, R.; Moran, J.; Borji, R.; Sahli, S.; Rebai, H. Effect of a 16-week combined strength and plyometric training program followed by a detraining period on athletic performance in pubertal volleyball players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2019, 33, 2117–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, G.H.; Clark, B.C.; Li, S.; Vaillancourt, D.E. Understanding Neuromuscular System Plasticity to Improve Motor Function in Health, Disease, and Injury. Neural Plast. 2017, 2017, 2425180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaleff, Z.A.; Kamper, S.J. Effects of resistance training in children and adolescents: A meta-analysis. Br. J. Sports Med. 2011, 45, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flórez Gil, E.; Vaquera, A.; Ramírez-Campillo, R.; Sanchez-Sanchez, J.; Rodríguez Fernández, A. Can complex training improve acute and long-lasting performance in basketball players? A systematic review. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cormie, P.; McCaulley, G.O.; McBRIDE, J.M. Power versus strength-power jump squat training: Influence on the load-power relationship. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2007, 39, 996–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos’Santos, T.; Thomas, C.; Jones, P.A.; Comfort, P. Assessing Asymmetries in Change of Direction Speed Performance: Application of Change of Direction Deficit. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2019, 33, 2953–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Study ID | Group | N | Age | Gender | Sport/Level | CNT Interventions | COD Measures |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Villanueva-Guerrero, 2024 [23] | CNT CON | 14 14 | 17 | M | Futsal/E | ST + PT + CST; 1 session; 8 week | V-Cut test |
| Bin Wang, 2024 [6] | CNT ST | 16 16 | 20 | F | Basketball/A | ST + PT; 70–100% 1RM; 2–3 sessions; 8 weeks | 505 Test; Illinois test |
| Barra-Moura, 2024 [60] | CNT1 CNT2 CON | 6 7 8 | 15 | M | Soccer/A | ST + Sprint + PT; 80–90% 1RM; 2/3 sessions; 6 weeks | 505 Test |
| Thapa, 2023 (A) [61] | CNT CON | 8 8 | 20 21 | M | Soccer/A | ST + PT; 65–85% 1RM; 2 sessions; 6 weeks | Modified T-Test |
| Thapa, 2023 (B) [15] | CNT CON | 8 6 | 21 22 | M | Hockey/A | ST + PT; 65–85% 1RM; 3 sessions; 6 weeks | Modified T-Test |
| Piotr Biel, 2023 [9] | CNT AT | 13 11 | 24 21 | M | Basketball/A | ST + PT; 80–85% 1RM; 2 sessions; 8 weeks | Shuttle Test |
| Pauil, 2023 [10] | CNT DT | 9 9 | 20 | M | Futsal/E | ST + Sprint; 60% 1RM; 2 sessions; 8 weeks | Illinois test |
| Hammami, 2022 [62] | CNT CON | 19 19 | 16 | F | Handball/A | ST + PT; 2 sessions; 10 weeks | Modified Illinois test |
| Erol, 2022 [63] | CNT DT | 13 10 | 23 21 | M | Soccer/A | ST + Sprint + PT; 70–85% 1RM; 3 sessions; 8 weeks | T-Test |
| Gee, 2021 [22] | CNT AT | 9 8 | 17 | M | Soccer/E | ST + PT/OLS; 85% 1RM; 2 sessions; 10 weeks | Arrowhead test |
| Hammami, 2019 [51] | CNT PT CON | 14 14 12 | 16 | M | Soccer/A | ST + PT + Sprint; 70–90% 1RM; 2 sessions; 8 weeks | S4 × 5 Test |
| Ali, 2019 [52] | CNT DT CON | 12 12 12 | 22 | M | Soccer/A | ST + PT; 80% 1RM; 3 sessions; 6 weeks | T-Test |
| Hammami, 2018 [53] | CNT CON | 14 14 | 17 | F | Handball/A | ST + PT + Sprint; 75–90% 1RM; 2 sessions; 10 weeks | Modified T-Test; Modified Illinois test |
| Spineti, 2018 [7] | CNT ST | 10 12 | 18 | M | Soccer/E | ST + PT + Sprint; 90% 1RM; 3 sessions; 8 weeks | Zigzag pattern test |
| Freitas, 2018 [54] | CNT ST | 9 9 | 21 | M | Basketball/E | ST + OLT; 80% 1RM; 2 sessions; 6 weeks | T-Test |
| Nikolic, 2017 [24] | CNT CON | 16 15 | 17- 18 | M | Basketball/A | ST + PT; 60–80% 1RM; 2 sessions; 12 weeks | 10 × 5 m Shuttle test |
| Kobal, 2017 [14] | CNT DT AT | 9 9 9 | 19 | M | Soccer/E | ST + PT; 60–80% 1RM; 2 sessions; 8 weeks | 505 Test |
| Hammami, 2017 (A) [56] | CNT ST CON | 16 16 12 | 16 | M | Soccer/A | ST + PT + Sprint; 70–90% 1RM; 2 sessions; 8 weeks | S4 × 5 Test; Shuttle run S180°; Shuttle run SBF |
| Hammami, 2017 (B) [55] | CNT CON | 17 12 | 17 | M | Soccer/A | ST + PT + Sprint; 70–90% 1RM; 2 sessions; 8 weeks | S4 × 5 Test; Shuttle run S180°; Shuttle run SBF |
| Parrow, 2016 [8] | CNT ST PT | 10 10 10 | 17 | M | Handball/A | ST + PT; 50–60% 1RM; 3 sessions; 4 weeks | T-Test |
| Cavaco, 2014 [58] | CNT1 CNT2 CON | 5 5 6 | 14 | M | Soccer/A | ST + Sprint; 85% 1RM; 1/2 sessions; 6 weeks | Agility with the ball |
| García-Pinillos, 2014 [57] | CNT CON | 17 13 | 16 | M | Soccer/A | ST + PT; body weight; 2 sessions; 12 weeks | Balsom agility test |
| Faude, 2013 [59] | CNT CON | 8 8 | 23 | M | Soccer/E | ST + PT + Sprint; 50–60% 1RM; 2 sessions; 7 weeks | shuttle sprint and dribble test |
| Alves, 2010 [16] | CNT1 CNT2 CON | 9 8 6 | 17 | M | Soccer/E | ST + PT + Sprint; 80–90% 1RM; 1/2 sessions; 6 weeks | 505 Test |
| Dodd, 2007 [13] | CNT PT ST | 32 28 31 | 18–23 | M | Baseball/A | ST + PT; 80–90% 1RM; 2 sessions; 4 weeks | T-Test |
| Intervention | No. | Hedges’ g (95% CI) | Interpret | I2 | τ2 | Effect Model | Egger’s Test (p) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNT vs. CON | 15 | 1.24 (0.88, 1.61) | Large | 65.1% | 0.4993 | RE | 0.377 |
| CNT vs. ST | 6 | 0.88 (0.41, 1.36) | Moderate | 63.0% | 0.3229 | RE | 0.215 |
| CNT vs. PT | 3 | 0.65 (0.18, 1.12) | Moderate | 0.0% | 0.0000 | FE | 0.055 |
| CNT vs. DT | 4 | −0.08 (−0.56, 0.39) | Trivial | 0.0% | 0.0000 | FE | 0.663 |
| CNT vs. AT | 3 | 0.19 (−0.28, 0.66) | Trivial | 0.0% | 0.0000 | FE | 0.421 |
| Subgroup | No. | Hedges’ g (95% CI) | I2 (%) | Pdiff |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | ||||
| <18 | 12 | 1.13 (0.84, 1.42) | 51.6 | 0.017 * |
| ≥18 | 13 | 0.56 (0.19, 0.93) | 65.8 | |
| Gender | ||||
| Female | 3 | 1.59 (0.82, 2.37) | 76.8 | 0.049 * |
| Male | 22 | 0.78 (0.54, 1.03) | 58.0 | |
| Sport | ||||
| Basketball | 4 | 0.50 (−0.33, 1.33) | 81.3 | 0.361 |
| Soccer | 14 | 0.87 (0.62, 1.13) | 41.2 | |
| Handball | 3 | 1.34 (0.53, 2.16) | 73.2 | |
| Level | ||||
| Amateur | 17 | 1.02 (0.75, 1.28) | 68.4 | 0.044 * |
| Elite | 8 | 0.46 (0.00, 0.93) | 61.0 | |
| Intervention | ||||
| Intensity | ||||
| <85% 1RM | 18 | 1.00 (0.67, 1.32) | 70.8 | 0.139 |
| ≥85% 1RM | 7 | 0.65 (0.33, 0.98) | 29.7 | |
| Frequency | ||||
| <3 week−1 | 20 | 0.93 (0.65, 1.31) | 67.9 | 0.415 |
| ≥3 week−1 | 6 | 0.69 (0.19, 1.19) | 43.4 | |
| Duration | ||||
| >6 weeks | 16 | 0.98 (0.65, 1.31) | 72.4 | 0.135 |
| ≤6 weeks | 9 | 0.64 (0.33, 0.95) | 19.9 | |
| Measures | ||||
| Turn ≤ 3 | 9 | 0.51 (0.24, 0.78) | 0.0 | 0.008 * |
| Turn > 3 | 17 | 1.08 (0.75, 1.41) | 72.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, S.; Yan, Z.; Xu, T.; Xie, H.; Liu, R. Effect of Complex Contrast Training on Change of Direction Performance in Team-Sport Athletes: A Meta-Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 7385. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137385
Lin S, Yan Z, Xu T, Xie H, Liu R. Effect of Complex Contrast Training on Change of Direction Performance in Team-Sport Athletes: A Meta-Analysis. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(13):7385. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137385
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Shengfa, Zhijie Yan, Tengyu Xu, Huisong Xie, and Ruidong Liu. 2025. "Effect of Complex Contrast Training on Change of Direction Performance in Team-Sport Athletes: A Meta-Analysis" Applied Sciences 15, no. 13: 7385. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137385
APA StyleLin, S., Yan, Z., Xu, T., Xie, H., & Liu, R. (2025). Effect of Complex Contrast Training on Change of Direction Performance in Team-Sport Athletes: A Meta-Analysis. Applied Sciences, 15(13), 7385. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15137385






